Abstract
Railway systems are sometimes faced with the necessity of decommissioning railway stations due to issues in the electricity supply system, control system failures, or a decrease in train traffic. In order for fully or partially decommissioned stations to maintain functionality and turnout availability, the researchers propose the use of a computer system utilizing GSM technology. Using AES-encrypted SMS messages, GSM signaling can be applied to a wide range of electrical equipment at decommissioned stations, enabling monitoring and control of these installations remotely, as well as allowing for integration into an existing SCADA system. This study attempts to estimate the reduction in total delays and operating cost that would arise when implementing this control system in a low-resource setting. An impact and cost analysis was performed on a rail section with partially decommissioned stations (Brașov–Codlea, Romania), to ascertain whether this control method would result in significant delay and cost reductions. The analyzed data show that the proposed control system can significantly reduce delays and costs on railway lines with decommissioned stations, thus allowing for a more efficient use of resources. By leveraging technology to monitor and control electrical installations remotely, the need for physical presence at the decommissioned station is eliminated. Overall, the research described represents a significant step towards the more efficient and safe use of railway infrastructure, and could potentially lead to the reactivation of previously decommissioned stations, providing benefits for both passengers and freight transport operators.
1. Introduction
The industrial revolution brought us railway transportation, and with it, a fast and reliable way of connecting cities and industries. In the past century, railway systems have grown exponentially, thanks to the construction of intricate and abundant railway networks and with the development of high-speed trains [1]. However, such a complex and high-speed capable railway system needs an up-to-date fail-safe control infrastructure, as even minor failures or desynchronizations could lead to delays or even accidents, with human casualties and loss of valuable resources. In order to ensure the safe, sustainable, and efficient movement of an increasing number of high-speed traveling trains, a centrally controlled supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) railway system, connected to multiple, remote, GSM-operated PLCs (programmable logic controller), is necessary for the operation of interlocking and signaling systems, railway switches, train detection but also for collecting data referring to energy consumption and modes, voltage, and power flow [2,3].
However, in low-resource settings, reliable physical infrastructure is not always provided. Such is the case with decommissioned stations, due to failure of track circuits, axle counters, CAS (condition assessment systems), switches, and many other essential components [4]. Another reason for decommissioning is the lack of trained personnel to manually operate various components, a situation encountered especially in hard to reach areas and remote railway stations with low railway traffic. Therefore, such stations need to be equipped with RCS (remote-controlled systems) and monitoring systems, to ensure safe railway traffic and reduce time and operational costs [5].
GSM-R (global system for mobile communications railways) is an example of wireless rail traffic management, using radio waves on specific frequency bands, allocated to railway communications only. It is part of the European train control system (ETCS) and European rail traffic management system (ERTMS) used in Europe, and it works by collecting data from the input parts (sensors, push buttons, and contact limit switches) regarding the positioning and velocity of rail vehicles, and transmitting the aforementioned data through the ETML (European traffic management layer) to the ETCS, in order to control the output parts (signaling or moving parts). It operates via infrastructure located only near railway lines and is subject to radio network planning challenges, including meeting the signal coverage requirements of the ETCS on designated railway lines and optimizing operational capacity for voice and other services in the GSM-R system [6].
The ETCS is classified on three levels of operation from a functionality and data integration point of view, with an additional level 0 for situations regarding ETCS-compliant rolling stock interacting with non-ETCS lines, due to lack of equipment or non-ETCS compliant equipment. While the GSM-R system has a communication-only purpose in the ETCS-1 system, it has a role in train detection, train monitoring, and automatic train control in the ETCS-2 system [7]. Such an interface is safety critical, and therefore it needs protection from wireless interferences and attacks [8,9,10]. Advanced Encryption System (AES) encryption of SMS data is a possible way of shielding this system [11].
Managing decommissioned stations can be a challenge, due to the heating of railway switches. For example, Russian Railways (JSC RZD) employs automatic snow and ice buildup removal systems, such as SCRS, to address this issue. However, the current systems have been found to have deficiencies in switch rail surface cleaning and power consumption efficiency. Therefore, an effective and efficient solution is needed, to comply with current operational standards of railway switch heating systems. This can be achieved through the integration of data collection and control functions into the system, as discussed in article [12].
The electronic data processing unit, with special software, continuously receives signals from rail temperature, outdoor temperature, and precipitation sensors. The signals are then compared, according to a certain algorithm, and the first and second stepless voltage control units transmit voltage to flat oval electric heaters. This maintains the required heating temperature of the frame rails, depending on air temperature and ambient humidity. This device for cleaning snow and ice by electrical heating, can reduce energy consumption by up to 60% compared to existing systems, preventing icing and removing ice and snow in the area of the wits and frame rails. It ensures uninterrupted train movement during snowfalls and blizzards, and provides continuous operation of turnouts in winter, regardless of precipitation [13].
To evaluate the efficiency and performance of systems for maintaining required temperature parameters of railway switch control surfaces without using expensive equipment, computer simulation modeling is currently used for testing and experimenting in applied research. SIMULINK, a general-purpose simulation environment, is a powerful tool for testing and analyzing simulated preventive adjustment control systems applied to railway switch electric heating systems. Simulation allows for the testing and verification of models for performance. The algorithm for measuring snow and ice buildup presence on the control surface, required development and testing of a computer simulation model in the MATLAB environment [14].
The aim of this paper is to propose a GSM control system for fully or partially decommissioned railway stations, which could improve the flow and efficiency of train traffic, by reducing the number of minutes of delay on partially decommissioned railway lines, with the added benefit of SCADA compatibility. It also proposes a way to protect the aforementioned system from accidental or malicious attempts to interfere with the wireless network and its adjacent components, and to perform an estimated analysis of the reduction in delays and costs this method could achieve. The main hypothesis tested is whether the proposed control method would result in significant delay and cost reductions on railway lines with decommissioned stations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Initial Situation
2.1.1. Rail Traffic and Handling Facilities
It is possible to change the path of trains from one railway line to another, by using a specialized device called a track changer. The railway switch is a crucial component of the track changer, consisting of point blades, sliding supports, and two fixed rails. The handling device operates the point blades through a traction bar. To ensure that the switches work correctly, even in harsh conditions such as heavy snow or low temperatures, each switch is equipped with a heating system, comprising four resistive elements mounted on both fixed and movable parts [15]. Figure 1 displays a switch equipped with a resistive heating system.
