Abstract
Thermal infrared detection technology can enable night vision and is robust in complex environments, making it highly advantageous for various fields. However, infrared images have low resolution and high noise, resulting in limited detailed information being available about the target object. This difficulty is further amplified when detecting small targets, which are prone to occlusion. In response to these challenges, we propose a model for infrared target detection designed to achieve efficient feature representation. Firstly, an interval sampling weighted (ISW) module is proposed, which strengthens the fusion network’s spatial relationship modeling, thereby elevating the model’s generalization capability across diverse target-density regions. Next, a detection head founded on 3D attention (TAHNet) is introduced, which helps the network more comprehensively understand the feature details of the target. This enhances the accuracy of the model in identifying the target object’s location, reduces false positives and false negatives, and optimizes the network’s performance. Furthermore, to our model, we introduce the C2f module to transfer gradient information across multiple branches. The features learned using diverse branches interact and fuse in subsequent stages, further enhancing the model’s representation ability and understanding of the target. Experimental outcomes validate the efficacy of the proposed model, showcasing state-of-the-art detection performance on FLIR and KAIST thermal infrared datasets and showing strong antiocclusion and robustness in complex scenes.
1. Introduction
Object detection is a crucial task within the domain of deep learning computer vision, which aims to recognize a particular object within an image or video, pinpointing both its location and category [1].
Notably, significant progress has been achieved in object detection through convolutional neural networks (CNNs), especially in visible light conditions where the algorithm performs exceptionally well. Nevertheless, under conditions of low visibility and extreme weather, object detection is inevitably affected by various factors, which interfere with the identification and localization of the target object, suffering from problems such as missed detection and false alarms in practical applications. This leads to a sharp decline in performance. To tackle this puzzle, infrared detection technology has emerged, finding widespread use in diverse domains like cellular tumor diagnosis [2], privacy preservation [3], marine rescue [4,5], UAV navigation [6,7], and autonomous driving [8,9]. As a result, detecting infrared objects in real time with precision within low-contrast conditions has become a challenge to solve.
Traditional infrared target detection algorithms exhibit instability under such extreme conditions, making infrared detection complicated and elusive. Researchers have made efforts to overcome these difficulties, and some advanced research results have been achieved in the field of infrared target detection based on deep learning [10]. Luo et al. [11] proposed guided attention to color thermal infrared images in a richer semantic encoding way to enable the perception of the environment at night. However, this novel colorization strategy has insufficient generalization ability for different scenes and lighting conditions. Colorization may distort the colors in the image, creating confusion and thus reducing accuracy. Chen et al. [12] attempted to use optical images to compensate for the missing information in infrared images by proposing an integrated detector to fuse the features of thermal and multiple RGB modalities. This competitive approach, however, introduces noise and inconsistency among the data from different modalities, which diminishes the quality of the integrated information. Chen et al. [13] achieved the fusion of encoding and decoding features of input features by using the features generated by a deconvolution scaling decoder, but, in fact, the use of deconvolution layers leads to the loss of spatial information. Zhao et al. [14] introduced a contrast enhancement coefficient as the weighted part of the loss function, aiming to boost the accuracy of small infrared targets. Yet, such adjustment creates a more complicated loss function, which relies too much on prior assumptions and is effective in some specific scenarios but cannot adapt to all intricate scenarios. Although the above methods have achieved leading results in some environments, distinguishing between target and background in realistic, involved, and diverse scenes where color and texture information are lacking in infrared images is still a difficult task, and the performance o the developed methods is often unsatisfactory in practical applications. For this reason, in the face of complex scenes of infrared target detection, it is urgent to establish a powerful and robust model to advance the ability of feature expression and create new breakthroughs for infrared exploration in intricate environments.
In general, object detection can be achieved through two primary detection strategies. The first strategy follows a two-stage approach, with faster R-CNN [15] serving as an example. This approach comprises two key phases: initially, potential object regions are generated by the algorithm, and then the generated candidate regions are classified and adjusted more finely by the CNN. While this strategy offers heightened accuracy, it tends to be time-consuming and not suitable for practical scenarios like unmanned driving. The other is an end-to-end single-stage strategy, including YOLO series [16,17,18], SSD [19], RetinaNet [20], etc., which tries to solve the problem of object boundary box localization using regression methods and completes object detection and localization simultaneously without the need for additional region proposal steps. It significantly surpasses the two-stage model in speed and can provide real-time detection, making it particularly well suited for scenarios with stringent real-time requirements, like running on edge devices [21]. Hence, more and more scholars focused on single-stage detection algorithms and developing more robust and efficient network models to design detectors. This trend indicates that the demand for accuracy, reliability, and efficiency is constantly increasing, which also means that object detection algorithms need to be continuously optimized to meet these new requirements.
The one-stage object detection model generally comprises three key components: a fundamental backbone, a feature-enhanced fusion network in the neck, and a parallel head. These three components collaboratively capture elements from the feature map, ensuring precise object detection [22]. The backbone captures the encoding of features in the input image at different levels. The enhanced feature fusion network acts as a bridge between the backbone network and the head to further refine features. Through upsampling and downsampling operations, the features of diverse dimensions are obtained, and features of diverse scales are fused and compressed to optimize the overall performance of object detection. The prediction network performs object classification and regression of bounding box positions to generate object detection results employing enhanced features. This means that the quality of the feature extraction plays a pivotal role in determining the outcome of the ultimate prediction. Wen et al. [23] used lightweight PConv to replace the original convolutional layer to reduce parameters and introduced coordinate attention in the backbone to enhance the ability to position the target. Du et al. [24] introduced BIFPN to improve the fusion network so that it could capture and utilize multiscale features more effectively, thus enhancing the performance of the object detector. Wei et al. [25] proposed the use of a radius-aware loss function to consider the radius between the prediction result and the target to better evaluate the accuracy of the prediction. Regarding architecture, the head can be categorized into two main methods: anchor-based and anchor-free detection approaches [26]. Among them, the former has stable training, accurate target position regression, and is advantageous when dealing with dense target distribution. In contrast, the anchor-free detection method has higher detection speed, lower computational complexity, but may behave unstably when the target is occluded. Since there is no predefined anchor box, the algorithm may have difficulty in handling cases of occluded targets, resulting in decreased detection accuracy. It is worth mentioning that the current one-stage model YOLOv5, which achieves a flawless blend of accuracy and pace, uses an anchor-based detection method.
