Commercially Biochar Applied for Tartrazine Removal from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Adsorption Process
2.3. Desorption and Recycle Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biochar Characterization
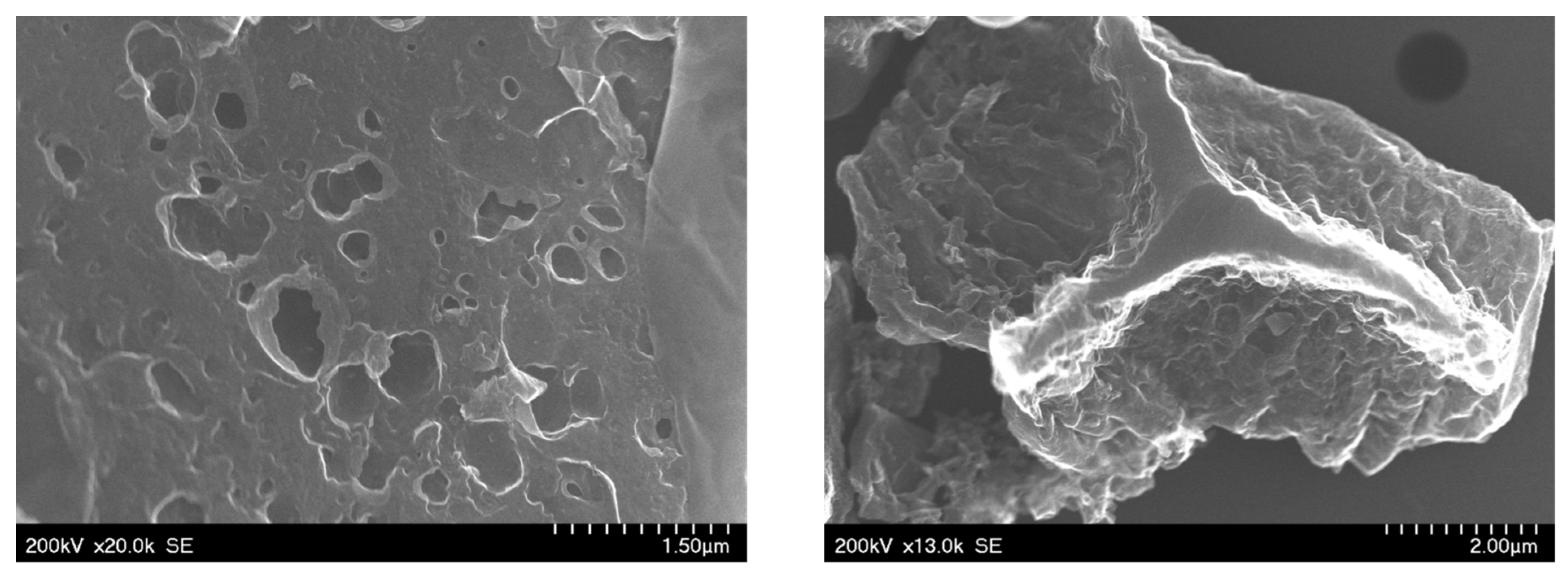
3.1.1. Morphological Characterization
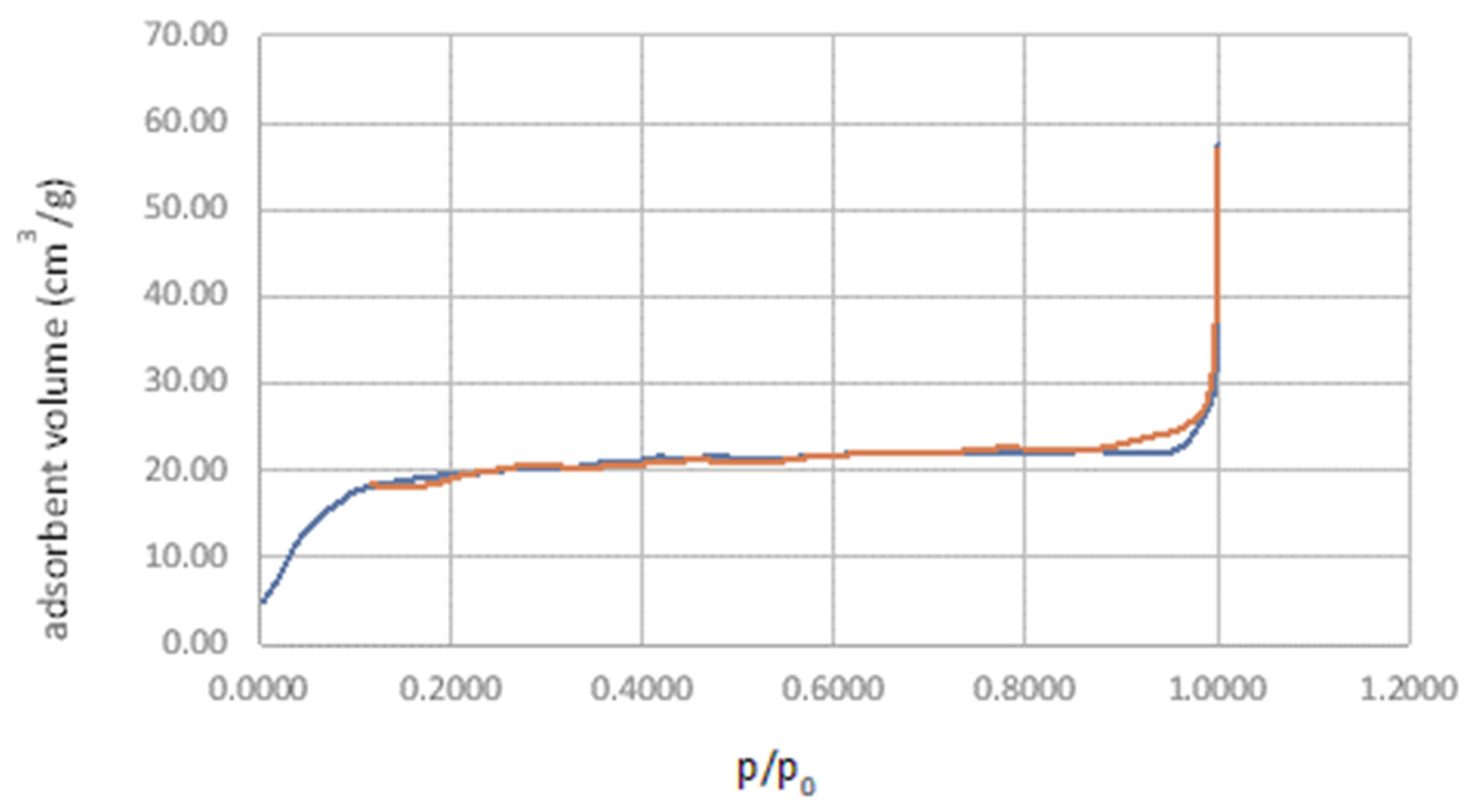
3.1.2. Surface Area
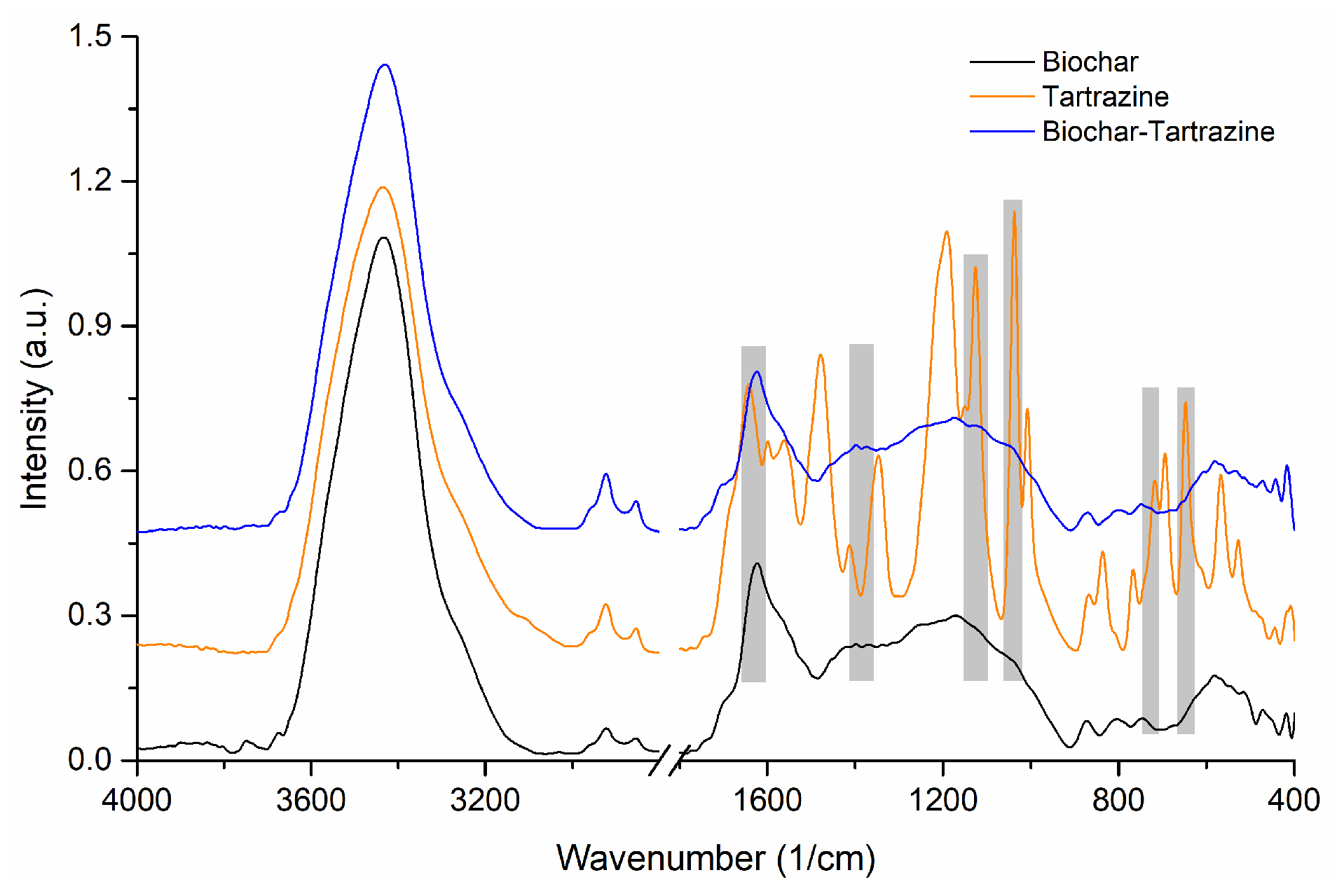
3.1.3. FTIR Analysis
3.1.4. pH at Point of Zero Charge (pHpzc) of Biochar
3.2. Testing the Biochar Efficiency as Tartrazine Adsorbent from Synthetic Aqueous Solutions
3.2.1. The Influence of the Initial pH of the Aqueous Solution on the Adsorption Process
3.2.2. The Influence of the Temperature of the Solution on the Adsorption Process
3.2.3. The Influence of the Adsorbent Dose on the Adsorption Process
3.2.4. The Influence of the Tartrazine Initial Concentration on the Adsorption Process
3.2.5. The Influence of the Contact Time on the Adsorption Process
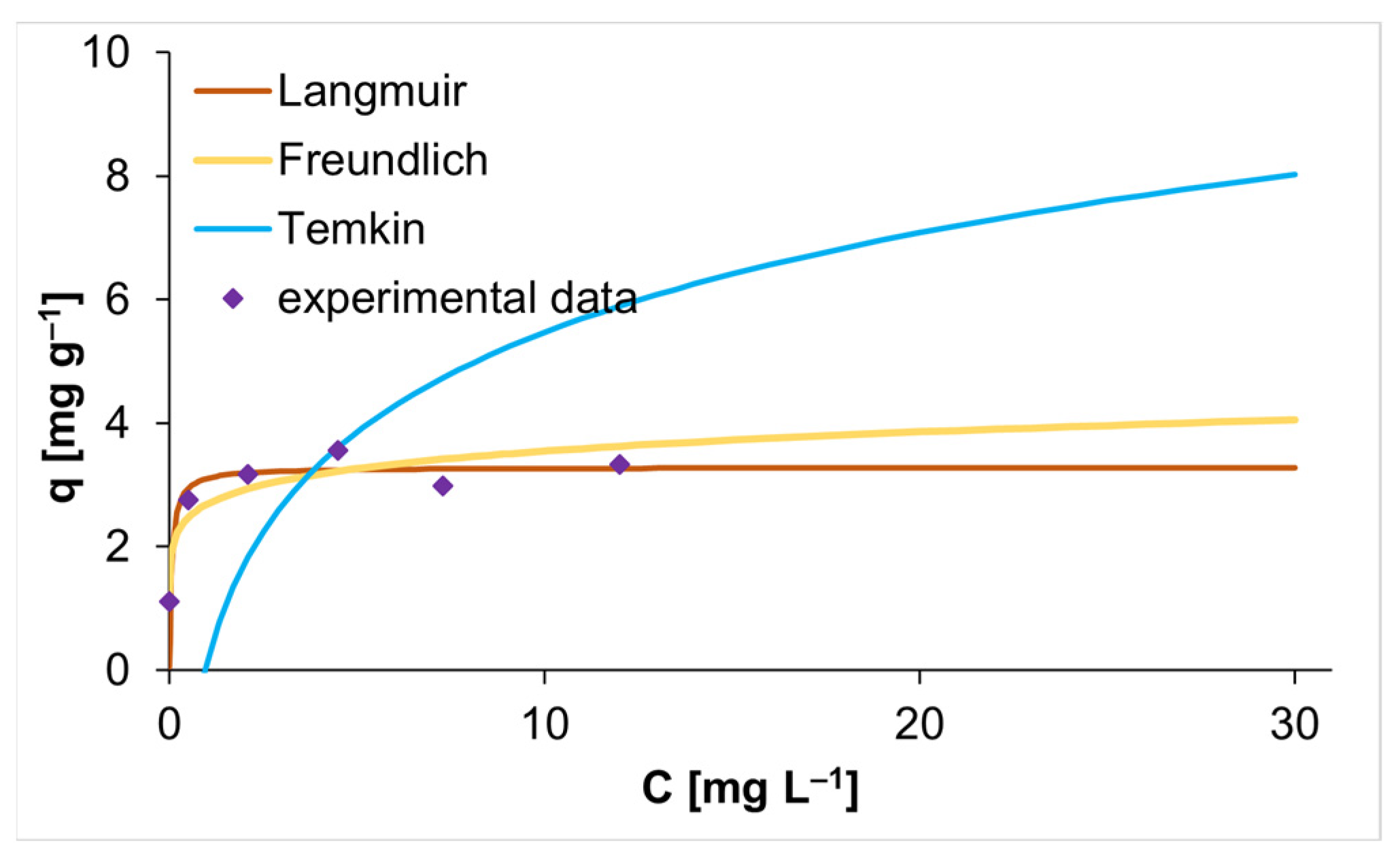
3.3. Adsorption Isotherm
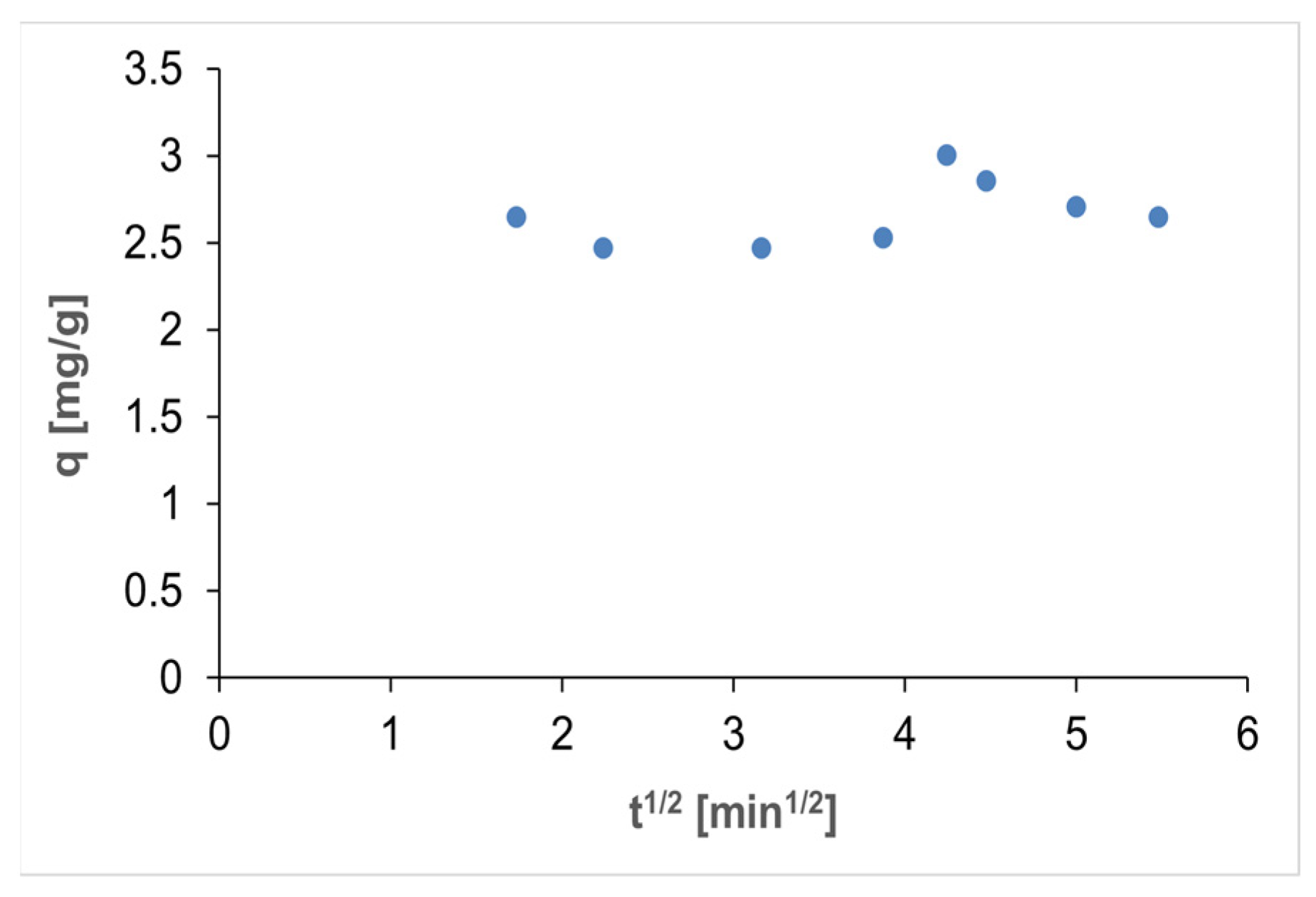
3.4. Kinetic Studies of the Adsorption Process
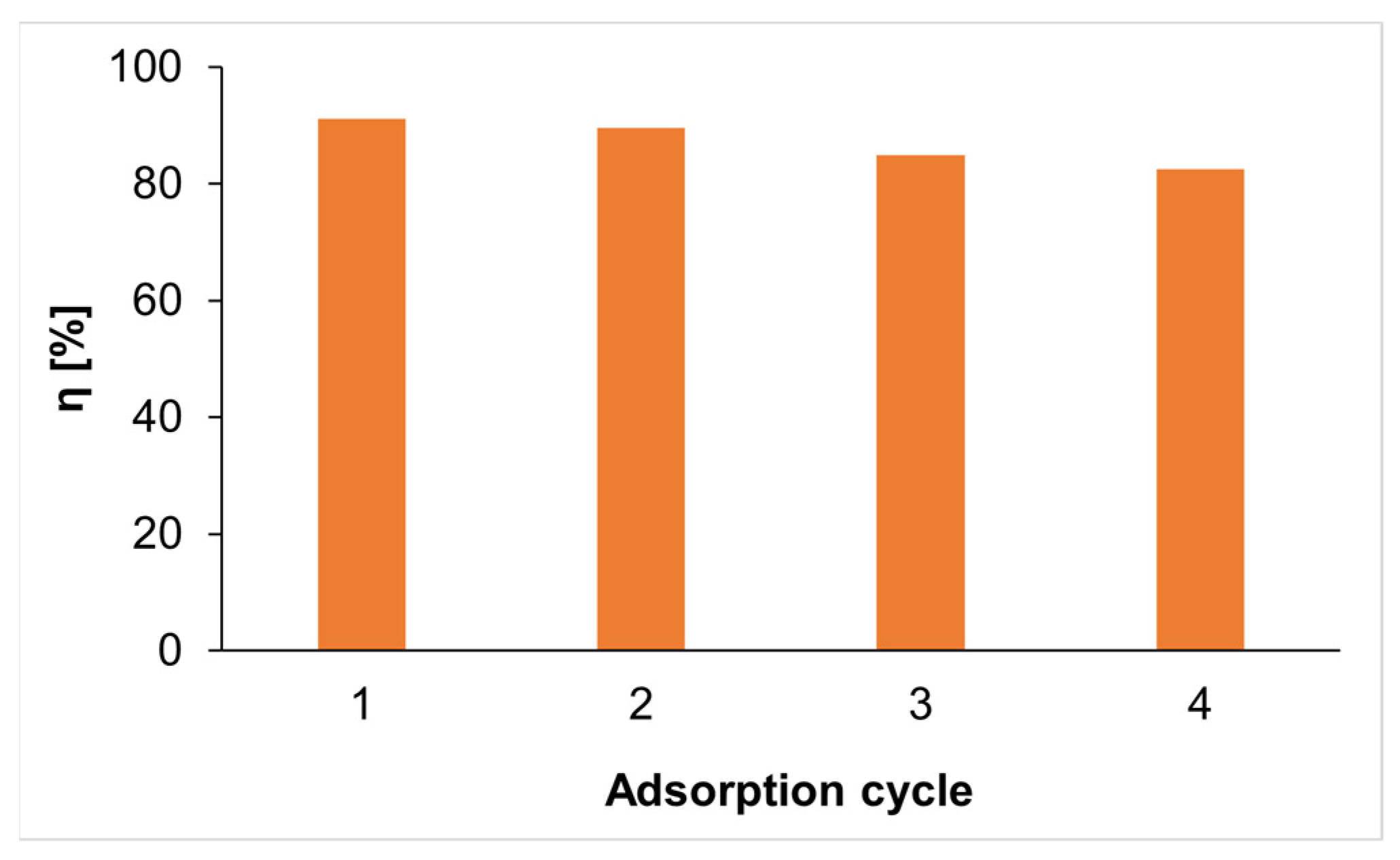
3.5. Reusability of Biochar
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fiorito, S.; Epifano, F.; Palumbo, L.; Collevecchio, C.; Bastianini, M.; Cardellini, F.; Spogli, R.; Genovese, S. Efficient removal of tartrazine from aqueous solutions by solid sorbents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 290, 120910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobylewski, S.; Jacobson, M.F. Toxicology of food dyes. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2012, 18, 220–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amchova, P.; Kotolova, H.; Ruda-Kucerova, J. Health safety issues of synthetic food colorants. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 73, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micheletti, D.H.; da Silva, J.G.S.; Porto, C.E.; Alves, B.H.M.; de Carvalho, F.R.; Sakai, O.A.; Batistela, V.R. A review of adsorbents for removal of yellow tartrazine dye from water and wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 24, 101598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhkim, M.O.; Héraud, F.; Bemrah, N.; Gauchard, F.; Lorino, T.; Lambré, C.; Frémy, J.M.; Poul, J.M. New considerations regarding the risk assessment on Tartrazine: An update toxicological assessment, intolerance reactions and maximum theoretical daily intake in France. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 47, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maekawa, A.; Matsuoka, C.; Onodera, H.; Tanigawa, H.; Furuta, K.; Kanno, J.; Jang, J.J.; Hayashi, Y.; Ogiu, T. Lack of carcinogenicity of tartrazine (FD & C Yellow No. 5) in the F344 rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1987, 25, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borzelleca, J.F.; Hallagan, J.B. Chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity studies of FD & C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine) in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1988, 26, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borzelleca, J.F.; Hallagan, J.B. A Chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity studies of FD & C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine) in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1988, 26, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, Y.F.; Kawaguchi, S.; Kamaya, A.; Ohshita, M.; Kabasawa, K.; Iwama, K.; Taniguchi, K.; Tsuda, S. The comet assay with 8 mouse organs: Results with 39 currently used food additives. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2002, 519, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzig, B.; Kojok, R.; Khalifa, E.B.; Magnacca, G.; Lahssini, T.; Hamrouni, B.; Bellakhal, N. Adsorption performance of tartrazine dye from wastewater by raw and modified biomaterial: Equilibrium, isotherms, kinetics and regeneration studies. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, C.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, Q.; Niu, T.; Pan, L.; Xu, P.; Zhang, F.; Wu, W.; Ni, T. Facile synthesis of three-dimensional hollow porous carbon doped polymeric carbon nitride with highly efficient photocatalytic performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 438, 135623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, C.; Ni, T.; Gao, R.; Ge, J.; Zhang, F.; Wu, W.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q. 3D interconnected porous g-C3N4 hybridized with Fe2O3 quantum dots for enhanced photo-Fenton performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 555, 149677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, T.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, L.; Guo, W.; Pan, L.; Yang, Z.; Chang, K.; Ge, C.; Liu, D. Peroxymonosulfate activation by Co3O4/SnO2 for efficient degradation of ofloxacin under visible light. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2022, 615, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambaye, T.G.; Vaccari, M.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Amrane, A.; Rtimi, S. Mechanisms and adsorption capacities of biochar for the removal of organic and inorganic pollutants from industrial wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 3273–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Goyal, A.