Aminated Covalent Organic Polymers for Anionic Dye Adsorption in Aqueous Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Materials
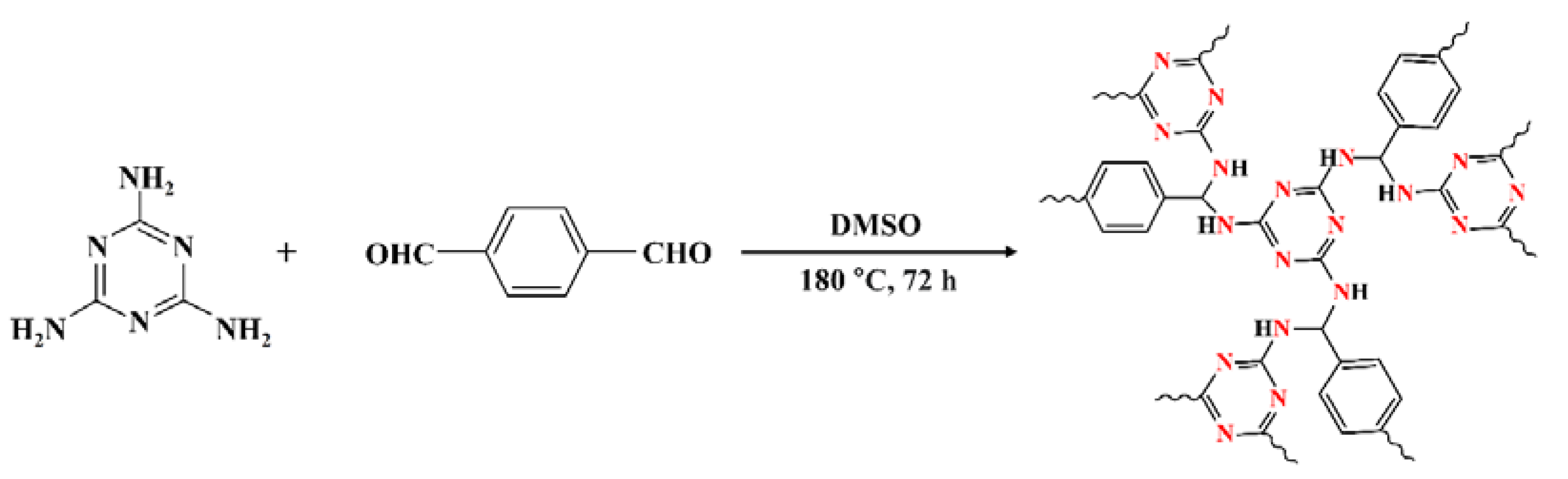
2.2. ACOP Synthesis
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
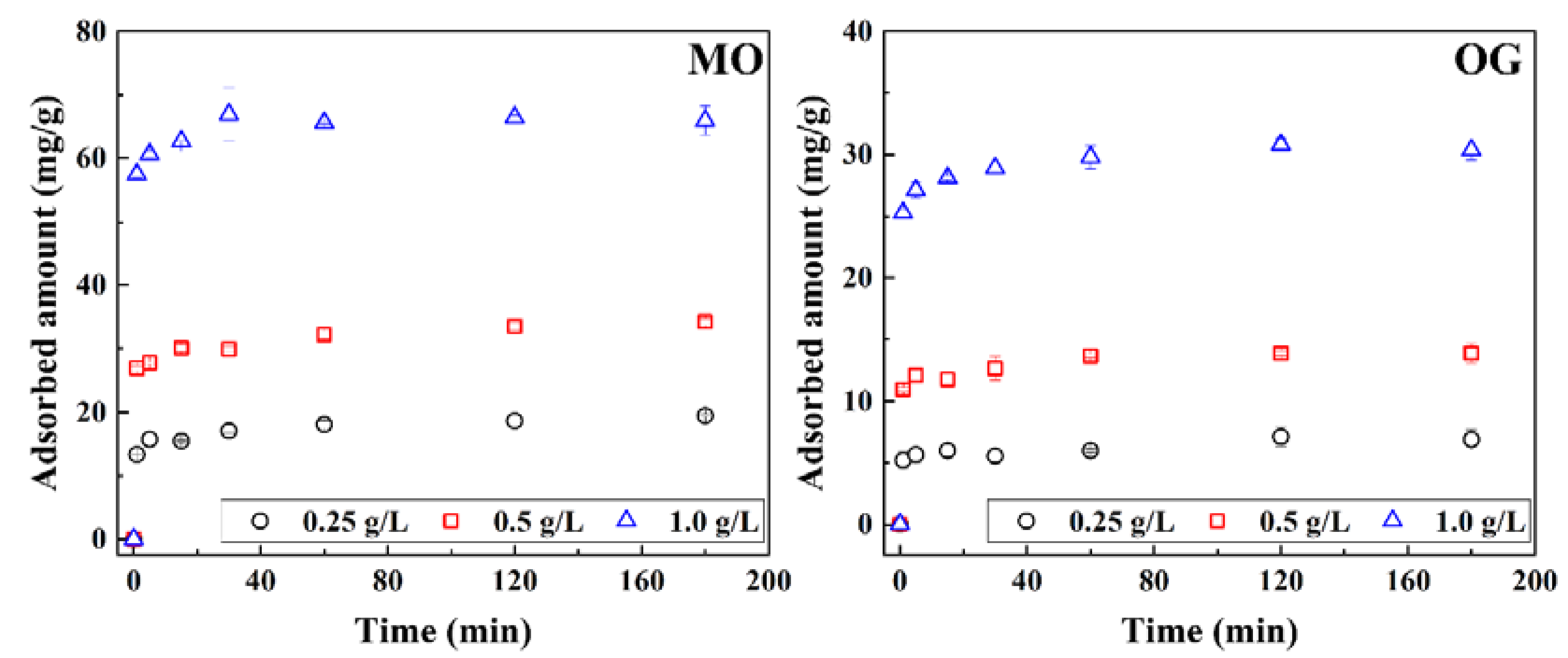
2.4.1. Adsorption Kinetic Experiments
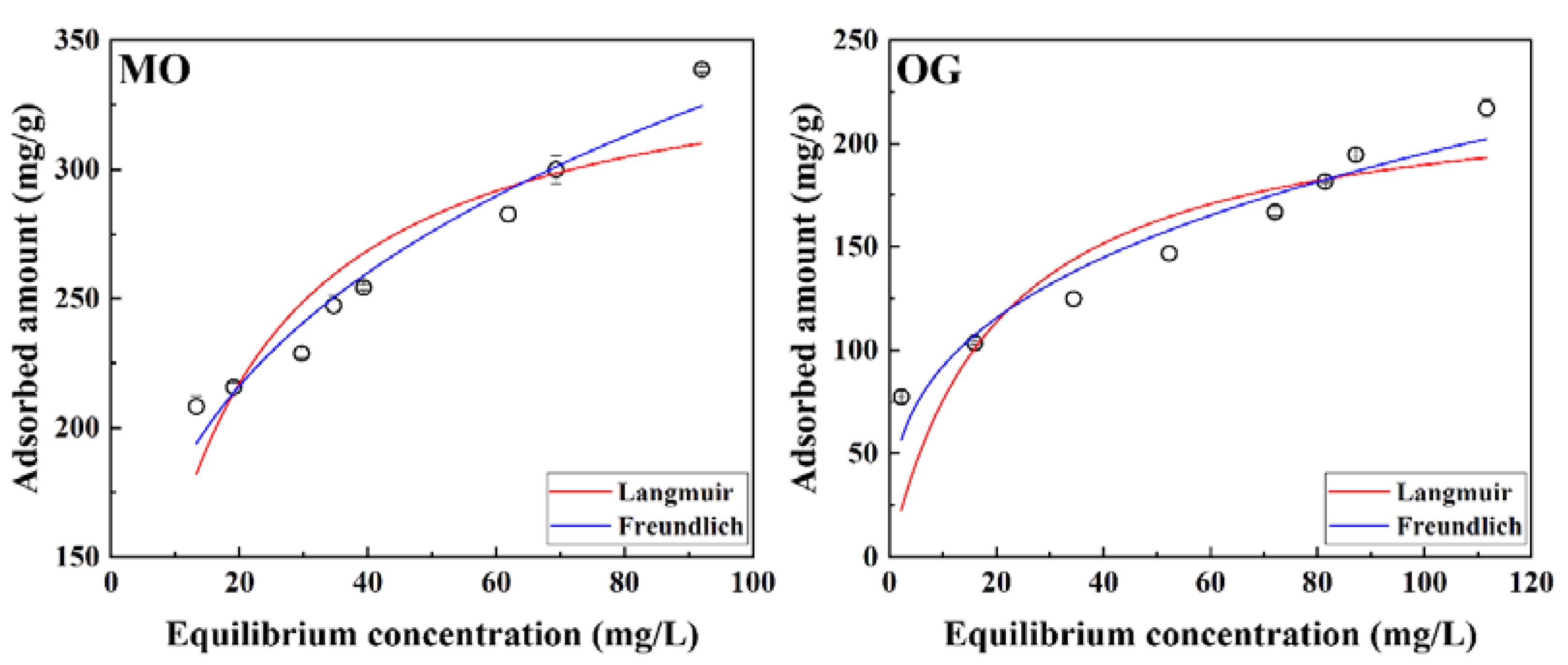
2.4.2. Adsorption Isotherm Experiments
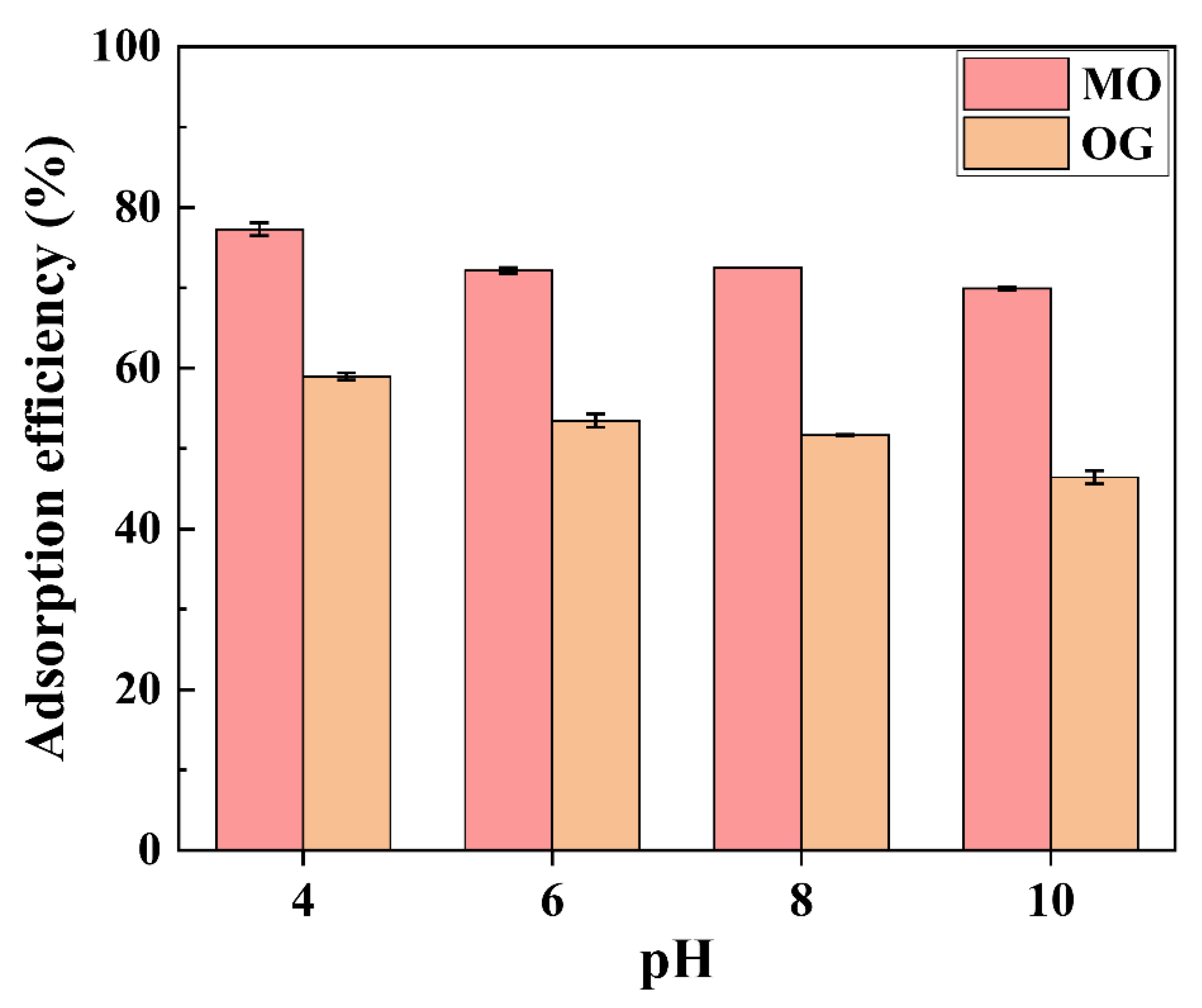
2.4.3. Effect of pH on Adsorption of Dye Molecules
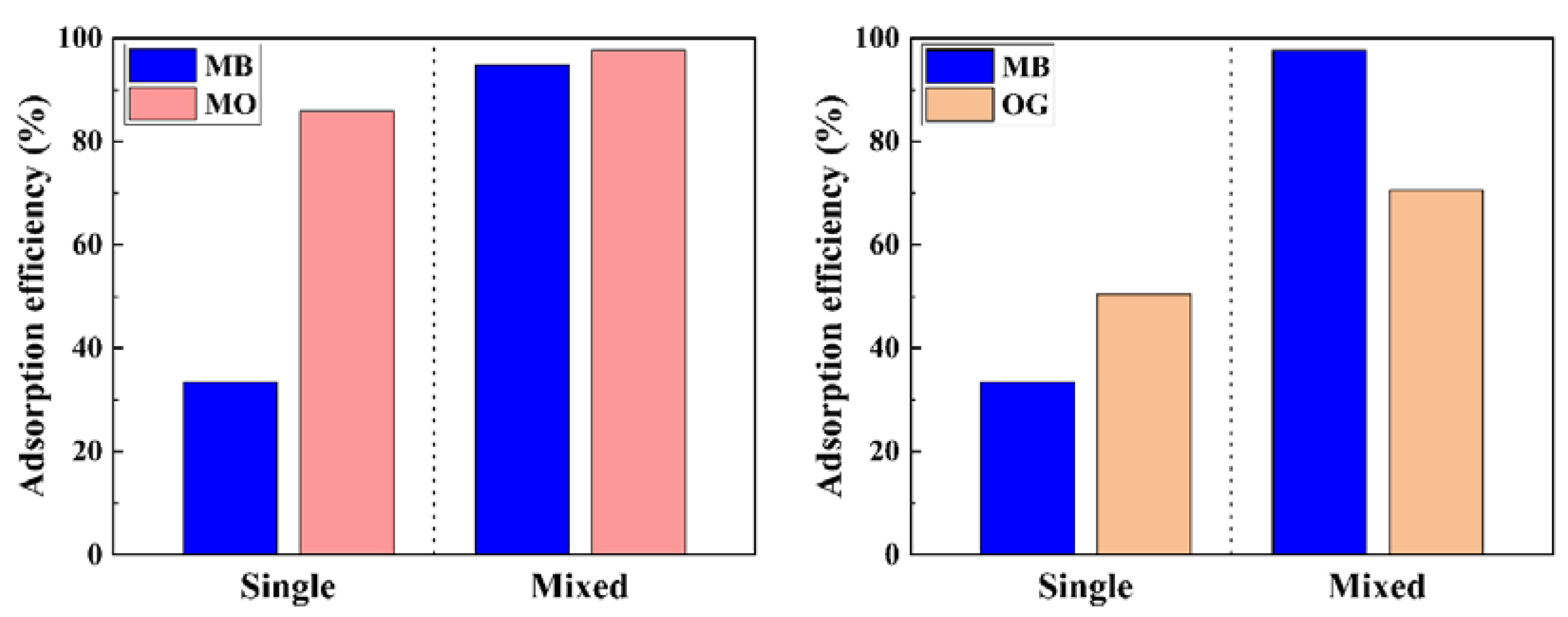
2.4.4. Adsorption of Anionic Dyes from Mixed-Dye Solutions and Real Water Sample
3. Results and Discussion
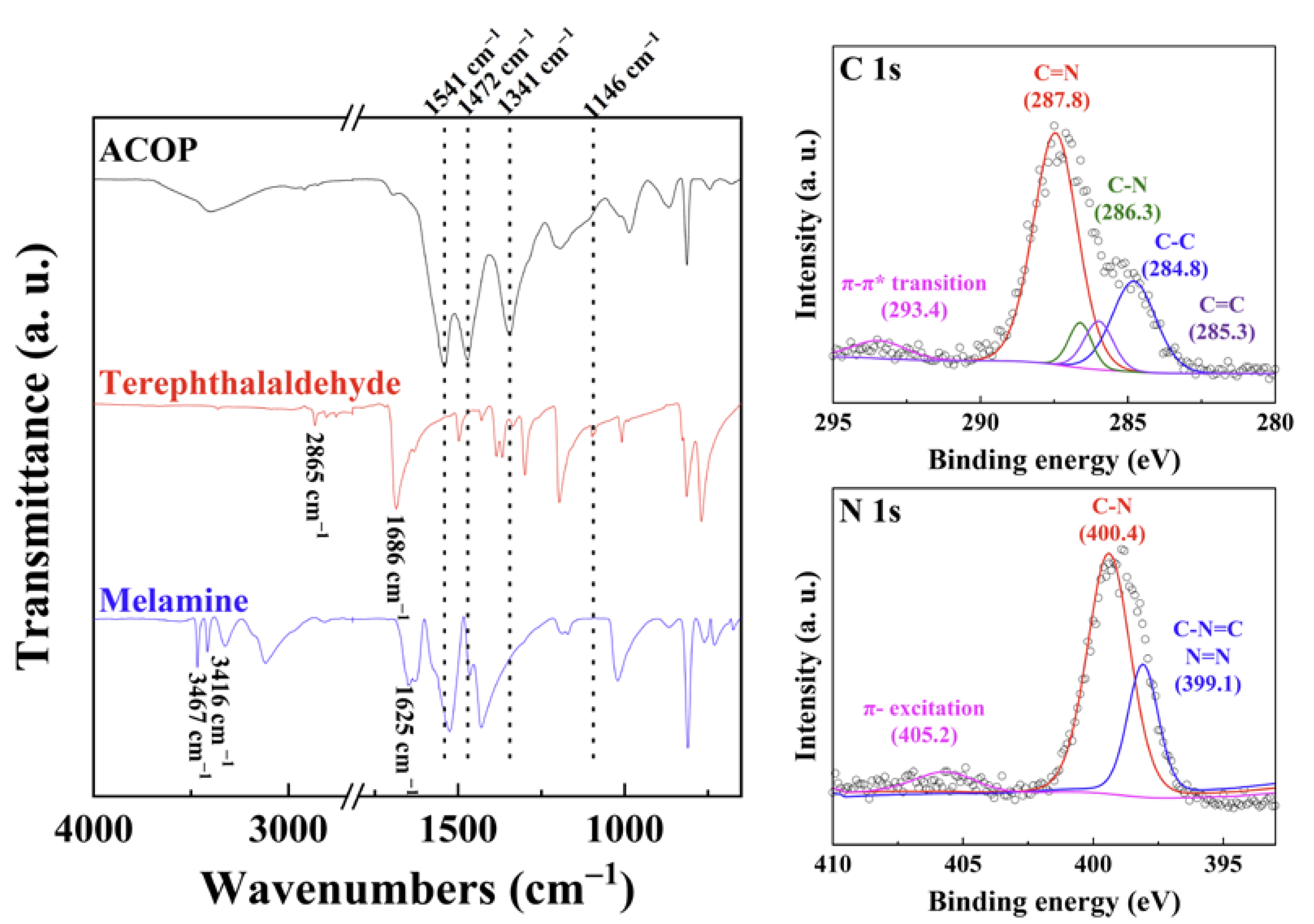
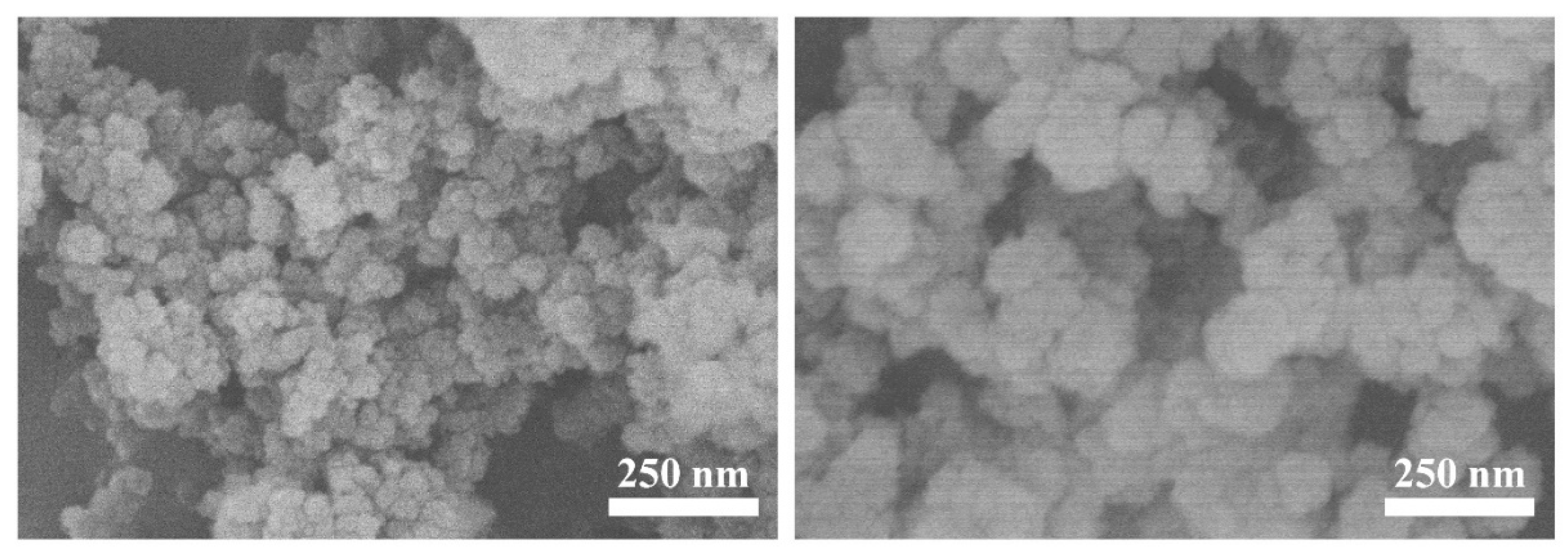
3.1. Characterization of Prepared ACOP
3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
3.3. Adsorption Isotherm
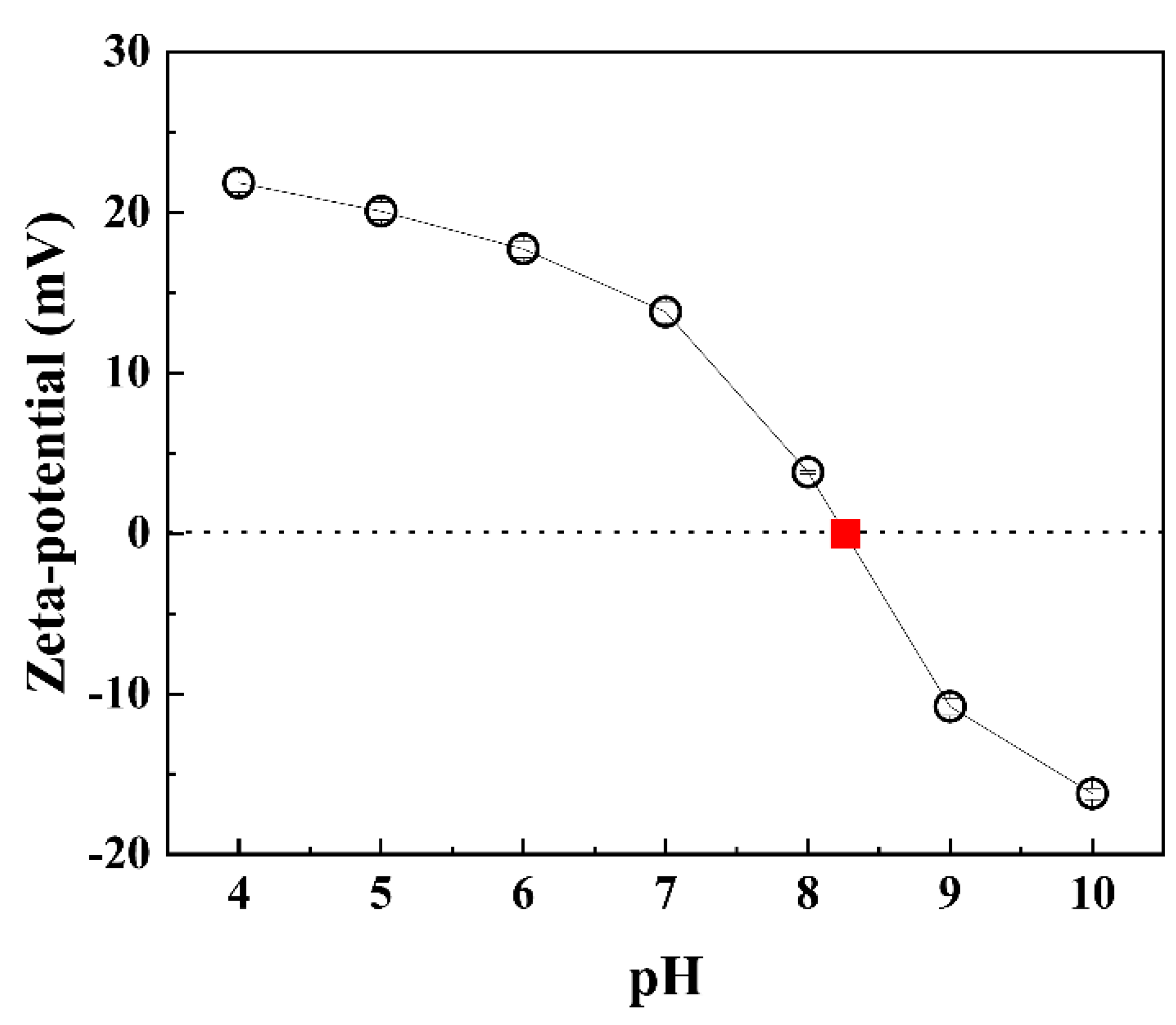
3.4. pH Effect
3.5. Adsorption Experiments in Mixed-Dye System and Real Water Sample
3.6. Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dashtian, K.; Porhemat, S.; Rezvani, A.R.; Ghaedi, M.; Sabzehmeidani, M.M. Adsorption of semisoft pollutants onto Bi2S3/Ag2S-AC under the influence of ultrasonic waves as external filed. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 60, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzen, M.; Sarı, A.; Saleh, T.A. Response surface optimization, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for effective removal of rhodamine B by magnetic AC/CeO2 nanocomposite. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshari, M.; Dinari, M.; Moradi, H.; Noori, Z. Polyaniline/sulfonated-covalent organic polymer nanocomposite: Structural and dye adsorption properties. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 31, 2433–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, C.I.; Lloyd, J.R.; Guthrie, J.T. The removal of colour from textile wastewater using whole bacterial cells: A review. Dyes Pigment. 2003, 58, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Kumar, R.; Nayak, A.; Saleh, T.A.; Barakat, M.A. Adsorptive removal of dyes from aqueous solution onto carbon nanotubes: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 193–194, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jejurkar, V.P.; Yashwantrao, G.; Saha, S. Tröger’s base functionalized recyclable porous covalent organic polymer (COP) for dye adsorption from water. New, J. Chem. 2020, 44, 12331–12342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türgay, O.; Ersöz, G.; Atalay, S.; Forss, J.; Welander, U. The treatment of azo dyes found in textile industry wastewater by anaerobic biological method and chemical oxidation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 79, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Carr, C.M. A critical review on recent advancements of the removal of reactive dyes from dyehouse effluent by ion-exchange adsorbents. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saruchi; Kumar, V.; Kaith, B.S.; Jindal, R. Synthesis of hybrid ion exchanger for Rhodamine B dye removal: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 10492–10499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.; Kadam, A.A.; Govindwar, S.P.; Kumar, P.; Varshney, L. An insight into the influence of low dose irradiation pretreatment on the microbial decolouration and degradation of Reactive Red-120 dye. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 1348–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njoku, V.O.; Foo, K.Y.; Asif, M.; Hameed, B.H. Preparation of activated carbons from rambutan (Nephelium lappaceum) peel by microwave-induced KOH activation for acid yellow 17 dye adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 250, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Gupta, B.; Rastogi, A.; Agarwal, S.; Nayak, A. A comparative investigation on adsorption performances of mesoporous activated carbon prepared from waste rubber tire and activated carbon for a hazardous azo dye—Acid Blue 113. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Lazaridis, N.K.; Mitropoulos, A.C. Removal of dyes from aqueous solutions with untreated coffee residues as potential low-cost adsorbents: Equilibrium, reuse and thermodynamic approach. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 189–190, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Sorption of dyes and copper ions onto biosorbents. Process. Biochem. 2003, 38, 1047–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulkumar, M.; Sathishkumar, P.; Palvannan, T. Optimization of Orange G dye adsorption by activated carbon of Thespesia populnea pods using response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Iqbal, M.; Javed, A.; Aftab, K.; Nazli, Z.-i.-H.; Bhatti, H.N.; Nouren, S. Dyes adsorption using clay and modified clay: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 256, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brião, G.V.; Jahn, S.L.; Foletto, E.L.; Dotto, G.L. Highly efficient and reusable mesoporous zeolite synthetized from a biopolymer for cationic dyes adsorption. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 556, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.G.; EL-Mahdy, A.F.M.; Meng, T.-S.; Samy, M.M.; Kuo, S.-W. Multifunctional hypercrosslinked porous organic polymers based on tetraphenylethene and triphenylamine derivatives for high-performance dye adsorption and supercapacitor. Polymers 2020, 12, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Tang, K.; Kim, T.-H.; Hwang, Y. Selective removal of cationic organic pollutants using disulfide-linked polymer. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 288, 120522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, S.; Lu, C.; Liu, D.; Pan, Y.; Sakiyama, H.; Muddassir, M.; Liu, J. A new magnetic adsorbent of eggshell-zeolitic imidazolate framework for highly efficient removal of norfloxacin. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 18016–18026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernomorova, M.A.; Myakinina, M.S.; Zhinzhilo, V.A.; Uflyand, I.E. Analytical Determination of Cephalosporin Antibiotics Using Coordination Polymer Based on Cobalt Terephthalate as a Sorbent. Polymers 2023, 15, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthiaraj, P.; Lee, Y.-R.; Zhang, S.; Ahn, W.-S. Triazine-based covalent organic polymers: Design, synthesis and applications in heterogeneous catalysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 16288–16311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Cao, D.; Dai, L. Well-defined two dimensional covalent organic polymers: Rational design, controlled syntheses, and potential applications. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 1896–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Zhou, Z.; Guo, J.; Xiang, Z. Well-defined 2D covalent organic polymers for energy electrocatalysis. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, S.; Deo, K.A.; Gaharwar, A.K. 2D covalent organic frameworks for biomedical applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhuang, S. Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) for environmental applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 400, 213046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhang, M.; Huang, X.; Chen, B.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, D.G.; Kim, I. Smart l-borneol-loaded hierarchical hollow polymer nanospheres with antipollution and antibacterial capabilities. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 26, 101252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Varyambath, A.; Ding, Y.; Chen, B.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, D.