Abstract
This paper introduces a direct predictive torque control (DPTC) method to minimize the torque ripple and copper loss of the switched reluctance motor (SRM). Generally, there is a problem with torque ripple during the SRM’s commutation. In this method, the commutation optimization is provided by a direct predictive torque control algorithm. Firstly, the reachable range of phase torques is predicted and the boundary of two continuous phases is modified. By dividing the torque range directly to determine the torque allocation set, the suppression of torque ripple becomes simple. Secondly, considering the optimization problem of copper loss during commutation, a cost function only related to the phase current is constructed. Further, the minimization of copper loss can be achieved by solving the cost function, and the work of setting weight parameters is not required. Finally, the proposed DPTC method is tested by simulation and experiment in a three-phase 12/8-pole SRM drive system and the results are compared with the existing predictive torque control methods. The results show that the proposed method has less torque ripple and copper loss, which effectively improves the torque control performance.
1. Introduction
Switched reluctance motors (SRMs) have gained increasing attraction in industry and academia because of their reliable structure, wide speed range, and high fault tolerance [1,2]. However, the application of SRMs is limited by its inherent noise and torque ripple issues [3,4]. These issues can be improved by optimizing the physical structure of the motor, but this approach does not apply to SRMs that have been produced or used. Therefore, many researchers are interested in solving the noise or torque ripple issue by using the advanced control strategy [5]. Many torque ripple optimization methods have been designed, and these methods can be roughly classified as indirect methods and direct methods.
The indirect methods focus on splitting the total torque signal into phase reference signals using a torque sharing function (TSF) and keeping the total output torque constant by controlling the phase current. In [6,7,8], it is also proved that the phase torque can be controlled indirectly by adjusting the phase current. Since the phase reference signals are calculated from the sharing function, the control effect of this method is directly affected by the TSF [9]. In [10], the torque ripple suppression capabilities of linear, sinusoidal, cubic, and exponential TSFs are evaluated and improved, respectively. In conventional TSFs, due to their fixed parameters and limited voltage source, problems such as high current peak, high copper loss, and low-speed range may be generated [11,12]. Therefore, many types of TSF are designed to accomplish the optimization of multiple control objectives simultaneously. In [13], in order to expand the applicable speed range of the TSF method, the commutation process is defined as two cases and a torque error proportional compensator is designed to reduce the maximum change rate of the flux linkage. In [14], an offline TSF is designed to optimize both torque ripple and copper loss. Since only one weight parameter is included in the objective function, the application of this method is simplified. In [15], an optimization problem is formulated based on the offline TSF, and the GA optimization algorithm is used to minimize the torque ripple and copper loss. In [16], an online optimization method for the TSF is developed to smooth the total output torque by compensating for the tracking error of the phase torque. Since the phase current is a direct control variable in the TSF method, it is also necessary to design an additional current controller. In [17], a PWM current controller with parameter adaption is proposed, which aims to improve the response speed and control accuracy of the phase current. In [18], in order to reduce the torque ripple, a predictive current controller is designed. Additionally, considering the disturbance in the system, an additional disturbance observer is proposed to improve the robustness of the current controller. In [19], a deadbeat predictive current controller is developed to achieve low torque ripple over the full speed range.
The direct methods usually control the output state of the converter directly through the pre-established rule. Direct torque control (DTC) is a direct method to control flux linkage and torque simultaneously and was first applied to the SRM in [20]. In [21], the original six sectors in DTC are re-divided into nine and twelve sectors, and a new conduction rule is formulated to reduce the torque ripple. In [22], a new sector division method is developed to improve drive efficiency by avoiding the current extension into the negative torque region in the traditional DTC. The magnitude of flux linkage is required to be constant in the DTC, but this does not mean that the output torque is also constant, so it is pointed out in [23] that the closed loop of flux linkage should be removed. Direct instantaneous torque control (DITC) is another direct method with a simpler structure than DTC, which requires only hysteresis control of the torque [24]. The DITC strategy is extended in [25] to achieve the four-quadrant operation of the SRM. In [26], a new hysteresis rule for DITC is formulated and the system efficiency is improved by modifying the conduction angles. In order to improve the torque control performance and system efficiency, an online optimization strategy for DITC based on the genetic algorithm is proposed in [27]. In [28], the pulse width modulation (PWM) technology is introduced into DITC to reduce the torque ripple.
The model predictive torque control (MPTC) is also an excellent direct method due to its ease of implementation and well-known ability to optimize the multi-objective performance of the SRM [29]. In the MPTC method, the operating modes of the converter are usually divided into finite control sets, and the optimal switching scheme is determined by minimizing the cost function. As can be seen from the application of MPTC in the transformer in [30], it has a well-known ability to deal with nonlinear transformers. The MPTC method is first applied to the SRM drive system in [31] to improve the torque ripple and copper loss. In [32], the performance of the MPTC is improved using the sector partition technique, and the realizability of this method is enhanced by compensating for the computation delay. To further reduce the computational burden of MPTC, a finite control set with only 6 switching states is proposed in [33], and the feasibility of the method is demonstrated experimentally. In addition, the MPTC can also be integrated with TSF [34] and DTC [35] to improve the performance of traditional torque control methods. Nevertheless, in the above MPTC method, the converter state is constant within each control step and the switching frequency is also variable, which leads to a relatively large torque ripple and is not conducive to the filter design. It is pointed out in [9,36] that the MPTC method with fixed switching frequency is a promising work to be explored.
