Abstract
There is a general agreement in referring the deposition of calcareous tufa to climatic causes. Warm climates are believed to favor calcareous tufa formation due to higher concentrations of biogenic CO2 in soils, enhancing the dissolution rates of CaCO3 and the broader development of aquatic plants that remove CO2 from spring waters. Conversely, cold climates are considered less favorable because of the reduced biological activity of soils and the lesser development of aquatic plants. Dry climates are also considered unfavorable to the deposition of calcareous tufa due to scarcity of rainwater and the consequent reduction of water circulating in the ground and spring discharge contrary to humid climates, which, besides allowing abundant water infiltration and emergence, favor the spreading of vegetation cover, the development of biogenic processes in the soils, and the growth of aquatic plants. An additional factor controlling calcareous tufa deposition may be the temperature difference between the ground surface and the aquifer in connection with major climatic changes due to the low thermal conductivity of the limestone bedrock. With climate warming, the infiltrating water, made highly acidic when crossing the soil due to the elevated partial pressure of biogenic CO2 present therein, percolating through the progressively colder levels of the aquifer, induces a relevant dissolution of CaCO3, definitely higher than in normal conditions. At emergence, because of the higher surface temperatures, running water turbulence, photosynthetic activity of mosses and algae, and evaporation of spray droplets, the groundwater loses CO2, becoming oversaturated with CaCO3 and causing tufa deposition, even at a great distance from the spring. Opposite effects, such as the deposition of dissolved carbonate in the upper bedrock layers and the emergence of spring waters undersaturated with CaCO3, capable of further dissolution, are expected to occur with major climatic changes to cold conditions. This model appears to be confirmed by the deposition/erosion stages of calcareous tufa, which repeatedly occurred during the Holocene and the late Pleistocene in different parts of the world.
1. Calcareous Tufa
The term calcareous tufa, or freshwater travertine, is widely used in the scientific literature to describe carbonate deposits precipitated from cool groundwaters of meteoric origin enriched in CO2 (carbon dioxide) by percolating through organic soils and, therefore, capable of attacking CaCO3 (calcium carbonate) in limestone aquifers and dissolving it as Ca (HCO3)2 (calcium bicarbonate) according to the equation: [1]
CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O ↔ Ca + (HCO3)2
Calcareous tufa deposits form from the degassing of carbon dioxide and related shifting of the above equation induced by flowing water turbulence and the photosynthetic process by vegetal organisms typical of aquatic environments such as bacteria, blue-green algae, and mosses whose remnants are usually present in the deposit structure [1,2,3] together with fossil fauna such as ostracods and mollusk shells [4,5]. Similar in origin to calcareous tufa are cave speleothems [6]. Carbonate deposits precipitated from geothermal waters highly enriched with concentrations of CO2 are called thermogene travertines [6] or, more simply, travertines [7]. Calcareous tufa deposition has taken place in various environmental conditions since the earliest geological times [6], even though most deposits are referred to the Middle-Upper Pleistocene and Holocene ([8,9,10,11] and references therein).
2. Calcareous Tufa Deposition/Erosion and the CaCO3·CO2·H2O System
The dissolution rate of CaCO3 in water is very low [12]. However, if the solution includes some CO2, CaCO3 is easily dissolved as Ca(HCO3)2. The dissolved free carbon dioxide (not combined in the previous equation) is called equilibrium CO2 [13]: With concentrations of dissolved CO2 lower than the equilibrium values, precipitation of CaCO3 will occur, while with higher concentrations, further dissolution of CaCO3 will be possible. The carbon dioxide concentration above the equilibrium value is called independent CO2 [12].
The solubility of CaCO3 in water directly depends on the partial pressure of CO2 in the surrounding atmosphere [14,15]. It is very low in the open air but strongly increases in soils, where the partial pressure of CO2 produced by biological processes and the decay of organic matter can attain values up to 1000 times higher than in the atmosphere [16]. The temperature also controls the CO2 solubility: Water at 0 °C dissolves CO2 about three times more than at 30 °C [12]. Then, the water reaches the phreatic zone where the only sources of additional CO2, apart from a possible endogenous supply, is from the oxidation of minor amounts of transported organic matter or bacterial activity [17]. However, in such conditions, the total amount of CO2 may be considered practically constant, but the relative amounts of free CO2 (equilibrium plus independent CO2) and combined CO2 (to form CaCO3 and Ca(HCO3)2) may change with variations of pressure and temperature. In a closed system, free CO2 may also be derived from the mixture of solutions saturated with different concentrations of CaCO3 [18].
Several factors may cause CaCO3 precipitation [6,8]: Lower partial pressure of CO2 at the groundwater emergence, increasing groundwater temperature at the emergence, consumption of CO2 by aquatic plants, loss of dissolved CO2 (degassing) induced by turbulence and pulverization of stream waters at waterfalls, breaks, and roughness reaches of the river profile, even at a great distance from the spring [19,20].