-g.; Kim, I.; Song, W. Porous organic polymers for drug delivery: Hierarchical pore structures, variable morphologies, and biological properties. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 5369–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.; Patel, H.A.; Thirion, D.; Yavuz, C.T. Charge-specific size-dependent separation of water-soluble organic molecules by fluorinated nanoporous networks. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, D.; Lee, J.S.; Patel, H.A.; Jakobsen, M.H.; Hwang, Y.; Yavuz, C.T.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Andersen, H.R. Selective removal of heavy metal ions by disulfide linked polymer networks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 332, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, K.; Cheng, B.; Liang, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, R. The aminated covalent organic polymers for reversible removal of concurrent perfluorooctane sulfonate and dichromate. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, M.G.; Fassbender, B.; Spiess, H.W.; Thomas, A.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K. Catalyst-free preparation of melamine-based microporous polymer networks through Schiff Base chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7216–7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisova, N.E.; Reshetova, M.D.; Ustynyuk, Y.A. Metal-free methods in the synthesis of Macrocyclic Schiff Bases. Chemical Reviews 2007, 107, 46–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, F.; Dinari, M. Cu nanoparticles embedded in the porous organic polymer as highly effective catalysts for nitroaromatics reduction. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 325, 111339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, F.; Dinari, M. Novel covalent organic polymer-supported Ag nanoparticles as a catalyst for nitroaromatics reduction. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 618, 126441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Sun, Y.; Che, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Bosch, M.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Smith, M.; Yuan, S.; et al. Porous organic polymers for post-combustion carbon capture. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Jia, S.; Diercks, C.S.; Yang, X.; Alshmimri, S.A.; Yaghi, O.M. Amidation, esterification, and thioesterification of a carboxyl-functionalized covalent organic framework. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 2020, 59, 2023–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Deng, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, K.