In this paper, a DPTC method using the fixed frequency PWM technique is developed to enhance the torque control performance of the SRM drive. This method enhances the predictive PWM-DITC algorithm published in [36] and solves the problem of uncontrollable current. Additionally, the shortcoming of large torque ripple in the conventional MPTC method is improved. In the proposed method, the attainable range of phase torque is predicted and the torque allocation set is divided directly after modifying the torque boundary. Therefore, each allocation scheme in the torque allocation set is achievable. Afterward, in order to minimize the copper loss, a single-objective cost function is defined. It is worth noting that the torque ripple has been optimized in the torque allocation set, so the optimization objective is only related to the phase current, which avoids the work of setting weight parameters. By minimizing the cost function, the scheme to minimize the copper loss can be found in the torque allocation set. Furthermore, the optimizable speed boundary is also determined to avoid negative torque. Since the proposed method provides the phase reference torque throughout the optimizable region, the effectiveness of the optimization operation is guaranteed. The proposed DPTC method is simulated and experimentally verified on a three-phase 12/8-pole SRM and compared with several existing torque control methods.
2. SRM Model
The advantages of SRM’s simple structure and high reliability can be attributed to the absence of magnets and windings on its rotor. A typical three-phase 12/8-pole SRM has 12 stator and 8 rotor poles, each phase contains four coil windings that can be excited simultaneously. The topology of the SRM and its asymmetric half-bridge converter is shown in Figure 1a. The anti-clockwise direction is the positive direction of the rotor angular position, and the aligned and unaligned positions of the rotor are defined as and , respectively. When a phase is energized, the rotor tends to align with the energized stator poles and generates torque. In general, the phase torque can be expressed by the co-energy as
where p is the identifier of the phases. , , and are the rotor angle, phase current, and phase flux linkage, respectively. The phase flux linkage can be represented by the phase inductance and phase current as
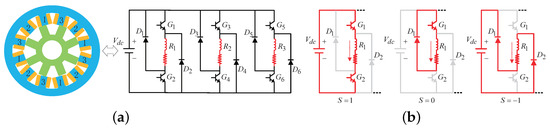
Figure 1.
SRM with excitation circuit and three switching states of the asymmetric bridge converter. (a) SRM with excitation circuit; (b) three switching states of the asymmetric bridge converter.
The highly nonlinear electromagnetic characteristics of the SRM make Equation (1) difficult to solve. The linear model shown in (3) can simplify the calculation effectively, but it is usually used for principle analysis because of the large difference from the actual model. Therefore, considering the model accuracy and computational complexity, the nonlinear model proposed in [4] is adopted and look-up tables (LUTs) are established to realize the proposed control strategy.
The asymmetric half-bridge converter is very popular in the SRM drive system due to its high single-phase control flexibility and low hardware cost. Taking phase 1 as an example, three operating modes of 1, 0, and −1 shown in Figure 1b can be generated by turning on and off the two switches in each bridge arm. The red lines and arrows represent the path and direction of the current, respectively. In mode , the switches and are both turned on and the DC bus voltage is acted on the phase winding through the switches to make it excited. This mode can increase the phase output torque during torque generation. In mode , the switches and are turned on and off, respectively, and the phase winding is in the freewheeling mode through the switch and diode . During torque generation, this mode can make the current decrease slowly, and the phase output torque can be reduced when the inductance rise rate is less than the square of the current decrease. In mode , the switches and are turned off, and the phase winding is in the demagnetization mode. This mode can reduce the phase output torque by rapidly reducing the amplitude of the phase current during torque generation.
In the asymmetric half-bridge converter, considering the voltage drop on the phase resistance and components, the phase voltages are expressed separately as
where represents the phase winding voltage drop; and are the phase voltage and DC voltage, respectively; and are the voltage drop across the semiconductor switch and diode, respectively. Since the values of and are very small, they are usually ignored to simplify the calculation.
3. Theoretical Background of the Predictive Torque Control
3.1. Predictive Torque Control Based on PWM
Many control strategies have been proposed to enhance the torque control performance of the SRM [31,33]. The core idea of the MPTC is to carry out the control process in steps, which is very suitable for the discrete working mode of the SRM. The PWM technology allows precise adjustment of the phase output torque at each sampling time. Nevertheless, the operating states of the converter are discretized into a finite set making the conventional MPTC unsuitable for PWM. Therefore, it is necessary to propose an improved MPTC method. The structure diagram of the improved MPTC method is shown in Figure 2.
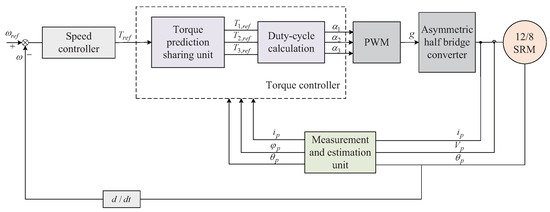
Figure 2.
Block diagram of SRM drive system based on the improved MPTC.
In Figure 2, the total reference torque signal is output by the speed controller and used as an input to the torque controller. Then, the duty cycle of each phase is calculated using the phase reference torque and output to the PWM unit. Finally, the converter controls the SRM to output the corresponding torque. In this paper, the speed controller is a proportional-integral (PI) controller, and the torque controller is designed by the control algorithm proposed in this section. In the torque controller, the phase reference torque is output by the torque prediction sharing unit. Therefore, to make the phase torque track its reference signal, (5) is usually used to calculate the duty cycle.
