Microbiota Alterations in Patients with Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid and Pemphigus Vulgaris: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
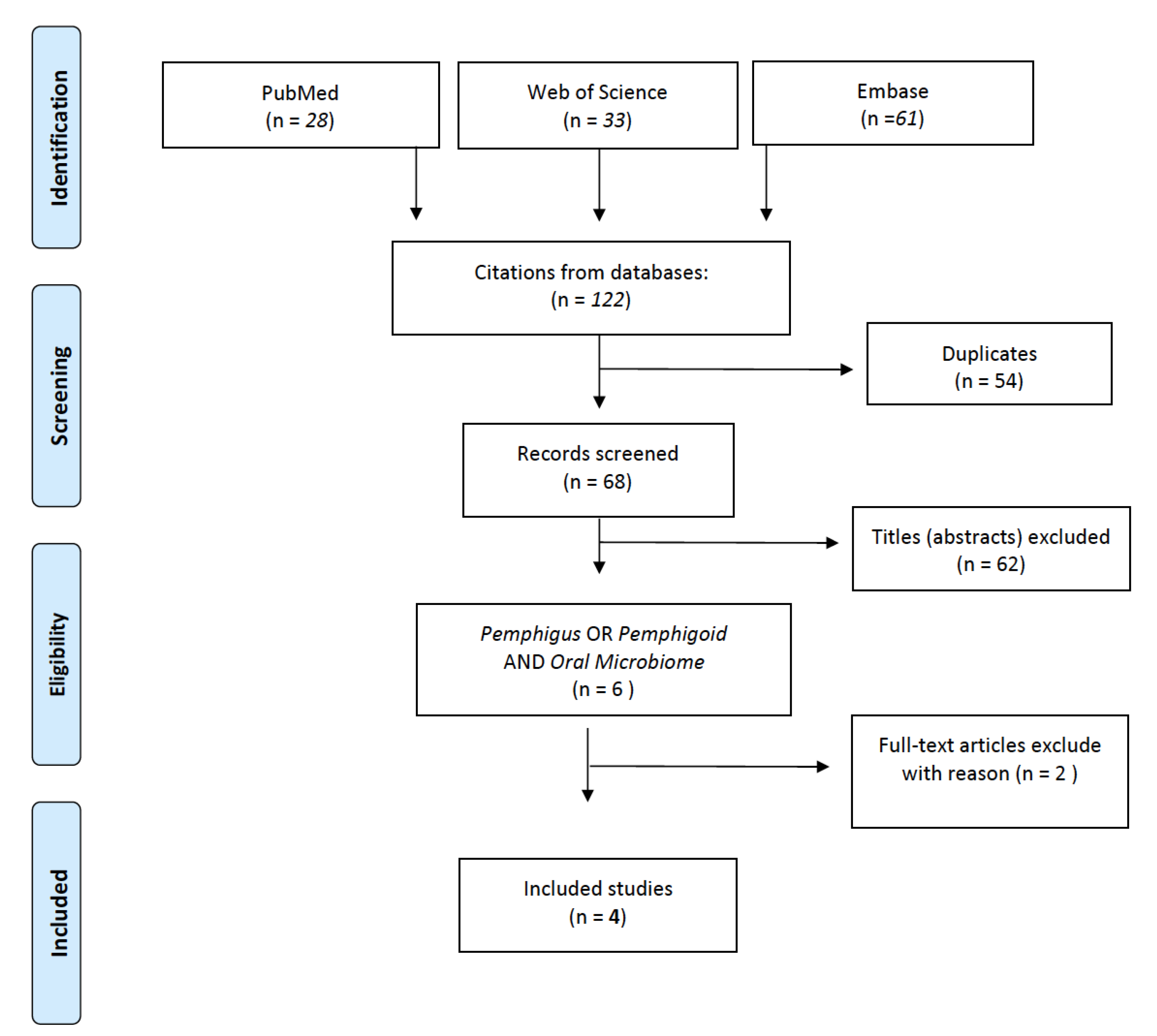
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Risk of Bias in Individual Studies
3.2. Pemphigus Vulgaris
3.3. Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verma, D.; Garg, P.K.; Dubey, A.K. Insights into the Human Oral Microbiome. Arch. Microbiol. 2018, 200, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaura, E.; Nicu, E.A.; Krom, B.P.; Keijser, B.J.F. Acquiring and Maintaining a Normal Oral Microbiome: Current Perspective. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcaraz, L.D.; Belda-Ferre, P.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Romero, H.; Simon-Soro, A.; Pignatelli, M.; Mira, A. Identifying a Healthy Oral Microbiome through Metagenomics. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; Knight, R.; Abubucker, S.; Badger, J.H.; Chinwalla, A.T.; Creasy, H.H.; Earl, A.M.; Fitzgerald, M.G.; Fulton, R.S.; et al. Structure, Function and Diversity of the Healthy Human Microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gao, H.; Mihindukulasuriya, K.A.; Rosa, P.S.L.; Wylie, K.M.; Vishnivetskaya, T.; Podar, M.; Warner, B.; Tarr, P.I.; Nelson, D.E.; et al. Biogeography of the Ecosystems of the Healthy Human Body. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.X.; Hu, Y.J.; Gao, L.; He, Z.Y.; Zhu, C.L.; Ma, R.; Huang, Z.W. The Impact of Various Time Intervals on the Supragingival Plaque Dynamic Core Microbiome. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.N.; Feazel, L.M.; Bessesen, M.T.; Price, C.S.; Janoff, E.N.; Pace, N.R. The Human Nasal Microbiota and Staphylococcus Aureus Carriage. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kort, R.; Caspers, M.; van de Graaf, A.; van Egmond, W.; Keijser, B.; Roeselers, G. Shaping the Oral Microbiota through Intimate Kissing. Microbiome 2014, 2, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewhirst, F.E.; Chen, T.; Izard, J.; Paster, B.J.; Tanner, A.C.R.; Yu, W.H.; Lakshmanan, A.; Wade, W.G. The Human Oral Microbiome. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 5002–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, E.; Maukonen, J.; Hyytiäinen, T.; Kieseppä, T.; Orešič, M.; Sabunciyan, S.; Mantere, O.; Saarela, M.; Yolken, R.; Suvisaari, J. Analysis of Microbiota in First Episode Psychosis Identifies Preliminary Associations with Symptom Severity and Treatment Response. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 192, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; De Jesus-Laboy, K.M.; Shen, N.; Cox, L.M.; Amir, A.; Gonzalez, A.; Bokulich, N.A.; Song, S.J.; Hoashi, M.; Rivera-Vinas, J.I.; et al. Partial Restoration of the Microbiota of Cesarean-Born Infants via Vaginal Microbial Transfer. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goleva, E.; Jackson, L.P.; Harris, J.K.; Robertson, C.E.; Sutherland, E.R.; Hall, C.F.; Good, J.T.; Gelfand, E.W.; Martin, R.J.; Leung, D.Y.M. The Effects of Airway Microbiome on Corticosteroid Responsiveness in Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, J.C.; Pehrsson, E.C.; Blaser, M.J.; Sandhu, K.; Gao, Z.; Wang, B.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Contreras, M.; Noya-Alarcón, Ó.; et al. The Microbiome of Uncontacted Amerindians. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.; Saunier, K.; Hanisch, C.; Norin, E.; Alm, L.; Midtvedt, T.; Cresci, A.; Silvi, S.; Orpianesi, C.; Verdenelli, M.C.; et al. Differences in Fecal Microbiota in Different European Study Populations in Relation to Age, Gender, and Country: A Cross-Sectional Study. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, R.