Abstract
Multiplexed positron emission tomography (PET) imaging provides perfectly registered simultaneous functional and molecular imaging of more than one biomarker. However, the separation of the multiplexed PET signals within a single PET scan is challenging due to the fact that all PET tracers emit positrons, which, after annihilating with a nearby electron, give rise to 511 keV photon pairs that are detected in coincidence. Compartment modelling can separate single-tracer PET signals from multiplexed signals based on the differences in bio-distribution kinetics and radioactive decay. However, the compartment-modelling-based method requires staggered injections and assumes that each tracer’s input function is known. In this paper, we propose a deep-learning-based method to simultaneously separate dual-tracer PET signals without explicitly knowing the input functions. We evaluate the proposed deep-learning-based separation method on dual-tracer [F]FDG and []MET PET simulations and compare its separation performance to that of the compartment-modelling-based method, assessing performance dependence on the time interval between tracer injections as well as on the amount of training data. It is shown that the proposed method implicitly denoises the separated images and offers reduced variance in the separated images compared to compartment modelling.
1. Introduction
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a potent functional molecular imaging technology having applications to the imaging of the heart [1], brain [2] and cancer [3]. Conventional PET scans rely on imaging a single tracer to provide detailed functional or molecular imaging information typically connected to disease, meaning that images of different processes can only be acquired separately through multiple scans, e.g., a -fluorodeoxyglucos (FDG) PET scan to examine glucose metabolism and a subsequent separate -methionine (MET) scan to image protein synthesis to determine the boundaries of a brain tumour [4,5].
With multiplexed PET imaging, multiple targets of interest for different tracers can be observed simultaneously in a single scan, providing complementary information for clinical decision making [6,7,8,9]. Additionally, using multi-tracers in a single PET scan was thought to be beneficial for shortening the examination time and thereby improving diagnostic efficiency [10]. Multiplexed PET involves injecting different tracers with an offset of several minutes or even simultaneously and recovering the dynamic/static imaging measurements of each individual tracer in a single PET scan. To the best of our knowledge, the initial proof-of-principle of such an approach, has been applied to studies with phantom [11], simulated brain imaging [12] and cardiac imaging [13]. The main challenge with simultaneous multiplexed PET imaging, however, is that positrons from the PET radionuclides will emit 511 keV photon pairs when they annihilate with electrons, resulting in no unique energy information for identifying or differentiating the source of each photon pair. As a result, the PET scanner measures the sum of the PET signals of all tracers [14].
Several dual-tracer separation methods based on staggered injection protocols and dynamic imaging techniques have been proposed. Huang et al. [11] initially considered separating dual-tracer signals based on the difference in physical decay rates of tracers. A feasibility study of this method in small animals employing FDG and was shown in [15]. Further investigations of this method were also conducted and presented in [6,16]. However, this method requires significant differences between the half-lives of the two tracers. Another widely studied method is based on a parallel multi-tracer compartment model (CM), where the single-tracer signals are separated by fitting the superposed pharmacokinetic models of the corresponding tracers to the time activity curves (TACs) extracted from the reconstructed dynamic dual-tracer PET images; see Section 3.3 for details. The CM-based separation method was first introduced in [17] to estimate the kinetic parameters of -labeled tracers. The feasibility of this method for separating different tracer pairs was examined through simulation [18,19,20,21,22], animal studies [23,24] and a three-tracer (FDG, ATSM and PTSM) separation task [25].
The CM-based method is susceptible to noise and is prone to fall into local minima, leading to inaccurate separation results. Several methods have been proposed to improve the separation quality based on the CM-based method, e.g., separating the linear from the non-linear in the fitting process to reduce the parameter space [26,27], integrating the spatial and temporal information for dual-tracer separation by incorporating model fitting into the image reconstruction process [28] and simultaneous signal separation and reconstructions based on the dual-tracer kinetic model [29]. However, each of the aforementioned approaches was built on the assumption that the arterial input function (AIF) of each tracer is known, which restricts their practical feasibility. Verhaeghe and Reader [30,31] tackled this problem by using a set of temporal basis functions to model the TACs of each tracer. This temporal model is then incorporated into a global 4D PET reconstruction strategy [32]. However, the solution of the fitting problem was not unique in this method.
Although additional non-CM-based methods have also been suggested, including reference-tissue model-based dual-tracer separation [21], principal component analysis (PCA) [19], generalised factor analysis of dynamic sequences [33] and basis pursuit [34], their accuracy is still insufficient, and a long time-delayed injection protocol is required. A machine-learning-based dual-tracer separation method was conducted in [35], where a recurrent extreme gradient boosting (rXGBoost) algorithm [36] was presented to separate the dual-tracer TACs for a region of interest (ROI). It permits a shorter delay (5 min) between the injection of two tracers than that described in the literature [19,20,22,25,34], while high separation accuracy is still maintained. This method, however, only employs the temporal information of the measured signals for separation and still requires the knowledge of the AIFs of each tracer.
Over the years, deep learning has provided powerful new tools for the separation of dual-tracer PET signals. The DL-based method has two advantages over the aforementioned ones: (i) the ability to separate dual-tracer signals without explicitly knowing the input functions, (ii) use of spatiotemporal information for dual-tracer separation, and (iii) fast separation and processing using a trained network. Two main (supervised) deep learning strategies have been proposed for dual-tracer PET image separation in the literature. The indirect strategy employs a neural network to separate the dynamic dual-tracer images reconstructed using traditional reconstruction algorithms into dynamic single-tracer images [37,38,39,40,41,42,43]. Alternatively, the direct strategy incorporates the reconstruction task with the separation task to perform an end-to-end learning from dual-tracer dynamic sinograms to separated single-tracer dynamic images using a neural network [44,45,46]. In [47], an unsupervised joint method based on a GAN (pix2pix [48]) is presented to separate simultaneous dual-tracer PET signals and perform ROI segmentation. However, only a simultaneous injection protocol was considered in all the aforementioned deep-learning-based dual-tracer separation methods, neglecting the investigation of the impact of the time interval between the injections of the two tracers.
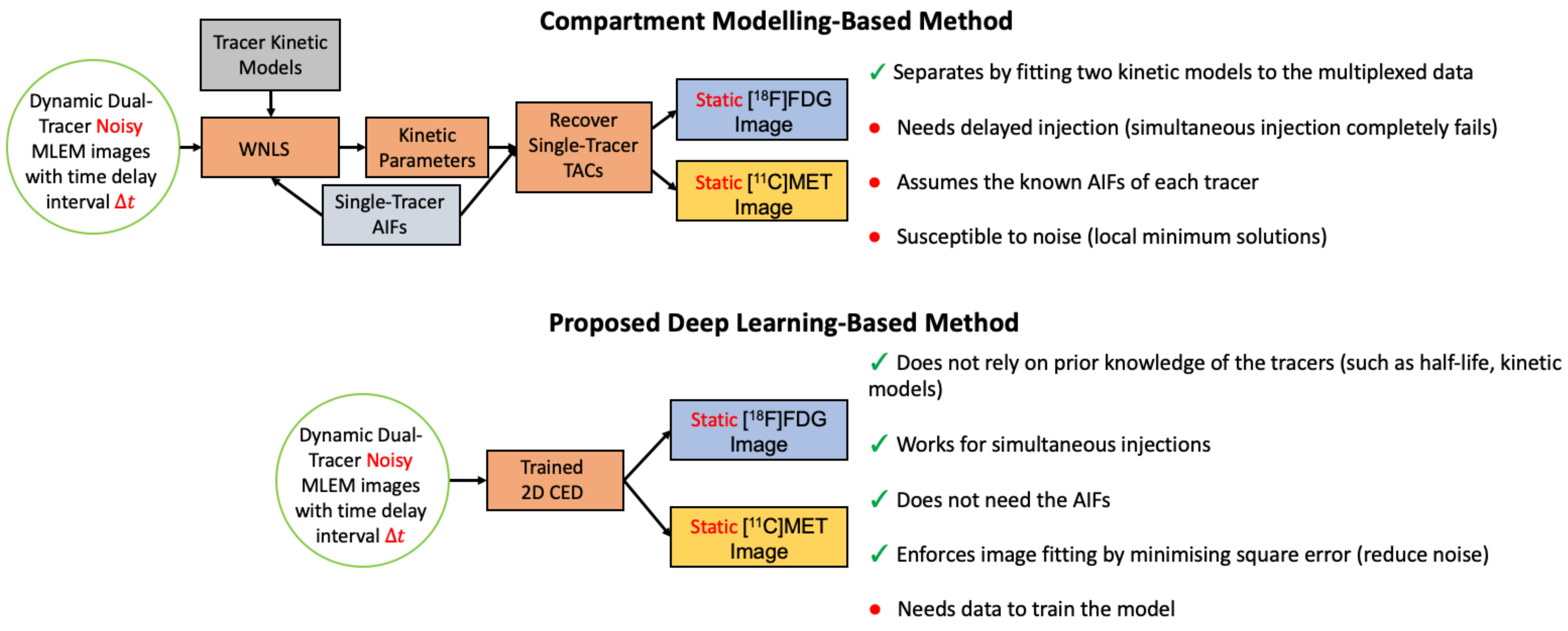
In this work, we investigate the impact of the number of training pairs and for indirect deep learning dual-tracer separation and conduct a comparative analysis between the proposed method and the CM-based method, which has not thus far been reported anywhere in the literature. In particular, we construct a customised 2D CED to separate dynamic and dual-tracer images into two static single-tracer images, one for each tracer, in a single dynamic scan when two tracers are injected sequentially with a specified short time interval . The proposed DL-based method and the CM-based method are summarised in Figure 1. The reminder of the paper is organised as follows. In Section 2, we outline our proposed methodology. Section 3 describes the design of the simulated experiments. In Section 4, we demonstrate the separation performance of our framework in the simulation study. Section 5 and Section 6 provide outlook and conclusions.
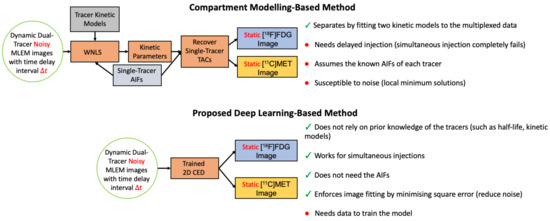
Figure 1.
Flowchart diagram of the DL-based method and the CM-based method for dual-tracer [F]FDG and [C]MET separation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dual-Tracer Single-Acquisition PET Measurement
Dynamic PET scanning can capture the spatiotemporal distribution of a radiotracer within a living organism. The activity concentration of a radiotracer of an image voxel at time t (i.e., TAC) can be described by the following model [49]
where represents the kinetic parameters that determine the tracer uptake in the tissue, is the tracer concentration in whole blood (we assume that the tracer concentration in whole blood is known and is equal to for simplicity), is the AIF representing the whole blood activity concentration, is the impulse response function, specified by a certain compartment model and corresponding kinetic parameters , is the fractional volume of blood in the tissue, and ⊗ denotes the convolution operator. In our work, we consider a reversible two-tissue compartment model for both FDG and MET.
Since in dual-tracer PET, the PET scanner measures the sum of the PET signals of two tracers, the dual-tracer activity concentration can be modelled as the sum of the activity concentrations of each tracer
where is the rate of radioactive decay of , is the rate of radioactive decay of , and the vector contains the kinetic parameters of each tracer. The single-tracer activity concentration is multiplied by the decreasing exponential term in the right-hand side of (2), which models the radioactive decay of each tracer. A dynamic PET scan measures the activity of both tracers at multiple consecutive time frames. In each frame, the coincidence events were recorded from the start of the frame until the end of the frame. The intensity of the dual-tracer image at pixel j in the mth frame can be expressed as [50]
where and represent the start and end points of frame m, respectively. The expectation of the projection data in time frame m can be expressed as
where the (i, j)th element of the system matrix is the probability of detecting an event originating in voxel j by detector pair i, is the expectation of scattered and random events in the mth frame, and M and N are the total number of detector pairs and image voxels, respectively.
