Abstract
Online education review data have strong statistical and predictive power but lack efficient and accurate analysis methods. In this paper, we propose a multi-modal emotion analysis method to analyze the online education of college students based on educational data. Specifically, we design a multi-modal emotion analysis method that combines text and emoji data, using pre-training emotional prompt learning to enhance the sentiment polarity. We also analyze whether this fusion model reflects the true emotional polarity. The conducted experiments show that our multi-modal emotion analysis method achieves good performance on several datasets, and multi-modal emotional prompt methods can more accurately reflect emotional expressions in online education data.
1. Introduction
Online education is a new form of education with a significant impact on the current mode of communication in higher education. Compared with traditional offline education, online education has distinct characteristics and advantages [1,2]. For example, online education platforms, through the use of new technologies, are more convenient for spreading high-quality educational resources and promoting the principle of educational fairness [3]. Through online education, students can fully express their personality and increase their sense of achievement, which also promotes students’ interest in learning and motivation for continuous learning. However, with the current explosive growth of online education, the educational resources of various platforms are uneven [4] and the platforms are not interconnected, which leads to inconsistent student participation and to some students’ online education being ineffective [5]. An analysis of data on the current state of students’ online education can also reflect their learning situation, especially by looking at students’ comments on different courses [6] which directly reflect the students’ attitudes toward their current courses [7]. If this part of the data can be fully exploited, it can be successfully fed back to course instructors, improve the utilization of online education resources [8], and improve the effects of online education on students.
However, in view of the diversity of the current education platform data, it is difficult to unify the evaluation criteria. Many analyses of education data focus on the advantages and disadvantages of educational resources. This part can be successfully evaluated by measuring the amount of playing and the length of click learning. However, for a student participating in learning, their attention is not sufficient and cannot be reflected in more detail [9,10]. In our study, we analyzed data on students’ comments on the current curriculum based on their individual comments. At the same time, we designed an online education emotion analysis method for individual students using multi-modal learning methods and integrating text and emotional expression data. In this process, we paid attention not only to the education resource data but also, and more importantly, to the personalized demand data. This way, we could focus on modifying the education resources so that we can more accurately serve students and improve the quality of the online education platform. Emotional classification using emojis as features has a wide range of applications, such as synchronizing images and text in movies and predicting the emotional tendency of speech using a combination of facial expressions and text. Chen et al. [11] proposed a new method named Visual Voice Cloning (V2C), which can convert text to speech with emotion. Cong et al. [12] proposed a method for switching the frame level of dubbing to the phoneme level, which captures the speaking style while considering the emotion.
The expression of emotion happens jointly through expressions, text, and voice messages. An efficient and accurate analysis of these data is crucial for understanding their characteristics. For multi-modal data that include images and text, current research methods focus on semantically aligning the image and text information, mapping it into a multi-modal space and relying on feature extraction algorithms to ultimately obtain emotional polarity. This approach requires a large amount of high-quality multi-modal data, and while it enhances the accuracy of multi-modal sentiment analysis, it also incurs significant computational cost and data expenses. Moreover, our online education data, especially the comments from students, were often limited in quantity and could not support such large-scale pre-training requirements. Therefore, in this study, we utilized a symbolic emoticon prompt learning method to enhance the emotional polarity of the data. Prompt learning fuses emoticons and text data to jointly constitute multi-modal data features and judge whether emoticon prompts meet the emotional polarity in the classification results.
The format of the collected online education platform comment data is shown in Figure 1. The comment data include text data and emoji data. Generally, emoji data are used as a supplement to text data, that is, the emotional polarity reflected by emoji data is consistent with the text data. However, in some comment data, the text polarity and emoji polarity were inconsistent. In this case, our processing method was primarily based on the polarity of the text expression. In fact, in our research, the emotions expressed by means of emoji data were used as a part of the prompt learning and as a supplement to the semantics of the text data. Each emoji corresponds to one or more emotional labels. For emojis with a clear sentiment polarity, the emotional labels are usually definite. For emojis with uncertain emotional expression, confirmation is needed based on the emotional characteristics of the text. By further optimizing the model, we can control the emotional polarity of emoji symbols within a certain range of emotional polarity thresholds.