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human Gut Microbiome Viewed across Age and Geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.M.; Patel, S.; Forsberg, K.J.; Wang, B.; Bentley, G.; Razia, Y.; Qin, X.; Tarr, P.I.; Dantas, G. Pediatric Fecal Microbiota Harbor Diverse and Novel Antibiotic Resistance Genes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stecher, B.; Denzler, R.; Maier, L.; Bernet, F.; Sanders, M.J.; Pickard, D.J.; Barthel, M.; Westendorf, A.M.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Walker, A.W.; et al. Gut Inflammation Can Boost Horizontal Gene Transfer between Pathogenic and Commensal Enterobacteriaceae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Bihan, M.; Methé, B.A. Analyses of the Stability and Core Taxonomic Memberships of the Human Microbiome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aas, J.A.; Paster, B.J.; Stokes, L.N.; Olsen, I.; Dewhirst, F.E. Defining the Normal Bacterial Flora of the Oral Cavity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5721–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Bhatia, S.; Singh Sodhi, A.; Batra, N. Oral Microbiome and Health. AIMS Microbiol. 2018, 4, 42–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizani, S.; Papaioannou, W.; Haffajee, A.D.; Kavvadia, K.; Quirynen, M.; Papagiannoulis, L. Distribution of Selected Cariogenic Bacteria in Five Different Intra-Oral Habitats in Young Children. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2009, 19, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnenburg, J.L.; Fischbach, M.A. Community Health Care: Therapeutic Opportunities in the Human Microbiome. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 13, 78ps12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamont, R.J.; Koo, H.; Hajishengallis, G. The Oral Microbiota: Dynamic Communities and Host Interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papapanou, P.N.; Park, H.; Cheng, B.; Kokaras, A.; Paster, B.; Burkett, S.; Watson, C.W.M.; Annavajhala, M.K.; Uhlemann, A.C.; Noble, J.M. Subgingival Microbiome and Clinical Periodontal Status in an Elderly Cohort: The WHICAP Ancillary Study of Oral Health. J. Periodontol. 2020, 91 (Suppl. S1), S56–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark Welch, J.L.; Rossetti, B.J.; Rieken, C.W.; Dewhirst, F.E.; Borisy, G.G. Biogeography of a Human Oral Microbiome at the Micron Scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E791–E800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, M.; Costello, E.K.; Hidalgo, G.; Magris, M.; Knight, R.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G. The Bacterial Microbiota in the Oral Mucosa of Rural Amerindians. Microbiology 2010, 156, 3282–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pride, D.T.; Salzman, J.; Relman, D.A. Comparisons of Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats and Viromes in Human Saliva Reveal Bacterial Adaptations to Salivary Viruses. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 2564–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pride, D.T.; Salzman, J.; Haynes, M.; Rohwer, F.; Davis-Long, C.; White, R.A.; Loomer, P.; Armitage, G.C.; Relman, D.A. Evidence of a Robust Resident Bacteriophage Population Revealed through Analysis of the Human Salivary Virome. ISME J. 2012, 6, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.P.; Kreth, J. The Impact of Horizontal Gene Transfer on the Adaptive Ability of the Human Oral Microbiome. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krom, B.P.; Kidwai, S.; Ten Cate, J.M. Candida and Other Fungal Species: Forgotten Players of Healthy Oral Microbiota. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, A.; Nuzzo, A.; Prouvost, B.; Diallo, D.; Hamdan, S.; Meseguer, E.; Guidoux, C.; Lavallée, P.; Amarenco, P.; Lesèche, G.; et al. Oral Microbiota and Atherothrombotic Carotid Plaque Vulnerability in Periodontitis Patients. A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Periodontal Res. 2021, 56, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contaldo, M.; Romano, A.; Mascitti, M.; Fiori, F.; della Vella, F.; Serpico, R.; Santarelli, A. Association between Denture Stomatitis, Candida Species and Diabetic Status. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2019, 33, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.A.; Koh, A.Y. Adaptation of Candida Albicans during Gastrointestinal Tract Colonization. Curr. Clin. Microbiol. Rep. 2018, 5, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, I.; Fusco, A.; Grimaldi, E.; Perillo, L.; Coretti, L.; Di Domenico, M.; Cozza, V.; Lucchese, A.; Contaldo, M.; Serpico, R.; et al. Assessment of Host Defence Mechanisms Induced by Candida Species. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2013, 26, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, T.; Sultan, A.S.; Montelongo-Jauregui, D.; Jabra-Rizk, M.A. Oral Candidiasis: A Disease of Opportunity. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- della Vella, F.; Lauritano, D.; Lajolo, C.; Lucchese, A.; Di Stasio, D.; Contaldo, M.; Serpico, R.; Petruzzi, M. The Pseudolesions of the Oral Mucosa: Differential Diagnosis and Related Systemic Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stasio, D.; Lauritano, D.; Minervini, G.; Paparella, R.S.; Petruzzi, M.; Romano, A.; Candotto, V.; Lucchese, A. Management of Denture Stomatitis: A Narrative Review. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2018, 32 (Suppl. 1), 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Abrantes, P.M.D.S.; Africa, C.W.J. Measuring Streptococcus Mutans, Streptococcus Sanguinis and Candida Albicans Biofilm Formation Using a Real-Time Impedance-Based System. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 169, 105815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Grier, A.; Faustoferri, R.C.; Alzoubi, S.; Gill, A.L.; Feng, C.; Liu, Y.; Quivey, R.G.; Kopycka-Kedzierawski, D.T.; Koo, H.; et al. Association between Oral Candida and Bacteriome in Children with Severe ECC. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 1468–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartnicka, D.; Karkowska-Kuleta, J.; Zawrotniak, M.; Satała, D.; Michalik, K.; Zielinska, G.; Bochenska, O.; Kozik, A.; Ciaston, I.; Koziel, J.; et al. Adhesive Protein-Mediated Cross-Talk between Candida Albicans and Porphyromonas Gingivalis in Dual Species Biofilm Protects the Anaerobic Bacterium in Unfavorable Oxic Environment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contaldo, M.; Fusco, A.; Stiuso, P.; Lama, S.; Gravina, A.G.; Itro, A.; Federico, A.; Itro, A.; Dipalma, G.; Inchingolo, F.; et al. Oral Microbiota and Salivary Levels of Oral Pathogens in Gastro-Intestinal Diseases: Current Knowledge and Exploratory Study. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konig, M.F. The Microbiome in Autoimmune Rheumatic Disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 34, 101473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, F.; Shoenfeld, Y. The Microbiome in Autoimmune Diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2018, 195, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wu, W.; Liu, Z.; Cong, Y. Microbiota Metabolite Short Chain Fatty Acids, GPCR, and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriachan, D.; Suresh, R.; Janardhanan, M.; Savithri, V. Oral Lesions: The Clue to Diagnosis of Pemphigus Vulgaris. Case Rep. Dent. 2015, 2015, 593940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofan, E.C.; Părlătescu, I.; Ţovaru, Ş.; Nicolae, C.; Preda, A.S.; Funieru, C. Desquamative Gingivitis—A Clinicopathological Review. Curr. Heal. Sci. J. 2018, 44, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-D.; Chen, W.