3. Types of Calcareous Tufa
Calcareous tufa may be divided into two main groups: autochthonous tufa, deriving from in situ encrusted organisms, and allochthonous tufa, consisting of phytoclasts (encrusted fragments of plants) arenitic (microdetrital facies) and ruditic (macrodetrital facies) in size [21,22,23,24,25]. Based on the sedimentary facies, autochthonous tufa may be distinguished:
- -
- stromatolithic tufa, including sequences of laminae (usually 1–10 mm in thickness) formed during short depositional intervals characterized by the presence of particular encrusting microorganisms (Figure 1);
- -
- microhermal tufa, consisting of strata lens whose fabric reveals the structure of constructing organisms (usually mosses or algae) encrusted in growth position;
- -
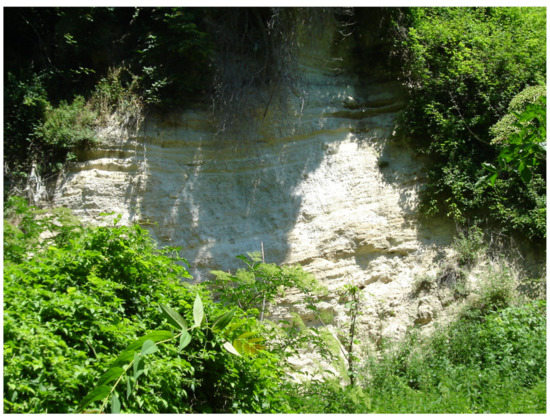

Figure 1.
Stratified stromatolithic tufa in the upper basin of the Esino River (Marche, Italy).
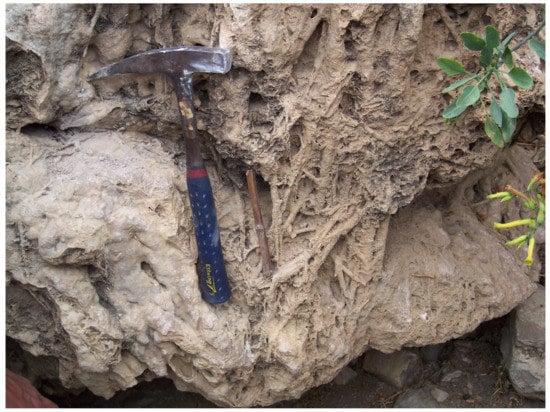

Figure 2.
Plant remains encrusted in phytohermal tufa at the Romanatt dam (Tigray, Ethiopia).
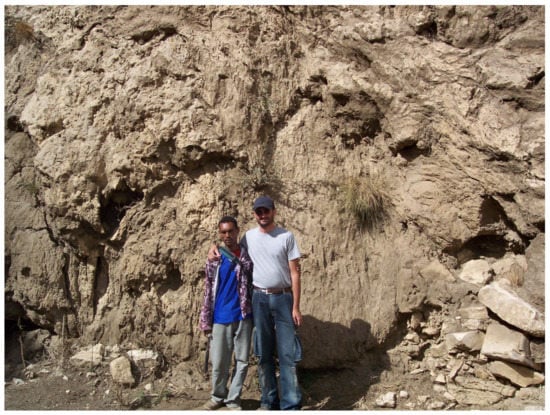

Figure 3.
Phytohermal tufa at Romanatt Dam (Tigray, Ethiopia).
Allochthonous tufa deposits have a typical clastic texture with fragments of incrustations on vegetal organisms sometimes providing information (e.g., clast orientation, imbrication, etc.) about their transporting flow. Fragments with an irregularly laminated cortex of calcium carbonate, often characterized by a spheroidal to oblate shape and usually referred to as oncoids [26], are common components of allochthonous tufa deposited in streams, rivers, and lakes. Pedley [24] attributes the spheroid shapes of grains to high competence flow, the elongated shapes to slow flow, and the irregular shapes to calm waters.
Clastic fragments cemented by calcareous tufa are sometimes found inside terraced alluvial or slope deposits. They form mainly in the first stages of tufa deposition [27].
Following Choquette and Pray [28], the porosity of calcareous tufa limestone may be distinguished into non-fabric porosity (produced by fracturing, karstic dissolution, and burrowing invertebrates) and fabric porosity.
Depending upon the cohesion between the constituting crystals, calcareous tufa deposits range from soft and chalky to dense and highly indurated [6].
Tufa deposits are affected by meteoric diagenesis soon after deposition when exposed at the surface and by burial diagenesis when overlain by more recent thick sediments [6,25,29].
The principal changes caused by meteoric diagenesis are related to the dissolution/precipitation of calcium carbonate (void filling, cementation) induced by percolating rainwater or groundwater; other diagenetic effects are recrystallization, microbial micritization, bioturbation, oxidation of organic matter and sparmicritization, a term introduced by Kahle [30] to describe the etching action of microorganisms at or near the tufa surface [6]. Burial diagenetic effects resulting from increased lithostatic and hydrostatic pressure, heating, and the ingress of mineral-enriched solutions include compaction and porosity reduction resulting from further cementation, dissolution of the original fabric, sometimes with replacement by other minerals, and reactions between the original carbonate component and accessory minerals [6].
The original differences in porosity combined with those due to diagenesis make the permeability of tufa deposits extremely variable.
4. Calcareous Tufa Deposits and Landforms
The deposition of calcareous tufa may give rise to construction landforms such as small mounds at springs and dams across the riverbeds or coatings of steep slopes, rough river beds, or swamp/lake bottoms generally lacking a recognizable shape [6,31,32]. These features are geologically not durable as the construction process can be interrupted, and landforms can be destroyed, in whole or in part, by erosion [6]. Bedding within the deposit, where present, is usually inclined and undulated and rarely horizontal; thin laminations resulting from daily/seasonal variations are often recognizable [6].