Figure 1.
An illustration of the style of online text and emoji data.
We highlighted the words expressing emotional polarity, such as comment 1/2/3. In addition, if no emotional polarity words were detected in the comment, we chose an emotional semantic expression, such as “don’t understand” in comment 1/4.
The main contributions of this paper are as follows:
- In multi-modal sentiment recognition, we used emoji emoticons as prompts, rather than relying solely on text data.
- We studied the effectiveness of emoji emoticons as features in multi-modal pre-training.
2. Related Works
At present, the automatic and intelligent processing of large amounts of data on emotional trends and public opinion are hot research topics [13,14]. On the one hand, emoticons and sticker pack data have become crucial information in people’s daily communications and interactions. Often, a single emoticon can express a more accurate emotional polarity. Therefore, emoticons are widely used and popular in communication. However, data on emoticons are rich and diverse, posing a significant challenge to sentiment analysis models. Examples include effectively incorporating symbolic data into natural language processing (NLP) models and obtaining a multi-modal feature extraction model through semantic alignment. There are many studies on online education, most of which focus on the analysis of education resources and platforms [15,16]. However, there are relatively few analyses of students’ learning effectiveness. Yang et al. [17] proposed multi-channel graph neural networks with sentiment awareness (MGNNS) for sentiment detection in images and text, which introduces multi-channel graph neural networks to learn multi-modal representations based on the global characteristics of the dataset. Liang et al. [18] proposed a method to extract emotional attributes by constructing a knowledge graph and taking each emotional attribute as a node in a graph. Chen et al. [19] proposed an end-to-end reinforcement learning framework that jointly performs counterfactual data generation and dual-sentiment classification. Ashwin et al. [20] proposed a simple sentiment analysis method that uses bag-of-words (BOW) and TF-IDF for classification. Li and Liang et al. [21,22] proposed a dual-graph convolutional network model that fuses syntax structures and semantic correlations simultaneously. Mrityunjay et al. [23] proposed a sentiment analysis method to assess the impact of coronavirus on social life using the BERT model. Jing et al. [24] proposed a hybrid model that applies a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural network to analyze the stock market. Li et al. [25] analyzed the e-word-of-mouth for user behavior. Dashtipour et al. [26] proposed a novel, context-aware, deep-learning-driven Persian sentiment analysis approach [27] that is used to determine the sentiments expressed in movie reviews. Tobias et al. [28] proposed a method that leverages the textual and contextual information of a record for fine-grained sentiment analysis. Zhao et al. [29] proposed a model based on graph representation that embeds knowledge graph information into a language model to improve the sentiment classification accuracy. Dong et al. [30] proposed a model called AdaRNN, which adaptively propagates the sentiments of words to a target depending on the context and syntactic relationships. Wang et al. [31] proposed an attention-based Long Short-Term Memory network for aspect-level sentiment classification, which can concentrate on different parts of a sentence when different parts are used as input. Xue et al. [32] proposed a model based on convolutional neural networks and gating mechanisms that are more accurate and efficient. Li et al. [33] proposed a novel approach that clusters barrages from the same commander in order to solve the problem of repetitive emotional polarity.
Current multi-modal sentiment recognition methods, which utilize text processing and image processing techniques, obtain the textual sentiment features and emoticon features of the input data separately and map these features together into a feature space. Through feature alignment and data similarity processing, they obtain consistent integrated sentiment features and use them for sentiment polarity classification of the data. These methods have achieved certain targets in multi-modal sentiment recognition; however, they require a larger amount of multi-modal data. In this study, based on the particularity of online education review data, we modeled symbolic emoticon data as part of the learning enhancement. Compared to using text as a prompt, using emoticon data can enhance the model’s perception of multi-modal data, and these data can more accurately contribute to the feature extraction of sentiment recognition. In subsequent experiments, we verified the true expressive power of the fusion model through emoticon data prompt learning. Especially in training data where the emotional expressions are not rich, the accuracy of sentiment classification has steadily improved through the enhancement of the emoticon data.