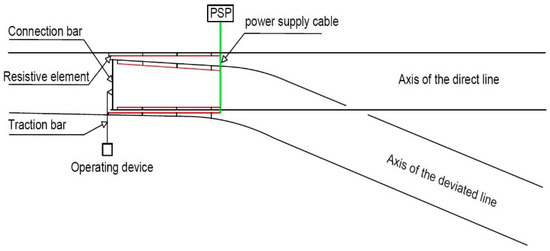
Figure 1.
Diagram of a switch equipped with a resistive heating system. PSP = power supply panel.
Switches are located at various points in railway stations, including entry points from open lines, access to different lines within stations, and exit points, for changing the train’s path. The distance between the entry switches and the exit switches of a station determines the size or limit of the station. Figure 2 shows a double-line railway station and displays the normal position and numbering of switches, and the distribution of the power supply panels (PSP) for the switch heaters.
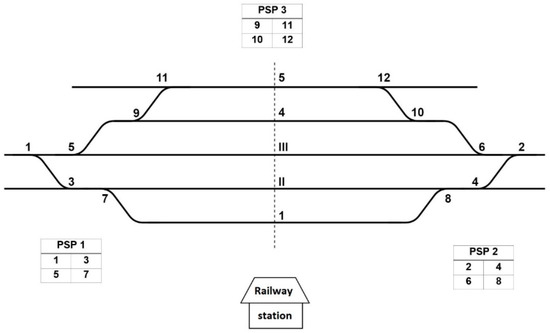
Figure 2.
Schematic of a double-track railway station, switch position, and heater power supply position on the panels. PSP = power supply panel.
At present, the process of coupling or decoupling the heaters’ power supply, involves the use of control keys situated within the railway station, as well as cables that connect to the PSPs using wires. Due to the elevated danger of control cable malfunction in the vicinity of the railway, alternative methods for transmitting this command have been suggested [16]. This paper presents a potential solution to address this issue, by proposing the use of a SCADA-compatible GSM support as a replacement for the unreliable physical control method [17]. The method consists of interfacing a GSM modem with a SCADA RTU (remote terminal unit), and controlling said GSM modem through the SCADA central station. This expands on the previous use for GSM technology, namely for the control of electrical installations of resistor heaters in railway switches, where control cable failure led to decommissioning [18].
2.1.2. The Power Supply Installation of the Railway Station
The power supply installation comprises lighting and power circuits that supply the illumination system for platforms, waiting rooms, relay rooms, and the employee (train dispatcher) activity room. The sources of electrical energy for a railway station are depicted in Figure 3.
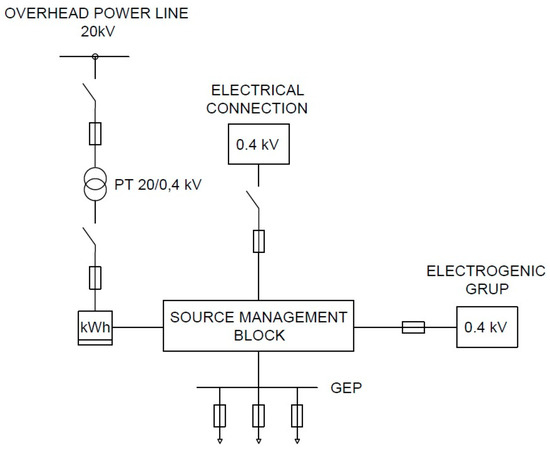
Figure 3.
The power supply diagram of a railway station.
In the initial situation, the source management block (SMB) is composed of switches manually operated by the operational servicing personnel of the railway station. By deactivating the station and withdrawing the personnel, in the event of a failure of the source that supplies the railway station installations, it becomes impossible to switch to a reserve source. The platform lighting system consists of lamps installed along the length of each railway track, which are supplied with power from the PSPs and controlled by authorized personnel, using control keys and relays. Figure 4 illustrates the lighting equipment layout of a railway station.
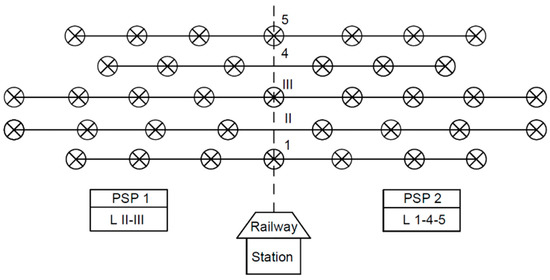
Figure 4.
Platform lighting scheme for a railway station. PSP = power supply panel; L = rail line, Roman numerals = direct lines; Arabic numerals = branching lines.
The energy supply and train running and handling facilities, are part of the category of critical railway installations, which must be kept permanently in operation at a level of safety imposed by the railway safety authorities of each state [19,20].
The lack of electricity supply to a railway station, leads to the inability to carry trains on that section, and so to the occurrence of delays and bottlenecks in rail traffic.
2.2. System Architecture
2.2.1. Initial Development
The process of coupling or decoupling switch heaters, involves transmitting a written message (e.g., ON as 01 and OFF as 10) from a mobile terminal, which is received by a GSM modem in the power supply box, located near the switches. The modem then delivers the message to the remote control system (RCS) as an electrical signal, which triggers the coupling or uncoupling of the power contacts supplying the PSPs. Upon execution, a confirmation message is sent back to the mobile device. Figure 5 illustrates the control system of a resistive heater remote, through the GSM network [20,21].