Slope deposits essentially consist of wedge-shaped, layered bodies of microhermal tufa locally passing to stromatolithic tufa with minor intercalations of phytoclastic tufa. Calcareous tufa systems may develop either along slopes forming wedge-shaped sedimentary bodies with the thickest accumulation downstream and transforming the original water flow into a system of hanging channels, low barrages, ponds, and terraces, or across rivers giving rise to dams with pools or larger basins on their backside [6,22].
Dams are the showiest construction bodies of calcareous tufa (Figure 4). They may reach heights up to several tens of meters in correspondence with breaks or obstructions of riverbeds that reduce erosion by flowing water, thus allowing CaCO3 precipitation [6,33,34,35]. These features mainly consist of massive phytohermal tufa encrusted on a skeleton made of remnants of vegetal organisms. In addition to growing upward, the aggradation of tufa progrades onward, forming sub-vertical layers unconformably covering the earlier deposits, including those of the basin down valley (Figure 4) [21,24,36]. On the backside of dams, water basins form (ranging in size from small pools to vast lacustrine basins) whose bottom hosts tufa sands (deriving from dismantling tufa deposits upstream), phytoclastic tufa, and stromatolithic tufa, interspersed with clayey sediments and peaty layers (Figure 5) [1,21,24,33,34,37].
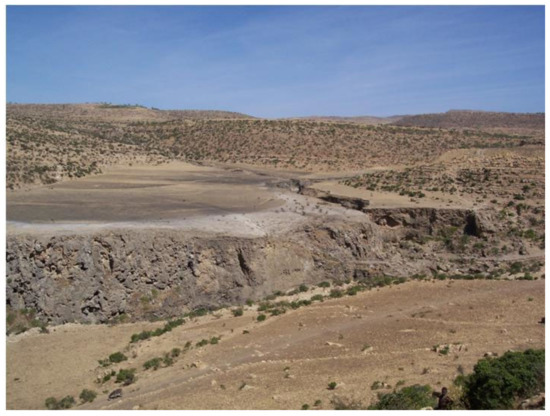

Figure 4.
The imposing Holocene tufa dam of May Makden in Tigray (northern Ethiopian Highlands).

Figure 5.
The backfill deposits of the May Makden tufa dam: a complex sequence of stromatolithic tufa levels, lacustrine clay, peat, alluvial gravels, and buried soils testifying repeated aggradation/erosion phases.
Dams and backside pools usually follow one another along the watercourse forming characteristic depositional systems (Figure 6) [6,21,24].
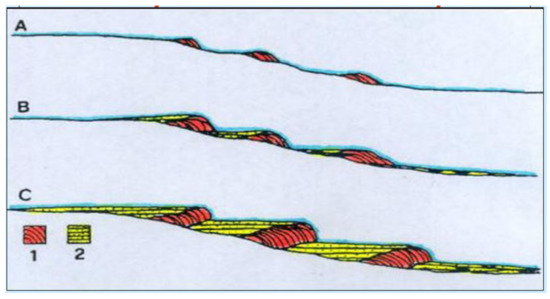
Figure 6.
Evolutionary scheme (from initial phase A to final phase C) of tufa dams and backside pools along a watercourse: 1. phytohermal tufa; 2. stromatolithic and phytoclastic tufa.
The growth of tufa dams occurs where the deposition rate of calcium carbonate from water is high enough to balance the streamflow erosion [38].
In correspondence with significantly high steps in the riverbed profile, dams often fail to grow due to the erosion exerted by rapid water flow, and the deposition of tufa mainly progresses downstream from the tufa dam, giving rise to a “cascade tufa” deposits (Figure 7) [6].
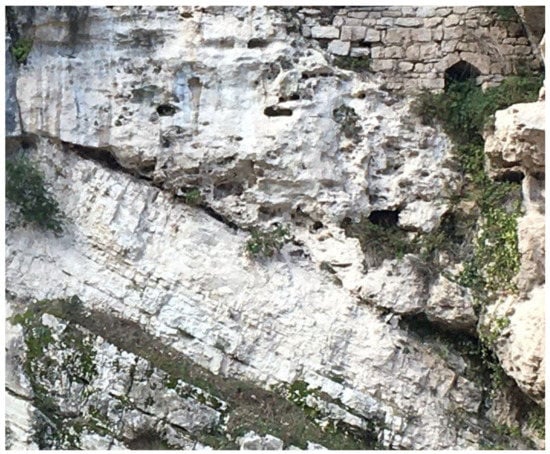

Figure 7.
Cascade tufa overlying Mesozoic limestone in the upper Esino River basin (Central Italy).
5. Factors Controlling Calcareous Tufa Deposition/Erosion
There is general agreement in referring the development of calcareous tufa to climatic causes [6,8,39,40,41].
Warm climates are believed to favor calcareous tufa formation due to higher concentrations of biogenic CO2 in soils [6,8,14,39,40,41,42,43,44,45] enhancing the dissolution rates of CaCO3 [12] and increasing photosynthetic activity by aquatic plants [1,8,25,46]. Conversely, cold climates are considered less favorable because of the reduced biological activity of soils and the lesser development of aquatic plants [6,45].
Humid climates are generally considered favorable for tufa deposition by allowing abundant water infiltration and emergence, enhancing the development of vegetation covers and related biogenic processes in the soils, and promoting the growth of aquatic plants. This is contrary to dry climates where there is a scarcity of rainwater and a consequent general reduction in water circulating in the ground and discharging at springs. However, delayed responses to climate aridification of deep aquifers reached by river incision may locally result in tufa deposition, even during dry periods [47,48].