-T.; Chi, C.-C. Association between Medication Use and Bullous Pemphigoid. JAMA Dermatol. 2020, 156, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, B.; Setterfield, J. Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid and Oral Blistering Diseases. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 44, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stasio, D.; Romano, A.; Paparella, R.S.; Gentile, C.; Serpico, R.; Minervini, G.; Candotto, V.; Laino, L. How Social Media Meet Patients Questions: YouTube Review for Mouth Sores in Children. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2018, 32 (Suppl. 1), 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Lucchese, A.; Mittelman, A.; Tessitore, L.; Serpico, R.; Sinha, A.A.; Kanduc, D.; Lucchese, A.; Mittelman, A.; Tessitore, L.; Serpico, R.; et al. Proteomic Definition of a Desmoglein Linear Determinant Common to Pemphigus Vulgaris and Pemphigus Foliaceous. J. Transl. Med. 2006, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kridin, K.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Bergman, R. Mortality and Cause of Death in Patients with Pemphigus. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2017, 97, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Zenzo, G.; Amber, K.T.; Sayar, B.S.; Müller, E.J.; Borradori, L. Immune Response in Pemphigus and beyond: Progresses and Emerging Concepts. Semin. Immunopathol. 2016, 38, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kridin, K. Pemphigus Group: Overview, Epidemiology, Mortality, and Comorbidities. Immunol. Res. 2018, 66, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, L.C.; Phoon, Y.W.; Pang, S.M.; Lee, H.Y. Pemphigoid and Pemphigus: Comparative Analysis of Clinical Epidemiology, Course and Outcome in an Asian Academic Medical Centre. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2021, 62, e288–e290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagi, L.; Baum, S.; Agmon-Levin, N.; Sherer, Y.; Katz, B.S.P.; Barzilai, O.; Ram, M.; Bizzaro, N.; SanMarco, M.; Trau, H.; et al. Autoimmune Bullous Diseases the Spectrum of Infectious Agent Antibodies and Review of the Literature. Autoimmun. Rev. 2011, 10, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stasio, D.; Lauritano, D.; Romano, A.; Salerno, C.; Minervini, G.; Minervini, G.; Gentile, E.; Serpico, R.; Lucchese, A. In Vivo Characterization of Oral Pemphigus Vulgaris by Optical Coherence Tomography. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2015, 29, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Petruzzi, M.; Tampoia, M.; Serpico, R.; Lauritano, D.; Lajolo, C.; Lucchese, A.; Della Vella, F. Evaluation of BP180-NC16A ELISA in Exclusive Oral Pemphigoid Diagnosis. A Comparative Study. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bağcı, I.S.; Horváth, O.N.; Ruzicka, T.; Sárdy, M. Bullous Pemphigoid. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonavoglia, A.; Leone, P.; Dammacco, R.; Di Lernia, G.; Petruzzi, M.; Bonamonte, D.; Vacca, A.; Racanelli, V.; Dammacco, F. Pemphigus and Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid: An Update from Diagnosis to Therapy. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 88, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Di Stasio, D.; Lauritano, D.; Lajolo, C.; Fiori, F.; Gentile, E.; Lucchese, A. Topical Photodynamic Therapy in the Treatment of Benign Oral Mucosal Lesions: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2020, 50, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arduino, P.G.; Romano, F.; Sasia, D.; Broccoletti, R.; Ricceri, F.; Barbui, A.M.; Brossa, S.; Cipriani, R.; Cricenti, L.; Cabras, M.; et al. Subgingival Microbiota in White Patients with Desquamative