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Khatri, M.; Bhardwaj, N. Highly robust UiO-66@PVDF metal–organic framework beads for tartrazine removal from aqueous solutions. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2023, 288, 116165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amdeha, E. Biochar-based nanocomposites for industrial wastewater treatment via adsorption and photocatalytic degradation and the parameters affecting these processes. Biomass Convers. Biorefn. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godiya, C.B.; Ruotolo, L.A.M.; Cai, W. Functional biobased hydrogels for the removal of aqueous hazardous pollutants: Current status, challenges, and future perspectives. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 21585–21612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Recent advances for dyes removal using novel adsorbents: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarnaghasha, N.; Rezaeia, R.; Hayatib, P.; Doroodmand, M.M. Selective ultrasonic assisted synthesis of iron oxide mesoporous structures based on sulfonated melamine formaldehyde and survey of nanorod/sphere, sphere and core/shell on their catalysts properties for the Biginelli reaction. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 104, 109975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamer, B.M.; Aldalbahi, A.; Moydeen, A.M.; El-Hamshary, H.; Al-Enizi, A.M.; El-Newehy, M.H. Effective adsorption of Coomassie brilliant blue dye using poly(phenylene diamine)grafted electrospun carbon nanofibers as a novel adsorbent. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 234, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, C.; Samoila, P.; Pascariu, P. Chitosan-based magnetic adsorbent for removal of water-soluble anionic dye: Artificial neural network modeling and molecular docking insights. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Gupta, B.; Srivastava, S.K.; Gupta, A.K. Recent advances on the removal of dyes from wastewater using various adsorbents: A critical review. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 4497–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgal, D.; Yadav, N.; Singh, J.; Srivastava, G.K.; Mishra, V. Xanthan gum-based copper nano-magnetite doped carbon aerogel: A promising candidate for environmentally friendly catalytic dye degradation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praveen, S.; Jegan, J.; Bhagavathi Pushpa, T.; Gokulan, R.; Bulgariu, L. Biochar for removal of dyes in contaminated water: An overview. Biochar 2022, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, M.B.