In all conditions, tectonics strongly influences tufa deposition by opening waterways in fractured rocks and giving rise to fault steps across rivers, thus favoring the growth of tufa dams [49].
6. Calcareous Tufa Deposition/Decline during Holocene
As shown by investigations carried out in different parts of the world, widespread deposition of tufa occurred in the early-middle Holocene from 10,000 to 4600 yr B.P. and declined or ceased entirely in the late Holocene [8,9,20,33,34,37,40,45].
According to Geurts [50], the tufa deposition rates in Belgium during the Holocene were 12 mm/yr in the Pre-Boreal, 26 mm/yr in the Boreal, 6 mm/yr in the Atlantic and 1 mm/yr in the Sub-Boreal. Moreover, the Holocene formation of speleothems shows a similar trend [43,51].
Two explanation models for the late Holocene decline of tufa deposition have been proposed: a “climatic” model [50,52] and a “human impact” model [8,9,39,40,45].
The first model stresses the role of the progressive cooling and wetting of climate that should have affected middle-high latitudes, as indicated by the reduction of thermophile vegetation species and the southward migration of the boreal forest [53]. In addition, these new conditions would have induced a general deepening of river incision and a related lowering of water tables, resulting in a widespread modification of water regimes and tufa depositional systems [52]. However, more recent research [54] indicates a general shift of climate towards cooler and drier conditions in both middle-high and low latitudes, where tufa formation also declined [20,33,34].
The second model points to the effects of human impact on slopes for agricultural or pastoral use. In particular, the widespread forest clearing started locally in the Early Holocene and widely developed after 5000 yr B.P. would have drastically lowered the biogenic CO2 in soils, the CaCO3 dissolution in the limestone aquifers, and the deposition rates of tufa from spring groundwaters. Other possible human-induced factors unfavorable to tufa deposition would have been changes in the chemical characteristics of ground/surface water, changes in stream hydrology, increasing water turbidity, and water pollution [39]. However, even if the above factors could have been effective in reducing/preventing tufa deposition, it seems difficult to explain all the cases of tufa deposition decline observed in different parts of the world as being due to the impact of human activities [50]. Moreover, the “human impact” theory cannot explain the cases of tufa deposition decline which repeatedly occurred before the Holocene [10,11,52,55].
7. The Ground Thermal Gradient Model
A further explanatory model for the late Holocene decline of tufa deposition rates and, more in general, for the increase/decrease of tufa deposition rates refers to the variations of thermal gradient in the bedrock by significant climate changes [56].
Due to the low thermal conductivity of bedrock [57,58], major climatic changes to warmer conditions, such as the rapid increase in air temperature (up to several degrees) which occurred everywhere on the planet at the Late Pleistocene-Holocene transition [59], induces a significant thermal contrast between surface and ground and reverses thermal gradients in the deep limestone aquifers. With climate warming, the infiltration water, made highly acidic when crossing the soil due to the elevated partial pressure of biogenic CO2 present therein, percolating through the progressively colder levels of the aquifer, induces a relevant dissolution of CaCO3 [14,60], higher than in normal conditions. At the emergence, because of the higher surface temperatures, the groundwater loses CO2, becoming oversaturated with CaCO3 and causing tufa deposition, even at a great distance from the spring; favored by the running water turbulence, photosynthetic activity of mosses and algae, and evaporation of spray droplets.
Opposite effects, such as the deposition of dissolved carbonate in the upper bedrock layers and the emergence of spring waters undersaturated with CaCO3, are expected to occur with major climatic changes to cold conditions. This could explain the occurrence of carbonate concretions in the bedrock fissures and tufa deposits and their erosion in the colder Quaternary stages [11,56,61,62].
Changes in temperature of different amplitude ranging in timescales from years to millions of years have repeatedly affected the Earth’s surface, inducing thermal variations in the ground of increasing depth, as a function of the magnitude and duration of the change [58]. With ground temperatures below 0 °C, groundwater freezes (permafrost) [63], preventing water circulation and the formation of calcareous tufa.
Convective circulation in the groundwater may facilitate heat transfer, reducing the amplitude and duration of thermal differences between the upper and deeper levels of the bedrock [58]. However, in the case of massive limestones, the process mentioned above may not be significant since groundwater percolates down to the water table in a network of enlarged fissures, channels, and cavities within a much larger volume of almost or completely dry rock, with rock mass porosity values as low as 0.5% [64].
Furthermore, convective heat transfer may be reduced even in the saturated zone [56], considering that most of the phreatic water circulates at an extremely slow velocity in very narrow fractures and that the spacing between large fractures may reach several hundreds of meters [65].
As demonstrated by Benderitter [66], water temperature records at the outlet of a fractured carbonate system during an annual cycle show two types of variations, slow variations over a small range, resulting from the thermal equilibrium between water and rock in the aquifer, and more rapid variations over a broader range, transmitted more quickly due to the inflow of water through fractures or karstic pipes.
The heat exchange between rock mass and circulating water in the saturated zone is low, even though thermal disequilibrium may disappear over a long distance [67]. Disturbances of ground temperatures reaching depths down to several hundreds of meters were induced by the 100,000 years (glacials-interglacials) and the 41,000–21,000 (stadials-interstadials) climatic oscillations which occurred during the Quaternary [68].
Ultimately, the differences in temperature between the surface and the aquifer have the effect of increasing (warmer surface) or reducing (colder surface) the concentrations of dissolved calcium carbonate at the source and, consequently, the deposition rates of the calcareous tufa. With surface temperatures much warmer than those of the aquifer, it is possible to have undersaturated spring waters that may exert chemical erosion on previous tufa deposits.