Therefore, it is possible to set the phase voltage to any value between and by adjusting the duty cycle. The phase electric balance equation of the SRM is
Since the phase resistance is very small, the phase voltage in Equation (6) can be considered to be mainly relevant to the change rate of the phase flux linkage. Furthermore, Ref. [20] shows that the phase torque can be controlled by adjusting the phase flux linkage. Using the standard forward-Euler approximation, the discrete expression of (6) is obtained as
where is the discrete control period, is the sampling current at the starting of the control period k, and is the expected change of flux linkage at the end of this control period (or the starting of the next control period ). Therefore, it is necessary to extrapolate the rotor position at the end of the period. Assuming that the phase reference torque and speed are constant in each control period, we have
The phase reference flux linkage and the phase flux linkage are obtained from the LUT and LUT . The expected change of the flux linkage is described as
Further, by combining (9) and (7), the duty cycle can be rewritten as
Therefore, with the reference phase torque given, the phase torque can track its reference signal through the duty cycle calculated from (10). Based on the excitation sequence of the three-phase 12/8-pole SRM, its excitation period () can be divided into six parts, as shown in Figure 3. In the single-phase excitation interval, the total reference torque is served as the reference signal for the excitation phase. During commutation, the two consecutive phases overlap, and the relation (11) should be satisfied.
where is the total reference torque, and and are the reference torques of the incoming phase (excitation phase) and outgoing phase (demagnetization phase), respectively. To keep a constant superposition torque, it is necessary to reduce the outgoing phase torque gradually and build up the incoming phase torque simultaneously. However, discrete commutation usually leads to the problem of torque ripple during commutation, which makes the reasonable allocation of phase torque a challenge.
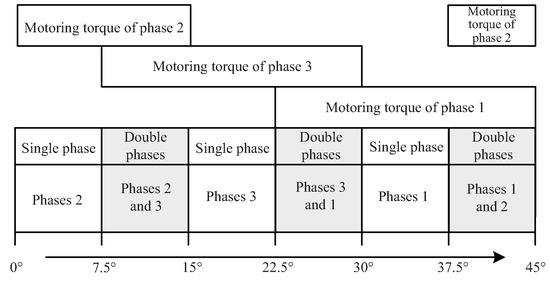
Figure 3.
Sector definitions of the electric cycle for three-phase 12/8-pole SRM.
3.2. Predictive PWM-DITC Algorithm
To minimize the torque ripple, a predictive PWM-DITC algorithm has been developed. This method allocates the phase reference torque within the reachable range and has a remarkable effect on suppressing the torque ripple. When commutation starts, the incoming phase is excited and provides as much output torque as possible. Afterward, the remaining reference torque is tracked by the outgoing phase until its value decreases to zero. Sometimes the outgoing phase cannot reduce its torque as required. In this case, the phase reference torque is reallocated to ensure that the reference torque for both phases is within their reachable range.
To predict the range of phase output torque, it is assumed that the duty cycle is 1 and −1, respectively, in a control period , then the maximum and minimum values of the flux linkage can be calculated as
where and are the two cases in (4), and . Further, using the LUT and LUT , the phase reference torque of the next period is expressed as
After determining the capacity of each phase to deliver torque, the total reference torque needs to be allocated. In commutation, the incoming phase always has the priority of delivering torque. Subsequently, in order to ensure the tracking effect of the outgoing phase on the remaining reference torque, the following inequality constraint is constructed:
where is the minimum output torque of the outgoing phase, and is the maximum output torque of the incoming phase. When relationship (14) is satisfied, the phase reference torque is directly expressed as
However, the outgoing phase sometimes fails to reduce its torque immediately and the inequality (14) cannot be satisfied. In this case, the reference torque of the incoming phase is corrected as
The reference torque of the outgoing phase is expressed as
Therefore, according to the above torque allocation rules, the corresponding duty cycles are calculated by (10), so that the suppression of torque ripple is realized.
4. Direct Predictive Torque Control Algorithm for SRM
4.1. Purpose of the Algorithm
Torque ripple is a non-negligible problem for torque control of the SRM, but a higher copper loss is also undesirable [9]. It can be seen from the previous section that the PWM-DITC algorithm maintains the reachability of the phase reference torque, and the sum of the phase reference torque is always equal to the total reference torque. However, the phase current during commutation is not optimized, and undesirable results, such as a higher copper loss in the phase winding, may occur. Therefore, a novel DPTC algorithm is proposed in this section for optimizing the commutation operation of the SRM.
The DPTC algorithm aims to improve the torque control performance and minimize the copper loss during commutation. This algorithm solves the problem of uncontrollable current in the PWM-DITC algorithm, and the principle of commutation is shown in Figure 4. In the PWM-DITC algorithm, once the incoming phase is excited, the phase commutation is completed as soon as possible. The available positive torque area is underutilized. The proposed method eliminates this shortcoming. In the DPTC method, the reference torque is directly divided within the reachable range of the phase torque, and the effective commutation at each operating point is achieved by a cost function.
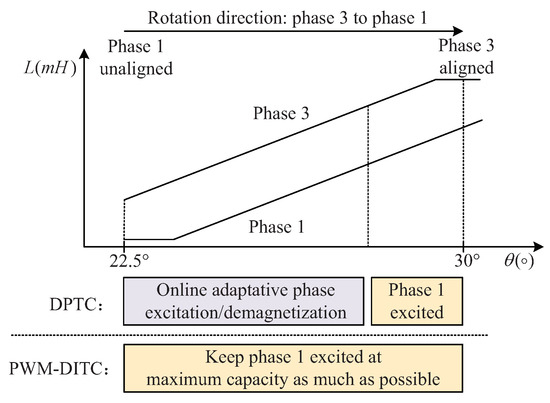
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of the DPTC and PWM-DITC algorithms.