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Abbas, F.; Bibi, I.; Riaz, M.; Khalil, U.; Niazi, N.K.; Rinklebe, J. A review of biochar-based sorbents for separation of heavy metals from water. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2020, 22, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.; Dey, S. Review on biochar as an adsorbent material for removal of dyes from waterbodies. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 9335–9350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, B.R.; Mukherjee, A.; Nanda, S.; Dalai, A.K. Biochar production, activation and adsorptive applications: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2237–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Ho, S.H.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, N.Q. Highly efficient adsorption of dyes by biochar derived from pigments-extracted macroalgae pyrolyzed at different temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 259, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharm, A.E.; Naeem, G.A.E.; Soliman, H.M.A.; Abd-Elhamid, A.I.; El-Bardan, A.A.; Kassem, T.S.; Nayl, A.A.; Bräse, S. Fabrication and characterization of effective biochar biosorbent derived from agricultural waste to remove cationic dyes from wastewater. Polymers 2022, 14, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokulan, R.; Balaji, S.; Sivaprakasam, P. Optimization of remazol black b removal using biochar produced from caulerpascalpelliformis using response surface methodology. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1535823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Sheng, G.D. Effectiveness and mechanisms of dye adsorption on a straw-based biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5348–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xu, J.; Luo, X.; Shi, J. Efficient adsorption of dyes from aqueous solution using a novel functionalized magnetic biochar: Synthesis, kinetics, isotherms, adsorption mechanism, and reusability. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, F.; Ji, G.; Irfan, M.; Gao, Y.; Shafiq, F.; Sun, Y.; Ain, Q.U.; Li, A. Adsorption performance and mechanism of cationic and anionic dyes by KOH activated biochar derived from medical waste pyrolysis. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Su, L.; Cheng, C.; Cheng, H.; Chang, M.; Liu, F.; Liu, N.; Oh, K. A new type of calcium-rich biochars derived from spent mushroom substrates and their efficient adsorption properties for cationic dyes. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1007630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Reis, G.S.; Bergna, D.; Grimm, A.; Lima, E.C.; Hu, T.; Naushad, M.; Lassi, U. Preparation of highly porous nitrogen-doped biochar derived from birch tree wastes with superior dye removal performance. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 669, 131493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Pillai, S.C.; Bolan, N.; He, J.; Li, N.; Xu, S.; Chen, X.; Lin, Q.; et al. Activated peroxydisulfate by sorghum straw-based biochar for enhanced tartrazine degradation: Roles of adsorption and radical/nonradical processes. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perveen, S.; Nadeem, R.; Nosheen, F.; Asjad, M.I.; Awrejcewicz, J.; Anwar, T. Biochar-mediated zirconium ferrite nanocomposites for tartrazine dye removal from textile wastewater. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Abdelfattah, A.M.; Tharwat, R.M.; Nabil, G.M. Adsorption of negatively charged food tartrazine and sunset yellow dyes onto positively charged triethylenetetramine biochar: Optimization, kinetics and thermodynamic study. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 318, 114297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademoriyo, C.O.; Enyoh, C.E. Batch adsorption studies of sunset yellow and tartrazine using coconut and groundnut shells. J. Biomed. Res. Environ. Sci. 2020, 6, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, I.M.; Paixao, R.M.; Bergamasco, R.; Vieira, M.F.; Vieira, A.M.S. Removal of tartrazine from aqueous solutions using adsorbents based on activated carbon and Moringa oleifera seeds. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villabona-Ortíz, A.; Figueroa-Lopez, K.J.; Ortega-Toro, R. Kinetics and adsorption equilibrium in the removal of azo-anionic dyes by modified cellulose. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albroomi, H.I.; Elsayed, M.A.; Baraka, A.; Abdelmaged, M.A. Batch and fixed-bed adsorption of tartrazine azo-dye onto activated carbon prepared from apricot stones. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2063–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, G.; Tahir, H.; Sultan, M.; Akhtar, N. Synthesis and characterization of cupric oxide (CuO) nanoparticles and their application for the removal of dyes. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 6650–6660. [Google Scholar]