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Ma, D. Evaluation of an ionic porous organic polymer for water remediation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 39404–39413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Pang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, N.; Mao, L.; Qiu, M.; Hu, B.; Yang, H.; Wang, X. Orderly porous covalent organic frameworks-based materials: Superior adsorbents for pollutants removal from aqueous solutions. Innovation 2021, 2, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Sa, R.; Li, P.; Yuan, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, R. Metalloporphyrin-based covalent organic frameworks composed of the electron donor-acceptor dyads for visible-light-driven selective CO2 reduction. Sci. China Chem. 2020, 63, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Aguila, B.; Earl, L.D.; Abney, C.W.; Wojtas, L.; Thallapally, P.K.; Ma, S. Covalent organic frameworks as a decorating platform for utilization and affinity enhancement of chelating sites for radionuclide sequestration. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Über die adsorption in lösungen. Z. Für Phy. Chem. 1907, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoul Waterworks Authority. Report on Arisu Water Quality; Seoul Waterworks Authority: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mircescu, N.E.; Oltean, M.; Chiş, V.; Leopold, N. FTIR, FT-Raman, SERS and DFT study on melamine. Vib. Spectrosc. 2012, 62, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaygan, S.; Pasdar, H.; Foroughifar, N.; Davallo, M.; Motiee, F. Cobalt (II) complexes with Schiff Base ligands derived from terephthalaldehyde and ortho-substituted anilines: Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.; Gharib, M.; Najafi, M.; Janczak, J. Room temperature synthesis of a Zn(II) metal-organic coordination polymer for dye removal. J. Solid State Chem. 2016, 235, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Lim, S.M.; Ramasamy, K.; Vasudevan, M.; Shah, S.A.A.; Narasimhan, B. Bis-pyrimidine acetamides: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation. Chem. Cent. J. 2017, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Yan, H.; Li, K.; You, J.; Han, W. A covalent organic framework–MnO2 nanosheet system for determination of glutathione. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 10022–10034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yu, H.; He, Y.; Liu, Z.; Qin, C.; Liu, B.; Li, Y. Porous three-component hybrid hydrogen-bonded covalent organic polymers: Design, synthesis and ciprofloxacin adsorption. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 123, 109445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarasinghe, S.A.S.C.; Chuah, C.Y.; Li, W.; Sethunga, G.S.M.D.P.; Wang, R.; Bae, T.-H. Incorporation of CoIII acetylacetonate and SNW-1 nanoparticles to tailor O2/N2 separation performance of mixed-matrix membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 223, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Yang, H.; Li, A.; Cheng, R. pH-tunable surface charge of chitosan/graphene oxide composite adsorbent for efficient removal of multiple pollutants from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, N.; Akbar Razavi, S.A.; Morsali, A.; Hu, M.-L. High capacity Hg(II) and Pb(II) removal using MOF-based nanocomposite: Cooperative effects of pore functionalization and surface-charge modulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneechakr, P.; Karnjanakom, S. Environmental surface chemistries and adsorption behaviors of metal cations (Fe3+, Fe2+, Ca2+ and Zn2+) on manganese dioxide-modified green biochar. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 24074–24086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darmograi, G.; Prelot, B.; Layrac, G.; Tichit, D.; Martin-Gassin, G.; Salles, F.; Zajac, J. Study of adsorption and intercalation of Orange-type dyes into Mg–Al layered double hydroxide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 23388–23397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, B.H.; Salman, J.M.; Ahmad, A.L. Adsorption isotherm and kinetic modeling of 2,4-D pesticide on activated carbon derived from date stones. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Shi, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, Q. A novel covalent organic polymer with hierarchical pore structure for rapid and selective trace Hg(II) removal from drinking water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 285, 120306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Bing, H.; Feifei, X.; Xiaofeng, C. Equilibrium and kinetic studies of methyl orange adsorption on multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Yue, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, C. Equilibrium and kinetic studies of methyl orange and methyl violet adsorption on activated carbon derived from Phragmites australis. Desalination 2010, 252, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.-M.; Xia, S.-J.; Wang, L.-G.; Xing, F.-F.; Pan, G.