It is well known that the higher the motor speed, the less commutation time is available. In this case, the commutation should be completed as soon as possible to avoid negative torque. Thus, the optimization of commutation by the DPTC is not included in high-speed operation. Nevertheless, this method is still very advantageous at low speeds, especially in the operating area where the copper loss is dominant. Furthermore, please note that the torque ripple is suppressed in all the torque allocation schemes of the DPTC method, which is different from the conventional MPTC. Therefore, the cost function is only used to select the torque allocation scheme with the minimum copper loss.
4.2. The DPTC Algorithm
During commutation, the incoming phase is always expected to provide torque in place of the outgoing phase. Therefore, when the torque needs to be increased, the incoming phase torque should be increased first. When the torque needs to be reduced, the outgoing phase torque should be reduced preferentially.
In the DPTC algorithm, the commutation operation is determined by predicting the torque that the present flux linkage value can generate in the next period. Specifically, assume that the flux linkage is constant in the present period k, i.e., . Then, by combining the angle calculated in (8) and using LUT and LUT , the phase torque of the next period can be estimated. Further, the total torque is obtained as . To assist the commutation, a commutation factor shown in (18) is defined, and the torque allocation scheme of the DPTC can be determined by judging the value of .
When , it indicates that the present flux linkage is insufficient to generate the reference torque. In this case, the flux linkage of the incoming phase should be increased appropriately to keep the total output torque constant. To ensure that the phase torque is reachable, the torque boundary of the incoming phase is rewritten as
Thus, the maximum increment in torque of the incoming phase is calculated as
where the estimation method of the maximum/minimum torque is the same as (12) and (13). The torque allocation set for both consecutive phases can be given as
where and are the torque allocation set of the incoming phase and outgoing phase, respectively. Please note that the value of n is determined according to the computing power of the processor, and its minimum value of 1 guarantees the commutation operation.
Similarly, when , the flux linkage of the outgoing phase should be reduced preferentially to keep the total output torque constant. At this point, the torque of the outgoing phase is reduced and its torque boundary can be defined as
The maximum decrease in torque of the outgoing phase is calculated as
According to (23), should be a nonpositive number to ensure that the torque of the outgoing phase is not increased. However, when the outgoing phase cannot be demagnetized to zero at the stator–rotor alignment position, this may not be satisfied, and an undesired negative torque is generated. A solution to this situation is given in the next subsection. At this point, the set of torque allocations for the consecutive phases is defined as
From the above commutation principle, the torque ripple is suppressed under each scheme of the torque allocation set. Therefore, it is only necessary to find the scheme that minimizes the copper loss in the torque allocation set to determine the optimal commutation operation. Since the copper loss is proportional to the root mean square (RMS) of the phase current, the cost function is constructed as
where the phase current is estimated using the LUT .
To ensure that the proposed DPTC algorithm can be applied safely, the constraint on the current needs to be defined. Therefore, the cost function is rewritten as
where the function is defined as (27) to ensure that the phase current does not exceed the maximum admitted current .
Therefore, by minimizing the cost function (26), the optimal torque allocation scheme can be determined to improve both torque ripple and copper loss. It is worth noting that since the cost function is only related to the phase current, the proposed DPTC method avoids the work of setting weighting parameters compared to the traditional MPTC method. However, in the actual application of the algorithm, because the execution of the algorithm requires a certain time cost, there is usually a problem of time delay. If this delay problem is ignored, the control effect will be affected. In this paper, the problem is solved by the method of delay compensation. The cost function (26) is rewritten as
To demonstrate the optimization process of the proposed DPTC algorithm, the flowchart shown in Figure 5 is given. The execution process of the proposed algorithm can be described as:
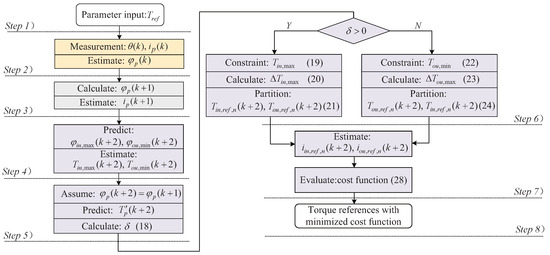
Figure 5.
Flowchart of the proposed DPTC algorithm.
Step 1: Obtain the total torque command from the speed controller.
Step 2: and are sampled at the beginning of period k, and the phase flux linkage is estimated.
Step 3: Calculate the expected flux linkage at the end of this control period (namely as ) by the duty cycle calculated previously. Then, the corresponding phase current can be estimated.
Step 4: The flux linkage boundaries and at the end of period are predicted by setting the duty cycle in (10) to 1 and −1, respectively. Then, the corresponding torque boundaries and are estimated.
Step 5: Assuming that the flux linkage in the control period is constant, predict the torque value and calculate the commutation factor using (18).
Step 6: Partition the commutation into two cases with and modify the torque boundary. Then, the torque allocation set is obtained by formulas (21) and (24).
Step 7: Evaluate the torque allocation scheme using the cost function (28).
Step 8: Determine the optimal torque allocation scheme that minimizes the cost function.
5. The Switching Strategy
Under a certain speed level, the DPTC algorithm can reduce copper loss and achieve effective commutation. If the speed limit is exceeded, the delayed demagnetization caused by the optimization operation may increase the copper loss. However, if this speed limit is determined, the DPTC algorithm provides the optimization operation over the entire allowable range. The rate of change of flux linkage relative to the rotor position is an important criterion for evaluating the torque–speed performance [13]. The maximum is denoted as
where is the decreasing flux linkage of the outgoing phase, and is the increasing flux linkage of the incoming phase.