2.2. Deep Learning Dual-Tracer Separation
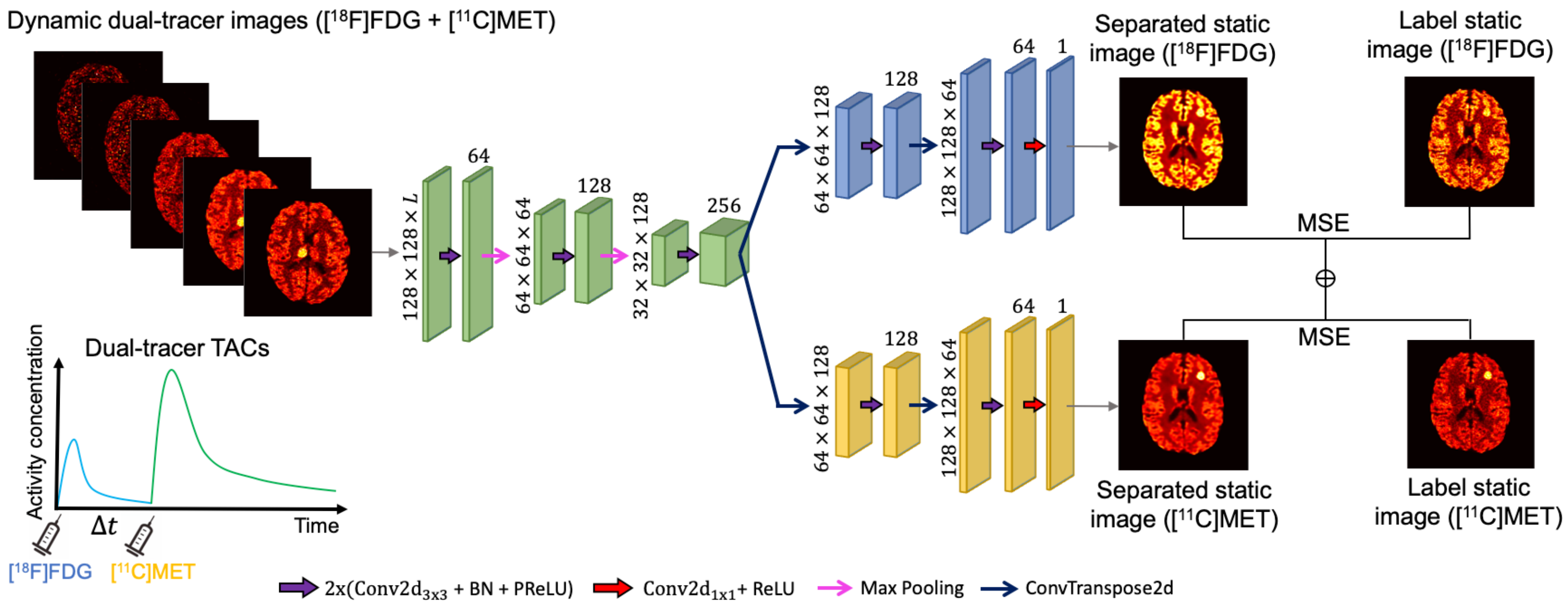
In deep learning for dual-tracer signal separation, the designed network is usually trained to simultaneously infer the separated images of each tracer, which can be considered as a multi-task learning problem [44,45,46]. Our proposed architecture is based on the hard parameter sharing approach commonly employed in multi-task learning [51], where a common space representation is shared for all tasks, with additional layers that are specific to each task. Since all tasks are learned simultaneously, the hard parameter sharing helps our model generalise better and reduce the risk of overfitting [52]. Specifically, our network is based on a CED architecture, but it contains two decoders. The specifics of the tailored CED architecture are shown in Figure 2. It consists of repeated applications of (1) double convolutional layers, (2) a batch normalisation (BN) layer, (3) a PReLU layer, (4) max-pooling for down-sampling, (5) a 2D transposed convolution layer for up-sampling, (6) a convolutional layer, and (7) a ReLU layer. The number of trainable parameters for this 2D CED is around 2.2 million.
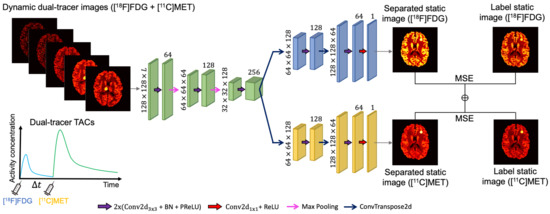
Figure 2.
The proposed 2D CED structure. The input is the dynamic dual-tracer images with L consecutive frames. The numbers shown in the plot are based on the simulation study described in Section 3.1.
The inputs to the CED are dynamic dual-tracer MLEM images reconstructed from a sinogram sequence obtained during a single PET scan with a time-delayed interval between tracer injections. The dynamic dual-tracer MLEM images, i.e., dual-tracer TACs of each voxel, are mapped to a latent representation via a series of 2D convolutions, batch-normalisation, non-linearities, and down-sampling in the encoder of the CED. The correlations between each frame of the dynamic dual-tracer images are encoded in this latent representation during training and allow prediction of the separated static single-tracer images. The two decoders of the CED separate and decode the latent representation to output static images corresponding to each tracer (in blue for FDG and yellow for MET). A ReLU layer was added prior to the output in order to introduce the non-negative constraint on the separated images.
As the network outputs contain the static images of two individual tracers, the mean squared error (MSE) loss function is applied to both the static single-tracer images and can be written as
where denotes the total number of training pairs, and are the network’s outputs, and and are the label static single-tracer images.
3. 2D Simulation Study
3.1. 2D Dataset Simulation
The proposed DL-based dual-tracer separation method was validated through 2D numerical simulations. A total of 5 non-contiguous slices were selected from each of the 20 3D BrainWeb phantoms (the BrainWeb dataset is available from https://brainweb.bic.mni.mcgill.ca/, accessed on 1 July 2021) to generate the simulated dataset of 2D brain phantoms [53]. The simulated dataset consists of 100 brain images. Each image is of resolution , assuming a uniform voxel size , and contains gray matter (GM) and white matter (WM). Randomised structures were introduced, and a tumour region with random radii of 2.5–4 mm and random locations was added to each phantom (the BrainWeb-based image processing toolbox is available from https://github.com/casperdcl/brainweb, accessed on 1 July 2021).
The combination of two tracers of different isotopes, FDG and MET, with radioactive decay rates of and , respectively, was considered in our simulation study. Following the simulation process in [46,54,55], each kinetic parameter was modelled as a Gaussian variable with the coefficient of variation equal to 0.1 to simulate the population variation in the dataset [54,55]. The mean values of the kinetic parameters were taken from [28] and are presented in Table 1. Feng’s input function model [56] was used to generate the FDG and MET AIFs. The parameters for Feng’s model were selected to match the shapes of the AIFs presented in [28]; see Table A1 for the details.

Table 1.
Mean values of the ground-truth kinetic parameters of FDG and MET for different tissue ROIs.
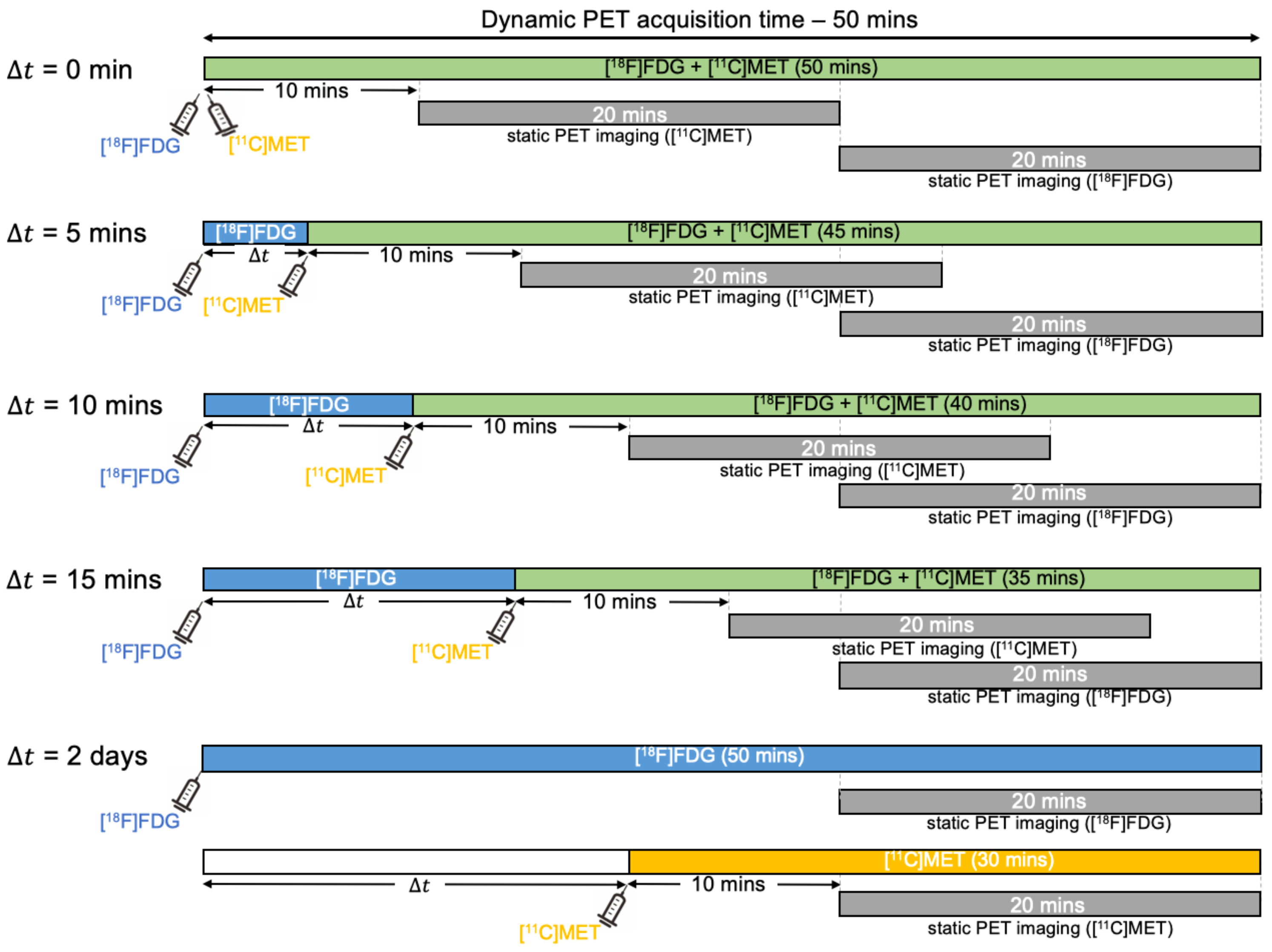
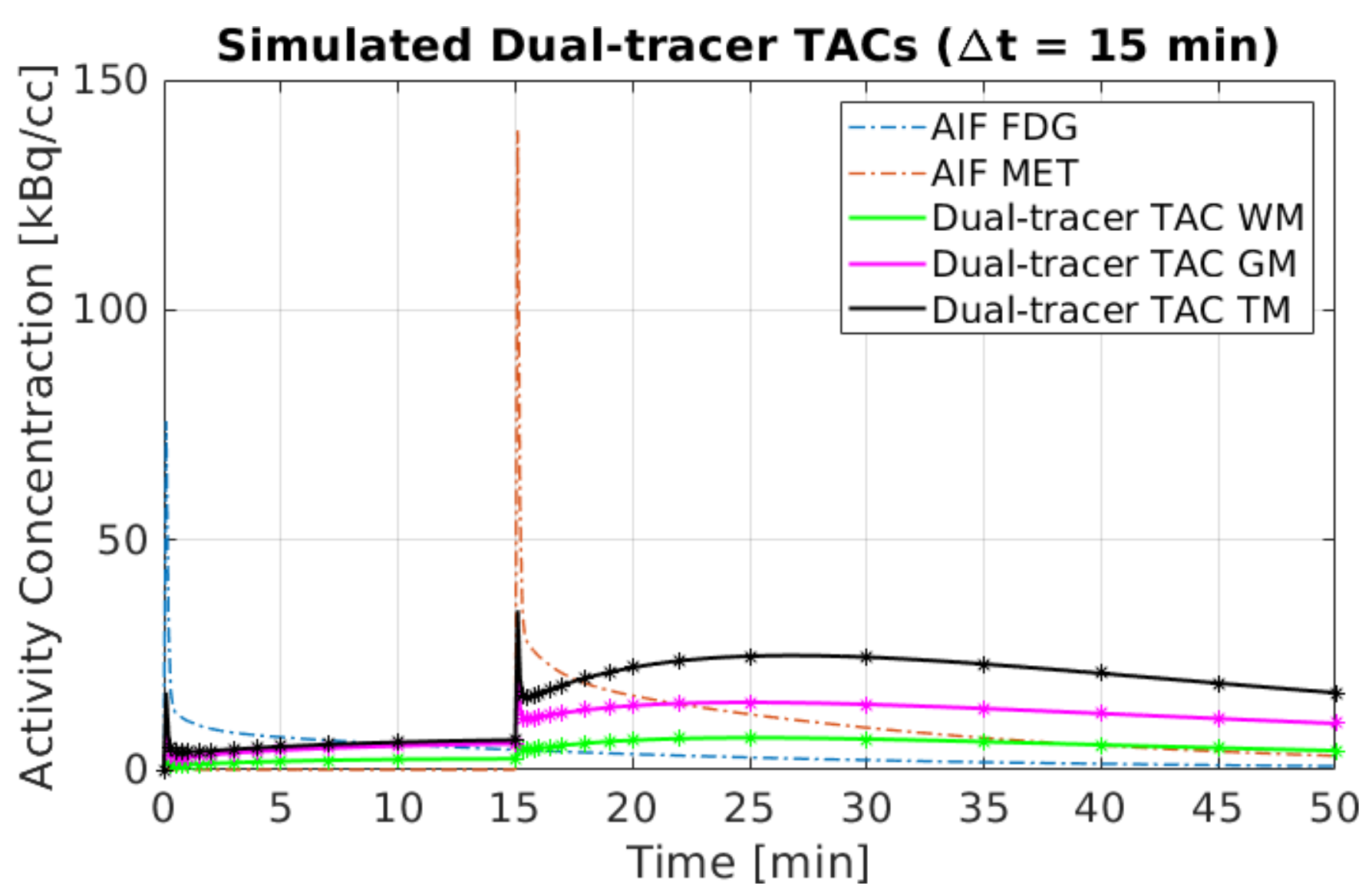
Figure 3 depicts the dynamic dual-tracer PET scanning protocols for different , as well as the static PET scanning protocols for each tracer in our simulation. We consider a 50 min dual-tracer PET scan: the MET injection was followed by the injection of FDG with a time delay . To explore the impact of the time-delayed interval, different were taken into account in our experiments, e.g., 0 min, 5 min, 10 min, 15 min and 2 days. The reversible two-tissue compartment model was used to simulate the 50 min dual-tracer TACs. The AIFs and a simulation of a dual-tracer TAC for min without decay correction are shown in Figure 4. We note that the dual-tracer signals were entirely separated in time by = 2 days since FDG was metabolised and cleared from brain tissues prior to the injection of MET. In this instance, two separate dynamic PET scans were performed, one for each tracer.