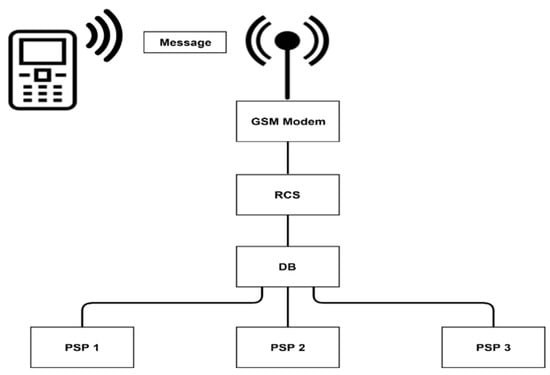
Figure 5.
Diagram of the command system of resistive heating of railway switches using GSM networking. RCS = remote control system; DB = distribution block; PSP = power supply panel.
The RCS assembly consists of several components, including an 8-bit microcontroller, a GSM modem, a voltage regulator, an RS232 serial communication module, and other electronic parts such as optocouplers, diodes, transistors, capacitors, and a 12 V relay. These components are mounted on wiring made in ExpressPCB, as shown in Figure 6 [22,23].
The 40-pin, 8-bit PIC16F887 microcontroller (Microchip, Chandler, AZ, USA), uses nanoWatt technology and has a 40-pin design. Its low cost and user-friendly architecture, make it affordable and simple to use and modify. The GSM Maestro 100 modem is used by the microcontroller to implement communication between the railroad switch and the SMS sender, at a speed of 300 bits per second (bps) over the serial port. A voltage regulator, LM2575-5 (Texas Instruments, Dallas, TX, USA), of 1 A, is utilized to reduce the supply voltage from 12 V continuous to 5 V continuous, which is needed for the PIC microprocessor (Microchip, Chandler, AZ, USA) and MAX232IN (Texas Instruments, Dallas, TX, USA) circuit. Using a 330-H coil and the voltage regulator mentioned above, a consistent power supply distribution is created [22,24].
The MAX232IN integrated circuit is used as a converter of logical (0/1 logic) impulses into RS232 signals (+8/–8 V), that are accepted by the GSM modem.
In addition, for added security, the LTV825 optocoupler is used, which acts as a bridge between the microcontroller’s logic levels of control (0/1) and the final command transistor BD139. A continuous voltage level of 12 V and a maximum current of 1.5 A pass through the transistor. This signal is used to control a relay for a railroad switch, and the relay in question will direct a 220 V AC voltage level to a power contactor. Upon decoupling, the 1N4007 diode, in series with the 12 V relay coil, achieves the protection of the BD139 transistor.
The microcontroller issues the command to the optocoupler through the output pin. By passing the ground connection through an auxiliary contact on the 12 V relay, the (open/closed) state of the relay is read. The microcontroller’s input pin 10 (RE2 pin), which is designated as the input pin, detects the presence or absence of the ground. The two-pin modem and the PIC16F887 communicate via MAX232: TX for transmission and RX for receiving characters from the modem.
AT commands are a set of instructions used to control modems, where AT stands for attention. Each command line must start with “AT” followed by the specific command. The system described in this study utilizes the following AT commands: AT + CMGD = 1.4, for deleting all messages stored in the SIM card; AT + CMGS, for sending SMS messages; and AT + CMGR, for reading SMS messages received by the modem and processed by PIC16F887.
The programming of PIC16F887 was carried out using the PICKit 2 programmer and written in the C language. The integrated development environment (IDE) utilized, was MPLAB v8.10, and the compiler HI-TECH PIC C Lite 9.60 was used to compile the program. The resultant hexadecimal (.hex) file was written into the program memory of PIC16F887 (Microchip, Chandler, AZ, USA) using the PICKit 2 programmer (Microchip, Chandler, AZ, USA), in MPLAB IDE v8.10.
2.2.2. Software Description
The software application was developed in the C language and includes a configuration process that sets the prescaler resolution to 8 bits for timer 0, configures the watchdog timer timeout, and sets the input/output pins. To restore the last relay value, a read operation is performed from the electrically erasable programmable read-only memory (EEPROM). If the relay was previously opened, the system will send a command to reopen it. This feature is useful in the event of a voltage drop during board restart, as it ensures that the relay is set to the previous command. Figure 6 provides further details on this process.
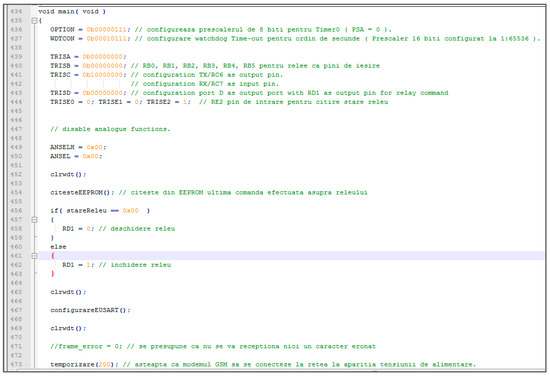
Figure 6.
Main code with configurations and fail-safe features.
The next step, is to configure the EUSART (enhanced universal asynchronous receiver transceiver) module, where the baud rate is configured at 300 bps, along with other configurations (frequencies, asynchronous mode, enable the interrupts for reception). If the power is down, the modem needs some time (almost 70 s) to connect to the nearby mobile cell tower. For this, a waiting time delay of 70 s was introduced. Because this fail-safe mechanism is very important, firstly, a message which specifies that a problem has been detected and a voltage drop-out has occurred, is sent, alongside the state of the relay (if it is ON or OFF), so that the user will know for sure if the data from the EEPROM was successfully restored and if it is correct. Secondly, the code will enter into a continuous loop, also known as a while loop, that will check regularly if an SMS was received from the user. If it receives a message and it is not an accepted command, it will react immediately with ‘invalid command’. If the request is valid, then, firstly it will send the command to the relay via RD1, and then, if the PIN was set, it will save it into the EEPROM. A feedback message will be sent confirming the command and the relay were set to the desired position. The available commands are made up on 4-byte buffers, and they are as follows: “01ON” to turn on the relay, “1OFF” to turn off the relay, and for the current status of the relay, the command is “STAT”.