-X. Treatment of methyl orange by calcined layered double hydroxides in aqueous solution: Adsorption property and kinetic studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 316, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.-X.; Yao, Z.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-H. A covalent organic framework exhibiting amphiphilic selective adsorption toward ionic organic dyes tuned by pH value. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 133, 109764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Meng, X.; Luo, H.; Yao, L.; Song, X.; Liang, Z. Post-synthetic modification of conjugated microporous polymer with imidazolium for highly efficient anionic dyes removal from water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 284, 120245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, M.; Xie, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, A. Performance of defective Zr-MOFs for the adsorption of anionic dyes. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 5438–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benselka-Hadj Abdelkader, N.; Bentouami, A.; Derriche, Z.; Bettahar, N.; de Ménorval, L.C. Synthesis and characterization of Mg–Fe layer double hydroxides and its application on adsorption of Orange G from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 169, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, Z.; Guo, X.; Jiang, X.; Liu, R. Process optimization, kinetics and equilibrium of orange G and acid orange 7 adsorptions onto chitosan/surfactant. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 197, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, P.; Lu, N.; Chen, H.; Zhang, C.; Hou, X. Facile fabrication of Fe3O4/MIL-101(Cr) for effective removal of acid red 1 and orange G from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 295, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsini, A.; Essekri, A.; Aarab, N.; Laabd, M.; Ait Addi, A.; Lakhmiri, R.; Albourine, A. Elaboration of novel polyaniline@Almond shell biocomposite for effective removal of hexavalent chromium ions and Orange G dye from aqueous solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 15245–15258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Lee, H.J.; Jhung, S.H. Covalent-organic polymer-derived carbons: An effective adsorbent to remove sulfonamide antibiotics from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 135386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalilzadeh Shirazi, E.; Metzger, J.W.; Fischer, K.; Hassani, A.H. Removal of textile dyes from single and binary component systems by Persian bentonite and a mixed adsorbent of bentonite/charred dolomite. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 598, 124807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


