An Improved YOLOv5 Algorithm for Drowning Detection in the Indoor Swimming Pool
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methods
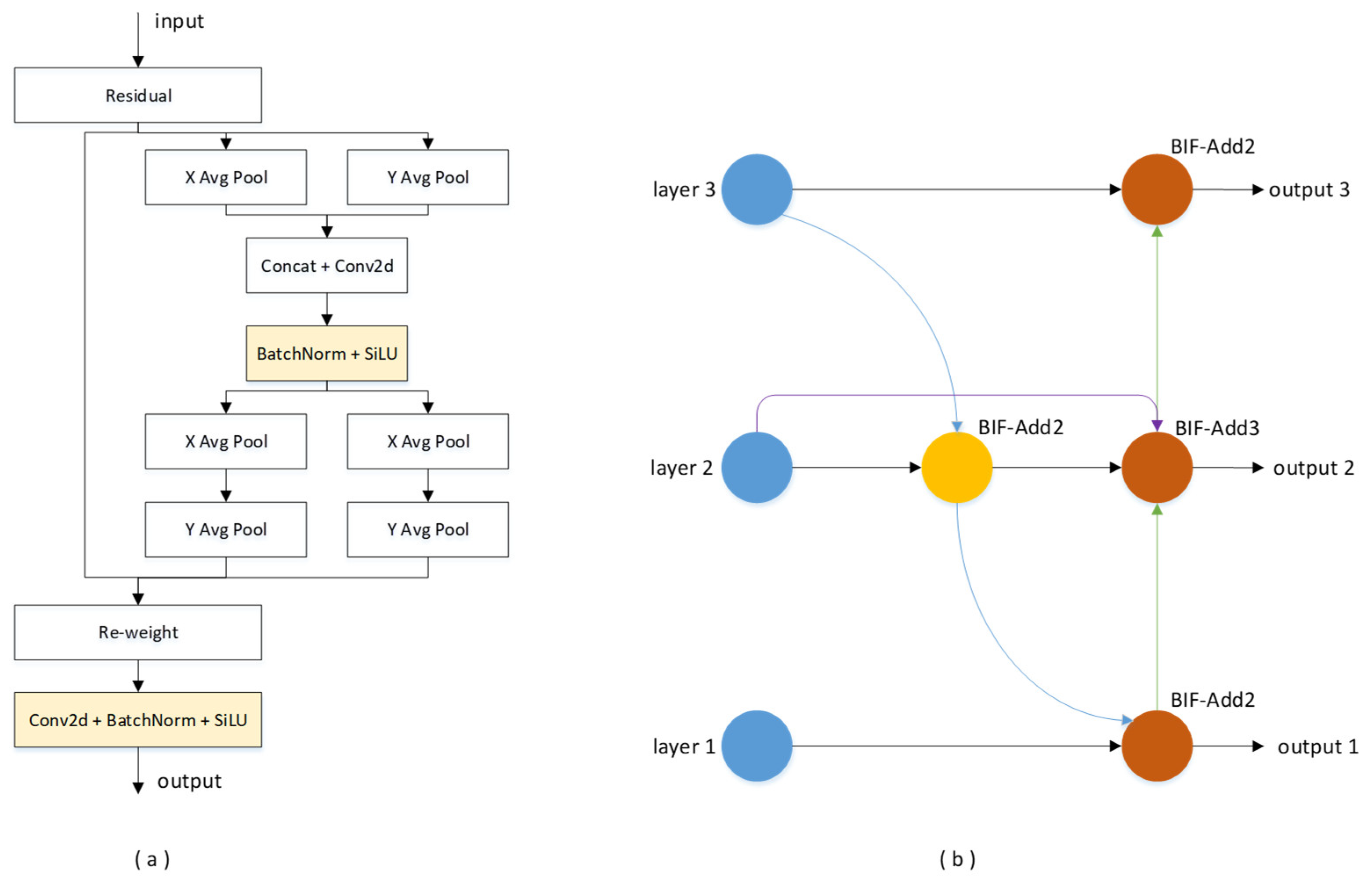
3.1. ICA Module and BiFPN Mechanism
3.2. Improved YOLOv5 Algorithm
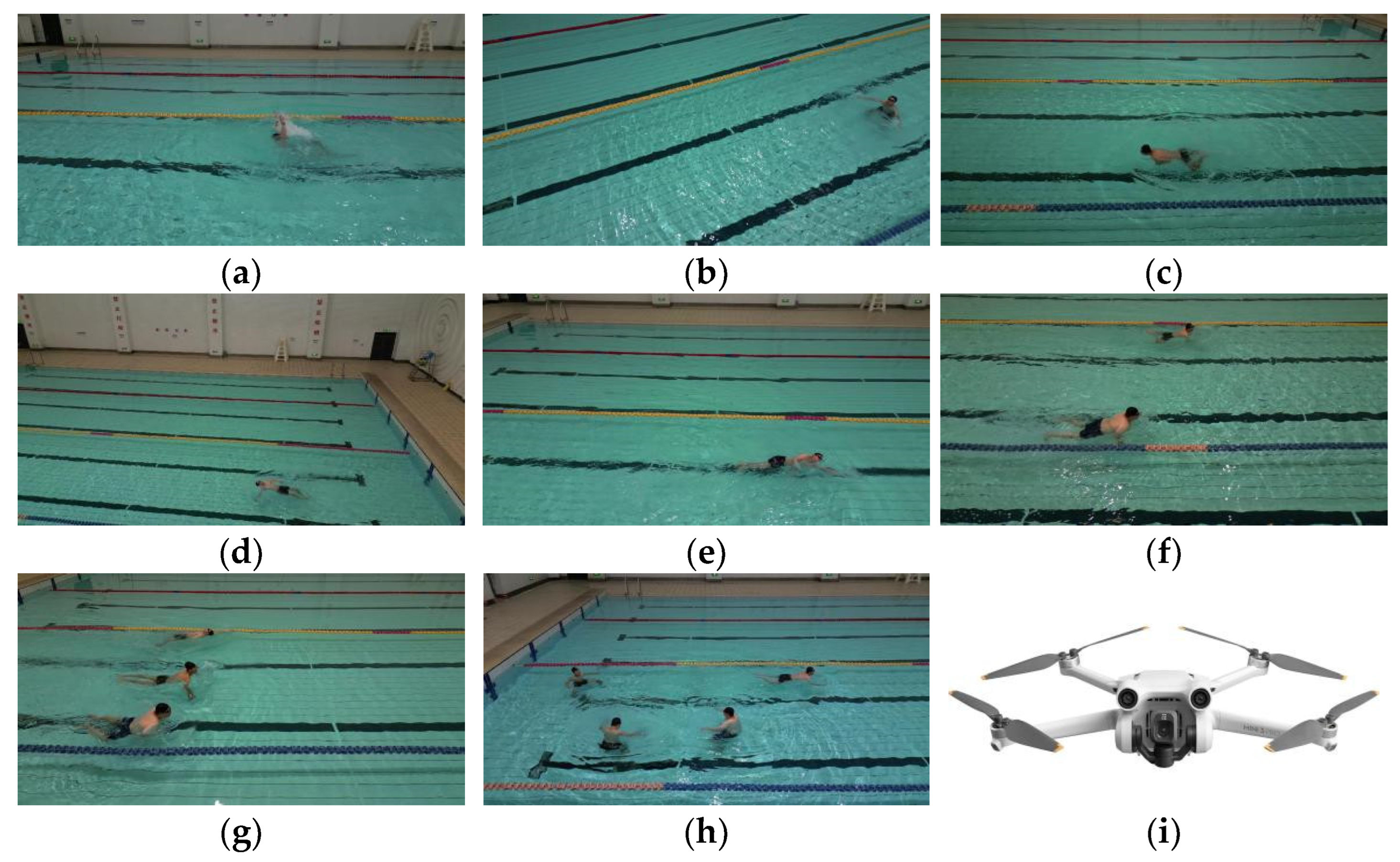
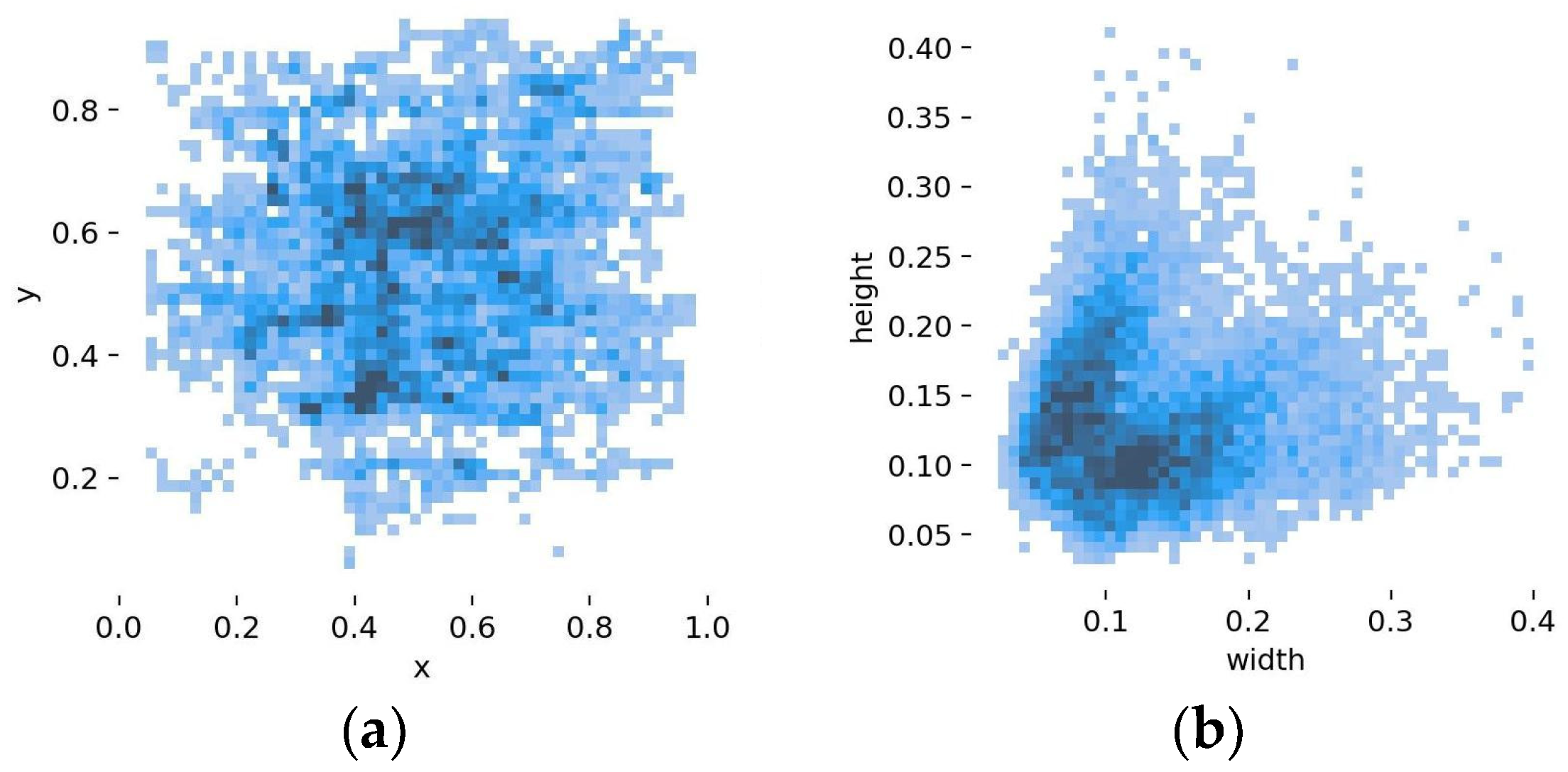
3.3. Self-Made Dataset
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Environment and Configuration
4.2. Evaluation Indicators
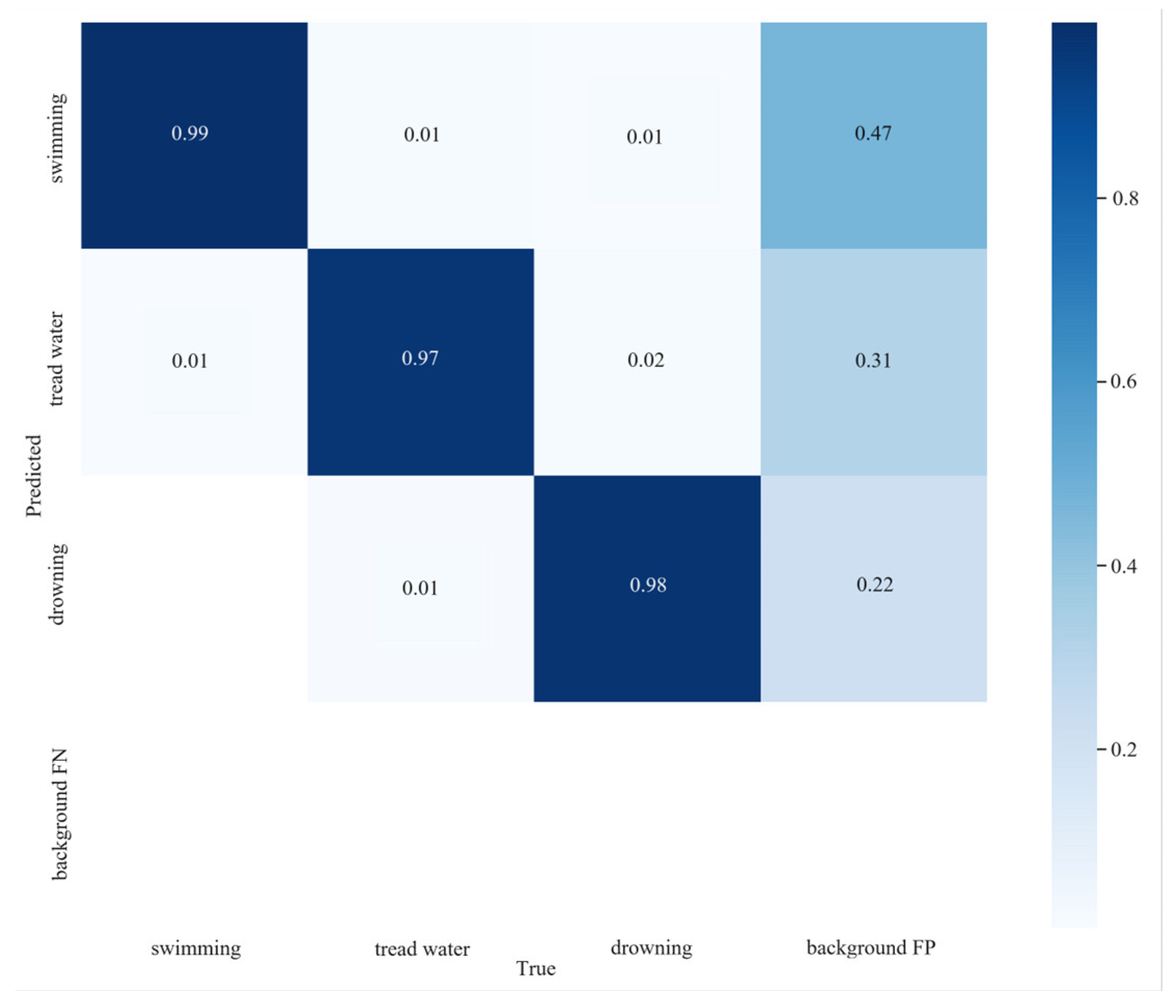