The mobile phone number where the messages can be sent, is configurable from the source code. The new code can be flashed on the PIC microcontroller with the updated number. The panel-mounted control module is shown in Figure 7.
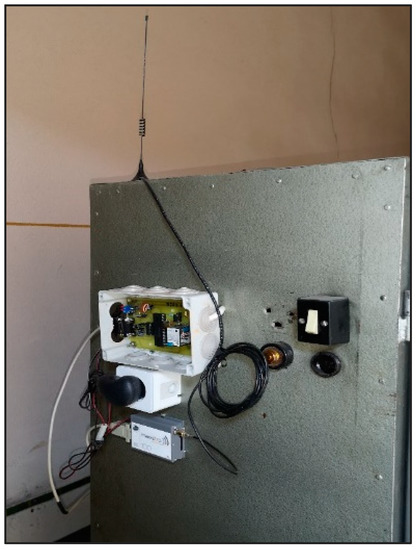

Figure 7.
Switch heating remote control device, mounted on a metal panel.
This C-module has in total 12 functions, including the main function, and it uses a 68-byte buffer, used for storing the messages from the GSM modem along with some safety checks (in the case of the message being longer than 68 bytes, the buffer will be overwritten!) [22].
The development and integration of the system into SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) involved the following stages:
- Replacement of the mobile terminal with the SCADA system implemented in the dispatch center;
- Installation of an RTU connected to the GSM modem at the station;
- Outfitting of SMBs (source management blocks) and PSPs with digital relays.
A block diagram of the control system consisting of the PC unit on which the SCADA system is installed, the GSM modem that enables bidirectional transmission of information, and the RTU unit installed at the railway station, is shown in Figure 8 [25].
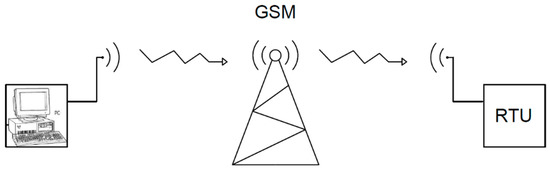
Figure 8.
Block diagram of the GSM-based control system of the railway station. GSM = global system for mobiles; RTU = remote terminal unit.
In this implementation, the existing SCADA system at the dispatching point, was enhanced with a software package that collects data from the field, transmitted by the RTU, and generates corrective commands if the RTU has not already done so. The RTU developed for this implementation is described in Figure 9.
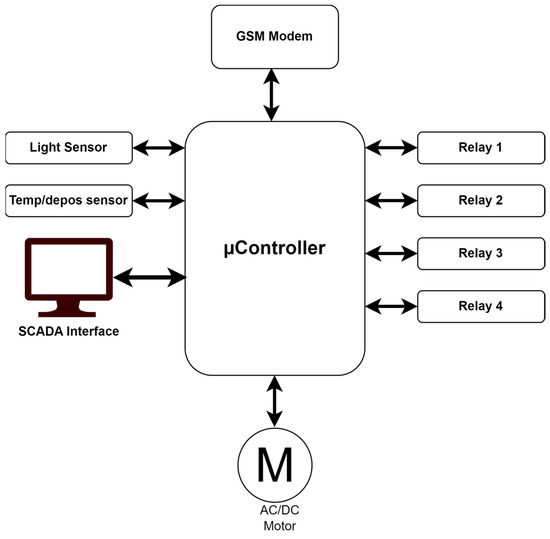
Figure 9.
Diagram of a remote terminal unit.
The remote terminal unit (RTU) is typically defined as a communication satellite within the SCADA system, and is installed at the railway station. The RTU collects data from sensors located in the field, stores them in its own memory, analyzes them, and initiates a command if necessary. Periodically, this information is sent to the SCADA system dispatch point, which can intervene with response commands. The developed RTU utilizes a PIC16F887 microchip and an 8-bit microcontroller with eight analog input channels. The controller programming and project development are performed similarly to the previously developed version, as it has been found that the programming tools available for these controllers are easy to use.
Temperature sensors read the temperature from the switch points at each end of the railway station, while deposit sensors are mounted on each switch point and record the presence or absence of snow deposits on their surface. This information is transmitted in the form of an electrical voltage, that varies between 0 and 5 V. The four relays are interfaced with the PC16F887 microcontroller (Microchip, Chandler, AZ, USA), to control the switch point heating system and platform lighting system. Figure 10 depicts the setup of the control system applied in the field.
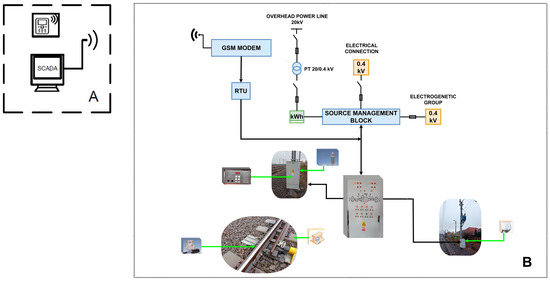
Figure 10.
Setup of the control system applied in the field. RTU = remote terminal unit.
The AC/DC motor was interfaced to be able to act in both directions on the 20 kV three-pole LEA separator. The GSM modem was interfaced with the RTU and the PC unit on which the SCADA system is installed. Both units communicate serially with the GSM module through AT command sets. The GSM infrastructure for communication between the dispatch post and the railway station was chosen, because it has the lowest implementation cost, and safety and efficiency in operation.