Gingivitis: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gireeva, A.I.; Polyakova, M.A.; Lalaev, K.V.; Babina, K.S.; Sokhova, I.; Doroshina, V.Y.; Seli-Fanova, E.I.; Eshtieva, A.A.; Kadzhoyan, A.G.; Podkhvatilina, A.S.; et al. Oral Hygiene Level and Composition of Oral Microbiota in Patents with Pemphigus Vulgaris during the Periods of Exacerbation and Remission. New Armen. Med. J. 2021, 15, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Scaglione, G.L.; Fania, L.; De Paolis, E.; De Bonis, M.; Mazzanti, C.; Di Zenzo, G.; Lechiancole, S.; Messinese, S.; Capoluongo, E. Evaluation of Cutaneous, Oral and Intestinal Microbiota in Patients Affected by Pemphigus and Bullous Pemphigoid: A Pilot Study. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2020, 112, 104331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorba, M.; Melidou, A.; Patsatsi, A.; Poulopoulos, A.; Gioula, G.; Kolokotronis, A.; Minti, F. The Role of Oral Microbiome in Pemphigus Vulgaris. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 2237–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruzzi, M.; Romano, A.; Baroni, A.; Borgia, R.; Fusco, A.; Donnarumma, G.; Contaldo, M.; Serpico, R. Oral Microbioma and Pemphigus Vulgaris. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2022, 36, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchese, A.; Petruzzi, M.; Lauritano, D. Crossreactivity: The Possible Role of Oral Microbiota in Oral Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.-F.; Dou, X.-Y. Gastrointestinal Microbiome and Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Review of the Literature and Conclusions. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 15, 1864–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Sun, W.; Wang, M.; Li, M. Characteristics of Gut Microbiota in Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome in Northern China. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0277270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, W.; Cheng, D.; Howe, P.H.; Bian, C.; Kamen, D.L.; Luo, Z.; Fu, X.; Ogunrinde, E.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; et al. Staphylococcus Aureus Peptidoglycan (PGN) Induces Pathogenic Autoantibody Production via Autoreactive B Cell Receptor Clonal Selection, Implications in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 131, 102860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, W.A.; Quraishi, M.N.; Iqbal, T.H. Gut Microbiome and Autoimmune Disorders. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2022, 209, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosang, L.; Canals, R.C.; van der Flier, F.J.; Hollensteiner, J.; Daniel, R.; Flügel, A.; Odoardi, F. The Lung Microbiome Regulates Brain Autoimmunity. Nature 2022, 603, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildner, G. Antigenic Mimicry—The Key to Autoimmunity in Immune Privileged Organs. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 102942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanduc, D.; Lucchese, A.; Mittelman, A. Non-Redundant Peptidomes from DAPs: Towards “The Vaccine”? Autoimmun. Rev. 2007, 6, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauritano, D. Designing a Peptide-Based Vaccine against Porphyromonas Gingivalis. Front. Biosci. 2013, S5, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitakis, N.G.; Papaioannou, W.; Sakkas, L.I.; Kousvelari, E. The Autoimmunity–Oral Microbiome Connection. Oral Dis. 2017, 23, 828–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittelman, A.; Lucchese, A.; Sinha, A.A.; Kanduc, D. Monoclonal and Polyclonal Humoral Immune Response to EC HER-2/NEU Peptides with Low Similarity to the Host’s Proteome. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 98, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willers, J.; Lucchese, A.; Mittelman, A.; Dummer, R.; Kanduc, D. Definition of Anti-Tyrosinase MAb T311 Linear Determinant by Proteome-Based Similarity Analysis. Exp. Dermatol. 