The geomorphological-stratigraphic analysis of tufa dams from Eastern Africa (Northern Ethiopia) and the Mediterranean basin (Central Italy) highlights the control exerted by climate changes at the global scale [69,70,71]. Despite the differences in latitude and climate, the aggradation of tufa dams started in both cases at the Pleistocene-Holocene transition (before 9510 ± 100 14C yr BP—11,080–10,590 yr cal BP in Northern Ethiopia and before 9310 ± 100 14C yr BP—10,211–10,184 yr cal BP in Central Italy) and turned to decline in the Middle Holocene (around 5610 ± 70 14C yr BP—6450–6305 yr cal BP in Northern Ethiopia and around 6190 ± 70 14C yr BP—7240–6990 yr cal BP in Central Italy) followed by short-lived alternating stages of incision/ deposition (since ca. 4710 ± 70 14C yr BP—5580–5320 yr cal BP in Northern Ethiopia and 4610 ± 100 14C yr BP—5600–5050 yr cal BP in Central Italy) until the end of tufa deposition (after 2380 ± 50 14C yr BP—2710–2340 yr cal BP in Northern Ethiopia and 2826 ± 60 14C yr BP—3060–2840 yr cal BP in Central Italy) with the subsequent incision of the dams down to the underlying bedrock [20] (Figure 8).

Figure 8.
The final incision down to the bedrock of the Holocene tufa dam of Triponzo (Central Italy).
Comparing the ages of tufa deposits with the Holocene climate changes [69,70,71] confirms the ground thermal gradient model reliability: It is interesting to notice that both in Eastern Africa and south-central Europe the deposition occurred with warming stages, while a general absence of tufa deposits and the erosion of previous ones characterizes cooling stages, even with temperatures not low enough to prevent tufa deposition [20,33,37].
Good support for the ground thermal gradient model comes from the temporal distribution of tufa deposits in the northern hemisphere during the Late Pleistocene (MIS 2-3-4), a time interval characterized by the abrupt occurrence of several very cold periods known as Heinrich (H) events [72,73] and changes toward much warmer periods named Dansgaard-Oeschger (D-O) events [70,74]. Comparing the U/Th dates of tufa deposits with the distribution of the relevant warm/cold temperatures peaks (Table 1) shows that, apart from a few exceptions, the overwhelming majority formed with rising temperatures to warm peaks, even in very low thermal conditions [11].

Table 1.
U/Th dates of calcareous tufa deposits from different countries and cold/warm peaks in the MIS 2-3-4 chronological interval; modified from Fubelli et al., 2021 [11].
Even if with exceptions [48,75], the aridification trend recorded in southern Europe and Eastern Africa since the middle Holocene [76,77,78,79,80,81] also contributed to the progressive decline of tufa deposition, the short-lived phases of tufa erosion/aggradation recorded in both areas since the Middle Holocene [20,34] may have been the combined effect of the high-frequency cold/warm and dry/wet climatic fluctuations which affected southern Europe [70,80,81] and East Africa [78,79], recorded by a pronounced erosion phase of the tufa dam at Triponzo, Italy [38] and by a clear gap in the backfill sequence at Mai Makden, Ethiopia [37].
Calcareous tufa deposition is currently highly reduced [82,83] or completely absent, likely due to the progressive climate cooling and, most likely, the Little Ice Age cold spell [70,84]. A renewed increase of tufa deposition rates could result from ongoing global warming [85].
8. Conclusions
In conclusion, the deposition rates of calcareous tufa may be controlled concurrently by changes in surface temperature and wet-dry fluctuations.
Warm/humid climates favor calcareous tufa formation due to higher concentrations of biogenic CO2 in soils, enhancing the dissolution rates of CaCO3 and increasing photosynthetic activity by aquatic plants. Conversely, cold/dry climates are considered less favorable because of the reduced biological activity of soils and the lesser development of aquatic plants.
Both highly cold and extremely arid climates make the deposition of calcareous tufa impossible due to the disappearance of the vegetation cover and the blocking of groundwater circulation due to ground freezing (permafrost) and the lack of meteoric water, respectively.
A relevant role in determining the deposition rates of calcareous tufa is played by the major warming/cooling climate changes, such as those that have repeatedly occurred over geological times.
An abrupt transition to significantly warmer conditions and the resulting thermal contrast between the surface and aquifer may increase the deposition rates of calcium carbonate that reach their maximum values with well-developed forest covers, as happened in the Early Holocene.