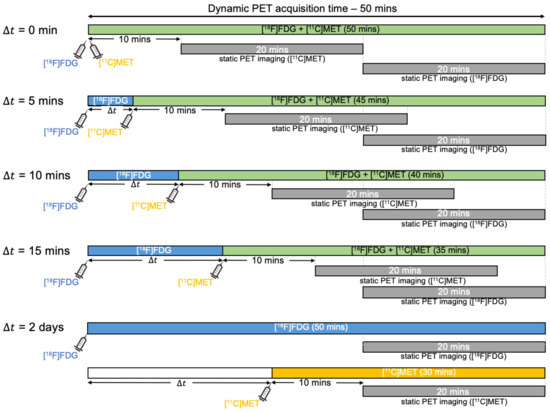
Figure 3.
Diagrams of the proposed protocols for dynamic dual-tracer FDG and MET PET scans for 0 min, 5 min, 10 min, 15 min and 2 days, along with the static PET scanning protocols of each tracer.
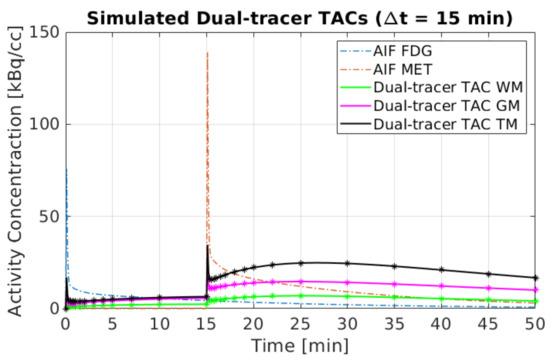
Figure 4.
A simulated example of dual-tracer ([F]FDG and [C]MET) TACs with = 15 min.
For the single-tracer PET scan, a static PET scan was taken for 20 min starting 30 min after the injection of FDG to ensure that the radioactive compound was sufficiently trapped. Following the protocol outlined in [57], a static MET PET scan was conducted separately for 20 min, starting 10 min after injection. The single-tracer TACs were simulated for (50 min) and (30 min) based on the proposed protocols for a static PET scan of each tracer. However, only the last 20 min activity concentration was assessed in the static PET scan for each tracer. For a fair comparison, we determined the total acquisition time for the dynamic single-tracer PET scans to be 50 min for FDG and 30 min for MET for = 2 days based on the aforementioned dynamic and static scan protocols.
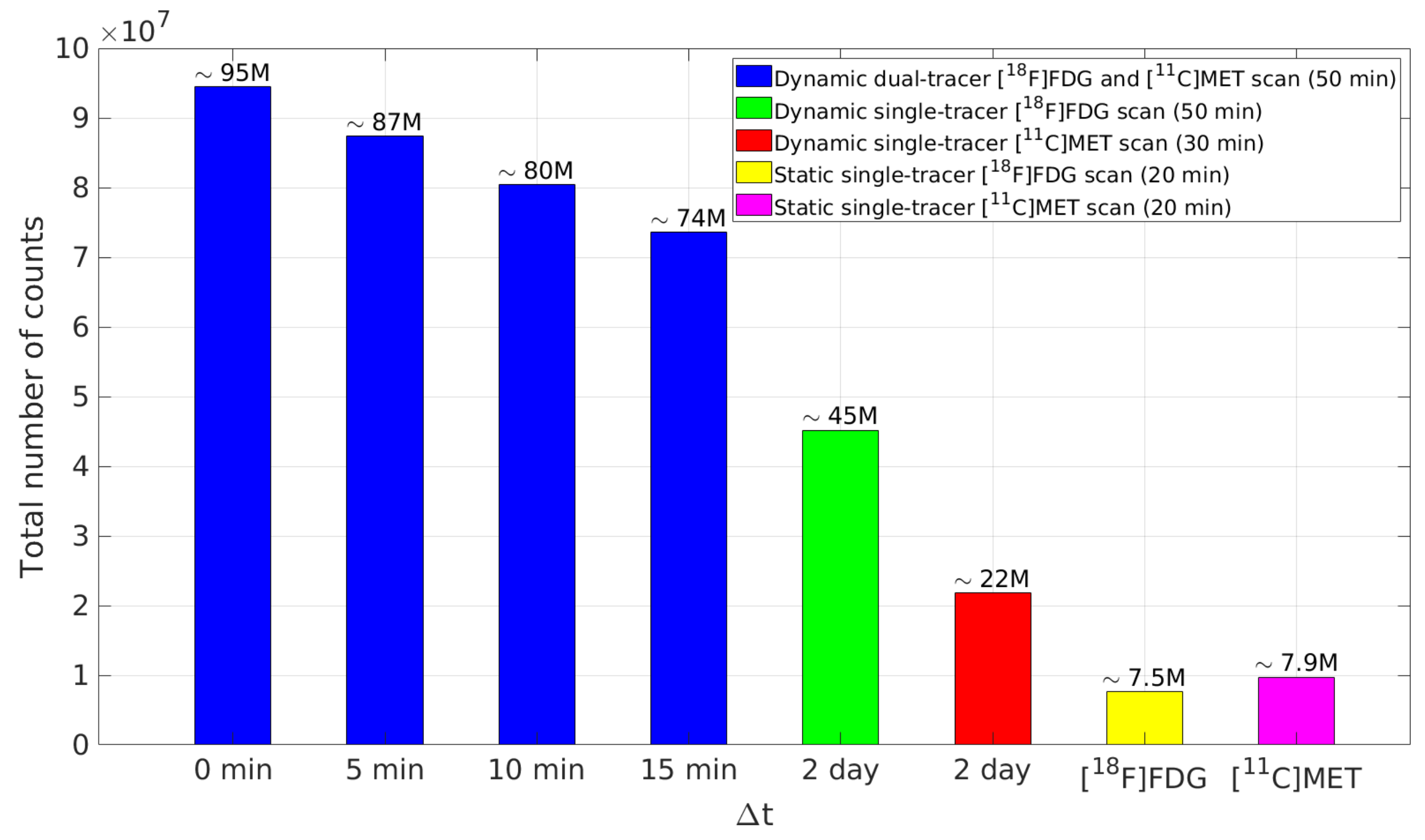
Dynamic and static PET scans were simulated for a GE DST PET scanner with system sensitivity ∼2 cps/kBq in 2D mode (specifications of the GE Discovery ST scanner are available from https://www.amberusa.com/equipment/pet-ct/pet-ct/ge-discovery-st-8-slice, accessed on 1 July 2021). The simulated single-tracer TACs (the last 20 min for both tracers) were integrated, assigned to different brain tissues and then forward projected to produce the noise-free static sinograms of each tracer. To generate the noise-free dynamic sinograms, the simulated dual-tracer TACs (50 min) were integrated and assigned to different brain tissues for each time frame, then forward projected to the sinogram domain. The forward projection model included object self-attenuation, which was simulated using the DIRECT package (the MATLAB toolbox DIRECT developed for dynamic PET image reconstruction is available from https://wanglab.faculty.ucdavis.edu/code, accessed on 1 July 2021). A total of 20% scattered and 20% random events were included in this simulation. Poisson noise was then introduced. We followed the same framing scheme as presented in [28] for [F]FDG and [C]MET dual-tracer TACs simulation with = 15 min and further addressed the frame widths according to the measurement points for different (see Table 2 for details). A simulation of the total number of counts of the static single-tracer PET scans (20 min) and dynamic dual-tracer scans (50 min) for different are shown in Figure 5.

Table 2.
Framing scheme of dynamic dual-tracer PET scans for different .
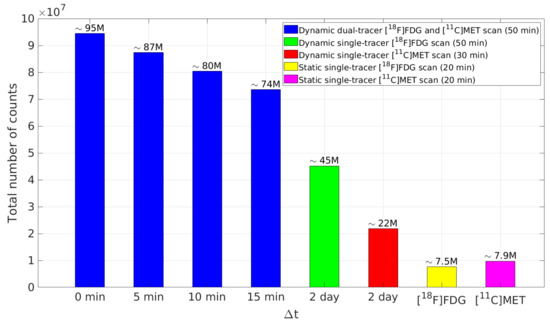
Figure 5.
A simulated example of the total number of counts of the static single-tracer PET scans (20 min) and dynamic dual-tracer scans (50 min) for different .
3.2. Implementation of Deep-Learning-Based Dual-Tracer Separation Method
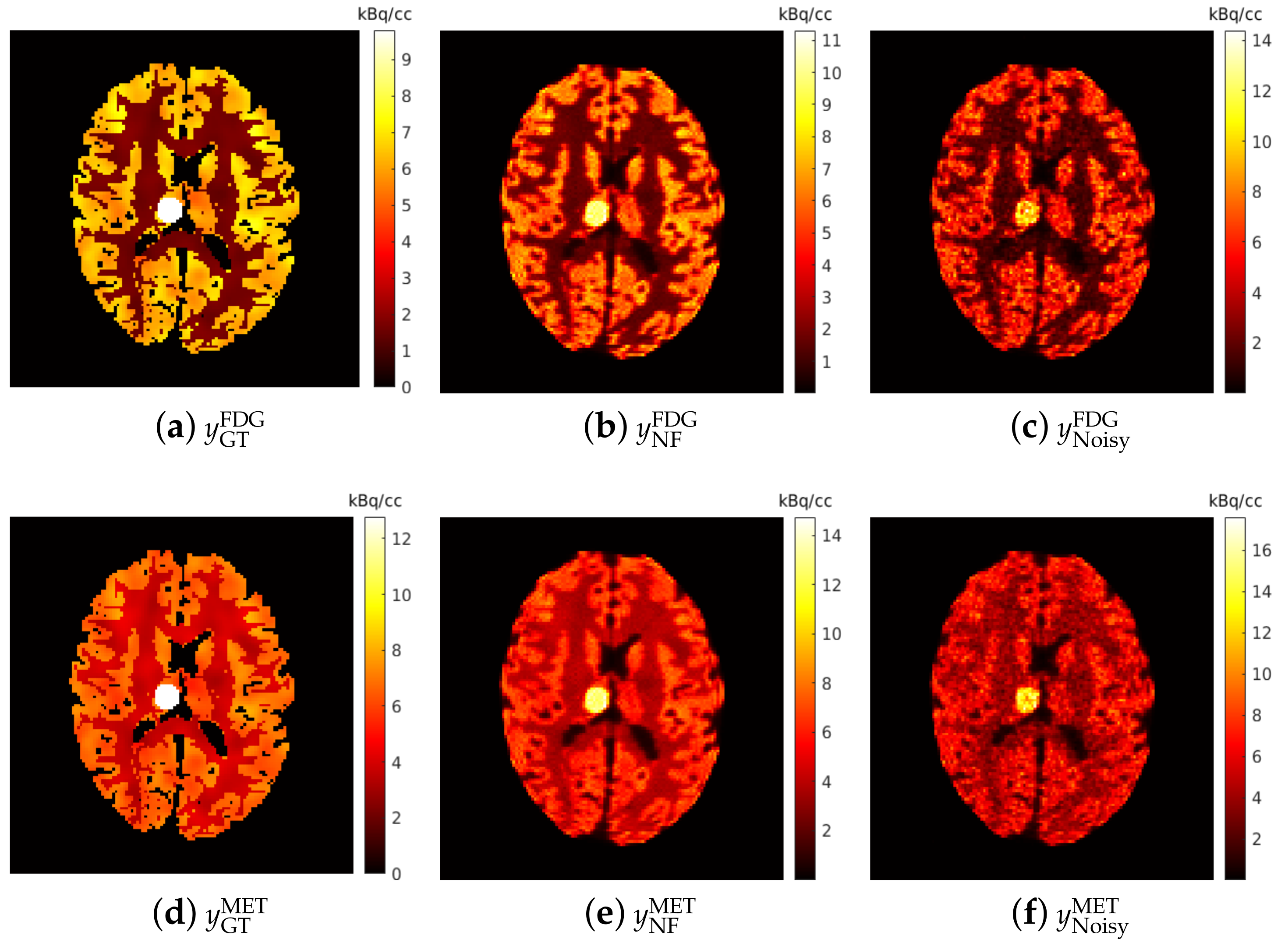
The simulated brain phantoms were reconstructed using the classic maximum-likelihood expectation maximization (MLEM) algorithm [58]. A total of 128 iterations were used for EM reconstruction to maintain the balance between bias and noise as suggested in [28,59]. Given that the PET scanner measures average activity concentration over time, the reconstructed dynamic dual-tracer images were further normalised by frame widths, e.g., for the mth frame, to obtain the (non-decay corrected) dual-tracer TACs of each voxel. The reconstructed single-tracer images were also normalised by 20 min static acquisition time to obtain the activity distributions. The reconstructed dynamic dual-tracer images and the reconstructed static single-tracer images were used as network inputs and training labels, respectively. Examples of reconstructed static single-tracer noisy MLEM images are shown in Figure 6c,f, together with the corresponding noise-free MLEM reconstructions (NF) (b,e) and the ground truths (a,d). When 2 days, the dual-tracer signals were entirely separated (reasons for which are discussed in Section 3.1), and thus two reconstructed dynamic single-tracer images were obtained, one for each tracer. In this case, the reconstructed dynamic single-tracer images (either FDG or MET) were employed as the network input. In this special case, the MSE loss is only applied to either FDG or MET, depending on the choice of the tracer considered in the network input. Notice that the decay correction cannot be performed in dual-tracer PET prior to separation because the proportion of each tracer (and hence its decay correction factor) is unknown prior to separation. While we do model decay, we do not seek to include decay correction in this present work.
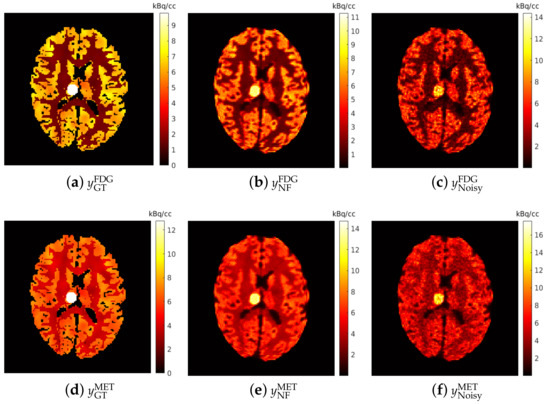
Figure 6.