The maximum value of during commutation is mainly determined by the demagnetization ability of the outgoing phase. The maximum demagnetization voltage is represented by the case of in (4). Therefore, the maximum permissible speed of the algorithm can be expressed as
When this maximum speed is exceeded, undesired negative torque is generated and copper loss is increased. To avoid this case, it is necessary to ensure that the flux linkage of the outgoing phase at the aligned position is zero under the action of the maximum demagnetization voltage. In the three-phase 12/8-pole SRM, the alignment position is 45°. Therefore, according to the phase flux linkage , phase current and rotor position , the speed limit condition is finally defined as
The maximum permissible speed of the proposed DPTC algorithm is provided by (31). When the rotor speed satisfies the constraint , the commutation operation is provided by the DPTC algorithm. When the constraint is not satisfied, i.e., , the delayed demagnetization will increase the copper loss. In this case, the commutation operation switches to the regular PWM-DITC strategy to demagnetize the outgoing phase as quickly as possible. Through this switching strategy, the generation of negative torque can be avoided and the optimization of copper loss is guaranteed. Please note that the trigger condition is based on a speed hysteresis, which avoids frequent switching of the strategies caused by speed fluctuation.
6. Simulation Results
The relevant simulation verifications are carried out in this section by MATLAB/ Simulink. The detailed parameters of the selected SRM are listed in Table 1. The DITC method is common in SRM torque control. Therefore, the simulation results of the DITC method, the MPTC method in [31], and the PWM-DITC method in [36] under the same conditions are also given for comparison. The sampling frequency and control frequency are both set at 10 kHz to ensure the consistency of simulation verification and experimental verification. Since the total reference torque signal is calculated by the speed controller, the PI speed controller of the same specification ( = 0.14, = 0.18) is used in the verification of the above methods. In the torque controller, the parameters in the MPTC method are determined by the rules in [31]. On the other hand, the cost function in the proposed DPTC method is only related to the current, which avoids the adjustment of parameters and reduces the difficulty of algorithm application.

Table 1.
Specifications of the SRM.
The simulation results of the four methods at 200, 400, and 800 rpm speeds when the load is 5 Nm are shown in Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8. From the current waveforms, it can be seen that both the DITC and PWM-DITC have a peak current of approximately 6 A. The MPTC and the proposed DPTC methods have smaller current peaks due to their optimization of the phase torque allocation during commutation. However, the MPTC shows a large current ripple, which is caused by a large variation in terminal voltage due to its fixed switching vector (−1, 0, 1). On the contrary, the proposed DPTC method makes the change of terminal voltage relatively continuous by calculating the duty cycle, so that the phase current surrounds the reference signal tightly. This advantage is also reflected in the torque. Undoubtedly, in the torque waveforms, the DPTC method has a lower torque ripple than the MPTC method.
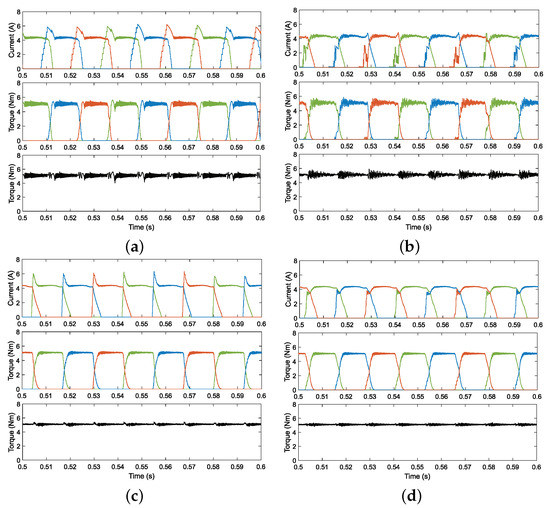
Figure 6.
Simulation results of (a) the DITC method, (b) the FCS MPTC method in [31], (c) the PWM-DITC method in [36], and (d) the proposed DPTC method at 200 rpm with a load of 5 Nm.
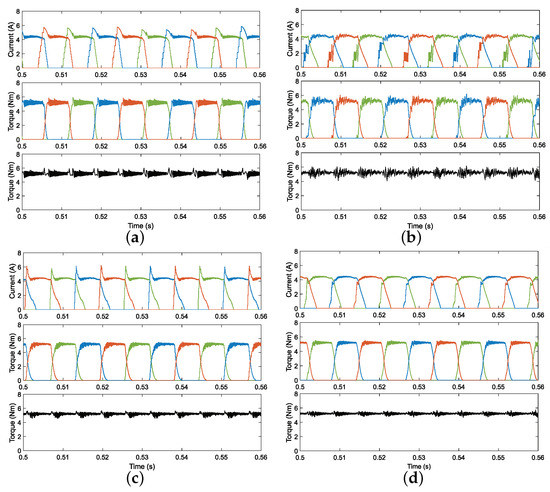
Figure 7.
Simulation results of (a) the DITC method, (b) the FCS MPTC method in [31], (c) the PWM-DITC method in [36], and (d) the proposed DPTC method at 400 rpm with a load of 5 Nm.