- Lung, I.; Soran, M.L.; Stegarescu, A.; Opriș, O.; Gutoiu, S.; Leoștean, C.; Lazar, M.D.; Kacso, I.; Silipas, T.D.; Porav, A.S. Evaluation of CNT-COOH/MnO2/Fe3O4 nanocomposite for ibuprofen and paracetamol removal from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Feng, Q.; Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Gielen, G.; Wu, W. Rice (Oryza sativa L.) plantation affects the stability of biochar in paddy soil. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.; Deb, M.K. Modified silver nanoparticles-enhanced single drop microextraction of tartrazine in food samples coupled with diffuse reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic analysis. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 3552–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leulescu, M.; Rotaru, A.; Pălărie, I.; Moanţă, A.; Cioateră, N.; Popescu, M.; Morîntale, E.; Bubulică, M.V.; Florian, G.; Hărăbor, A.; et al. Tartrazine: Physical, thermal and biophysical properties of the most widely employed synthetic yellow food-colouring azo dye. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 134, 209–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.D.; Mandavgane, S.A.; Kulkarni, B.D. Fruit peel waste: Characterization and its potential uses. Curr. Sci. 2017, 113, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwala, R.; Mulky, L. Adsorption of dyes from wastewater: A comprehensive review. ChemBioEng Rev. 2023, 10, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar]
- Temkin, M.I.; Pyzhev, V. Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted ion catalyst. Acta Physicochem. 1940, 12, 217–222. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, R.K.; Reddy, D.D. Crop residue ashes as adsorbents for basic dye (methylene blue) removal: Adsorption kinetics and dynamics. Clean Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, D.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Chen, Q.; Wang, C.; Wu, T.; Xu, M. Adsorptive removal of organic dyes via porous materials for wastewater treatment in recent decades: A review on species, mechanisms and perspectives. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X. Modeling of experimental adsorption isotherm data. Information 2015, 6, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahnoun, S.; Boutahala, M.; Tiar, C.; Kahoul, A. Adsorption of tartrazine from an aqueous solution by octadecyltrimethylammonium bromide-modified bentonite: Kinetics and isotherm modeling. C. R. Chimie 2018, 21, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaku, J.F.; Taziwa, R. Thermodynamics, kinetics and isothermal studies of tartrazine adsorption onto microcline/MWCNTs nanocomposite and the regeneration potentials. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahnoun, S.; Boutahala, M. Adsorption removal of tartrazine by chitosan/polyaniline composite: Kinetics and equilibrium studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacioiu, I.G.; Stoica, L.; Constantin, C.; Stanescu, A.M. Removal of tartrazine from aqueous solution by adsorption on activated red mud. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwuemeka-Okorie, H.O.; Ekuma, F.K.; Akpomie, K.G.; Nnaji, J.C.; Okereafor, A.G. Adsorption of tartrazine and sunset yellow anionic dyes onto activated carbon derived from cassava sievate biomass. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennouh, R.; Benturki, O.; Mokhati, A.; Benturki, A.; Belhamdi, B.; Trari, M. Preparation and characterization of highly mesoporous activated carbon from Ziziphus Spina-Christi for tartrazine adsorption from a simulated effluent. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption kinetic models: Physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. J. Hazard Mater. 2020, 390, 122156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagergren, S. Zur theorie der sogennanten adsorption geloster stoffe. K. Sven. Vetensk. Akad. Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; Mckay, G. The kinetics of sorption of basic dyes from aqueous solution by sphagnum moss peat. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1998, 76, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of adsorption carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. Am. Soc. Civil Eng. 1963, 89, 31–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harby, N.F.; Albahly, E.F.; Mohamed, N.A. Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic studies for efficient adsorption of congo red dye from aqueous solution onto novel cyanoguanidine-modified chitosan adsorbent. Polymers 2021, 13, 4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, W.S.W.; Md Ariff, N.F.; Hanafiah, M.A.K.M. Preparation, characterization, and environmental application of crosslinked chitosan-coated bentonite for tartrazine adsorption from aqueous solutions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 206, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Isotherm Model | Linear Form | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | [50] | |
| Freundlich | [51] | |
| Temkin | [52] |
| Isotherm Model | Constants | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | qm [mg g−1] | 3.2841 |
| KL [L g−1] | 17.4000 | |
| R2 | 0.9936 | |
| Freundlich | KF [L mg−1] | 2.6878 |
| 1/n | 0.1207 | |
| R2 | 0.9451 | |
| Temkin | KT [L mg−1] | 1.0486 |
| bT [J mol−1] | 1046.5724 | |
| R2 | 0.3315 |
| Adsorbent | q [mg g−1] | References |
|---|---|---|
| positively charged triethylenetetramine biochar | 85.47 | [38] |