In this SCADA implementation, unique proprietary protocols were used for communication between field devices and the main terminal unit. The security of SCADA systems is based on the secrecy of these protocols, which we have defined as our own protocols for both transmission and reception.
2.2.3. SCADA Functional Architecture
The functional architecture of a control system is designed to be modular, and consists of three functional levels: the control level, the supervision level, and the execution/signal level. The control level provides the following functions: communication with the railway energy dispatcher, initiation of commands, validation of commands, ensuring safety conditions, interpretation and display of control information from the remote terminal unit (RTU).
The supervision level provides the following functions: verification and validation of transmitted commands, monitoring of command execution, validation of control information received from the execution level, and monitoring of system operation. The execution/signal level provides the following functions: control of terminal equipment, processing of status signals collected from the field into operable digital signals by the computer system, and transmission of information to the dispatch point.
In Figure 11, the functional architecture of the control system for power supply installations in a railway station is described. This functional architecture provides a framework for the development and implementation of control systems that are safe, efficient, and reliable. By separating the functions of control, supervision, and execution/signal processing into distinct functional levels, the system can be designed, tested, and maintained more easily, with clear interfaces and well-defined responsibilities for each level.
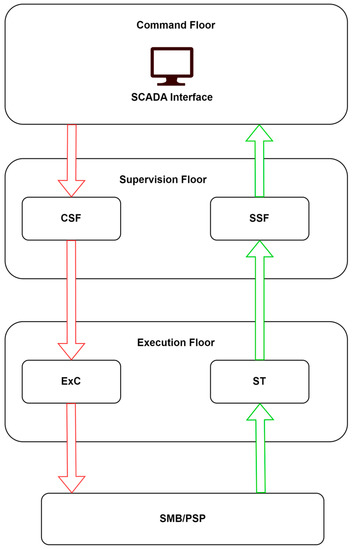
Figure 11.
The functional architecture of the control system for power supply installations in a railway station. CSF—control safety filter; SSF—signal safety filter; ExC—execution of commands; ST—signaling transmission; SMP/PSP—source management block/power supply panels.
2.2.4. Security and Encryption
Controlling relays via SMS messages poses a security risk, as anyone with access to the mobile number can potentially turn on or off the relay. To address this issue, we propose a secure relay control system, using an OTP algorithm and AES encryption. To make sure that only authorized users may turn on or off the relay, the system utilizes a one-time password, the so-called OTP technique. The OTP is more secure against possible attacks, since it is created or stored locally on the microcontroller and is not reliant on the current time or sent via SMS. To increase security even further, the OTP is encrypted using the AES encryption, using a shared key. SMS messages delivered to the GSM shield, which talks with the microcontroller, trigger the relay depending on the OTP and shared key.
A microcontroller board and a GSM shield are used in the system, to connect to the mobile network. By sending an SMS message to the GSM shield, the relay, which is attached to the relay (actuator) pin, may be switched on or off. The SMS message is made up of a frame that includes the relay status, shared key, and OTP (on or off).
A random number generator is used locally, to create the OTP, that is stored on the chip and available only for the sender. The OTP is more resistant to possible assaults, since it is a 24-bit value that is maintained in memory, and is not reliant on the current time. The OTP is delivered to the microcontroller, together with the shared key, when a user sends an SMS to activate or deactivate the relay.
With AES encryption, the shared key is a 256-bit key. The OTP and relay status, as shown in Figure 12, are encrypted using the shared key, which is only known to the sender and recipient of the SMS message. The microcontroller receives the encrypted frame and uses the shared key to decode it, before verifying the OTP. Depending on the relay status in the frame and if the OTP is valid, the Arduino switches the relay on or off.
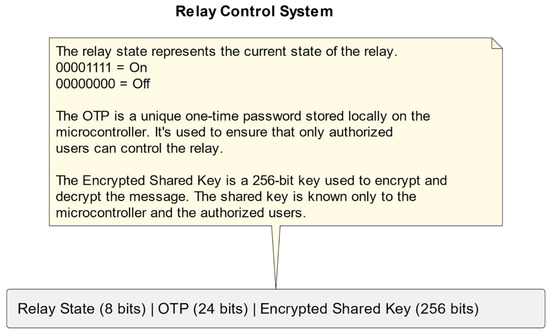
Figure 12.
Improving relay control security using AES encryption.
The full frame would consist of:
- 8 bits for the state (0 for off, 00001111 for on);
- 24 bits for the OTP;
- 256 bits for the shared key using AES encryption.
The complete frame size would be:
8 bits + 24 bits + 256 bits = 288 bits
Or, in bytes:
(8 bits + 24 bits + 256 bits)/8 = 36 bytes
Here is an example of AES encryption of a 288-bit frame message, with the following structure:
|8-bit command|24-bit OTP|256-bit AES encrypted payload|
With the 8-bit command, you can control whether the relay is on or off (command = 0x0F or 0x00). The one-time password (OTP) is a 24-bit number created by the sender and stored on the microcontroller. The payload is encrypted using the advanced encryption standard (AES) method, with a shared secret key, utilizing the remaining bits (256 bits).
To encrypt the payload, we concatenate the command, secret key, and OTP into a single string as the initial stage. For example, if the command is 0x0F, the OTP is 0x123456, and the shared secret key is “my$ecr3tkey”, the resulting string would then be “my$ecr3tkey0F123456”. As the second step, the shared secret key is then used to create an AES key, using a key derivation algorithm (KDF). For instance, we may generate a 256-bit AES key using the PBKDF2 algorithm. As a final step, the final 256-bit encrypted payload is created by encrypting the concatenated string, using the AES algorithm and the generated/stored key. As an example of an SMS, the following values would be used to build a 288-bit frame, that would be used to send an SMS message to the relay to activate it:
| 0x0F | 0x12ab5c |
d6e615e72c50b8a156789a637a114c5f8d14drg58127a524e16621d10d3f3f9e |
The OTP would be extracted from the frame when the message was received by the recipient, who would then compare it to the OTP that was kept locally. If the OTP is legitimate, it would use the shared secret key to decode the payload and carry out the relay-activation command.