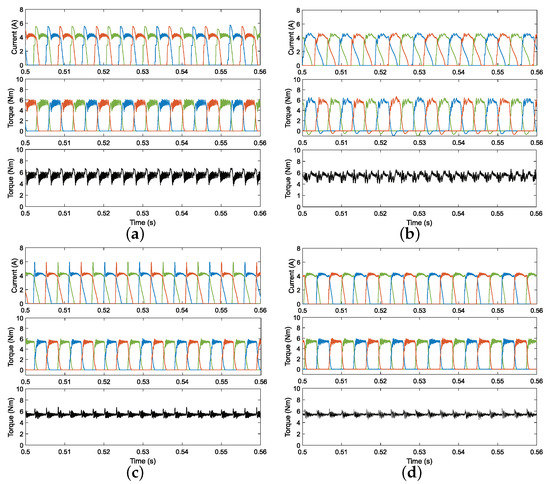
Figure 8.
Simulation results of (a) the DITC method, (b) the FCS MPTC method in [31], (c) the PWM-DITC method in [36], and (d) the proposed DPTC method at 800 rpm with a load of 5 Nm.
To quantitatively compare the simulation results of the above methods, three performance indices, namely the peak torque ripple , the RMS of the torque ripple, and the copper loss index , are given. The expressions of , , and are shown in (32)–(34), where is the total output torque, is the average torque, and and are the maximum and minimum values of the torque ripple, respectively. The calculation results are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Simulation performance comparison at various speeds.
From Table 2, the DITC method is the worst choice among all the methods with respect to the speeds of 200, 400, and 800 rpm, which is caused by the hysteresis effect of the hysteresis control. In terms of torque ripple, DITC has a relatively high torque ripple index of 39.1%, 42.9%, and 58.4%, respectively. Similarly, the of MPTC at different speeds are 38.2%, 41.8%, and 53.2%, respectively. In contrast, the proposed DPTC method reduces the torque ripple to 17.9%, 29.4%, and 38.6%, respectively. This shows that compared with the MPTC method, the proposed method reduces the torque ripple by 53.14%, 29.67%, and 27.44%, respectively. Since the PWM-DITC method also calculates the duty cycle, it has a similar torque ripple as the proposed DPTC method. Moreover, Table 2 clearly shows that the copper loss index of the PWM-DITC method at the speeds of 200, 400, and 800 rpm are 4.6230, 4.8113, and 5.2329, respectively. On the other hand, the proposed DPTC method is optimized for phase torque allocation, so the index are 4.2109, 4.4360, and 4.9058, respectively. The result shows that the proposed DPTC method reduces the copper loss index in the PWM-DITC method by 8.96%, 7.80%, and 6.25%, respectively. Although the PWM-DITC can reduce the copper loss by trial and error of the turn-on angle, the proposed method avoids this work. It is worth noting that the optimization degree of the proposed DPTC method for copper loss decreases with the increase of the speed. This is because as the speed increases, the operable optimization time decreases. At this point, the optimization operation may generate undesired negative torque and reduce the optimization effect, which can be seen from the index of the MPTC method at 800 rpm. In the proposed DPTC method, this situation is avoided by setting a speed limit to ensure the optimization effect of the copper loss. Thus, the proposed method has a significant advantage when the speed is lower or the copper loss is dominant. To sum up, the above comparison results illustrate the advantages of the proposed DPTC method in torque control.
7. Experimental Results
To verify the practicability of the proposed DPTC method, relevant experimental tests are conducted on the SRM experimental bench. The relevant devices of the experimental bench are shown in Figure 9, which mainly include SRM, SRM controller, power converter, and oscilloscope. The load torque is generated by a magnetic powder brake, and the output torque is controlled by the predefined control algorithm. In the experimental test, the control algorithm is operated by a dSPACE-1103 controller. Because the oscilloscope used has only two channels, only the phase current and total output torque can be captured. In addition, to ensure consistency between the experiment and simulation, the parameters of the algorithms and the specification of the SRM are the same as in the simulation.
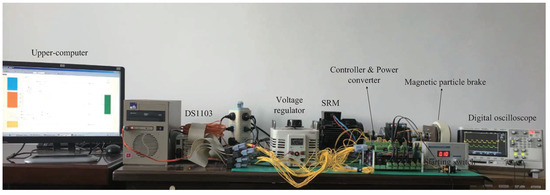
Figure 9.
Experimental bench.
Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12 show the experimental results of the four methods at 200, 400, and 800 rpm speeds when the load is 5 Nm. From the current waveform of the above methods, it can be seen that the DITC and PWM-DITC still have larger current peaks than the other two methods, which is not expected during the experiment. Moreover, the proposed DPTC method has smoother phase current and phase torque curves than the MPTC method.
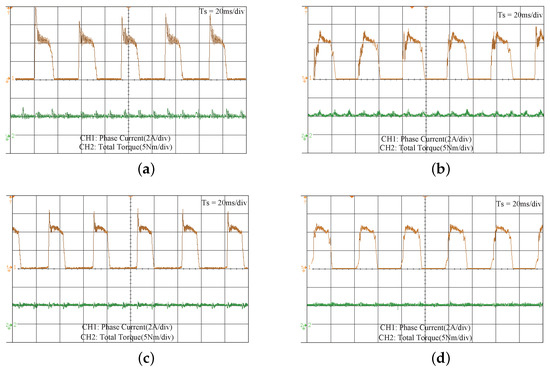
Figure 10.
Experimental results of (a) the DITC method, (b) the FCS MPTC method in [31], (c) the PWM-DITC method in [36], and (d) the proposed DPTC method at 200 rpm with a load of 5 Nm.