| octadecyltrimethylammonium bromide-modified bentonite | 43.20, 145.80, 175.80, and 201.00 | [56] |
| raw sawdust | 0.80 | [10] |
| activated sawdust | 127.00 | [10] |
| microcline | 37.96 | [57] |
| microcline/MWCNTs | 67.17 | [57] |
| chitosan/polyaniline | 584.00 | [58] |
| activated red mud | 136.98 | [59] |
| activated carbon derived from cassava sievate | 20.83 | [60] |
| activated carbon from Ziziphus Spina-Christi | 160.00 | [61] |
| commercial biochar | 3.28 | present study |
| Kinetic Model | Linear Form | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order kinetic | [63] | |
| Pseudo-second-order kinetic | [64] | |
| Intraparticle diffusion | [65] |
| Kinetic Model | Constants | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order kinetic | qe [mg g−1] | 0.1313 |
| k1 [min−1] | 0.0355 | |
| R2 | 0.1867 | |
| Pseudo-second-order kinetic | qe [mg g−1] | 2.7579 |
| h [mg g−1 min−1] | 2.1245 | |
| k2 [g mg−1 min−1] | 1.0603 | |
| R2 | 0.9889 | |
| Intraparticle diffusion | kid [mg g−1 min1/2] | 0.0630 |
| C | 2.4296 | |
| R2 | 0.1912 |
| Adsorbent | References |
|---|---|
| raw sawdust | [10] |
| activated sawdust | [10] |
| octadecyltrimethylammonium bromide-modified bentonite | [38] |
| cellulose from wheat straw residues | [41] |
| cetyltrimethylammonium chloride-modified cellulose | [41] |
| microcline/MWCNTs nanocomposite | [57] |
| chitosan/polyaniline | [58] |
| activated red mud | [59] |
| activated carbon derived from cassava sievate | [60] |
| crosslinked chitosan-coated bentonite | [67] |
| commercial biochar | this study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soran, M.-L.; Bocșa, M.; Pintea, S.; Stegarescu, A.; Lung, I.; Opriş, O. Commercially Biochar Applied for Tartrazine Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010053
Soran M-L, Bocșa M, Pintea S, Stegarescu A, Lung I, Opriş O. Commercially Biochar Applied for Tartrazine Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(1):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010053
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoran, Maria-Loredana, Mariana Bocșa, Stelian Pintea, Adina Stegarescu, Ildiko Lung, and Ocsana Opriş. 2024. "Commercially Biochar Applied for Tartrazine Removal from Aqueous Solutions" Applied Sciences 14, no. 1: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010053
APA StyleSoran, M.-L., Bocșa, M., Pintea, S., Stegarescu, A., Lung, I., & Opriş, O. (2024). Commercially Biochar Applied for Tartrazine Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Applied Sciences, 14(1), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010053






