Helicobacter pylori—The Bridge between Local and Systemic Inflammation in Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Ethical Statements
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salama, N.R.; Hartung, M.L.; Müller, A. Life in the Human Stomach: Persistence Strategies of the Bacterial Pathogen Helicobacter Pylori. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mărginean, C.D.; Mărginean, C.O.; Meliț, L.E. Helicobacter Pylori-Related Extraintestinal Manifestations-Myth or Reality. Children 2022, 9, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amieva, M.; Peek, R.M. Pathobiology of Helicobacter Pylori-Induced Gastric Cancer. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkin, D.M.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Pisani, P. Global Cancer Statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2005, 55, 74–108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Săsăran, M.O.; Meliț, L.E.; Dobru, E.D. MicroRNA Modulation of Host Immune Response and Inflammation Triggered by Helicobacter Pylori. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guclu, M.; Faruq Agan, A. Association of Severity of Helicobacter Pylori Infection with Peripheral Blood Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Mean Platelet Volume. Euroasian J. Hepatogastroenterol. 2017, 7, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meliţ, L.E.; Mărginean, M.O.; Mocan, S.; Mărginean, C.O. The Usefulness of Inflammatory Biomarkers in Diagnosing Child and Adolescent’s Gastritis: STROBE Compliant Article. Medicine 2019, 98, e16188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, M.; Gravina, A.G.; Eusebi, L.H.; Pellegrino, R.; Palladino, G.; Frazzoni, L.; Dajti, E.; Gasbarrini, A.; Di Mario, F.; Zagari, R.M.; et al. Management of Helicobacter Pylori Infection: Guidelines of the Italian Society of Gastroenterology (SIGE) and the Italian Society of Digestive Endoscopy (SIED). Dig. Liver Dis. 2022, 54, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, V.; Memar, B.; Momtazi, A.A.; Sahebkar, A.; Gholamin, M.; Abbaszadegan, M.R. Cytokine Networks and Their Association with Helicobacter Pylori Infection in Gastric Carcinoma. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 2791–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, K.; Karin, M. IL-6 and Related Cytokines as the Critical Lynchpins between Inflammation and Cancer. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, C.; Kushner, I. Acute-Phase Proteins and Other Systemic Responses to Inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, D.; Liu, J.; Lau, C.W.; Huang, Y. IL-6 in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Complications. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 3595–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dincă, A.L.; Meliț, L.E.; Mărginean, C.O. Old and New Aspects of H. Pylori-Associated Inflammation and Gastric Cancer. Children 2022, 9, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fond, G.; Hamdani, N.; Kapczinski, F.; Boukouaci, W.; Drancourt, N.; Dargel, A.; Oliveira, J.; Le Guen, E.; Marlinge, E.; Tamouza, R.; et al. Effectiveness and Tolerance of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs’ Add-on Therapy in Major Mental Disorders: A Systematic Qualitative Review. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2014, 129, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güzel, M.; Sönmez, M.F.; Baştuğ, O.; Aras, N.F.; Öztürk, A.B.; Küçükaydın, M.; Turan, C. Effectiveness of Lycopene on Experimental Testicular Torsion. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2016, 51, 1187–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradipour, A.; Khosravi, A.; Piri, F. Fecal Helicobacter Pylori GlmM and 16S RRNA Genes Correlate with Serum TNF-α and IL-1β Cytokine Fluctuations. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2018, 65, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusters, J.G.; van Vliet, A.H.M.; Kuipers, E.J. Pathogenesis of Helicobacter Pylori Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 449–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganuma, M.; Watanabe, T.; Sueoka, E.; Lim, I.K.; Fujiki, H. Role of TNF-α-Inducing Protein Secreted by Helicobacter Pylori as a Tumor Promoter in Gastric Cancer and Emerging Preventive Strategies. Toxins 2021, 13, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, R.; Khamisy-Farah, R. Association of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio with Presence and Severity of Gastritis Due to Helicobacter Pylori Infection. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2014, 28, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atayan, Y.; Hacisalihoglu, P. The Correlation between Tissue Helicobacter Pylori Severity and the Increase in Serum Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Active Chronic Gastritis. Biomed. Res. 2017, 28, 4874–4877. [Google Scholar]