4.3. Comparison of Detection Results on the Self-Made Dataset
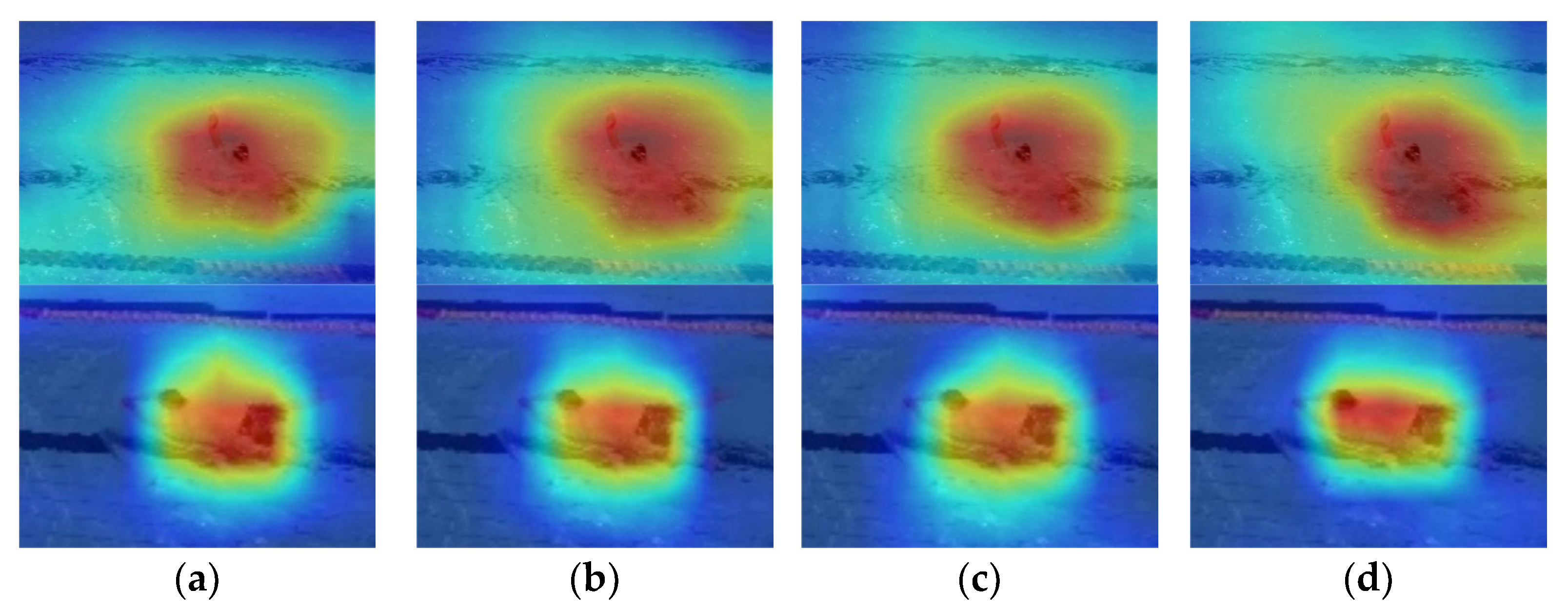
4.4. Ablation Experiments
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Two key improvements were implemented to augment the original YOLOv5 algorithm. Firstly, the ReLU activation function in the coordinated attention (CA) module was replaced with the SiLU activation function, resulting in a refined coordinated attention module (ICA). Additionally, the PAN module was substituted with the bi-directional feature pyramid network (BiFPN).