3. The Proposed Method
A block diagram of this study is shown in Figure 2. Our method mainly includes three modules: education data collection and pre-processing, multi-modal emotion analysis, and a fusion prediction module. Next, we introduce the three modules in detail.
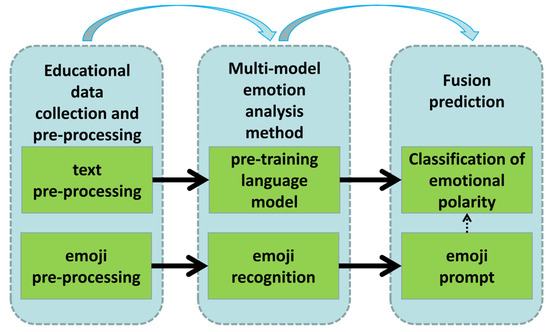
Figure 2.
Overview of proposed approach.
3.1. Educational Data Collection and Pre-Processing
The collection of education data was mainly conducted on several representative online platforms of Chinese higher education, MOOC platforms of Chinese universities (https://www.icourse163.org/, accessed on 1 September 2023), and the national intelligent education platform of higher education (https://higher.smartedu.cn/, accessed on 5 January 2024). For the collected preliminary test data, we first eliminated duplicates and spam data. Repeated screen-swiping comments were deleted. At the same time, some garbage data, such as comments that were unrelated to education, aimless abusive comments, and advertising and marketing comments, were removed. After preliminary data processing, we had 62,340 comment data points from two platforms, comprising 41,820 positive comments and 20,520 negative comments. The proportion of positive to negative comments was approximately 2:1.
For text data, to facilitate batch processing, we limited the length of the comment data. The length of each comment did not exceed 50 characters, and comments exceeding 50 characters were automatically blocked. According to our statistics, comments with more than 50 characters accounted for less than 0.1%, so the deleted characters did not affect the final result trend. In contrast, if a comment was less than 50 characters, it was assigned a null value, which does not express any semantics, and was not given further semantics in the subsequent pre-training process.
We selected two groups of emoji data with strong emotional polarities, as shown in Figure 3. When the emoji data were included in the comment data, we first separated the text and emoji data. For the separated emoji data, we directly identified the emoji’s emotional polarity through the emoji recognition module. In this process, we used a simple emoji-matching method, because each emoji expression corresponds to an emotional polarity; when the emoji expression was effectively recognized, its corresponding emotional polarity value was directly obtained.

Figure 3.
Two groups of emoji data with strong emotional polarities.
3.2. Multi-Modal Emotion Analysis Method
The multi-modal emotion analysis method was divided into two parts: text pre-training and emoji data recognition.
Text pre-training: First, we performed basic operations such as word segmentation and the removal of stop words from the collected text data. The Jieba (https://github.com/fxsjy/jieba, accessed on 1 January 2023) Chinese word segmentation package was used for word segmentation. The Chinese word segmentation package can accurately segment words with semantic relevance into word groups, with an accuracy rate of more than 99.8%. Second, part of the speech tagging was performed on the text data after word segmentation. The purpose of this step is to identify adjectives and adverbs with rich emotional polarity. Of course, entity and functional verbs were also tagged. These words also play a role in semantic recognition.
For training, we used the current efficient BERT model based on an attention mechanism. Specifically, we used random MASK to cover up adjectives or adverbs that represent emotional polarity. In the prediction stage, we predicted the words that were covered to judge the accuracy of model prediction. If the predicted emotional word polarity did not change, the prediction was considered accurate. The final accuracy was calculated from all of the prediction results. The calculation formula (Formula (1)) is as follows:
where the accuracy rate comprises two parts: the prediction accuracy rate of positive emotion words and the prediction accuracy rate of negative emotion words. The final accuracy rate is the average of the two. represents the number of correctly predicted positive emotion texts, represents the number of all positive emotion texts in the test set, represents the number of correctly predicted negative emotion texts, and represents the number of all negative emotion texts in the test set.