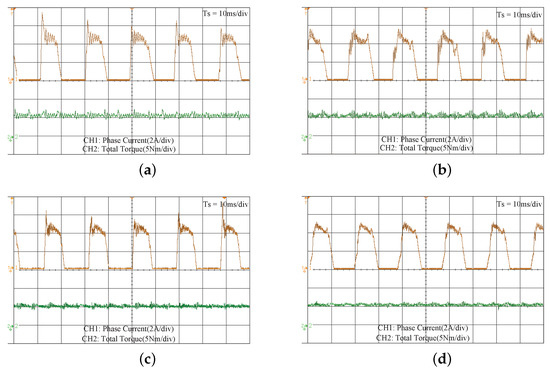
Figure 11.
Experimental results of (a) the DITC method, (b) the FCS MPTC method in [31], (c) the PWM-DITC method in [36], and (d) the proposed DPTC method at 400 rpm with a load of 5 Nm.
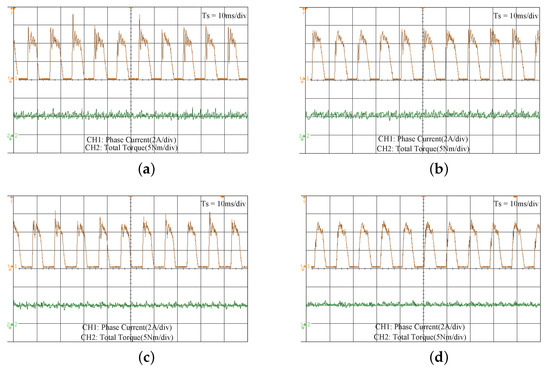
Figure 12.
Experimental results of (a) the DITC method, (b) the FCS MPTC method in [31], (c) the PWM-DITC method in [36], and (d) the proposed DPTC method at 800 rpm with a load torque of 5 Nm.
To quantitatively evaluate the experimental results of the above methods, the performance indices , , and have been calculated using (32)–(34) and summarized in Table 3. As can be seen from Table 3, the DITC method still has the largest torque ripple index of 42.4%, 51.3%, and 63.8% at 200, 400, and 800 rpm, respectively. Although the torque ripple is optimized in the MPTC method, it is still relatively large at 41.2%, 47.8%, and 56.3%, respectively. Undoubtedly, the proposed DPTC method has a smaller torque ripple than the MPTC method with 22.4%, 33.2%, and 39.4%, respectively. This shows that the proposed method reduces the torque ripple by 45.63%, 30.54%, and 30.02%, respectively, which has a high agreement with the simulation results. In terms of the copper loss, since the PWM-DITC method adheres to the principle of completing the commutation as soon as possible, compared with the proposed DPTC method, it has a higher copper loss index of 4.7106, 4.8742 and 5.3400 respectively. In contrast, the proposed DPTC method results in the copper loss index of 4.3065, 4.5218, and 4.9945 by optimizing the demagnetization and magnetization of two consecutive phases. This shows that the proposed method reduces the copper loss index by 8.58%, 7.23%, and 6.47%, respectively. Through the comparison results of the above experiments, the same conclusion as the simulation verification can be concluded, i.e., the proposed DPTC method has relative advantages in the torque ripple and copper loss, and the effectiveness of the proposed method is proved.

Table 3.
Experimental performance at various speeds.
8. Conclusions
In this paper, a novel direct predictive torque control algorithm for the SRM drive system is proposed. In the proposed DPTC method, the torque allocation set is obtained by directly dividing the reachable range of phase torque. Afterward, the optimal torque allocation scheme is obtained by using a cost function. Compared with the MPTC method, the proposed DPTC method solves the problems of unfixed switching frequency and large torque ripple. In addition, the proposed method takes into account the computing power of the hardware, thus ensuring the feasibility of the algorithm. In the torque predictive control of the SRM, the cost function is usually used to balance the contradiction between torque ripple and copper loss, which increases the difficulty of parameter setting and reduces the control effect. In the proposed method, the cost function only includes the penalty for phase currents, so the complexity of the algorithm is reduced. Finally, several algorithms are verified and compared by the simulation and experiment. The comparison results indicate that the proposed DPTC method not only outperforms the PWM-DITC method in terms of copper loss but also has significantly lower torque ripple than the MPTC method, thus proving the effectiveness of the proposed method. In future work, a simple SRM model will be considered to implement the proposed method, so as to ensure the control effect while reducing the memory space occupation of LUTs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.S. and G.W.; methodology, L.S.; software, L.S. and Y.F.; validation, L.S. and J.L.; formal analysis, L.S.; investigation, L.S. and D.L.; resources, L.S. and D.M.; data curation, L.S.; writing—original draft preparation, L.S.; writing—review and editing, L.S. and G.W.; visualization, L.S.; supervision, Y.F.; project administration, G.W.; funding acquisition, Y.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant number 2022YFB4301401), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number 61976033), Pilot Base Construction and Pilot Verification Plan Program of Liaoning Province of China (Grant number 2022JH24/10200029), Key Development Guidance Program of Liaoning Province of China (Grant number 2019JH8/10100100), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant number 2022M710569).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sahoo, S.K.; Dasgupta, S.; Panda, S.K.; Xu, J.X. A Lyapunov Function-Based Robust Direct Torque Controller for a Switched Reluctance Motor Drive System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lun, H.; Dai, L.C.; Fang, C.; Chen, Z.H. Networked control strategy of dual linear switched reluctance motors based time delay tracking system. ISA Trans. 2022, 129, 605–615. [Google Scholar]
- Ralev, I.; Qi, F.; Burkhart, B.; Klein-Hessling, A.; De Doncker, R.W. Impact of Smooth Torque Cont-rol on the Efficiency of a High-Speed Automotive Switched Reluctance Drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 5509–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, G.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Fan, Y. A Novel Method for Modeling the Electromagnetic Characteristics of Switched Reluctance Motors. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Zhang, W. A Simple Strategy for Parameters Identification of SRM Direct Instantaneous Torque Control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 3622–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustun, O.; Onder, M. An improved torque sharing function to minimize torque ripple and increase average torque for switched reluctance motor drives. Electr. Power Components Syst. 2020, 48, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bober, P.; Ferkova, Z. Comparison of an off-line optimized firing angle modulation and torque sharing functions for switched reluctance motor control. Energies 2020, 13, 2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Chen, Z.; Chen, H. Smooth torque speed characteristic of switched reluctance motors. J. Power Electron. 