To ensure the stability and adaptability of an infrared detection model in complex scenes, this study selected the lightweight YOLOv5 framework as the benchmark model for infrared detection. This study identified three areas where the model needs improvement: (1) Due to the complexity of the real environment and the very weak characteristics of infrared targets, there are still problems such as weak anti-interference ability in the face of multi-scale targets. For example, in the verification of some occluded targets, the model cannot accurately identify them, resulting in reduced accuracy. (2) The fusion feature map is not weighted by the prediction network, which leads to the neglect of important information; yet, in real-life scenes, there is often intricate and abundant contextual information around the object to be detected. (3) Enhancements are required for feature extraction in the model’s backbone. Fine-grained features, including basic contour and texture, are crucial for object detection. However, the current model has shortcomings in low-level feature extraction, resulting in the omission of part of the crucial information about the target. This inadequacy prevents the accurate expression of features for the target to be detected, consequently reducing the detection precision. To tackle these issues, through a series of experiments, it was proven that the improved model significantly optimizes the average precision while maintaining the original running speed. Notably, improving these points proves advantageous in achieving more accurate detection, especially in the case of small infrared targets that are easily occluded in complex scenes. The following are the contributions of this paper:
- We propose a novel interval sampling weighting module in the neck-strengthening feature fusion network; the ISW module converts the feature information from the plane dimension to the channel dimension through interval sampling, which helps to retain more comprehensive positional information. Furthermore, a multidimensional collaborative attention mechanism is introduced to screen and strengthen the features before dimensionality reduction, so that the network focuses on the regions related to the target in the image, thereby expanding the perception range, improving the accuracy, and reducing unnecessary information.
- A 3D-attention-based detection head is proposed. TAHNet boosts model target sensitivity, so that the model may correctly locate and recognize the target. Especially in the face of complex scenes or occlusion, it is helpful for weakening the interference of background noise and optimizing the precision in model detection.
- The C2f is employed as the core feature extraction module of the model. By paralleling more gradient flow branches, the model can obtain more plentiful and hierarchical feature representations, which can accelerate the speed of feature extraction and effectively handle objects of diverse scales and shapes, thereby improving the model’s resilience.
2. Related Studies
The attention mechanism plays a pivotal role in an object detection model, empowering it to concentrate on particular areas within the input information, understanding and processing essential information in the image more accurately [27]. By selectively dampening invalid information, the model’s perception ability is refined. Conventional attention methods comprise spatial attention [28] and channel attention [29]. Spatial attention prioritizes the spatial information of the image while disregarding channel-level details. This may result in the model lacking a profound understanding of the image’s semantics. Improperly designed channel attention, in some cases, may cause the model to excessively rely on certain feature channels, ultimately compromising its generalization ability. However, hybrid attention methods, like CBAM attention [30], follow a two-step approach to learning channel and spatial information, independently calculating weights for the channel and spatial dimensions, which inevitably increases the computation time. In light of this concern, this study opted for a more efficient multidimensional attention method that processes weights between different dimensions synchronously.
2.1. Multidimensional Collaborative Attention
The MCA [31] is a generalized lightweight multidimensional collaborative attention module. Depicted in Figure 1 is the network framework, which designs adaptive squeeze and excitation conversion operations to collect dependencies across three dimensions: width, height, and channel. It operates on an input feature tensor of dimensions , in which the channel direction feature () is directly mapped to the adaptive process of squeeze and excitation conversion. The channel direction weight is then computed utilizing the . Similarly, in the width and height branches, the dimensions of the input feature tensor undergo reordering (the width and height dimensions after conversion are and , respectively), and the weights along the width and height dimensions are determined through employing adaptive transformation operation and the function. Upon completing these operations, the two dimensions of the space are arranged into the original dimensional features (). Finally, the aggregated features from the three branches are integrated by computing their average values. The output is a weighted refined feature layer that encapsulates the collective information obtained through the collaborative attention mechanism acrossmthe width, height, and channel dimensions.
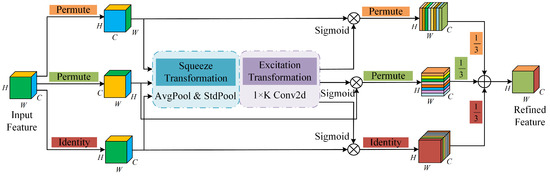
Figure 1.
MCA network structure.
In the case of the width direction, this mechanism can be implemented using the following mathematical formula:
where represents a counterclockwise rotation along the H axis; is the dimension after rotation; and define squeeze conversion and excitation conversion procedures, respectively; is a clockwise rotation to convert to the original dimension; is the weight after processing; is used to obtain the feature layer after conversion to the original dimension.