Brain phantom: an example of the simulated static single-tracer images (tracer activity distributions) for and : (a,d) ground-truth static images; (b,e) noise-free MLEM reconstructions; (c,f) noisy MLEM reconstructions.
In our experiments, an individual 2D CED was trained for each to investigate the impact of the time delay interval between the injections of the two tracers. We used 80 simulated 2D brain phantoms to generate the training pairs (dynamic dual-tracer reconstructed images and static single-tracer reconstructed images), 10 for validation and 10 for testing. We also retrained each CED using a different sample size (1, 4, 8 and 40 training pairs) to assess the impact of the number of training pairs. All network training was performed in the same manner. We chose Adam [60] as the optimizer with Xavier initialization [61] and a learning rate of 0.005. Different batch sizes were chosen based on the number of training pairs; see Table A2 for additional information. To prevent overfitting, all networks were trained for 1000 epochs, with early stopping when the validation metrics no longer improved along with the training metrics. The training and evaluation of each network were implemented with PyTorch 1.11.0. All computations were conducted on a Quadro P6000 GPU with 24 GB memory.
3.3. Implementation of Compartment Model-Based Dual-Tracer Separation Method
We compared the performance of the proposed DL-based method with the (voxel-wise) CM-based method for dual-tracer separation (a flowchart diagram can be found in Figure 1). In the CM-based method, dual-tracer TACs of each voxel (denoted with ) were first extracted from the reconstructed dynamic dual-tracer MLEM images. The kinetic parameters were estimated for each tracer by fitting the dual-tracer kinetic model (2) to the measured dual-tracer TACs
where L is the total number of frames, is the weight factor of the mth frame, and is the mid-time of the mth frame. We chose in accordance with the recommendation made in [30], where denotes the TAC value for a given voxel at frame m, and denotes the frame width for the mth frame. The trust-region-reflective algorithm [62,63] (implemented in the Matlab function ) was used to performed a voxel-wise weighted non-linear least squares (WNLS) fitting to solve (4). The initial values of each of the kinetic parameters contained in were set at 0.05 for all voxels, and the lower and upper bounds of each parameter were set to 0 and 1, respectively. Stopping criteria were set such that the optimization procedure terminated when the change of the objective function was less than or after 2000 iterations.
Given the estimated kinetic parameter vector and the AIFs of each tracer, the single-tracer TACs of each voxel can be calculated using Equation (1) (physical decay of each radioactive tracer was considered). According to the static single-tracer PET protocol described in Section 3.1, the recovered single-tracer TACs (the last 20 min for both tracers) were integrated and assigned to each voxel to recover the static single-tracer images, which were then normalised by the entire static acquisition time of 20 min to represent the mean activity distributions. Although, for 2 days, dynamic dual-tracer signals have been entirely separated due to a sufficiently long (see the discussion in Section 3.1), the CM-based method is still valid by assuming either the activity concentration or activity concentration to be zero in Equation (2). In this case, the CM-based method estimates the kinetic parameters of each tracer by fitting the single-tracer kinetic model (1) to the measured single-tracer TACs extracted from the reconstructed dynamic single-tracer MLEM images.
3.4. Image Evaluation
The separated static FDG and MET images were evaluated at the pixel level using the normalised root mean square error (NRMSE) over a masked region of the images (denoted with )
with the bias given by
and the standard deviation (SD) given by
where is the mean value for voxel j in the separated image , obtained by averaging noise realisations, and is a reference image for error calculation.
The ROI level metrics were also computed for evaluating the separation performance, with the ROI bias given by
and the ROI standard deviation given by
where and are the mean values obtained by averaging S voxels within the ROI in the separated image and the reference image , respectively.
4. Results
4.1. DL-Based Dual-Tracer Separation Results
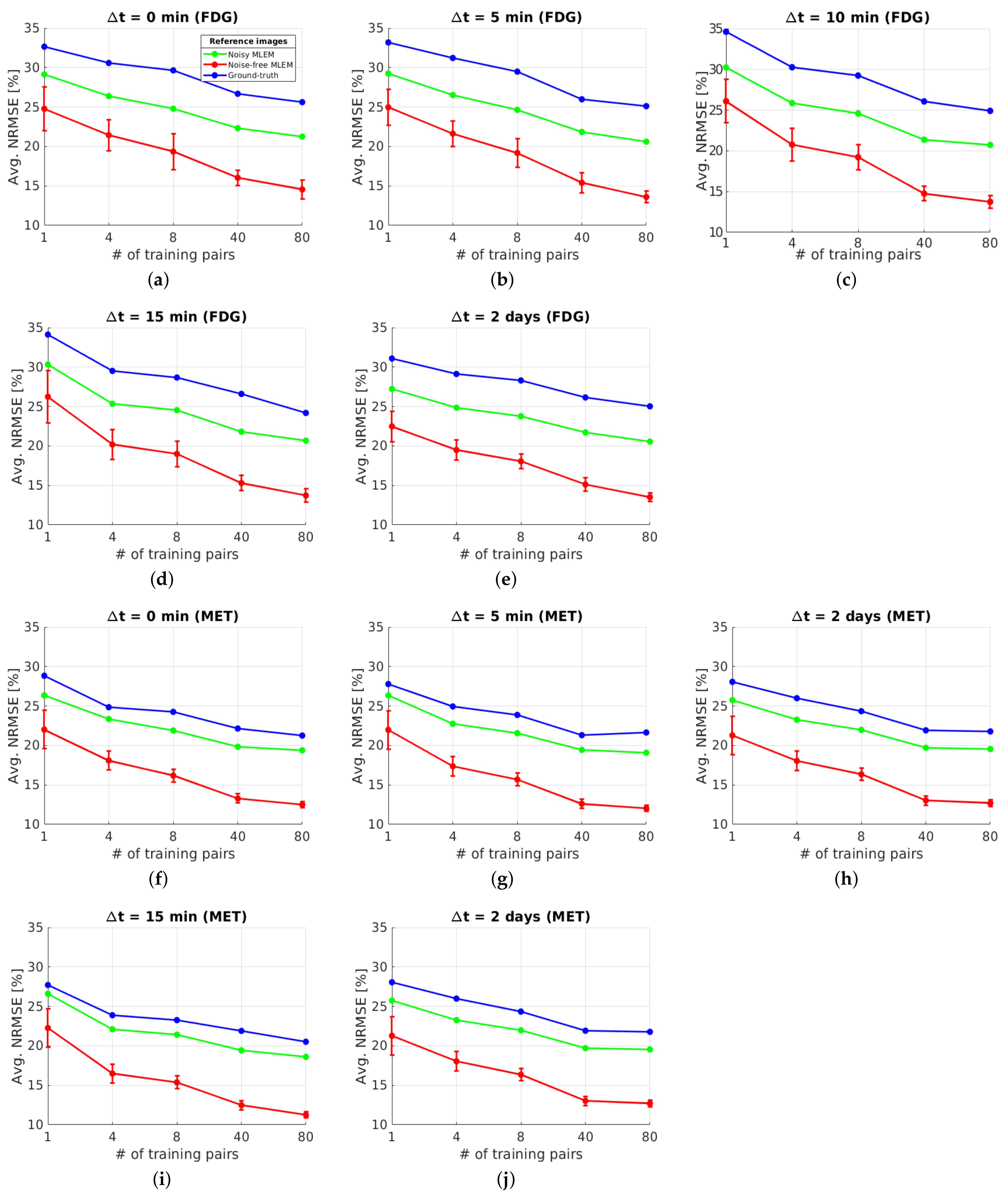
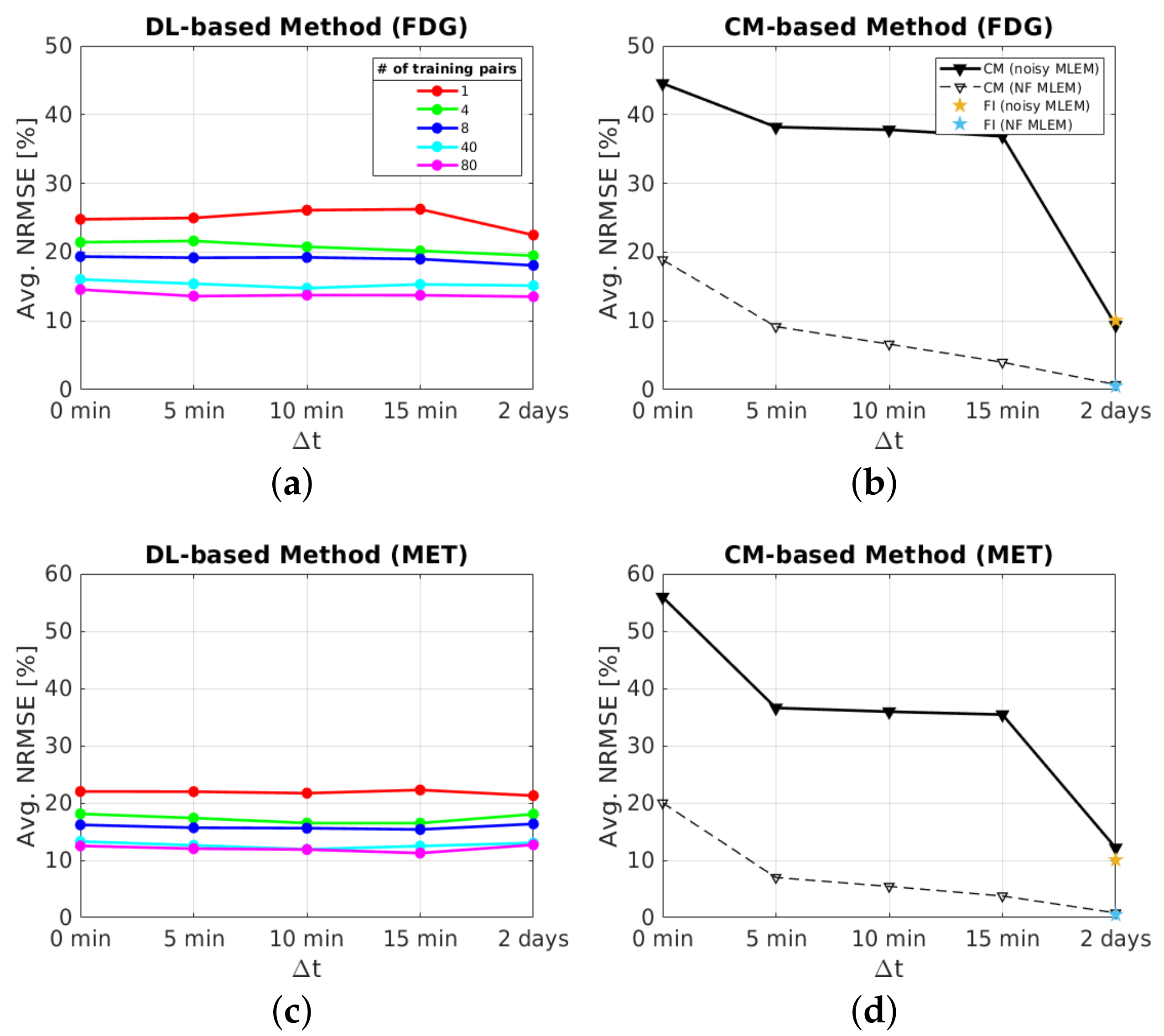
The whole brain region , where the activity concentration is non-zero in the ground-truth images of each tracer, was assessed for testing the separation quality at the pixel level. Figure 7 shows the NRMSE averaged over the entire test set (10 test datasets) as a function of the number of training pairs for the DL-based method. More specifically, the figure shows the NRMSE with respect to three different reference images: the static single-tracer ground-truth images , the reconstructed static single-tracer noisy MLEM images and the reconstructed static single-tracer noise-free MLEM images , where * denotes either FDG or MET; see Figure 6 for an illustration of the reference images. For each , the separation error of the DL-based method in terms of the average NRMSE with respect to was higher than when and were used as reference images. This is due to the fact that noise-free or noisy MLEM will not give perfect results with respect to the ground truths. Comparing our DL-based separation results to MLEM is therefore helpful as the perfectly separated MLEM images are not achieving the ground truths. While the proposed network was trained with noisy labels , the separation results achieved better average NRMSE values across all when noise-free images were used as references. This is a consequence of using MSE as a loss function in our task. We note that the arithmetic mean of the observations z, i.e., , is found to be the minimum of the loss in MSE. This indicates that a neural network learns to output the average of all plausible explanations when trained with MSE loss. Therefore, our proposed network can be trained using noisy labels with MSE loss to learn to separate the dual-tracer signals and output the estimation of the mean images of each tracer, and as a result, the separated images are closer to . For the remainder of the paper, we use the reconstructed static single-tracer noise-free MLEM images as the reference images to calculate the error metrics in all cases.
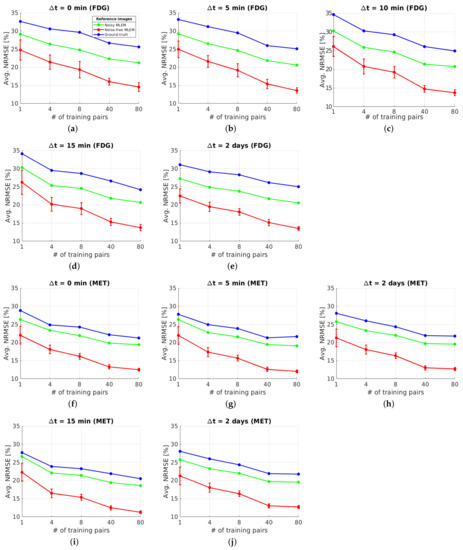
Figure 7.