- (2)
- To evaluate the accuracy of the improved YOLOv5 algorithm, a self-made dataset was generated. Four college students simulated drowning scenarios and various water poses under drone surveillance, with relevant images extracted to form a dataset comprising 8572 images.
- (3)
- The improved YOLOv5 algorithm exhibited a noteworthy 1.3% improvement in precision compared to the original YOLOv5 algorithm. It achieved a recall rate of 98.0% and mean average precision (mAP) values of 98.5% and 73.3% at 0.5 to 0.9 IOU thresholds, respectively, meeting the stringent accuracy requirements for drowning detection.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| BatchNorm, BN | batch normalization |
| BiFPN | bi-directional feature pyramid network |
| BIF-Add2 | BiFPN feature fusion of 2 inputs |
| BIF-Add3 | BiFPN feature fusion of 3 inputs |
| CA | coordinated attention module |
| Conv2d | ordinary convolution |
| DJI Mini3pro | drones made by Shenzhen Dajiang Innovation Technology Co., Ltd. in China |
| FN | false negative |
| FP | false positive |
| ICA | improved coordinated attention module |
| IOU | intersection over union |
| mAP | mean average precision |
| PAN | pyramid attention network |
| ReLU | rectified linear unit |
| SiLU | sigmoid-weighted linear unit |
| SPPF | spatial pyramid pooling-fast |
| TN | true negative |
| TP | true positive |
| X Avg Pool | average pool in X direction |
| Y Avg Pool | average pool in Y direction |
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789240046726 (accessed on 23 October 2023).