2.2. SimAM Module
SimAM [32] is a parameter-free and efficient three-dimensional attention. According to the importance of information carried by neurons in various regions, different attention is allocated, making the network prioritize crucial features within the target district, thereby enhancing the feature representation of the target. Different from traditional methods, the 3D weights obtained by the module are directly calculated using a specific energy function, and no additional subnetworks are needed to generate them. The analytical solution defined by the function can infer the 3D weights for the current neuron. It is worth explaining that the existing attention module treats all neurons of the same dimension equally. This module distributes an exclusive weight to individual neurons while simultaneously considering the importance of both channel and spatial dimensions, which is more in line with the characteristics of human attention. In addition, the SimAM module has been embedded into some classical network structures to verify its generalization in disparate tasks.
In visual neuroscience, neurons carrying different amounts of information activate in diverse ways, and the way to find neurons carrying more important information is to determine whether the target neuron and surrounding neurons are linearly separable. Linear separability can be achieved by minimizing the energy function formulation. First, the energy function after introducing the regularization term is described as follows:
where t and are the target and surrounding neurons of the input feature in a single channel, respectively; represents the quantity of neurons within that channel; and i denotes the index of the spatial location. and are the weight and bias transforms.
Secondly, the specific forms of the analytical solutions of and are defined using Equations (6) and (7).
where and represent the mean and variance of every neuron except t, respectively. Then, the minimum energy can be calculated as follows:
Here, and . Equation (5) shows that the lower the energy, the more pronounced the distinction between the target neuron and other neurons, so the significance of the target neuron may be represented using . At this point, we use to define across all channels and spatial dimensions, and then we apply the to as the 3D weight and multiply it by the original input feature.
3. Proposed Methods and Model Architecture
3.1. Overall Framework of the Proposed Model
In order to increase the model’s detection accuracy, an infrared target detection framework with high feature expression ability was developed and is presented in Figure 2. The C2f module is introduced as the backbone feature extraction module of the model, and the gradient information flows into multiple branches to improve the efficiency of data calculation. Each branch can focus on different features, such as edge, texture, color, etc., thereby heightening the expression capacity of the network. Furthermore, enhancing the gradient mobility in the network helps with mitigating the vanishing gradient problem, leading to more efficient training. Specifically, the module contains two convolutional layers and adopts a channel-splitting structure. One branch uses residual maps and the other branch processes information by stacking bottlenecks to form n paths. The C2f_ 2 of the backbone in Figure 2 represents n = 2. SPPF is used in the final phase of the backbone network to mitigate the loss in the receptive field, enabling the capture of multiscale information from the input data, which is very important for detecting objects with different scales in the image. At the same time, the feature layers P3, P4, and P5 are selected to integrate with the abstract feature mapping enhanced by the neck network, and the spatial detail information in the deep features is further extracted through the ISW module to increase the model’s the information representation power, which can capture more comprehensive local and global information, thereby improving detection precision. Additionally, we selected TAHNet as the head prediction network. The postprocessing part follows the original advanced method of YOLOv5, and the bounding box loss function employs CIOU [33], whose expression is described in Equation (10), which is mainly employed to assess the alignment between the predicted box and the real box. Finally, through a series of comparative test evaluations, it is demonstrated that the network model proposed in the study shows excellent performance in complex conditions.
where stands for the ratio of the intersection region of the predicted box and the actual box to the union area. reflects the center distance term and the diagonal length term. v characterizes the width-to-height ratio term, and is an equilibrium coefficient. and stand for the width and height of the true target box, and w and h denote the width and height of the predicted box.
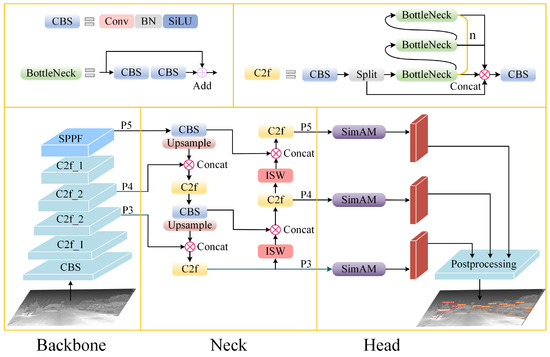
Figure 2.
The global network framework of the detection model. The backbone network uses the C2f module for feature extraction, where C2f_ 2 indicates that the channel split parallelizes two bottleneck structures.
3.2. SPPF Module
Drawing inspiration from the He Kaiming SPPNet [34], the SPP module processes features across distinct levels through parallel multiple max pooling layers. Employing pooling kernels with a consistent step size but distinct sizes (specifically, a pooling layer of , , and ) to process features. The output information layer of each pooling operation maintains the same scale. Following this, the feature maps generated by the four branches are concatenated and spliced according to the channel direction. The SPPF module extends the functionality of the SPP module while improving the efficiency under the same calculation results. Its structure is indicated in Figure 3, which adopts serial mode to connect three pooling layers with pooling cores. Through this sequential pooling operation, the receptive field of each pooling layer can be expanded, enabling the network can grasp the broader scope of global context features. In addition, this approach helps mitigate the loss of spatial information, ultimately enhancing the model’s robustness.
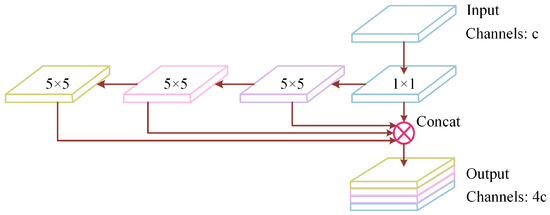
Figure 3.
The SPPF network structure composition. is the convolution layer, and is the maximum pooling operation.