Because the predicted emotional words are not always the ideal masked words, in most cases, the predicted emotional words will be the most likely emotional words, selected by means of the calculated probability, which means that the predicted emotional words and the masked emotional words cannot match completely. Therefore, in the actual experiment, we measured the similarity between the predicted emotional words and the masked emotional words, and the number of accurate predictions was calculated by setting the threshold of similarity. The calculation method for the threshold is shown in Formula (2):
where and represent the predictive and masked sentiment words, respectively. cos () calculates the cosine similarity between the two values. The threshold value was initially set to 0.5. When > 0.5, the current prediction is correct. When < 0.5, this indicates that the current prediction is incorrect. Finally, we calculated the number of correctly predicted texts.
Emoji prompt: The emoji prompt improves the accuracy of multi-modal recognition through the prompt method. In most cases, an emoji prompt is used as an aid for emotion classification. The first case includes text and emoji modal data. If the prediction polarity of the text and emoji is the same, the final emotional result is the polarity of the text and emoji. If the predicted polarities of the text and emoji are different, the final emotional result depends on the predicted polarity of the text. In the first case, the polarity of the emoji has no effect. In the second case, the data only include text data but lack emoji data. In this paper, we randomly selected positive and negative emoji expressions from the emoji expression data and added the selected emoji expressions to the relevant text data to predict the emotional polarity after adding positive and negative emoji data. The first case can be used as the prediction result.
In this paper, we automatically added a positive and negative emoji to a piece of text. By means of joint training and ultimately outputting the emotional polarity, we evaluated and judged whether the added emojis were correct. Relying on network training, we ultimately obtained emojis with higher matching degrees and enhanced the model’s accuracy in multi-modal emotion recognition. The structure contains three parts: text input, emoji prompt and polarity prediction, and emoji judgment. The structural diagram of this process is shown in Figure 4.
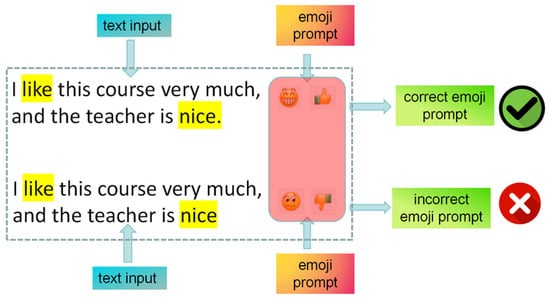
Figure 4.
The structure of emoji prompt.
For an input text, we first recognized the sentiment words. For example, in Figure 4, the words “like” and “nice” can be extracted, and then, the text can be annotated using emojis; following this, the pre-training network determines whether this emoji annotation is correct and whether it accurately matches the text. In actual experiments, each emoji corresponds to one or more emotional labels. For emojis with a clear sentiment polarity, the emotional labels are usually definite. For emojis with uncertain emotional expressions, confirmation is needed based on the emotional characteristics of the text. During training, the embedding vector of each expression corresponds to the embedding vector of its label. This maintains consistency across modal spaces and integrates the expression information into the textual information. Although this method is overly simplistic and direct, it can enhance the accuracy of emotional classification to a certain extent.
In practice, each emoji contains a label, and for ambiguous emojis, there are multiple candidate labels. When the model is uncertain about the true emotion of an emoji, it utilizes textual information to preliminarily determine the sentiment polarity and then selects the final emotional label based on the sentiment polarity.
Fusion prediction: Fusion prediction includes an emotion polarity classification module and an emoji prompt module. For the classification of emotional polarity, we used square loss to correct the back-propagation error, and the calculation method is as follows (Formula (3)):
where represents the predicted value, and represents the real data value.
4. Experimental Results and Analyses
In this section, we first introduce the benchmark datasets, and the parameter settings for our experiments are described. Finally, we compare the performance of several models.