2.3. Delay Estimation Based on Train Traffic Data
We chose the Brașov–Codlea route for the analysis, with two partially decommissioned stations (Bartolomeu and Ghimbav). It should be noted that the choice of the mainline took into account the following:
- The occupancy rate of passenger trains should be between 90% and 100%;
- It should be a route with heavy traffic;
- It should be intended for commuting to the workplace for the majority of passengers;
- It should include partially or fully deactivated railway stations.
The research was restricted to four successive railway stations positioned along the mainline route, and the layout and characteristics of the section are represented in Figure 13.
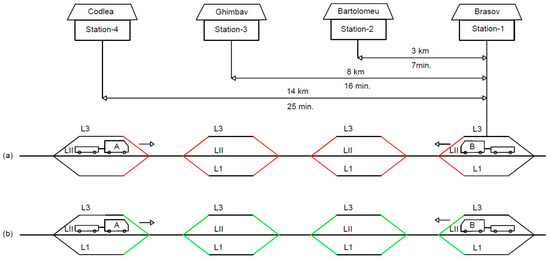
Figure 13.
Layout of the four railway stations. (a) The red colored route represents the blocked turnouts that do not allow access to adjacent lines, and (b) the same route but with turnouts and adjacent lines in operation, depicted in green. A,B = trains; L = rail line, Roman numerals = direct lines, Arabic numerals = branching lines.
In order to estimate the delay with and without turnout availability, train movement data was collected from the internal train signal register used on this line, “Registrul Unificat de Căi Libere, Comenzi si Miscare”, which translates to “unified registry of clear railways, commands and train movement”. In Figure 13, the distance from CF1 station and the time required to travel the route, are displayed. Two passenger trains (A and B) have been selected, which, according to the train schedule, are supposed to depart from CF1 and CF4 at the same time. Above each railway station, the distance from station CF1, and the time required to travel the route, are displayed. For freight trains, these times are expected to be doubled, given that these run at half the speed. The data was analyzed for the two situations described in Figure 13, for passenger trains and freight trains.
3. Results
The analyzed data show that, for passenger trains:
- Situation 1: L1 and L3 are unavailable at each railway station -> Train B departs from CF1 to CF4, Train A waits at CF4 for the arrival of Train B -> Train A arrives at CF1 with a delay of 25 min.
- Situation 2: L1 and L3 are available at each railway station -> Train B departs from CF1 to CF4, Train A departs from CF4 to CF3, the journey takes 9 min, and waits for Train B, which arrives after 7 min on Line 1 or 3. After this intersection, the trains continue their route, Train B arrives at CF4 according to the schedule, and Train A arrives at CF1 with a delay of only 7 min.
This reasoning was multiplied for the entire distance studied, for all passenger and freight trains that need to intersect at railway stations.
In Table 1, the minutes of delay due to situation 1 and the fare/minute for passenger and freight trains have been entered.

Table 1.
Delay and cost data for the two analyzed situations.
For freight trains:
Situation 1: L1 and L3 are unavailable at each railway station -> Train B departs from CF1 to CF4, Train A waits at station CF4 for the arrival of Train B -> Train A will arrive at CF1 with a delay of 50 min.
Situation 2: L1 and L3 are available at each railway station -> Train B departs from CF1 to CF4, Train A departs from CF4 to CF3, the journey takes 21.42 min, and waits for Train B, which arrives at CF3 after 7.14 min (28.56 min delay) on line 1 or 3. After this intersection, the trains continue their route, Train B arrives at CF4 according to the schedule, and Train A arrives at CF1 with only a 7.14 min delay.
The comparative cost analysis for passenger and freight trains passing through the described section, in both situations, is shown in Table 1.
The state-owned railway companies SNCFR Călători SA (National Railway Passengers Transport Company, Bucharest, Romania) and SNTFM CFR Marfă SA (National Railway Freight Transport Company, Bucharest, Romania), provide internal guidelines for determining the cost of delays, mainly to establish the compensation owed to passengers and freight companies. The tariff for passenger trains is set at RON 12.3 (EUR ~2.5) per minute, while the tariff for freight trains is RON 0.2 (EUR 0.041) per minute. We used these tariffs to assess the cost impact of the potential delay reduction made possible by the measures proposed above.
According to the analysis of the information presented in Table 1, implementing the proposed solution would result in an 80.07% reduction in total delay time. This would enhance the efficiency of both passenger and freight transportation on the studied rail segment and generate a potential annual benefit of RON 36,041,895.8.
4. Discussion
In order to be able to maintain the safe and efficient management of crucial structures in the decommissioned stations of our railway system, it is of the utmost necessity to install GSM-R technology coupled with a SCADA interface model, to remotely operate various applications (railway switches with their adjacent heating system, illumination and signaling systems on platforms) and the auxiliary transformers that supply the required voltage to run such applications [26]. Moreover, Romania is part of the ERTMS, with a national implementation plan for various level 1 and level 2 ETCS lines being proposed since 2018, and ETCS lines currently rely on GSM-R technology [27].