3.3. Interval Sampling Weighted Module
Pooling and convolution with a step size of two are usually used for downsampling in object detection, but these two traditional downsampling methods introduce information loss because they directly discard part of the information. In contrast, interval sampling avoids the risk of feature loss through selectively decreasing the sampling rate. More importantly, the downsampling mode of interval sampling is more in line with the characteristics of deep features, so can retain more comprehensive spatial information, alleviate the spatial mismatch problem, and help capture the overall structure and global context of the target. The neck region has more abundant contextual and semantic information and usually contains object information of distinct scales. The interval sampling downsampling method can not only be used to balance the training importance of the target dense region and the target sparse region but also can better adapt to the objects of these distinct scales to more precisely retain and transfer the relevant information in the feature fusion process.
According to the above viewpoint, this paper proposes an interval sampling weighting (ISW) module. Combined with the module framework chart illustrated in Figure 4 and the following equation, the input feature tensor is set as . Firstly, the original tensor is split into four portions of the spatial dimension information () employing interval sampling, and then the channel dimension information is merged in the direction of the channel to comprehensively obtain abstract semantic features. In addition, the use of multi-imensional collaborative attention before convolution dimensionality reduction to dynamically adjust sample weights and suppress irrelevant or redundant features makes the model focus on the features that are more challenging for network training and generalization. At the same time, the noise in the convolutional input is weakened, which is beneficial for the target detection task with large context dependence and elevates the precision of detecting targets. The final output feature layer is .
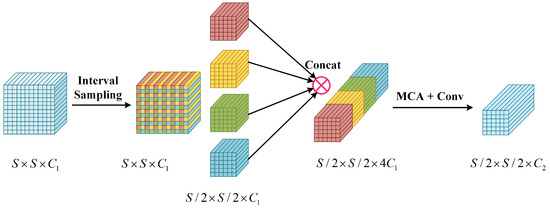
Figure 4.
ISW module network structure.
3.4. TAHNet
The detection head body of YOLOv5 includes three detectors, three scales of grid-based preset prior boxes allocated in each prediction feature layer, and the predictor is utilized to slide the processed fusion feature layer [35]. When the predictor slides to a specific grid, its confidence parameters and regression parameters are predicted for each prior box. However, while this process is efficient, it ignores the fact that diverse regions in each feature map differ in importance. This means that the prediction network does not take into account the correlation between the information features, which may result in a diminished capacity for the model to generalize effectively and thus hinders its adaptation to complex and diverse scenarios.
Intending to verify the preceding ideas, this paper puts forward a detecting head (TAHNet) based on three-dimensional attention, as depicted in Figure 5. Before the fusion feature map derived from the neck network serves as the input for the head prediction network, the SimAM module is introduced to perform three-dimensional weighting processing on the input feature map, which can specifically select and highlight the target area, supply more accurate important feature information in the local region of interest, and give more weight to the features related to the target. Thus, the global abstract information can be effectively utilized. The integration of global features helps with understanding image semantics more accurately and supplies richer feature representations, which improve both the detection precision and the model’s generalization power. The TAHNet detection head output feature layer effects are illustrated in Figure 6.
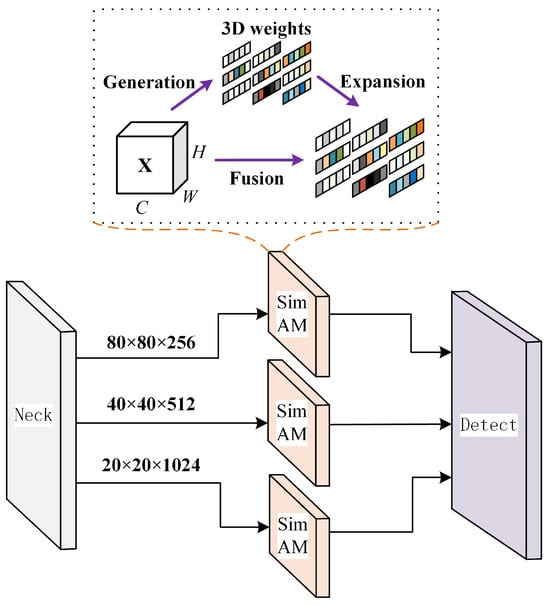
Figure 5.
TAHNet structure rendering.
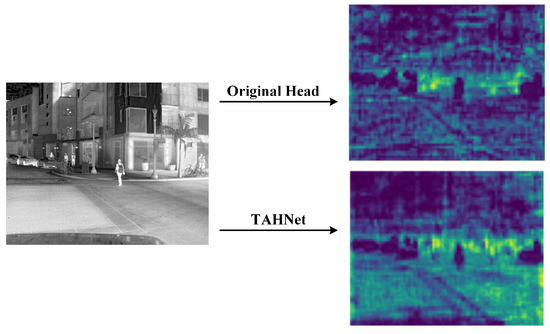
Figure 6.
Visual comparison between TAHNet and original detection head heat map.
4. Experiment and Analysis
4.1. Dataset and Experimental Environment
In this study, we chose the FLIR and KAIST datasets for the exploitation of thermal infrared target detecting and the evaluation of algorithm performance.
FLIR dataset: The FLIR dataset mainly contains thermal infrared images, which are images captured by thermal infrared cameras to capture the heat distribution of objects in the scene, making it able to provide unique information at night and in low-light conditions. The acquisition of infrared data was completed on streets and highways in California during both day and night, covering a range of scenes, involving but not confined to outdoor environments, day and night changes, buildings, and traffic scenes. We selected 10,228 frames of infrared images with annotated resolution in the dataset, which included the categories person, bicycle, and car. To increase the diversity of the dataset and balance the sample distribution, we repartitioned the training dataset and the testing dataset, where the quantity of samples was 8862 and 1366, respectively. In addition, negative samples were introduced in the training phase to help the network study the background information of the object more accurately, increase the model’s generalization capacity, and make the detecting model better-adapted to a variety of different scenarios in the testing phase.