4.1. Datasets and Baseline Methods
Datasets: In this article, in order to verify the effect of our model, we used three public benchmark datasets for evaluation. The datasets are from the Restaurant and Laptop dataset of Sem-eval ABSA and the Twitter dataset of Dong et al. [30]. ABSA provides 19 training and 20 testing datasets, which contain eight languages and seven domains [34], and the kinds of tasks include sentence-level and aspect-level categorization, opinion target expression, and sentiment polarity recognition. The dataset includes Chinese categories, which meet the model’s requirements for feature extraction from Chinese text. The Twitter dataset contains more shot texts, which can obtain features for few-shot data. We chose three categories, Restaurant, Laptop, and Twitter, for our benchmark datasets. The positive and negative numbers in the three datasets are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Statistics for 3 benchmark datasets.
The online comment data were colloquial and concise. To accurately identify emotional words, we collected emotionally opposite words that appeared frequently in comments as seed words. These words are characterized by networking and colloquialism. Some of these words are from the literature [30]. The results are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Positive and negative sentiment feed words.
In this study, we selected several baseline methods for comparative experiments. In this section, we briefly introduce these.
ATAE-LSTM [31] is an attention-based Long Short-Term Memory network for aspect-level sentiment classification.
GTRU [32] is a model based on convolutional neural networks and gating mechanisms that is more accurate and efficient.
AA-LSTM [35] is a novel variant of LSTM, which incorporates aspect information into LSTM cells in the context modeling stage before the attention mechanism.
CapsNet [36], each sentence contains at least two different aspects with different sentiment polarities.
AS-Capsules [37] is capable of performing aspect detection and sentiment classification simultaneously.
GIN/GIN-BERT [38] adopts two attention-based networks to learn the contextual sentiment for the entity and attribute it independently and interactively.
MIMLLN/MIMLLN-BERT [39] treats sentences as bags, words as instances, and the words indicating an aspect category as the key instances of the aspect category.
BERT [40] creates pre-trained deep bidirectional representations from unlabeled text by jointly conditioning both the left and right side in all layers.
Hier-GCN-BERT [41] contains a hierarchy output structure to first identify multiple aspect categories in a review sentence and then jointly predict the sentiment for each of the identified categories.
4.2. Experiments and Discussion
In the experiment, we used the accuracy and F1 values as evaluation indicators. Specifically, the calculation formulae for the accuracy and F1 values are shown in Equations (4) and (5).
where TP/TN/FP/FN denote true positives, true negatives, false positives, and false negatives, respectively. In the formula for F1, P and R denote precision and recall, respectively.
In the first group of experiments, we compared the performance of several models on three datasets, and the results are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
The accuracy/F1 of the compared systems on 3 benchmark datasets.
From Table 3, we can see that our model performs best in the Restaurant and Laptop datasets, but not in the Twitter dataset, where it is, however, still competitive. In addition to the comparison of different models, in the second group of experiments, the specific performances of the different models on educational learning data were compared.
Due to the simple initial matching method used for emoji symbols, there is a high likelihood of model misidentification. To address this, we utilized seed-word-assisted verification to correct misclassification results. Table 4 illustrates the results of the auxiliary error correction, which shows the actual performance of the model before and after the application of seed words.

Table 4.
The accuracy/F1 of the compared systems with/without the use of seed word prompts.
From Table 4, we can see that without the use of seed word prompts and error correction, the model’s accuracy and F1 score both decreased by about 3 percentage points, especially for the Twitter data, which include a richer set of emoji symbols, where the decline is even more pronounced.
Several models based on BERT were selected for comparison: BERT [40], GIN-BERT [38], MIMLLN-BERT [39], and Hier-GCN-BERT [42]. The P-R curves are shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6. Figure 5 shows the performance of different models on the education data, on which our model performs best, and Figure 6 shows the ablation experiment; after using the emoji expression data as the prompt, the performance of the model improved to a certain extent, which also shows that our model is effective in introducing emoji data.
