Colorectal Cancer Cell Spheroids Co-Cultured with Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescent Particles Targeting Sialic Acid Show Preserved Cell Viability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. SA-MIP Synthesis
2.3. HT29 Spheroid Cell Cultures
2.4. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.5. Confocal Imaging
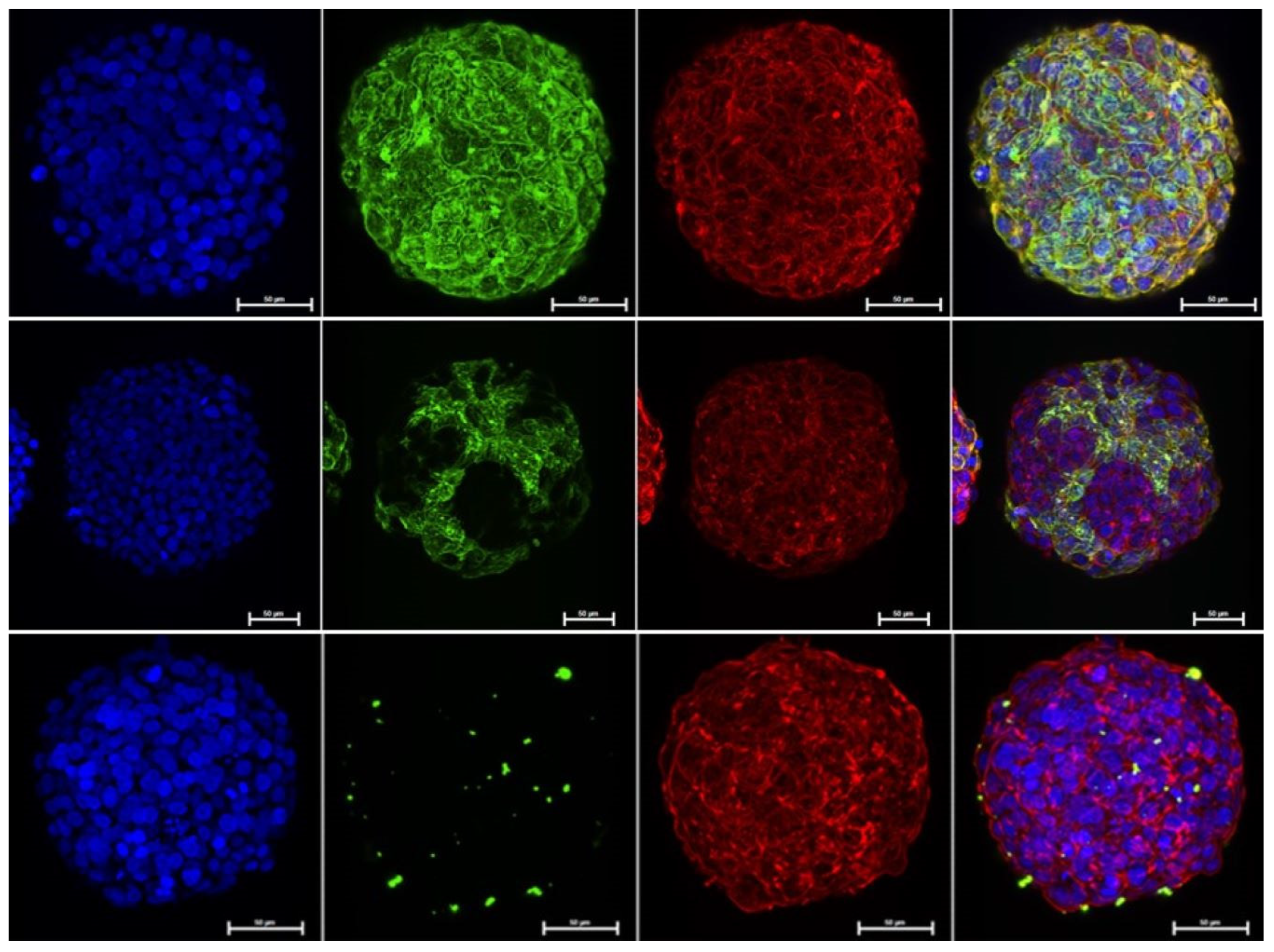
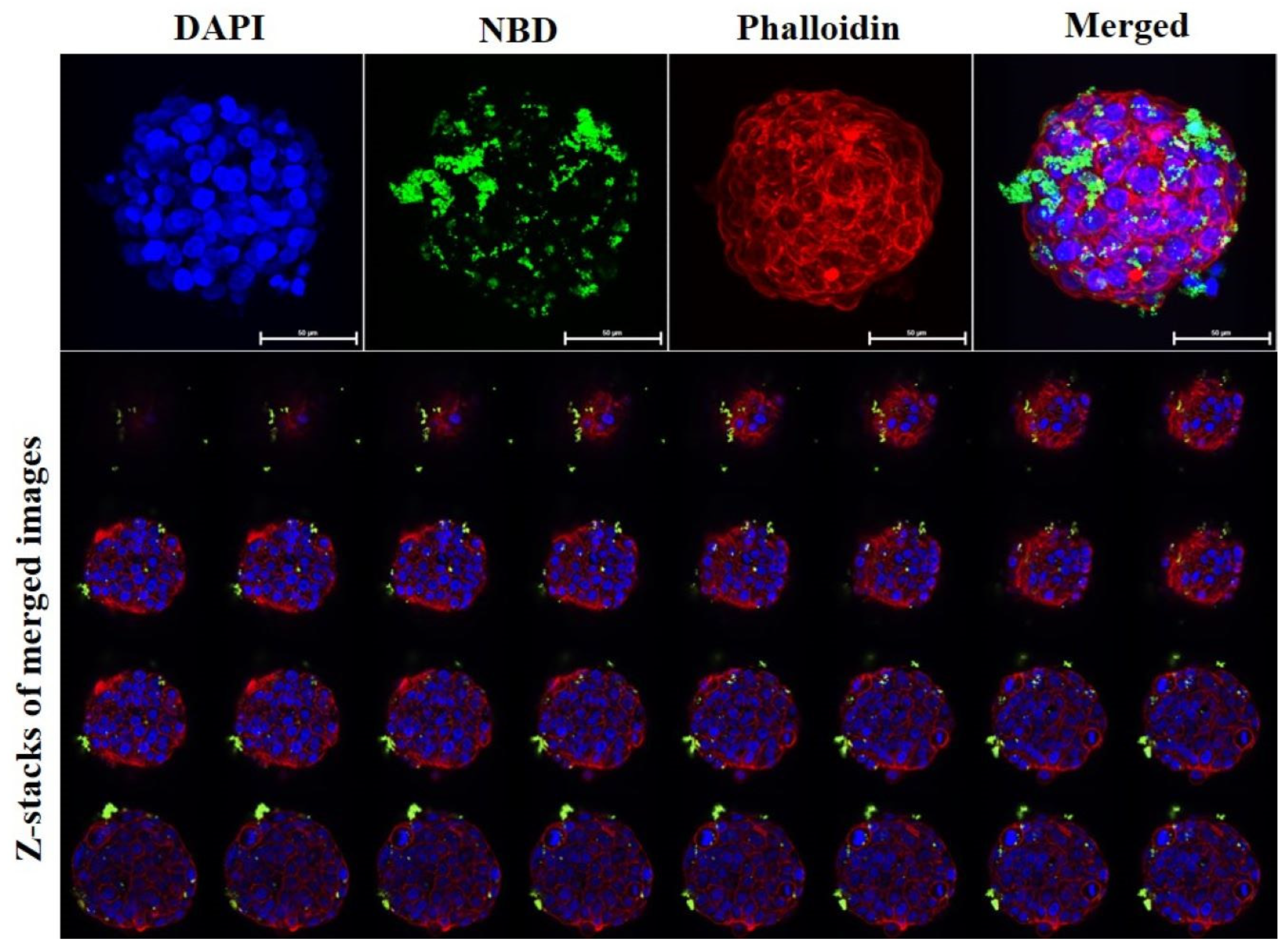
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardiello, D.; Vitiello, P.P.; Cardone, C.; Martini, G.; Troiani, T.; Martinelli, E.; Ciardiello, F. Immunotherapy of colorectal cancer: Challenges for therapeutic efficacy. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2019, 76, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habanjar, O.; Diab-Assaf, M.; Caldefie-Chezet, F.; Delort, L. 3D cell culture systems: Tumor application, advantages, and disadvantages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, C.; Teng, Y. Is it time to start transitioning from 2D to 3D cell culture? Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazic, S.E.; Williams, D.P. Improving drug safety predictions by reducing poor analytical practices. Toxicol. Res. Appl. 2020, 4, 2397847320978633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, G.; Guan, F. Biological functions and analytical strategies of sialic acids in tumor. Cells 2020, 9, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Schich, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Feith, M.; Beyer, S.; Sternbæk, L.; Ohlsson, L.; Stollenwerk, M.; Wingren, A.G. Molecularly imprinted polymers in biological applications. Biotechniques 2020, 69, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.; El-Schich, Z.; Malakpour, A.; Wan, W.; Dizeyi, N.; Mohammadi, R.; Rurack, K.; Gjörloff Wingren, A.; Sellergren, B.R. Sialic acid-imprinted fluorescent core–shell particles for selective labeling of cell surface glycans. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 13908–13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, S.; Kimani, M.; Zhang, Y.; Verhassel, A.; Sternbæk, L.; Wang, T.; Persson, J.L.; Härkönen, P.; Johansson, E.; Caraballo, R. Fluorescent Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Layers against Sialic Acid on Silica-Coated Polystyrene Cores—Assessment of the Binding Behavior to Cancer Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimani, M.; Beyer, S.; El-Schich, Z.; Gawlitza, K.; Gjorloff-Wingren, A.; Rurack, K. Imprinted particles for direct fluorescence detection of sialic acid in polar media and on cancer cells with enhanced control of nonspecific binding. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 2363–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, K.; Rangel, P.X.M.; Bui, B.T.S. Molecularly imprinted polymers: Antibody mimics for bioimaging and therapy. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 9554–9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, Y.L.; Keirouz, A.; Leese, H.S. Molecularly imprinted polymers in diagnostics: Accessing analytes in biofluids. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 7418–7449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfarotta, F.; Lezina, L.; Guerreiro, A.; Czulak, J.; Petukhov, A.; Daks, A.; Smolinska-Kempisty, K.; Poma, A.; Piletsky, S.; Barlev, N.A. Specific drug delivery to cancer cells with double-imprinted nanoparticles against epidermal growth factor receptor. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 4641–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternbæk, L.; Kimani, M.; Gawlitza, K.; Rurack, K.; Janicke, B.; Alm, K.; Wingren, A.G.; Eriksson, H. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Exhibit Low Cytotoxic and Inflammatory Properties in Macrophages In Vitro. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Läubli, H.; Nalle, S.C.; Maslyar, D. Targeting the Siglec–Sialic Acid Immune Axis in Cancer: Current and Future Approaches. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2022, 10, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar]
- Badr-Eldin, S.M.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Kotta, S.; Deb, P.K.; Venugopala, K.N. Three-Dimensional In Vitro Cell Culture Models for Efficient Drug Discovery: Progress So Far and Future Prospects. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Schich, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Göransson, T.; Dizeyi, N.; Persson, J.L.; Johansson, E.; Caraballo, R.; Elofsson, M.; Shinde, S.; Sellergren, B. Sialic acid as a biomarker studied in breast cancer cell lines in vitro using fluorescent molecularly imprinted polymers. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3256. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, M.; Feith, M.; Janicke, B.; Alm, K.; El-Schich, Z. Evaluation of the impact of imprinted polymer particles on morphology and motility of breast cancer cells by using digital holographic cytometry. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutia, S.K.; Panda, P.K.; Sinha, N.; Praharaj, P.P.; Bhol, C.S.; Panigrahi, D.P.; Mahapatra, K.K.; Saha, S.; Patra, S.; Mishra, S.R. Plant lectins in cancer therapeutics: Targeting apoptosis and autophagy-dependent cell death. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 144, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.R.; Ray, U.; Chatterjee, B.P.; Roy, S.S. Targeted apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells through mitochondrial dysfunction in response to Sambucus nigra agglutinin. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaneckova, T.; Bezdekova, J.; Han, G.; Adam, V.; Vaculovicova, M. Application of molecularly imprinted polymers as artificial receptors for imaging. Acta Biomater. 2020, 101, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaat, D.; Aggour, M.G.; Farghali, A.A.; Mahajan, R.; Wiklander, J.G.; Nicholls, I.A.; Piletsky, S.A. Strategies for molecular imprinting and the evolution of MIP nanoparticles as plastic antibodies—Synthesis and applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büll, C.; Heise, T.; Adema, G.J.; Boltje, T.J. Sialic acid mimetics to target the sialic acid–Siglec axis. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, C.; Boltje, T.J.; van Dinther, E.A.; Peters, T.; de Graaf, A.M.; Leusen, J.H.; Kreutz, M.; Figdor, C.G.; den Brok, M.H.; Adema, G.J. Targeted delivery of a sialic acid-blocking glycomimetic to cancer cells inhibits metastatic spread. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sjöberg, T.; El-Schich, Z.; Rurack, K.; Gjörloff Wingren, A. Colorectal Cancer Cell Spheroids Co-Cultured with Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescent Particles Targeting Sialic Acid Show Preserved Cell Viability. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5330. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095330
Sjöberg T, El-Schich Z, Rurack K, Gjörloff Wingren A. Colorectal Cancer Cell Spheroids Co-Cultured with Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescent Particles Targeting Sialic Acid Show Preserved Cell Viability. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(9):5330. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095330
Chicago/Turabian StyleSjöberg, Thomas, Zahra El-Schich, Knut Rurack, and Anette Gjörloff Wingren. 2023. "Colorectal Cancer Cell Spheroids Co-Cultured with Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescent Particles Targeting Sialic Acid Show Preserved Cell Viability" Applied Sciences 13, no. 9: 5330. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095330
APA StyleSjöberg, T., El-Schich, Z., Rurack, K., & Gjörloff Wingren, A. (2023). Colorectal Cancer Cell Spheroids Co-Cultured with Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescent Particles Targeting Sialic Acid Show Preserved Cell Viability. Applied Sciences, 13(9), 5330. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095330