- Tamhane, U.U.; Aneja, S.; Montgomery, D.; Rogers, E.-K.; Eagle, K.A.; Gurm, H.S. Association between Admission Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Outcomes in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 102, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemal, Y.; Yucel, I.; Ekiz, K.; Demirag, G.; Yilmaz, B.; Teker, F.; Ozdemir, M. Elevated Serum Neutrophil to Lymphocyte and Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratios Could Be Useful in Lung Cancer Diagnosis. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 2651–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.-F.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Q.-X. Preoperative Platelet Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR) is Superior to Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) as a Predictive Factor in Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 12, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardelean, C.L.; Pescariu, S.; Lighezan, D.F.; Pleava, R.; Ursoniu, S.; Nadasan, V.; Mihaicuta, S. Particularities of Older Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Heart Failure with Mid-Range Ejection Fraction. Medicina 2019, 55, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borka Balas, R.; Meliț, L.E.; Mărginean, C.O. Worldwide Prevalence and Risk Factors of Helicobacter Pylori Infection in Children. Children 2022, 9, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehata, S.; Parajuli, K.R.; Pant, N.D.; Rayamajhee, B.; Yadav, U.N.; Mehta, R.K.; Jha, P.; Mehta, N.; Dhimal, M.; Singh, D.R. Prevalence and Correlates of Helicobacter Pylori Infection among Under-Five Children, Adolescent and Non-Pregnant Women in Nepal: Further Analysis of Nepal National Micronutrient Status Survey 2016. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordin, D.S.; Voynovan, I.N.; Andreev, D.N.; Maev, I.V. Current Helicobacter Pylori Diagnostics. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefano, K.; Rosalia, A.; Chiara, B.; Federica, G.; Marco, M.; Gioacchino, L.; Fabiola, F.; Francesco, D.M.; Gian, L. de’Angelis Non-Invasive Tests for the Diagnosis of Helicobacter Pylori: State of the Art. Acta Biomed. 2018, 89, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; O’Morain, C.A.; Gisbert, J.P.; Kuipers, E.J.; Axon, A.T.; Bazzoli, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Atherton, J.; Graham, D.Y.; et al. Management of Helicobacter Pylori Infection-the Maastricht V/Florence Consensus Report. Gut 2017, 66, 6–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, C.A.; Gonzáez, C.G.; Rollan, A.R.; Duarte, I.; Torres, J.; Peña, A.J.; Harris, P.R. Lack of Diagnostic Utility of Specific Immunoglobulin M in Helicobacter Pylori Infection in Children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2008, 47, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, A.; Emdin, M.; Passino, C.; Michelassi, C.; Battaglia, D.; Cocci, F. Predictive Value of Elevated Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio on Cardiac Mortality in Patients with Stable Coronary Artery Disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2008, 395, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, L.; Britton, J.; Lewis, S.A.; McKeever, T.M.; Atherton, J.; Fullerton, D.; Fogarty, A.W. A Population-Based Epidemiologic Study of Helicobacter Pylori Infection and Its Association with Systemic Inflammation. Helicobacter 2009, 14, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinjo, K.; Sato, H.; Sato, H.; Shiotani, I.; Kurotobi, T.; Ohnishi, Y.; Hishida, E.; Nakatani, D.; Mizuno, H.; Sasaki, T.; et al. Prevalence of Helicobacter Pylori Infection and Its Link to Coronary Risk Factors in Japanese Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction. Circ. J. 2002, 66, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osawa, H.; Kawakami, M.; Fujii, M.; Kubo, N.; Iwanaka, H.; Yamamoto, W.; Saitoh, M.; Yaginuma, T.; Sugano, K. Helicobacter Pylori Infection and Coronary Heart Disease in Japanese Patients. Cardiology 2001, 95, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayr, M.; Kiechl, S.; Mendall, M.A.; Willeit, J.; Wick, G.; Xu, Q. Increased Risk of Atherosclerosis is Confined to CagA-Positive Helicobacter Pylori Strains: Prospective Results from the Bruneck Study. Stroke 2003, 34, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, F.; Niccoli, G.; Ferrante, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Baldi, A.; Candelli, M.; Feroce, F.; Saulnier, N.; Conte, M.; Roccarina, D.; et al. CagA Antigen of Helicobacter Pylori and Coronary Instability: Insight from a Clinico-Pathological Study and a Meta-Analysis of 4241 Cases. Atherosclerosis 2009, 202, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicano, R.; Parravicini, P.P.; Bigi, R.; Gandolfo, N.; Aruta, E.; Gai, V.; Figura, N.; Angelino, P.; Rizzetto, M.; Ponzetto, A. Infection by Helicobacter Pylori and Acute Myocardial Infarction. Do Cytotoxic Strains Make a Difference? New Microbiol. 2002, 25, 315–321. [Google Scholar]
- Whincup, P.; Danesh, J.; Walker, M.; Lennon, L.; Thomson, A.; Appleby, P.; Hawkey, C.; Atherton, J. Prospective Study of Potentially Virulent Strains of Helicobacter Pylori and Coronary Heart Disease in Middle-Aged Men. Circulation 2000, 101, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, L.J.; Bamford, K.B.; Kee, F.; McMaster, D.; Cambien, F.; Dallongeville, J.; Evans, A. Infection with Virulent Strains of Helicobacter Pylori is Not Associated with Ischaemic Heart Disease: Evidence from a Population-Based Case-Control Study of Myocardial Infarction. Atherosclerosis 2000, 149, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Tamura, T.; Mitsuda, Y.; Goto, Y.; Kamiya, Y.; Kondo, T.; Wakai, K.; Hamajima, N. Significant Association between Serum Interleukin-6 and Helicobacter Pylori Antibody Levels among H. Pylori-Positive Japanese Adults. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 142358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudkin, J.S.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Emeis, J.J.; Coppack, S.W. C-Reactive Protein in Healthy Subjects: Associations with Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Endothelial Dysfunction: A Potential Role for Cytokines Originating from Adipose Tissue? Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999, 19, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hull, J.; Thomson, A.; Kwiatkowski, D. Association of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Bronchiolitis with the Interleukin 8 Gene Region in UK Families. Thorax 2000, 55, 1023–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramis, I.B.; Vianna, J.S.; Gonçalves, C.V.; von Groll, A.; Dellagostin, O.A.; da Silva, P.E.A. Polymorphisms of the IL-6, IL-8 and IL-10 Genes and the Risk of Gastric Pathology in Patients Infected with Helicobacter Pylori. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2017, 50, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayraktaroğlu, T.; Aras, A.S.; Aydemir, S.; Davutoğlu, C.; Ustündağ, Y.; Atmaca, H.; Borazan, A. Serum Levels of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha, Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-8 Are Not Increased in Dyspeptic Patients with Helicobacter Pylori-Associated Gastritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2004, 13, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansilla-Vivar, R.; Serrano, C.A.; Palma, C.; Vera, M.; Hernandez, C.; Pizarro, M.; Torres, J.; Harris, P.R.; Fuentes-López, E.; Riquelme, A.; et al. High Helicobacter Pylori Bacterial Load and Low Cytokine Expression Levels Are Associated with Nodular Gastropathy. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larussa, T.; Leone, I.; Suraci, E.; Imeneo, M.; Luzza, F. Helicobacter Pylori and T Helper Cells: Mechanisms of Immune Escape and Tolerance. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 981328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourani, M.; Habibzadeh, M.; Karkhah, A.; Shokri-Shirvani, J.; Barari, L.; Nouri, H.R. Association of TNF-α but Not IL-1β Levels with the Presence of Helicobacter Pylori Infection Increased the Risk of Peptic Ulcer Development. Cytokine 2018, 110, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | H. pylori Gastritis Group (n = 14) n (%) | Non-H. pylori Gastritis Group (n = 26) n (%) | Control Group (n = 28) n (%) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 14.00 ± 2.717 | 13.50 ± 2.875 | 15.00 ± 2.617 | 0.0678 | |
| Gender | Female | 7 (50.00%) | 15 (57.69%) | 21 (75.00%) | 0.2159 |
| Male | 7 (50.00%) | 11 (42.31%) | 7 (25.00%) | ||
| Area | Rural | 11 (78.57%) | 11 (42.31%) | 11 (39.29%) | 0.0404 |
| Urban | 3 (21.43%) | 15 (57.69%) | 17 (60.71%) | ||
| CRP | Negative | 5 (55.56%) | 10 (58.82%) | 14 (66.67%) | 0.8096 |
| Positive | 4 (44.44%) | 7 (41.18%) | 7 (33.33%) | ||
| IgA anti-H. pylori | Positive | 5 (55.56%) | 2 (12.50%) | 1 (6.67%) | 0.0094 |
| Negative | 4 (44.44%) | 14 (87.50%) | 14 (93.33%) | ||
