Speech Emotion Recognition under Noisy Environments with SNR Down to −6 dB Using Multi-Decoder Wave-U-Net
Abstract
:1. Introduction
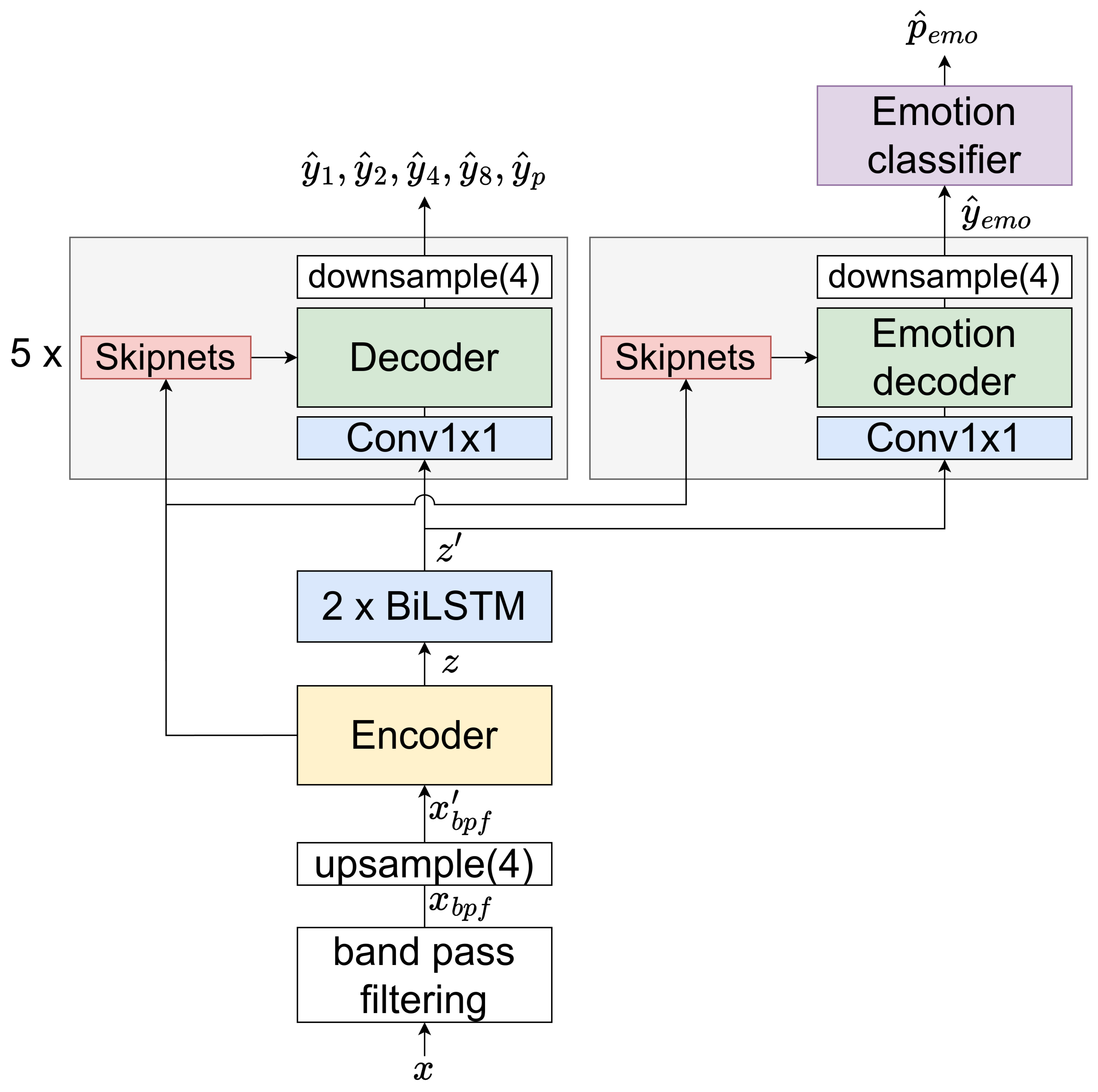
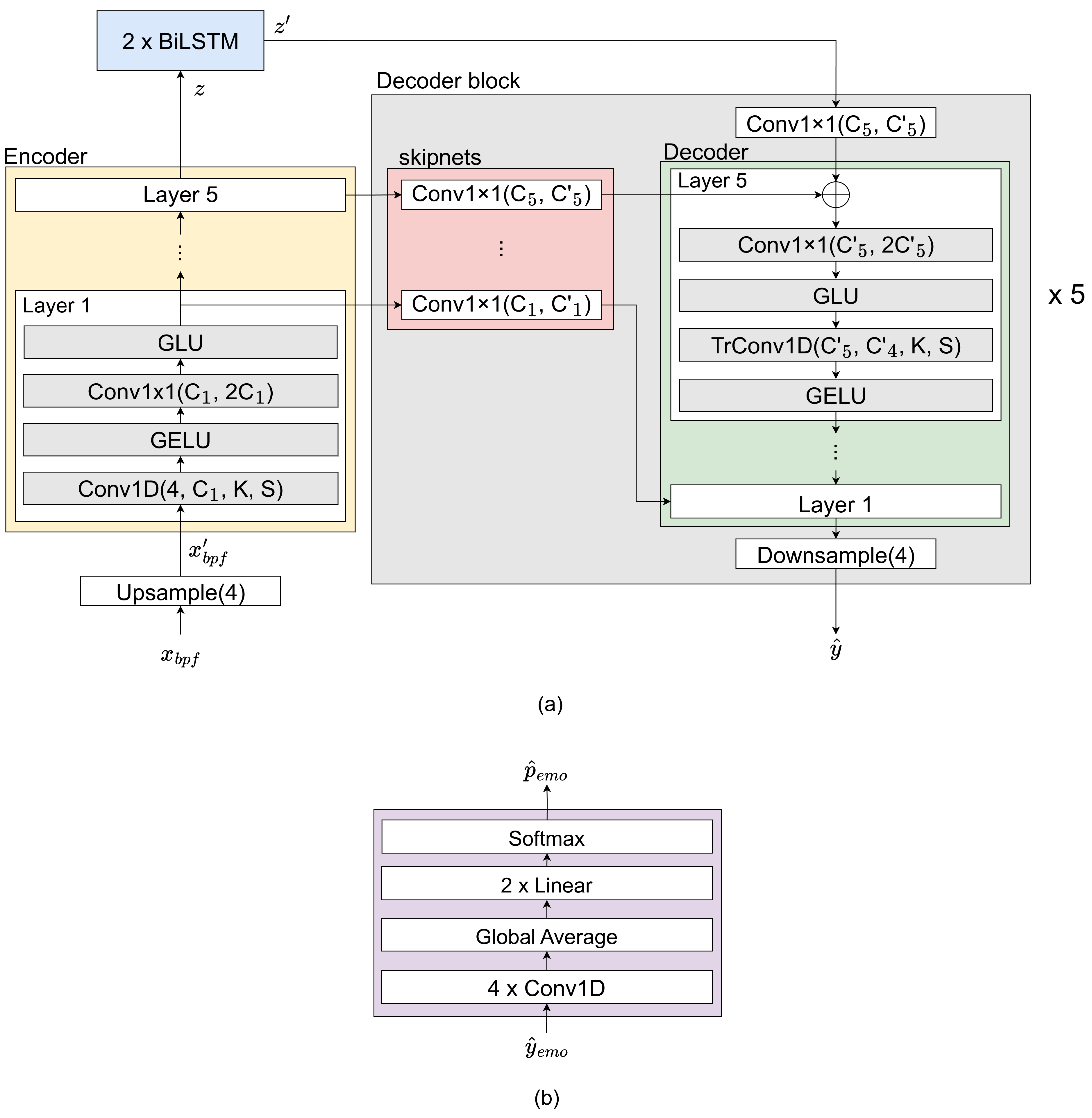
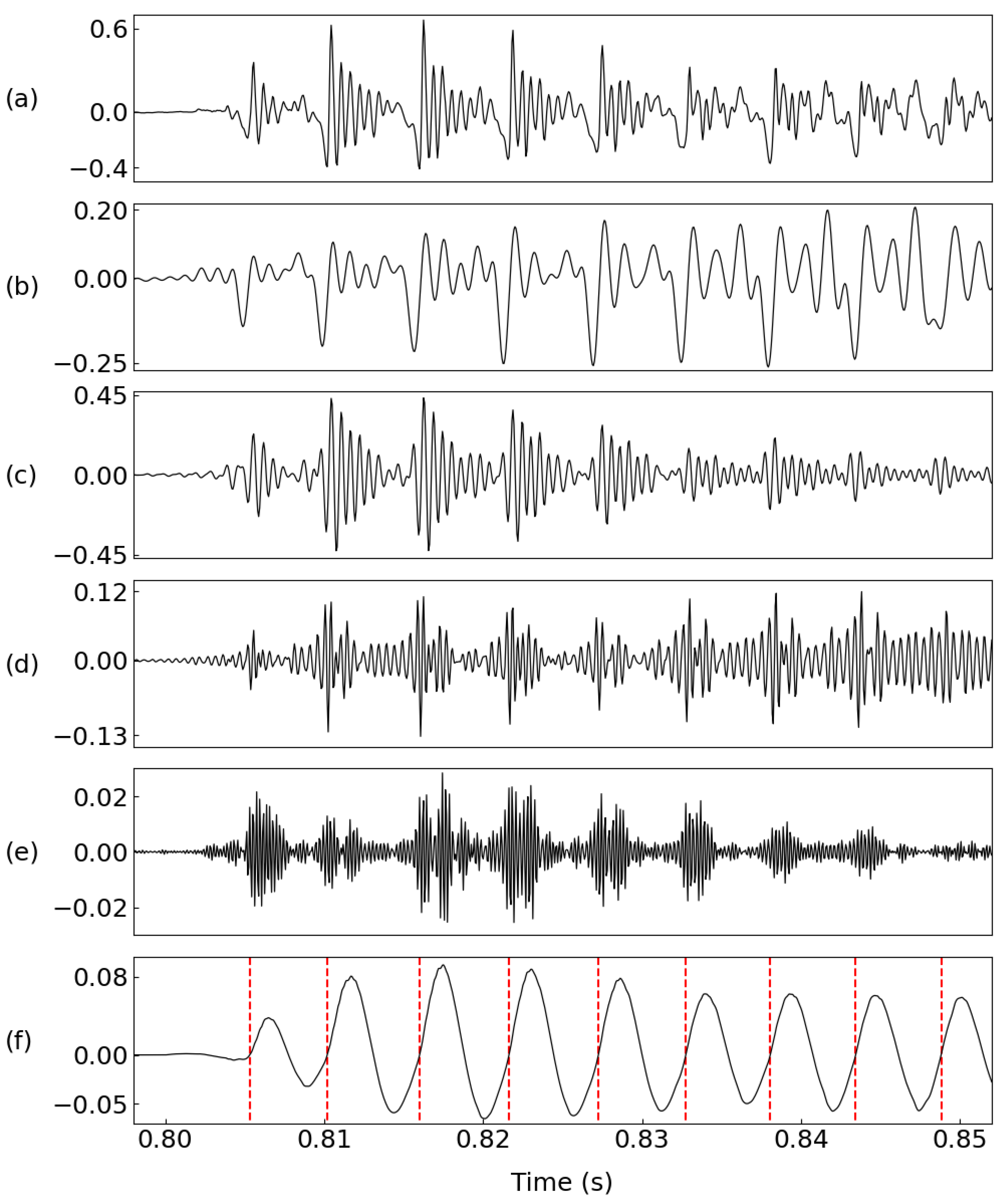
2. Proposed Deep Learning Model
3. Experimental Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dhuheir, M.; Albaseer, A.; Baccour, E.; Erbad, A.; Abdallah, M.; Hamdi, M. Emotion Recognition for Healthcare Surveillance Systems Using Neural Networks: A Survey. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing (IWCMC), Harbin, China, 28 June–2 July 2021; pp. 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kularatne, B.; Basnayake, B.; Sathmini, P.; Sewwandi, G.; Rajapaksha, S.; Silva, D.D. Elderly Care Home Robot using Emotion Recognition, Voice Recognition and Medicine Scheduling. In Proceedings of the 2022 7th International Conference on Information Technology Research (ICITR), Moratuwa, Sri Lanka, 7–9 December 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconi, D.; Mayora, O.; Lukowicz, P.; Arnrich, B.; Setz, C.; Troster, G.; Haring, C. Activity and emotion recognition to support early diagnosis of psychiatric diseases. In Proceedings of the 2008 Second International Conference on Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare, Tampere, Finland, 30 January–1 February 2008; pp. 100–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Garcia, J.M.; Penichet, V.M.R.; Lozano, M.D.; Fernando, A. Using emotion recognition technologies to teach children with autism spectrum disorder how to identify and express emotions. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 2021, 21, 809–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, M.; Bansal, M.; Ramesh, A.; Satvik, D.; D, U. Enhancing Safety in Vehicles using Emotion Recognition with Artificial Intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 8th International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT), Lonavla, India, 7–9 April 2023; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joel, J.S.; Ernest Thompson, B.; Thomas, S.R.; Revanth Kumar, T.; Prince, S.; Bini, D. Emotion based Music Recommendation System using Deep Learning Model. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), Lalitpur, Nepal, 26–28 April 2023; pp. 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, W. Head Fusion: Improving the Accuracy and Robustness of Speech Emotion Recognition on the IEMOCAP and RAVDESS Dataset. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 74539–74549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Koolagudi, S.G.; Kafley, S.; Rao, K.S. Emotion recognition using LP residual. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Students Technology Symposium (TechSym), Kharagpur, India, 3–4 April 2010; pp. 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.; Jang, D.; Lee, T. Speech emotion recognition using convolutional and Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 13–16 December 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahad, M.S.; Deepak, A.; Pradhan, G.; Yadav, J. DNN-HMM-Based Speaker-Adaptive Emotion Recognition Using MFCC and Epoch-Based Features. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 40, 466–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolagudi, S.G.; Reddy, R.; Rao, K.S. Emotion recognition from speech signal using epoch parameters. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Signal Processing and Communications (SPCOM), Bangalore, India, 18–21 July 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernekar, O.; Nirmala, S.; Chachadi, K. Deep learning model for speech emotion classification based on GCI and GOI detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 OPJU International Technology Conference on Emerging Technologies for Sustainable Development (OTCON), Raigarh, India, 8–10 February 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhangale, K.; Kothandaraman, M. Speech Emotion Recognition Based on Multiple Acoustic Features and Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Electronics 2023, 12, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.W. End-to-End Speech Emotion Recognition with Gender Information. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 152423–152438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, E.; Hoory, R.; Zhu, W.; Gat, I.; Damasceno, M.; Aronowitz, H. Speech Emotion Recognition Using Self-Supervised Features. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 6922–6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepino, L.; Riera, P.; Ferrer, L. Emotion Recognition from Speech Using Wav2vec 2.0 Embeddings. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.03502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, R.; Panda, A.; Pandharipande, M.; Joshi, S.; Kopparapu, S.K. Front-End Feature Compensation and Denoising for Noise Robust Speech Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Graz, Austria, 15–19 September 2019; pp. 3257–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Tian, K.; Wu, A.; Zhang, G. Research on Robustness of Emotion Recognition Under Environmental Noise Conditions. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 142009–142021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, U.; Soni, M.; Chakraborty, R.; Panda, A.; Kopparapu, S.K. Multi-Conditioning and Data Augmentation Using Generative Noise Model for Speech Emotion Recognition in Noisy Conditions. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 7194–7198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.; Lee, C. Cascaded convolutional neural network architecture for speech emotion recognition in noisy conditions. Sensors 2021, 21, 4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leem, S.G.; Fulford, D.; Onnela, J.P.; Gard, D.; Busso, C. Not all features are equal: Selection of robust features for speech emotion recognition in noisy environments. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 23–27 May 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 6447–6451. [Google Scholar]