KAIST dataset [36]: The KAIST dataset contains 95,328 aligned thermal infrared and visible images, each with a resolution of . With the intent of improving the training efficiency and reducing the risk of overfitting, the original dataset was cleaned to remove redundant or unnecessary samples. When training a model, a cleaner dataset can speed up the convergence process and reduce the overfitting of the model to noisy and abnormal conditions. The cleaned version of the dataset contained 9858 thermal infrared images with a 9:1 training and test set partition ratio, and we labeled the category “pedestrian”. We experimentally verified that cleaning data increased the overall quality of the data, ensured that the dataset met the requirements of the task, and helped with more accurately evaluating model performance.
Table 1 shows the configuration of the specific hardware devices used for model training and the evaluation framework of the software platform that provided environmental support.

Table 1.
Framework for the evaluation of the experimental platform.
Hyperparameter initialization holds a key position in object detecting tasks, and setting the appropriate intensity can make the model learn more efficiently. The hyperparameter configuration in this study is shown in Table 2. The input sample size of the network was set to ; the learning rate and momentum were 0.01 and 0.9; the selection of regularization technology weight attenuation and batch size was 0.005 and 16, respectively; and the training cycle length of the model was 100 epochs.

Table 2.
Hyperparameter settings for model training.
4.2. Performance Evaluation Metrics
Intending to analyze a model’s results for different categories and the overall performance, precision (P) is utilized to evaluate the veracity of the model predicting positive samples, recall (R) is employed to evaluate a model’s power to identify all positive samples, whereas the F1 score thinks about the overall performance of precision and recall. The average precision (AP) characterizes the area under the PR curve, representing the average of the model’s predicting precision over different classes, and the mean average precision (mAP) is the average of the average accuracy over all classes. These metrics enable a thorough evaluation of an object-detecting system’s performance in predicting both positive and negative classes and provide an overall insight into the effect of the model. Specifically, the expressions for precision and recall are:
where TP (true positive) stands for the quantity of true positive examples, FP (false positive) reflects the quantity of negative examples that are misjudged as positive examples, and FN (false negative) presents the quantity of positive examples that are misjudged as negative examples.
The F1 score is a comprehensive evaluation index, which is the harmonic mean between [recision and recall, and is suitable for the comparison of different model performances. Its equation is expressed as follows:
In object detection tasks, the average accuracy is evaluated by quantifying the area beneath the precision–recall (PR) curve. For each category, the values of the precision and recall under that category are calculated, and then the average accuracy is calculated based on the PR curve. The average accuracy mean provides a comprehensive performance assessment of the model over the entire dataset, taking into account multiple categories of prediction accuracy. The AP and mAP expressions are shown in Equations (18) and (19).
4.3. Analysis of Ablation Experiment
Ablation contrast experiments are scientific research methods designed to help researchers understand the effects of different components of a target detection model on its overall performance. This means that by modifying certain components, settings, or the model’s parameters, the contribution of these factors to the model’s performance can be fully deduced from the findings of the experiment. In this section, the detection performance effects of ISW, TAHNet, and C2f modules when used alone and in different combinations are discussed in detail. This experiment was verified on the public FLIR dataset, and a series of comparative tests were conducted based on the framework of the YOLOv5n model.
As illustrated in Table 3, when the three proposed modules act on the network at the same time, the model performance is the best. However, the interaction between modules is not all shared facilitation; for example, the recall of ISW+TAH modules combined in a stack is 0.7% lower than that of TAH modules alone. The reason for this phenomenon is that when two modules are used at the same time, if there is a lack of complementarity, involving overlapping information or trying to deal with conflicting information, information disharmony occurs, resulting in performance degradation. The optimal incremental order of different module combinations is given and the growth curve of its mAP is intuitively displayed in Figure 7.

Table 3.
Comparison of network performance under various combinations modules, where 🗸 stands for the module currently in use.
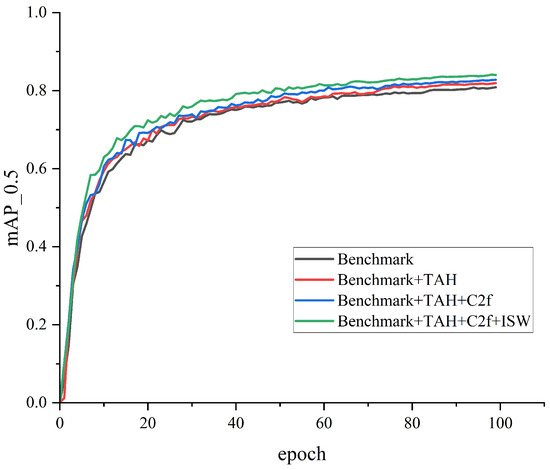
Figure 7.
The mAP performance curves for incremental ordering of modules. The curve shows that the combination of Benchmark+TAH+C2f+ISW has the best performance.
Benchmark module + TAH: First, select the detection header of the optimized network to increase the positioning ability of the model. When the improved TAH policy is applied to the network alone, the weight value is obtained via function mapping, and the new parameter number and complexity are not introduced. Compared to the benchmark model, the precision, recall, F1, and mAP of the improved detection head increase by 0.7%, 2.0%, 1.0%, and 1.1%, respectively, reducing the problem of missing detection targets.
Benchmark module + TAH + C2f: Secondly, to strengthen the feature extraction capability of the backbone, the C2f strategy is proposed to introduce more abundant gradient information. On the basis of TAH, C2f is added to network training to further improve the model’s detection effect. The test outcomes showed that the recall increased by 3.3%, mAP increased by 1.9%, and the generalization capacity of the network increased.