For our research we chose the Brașov–Codlea line, a line with heavily traffic, with two partially or fully decommissioned stations and accessory lines (level 0 ETCS), and two trains traveling in opposite directions on the same route, to showcase the importance of using remotely-controlled switches and signaling to facilitate the circulation of rolling stock, using the same main line passing through decommissioned stations. In situation 1, the accessory lines situated in the aforementioned stations cannot be used as temporary waiting lines, due to the lack of infrastructure and personnel to manually operate the railway switches and correctly signal the rolling stock. Therefore, two trains cannot use the same route simultaneously, this results in one of the trains being obliged to wait for the arrival of the other train in order to depart, thus accumulating tens of minutes of delay and additional costs. However, if the accessory lines could be opened, because of remote-controlled switching and signaling, and those operations being monitored remotely from a control center, the two trains could depart at their estimated departure times, with one of the trains using an accessory line after its arrival at one of the decommissioned stations, as a buffer zone. This allows the second train to use the main line unencumbered and arrive at its destination on time, while the first train has considerably less distance to recover after waiting on the accessory line, getting to its destination with a significantly reduced delay and operational cost, generating an annual benefit of over 36 million RON (over 7.3 million Euros). This situation works for both passenger trains and freight trains. In addition, the remotely-controlled switching system is operational in low temperatures thanks to the heating system the switches are equipped with, which can also be remotely controlled [18]. This is an important situation to consider, since the Brașov–Codlea line is situated near the mountain ranges of the Carpathian arc, with very low temperatures during the winter, with a temperature of −38.5 °C being recorded in a settlement near Brașov in 1942 [28].
The analysis presented in this paper, supports the hypothesis that implementing remote control measures in decommissioned and partially decommissioned railway stations, has the potential to result in significant delay reduction and cost reduction in railway systems in low-resource settings. Moreover, with relatively few and low cost improvements of such systems, such as installing on-board train modules that communicate their real-time position via GPS to the decommissioned stations and the command center, the railway warning and collision avoiding systems could be improved even further [29]. The scalability of the proposed solution, facilitates the introduction into existing, or under construction, control systems, providing an easy adaptation to changes in train traffic. In addition to the advantages described above, the results of this research respond to the request to increase the safety and security of critical infrastructures by global and Euro-Atlantic economic structures, and to bring Romania closer to a fully ERTMS-compliant railway network, and remove its outdated class B system from the trans-European corridors [30].
Limitations
The limitations of this research study are:
- In Romania, the development and implementation of the SCADA system for the control of the railway transport system is just beginning, there are very few dispatching points and railway stations that are outfitted with this technology. For the quick resolution of this situation, it is recommended to implement the solution proposed here, mobile phone terminals and GSM modem based control;
- The control system was tested on a single railway. However, considering the comprehensive description of the GSM module, it is plausible that the proposed control system can be replicated by implementing the same system on other railways that possess decommissioned stations. Such an approach would enable a comparative analysis of the outcomes achieved, thus strengthening the generalizability of the findings.
- The research did not include the automation of train circulation, and for this reason there was the need to maintain operative service personnel in railway stations, authorized for the execution of maneuvers related to the effective movement of trains;
- The research could not be performed on a larger sample of railway stations, due to the lack of a digitized system providing a database with the necessary information. Ideally, the energy cost would be monitored using a dedicated procedure and module, as previously described [23];
- Although during the research period the limitations mentioned above were discovered, comparative analysis of the two situations shows that the solution developed and proposed in this paper requires a minimum financial effort to obtain important economic results.
5. Conclusions
This paper presents a novel approach to managing partially or fully decommissioned railway stations using a SCADA-GSM system. The proposed method aims to ensure the electricity supply system, prevent system failures, reduce train traffic, and improve the overall efficiency of railway transportation.
To ensure the security of the SCADA system, the authors propose defining their own protocols for both transmission and reception. They use the advanced encryption standard (AES) method, with a shared secret key that utilizes the remaining bits (256 bits). The payload is encrypted by concatenating the command, secret key, and OTP into a single string, as the initial stage. The architecture of the control system is modular, and consists of three functional levels: the control level, the supervision level, and the execution/signal level.
To test the efficacy of the proposed method, the authors chose the Brașov–Codlea route, which has two partially decommissioned stations, Bartolomeu and Ghimbav. Data were analyzed for both passenger and freight trains, and the results showed an 80.07% reduction in total delay time. This reduction in delay time would significantly enhance the efficiency of both passenger and freight transportation on the studied rail segment and generate a potential annual benefit of more than 36 million Romanian Leu.
The proposed system’s scalability, makes it easy to integrate into existing control systems, or those under construction, and to adapt to changes in train traffic. This approach addresses the need for increasing the safety and security of critical infrastructure, and helps bring Romania closer to a fully compliant railway network.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.-F.P. and S.-A.M.; funding acquisition, S.-A.M.; investigation, A.-F.P.; methodology, A.-F.P., D.M.K., D.-V.B. and M.-A.Z.; visualization: D.M.K.; resources, S.-A.M.; software, A.-F.P., D.-V.B. and M.-A.Z.; supervision, S.-A.M.; writing—original draft, A.-F.P., D.-V.B., M.-A.Z. and S.-A.M.; writing—review and editing, A.-F.P., D.M.K., D.-V.B., M.-A.Z. and S.-A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Article Processing Charge was reimbursed by the Transilvania University of Brașov (Brașov, Romania) under decision nr. 1/2020, the registration number of this paper being 4223/04.04.2023. The publication fee of the article will be reimbursed according to the decision of the Transilvania University of Brașov’s Board of Administration, no. 11 of 2 September 2020, point 10, paragraph d).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, because, since it was an observational no-clinical study, it was not mandatory.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The raw train traffic data are not publicly available, due to internal confidentiality guidelines set by the railway company CFR SA.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Küster, H. Railways: Gateways between east and west in Europe. Promet-Traffic Transp. 2003, 15, 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov, A.A.; Lavrukhin, A.A.; Kuznetsova, M.A. Schemes and problems of scada system for electrical energy control on railway rolling stock. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Industrial Engineering, Applications and Manufacturing (ICIEAM), St. Petersburg, Russia, 16–19 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, S. A historical overview of railway signalling & control (or ‘from Bobbies to Balises’). In Proceedings of the IET 13th Professional Development Course on Electric Traction Systems, London, UK, 3–6 November 2014; pp. 4–18. Available online: https://digital-library.theiet.org/content/conferences/10.1049/cp.2014.1433 (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- Ramuhulu, M.; Chiranga, N. An Investigation into the Causes of Failures in Railway Infrastructure at Transnet Freight Rail—A Case of the Steel and Cement Business Unit. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Policy 2018, 7, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, M.; Bramani, M. The automation control systems for the efficiency of metro transit lines. In Proceedings of the 2015 AEIT International Annual Conference (AEIT), Naples, Italy, 14–16 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- European Union Agency for Railways. European Rail Traffic Management System (ERTMS). 2018. Available online: https://www.era.europa.eu/domains/infrastructure/european-rail-traffic-management-system-ertms_en (accessed on 12 March 2023).
