Cross-Domain Person Re-Identification Based on Feature Fusion Invariance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
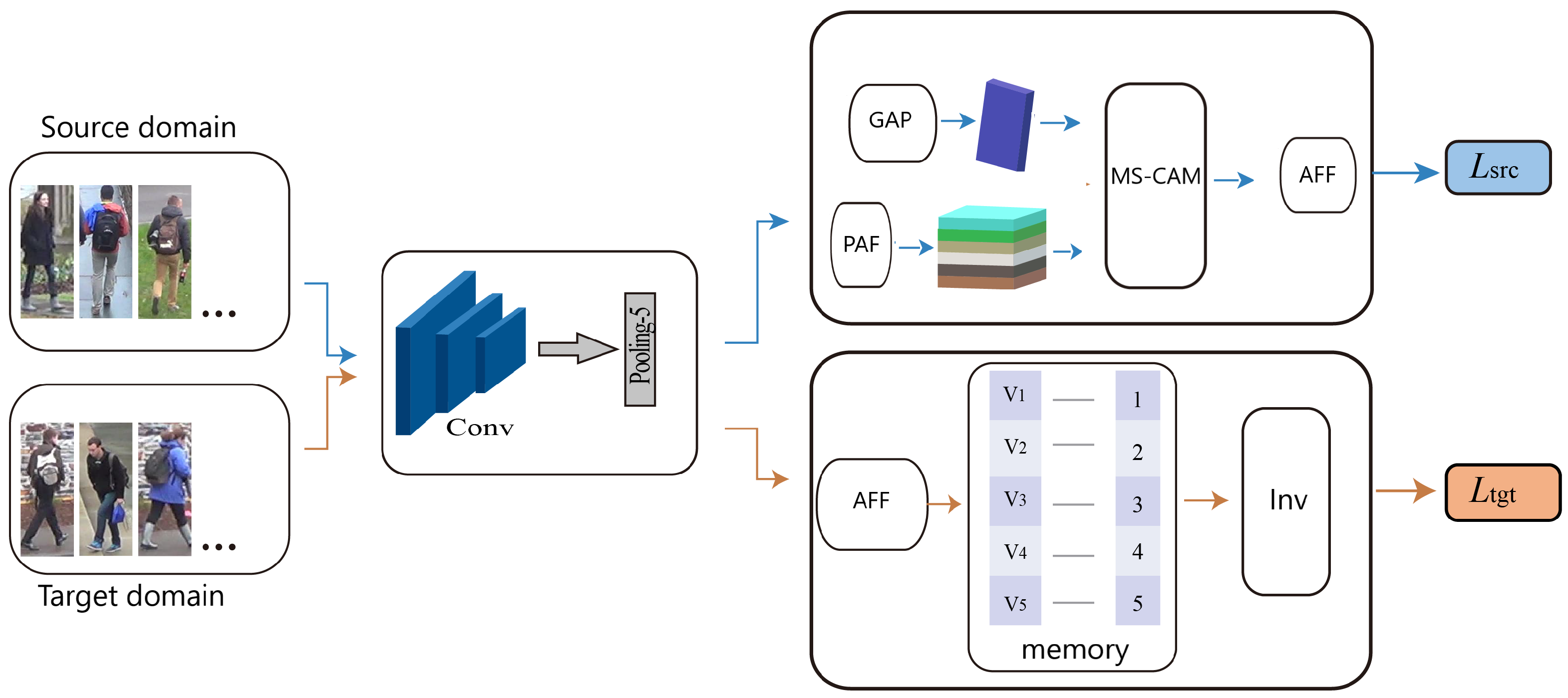
2.1. Framework Description
2.2. Integration Features
2.2.1. Global Feature
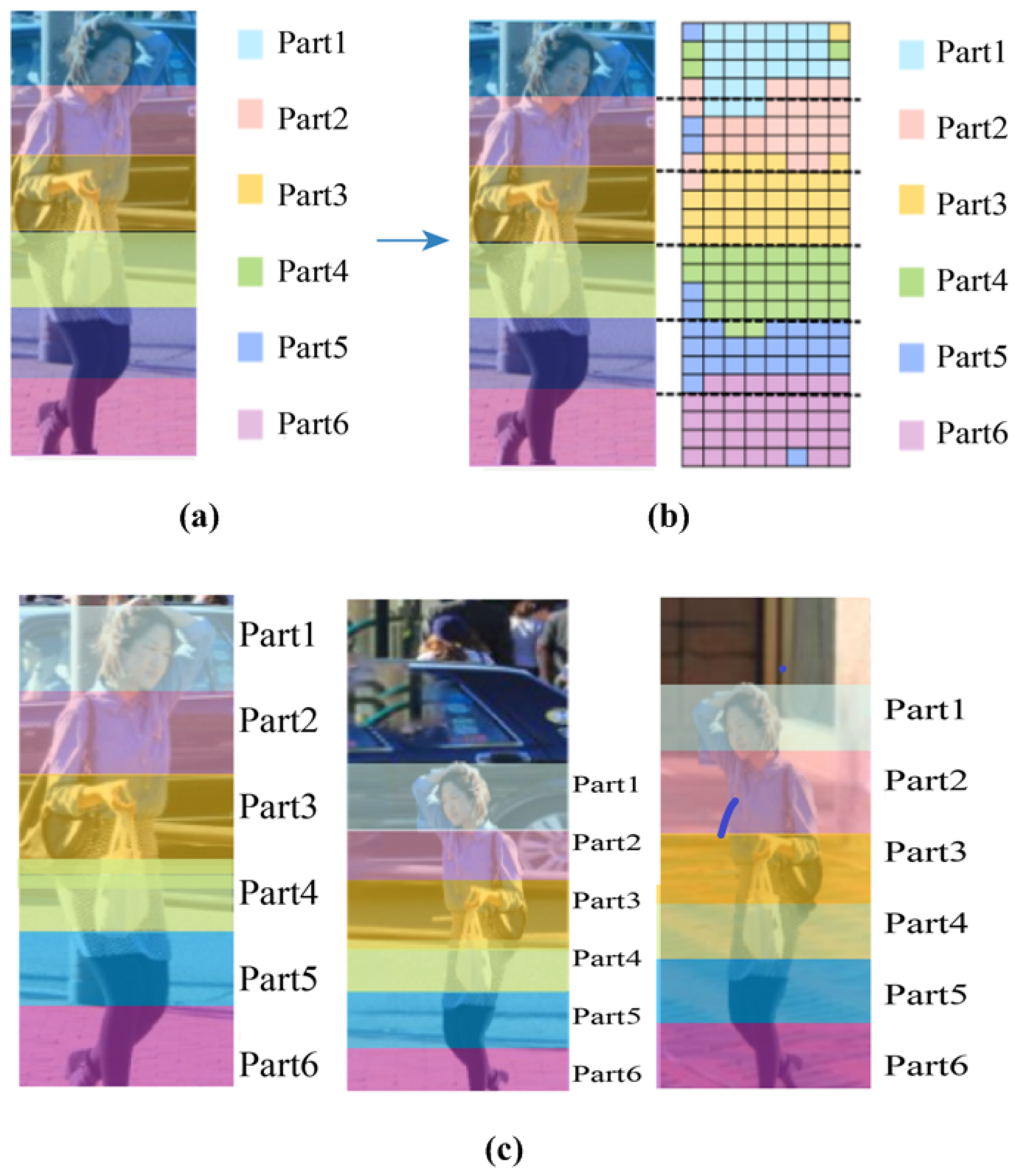
2.2.2. Local Feature
2.2.3. Fusion Features
2.3. Feature Memory
2.4. Feature Invariant Learning
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Ablation Experiment
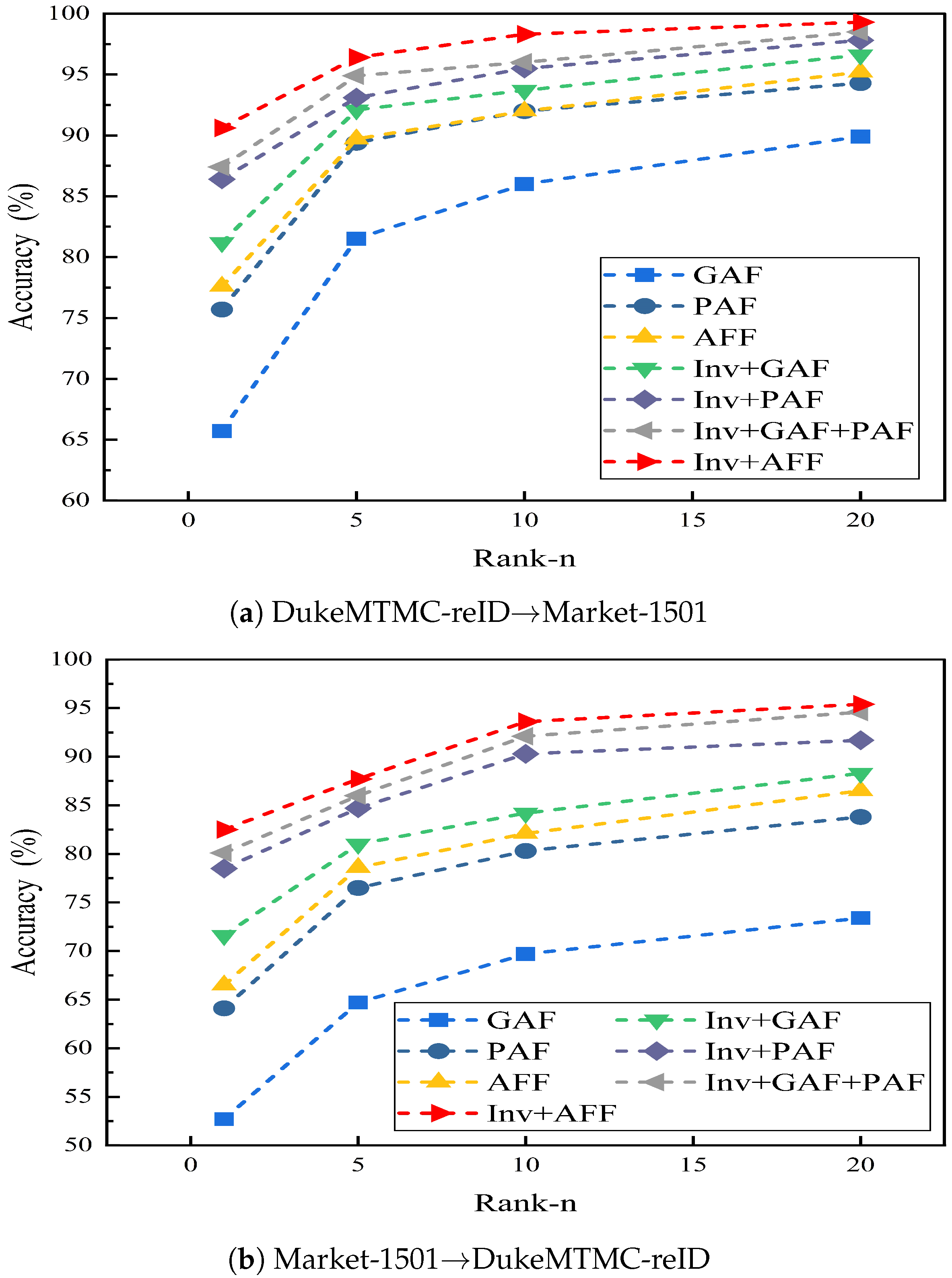
3.1.1. Invariance Analysis Based on Feature Fusion
- (1)
- Effectiveness analysis of local features
- (2)
- Effectiveness of feature fusion
- (3)
- Effectiveness of invariant learning
3.1.2. Analysis of the Importance of Feature Memory
3.2. Comparison Experiment with the Current First-Class Algorithm
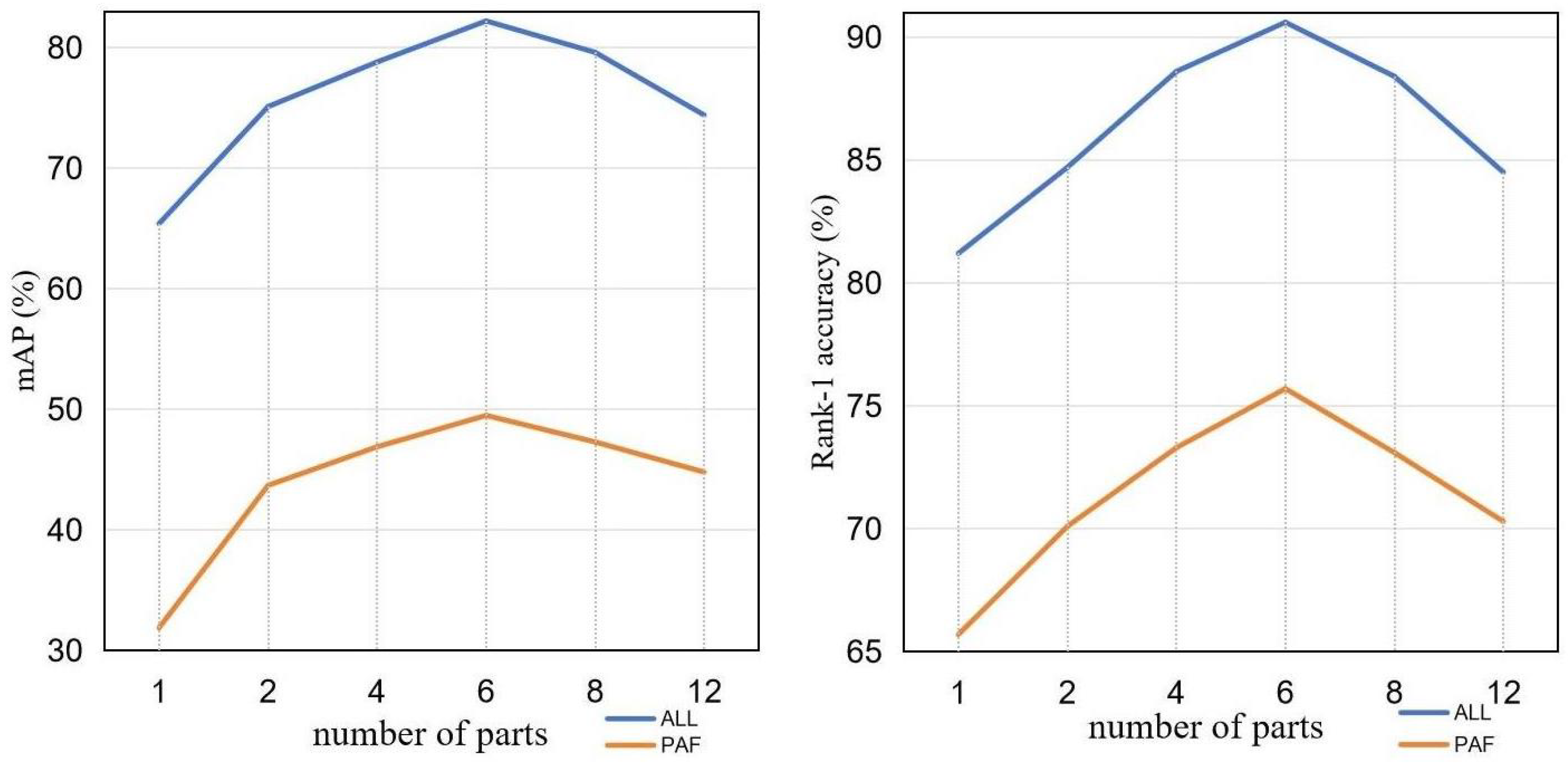
3.3. Parameters Analysis
- (1)
- The number of parts p.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yan, K. Deep transfer learning for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Fourth International Conference on Multimedia Big Data (BigMM), Xi’an, China, 13–16 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, R.; Dong, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yang, Y. Auto-reid: Searching for a part-aware convnet for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3750–3759. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Yao, J.G.; Han, K. Beyond human parts: Dual part-aligned representations for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3642–3651. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Yang, M.; Huang, T.; Dou, Z.; Yu, R.; Xu, Y. Deep-person: Learning discriminative deep features for person re-identification. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 98, 107036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Sun, J. Perceive where to focus: Learning visibility-aware part-level features for partial person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 393–402. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Wang, S. Beyond part models: Person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 480–496. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, H.; Tian, M.; Sheng, L.; Shao, J.; Yi, S.; Yan, J.; Wang, X. Hydraplus-net: Attentive deep features for pedestrian analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 350–359. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Ding, S.; Xie, J.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, W.; Yang, Y.; Ren, Z.; Wang, Z. Abd-net: Attentive but diverse person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 8351–8361. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zou, C.; Wang, M.; Xu, F.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, R.; Cheng, Y.; Chu, W. Dc-former: Diverse and compact transformer for person re-identification. Proc. Aaai Conf. Artif. Intell. 2023, 37, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, H.; Miao, C. Transg: Transformer-based skeleton graph prototype contrastive learning with structure-trajectory prompted reconstruction for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 22118–22128. [Google Scholar]
- Madadi, Y.; Seydi, V.; Nasrollahi, K.; Hosseini, R.; Moeslund, T.B. Deep visual unsupervised domain adaptation for classification tasks: A survey. IET Image Process. 2020, 14, 3283–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, X.; Gong, S. Instance-guided context rendering for cross-domain person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 232–242. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Fookes, C.; Baktashmotlagh, M.; Sridharan, S. Correlation-aware adversarial domain adaptation and generalization. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 100, 107124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.; Shin, Y.; Yoon, Y.; Ham, B. Camera-Driven Representation Learning for Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 11453–11462. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, L.; Peng, Y.; Wen, Z.; Ying, S. Manifold alignment and distribution adaptation for unsupervised domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Shanghai, China, 8–12 July 2019; pp. 688–693. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, H.; Song, J.; Luo, X.; Zheng, F.; Li, W.; Shen, H.T. Meta distribution alignment for generalizable person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2487–2496. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, H.; Li, Y.; Gao, L.; Shen, H.T.; Song, J. Part-aware transformer for generalizable person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 11280–11289. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, B.; Liu, L.; Gao, L.; Lin, G.; Yang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y. Dynamically transformed instance normalization network for generalizable person re-identification. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 285–301. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, N.; Zhong, Z.; Sebe, N.; Lew, M.S. A memorizing and generalizing framework for lifelong person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 13567–13585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Li, K.; Zhong, Z.; Luo, Z.; Sun, X.; Cheng, H.; Guo, X.; Huang, F.; Ji, R.; Li, S. Asymmetric co-teaching for unsupervised cross-domain person re-identification. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 12597–12604. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Xue, D.; Chen, D. Feature diversity learning with sample dropout for unsupervised domain adaptive person re-identification. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 5079–5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, F.