- People’s Daily Public Opinion Data Center and People’s Online. Available online: https://www.1608.cn/pptx/70444.html (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Alshbatat, A.I.N.; Alhameli, S.; Almazrouei, S.; Alhameli, S.; Almarar, W. Automated vision-based surveillance system to detect drowning incidents in swimming pools. In Proceedings of the Advances in Science and Engineering Technology International Conferences, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 20–23 February 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, M.R.; Rimajova, M.; Edgecombe, D.; Vickery, K. Childhood drowning: Barriers surrounding private swimming pools. Pediatrics 2003, 111, E115–E119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, P.; Branche, C.M.; Sacks, J.J.; Ryan, G.; Peddicord, J. Childhood drownings and fencing of outdoor pools in the United States, 1994. Pediatrics 1998, 101, E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atilgan, M.; Bulgur-Kirbas, D.; Akman, R.; Deveci, C. Fatal drowning caused by a swimming pool drainage system. Am. J. Forensic Med. Pathol. 2021, 42, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanagan-Leitzel, L.K.; Skow, E.; Moore, C.M. Great expectations: Perceptual challenges of visual surveillance in lifeguarding. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 2015, 29, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victoria, L.; David, C. The effect of lifeguard experience upon the detection of drowning victims in a realistic dynamic visual search task. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 2017, 32, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, F.; Zhu, H.; Tang, F.; Wang, X. Drowning behavior detection in swimming pool based on deep learning. Signal Image Video Process. 2022, 16, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kałamajska, E.; Misiurewicz, J.; Weremczuk, J. Wearable pulse oximeter for swimming pool safety. Sensors 2022, 22, 3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalalifar, S.; Kashizadeh, A.; Mahmood, I.; Belford, A.; Drake, N.; Razmjou, A.; Asadnia, M. A smart multi-sensor device to detect distress in swimmers. Sensors 2023, 22, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiurewicz, J.; Bruliński, K.; Klembowski, W.; Kulpa, K.S.; Pietrusiewicz, J. Multipath propagation of acoustic signal in a swimming pool—Source localization problem. Sensors 2022, 22, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, S.; Li, K.; Wang, X. An indoor pool drowning risk detection method based on improved YOLOv4. In Proceedings of the IEEE Advanced Information Management, Communicates, Electronic and Automation Control Conference, Chongqing, China, 16–18 December 2022; pp. 1559–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Drowning Detection System. Available online: https://poseidon-tech.com/ (accessed on 28 October 2023).
- Hasan, S.; Joy, J.; Ahsan, F.; Khambaty, H.; Agarwal, M.; Mounsef, J. A water behavior dataset for an image-based drowning solution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Green Energy and Smart Systems Conference, Long Beach, CA, USA, 1–2 November 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.; Bierens, J.J.L.M.; Lis, R.; Rowhani-Rahbar, A.; Morley, P.; Perkins, G.D. Predicting outcome of drowning at the scene: A systematic review and meta-analyses. Resuscitation 2016, 104, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.; Mack, C.; Schiff, M.A. Association of water temperature and submersion duration and drowning outcome. Resuscitation 2014, 85, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claesson, A.; Schierbeck, S.; Hollenberg, J.; Forsberg, S.; Nordberg, P.; Ringh, M.; Jansson, A.; Nord, A. The use of drones and a machine-learning model for recognition of simulated drowning victims-A feasibility study. Resuscitation 2020, 156, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seguin, C.; Blaquiere, G.; Loundou, A.; Michelet, P.; Markarian, T. Unmanned aerial vehicles (drones) to prevent drowning. Resuscitation 2018, 127, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, M.A.; Yang, G.; Iqbal, A. Mask R-CNN based real time near drowning person detection system in swimming pools. In Proceedings of the Mohammad Ali Jinnah University International Conference on Computing, Karachi, Pakistan, 27–28 October 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, A.H.; Lu, W.; Yau, W.Y. A video-based drowning detection system. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2002: 7th European Conference on Computer Vision, Copenhagen, Denmark, 28–31 May 2002; Volume 2353, pp. 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budiharto, W.; Gunawan, A.A.S.; Suroso, J.S.; Chowanda, A.; Patrik, A.; Utama, G. Fast object detection for quadcopter drone using deep learning. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems, Nagoya, Japan, 27–30 April 2018; pp. 