Benchmark module + TAH + C2f + ISW: In the end, to develop the feature fusion power of the network for multiscale targets, the ISW module was developed to capture spatial semantic information more comprehensively. The recall, precision, F1, and mAP of the overall model increased by 4.4%, 1.3%, 3.0%, and 3.1%, respectively, indicating that the detecting performance of the network on easily blocked infrared objects was effectively improved. Therefore, the experiment verified that these three modules have good complementarity and can make up for the defects of different modules to improve the overall performance and achieve optimal performance.
4.4. Comparison of Diverse Models on FLIR Dataset
To further verify the efficacy of the proposed method, several different single-stage target detection algorithms were selected by utilizing the uniform equipment and infrared dataset and setting the uniform experimental arguments. The performance of the infrared target detection algorithm in a complex environment was compared using various detection and evaluation indices.
Figure 8 includes the visual effect presentation of the original label, YOLOv5, YOLOv7-tiny, and the method proposed in this study. Obviously, our proposed model has excellent performance in detecting easily occluded infrared objects in intricate conditions, which improves the model’s resistance to noise and interference. For example, on account of the low contrast of infrared images in a real environment, the distinction between the target and the backdrop becomes blurred, increasing the difficulty of detection. During the detection using YOLOv5 and YOLOv7-tiny, there was a situation of missing detection, and no distant infrared small target was identified. However, the green circle marked in Figure 8 indicates that the network proposed in this paper could comprehensively identify all objects and avoid missing detection, indicating that the improved model has certain universality and adaptability, not limited to specific types of targets, provides a reliable solution for application in actual scenes, and can better maintain detection performance even in the case of intricate conditions or occlusion.
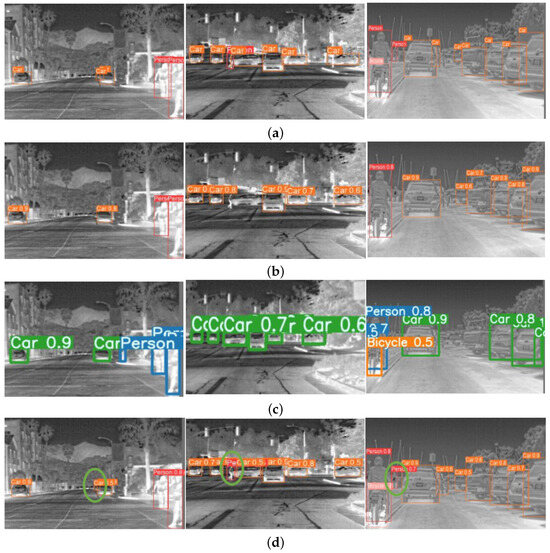
Figure 8.
Visual effects of diverse infrared detection models based on FLIR dataset. (a) Ground truth of the original label; (b) YOLOv5n; (c) YOLOv7-tiny; (d) ours.
The data in Table 4 clearly reveal that compared with the most advanced target-detecting models at present, the method in this study provides leading improvements in several indicators, with mAP, precision, and F1 scores reaching 84%, 86.8%, and 81%, respectively. Specifically, the proposed algorithm achieves mAP and F1 that are 16.1% and 13% higher than those of the SSD algorithm, while the model size is only one-fortieth, demonstrating improved detection results. In addition, our method mAP outperforms the latest lightweight YOLOv7-tiny algorithm by 5.2% in terms of precision. The above analysis illustrates that the method in this study has a strong feature expression ability, which is more in line with real needs and is more stable and reliable for practical use. Figure 9 concisely and intuitively illustrates the overall trend in the model across diverse metrics to better understand the holistic performance characteristics of the model.

Table 4.
Performance contrast of diverse one-stage models. The best data are described in bold.
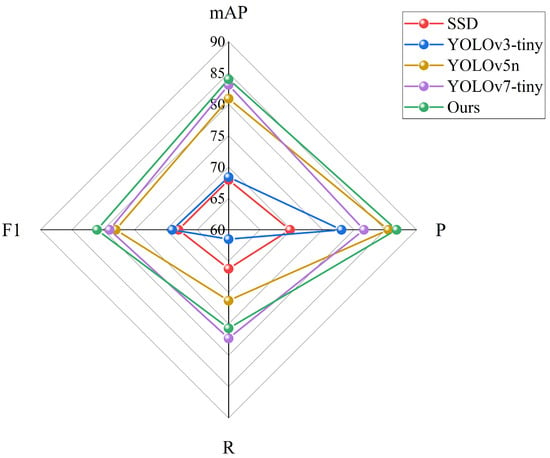
Figure 9.
Various one-stage models’ performance indicators comparison chart.
Within the realm of infrared detection, on account of the open source and data diversity of the FLIR dataset, many scholars have explored of infrared object detection with a basis in this public resource in recent years. Therefore, aiming at the three categories of AP and mAP indicators, this study selected the most popular and excellent infrared image detection methods to carry out a succession of comparative analyses. In addition to the YOLO series, the comparison method also included MMTOD-CG, TermalDet, CMPD, and other multimode detectors based upon the complementary information fusion of visible and infrared images. Table 5 lists the experimental results of all the above models.

Table 5.
Performance effect of various algorithms on FLIR dataset when IOU = 0.5. The best two data are described in bold.