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Tao, D.; Gao, X. Logical relation inference and multiview information interaction for domain adaptation person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (TNNLS) 2023. early access. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y.; Zhu, F.; Chen, D.; Zhao, R.; Wang, X.; Li, H. Structured domain adaptation With online relation regularization for unsupervised person Re-ID. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (TNNLS) 2024, 35, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Gieseke, F.; Oehmcke, S.; Wu, Y.; Barnard, K. Attentional feature fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Virtual, 5–9 January 2021; pp. 3560–3569. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, S.; Yao, H.; Gao, W.; Tian, Q. Glad: Global-local-alignment descriptor for pedestrian retrieval. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Mountain View, CA, USA, 23–27 October 2017; pp. 420–428. [Google Scholar]
- Veličković, P.; Cucurull, G.; Casanova, A.; Romero, A.; Lio, P.; Bengio, Y. Graph attention networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.10903. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Shen, L.; Tian, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Tian, Q. Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1116–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Ristani, E.; Solera, F.; Zou, R.; Cucchiara, R.; Tomasi, C. Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 17–35. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.; Zheng, L.; Ye, Q.; Kang, G.; Yang, Y.; Jiao, J. Image-image domain adaptation with preserved self-similarity and domain-dissimilarity for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 994–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, X.; Gong, S.; Li, W. Transferable joint attribute-identity deep learning for unsupervised person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 2275–2284. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, Z.; Li, S.; Yang, Y. Camstyle: A novel data augmentation method for person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Zheng, L.; Li, S.; Yang, Y. Generalizing a person retrieval model hetero-and homogeneously. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 172–188. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.; Zheng, L.; Luo, Z.; Li, S.; Yang, Y. Invariance matters: Exemplar memory for domain adaptive person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 598–607. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, H.; Huang, T.S. Self-similarity grouping: A simple unsupervised cross domain adaptation approach for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6112–6121. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, H. Mutual mean-teaching: Pseudo label refinery for unsupervised domain adaptation on person re-identification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations 2019, New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019. [Google Scholar]


| Method | Market-1501 | DukeMTMC-reID | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Src | R-1 | R-5 | R-10 | R-20 | mAP | Src | R-1 | R-5 | R-10 | R-20 | mAP | |
| GAP | DukeMTMC-reID | 65.7 | 81.5 | 86.0 | 89.9 | 31.9 | Market-1501 | 52.7 | 64.7 | 69.7 | 73.4 | 27.0 |
| PAF | 75.7 | 89.4 | 92.0 | 94.3 | 49.5 | 64.1 | 76.5 | 80.3 | 83.8 | 43.0 | ||
| AFF | 77.6 | 89.7 | 92.0 | 95.2 | 57.0 | 66.5 | 78.6 | 82.1 | 86.5 | 50.8 | ||
| Inv + GAP | 81.2 | 92.1 | 93.7 | 96.6 | 65.4 | 71.6 | 81.0 | 84.2 | 88.3 | 59.0 | ||
| Inv + PAF | 86.4 | 93.1 | 95.5 | 97.8 | 76.6 | 78.5 | 84.7 | 90.3 | 91.7 | 68.4 | ||
| Inv + GAP + PAF | 87.4 | 94.9 | 96.0 | 98.5 | 78.1 | 80.1 | 86.0 | 92.1 | 94.6 | 70.3 | ||