- Leem, S.G.; Fulford, D.; Onnela, J.P.; Gard, D.; Busso, C. Selective Acoustic Feature Enhancement for Speech Emotion Recognition with Noisy Speech. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2023, 32, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoller, D.; Ewert, S.; Dixon, S. Wave-U-Net: A Multi-Scale Neural Network for End-to-End Audio Source Separation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.03185. [Google Scholar]
- Talkin, D. REAPER: Robust Epoch And Pitch EstimatoR. 2015. Available online: https://github.com/google/REAPER (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Busso, C.; Bulut, M.; Lee, C.C.; Kazemzadeh, A.; Mower, E.; Kim, S.; Chang, J.N.; Lee, S.; Narayanan, S.S. IEMOCAP: Interactive emotional dyadic motion capture database. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2008, 42, 335–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, J.; Marxer, R.; Vincent, E.; Watanabe, S. The third ‘CHiME’ speech separation and recognition challenge: Dataset, task and baselines. In Proceedings of the ASRU, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 13–17 December 2015; pp. 504–511. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, C.K.A.; Beyrami, E.; Pool, J.; Cutler, R.; Srinivasan, S.; Gehrke, J. A Scalable Noisy Speech Dataset and Online Subjective Test Framework. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Graz, Austria, 15–19 September 2019; pp. 1816–1820. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, A.; Steeneken, H.J. Assessment for automatic speech recognition: II. NOISEX-92: A database and an experiment to study the effect of additive noise on speech recognition systems. Speech Commun. 1993, 12, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, S.R.; Russo, F.A. The Ryerson Audio-Visual Database of Emotional Speech and Song (RAVDESS): A dynamic, multimodal set of facial and vocal expressions in North American English. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhardt, F.; Paeschke, A.; Rolfes, M.; Sendlmeier, W.F.; Weiss, B. A database of German emotional speech. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Lisbon, Portugal, 4–8 September 2005; Volume 5, pp. 1517–1520. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Sisman, B.; Liu, R.; Li, H. Seen and unseen emotional style transfer for voice conversion with a new emotional speech dataset. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 920–924. [Google Scholar]