The superiority of the presented strategy is clearly observable in Table 5, where mAP reaches the highest level of 84% of all comparison models. Specifically, the latest multispectral pedestrian detection CMPD method achieves more reliable multimodal feature fusion by attaching a confidence subnetwork; BU(AT, T) adopts a domain adaptation strategy to retain more visible domain feature information; and these methods achieve good results. However, the average -recision in the Person category is 15.5% and 9% lower than ours, respectively. Among the other methods, the highest mAP value was achieved by the most advanced multistage detector Cascade R-CNN and anchor-free detection algorithm YOLOX; and our method achieved values 3.5% and 2.8% higher than theirs. The contrasting results of the data mentioned above prove the validity and rationality of the module presented in this study. In addition, Figure 10 displays the F1 score curve and the PR curve for each category of our model.
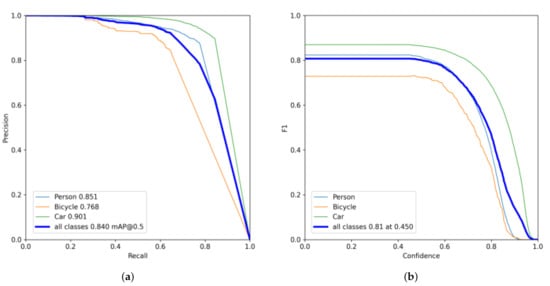
Figure 10.
Performance curves of the proposed infrared target detection method. (a) PR curves; (b) F1 curves.
4.5. Comparison of Various Models on KAIST Dataset
For the sake of evaluating the universality and reliability of the algorithm, the model’s performance was further verified on the cleaned KAIST pedestrian dataset in this study. The results, as displayed in Table 6, in comparison with the most progressive YOLO series models, the algorithm’s performance presented in this study is better, achieving ideal results in various evaluation indicators. This demonstrates that our model boasts a powerful capacity to generalize and can be flexible given the detecting requirements of various environments. Specifically, our precision, recall, F1 score, and mAP are as high as 96.6%, 92.2%, 94%, and 97.5%, outperforming the baseline model by 2.4%, 2.5%, 2%, and 2.7%, respectively. In general, our mAP is 2.7 to 17.9% higher than that of other methods, and the running time is reduced by 50 to 84%, confirming that our model is highly adaptable to different datasets and reduces the risk of performing well on a single dataset while having sufficient generalization ability. Figure 11 provides a more intuitive and clear data comparison trend to fully assess the overall effectiveness of the method as well as visually demonstrate the excellent performance of our approach on various performance indicators.

Table 6.
Performance data of different IR detection models based on the KAIST dataset. *-labeled model results are from [43], and the best data are described in bold.
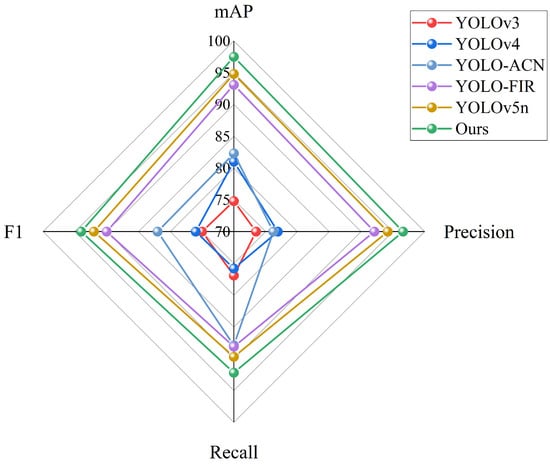
Figure 11.
Various YOLO series detection models’ performance indicators comparison chart.
From the visual detection effect diagram in Figure 12, it is observable that our model’s detecting efficacy in complex scenes perfectly coincides with the detection target box of the original mark. Even with interference in the vicinity or unsatisfactory conditions, the method maintains highly accurate detection, indicating that the proposed model has excellent target information feature transmission ability and generalization ability and can correctly identify and locate infrared targets in practical applications with excellent performance.

Figure 12.
Visual effects of detection based on original markers and the proposed model on KAIST pedestrian dataset.
5. Conclusions
To create an innovative solution to the challenges of background noise interference and target occlusion loss information in thermal infrared images, this study proposed an infrared object detecting algorithm with a basis in deep learning with efficient feature extraction in complex scenes. With superior accuracy and robustness compared to other mainstream models in this field, this algorithm effectively overcomes some of the obstacles posed by thermal infrared images. To achieve these results, our proposed method utilizes an ISW module to expand the perception field of the fusion network for input data, which is beneficial for dealing with different sizes and occluded targets in infrared images. Additionally, TAHNet enables the detection head to better handle various shapes and poses, further enhancing the model’s robustness. Finally, the C2f module optimizes the feature extraction process, comprehensively capturing different features in the image and more accurately identifying the infrared target.
Infrared target detection remains a dynamic research area with vast potential for exploration. The algorithm presented in this study has strong feature expression capacity; in the future, our primary research emphasis will be on developing a lightweight network framework, aiming to attain a harmonious balance between exceptional precision and swift computation. Simultaneously, we intend to validate the detection performance across a broader spectrum of infrared target datasets. With advancing technology and the development of more practical applications, we expect to see increasingly advanced systems that accurately detect infrared targets in real time.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Y. and H.W.; data curation, H.W. and S.L.; validation, J.Y., H.W. and S.L.; software, H.W. and S.L.; methodology, J.Y. and H.W.; formal analysis, J.Y. and S.L.; resources, J.Y.; investigation, S.L. and S.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, H.W.; visualization, H.W. and S.Z.; writing—review and editing, J.Y., H.W., S.L. and S.Z.; funding acquisition, J.Y.; project administration, S.Z.; supervision, J.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by EEG recognition and service robot control based on structure optimization deep network in the background of high noise, grant number 61673079.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. The FLIR dataset can be found at https://www.flir.com/oem/adas/adas-dataset-form/, accessed on 29 August 2022. The data presented in this study are openly available in KAIST at https://www.doi.org./10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298706, reference number [36].