On the contrary, in connection with an abrupt transition towards significantly colder conditions, the ground temperatures higher than the surficial ones can end the deposition of tufa and induce the chemical erosion of pre-existing deposits even with a still present forest cover.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hynes, H.B.N. The Ecology of Running Waters; University Press: Liverpool, UK, 1978; p. 378. [Google Scholar]
- Chafetz, H.S.; Folk, R.L. Travertines: Depositional morphology and bacterial constructed constituents. J. Sediment. Petrol. 1984, 54, 289–316. [Google Scholar]
- Pentecost, A. Moss growth and travertine deposition: The significance of photosynthesis, evaporation and degassing of carbon dioxide. J. Bryol. 1996, 19, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preece, R.C.; Robinson, J.E. Molluscan and ostracod faunas from Post-glacial tufaceous deposits in County Offaly. Proc. R. Ir. Acad. Sect. B Biol. Geol. Chem. Sci. 1982, 82B, 115–131. [Google Scholar]
- Krolopp, E. The importance of mollusc fauna in the study of travertine deposits. Földtany Közlöny 2003, 134, 219–225. [Google Scholar]
- Pentecost, A. Travertine; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2005; p. 445. [Google Scholar]
- Gandin, A.; Capezzuoli, E. Travertine versus calcareous tufa: Distinctive petrologic features and stable isotopes analysis. Alp. Mediterr. Quat. 2008, 21, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar]
- Gullentops, F.; Mullenders, W. Age et formation de dépôts de tuf calcaire Holocène en Belgique. In Proceedings of the Symposium International de Géomorphologie, Liège, Belgium, 29 June–4 July 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Goudie, A.S.; Viles, H.A.; Pentecost, A. The late-Holocene tufa decline in Europe. Holocene 1993, 3, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, N.; Braum, M.; Hambach, U.; Mangini, A.; Wagner, G. Warm period growth of travertine during last Interglaciation in Southern Germany. Quat. Res. 2000, 54, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fubelli, G.; Soligo, M.; Tuccimei, P.; Bonasera, M.; Dramis, F. Calcareous tufa deposition in connection with Late Pleistocene abrupt warming events. J. Ecol. Nat. Resour. 2021, 5, 000236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeller, H. Les Eaux Souterraines; Masson and Cie: Paris, France, 1962; p. 642. [Google Scholar]
- Tillmans, J. Die Chemische Untersuchung von Wasser und Abwasser, 2nd ed.; Wilhelm Knapp: Halle, Germany, 1932; Volume 1, p. 252. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, T.C. Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere of the unsaturated zone: An important control of hardness in limestones. J. Hydrol. 1977, 35, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, J.J. The effect of soil activity on the chemistry of carbonate groundwaters. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roques, H. Observations physico-chemiques sur les eaux d alimentation de quelques concretions. Ann. Speleol. 1963, 18, 377–404. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, G.W. Introduction to the origin of limestone caves. Natl. Speleol. Soc. Bull. 1960, 22, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Bőgli, A. Mischungskorrosion-ein Beitrag zum Verkarstungs-problem. Erdlcunde 1964, 18, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Merz-Preiss, M.; Riding, R. Cyanobacterial tufa calcification in two freshwater streams: Ambient environment, chemicalthresholds and biological processes. Sediment. Geol. 1999, 126, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dramis, F.; Fubelli, G.; Calderoni, G.; Esu, D. Holocene aggradation/degradation of tufa dams in northern Ethiopia and central Italy: A paleoclimatic comparison between East Africa and Mediterranean Europe. Z. Geomorphol. 2014, 58, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buccino, G.; D’Argenio, B.; Ferreri, B.; Brancaccio, L.; Ferreri, M.; Panichi CStanzione, D. I travertini della bassa valle del Tanagro (Campania). Studio geomorfologico, sedimentologico e geochimico. Boll. Della Soc. Geol. Ital. 1978, 97, 617–646. [Google Scholar]
- D’Argenio, B.; Ferreri, V.; Stanzione, D.; Brancaccio, L.; Ferreri, M. I travertini di Pontecagnano (Campania) geomorfologia, sedimentologia, geochimica. Boll. Della Soc. Geol. Ital. 1983, 102, 123–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreri, M. Criteri di analisi di facies e classificazione dei travertini pleistocenici dell’Italia meriodionale. Rend. Acc. Scienze. Fis. Mat. 1985, 52, 121–147. [Google Scholar]
- Pedley, H.M. Classification and environmental models of cool fresh-water tufas. Sediment. Geol. 1990, 68, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubic, S.; Violante, C.; Ferreri, V.; D’Argenio, B. Algal control and early diagenesis in Quaternary travertine formation (Rocchetta a Volturno, Central Apennines). Boll. Della Soc. Paleontol. Ital. 1993, 1, 231–247. [Google Scholar]
- Riding, R. Classification of microbial carbonates. In Calcareous Algae and Stromatolites; Riding, R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1991; pp. 21–51. [Google Scholar]
- Gradzinski, M.; Jach, R.; Stworzewicz, E. Origin of calcite-cemented Holocene slope breccias from the Dluga Valley (the Western Tatra Mountains). Ann. Soc. Geol. Pol. 2001, 71, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Choquette, P.N.; Pray, C. Geologic nomenclature and classification of porosity in sedimentary carbonates. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 1970, 54, 207–250. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Berriguete, A.; Alonso-Zarza, A.M.; Martín-García, R. Diagenesis of continental carbonate country rocks underlying surficial travertine spring deposits. Quat. Int. 2017, 437, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahle, C.F. Origin of subaerial Holocene calcareous crusts: Role of algae, fungi and sparmicritization. Sedimentology 1977, 24, 413–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julia, R. Travertines. In Carbonate Depositional Environments; Scholle, P.A., Bebout, D.G., Moore, C.H., Eds.; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1983; pp. 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Viles, H.A.; Goudie, A.S. Tufas, travertines and allied carbonate deposits. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 1990, 14, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berakhi, O.; Brancaccio, L.; Calderoni, G.; Coltorti, M.; Dramis, F.; Umer, M. The Mai Maikden sedimentary sequence: A reference point for the environmental evolution of the Highlands of Northern Ethiopia. Geomorphology 1998, 23, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dramis, F.; Fubelli, G. Tufa dams in Tigray (Northern Ethiopia) as Late Pleistocene -Holocene climate proxies. In Landscapes and Landforms of Ethiopia; Billi, P., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 201–211. [Google Scholar]