Brain phantom (whole brain region): NRMSE (over 10 test datasets) of separated static FDG images (a–e) and MET images (f–j) using the DL-based method for the whole brain region .
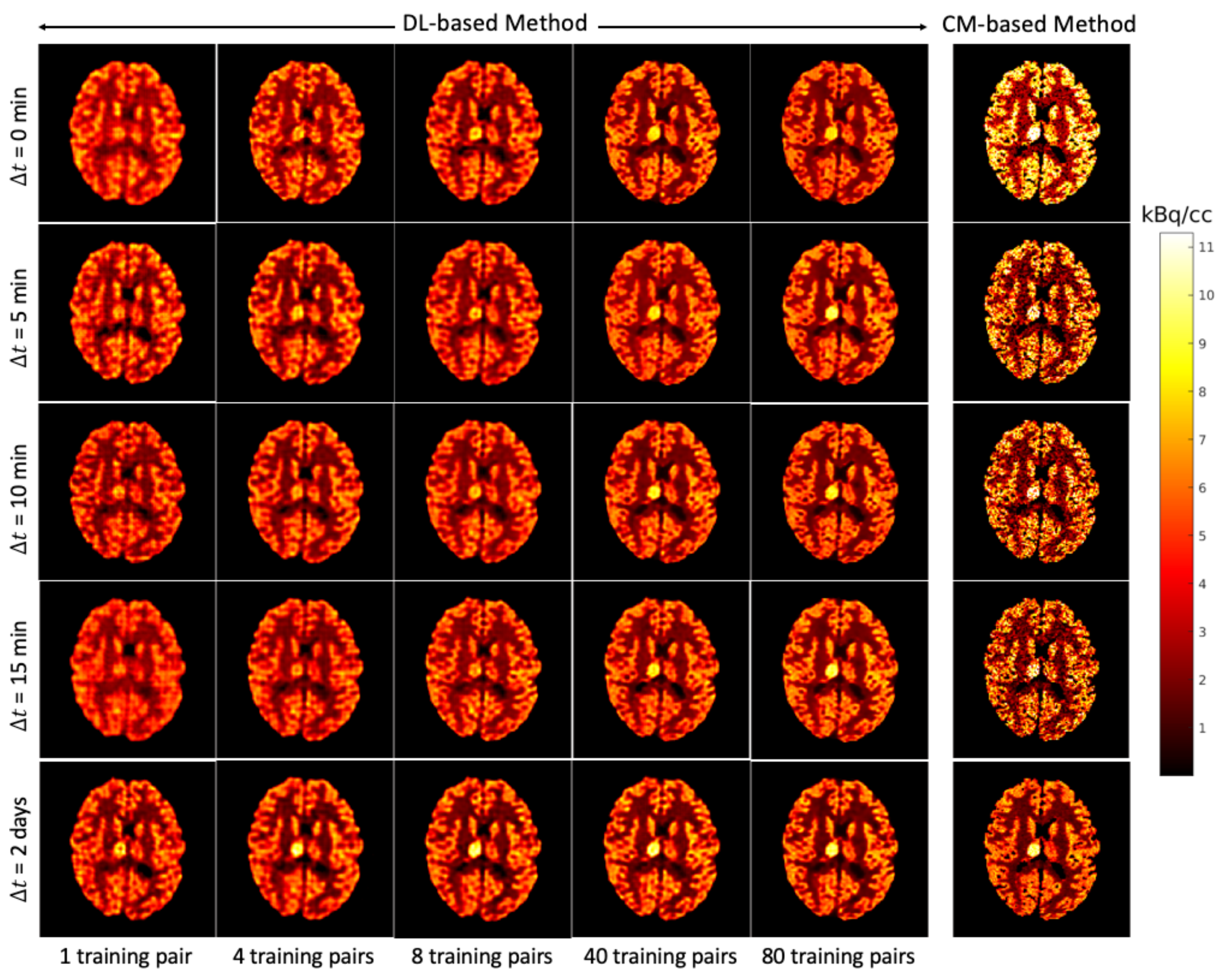
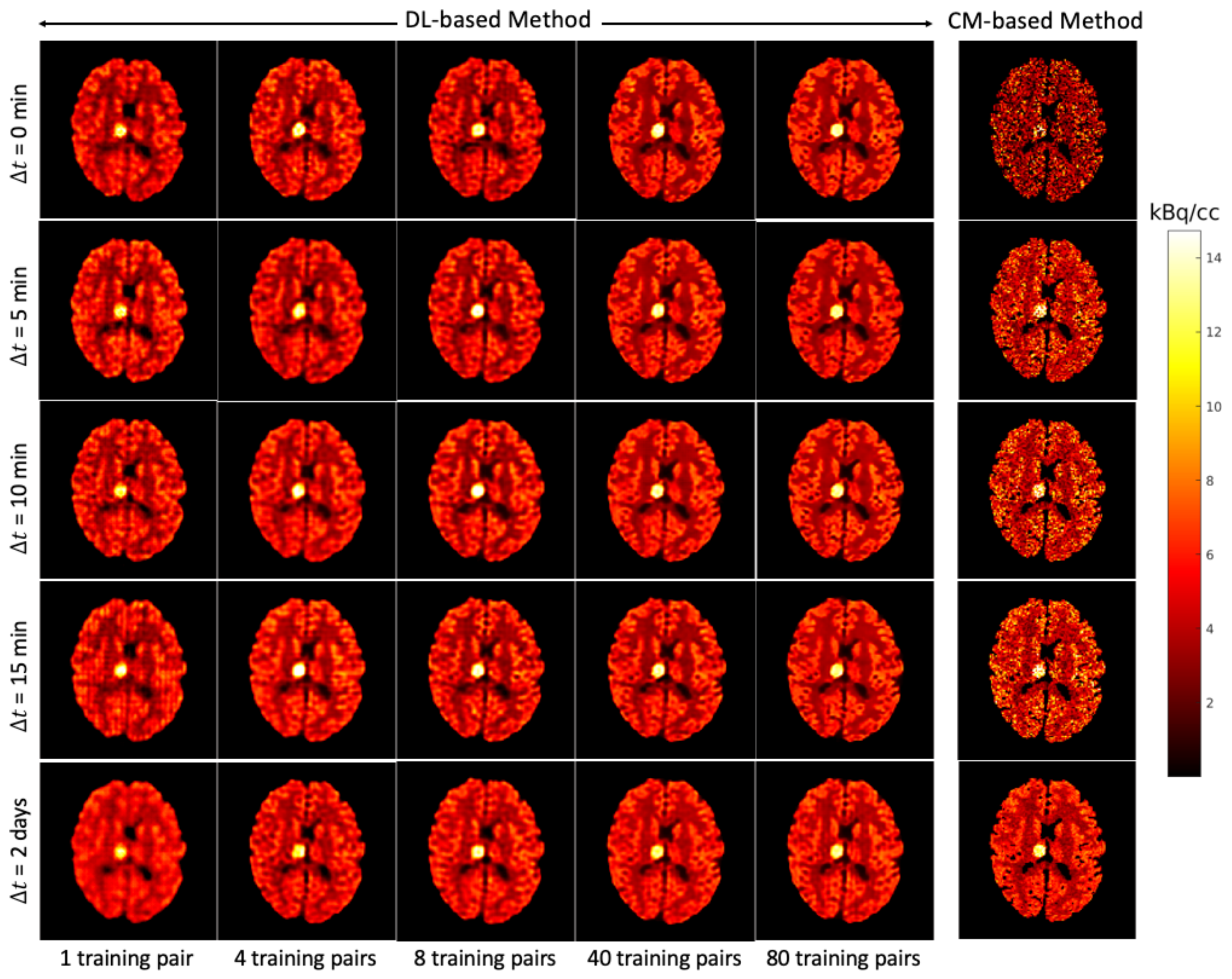
Figure 7 shows for each that the average NRMSE decreases and that a smaller SD is obtained in the test set as the number of training pairs increases from 1 to 80. This is consistent with the visual impression of the separations obtained by the DL-based method, as shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9. The first to fifth columns display the separated static single-tracer images (activity distributions) based on different numbers of training pairs (for plotting only, we limit the colour scale of the figures to fall within the same range as the reference images in Figure 6b for and Figure 6e for , respectively). Although all cases successfully recover the separated images, using more training pairs results in higher separation performance in terms of recovering the tumour regions, shapes and low contrast of the white and grey matter for . Figure 10a,c also suggest that the more training pairs used, the better the average NRMSE, which is in line with the results shown in Figure 7. With 80 training pairs, the DL-based method achieved average NRMSE values for FDG and MET of ∼15% and ∼12%, respectively, for the test set across all (see the magenta lines in Figure 10a,c).
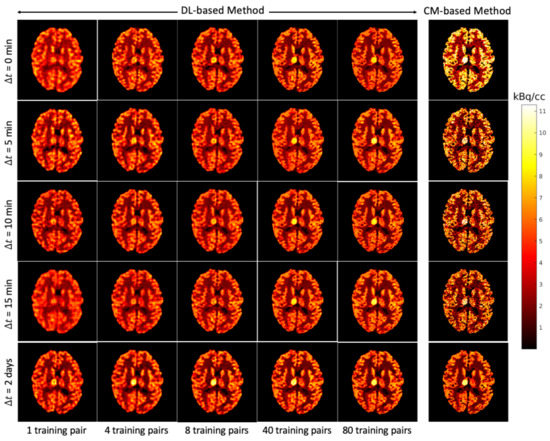
Figure 8.
Brain phantom (whole brain region): the static images recovered using the DL-based method (Columns 1 to 5) and the CM-based method (Column 6).
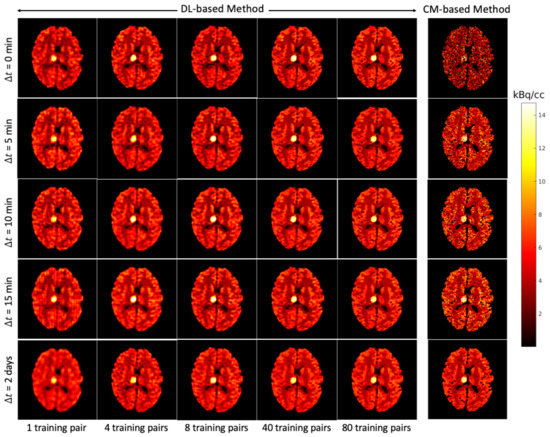
Figure 9.
Brain phantom (whole brain region): the static images recovered using the DL-based method (Columns 1 to 5) and the CM-based method (Column 6).
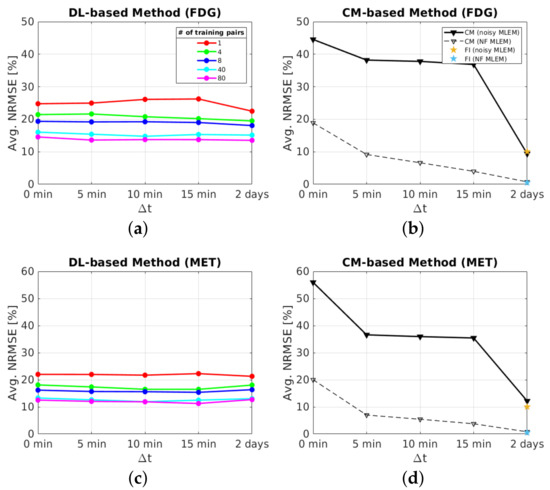
Figure 10.
Average NRMSE (over 10 test datasets) for the whole brain region: (a,c) DL-based method, (b,d) CM-based method and frame integrated (FI) method.
The impact of for the DL-based method using the same number of training pairs is shown in Figure 10a,c. The average NRMSE values of the DL-based separation results are at a similar level for all , which indicates that the separation performance of simultaneous injection is comparable to 5 min using the DL-based method. This is because the DL-based method uses both temporal and spatial information for dual-tracer separation, which effectively improves the separation performance even when simultaneous injection ( = 0 min) is considered.
4.2. CM-Based Dual-Tracer Separation Results
A test example of the separated images using the CM-based method is shown in the last column of Figure 8 (FDG) and Figure 9 (MET) for different . Compared to the results obtained from the DL-based method, the separated images using the CM-based method are much noisier because the model fitting (4) may fall into local minima even when the noise level is low. Although several strategies, such as using differing initial values or an exhaustive search algorithm [22], have been suggested to reduce local minima, their use in clinical practice is challenging because of their high computational cost.
We now investigate the impact of on the CM-based separation for dynamic dual-tracer noisy MLEM images. Figure 10b,d (solid lines) show longer results in more accurate separation using the CM-based method. High average NRMSE values were obtained (∼45% for FDG and ∼55% for MET) when a simultaneous injection protocol is used. The average NRMSE values improve rapidly (by ∼7% for FDG and and ∼20% MET) from simultaneous to 5 min delay and then gradually decrease for longer (10 and 15 min). This is because only the FDG signal was measured in the first 5 min, providing temporal prior information of a single tracer to aid in the disentangling of dual-tracer signals, whereas no prior information is given for simultaneous injection, which makes the dual-tracer separation problem more challenging. Longer means more temporal prior information of FDG is available before the MET injection, and thus the average NRMSE values steadily improve for the cases of = 10 and 15 min. For = 2 days, much lower average NRMSE values were obtained (∼10% for FDG and ∼12% for MET) as dual-tracer signals have been entirely separated by a large (see Section 3.1 for details). We also integrated the last 4 frames of the reconstructed dynamic single-tracer noisy MLEM images (we refer to herein as the frame integrated (FI) method) for = 2 days to estimate the target images (20 min static images of each tracer), and obtained a level of average NRMSE comparable to that of the CM-based method (see the pentagram markers in Figure 10b,d). This result indicates that the CM-based method is equivalent to the FI method for recovering the static single-tracer images from the dynamic single-tracer images when dual-tracer signals were separated by a sufficiently long time delay.