| Inv + AFF | 90.6 | 96.4 | 98.3 | 99.3 | 82.2 | 82.5 | 87.7 | 93.6 | 95.4 | 71.6 | ||
| Method | DukeMTMC-reID → Market-1501 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-1 | R-5 | R-10 | R-20 | mAP | |
| Minibatch | 76.4 | 79.5 | 82.3 | 85.6 | 66.2 |
| Minibatch + Memory | |||||
| Method | Market-1501 | DukeMTMC-relD | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-1 | R-5 | R-10 | mAP | R-1 | R-5 | R-10 | mAP | |
| SPGAN + LM [31] | 57.7 | 75.8 | 82.4 | 26.7 | 46.4 | 62.3 | 68.0 | 26.2 |
| TJ-AIDL [32] | 58.2 | 74.8 | 81.1 | 26.5 | 44.3 | 59.6 | 65.0 | 23.0 |
| CamStyle [33] | 58.8 | 78.2 | 84.3 | 27.4 | 48.4 | 62.5 | 68.9 | 25.1 |
| HHL [34] | 62.2 | 78.8 | 84.0 | 31.4 | 46.9 | 61.0 | 66.7 | 27.2 |
| ECN [35] | 75.1 | 87.6 | 91.6 | 43.0 | 63.3 | 75.8 | 80.4 | 40.4 |
| SSG [36] | 80.0 | 90.0 | 92.4 | 58.3 | 73.0 | 80.6 | 83.2 | 53.4 |
| MMT [37] | 88.4 | 96.2 | 97.8 | 74.6 | 75.1 | 87.3 | 91.2 | 61.0 |
| Ours | 90.6 | 96.4 | 98.3 | 82.2 | 82.5 | 87.7 | 93.6 | 71.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Song, H.; Wei, J. Cross-Domain Person Re-Identification Based on Feature Fusion Invariance. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4644. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114644
Zhang Y, Song H, Wei J. Cross-Domain Person Re-Identification Based on Feature Fusion Invariance. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(11):4644. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114644
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yushi, Heping Song, and Jiawei Wei. 2024. "Cross-Domain Person Re-Identification Based on Feature Fusion Invariance" Applied Sciences 14, no. 11: 4644. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114644
APA StyleZhang, Y., Song, H., & Wei, J. (2024). Cross-Domain Person Re-Identification Based on Feature Fusion Invariance. Applied Sciences, 14(11), 4644. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114644