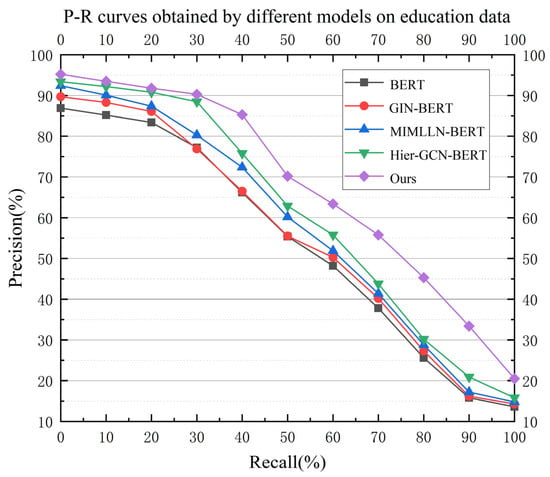
Figure 5.
P-R curves obtained using different models on education data.
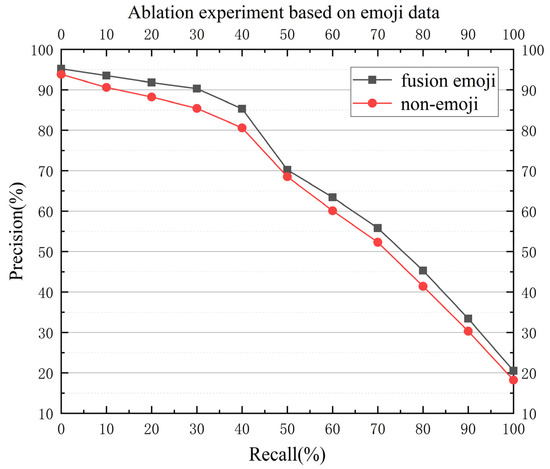
Figure 6.
Ablation curves based on emoji data.
5. Conclusions and Future Work
In this study, we designed a multi-modal emotion analysis method for online education data to assess students’ learning and evaluation. This method uses emoji usage to fuse text data in comments for emotion polarity classification. The biggest difference from the current multi-modal alignment methods is that we enhanced the ability to analyze emotional expressions through the prompt learning method using emoji data, especially for comment data where emotional characteristics were not prominent; the emoji prompt can effectively improve the accuracy of a sentiment analysis. Through comparative experiments, we established the feasibility of the model, and through ablation experiments, it was further proven that the fusion of emoji expression data can indeed improve the accuracy of emotion analysis. At the same time, the model also has some shortcomings. On the one hand, the module for integrating emoji data is too simplistic, relying solely on the simple matching of emoji data to obtain emotional polarity, which introduces significant errors. However, the model focuses more on textual features and uses a relatively simple and singular method for matching emoji data features, without designing more complex emotional feature models specifically for emoji data. This leads to a deficiency in the model’s extraction of emotional features from emoji data, and the feature fusion does not achieve the best results, increasing errors. Therefore, our model can only use emojis for prompt learning.
Our method integrates multi-modal features which can make use of emoji features to increase the dimension of emotion polarity, thus improving the accuracy of emotion analysis. However, our model relies solely on the label characteristics of the emojis and lacks the deep emotional features of the emojis, due to the low computational complexity of the direct matching method of emoji expressions and the lack of deep fusion of emotional features, thus needing to be enhanced in terms of model migration and robustness. In future work, according to the characteristics of the education platform we used, we will further enhance the enthusiasm of the students on the platform to participate, collect more comprehensive comment data, and use the large language model to enhance the data, so as to improve the emotion analysis accuracy of the model and the migration ability of the platform, while further optimizing the emoji emotion module, particularly for modeling prompted emoji data. We will extract more refined emotional features and optimize the fusion algorithm. At the same time, we will expand the dimensions of the multi-modal data further, such as by incorporating multi-frame audio and video data, to enhance the model’s robustness and applicability.