We then applied the CM-based method to the reconstructed dynamic dual-tracer noise-free MLEM images to examine the impact of the noise. Again, longer results in more accurate separation as illustrated in Figure 10b,d (dashed lines). The average NMRSE values of noise-free dual-tracer separations are substantially lower than those of noisy dual-tracer separations for all , indicating that noise has a massive effect on the separation performance when using the CM-based method. However, for both FDG and MET in the noise-free case, ∼20% average NRMSE values were obtained when = 0 min. The main reason is that the trust-region-reflective algorithm, which is used in the CM-based method to solve (4), may fall into local minima, leading to poor separation quality. When = 2 days, the dual-tracer signals have already been completely separated by a sufficiently long without the interference of noise, and thus the CM-based method exhibits almost perfect separation, which is equivalent to the results of using the FI method as highlighted in asterisk markers in Figure 10b,d.
4.3. DL-Based Method and CM-Based Method Comparison
The separation results between the DL-based method and CM-based method applied to the reconstructed dynamic dual-tracer noisy MLEM images were compared. For = 0, 5, 10 and 15 min, Figure 8 and Figure 9 show that in terms of visual assessment the CM-based method produces much nosier separated images than the DL-based method. This observation is consistent with better average NRMSE values of the DL-based separation results as illustrated in Figure 10. When using only 1 training pair, the DL-based method achieved high average NRMSE values across all (∼25% for FDG and ∼22% for MET). However, it nevertheless produces better average NRMSE values for = 0, 5, 10 and 15 min when compared to the separation results using the CM-based method. In fact, there are TACs contained in 1 training pair, one for each voxel; hence, in this instance, the proposed network was trained using TACs. Note that the DL-based method utilises both spatial and temporal information of the TACs from all voxels, but the CM-based method was implemented voxel by voxel, meaning only temporal information of one TAC was considered at each time. Therefore, for = 0, 5, 10 and 15 min, the DL-based method with 1 training pair yields better separation performance. When = 2 days, the CM-based method, in contrast to the DL-based method with 80 training pairs, achieved lower average NRMSE values for both FDG and MET. We believe this is the result of not enough training data which includes the case of = 2 days.
4.4. Bias and Standard Deviation Analysis (Pixel-Level)
To capture the variation of the separation caused by the random initialisation of the network parameters in network training, we retrained the proposed network for each scenario. Specifically, for each , the proposed network was independently retrained three times on the same dataset (with same number of training pairs) using different randomised weight initialization and random shuffling of the data per epoch during training. Armed with the retraining process, we can now compute the uncertainty of the separated image values of the retraining outcomes. The bias and standard deviation averaged from the three training reruns were used for analysis.
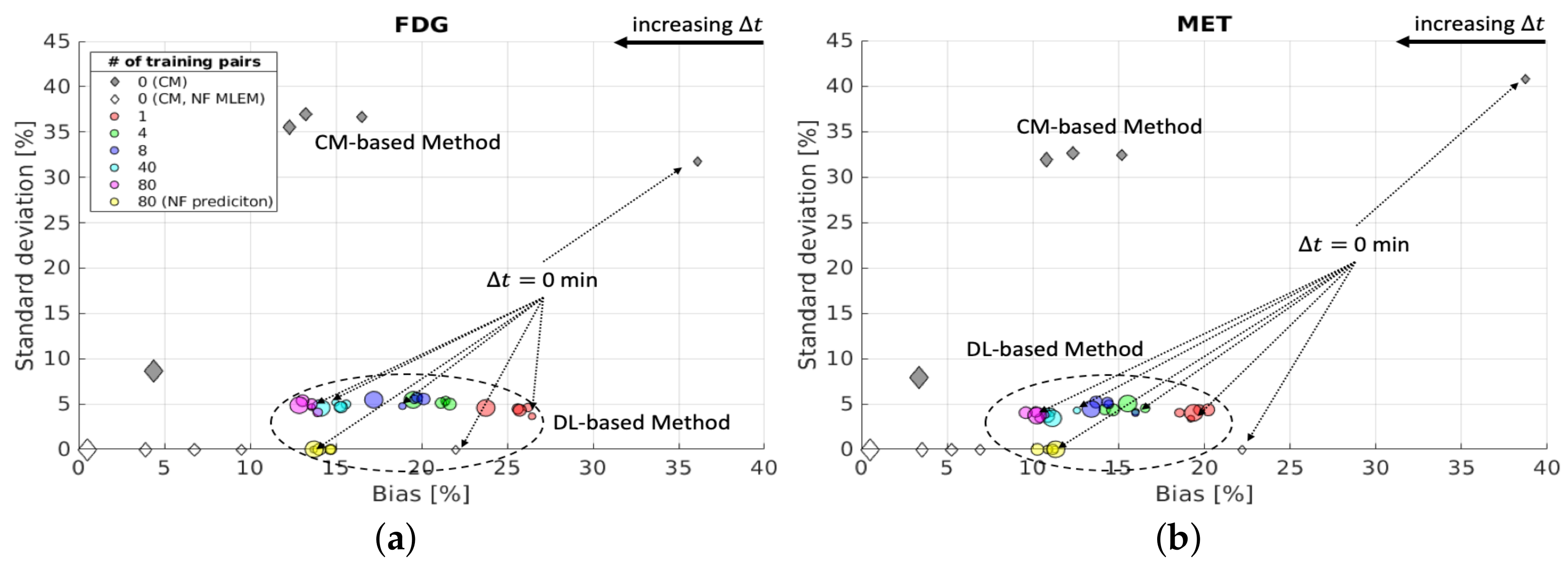
The bias and SD of the separation results for the whole brain region of one of the test data cases are shown in Figure 11. The scatter plots show that using more training pairs results in lower bias of the DL-based separation, which is referred to as the reducible epistemic uncertainty. However, their SD values are at a similar level for each , indicating that this uncertainty is irreducible by introducing more training data. We refer to this uncertainty as the irreducible aleatoric uncertainty, which is caused by the inherent noise of the dynamic input image data. We also evaluated the performance of the DL-based method (with 80 training pairs) applied to the reconstructed dynamic dual-tracer noise-free MLEM images, i.e., we trained the proposed networks (with 3 training reruns and 80 noisy training pairs), but the reconstructed dynamic dual-tracer noise-free MLEM images were used as the network inputs in the prediction stage. The separation results for the noise-free case reached ∼14% bias for FDG and ∼11% bias for MET, which are higher than the bias for the noisy case using the same trained networks. The reason for this is that the reconstructed dynamic dual-tracer noise-free MLEM images are out-of-domain data that were not observed during training, and hence the trained networks do not perform as well for out-of-domain predictions.
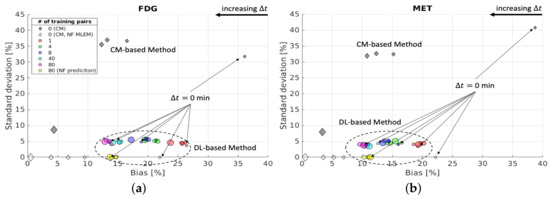
Figure 11.
Brain phantom (whole brain region): bias and SD of separated static FDG images (a) and MET images (b) using DL-based and CM-based methods for the whole brain region .
For the CM-based method, a longer helps to decrease bias and SD in the separation results for both tracers when the reconstructed dynamic dual-tracer noisy MLEM images separation was considered. The bias decreases gradually for = 5, 10 and 15 min after a sharp decline simultaneous to a 5 min delay; see the grey diamonds in Figure 11. When = 2 days, the CM-based method achieved ∼5% bias of the separated images for both tracers. High SD of the separation results (above 30% for both FDG and MET) were found using the CM-based method for = 0, 5, 10 and 15 min. The SD drastically decreased to ∼8% for both FDG and MET when the dual-tracer signals were entirely separated by = 2 days. The separation of the reconstructed dynamic dual-tracer noise-free MLEM images achieved a reduced bias for each when compared to the separation of noisy MLEM images using the CM-based method. In the noise-free case, the bias changed rapidly from 0 min (simultaneous) to 5 min, decreased gradually for = 5, 10 and 15 min and attained zero when = 2 days. The aforementioned results are consistent with the findings in Section 4.2, suggesting longer results in better separation using the CM-based method.
We now compare the bias and SD of the separation results between the DL-based method and the CM-based method on the reconstructed dynamic dual-tracer noisy MLEM images. The DL-based method achieved much smaller SD over all , even using a small number of training pairs. This is a consequence of training the proposed network with the MSE loss which implicitly learns to denoise the output images. The bias of the separation results using the CM-based method and the DL-based method (with 80 training pairs) reached a similar level when = 10 min for FDG and = 15 min for MET; see Figure 11). However, when = 2 days, the CM-based method surpassed the DL-based method (with 80 training pairs) in terms of bias. Note that as the number of training pairs increases, the bias of the separation results using the DL-based method decreases. We can reasonably anticipate that the DL-based method will achieve lower bias than the CM-based method for all if there are more data available.
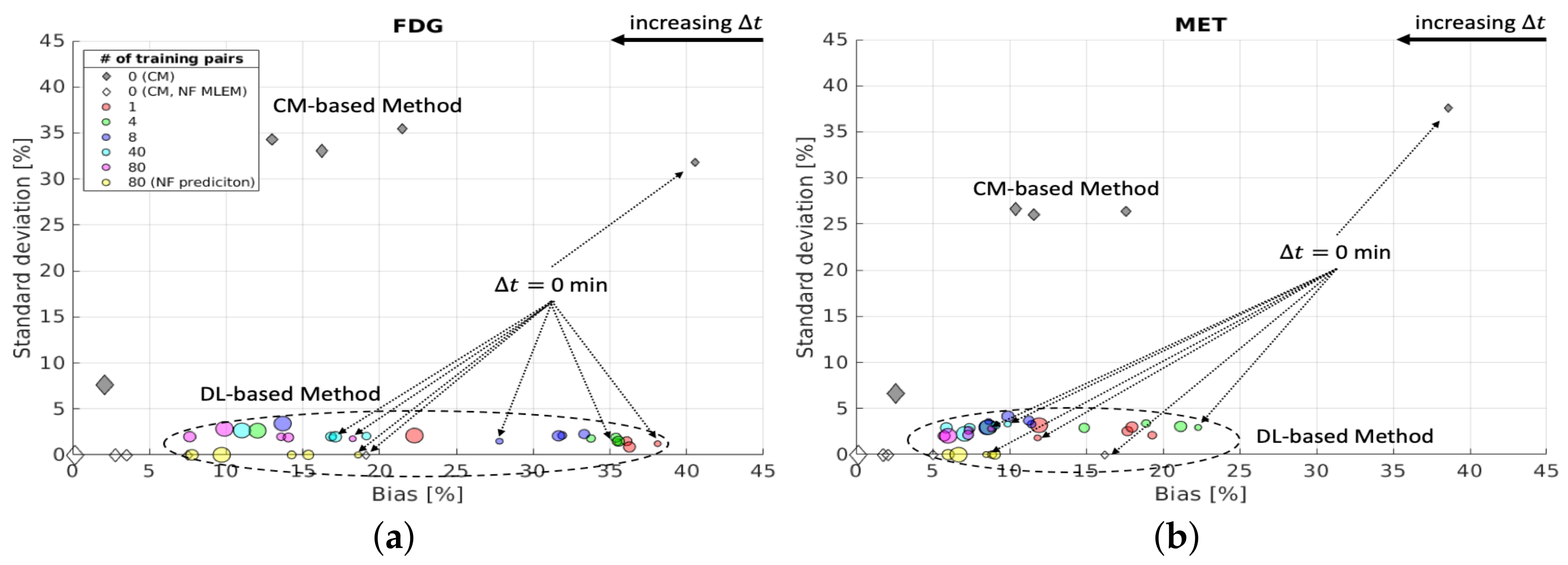
Next, we consider the bias and SD of the separation errors for a 10 pixel ROI within the tumour region (denoted with ) in the brain phantom. In general, using more training data yields lower mean values of the NRMSE for over all ; see Figure A1 in Appendix A for details. However, in some instances, the DL-based method with fewer training pairs was able to achieve superior mean values of the NRMSE as shown in Figure A1a,e,f,i. The reason for this is the fact that the proposed network was trained using a global loss function. The evaluation here focuses on a tiny local region at the pixel level, which is highly impacted by the stochastic network optimisation algorithm (Adam) and the random initialization of the learnable parameters. Figure 12 shows that, for each , using more training pairs gives lower bias for the DL-based separation for , while the SD values remain at a similar level due to the aleatoric uncertainty. A longer yields lower bias and SD of the separation results for using the CM-based method for both noisy and noise-free cases. Compared to the CM-based method, the DL-based method using 80 training pairs obtained lower bias and SD for min. However, when = 2 days, the CM-based method achieved even lower bias than the DL-based methods (with 80 training pairs), which again indicates that more training data which includes the case of = 2 days would likely be required to further enhance the separation performance for the tumour ROI.
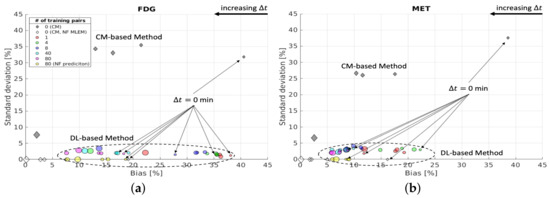
Figure 12.
Brain phantom (tumour ROI): bias and SD of separated static FDG images (a) and MET images (b) using DL-based and CM-based methods for the whole brain region .