| Parameters | H. pylori Gastritis Group (n = 14) Mean ± SD, (Median) | Non-H. pylori Gastritis Group (n = 26) Mean ± SD, (Median) | Control Group (n = 28) Mean ± SD, (Median) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erythrocytes (×106/µL) | 4.779 ± 0.4147 (4.685) | 4.782 ± 0.5510 (4.865) | 4.600 ± 0.5893 (4.750) | 0.3918 |
| MPV (fL) | 83.00 ± 5.088 (82.65) | 81.37 ± 4.522 (81.30) | 82.52 ± 5.080 (81.70) | 0.5365 |
| Htc (%) | 39.58 ± 3.081 (39.30) | 38.94 ± 4.809 (39.70) | 37.87 ± 5.601 (39.30) | 0.5653 |
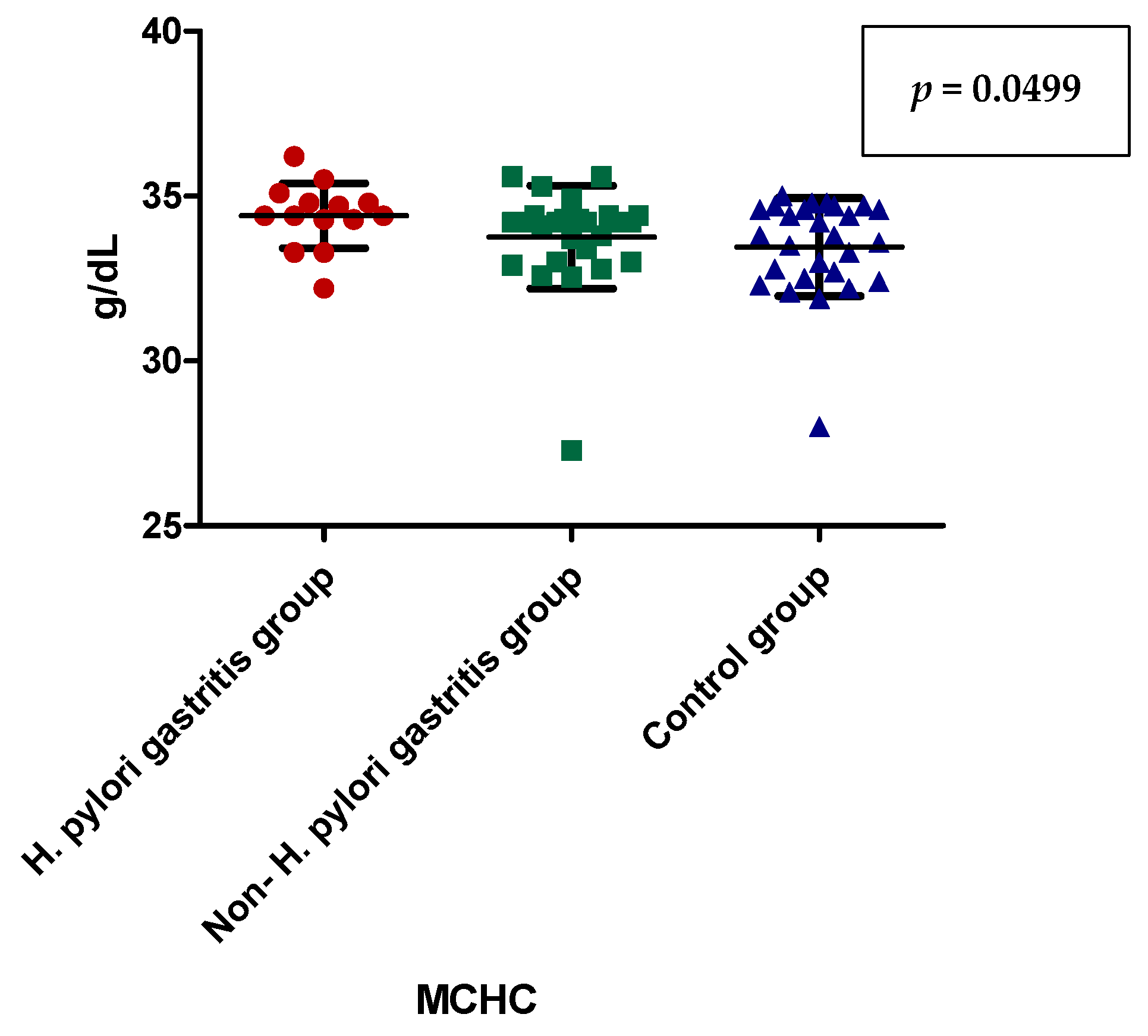
| MCHC (g/dL) | 34.41 ± 0.9856 (34.40) | 33.75 ± 1.562 (34.20) | 33.46 ± 1.486 (33.80) | 0.0803 |
| Hb (g/dl) | 13.64 ± 1.235 (13.75) | 13.18 ± 1.885 (13.55) | 12.74 ± 2.115 (13.25) | 0.3549 |
| Leukocytes (number/µL) | 8.106 ± 2.567 (7.630) | 7.104 ± 1.433 (6.925) | 8.290 ± 3.696 (6.870) | 0.6541 |
| Lymphocytes (number/µL) | 2.259 ± 0.5576 (2.100) | 2.660 ± 0.8269 (2.565) | 2.287 ± 0.5990 (2.160) | 0.1819 |
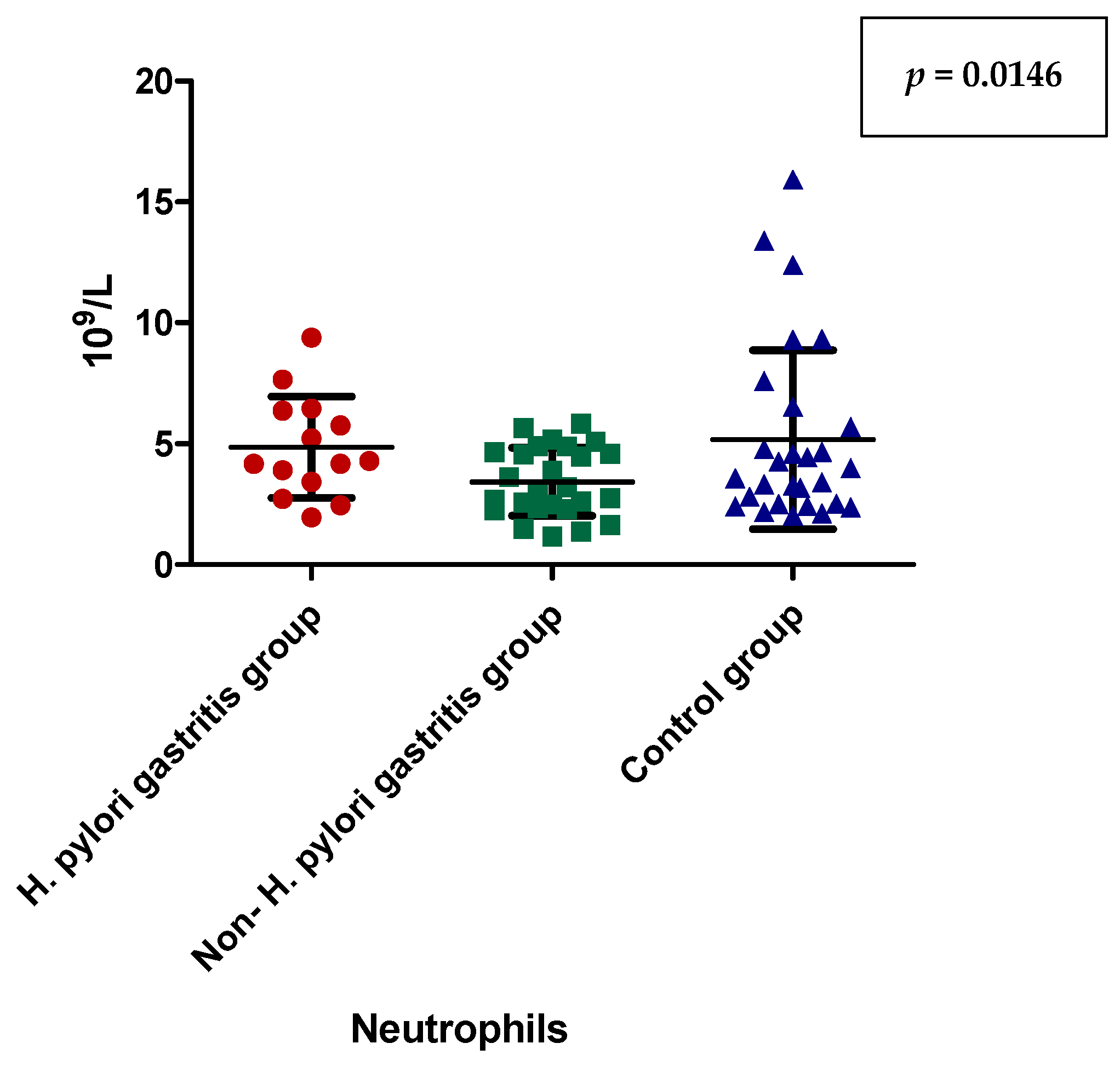
| Neutrophils (number/µL) | 4.855 ± 2.097 (4.235) | 3.431 ± 1.413 (3.075) | 5.177 ± 3.696 (3.780) | 0.1307 |
| NLR | 2.223 ± 1.034 (1.980) | 1.444 ± 0.8351 (1.260) | 2.263 ± 1.791 (1.790) | 0.0253 |
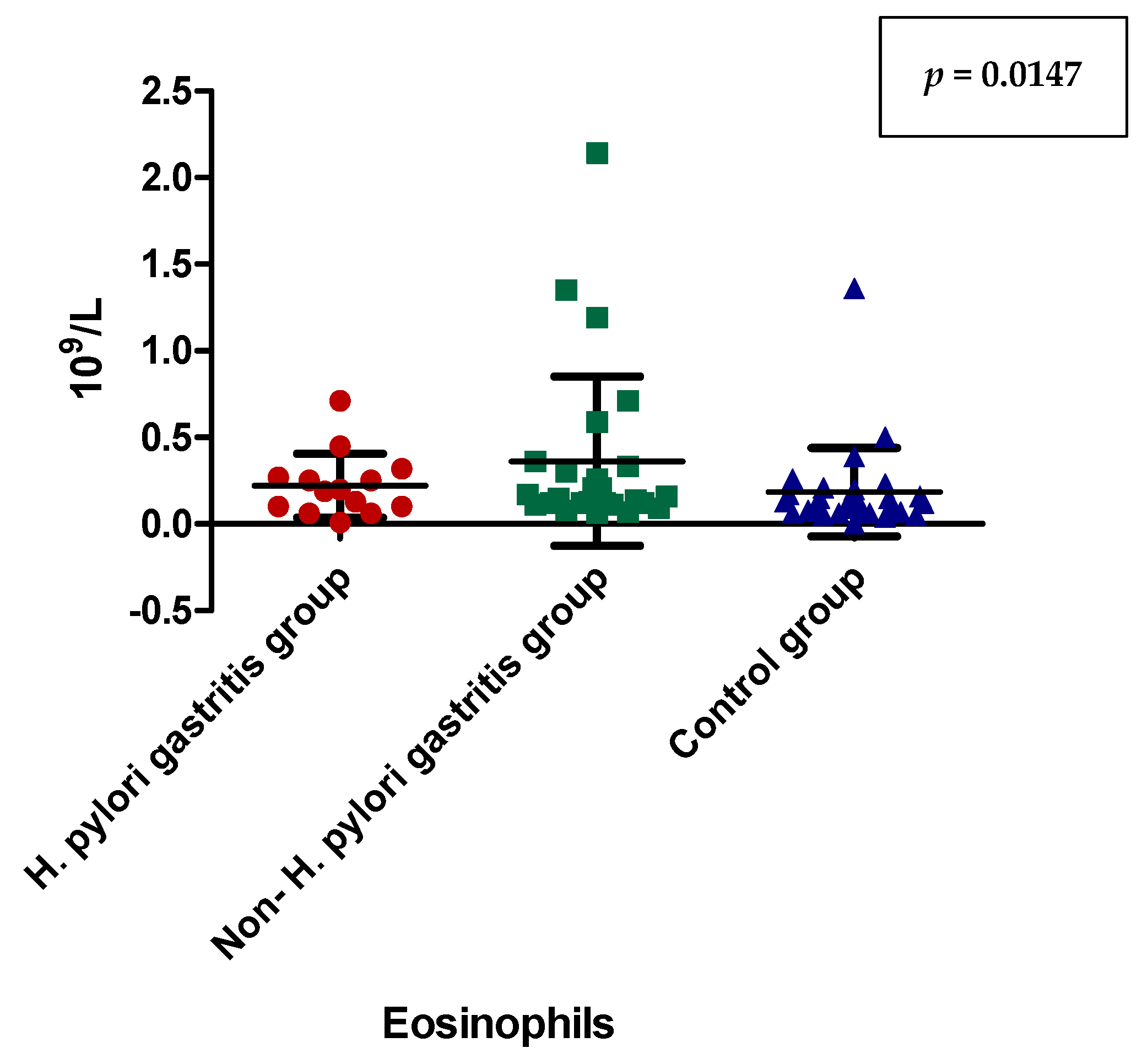
| Eosinophils (number/µL) | 0.2214 ± 0.1841 (0.1950) | 0.3615 ± 0.4889 (0.1550) | 0.1836 ± 0.2542 (0.1250) | 0.1017 |
| ESR (mmHg) | 15.75 ± 13.19 (14.00) | 11.91 ± 14.38 (8.000) | 15.00 ± 21.46 (11.00) | 0.2863 |
| Iron (µmol/L) | 18.91 ± 7.898 (20.25) | 16.16 ± 8.775 (14.15) | 13.84 ± 5.749 (14.68) | 0.2499 |
| AST (U/L) | 23.48 ± 8.569 (20.90) | 23.04 ± 16.14 (19.95) | 22.19 ± 11.16 (19.50) | 0.7679 |
| ALT (U/L) | 13.82 ± 4.853 (12.20) | 15.95 ± 12.09 (12.60) | 18.81 ± 24.45 (13.70) | 0.9612 |
| GGT (U/L) | 16.20 ± 6.546 (14.50) | 17.45 ± 20.19 (13.00) | 20.76 ± 30.70 (13.00) | 0.6024 |
| NLR | Dunn’s Multiple Comparison Test | Significant? p < 0.05? |
| H. pylori-induced gastritis vs. non-H. pylori gastritis | 0.0107 | |
| H. pylori-induced gastritis vs. control group | 0.3716 | |
| non-H. pylori gastritis vs. control group | 0.0581 |
| MCHC (g/dL) | Dunn’s Multiple Comparison Test | Significant? p < 0.05? |
| H. pylori-induced gastritis vs. non-H. pylori gastritis | 0.0499 | |
| H. pylori-induced gastritis vs. control group | 0.0489 | |