- Golubic, S. Cyclic and non cyclic mechanism in the formation of travertine. Verh. Int. Ver. Limnol. 1969, 17, 956–961. [Google Scholar]
- Calderoni, G.; Cilla, G.; Dramis, F.; Esu, D.; Magnatti, M.; Materazzi, M. La deposizione di travertino nelle aree prossimali dei fiumi Esino, Potenza e Chienti durante l’Olocene antico (Appennino Centrale Marchigiano). Quaternario 1996, 9, 481–492. [Google Scholar]
- Dramis, F.; Mohamed, U.; Calderoni, G.; Mitiku, H. Holocene climate phases from buried soils in Tigray (northern Ethiopia): Comparison with lake level fluctuations in the Main Ethiopian Rift. Quat. Res. 2003, 60, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fubelli, G.; Dramis, F.; Calderoni, G.; Cilla, G.; Materazzi, M.; Mazzini, I.; Soligo, M. Holocene aggradation/erosion of a tufa dam at Triponzo (Central Italy). Geogr. Fis. Din. Quat. 2013, 36, 259–266. [Google Scholar]
- Nicod, J. Facteurs physico-chimiques de 1’accumulation des formation travertineuses. Méditerranée 1986, 57, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisrock, A. Variations climatiques et périodes de sédimentation carbonatée à l’holocène. L’âge des dépôts. Méditerranée 1986, 57, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazdur, A.; Pazdur, M.F.; Starkel, L.; Szulc, J. Stable isotopes of Holocene calcareous tufa in southern Poland as paleoclimatic indicators. Quat. Res. 1988, 30, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, G.A.; Folkoff, M.E.; Box, E.O. A world model of soil carbon dioxide. Earh Surf. Processes Landf. 1983, 8, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, G.J.; Grun, R.; Brunnacker, K. Speleothems, travertines and paleoclimates. Quat. Res. 1983, 20, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifay, E. Origine et age des formations travertineuses de la Vallee de l’Huveaune entre Roquevaire et Auriol (Bouches du Rhone). Méditerranée 1986, 57, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaudour, J. Travertins holocenes et pression anthropique. Méditerranée 1986, 57, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, E.T. The agency of algae in the deposition of travertine and silica from thermal waters. Am. J. Sci. 1934, 28, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordonez, S.; Gonzalez Martin, J.A.; Garda del Cura, M.A.; Pedley, H.M. Temperate and semi-arid tufas in the Pleistocene to recent fluvial barrage system in the Mediterranean area: The Ruidera Lakes Natural Park (Central Spain). Geomorphology 2005, 69, 332–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viles, H.A.; Taylor, M.P.; Nicoll, K.; Neumann, S. Facies evidence of hydroclimatic regime shifts in tufa depositional sequences from the arid Naukluft Mountains, Namibia. Sediment. Geol. 2007, 195, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuera, J.; Alonso-Zarza, A.M.; Rodriguez-Berriguete, A.; Melendez, A. Variations of fluvial tufa sub-environments in a tectonically active basin, Pleistocene Teruel Basin, NE Spain. Sedimentology 2012, 59, 502–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurts, M.A. Genèse et stratigraphie des travertins de fond de vallée en Belgique. Acta Geogr. Louvanensia 1976, 16, 66. [Google Scholar]
- Gascoyne, M.; Schwarcz, H.P.; Ford, D.C. Uranium series ages of speleothems from North West England: Correlation with Quaternary climate. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Ser. B 1983, 301, 143–164. [Google Scholar]
- Preece, R.C.; Thorpe, P.M.; Robinson, J.E. Confirmation of an interglacial age for the Condat Tufa (Dordogne, France) from biostratigraphic and isotopic data. J. Quat. Sci. 1986, 1, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntley, B.; Birks, H.J.B. An Atlas of Past and Present Pollen Maps for Europe: 0–13,000 Years Ago; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Lamb, H.; Gasse, F.; Benkaddour, A.; El Hamouti, N.; van der Kaars, S.; Perkins, W.; Pear Roberts, C.N. Relation between century scale Holocene arid intervals in tropical and temperate zones. Nature 1995, 373, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soligo, M.; Tuccimei, P.; Barberi, R.; Delitala, M.C.; Miccadei, E.; Taddeucci, A. U/Th dating of freshwater travertine from Middle Velino Valley (Central Italy): Paleoclimatic and geological implications. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2002, 184, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dramis, F.; Materazzi, M.; Cilla, G. Influence of climatic changes on freshwater traverti ne deposition: A new hypothesis. Phys. Chem. Earth Part A Solid Earth Geod. 1999, 24, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasseur, G.; Bernard, P.H.; Van de Meulebrouck, J.; Kast, Y.; Jolivet, J. Holocene paleotemperatures deduced from borehole temperature data. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1983, 43, 237–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkonen, I.T.; Čermák, V.; Hurtig, E. Vertical variation of heath flow density in the continental crust. Terra Nova 1993, 5, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emiliani, C. Pleistocene temperature variations in the Mediterranean. Quaternaria 1955, 2, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Thrailkill, I. Chemical and hydrologic factors in the excavation of limestone caves. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1968, 79, 19–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.J.; Smith, N.W. The Frozen Earth. Fundamentals of Geocryology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1989; p. 306. [Google Scholar]