4.5. Bias and Standard Deviation Analysis (ROI-Level)
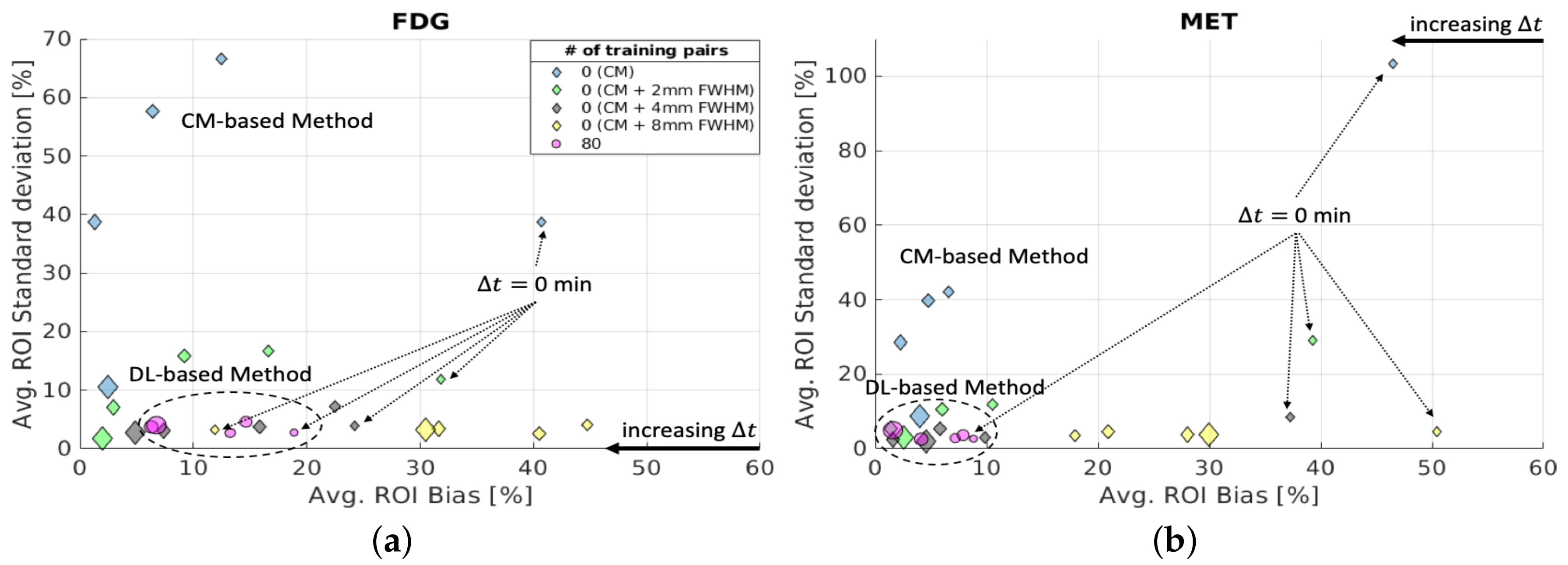
Finally, a comparison between the proposed DL-based method (with 3 training reruns, 80 training pairs) and the CM-based method (10 reruns with different random initial values of the kinetic parameters) was conducted for at the ROI level. To investigate the impact of the noise for the CM-based method at the ROI level, a full width at half maximum (FWHM) Gaussian kernel was used to denoise the separated images as a post-processing step. Figure 13 shows that the average of the CM-based separation results were sufficiently reduced by introducing an FWHM kernel after separation, and lower average bias was obtained for longer for the CM-based method with post-denoising. However, using a large FWHM kernel (8 mm) leads to higher average bias. The average of the DL-based method stays at a similar level for all , showing as the aleatoric uncertainty. For both [F]FDG and [C]MET, the average of the DL-based method is comparable to the CM-based method with a 4 mm FWHM kernel for different , which again indicates the DL-based method implicitly denoises the separated images as discussed in Section 4.1. For simultaneous injection ( = 0 min), the DL-based method overall delivers better separations at the ROI level than the CM-based method (with and without post-denoising) in terms of lower average and average . However, the CM-based method can still potentially surpass the DL-based method for at the ROI level by introducing an FWHM kernel (2–4 mm) as post-denoising for 5 min.
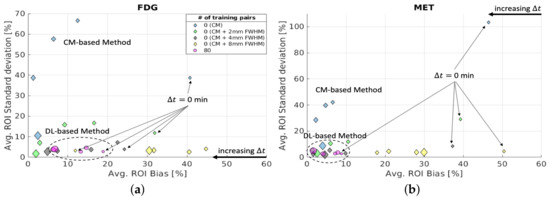
Figure 13.
Brain phantom (tumour ROI): average and average at the ROI level of separated static FDG images (a) and MET images (b) using DL-based and CM-based methods for the tumour ROI .
5. Discussion
Multiplexed PET imaging can reveal different aspects of physiology in a single dynamic scan, providing complementary information for diagnosis. The present study explored the feasibility of using an indirect deep learning method for dual-tracer FDG and MET imaging with 2D simulated brain data. A tailored 2D CED was designed to learn to separate the dynamic dual-tracer images into two static single-tracer images without explicitly knowing the input functions. The results showed that the proposed DL-based separation method implicitly denoised the separated images when noisy MLEM images were used for the training labels. We also investigated the impact of the number of training pairs and time delay interval on our proposed method and conducted a comparative analysis with the well-known compartment-modelling-based method. The performance of the proposed DL-based method was improved with more training pairs and achieved comparable results for different (0, 5, 10 and 15 min and 2 days) at the pixel level for the whole brain region. With a small number of training pairs, the proposed DL-based method still outperformed the CM-based method for a short time delay (0, 5, 10 and 15 min) in terms of NRMSE. However, for = 2 days, i.e., when the dual-tracer TACs were entirely separated by a sufficiently long , the CM-based method achieved lower NRMSE (similar observations were obtained in the pixel-level bias and standard analysis), indicating more training data would be required for the DL-based method with inclusion of data for = 2 days. We also performed a bias and standard deviation analysis for a tumour ROI. At the pixel level, much lower SD was obtained by the DL-based method compared to the CM-based method, and the SD stayed at a similar level for all due to the aleatoric uncertainty. Using more training data helped to reduce the bias for the DL-based method. For 15 min, the DL-based method using 80 training pairs achieved lower bias than the CM-based method. However, lower bias was found using the CM-based method when = 2 days. This is consistent with the aforementioned argument that the DL-based method needs more training pairs in order to surpass the CM-based method (as well as inclusion of = 2 days in its training data). For the DL-based method, the situation is accentuated at the ROI level for the tumour ROI. For simultaneous injection ( = 0 min), the DL-based method overall delivers lower average bias and SD at the ROI level than the CM-based method (with and without post-denoising). However, the CM-based method can surpass the DL-based method by introducing a 2–4 mm FWHM kernel as post-denoising for 5 min for the tumour ROI at the ROI level.
This study still has several limitations: (1) In the simulation study, we introduced 2D images with only 3 different homogeneous regions (white matter, gray matter and tumour region) and minor variations on the kinetic parameters. Further work is necessary to examine the proposed method for 3D PET images with multiple tissue classes and different levels of variation. (2) The total scan time was limited to 50 min, and the framing scheme was assumed to be the same for each dynamic scan with a given . The impact of the total scanning time and different framing schemes need to be investigated in order to optimise the separation performance. (3) The number of tracers was restricted to two. In the literature, a three-tracer separation task was feasible [25] using the CM-based method. Inspired by the proposed network architecture, it is possible to include multiple decoders, one for each tracer, to separate multi-tracer signals. It is noteworthy that our method does not rely on prior knowledge of the tracers, such as their half-lives, kinetic models or input functions. Theoretically, the proposed DL-based method can be extended to other tracer combinations.
The proposed method presupposes that there are enough training data available. However, this is usually not the case in medical imaging. Further developing more advanced network architectures to enable better separation performance based on small training sets is crucial. Lastly, our method will ultimately need to be rigorously evaluated with clinical data. Further study would need to focus on training the model using phantom and Monte Carlo simulation data. The model could then potentially be fine tuned with real patient data.
6. Conclusions
This paper presented a DL-based method for dual-tracer FDG and MET dynamic PET image separation. The method employed a 2D convolutional encoder–decoder to separate dynamic dual-tracer images acquired in a single scan to infer static single-tracer images. Our simulation results showed that the proposed DL-based method using different numbers of training pairs (up to 80) outperformed the CM-based method at the pixel level for short time delay intervals 15 min and even for simultaneous injections ( min).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, and formal analysis: B.P. and A.J.R.; software, data curation, validation and visualization: B.P.; writing—original draft preparation, B.P.; writing—review and editing, B.P. and A.J.R.; supervision, P.K.M. and A.J.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the EPSRC programme for Next Generation Molecular Imaging and Therapy with Radionuclides [EP/S032789/1, ‘MITHRAS’] and by core funding from the Wellcome/EPSRC Centre for Medical Engineering [WT 203148/Z/16/Z].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Wellcome Multiuser Equipment Radioanalytical Facility funded by Wellcome Trust (212885/Z/18/Z), and the EPSRC programme for Next Generation Molecular Imaging and Therapy with Radionuclides (EP/S032789/1, ‘MITHRAS’). This research was funded by EPSRC grant number EP/S032789/1. For the purposes of open access, the authors have applied a Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) licence to any Accepted Author Manuscript version arising, in accordance with King’s College London’s Rights Retention policy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| FDG | 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucos |
| MET | 11C-Methionine |
| TACs | Time-Activity Curves |
| AIF | Arterial Input Function |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| rXGBoost | Recurrent Extreme Gradient Boosting |
| ROI | Region of Interest |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| CED | Convolutional Encoder–Decoder |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network |
| WM | White Matter |
| GM | Grey Matter |
| TM | Tumour |
| MLEM | Maximum-Likelihood Expectation Maximization |
| GT | Ground-Truth |
| NF | Noise-Free |
| MSE | Mean Square Error |
| WNLS | Weighted Non-Linear Least Squares |
| NRMSE | Normalised Root Mean Square Error |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| FI | Frame Integrated |
| FWHM | Full Width at Half Maximum |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Feng’s Input Function Parameters
Table A1 contains the parameters used for generating the AIFs for FDG and MET based on Feng’s input function model.

Table A1.
Parameters used for generating the AIFs of FDG and MET based on Feng’s input function model.
Table A1.
Parameters used for generating the AIFs of FDG and MET based on Feng’s input function model.
| FDG | 4543.7089 | 5.7558 | 8.9690 | 19.6371 | 0.9830 | 0.0482 |
| MET | 8843.7089 | 10.7558 | 20.9690 | 20.6371 | 0.7830 | 0.0552 |
Appendix A.2. Batch Sizes for Network Training
Table A2 shows the batch sizes for network training based on the number of training pairs.

Table A2.
Batch sizes based on the number of training pairs.
Table A2.
Batch sizes based on the number of training pairs.
| # of Training Pairs (Images) | 1 | 4 | 8 | 40 | 80 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # of training pairs (TACs) | 1 × | 4 × | 8 × | 40 × | 80 × |
| Batch size | 1 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
Appendix A.3. NRMSE of Separated Static Images for the Tumour ROI
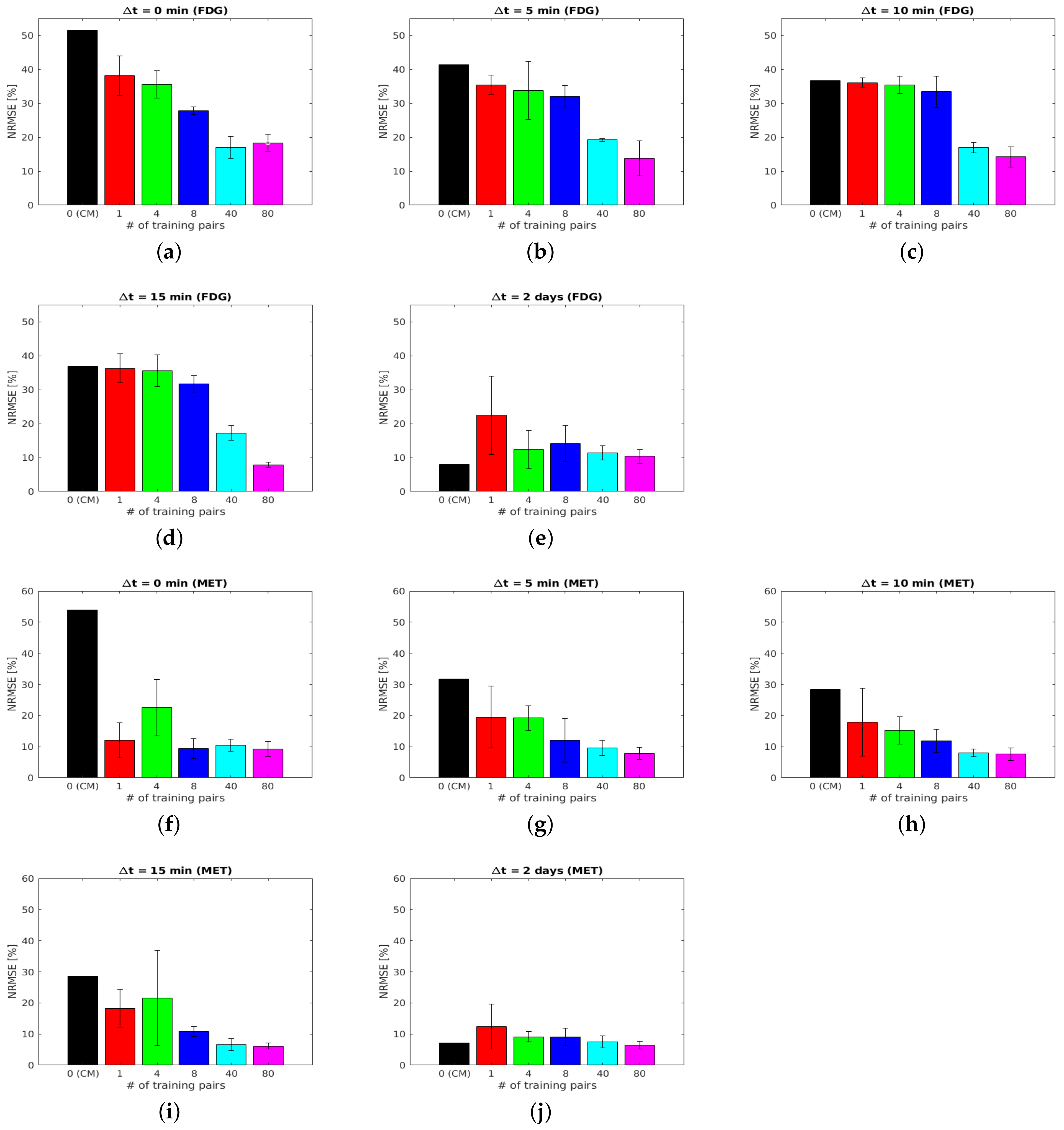
Figure A1 shows the NRMSE of separated static FDG images and MET images using the DL-based and the CM-based methods for the tumour ROI .