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çetin, E.; Barrado, C.; Pastor, E. Improving real-time drone detection for counter-drone systems. Aeronaut. J. 2021, 125, 1871–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Mei, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, X. Automatic real-time detection of infant drowning using YOLOv5 and Faster R-CNN models based on video surveillance. J. Social Comput. 2023, 4, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellen, D.A.R.; Kristalina, P.; Hadi, M.Z.S.; Patriarso, A. Effective searching of drowning victims in the river using deep learning method and underwater drone. In Proceedings of the International Electronics Symposium, Denpasar, Indonesia, 8–10 August 2023; pp. 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Lin, H.; Lu, K.; Cao, L.; Liu, Y. A forest fire detection system based on ensemble learning. Forests 2021, 12, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Lin, H.; Wang, F. A small target forest fire detection model based on YOLOv5 improvement. Forests 2022, 13, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13708–13717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, C.; Lu, X.; Wu, B. CME-YOLOv5: An efficient object detection network for densely spaced fish and small targets. Water 2022, 14, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfwing, S.; Uchibe, E.; Doya, K. Sigmoid-weighted linear units for neural network function approximation in reinforcement learning. Neural Netw. 2018, 107, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L. Analysis and research on YOLOv5s vehicle detection with CA and BiFPN fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE 4th Eurasia Conference on IOT, Communication and Engineering, Yunlin, Taiwan, 28–30 October 2022; pp. 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Xue, J.; Sun, H. Lightweight target detection for the field flat jujube based on improved YOLOv5. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 202, 107391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Ma, Z.; Ye, B.; Yu, G.; Tang, T.; Zheng, M. Detection of green asparagus in complex environments based on the improved YOLOv5 algorithm. Sensors 2023, 23, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carballo-Fazanes, A.; Bierens, J.J.; the International Expert Group to Study Drowning Behaviour. The visible behaviour of drowning persons: A pilot observational study using analytic software and a nominal group technique. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, Y. Dense crowd detection algorithm for YOLOv5 based on coordinate attention mechanism. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Algorithms, High Performance Computing and Artificial Intelligence, Guangzhou, China, 21–23 October 2022; pp. 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Lin, B.; Liu, Y. Research on the coordinate attention mechanism fuse in a YOLOv5 deep learning detector for the sar ship detection task. Sensors 2022, 22, 3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Training Configuration | Value |
|---|---|
| image size | 640 |
| batch size | 16 |
| works | 5 |
| momentum | 0.937 |
| learning rate | 0.01 |
| optimizer | SGD |
| Real Value | Predicted Value (Positive) | Predicted Value (Negative) |
|---|---|---|
| Positive | True Positive (TP) | False Positive (FN) |
| Negative | False Negative (FP) | True Negative (TN) |
| Algorithm | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.5:0.95 (%) | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5 | 96.8 | 98.1 | 98.9 | 73.2 | 7,018,216 |
| improved YOLOv5 | 98.1 | 98.0 | 98.5 | 73.3 | 7,272,073 |
| Algorithm | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.5:0.95 (%) | Parameters | Inference Speed (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5 | 96.8 | 98.1 | 98.9 | 73.2 | 7,018,216 | 3.5 |
| YOLOv5 + CA | 97.3 | 97.8 | 98.6 | 73.4 | 7,156,648 | 3.5 |
| YOLOv5 + ICA | 97.6 | 97.2 | 98.6 | 73.3 | 7,156,352 | 3.6 |
| improved YOLOv5 | 98.1 | 98.0 | 98.5 | 73.3 | 7,272,073 | 3.7 |
| Algorithm | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.5:0.95 (%) | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5 | 96.8 | 98.1 | 98.9 | 73.2 | 7,018,216 |
| YOLOv5 + CA | 97.3 | 97.5 | 98.8 | 73.3 | 7,437,848 |
| YOLOv5 + ICA | 97.5 | 97.8 | 98.9 | 73.2 | 7,437,848 |
| YOLOv5 + ICA + BIFPN | 97.8 | 97.5 | 98.6 | 73.3 | 7,586,337 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, R.; Wang, K.; Yang, L. An Improved YOLOv5 Algorithm for Drowning Detection in the Indoor Swimming Pool. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010200
Yang R, Wang K, Yang L. An Improved YOLOv5 Algorithm for Drowning Detection in the Indoor Swimming Pool. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(1):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010200
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Ruiliang, Kaikai Wang, and Libin Yang. 2024. "An Improved YOLOv5 Algorithm for Drowning Detection in the Indoor Swimming Pool" Applied Sciences 14, no. 1: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010200
APA StyleYang, R., Wang, K., & Yang, L. (2024). An Improved YOLOv5 Algorithm for Drowning Detection in the Indoor Swimming Pool. Applied Sciences, 14(1), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010200