- Blanc, J.J. Geodynamique et histoire du karst. Application au Sud-Est de la France. Quaternaire 1997, 8, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, S.W. Permafrost or Permanently Frozen Ground and Related Engineering Problems; Special Report Nc 62; US Army: Washington, DC, USA, 1945; p. 36. [Google Scholar]
- Castany, J. Traité Pratique des Eaux Souterraines; Dunod: Paris, France, 1967; p. 652. [Google Scholar]
- Klimentov, P.P. General Hydrogeology; Mir Publishers: Moscow, Russia, 1983; p. 239. [Google Scholar]
- Benderitter, Y.; Roy, B.; Tabbagli, A. Flow characterisation through heat transfer evidence in a carbonate fractured medium: First approach. Water Resour. Res. 1993, 29, 3741–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeannin, P.-Y.; Liedl, R.; Sauter, M. Some concepts about heat tranfer in karst systems. In Proceedings of the 12th International Congress of Speleology, La Chaux-de-Fonds, Switzerland, 10–17 August 1997; Volume 1, pp. 195–198. [Google Scholar]
- Labeyrie, L.; Cole, J.; Alverson, K.; Stocker, T. The history of climate dynamics in the late Quaternary. In Paleoclimate, Global Change and the Future; Global Change—The IGBP, Series; Alverson, K.D., Pedersen, T.F., Bradley, R.S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohling, E.J.; Casford, J.S.L.; Abu-Zied, R.; Cooke, S.; Mercone, D.; Thomson, J.; Croudace, I.; Jorissen, F.J.; Brinkhuis, H.; Kal lmeyer, J.; et al. Rapid Holocene climate changes in the Eastern Mediterranean. In Droughts, Food and Culture: Ecological Change and Food Security in Africa’s Later Prehistory; Hassan, F., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 35–47. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, G.C.; Showers, W.; Elliot, M.; Evans, M.; Lotti, R.; Hajdas, I.; Bonani, G.; Johnson, S. The North Atlantic’s 1–2 kyr climate rhythm: Relation to Heinrich events, Dansgaard/Oeschger cycles and the Little Ice Age. In Mechanisms of Global Change at Millennial Time Scales; Clark, P.U., Webb, R.S., Keigwin, L.D., Eds.; Geophysical Monograph 112, American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; pp. 59–76. [Google Scholar]
- Mayewski, P.A.; Rohling, E.E.; Stager, J.C.; Karlén, W.; Maasch, K.A.; Meeker, L.D.; Meyerson, E.A.; Gasse, F.; van Kreveld, S.; Holmgren, K.; et al. Holocene climate variability. Quat. Res. 2004, 62, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, H. Origin and consequences of cyclic Ice rafting in the northeast Atlantic Ocean during the past 130,000 years. Quat. Res. 1988, 29, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodell, D.A.; Evans, H.F.; Channell, J.E.T.; Curtis, J.H. Phase relationships of North Atlantic ice-rafted debris and surface-deep climate proxies during the last glacial period. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2010, 29, 3875–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansgaard, W.; Johnsen, S.; Clausen, H.; DahlJensen, D.; Gundestrup, N.; Hammer, C.U.; Hyldberg, J.P.; Steffesen, A.E.; Svelnbjomsdottlr, T.J.; Jouzel, T.; et al. Evidence for general instability of past climate from a 250 ka ice-core record. Nature 1993, 364, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Urbez, M.; Arenas, C.; Pardo, G. A sedimentary facies model for stepped, fluvial tufa systems in the Iberian Range (Spain): The Quaternary Piedra and Mesa valleys. Sedimentology 2012, 59, 502–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, R.; Street-Perrott, F.A.; Switzur, R. Post-glacial arid episodes in Ethiopia have implications for climate prediction. Nature 1983, 306, 680–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasse, F.; Van Campo, E. Abrupt post-glacial climate events in West Asia and North Africa monsoon domains. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1994, 126, 435–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasse, F. Hydrological changes in the African tropics since the Last Glacial Maximum. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2000, 19, 189–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umer, M.; Legesse, D.; Gasse, F.; Bonnefille, R.; Lamb, H.F.; Leng, M.J.; Lamb, A.A. Late Quaternary climate changes in the Horn of Africa. In Past Climate Variability through Europe and Africa; Developments in Paleoenvironmental Research; Battarbee, R.W., Gasse, F., Stickley, C.E., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 6, pp. 159–175. [Google Scholar]
- Drysdale, R.N.; Zanchetta, G.; Hellstrom, J.; Maas, R.; Fallick, A.; Pickett, M.; Cartwright, I.; Piccini, L. Late Holocene drought responsible for the collapse of Old World civilizations is recorded in an Italian cave flowstone. Geology 2006, 34, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraudi, C.; Mercuri, A.M.; Esu, D. Holocene palaeoclimate in the northern Sahara margin (Jefara Plain, northwestern Libya). Holocene 2013, 23, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeis, K.C.; Richnow, H.H.; Kempe, S. Travertine formation in Plitvice National Park, Yugoslavia: Chemical versus biological control. Sedimentology 1987, 34, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.; Simms, M.J. Active deposition of calcareous tufa in Wessex, UK, and its implications for thergille lacustrim “la te-Holocene tufa decline”. Holocene 1998, 8, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büntgen, U.; Hellmann, L. The Little Ice Age in scientific perspective: Cold spells and caveats. J. Interdiscip. Hist. 2014, 44, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, P.; Rangabhashiyam, S.; Srivastava, K.K. Global Climate Change; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; p. 442. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).