Author Contributions
The authors confirm their contribution to the paper as follows: study conception and design: X.Q. and J.L.; data collection: X.Q.; analysis and interpretation of results: J.L. and Y.Z.; draft manuscript preparation: X.Q. and J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (No. 2022GXNSFBA035510), the Guangxi Key Research and Development Program (No. Guike AB23075178), the Guangxi Key Laboratory of Image and Graphic Intelligent Processing (No. GIIP2207), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62267002).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Birjali, M.; Kasri, M.; Beni-Hssane, A. A comprehensive survey on sentiment analysis: Approaches, challenges and trends. Knowl. Based Syst. 2021, 226, 107134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Cao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Yang, A.; Li, X.; Jia, W.; Yu, S. A survey on deep learning for textual emotion analysis in social networks. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2022, 8, 745–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelke, N.; Chaudhury, S.; Chakrabarti, S.; Bangare, S.L.; Yogapriya, G.; Pandey, P. An efficient way of text-based emotion analysis from social media using LRA-DNN. Neurosci. Inform. 2022, 2, 100048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, H.V.; Karthikeyan, J. CNN based driver drowsiness detection system using emotion analysis. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2022, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandwani, P.; Verma, R. A review on sentiment analysis and emotion detection from text. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2021, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Gao, W. Metaverse-powered experiential situational English-teaching design: An emotion-based analysis method. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 859159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, M.K. A systematic review and meta-analysis of facial emotion recognition in autism spectrum disorder: The specificity of deficits and the role of task characteristics. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 133, 104518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Joshi, S.; Gautam, S.; Maharjan, S.; Khanal, S.R.; Reis, M.C.; Barroso, J.; de Jesus Filipe, V.M. Student engagement detection using emotion analysis, eye tracking and head movement with machine learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Technology and Innovation in Learning, Teaching and Education, Lisbon, Portugal, 31 August–2 September 2022; pp. 52–68. [Google Scholar]
- Iyer, A.; Das, S.S.; Teotia, R.; Maheshwari, S.; Sharma, R.R. CNN and LSTM based ensemble learning for human emotion recognition using EEG recordings. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 4883–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shen, Z.; Zeng, J.; Luo, X.; Lin, H. COSMIC: Music emotion recognition combining structure analysis and modal interaction. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 12519–12534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Tan, M.; Qi, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q. V2C: Visual voice cloning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 21242–21251. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, G.; Qi, Y.; Li, L.; Beheshti, A.; Zhang, Z.; Hengel, A.V.D.; Huang, Q. StyleDubber: Towards multi-scale style learning for movie dubbing. arxiv 2024, arXiv:2402.12636. [Google Scholar]
- Houssein, E.H.; Hammad, A.; Ali, A.A. Human emotion recognition from EEG-based brain–computer interface using machine learning: A comprehensive review. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 12527–12557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, G.; Wen, J.; Liu, C.; Jiang, D.; Cambria, E. Context-and sentiment-aware networks for emotion recognition in conversation. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2022, 3, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, W.; Tao, W.; Liotta, A.; Yang, D.; Li, X.; Gao, S.; Sun, Y.; Ge, W.; Zhang, W.; et al. A systematic review on affective computing: Emotion models, databases, and recent advances. Inf. Fusion 2022, 83, 19–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, C. An influence maximization method based on crowd emotion under an emotion-based attribute social network. Inf. Process. Manag. 2022, 59, 102818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Feng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D. Multimodal sentiment detection based on multi-channel graph neural networks. In Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), Bangkok, Thailand, 1–6 August 2021; pp. 328–339. [Google Scholar]