2014, 14, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Scalcon, F.P.; Xiao, D.; Vieira, R.P.; Gründling, H.A.; Emadi, A. Advanced Control of Switched Reluctance Motors (SRMs): A Review on Current Regulation, Torque Control and Vibration Suppression. IEEE Open J. Ind. Electron. Soc. 2021, 2, 280–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, P. Improvement of the torque-speed performance and drive efficiency in an SRM using an optimal torque sharing function. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, M.; Menaem, A.A.; Rezk, H.; Ibrahim, M.N.; Számel, L. An improved indirect instantaneous torque control strategy of switched reluctance motor drives for light electric vehicles. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujičić, V.P. Minimization of Torque Ripple and Copper Losses in Switched Reluctance Drive. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Bilgin, B.; Emadi, A. An Extended-Speed Low-Ripple Torque Control of Switched Reluctance Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 1457–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Bilgin, B.; Emadi, A. An Improved Torque Sharing Function for Torque Ripple Reduction in Switched Reluctance Machines. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 30, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Bilgin, B.; Nalakath, S.; Emadi, A. A New Torque Sharing Function Method for Switched Reluctance Machines with Lower Current Tracking Error. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 10612–10622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wu, J.H.; Gan, C.; Hu, Y.H.; Si, J.K. OCTSF for torque ripple minimisation in SRMs. IET Power Electron. 2016, 9, 2741–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Ye, J.; Emadi, A. A Digital PWM Current Controller for Switched Reluctance Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 7087–7098. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.H.; Du, Q.J.; Liu, X. Indirect predictive torque control for switched reluctance motor in EV application. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikail, R.; Husain, I.; Sozer, Y.; Islam, M.S.; Sebastian, T. A Fixed Switching Frequency Predictive Current Control Method for Switched Reluctance Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 3717–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrass, P.G.; Mecrow, B.C. Flux and torque control of switched reluctance machines. IET Electr. Power Appl. 1998, 6, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.D.; Zhao, X.C.; He, K.L.; Cao, Y.Z. Torque-ripple reduction of SRM using optimised voltage vector in DTC. IET Electr. Syst. Transp. 2018, 33, 3622–3630. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, P.K.; Ronanki, D.; Perumal, P. Efficiency improvement and torque ripple minimisation of four-phase switched reluctance motor drive using new direct torque control strategy. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2020, 14, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Cao, X.; Deng, Z. Direct Torque Control for Switched Reluctance Motor to Obtain High Torque–Ampere Ratio. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 5144–5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inderka, R.B.; De Doncker, R.W. DITC-direct instantaneous torque control of switched reluctance drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuengwarodsakul, N.H.; Menne, M.; Inderka, R.B.; De Doncker, R.W. High-dynamic four-quadrant switched reluctance drive based on DITC. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2005, 41, 1232–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wu, J.; Gan, C. Optimized Direct Instantaneous Torque Control for SRMs With Efficiency Improvement. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 2072–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Fang, G.; Hei, R.; Jiang, J.; Ma, R.; Liu, W. Torque Ripple and Efficiency Online Optimization of Switched Reluctance Machine Based on Torque per Ampere Characteristics. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 9608–9616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hu, Z.; Cui, X. Research on Novel Direct Instantaneous Torque Control Strategy for Switched Reluctance Motor. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 66910–66916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, D.F.; Tarvirdilu-Asl, R.; Garcia, C.; Rodriguez, J.; Emadi, A. Vision, Challenges, and Future Trends of Model Predictive Control in Switched Reluctance Motor Drives. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 69926–69937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, S.; Rodriguez, J.; Rivera, M.; Franquelo, L.G.; Norambuena, M. Model Predictive Control for Power Converters and Drives: Advances and Trends. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 935–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrl, H.; Papafotiou, G.; Morari, M. Model predictive torque control of a Switched Reluctance Motor. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, Churchill, VIC, Australia, 10–13 February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.H.; Wang, G.F.; Li, Y.; Xu, A.D. An improved finite-state predictive torque control for switched reluctance motor drive. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2017, 12, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Ye, J.; Xiao, D.; Xia, Z.; Emadi, A. Computational-Efficient Model Predictive Torque Control for Switched Reluctance Machines with Linear-Model-Based Equivalent Transformations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 5465–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cui, Z.; Ding, S.; Chen, F.; Guo, Y. Model Predictive Direct Torque Control of Switched Reluctance Motors for Low-Speed Operation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 37, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Shang, C.; Chen, J.; Zhu, J.; Han, L. A New Control Method Based on DTC and MPC to Reduce Torque Ripple in SRM. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 68584–68593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhaus, C.R.; Fuengwarodsakul, N.H.; Doncker, R.D. Predictive PWM-based direct instantaneous torque control of switched reluctance drives. In Proceedings of the 2006 37th IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Jeju, Republic of Korea, 18–22 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).