- ETCS Levels and Modes. Available online: https://transport.ec.europa.eu/transport-modes/rail/ertms/how-does-it-work/etcs-levels-and-modes_en (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- Prasad, C. GSM-R to LTE for Railways in India. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Global Conference on Wireless Computing and Networking (GCWCN), Lonavala, India, 23–24 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Holakar, A.; Mahendra, L.; Prasad, G.L.G.; Shetter, R. Secure interoperable gateway for wireless SCADA system. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Computation System and Information Proceedings of the Technology for Sustainable Solutions (CSITSS), Bengaluru, India, 6–8 October 2016; Available online: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7779408/ (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Baldini, G.; Nai Fovino, I.; Masera, M.; Luise, M.; Pellegrini, V.; Bagagli, E.; Rubino, G.; Malangone, R.; Stefano, M.; Senesi, F. An early warning system for detecting GSM-R wireless interference in the high-speed railway infrastructure. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. Prot. 2010, 3, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analysis of Different Encryption Standards on GSM Network. Available online: https://www.ijser.org/paper/ANALYSIS-OF-DIFFERENT-ENCRYPTION-STANDARDS.html (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- Barausov, V.A.; Bubnov, V.P.; Sultonov, S.K. Designing Automatic Railway Switch Heating System with Innovative Intelligent Sensors. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Transport Systems and Transport Security, St.Petersburg, Russia, 14 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Barausov, V.A.; Bubnov, V.P.; Sultonov, S.K. Control Software for surface ice and snow detecting device. In Proceedings of the Models and Methods of Information Systems Research Workshop (MMISR 2019), St. Petersburg, Russia, 4–5 December 2019; CEUR Workshop Proceedings: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2019; Volume 2556, pp. 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Barausov, V.A.; Bubnov, V.P.; Sultonov, S.K. Simulation modeling in methods and designs for detecting ice or snow buildup on control surface in MATLAB/SIMULINK dynamic modeling environment. In Proceedings of the Models and Methods of Information Systems Research Workshop 2020, St. Petersburg, Russia, 11–12 December 2020; CEUR Workshop Proceedings: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2020; pp. 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Golovash, A.N.; Esipenko, V.S.; Pimenov, I.Y. Switch Heating Device Bibliographic Data. Patent RU2232222 (C1) 2004, 15 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yantang, G. Electric Heating Snow Removing Device For Railway Points Bibliographic Data. Patent CN201433383 (Y), 31 March 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Baruchov, V.A.; Kochubey, V. Electrical Heating Device Of Track Switches Type Seit-04 Bibliographic Data. Patent RU2582627 (C1), 27 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, A.; Bratu, D.; Moraru, S. Remote Control of Railway Switch Heating Using GSM Modems. Ann. Dunarea Jos Univ. Galati Fascicle IX Metall. Mater. Sci. 2019, 42, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuesong, F.; Hanxiao, Z.; Yong, D.; Zhili, L.; Hongqin, P.; Bin, X. A Review Study on Traction Energy Saving of Rail Transport. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2013, 2013, 156548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, H.R.U.; Zaman, H.; Hanif, M. Scada Implementation Using Gsm Network For Communication. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Embedded Systems and Applications (ESA), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 18 July 2011; The Steering Committee of The World Congress in Computer Science, Computer Engineering and Applied Computing: Athens, Greece, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, D. GSM Remote Controler Heater, Technology and Comunication 2014. Available online: https://www.theseus.fi/handle/10024/79408 (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- Lukman, A.; Olayemi, M.O.; Kolo, J.; Ajao, A. Project-Based Microcontroller System Laboratory Using Bk300 Development Board With PIC16F887 Chip. Int. J. Embed. Syst. Appl. (IJESA) 2015, 5, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- ARC Electronics, RS232 Tutorial on Data Interface and Cables. Available online: http://www.arcelect.com/rs232.htm/ (accessed on 10 August 2022).
- Parab, J.S.; Shelake, V.G.; Kamat, R.K.; Naik, G.M. Exploring C for Microcontrollers: A Hands on Approach; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 50–76. [Google Scholar]
- Katte, S.; Kotecha, D.; Vora, J.; Mehendale, N. Wireless SCADA technology using GPRS. Technofocus 2011, 2, 37–40. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/305083329_Wireless_SCADA_technology_using_GPRS (accessed on 7 January 2023).
- Dange, A.; Fernando, E.; Zachariah, H.S.; Kallakuri, D. Real-time Alert System for Auxiliary Transformer Failures. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Students’ Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Science (SCEECS), Bhopal, India, 19–20 February 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, A.; Fratu, A.; Lepadat, I.; Helerea, E.; Cojanu, V. Monitoring the Cost of Energy for Powering the Railway Electric Traction System. In Proceedings of the 2019 8th International Conference on Modern Power Systems (MPS), Cluj Napoca, Romania, 21–23 May 2019; pp. 1–6. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8759724 (accessed on 6 January 2023).
- European Standard for the Automatic Train Protection (ATP)—Romania. Available online: https://transport.ec.europa.eu/transport-modes/rail/ertms/contributing/countries/romania_en (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- Rajkumar, R.I.; Sundari, G. Intelligent computing hardware for collision avoidance and warning in high speed rail networks. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Site-ul Administratiei Nationale de Meteorologie. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20090906221054/http://www.meteoromania.ro/index.php?id=489 (accessed on 14 March 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).