- Dhall, A.; Singh, M.; Goecke, R.; Gedeon, T.; Zeng, D.; Wang, Y.; Ikeda, K. Emotiw 2023: Emotion recognition in the wild challenge. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Paris, France, 9–13 October 2023; pp. 746–749. [Google Scholar]
| Step | Component | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Encoder | LSTM | Decoder Blocks | Emotion Classifier | ||
| Training | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.7 | 0.2 | 4.2 |
| Inference | 1.1 | 1.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 2.8 |
| Type | Dataset | Subset | Usage | Time (hours) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clean | IEMOCAP [25] | 5531 utterances of four classes (angry, happy, neutral, sad) | tr, va, te | 7.0 |
| Noise | CHIME3 [26] | backgrounds | tr, va | 8.4 |
| MS-SNSD [27] | noise_train | tr | 2.8 | |
| noise_test | va | 0.5 | ||
| NoiseX92 [28] | - | te | 1.0 |
| Methods | Input | Params | Accuracy (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∞ | 0 dB | diff. | |||
| [17] | MFCC | - | 51.2 | 32.1 | −19.1 |
| [18] | WPCC | - | 70 | 30 | −40 |
| [7] | MFCC | - | 72.3 | 48.0 * | −24.3 |
| [19] | 6552 vector | 19.7 M | 62.7 | 47.2 | −15.5 |
| This work | waveform | 4.2 M | 66.2 | 62.4 | −3.8 |
| Methods | Params | Accuracy (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∞ | 20 dB | 5 dB | 0 dB | −3 dB | −6 dB | ||
| [19] | 19.7 M | 62.7 | 60.5 | 51.6 | 47.2 | - | - |
| This work | 4.2 M | 66.2 | 65.5 | 63.8 | 62.4 | 61.0 | 59.0 |
| Methods | Accuracy (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∞ | 20 dB | 5 dB | 0 dB | −3 dB | −6 dB | |
| Proposed (six decoders) | 66.2 | 65.5 | 63.8 | 62.4 | 61.0 | 59.0 |
| speech waveform, pitch (three decoders) | 61.9 | 61.4 | 60.1 | 57.7 | 57.1 | 53.9 |
| speech waveform (two decoders) | 58.6 | 58.8 | 58.3 | 57.7 | 56.8 | 53.4 |