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to Yu for providing assistance with computing resources.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Su, Y.; Tan, W.; Dong, Y.; Xu, W.; Huang, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D. Enhancing concealed object detection in Active Millimeter Wave Images using wavelet transform. Signal Process. 2024, 216, 109303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, R.; Pramanik, P.; Sarkar, R. Breast cancer detection in thermograms using a hybrid of GA and GWO based deep feature selection method. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 219, 119643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieu, M.; Bagdanov, A.D.; Bertini, M. Bottom-up and layerwise domain adaptation for pedestrian detection in thermal images. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. (TOMM) 2021, 17, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Yang, Y.; Bai, H.; Zhang, J.; Guo, J. ISNet: Shape matters for infrared small target detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 877–886. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Du, S.; Liu, C.; Cao, Z. Interior attention-aware network for infrared small target detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5002013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddijn-Murphy, L.; Williamson, B.J.; McIlvenny, J.; Corradi, P. Using a UAV thermal infrared camera for monitoring floating marine plastic litter. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, Z. YOLO-ViT-Based Method for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Infrared Vehicle Target Detection. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Ren, H.; Ye, X.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, H.; Nan, Y.; Sun, M.; Ren, X.; Huo, H. Object detection from UAV thermal infrared images and videos using YOLO models. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 112, 102912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, S.; Zhou, S.; Wang, H. MSIA-Net: A Lightweight Infrared Target Detection Network with Efficient Information Fusion. Entropy 2023, 25, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, L.; Sun, W.; Gao, X. Near-infrared maritime target detection based on Swin-Transformer model. In Proceedings of the 2022 5th International Conference on Signal Processing and Machine Learning, Dalian, China, 4–6 August 2022; pp. 218–225. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, F.; Li, Y.; Zeng, G.; Peng, P.; Wang, G.; Li, Y. Thermal infrared image colorization for nighttime driving scenes with top-down guided attention. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 15808–15823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Shi, J.; Ye, Z.; Mertz, C.; Ramanan, D.; Kong, S. Multimodal object detection via probabilistic ensembling. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Cham, Switerland, 2022; pp. 139–158. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Shin, H. Pedestrian detection at night in infrared images using an attention-guided encoder-decoder convolutional neural network. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, J.; Su, N.; Yan, Y.; Xing, X. Low contrast infrared target detection method based on residual thermal backbone network and weighting loss function. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y. YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer: Cham, Switerland, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollar, P. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieu, M.; Bagdanov, A.D.; Bertini, M.; Del Bimbo, A. Task-conditioned domain adaptation for pedestrian detection in thermal imagery. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Cham, Switerland, 2020; pp. 546–562. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Lv, W.; Chang, Q.; Cui, C.; Deng, K.; Wang, G.; Dang, Q.; Wei, S.; Du, Y.; et al. PP-YOLOE: An evolved version of YOLO. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.16250. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Z.; Su, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Gan, G.; Zhang, S.; Fan, D. A lightweight small object detection algorithm based on improved YOLOv5 for driving scenarios. Int. J. Multimed. Inf. Retr. 2023, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Jiao, S.; Chu, K. Application research of bridge damage detection based on the improved lightweight convolutional neural network model. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wei, Y.; Lu, X. HD-YOLO: Using radius-aware loss function for head detection in top-view fisheye images. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2023, 90, 103715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, F. 2D and 3D object detection algorithms from images: A Survey. Array 2023, 19, 100305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.H.; Xu, T.X.; Liu, J.J.; Liu, Z.N.; Jiang, P.T.; Mu, T.J.; Zhang, S.H.; Martin, R.R.; Cheng, M.M.; Hu, S.M. Attention Mechanisms in Computer Vision: A Survey. Comput. Vis. Media 2022, 8, 331–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Spatial group-wise enhance: Improving semantic feature learning in convolutional networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.09646. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2018, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer: Cham, Switerland, 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Song, Z.; Tang, C. MCA: Multidimensional collaborative attention in deep convolutional neural networks for image recognition. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 126, 107079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, R.; Li, L.; Xie, X. SimAM: A Simple, Parameter-Free Attention Module for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Ren, D. Distance-IoU Loss: Faster and Better Learning for Bounding Box Regression. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 12993–13000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wu, T.; Zhou, S.; Pan, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W. An SAR Ship Object Detection Algorithm Based on Feature Information Efficient Representation Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Park, J.; Kim, N.; Choi, Y.; So Kweon, I. Multispectral pedestrian detection: Benchmark dataset and baseline. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1037–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Devaguptapu, C.; Akolekar, N.; Sharma, M.M.; Balasubramanian, V.N. Borrow From Anywhere: Pseudo Multi-Modal Object Detection in Thermal Imagery. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, C.; Hu, Q.; Fu, H.; Zhu, P. Confidence-aware fusion using dempster-shafer theory for multispectral pedestrian detection. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 3420–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Cai, W.; Yang, Z.; Xu, P.; Jiang, B. IARet: A Lightweight Multiscale Infrared Aerocraft Recognition Algorithm. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 2289–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, J.; Sun, J. You Only Look One-level Feature. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, H.; He, T. FCOS: Fully Convolutional One-Stage Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October 2019–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhu, X.; Su, Y. Every Feature Counts: An Improved One-Stage Detector in Thermal Imagery. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 5th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 6–9 December 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Xu, X. YOLO-FIRI: Improved YOLOv5 for Infrared Image Object Detection. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 141861–141875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Vasconcelos, N. Cascade R-CNN: Delving into High Quality Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. YOLOX: Exceeding YOLO Series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).