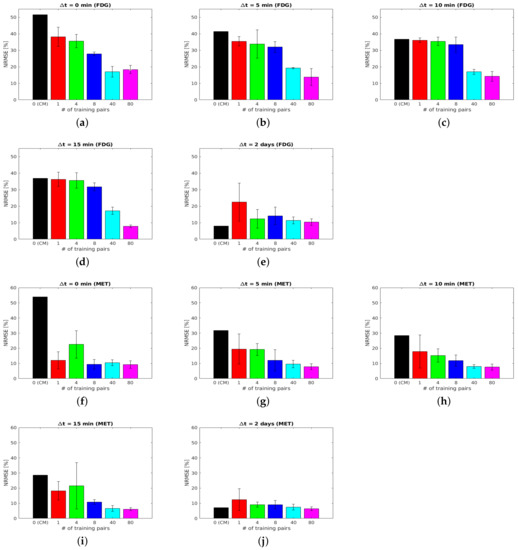
Figure A1.
Brain phantom (tumour ROI): NRMSE of separated static FDG images (a–e) and MET images (f–j) using DL-based and CM-based methods for the tumour ROI .
Figure A1.
Brain phantom (tumour ROI): NRMSE of separated static FDG images (a–e) and MET images (f–j) using DL-based and CM-based methods for the tumour ROI .
References
- Machac, J. Cardiac positron emission tomography imaging. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2005, 35, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunn, R.N.; Slifstein, M.; Searle, G.E.; Price, J.C. Quantitative imaging of protein targets in the human brain with PET. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, R363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, T.; Townsend, D.W.; Brun, T.; Kinahan, P.E.; Charron, M.; Roddy, R.; Jerin, J.; Young, J.; Byars, L.; Nutt, R. A combined PET/CT scanner for clinical oncology. J. Nucl. Med. 2000, 41, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, G.J.; Maisey, M.N.; Fogelman, I. Normal variants, artefacts and interpretative pitfalls in PET imaging with 18-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose and carbon-11 methionine. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 1999, 26, 1363–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.K.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, Y.; Paek, S.; Yeo, J.; Jeong, J.; Lee, D.; Jung, H.; Lee, M. Usefulness of 11C-methionine PET in the evaluation of brain lesions that are hypo-or isometabolic on 18F-FDG PET. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2002, 29, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearfott, K.J. Feasibility of simultaneous and sequentially administered dual tracer protocols for measurement of regional cerebral haematocrit using positron emission tomography. Phys. Med. Biol. 1990, 35, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.L.; Chen, S.; Yeung, D.W.; Cheng, T.K. Dual-tracer PET/CT imaging in evaluation of metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöll, M.; Carter, S.F.; Westman, E.; Rodriguez-Vieitez, E.; Almkvist, O.; Thordardottir, S.; Wall, A.; Graff, C.; Långström, B.; Nordberg, A. Early astrocytosis in autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease measured in vivo by multi-tracer positron emission tomography. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mapelli, P.; Partelli, S.; Salgarello, M.; Doraku, J.; Muffatti, F.; Schiavo Lena, M.; Pasetto, S.; Bezzi, C.; Bettinardi, V.; Andreasi, V.; et al. Dual tracer 68Ga-DOTATOC and 18F-FDG PET improve preoperative evaluation of aggressiveness in resectable pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Guo, N.; Lang, L.; Kiesewetter, D.O.; Xie, Q.; Li, Q.; Eden, H.S.; Niu, G.; Chen, X. 18F-alfatide II and 18F-FDG dual-tracer dynamic PET for parametric, early prediction of tumor response to therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.C.; Carson, R.E.; Hoffman, E.J.; Kuhl, D.E.; Phelps, M.E. An investigation of a double-tracer technique for positron computerized tomography. J. Nucl. Med. 1982, 23, 816–822. [Google Scholar]
- Koeppe, R.A.; Ficaro, E.P.; Raffel, D.M.; Minoshima, S.; Kilbourn, M.R. Temporally overlapping dual-tracer PET studies. In Quantitative Functional Brain Imaging with Positron Emission Tomography; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998; pp. 359–366. [Google Scholar]
- Rust, T.C.; DiBella, E.V.R.; McGann, C.J.; Christian, P.E.; Hoffman, J.M.; Kadrmas, D.J. Rapid dual-injection single-scan 13N-ammonia PET for quantification of rest and stress myocardial blood flows. Phys. Med. Biol. 2006, 51, 5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadrmas, D.J.; Hoffman, J.M. Methodology for quantitative rapid multi-tracer PET tumor characterizations. Theranostics 2013, 3, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiras, F.P.; Jiménez, X.; Pareto, D.; Gómez, V.; Llop, J.; Herance, R.; Rojas, S.; Gispert, J.D. Simultaneous dual-tracer PET imaging of the rat brain and its application in the study of cerebral ischemia. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2011, 13, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaeghe, J.; D’Asseler, Y.; Staelens, S.; Lemahieu, I. Noise properties of simultaneous dual tracer PET imaging. In Proceedings of the IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record, 2005, Fajardo, PR, USA, 23–29 October 2005; Volume 5, pp. 2611–2614. [Google Scholar]
- Koeppe, R.A.; Raffel, D.M.; Snyder, S.E.; Ficaro, E.P.; Kilbourn, M.R.; Kuhl, D.E. Dual-[11C]tracer single-acquisition positron emission tomography studies. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2001, 21, 1480–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikoma, Y.; Toyama, H.; Suhara, T. Simultaneous quantification of two brain functions with dual tracer injection in PET dynamic study. Int. Congr. Ser. 2004, 1265, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadrmas, D.J.; Rust, T.C. Feasibility of rapid multitracer PET tumor imaging. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2005, 52, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, T.C.; Kadrmas, D.J. Rapid dual-tracer PTSM + ATSM PET imaging of tumour blood flow and hypoxia: A simulation study. Phys. Med. Biol. 2005, 51, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.D.; Koeppe, R.A.; Fessier, J.A.; Kilbourn, M.R. Signal separation and parameter estimation in noninvasive dual-tracer PET scans using reference-region approaches. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2009, 29, 1346–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadrmas, D.J.; Rust, T.C.; Hoffman, J.M. Single-scan dual-tracer FLT + FDG PET tumor characterization. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Converse, A.K.; Barnhart, T.E.; Dabbs, K.A.; DeJesus, O.T.; Larson, J.A.; Nickles, R.J.; Schneider, M.L.; Roberts, A.D. PET Measurement of rCBF in the presence of a neurochemical tracer. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 132, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, N.F.; McJames, S.; Rust, T.C.; Kadrmas, D.J. Evaluation of rapid dual-tracer 62Cu-PTSM + 62Cu-ATSM PET in dogs with spontaneously occurring tumors. Phys. Med. Biol. 2007, 53, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, N.F.; McJames, S.; Kadrmas, D.J. Rapid Multi-Tracer PET Tumor Imaging with 18F-FDG and Secondary Shorter-Lived Tracers. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2009, 56, 2750–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadrmas, D.J.; Oktay, M.B. Generalized separable parameter space techniques for fitting 1K–5K serial compartment models. Med. Phys. 2013, 40, 072502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.L.; Morey, A.M.; Kadrmas, D.J. Application of separable parameter space techniques to multi-tracer PET compartment modeling. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Navab, N.; Huang, S.C.; Keller, U.; Ziegler, S.I.; Shi, K. Direct parametric image reconstruction in reduced parameter space for rapid multi-tracer PET imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 1498–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Liu, H.; Jian, Y.; Shi, P. Dynamic dual-tracer PET reconstruction. In Proceedings of the Information Processing in Medical Imaging: 21st International Conference, IPMI 2009, Williamsburg, VA, USA, 5–10 July 2009; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 38–49. [Google Scholar]
- Verhaeghe, J.; Reader, A.J. Accelerated PET water activation acquisition with signal separation methodology. Med. Phys. 2013, 40, 031909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaeghe, J.; Reader, A.J. Simultaneous water activation and glucose metabolic rate imaging with PET. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reader, A.J.; Matthews, J.C.; Sureau, F.C.; Comtat, C.; Trébossen, R.; Buvat, I. Fully 4D image reconstruction by estimation of an input function and spectral coefficients. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record, Honolulu, HI, USA, 26 October–3 November 2007; Volume 5, pp. 3260–3267. [Google Scholar]
- El Fakhri, G.; Trott, C.M.; Sitek, A.; Bonab, A.; Alpert, N.M. Dual-tracer PET using generalized factor analysis of dynamic sequences. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2013, 15, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C.; Puttick, S.; Rose, S.; Smith, J.; Thomas, P.; Dowson, N. Design and utilisation of protocols to characterise dynamic PET uptake of two tracers using basis pursuit. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Yu, J.; Zheng, C.; Fu, P.; Huang, Q.; Feng, D.D.; Yang, Z.; Wahl, R.L.; Zhou, Y. Machine Learning-Based Noninvasive Quantification of Single-Imaging Session Dual-Tracer 18F-FDG and 68Ga-DOTATATE Dynamic PET-CT in Oncology. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 41, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, D.; Liu, H. Separation of a mixture of simultaneous dual-tracer PET signals: A data-driven approach. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2017, 64, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, H. Deep-learning-based separation of a mixture of dual-tracer single-acquisition PET signals with equal half-Lives: A simulation study. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2019, 3, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, M.; Wan, Y.; Huang, W.; Xu, Y.; Liu, H. Separation of dual-tracer PET signals using a deep stacking network. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2021, 1013, 165681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Mesgarani, N. Tasnet: Time-domain audio separation network for real-time, single-channel speech separation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 696–700. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H. Single-scan dual-tracer separation network based on pre-trained GRU. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Multiscale Multimodal Medical Imaging, Shenzhen, China, 13 October 2019; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; pp. 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, H. Temporal information-guided dynamic dual-tracer PET signal separation network. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 4585–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, H. Spatiotemporal Attention Constrained Deep Learning Framework for Dual-Tracer PET Imaging. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Understanding and Analysis: 26th Annual Conference, MIUA 2022, Cambridge, UK, 27–29 July 2022; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland; pp. 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Liu, H. Three-dimensional convolutional neural networks for simultaneous dual-tracer PET imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 185016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Liu, H. Dual-tracer PET image direct reconstruction and separation based on three-dimensional encoder–decoder network. In Proceedings of the Optics in Health Care and Biomedical Optics X, Online, 11–16 October 2020; Volume 11553, pp. 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, F.; Fang, J.; Muhashi, A.; Liu, H. Direct reconstruction for simultaneous dual-tracer PET imaging based on multi-task learning. EJNMMI Res. 2023, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Ye, H.; Liu, H. Deep-learning based joint estimation of dual-tracer PET image activity maps and clustering of time activity curves. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2021: Physics of Medical Imaging, Online, 15–20 February 2021; Volume 11595, pp. 981–989. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, D.H. Compartmental Modeling and Tracer Kinetics; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, E.D.; Endres, C.J.; Schmidt, K.C.; Christian, B.T.; Muzic, R.F.; Fisher, R.E. Kinetic modeling in positron emission tomography. Emiss. Tomogr. 2004, 46, 499–540. [Google Scholar]
- Caruana, R. Multitask learning: A knowledge-based source of inductive bias. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Machine Learning, Amherst, MA, USA, 27–29 June 1993; pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Baxter, J.A. Bayesian/information theoretic model of learning to learn via multiple task sampling. Mach. Learn. 1997, 28, 7–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocosco, C.A.; Kollokian, V.; Kwan, R.K.; Pike, G.B.; Evans, A.C. Brainweb: Online interface to a 3D MRI simulated brain database. NeuroImage 1997, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Liu, H. FBP-Net for direct reconstruction of dynamic PET images. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 235008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Guan, J.; Kim, K.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Seo, Y.; El Fakhri, G.; Qi, J.; Li, Q. Iterative PET image reconstruction using convolutional neural network representation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 38, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Wong, K.P.; Wu, C.M.; Siu, W.C. A technique for extracting physiological parameters and the required input function simultaneously from PET image measurements: Theory and simulation study. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 1997, 1, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhou, Z.; Wen, J.; Xie, F.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Guan, Y.; et al. A nomogram modeling 11C-MET PET/CT and clinical features in glioma helps predict IDH mutation. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepp, L.A.; Vardi, Y. Maximum likelihood reconstruction for emission tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1982, 1, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Navab, N.; Ziegler, S.I.; Shi, K. Direct parametric image reconstruction of rapid multi-tracer PET. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Nagoya, Japan, 22–26 September 2013; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Glorot, X.; Bengio, Y. Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings, Sardinia, Italy, 13–15 May 2010; pp. 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, T.F.; Li, Y. An interior trust region approach for nonlinear minimization subject to bounds. SIAM J. Optim. 1996, 6, 418–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Coleman, T.F. On the convergence of reflective newton methods for large-scale nonlinear minimization subject to bounds. Math. Program. 1994, 67, 189–224. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).