- Neogi, A.S.; Garg, K.A.; Mishra, R.K.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Sentiment analysis and classification of Indian farmers’ protest using twitter data. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2021, 1, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xia, R.; Yu, J. Reinforced counterfactual data augmentation for dual sentiment classification. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, 7–11 November 2021; pp. 269–278. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, B.; Su, H.; Yin, R.; Gui, L.; Yang, M.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, X.; Xu, R. Beta distribution guided aspect-aware graph for aspect category sentiment analysis with affective knowledge. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Online and in the Barcelo Bavaro Convention Centre, Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, 7–11 November 2021; pp. 208–218. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Chen, H.; Feng, F.; Ma, Z.; Wang, X.; Hovy, E. Dual graph convolutional networks for aspect-based sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), Virtual Event, 1–6 August 2021; pp. 6319–6329. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, B.; Su, H.; Gui, L.; Cambria, E.; Xu, R. Aspect-based sentiment analysis via affective knowledge enhanced graph convolutional networks. Knowl. Based Syst. 2022, 235, 107643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Jakhar, A.K.; Pandey, S. Sentiment analysis on the impact of coronavirus in social life using the BERT model. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2021, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, N.; Wu, Z.; Wang, H. A hybrid model integrating deep learning with investor sentiment analysis for stock price prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 178, 115019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, Q.; Zhong, Z.; Gong, R.; Han, G. E-word of mouth sentiment analysis for user behavior studies. Inf. Process. Manag. 2022, 59, 102784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashtipour, K.; Gogate, M.; Adeel, A.; Larijani, H.; Hussain, A. Sentiment analysis of persian movie reviews using deep learning. Entropy 2021, 23, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashtipour, K.; Gogate, M.; Cambria, E.; Hussain, A. A novel context-aware multimodal framework for persian sentiment analysis. Neurocomputing 2021, 457, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daudert, T. Exploiting textual and relationship information for fine-grained financial sentiment analysis. Knowl. Based Syst. 2021, 230, 107389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Yu, Y. Knowledge-enabled BERT for aspect-based sentiment analysis. Knowl. Based Syst. 2021, 227, 107220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Wei, F.; Tan, C.; Tang, D.; Zhou, M.; Xu, K. Adaptive recursive neural network for target-dependent twitter sentiment classification. In Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (volume 2: Short papers), Baltimore, Maryland, 22–27 June 2014; pp. 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, L. Attention-based LSTM for aspect-level sentiment classification. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Austin, Texas, USA, 1–5 November 2016; pp. 606–615. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, W.; Li, T. Aspect based sentiment analysis with gated convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Melbourne, Australia, 15–20 July 2018; pp. 2514–2523. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Huang, G.; Zhou, Y. A Sentiment Classification Approach of Sentences Clustering in Webcast Barrages. J. Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 16, 718–732. [Google Scholar]
- Pontiki, M.; Galanis, D.; Papageorgiou, H.; Androutsopoulos, I.; Manandhar, S.; AL-Smadi, M.; Al-Ayyoub, M.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, B.; De Clercq, O. Semeval-2016 task 5: Aspect based sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the Pro-Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2016), San Diego, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2016; pp. 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, B.; Liao, L.; Song, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Huang, H. Earlier attention? aspect-aware LSTM for aspect-based sentiment analysis. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.07719. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q.; Chen, L.; Xu, R.; Ao, X.; Yang, M. A challenge dataset and effective models for aspect-based sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), Hong Kong, China, 3–7 November 2019; pp. 6280–6285. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, A.; Huang, M.; Zhu, X. Aspect-level sentiment analysis using as-capsules. In Proceedings of the World Wide Web Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 May 2019; pp. 2033–2044. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, R.; Su, H.; Liang, B.; Du, J.; Xu, R. Extracting the collaboration of entity and attribute: Gated interactive networks for aspect sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing: 9th CCF International Conference, NLPCC 2020, Zhengzhou, China, 14–18 October 2020; pp. 802–814. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yin, C.; Zhong, S.h.; Pan, X. Multi-instance multi-label learning networks for aspect-category sentiment analysis. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.02656. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; Tu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yu, J.; Xia, R. Aspect-category based sentiment analysis with hierarchical graph convolutional network. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Barcelona, Spain, 8–13 December 2020; pp. 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muffo, M.; Cocco, A.; Negri, E.; Bertino, E.; Sreekumar, D.V.; Pennesi, G.; Lorenzon, R. SBERTiment: A new pipeline to solve aspect-based sentiment analysis in the zero-shot setting. In Proceedings of the International FLAIRS Conference Proceedings, Clearwater, FL, USA, 14–17 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).