| Methods | Accuracy (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∞ | 20 dB | 5 dB | 0 dB | −3 dB | −6 dB | |
| Proposed | 66.2 | 65.5 | 63.8 | 62.4 | 61.0 | 59.0 |
| w/o 0∼1 kHz | 60.7 | 60.5 | 59.9 | 57.5 | 56.4 | 53.5 |
| w/o 1 kHz∼2 kHz | 61.9 | 61.4 | 60.0 | 58.7 | 57.1 | 54.9 |
| w/o 2 kHz∼4 kHz | 63.2 | 62.3 | 61.9 | 60.8 | 59.6 | 57.2 |
| w/o 4 kHz∼8 kHz | 62.1 | 62.5 | 62.2 | 60.8 | 59.0 | 56.6 |
| w/o pitch | 63.8 | 63.4 | 61.8 | 60.6 | 59.5 | 57.5 |
| Removing Component | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 0∼1 kHz | 1 kHz∼2 kHz | 2 kHz∼4 kHz | 4 kHz∼8 kHz | Pitch | |
| Avg. acc. (%) | 63.0 | 58.1 | 59.0 | 60.8 | 60.5 | 61.1 |
| Acc. deg. (%) | 0 | −4.9 | −4.0 | −2.2 | −2.5 | −1.9 |
| Training Dataset | Accuracy (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clean | 20 dB | 5 dB | 0 dB | −3 dB | −6 dB | |
| IEMOCAP | 47.2 | 47.3 | 46.3 | 45.3 | 45.1 | 44.6 |
| ESD * [31] | 48.7 | 48.8 | 48.4 | 47.5 | 46.1 | 44.3 |
| IEMOCAP + ESD | 58.8 | 58.7 | 57.9 | 56.4 | 55.1 | 52.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nam, H.-J.; Park, H.-J. Speech Emotion Recognition under Noisy Environments with SNR Down to −6 dB Using Multi-Decoder Wave-U-Net. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5227. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125227
Nam H-J, Park H-J. Speech Emotion Recognition under Noisy Environments with SNR Down to −6 dB Using Multi-Decoder Wave-U-Net. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(12):5227. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125227
Chicago/Turabian StyleNam, Hyun-Joon, and Hong-June Park. 2024. "Speech Emotion Recognition under Noisy Environments with SNR Down to −6 dB Using Multi-Decoder Wave-U-Net" Applied Sciences 14, no. 12: 5227. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125227
APA StyleNam, H.-J., & Park, H.-J. (2024). Speech Emotion Recognition under Noisy Environments with SNR Down to −6 dB Using Multi-Decoder Wave-U-Net. Applied Sciences, 14(12), 5227. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125227