2005, 14, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchese, A.; Willers, J.; Mittelman, A.; Kanduc, D.; Dummer, R. Proteomic Scan for Tyrosinase Peptide Antigenic Pattern in Vitiligo and Melanoma: Role of Sequence Similarity and HLA-DR1 Affinity. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 7009–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchese, A. From HSV Infection to Erythema Multiforme through Autoimmune Crossreactivity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, S.M.; Ghalayani, P.; Salehi, M.R.; Attarzadeh, H.; Shahmoradi, M. Human Papilloma Virus as a Possible Factor in the Pathogenesis of Oral Lichen Planus. Dent. Res. J. 2009, 6, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Yildirim, B.; Senguven, B.; Demir, C. Prevalence of Herpes Simplex, Epstein Barr and Human Papilloma Viruses in Oral Lichen Planus. Med. Oral Patol. Oral y Cir. Bucal 2011, 16, e170–e174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petti, S.; Rabiei, M.; De Luca, M.; Scully, C. The Magnitude of the Association between Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Oral Lichen Planus: Meta-Analysis and Case Control Study. Odontology 2011, 99, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viguier, M.; Bachelez, H.; Poirier, B.; Kagan, J.; Battistella, M.; Aubin, F.; Touzé, A.; Carmagnat, M.; Francès, C.; Gougeon, M.-L.; et al. Peripheral and Local Human Papillomavirus 16–Specific CD8 + T-Cell Expansions Characterize Erosive Oral Lichen Planus. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchese, A.; Serpico, R.; Crincoli, V.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Kanduc, D. Sequence Uniqueness as a Molecular Signature of HIV-1-Derived B-Cell Epitopes. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2009, 22, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Tian, E.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Z.; Peng, Q. Gut Microbiota and Its Roles in the Pathogenesis and Therapy of Endocrine System Diseases. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 268, 127291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, J.T.; Lin, P.; Asquith, M.; Costello, M.E.; Kenna, T.J.; Brown, M.A. Does the Microbiome Play a Causal Role in Spondyloarthritis? Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 33, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, P.; De Paz, B.; Rodríguez-Carrio, J.; Hevia, A.; Sánchez, B.; Margolles, A.; Suárez, A. Th17 Responses and Natural IgM Antibodies Are Related to Gut Microbiota Composition in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, O.; Lanham-New, S.A.; Corfe, B.M.; Gregson, C.L.; Darling, A.L.; Ahmadi, K.R.; Gibson, P.S.; Tobias, J.H.; Ward, K.A.; Traka, M.H.; et al. Role of the Microbiome in Regulating Bone Metabolism and Susceptibility to Osteoporosis. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2022, 110, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchese, G. From Toxoplasmosis to Schizophrenia via NMDA Dysfunction: Peptide Overlap between Toxoplasma gondii and N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptors as a Potential Mechanistic Link. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, M.; Ranjan, A.; Thompson, A.; Diaz, P.I.; Sobue, T.; Maas, K.; Dongari-Bagtzoglou, A. Candida Albicans Induces Mucosal Bacterial Dysbiosis That Promotes Invasive Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinan, J.; Wang, S.; Hazbun, T.R.; Yadav, H.; Thangamani, S. Antibiotic-Induced Decreases in the Levels of Microbial-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids Correlate with Increased Gastrointestinal Colonization of Candida Albicans. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noverr, M.C.; Huffnagle, G.B. Regulation of Candida Albicans Morphogenesis by Fatty Acid Metabolites. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 6206–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coit, P.; Sawalha, A.H. The Human Microbiome in Rheumatic Autoimmune Diseases: A Comprehensive Review. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 170, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contaldo, M.; Lucchese, A.; Lajolo, C.; Rupe, C.; Stasio, D.D.; Romano, A.; Petruzzi, M.; Serpico, R. The Oral Microbiota Changes in Orthodontic Patients and Effects on Oral Health: An Overview. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belvoncikova, P.; Maronek, M.; Gardlik, R. Gut Dysbiosis and Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Autoimmune Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marietta, E.; Mangalam, A.K.; Taneja, V.; Murray, J.A. Intestinal Dysbiosis in, and Enteral Bacterial Therapies for, Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 573079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrozzo, M.; Arduino, P.G.; Baldovino, S.; Di Zenzo, G.; Salzano, S.; Calabresi, V.; Roccatello, D. Minocycline in Combination with Mycophenolate Mofetil in Oral Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2008, 18, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrozzo, M.; Arduino, P.; Bertolusso, G.; Cozzani, E.; Parodi, A. Systemic Minocycline as a Therapeutic Option in Predominantly Oral Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid: A Cautionary Report. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 38, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Reference (First Author + Year) | N° Cases (Disease) and Controls | Sample | Bacteria | Study Type | Sample Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arduino 2017 [62] | 14 MMP and 33 controls affected by PG | Subgingival plaque samples | F. nucleatum E. corrodens Capnocytophaga spp. | Cross-sectional study | PCR technique |
| Gireeva 2021 [63] | 30 PV | Gingival fluid | P. intermedia, T. denticola, T. forsythensis, and P. gingivalis | Observation longitudinal study | Real-time PCR |
| Scaglione 2020 [64] | 7 PV | Oral cavity swabs | Firmicutes Fusobacteria | Cross-sectional study | NGS-based technologies |
| Zorba 2021 [65] | 15 PV and 15 healthy controls | Oral smear | Fusobacterium nucleatum Capnocytophaga leadbetteri Parvimonas micra | Case–control study | NGS-based technologies |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santoro, R.; Romano, A.; Morcaldi, M.C.; Fiori, F.; Di Spirito, F. Microbiota Alterations in Patients with Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid and Pemphigus Vulgaris: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4377. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074377
Santoro R, Romano A, Morcaldi MC, Fiori F, Di Spirito F. Microbiota Alterations in Patients with Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid and Pemphigus Vulgaris: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(7):4377. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074377
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantoro, Rossella, Antonio Romano, Maria Cristina Morcaldi, Fausto Fiori, and Federica Di Spirito. 2023. "Microbiota Alterations in Patients with Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid and Pemphigus Vulgaris: A Systematic Review" Applied Sciences 13, no. 7: 4377. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074377
APA StyleSantoro, R., Romano, A., Morcaldi, M. C., Fiori, F., & Di Spirito, F. (2023). Microbiota Alterations in Patients with Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid and Pemphigus Vulgaris: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences, 13(7), 4377. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074377