| non-H. pylori gastritis vs. control group | 0.5211 |
| Neutrophils (number/µL) | Dunn’s Multiple Comparison Test | Significant? p < 0.05? |
| H. pylori-induced gastritis vs. non-H. pylori gastritis | 0.0146 | |
| H. pylori-induced gastritis vs. control group | 0.5662 | |
| non-H. pylori gastritis vs. control group | 0.1769 |
| Eosinophils(number/µL) | Dunn’s Multiple Comparison Test | Significant? p < 0.05? |
| H. pylori-induced gastritis vs. non-H. pylori gastritis | 0.0147 | |
| H. pylori-induced gastritis vs. control group | 0.5662 | |
| non-H. pylori gastritis vs. control group | 0.1769 |
| Presence of TNF α (n/%) | Absence of TNF α (n/%) | Statistical Parameters | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gastritis (H. pylori-induced gastritis + non-H. pylori gastritis) group | 17 (85.00%) | 23 (47.92%) | RR = 3.967 IC (95%): 1.283–12.263 p = 0.0063 |
| Control goup | 3 (15.00%) | 25 (52.08%) |
| Presence of TNF α (n/%) | Absence of TNF α (n/%) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| H. pylori-induced gastritis group | 10 (50.00%) | 4 (8.33%) | 0.0002 |
| Non-H. pylori gastritis group | 7 (35.00%) | 19 (39.58%) | |
| Control group | 3 (15.00%) | 25 (52.08%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dincă, A.L.; Meliț, L.E.; Gurzu, S.; Mocan, S.; Ghiga, D.V.; Mărginean, C.O. Helicobacter pylori—The Bridge between Local and Systemic Inflammation in Children. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13042162
Dincă AL, Meliț LE, Gurzu S, Mocan S, Ghiga DV, Mărginean CO. Helicobacter pylori—The Bridge between Local and Systemic Inflammation in Children. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(4):2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13042162
Chicago/Turabian StyleDincă, Andreea Ligia, Lorena Elena Meliț, Simona Gurzu, Simona Mocan, Dana Valentina Ghiga, and Cristina Oana Mărginean. 2023. "Helicobacter pylori—The Bridge between Local and Systemic Inflammation in Children" Applied Sciences 13, no. 4: 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13042162
APA StyleDincă, A. L., Meliț, L. E., Gurzu, S., Mocan, S., Ghiga, D. V., & Mărginean, C. O. (2023). Helicobacter pylori—The Bridge between Local and Systemic Inflammation in Children. Applied Sciences, 13(4), 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13042162