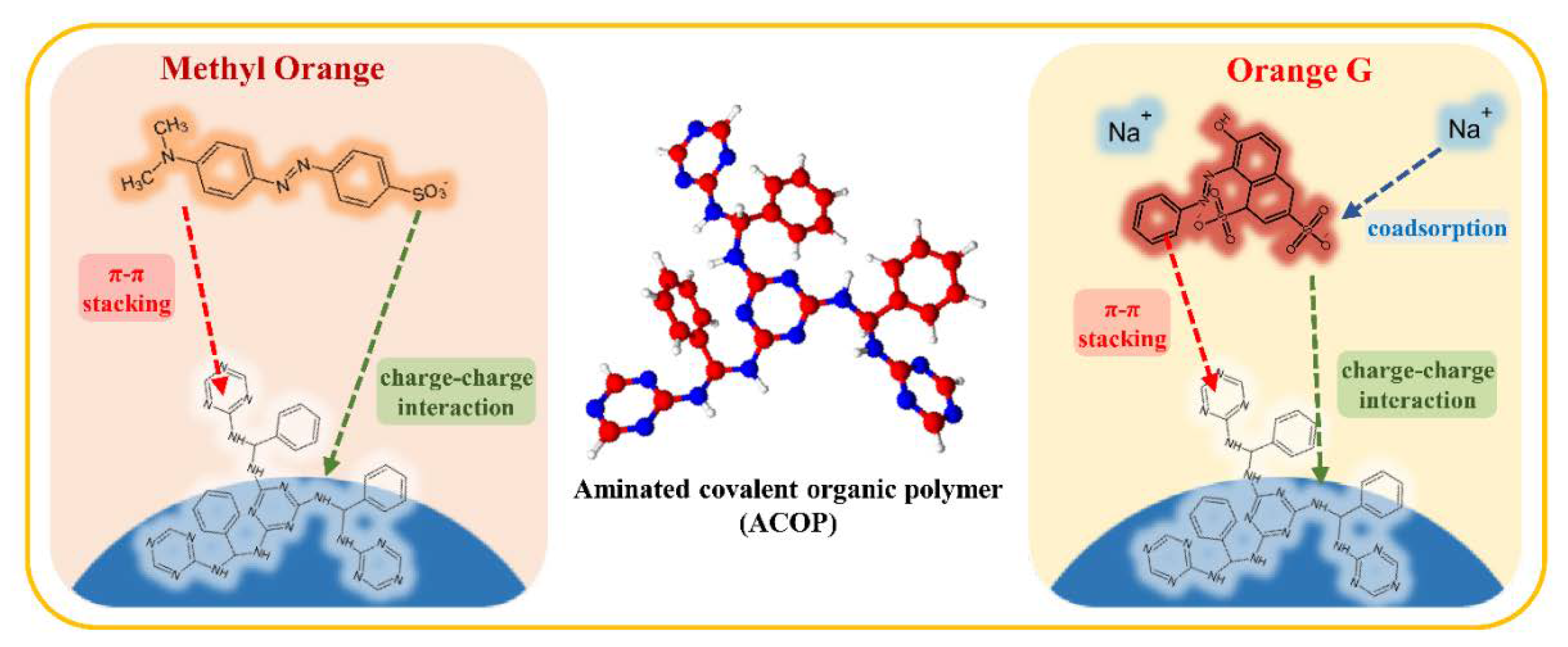
| Chemical Name | Chemical Formula | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | pKa (25 °C) | log Kow | Chemical Structure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anionic dye | Methyl Orange | C14H14N3NaO3S | 327.33 | 4.3 | −0.66 |  |
| Orange G | C16H10N2Na2O7S2 | 452.38 | 11.5 (−OH) 1.0 (−SO3H) | −4.56 | 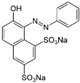 | |
| Cationic dye | Methylene Blue | C16H18ClN3S | 319.85 | 3.8 | 0.75 | 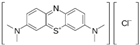 |
| Models | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | qm (mg/g) | aL (L/mg) | R2 | KF | n | R2 |
| MO | 351.9 | 0.0806 | 0.8341 | 97.34 | 3.753 | 0.9510 |
| OG | 227.9 | 0.0498 | 0.7170 | 43.59 | 3.072 | 0.9293 |
| Adsorbent | Dye | Dosing (g/L) | Initial Concentration (mg/L) | Contact Time (min) | qm (mg/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon nanotubes | Methyl orange | 0.3 | 20 | 180 | 35.4–64.7 | [60] |
| Activated carbon | 0.5 | 25–75 | 350 | 238.1 | [61] | |
| ZnAl-LDO | 0.5 | 100 | 120 | 200.0 | [62] | |
| Benzodiimidazole-COF | 1.0 | - | 160 | 256 | [63] | |
| CMP-Im | 0.25 | 100–600 | 720 | 588 | [64] | |
| MOF-808 | 0.2 | - | 240 | 540 | [65] | |
| ACOP | 1.0 | 180–350 | 180 | 351.9 | This study | |
| MgFe-LDO | Orange G | 1.0 | 50–800 | 1440 | 378.8 | [66] |
| Activated clay | 0.2 | 400 | 300 | 128.6 | [67] | |
| Fe3O4/MIL-101(Cr) | 0.6 | 40–80 | 120 | 200.0 | [68] | |
| MOF-808 | 0.2 | - | 240 | 197 | [65] | |
| PANI@AS biocomposites | 0.5 | 10–500 | 120 | 191.0 | [69] | |
| ACOP | 1.0 | 80–350 | 180 | 227.9 | This study |
| ACOP | C 1 s | N 1 s | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| π-π* transition | C=N | C-N | C=C | C-C | π-excitation | C-N | C-N=C N=N | |
| Peak position (eV) | 293.4 | 287.8 | 286.3 | 285.3 | 284.8 | 405.2 | 400.4 | 399.1 |
| Area(%) | 5.41 | 58.12 | 5.95 | 7.93. | 22.58 | 8.65 | 65.09 | 26.26 |
| ACOP-MO | C 1 s | N 1 s | ||||||
| π-π* transition | C=N | C-N | C=C | C-C | π-excitation | C-N | C-N=C N=N | |
| Peak position (eV) | 292.5 | 287.8 | 286.3 | 285.3 | 284.8 | 405.2 | 400.4 | 399.1 |
| Area (%) | 2.77 | 59.27 | 17.40 | 3.61 | 16.95 | 3.90 | 50.74 | 45.36 |
| ACOP-OG | C 1 s | N 1 s | ||||||
| π-π* transition | C=N | C-N | C=C | C-C | π-excitation | C-N | C-N=C N=N | |
| Peak position (eV) | 293.4 | 287.8 | 286.2 | 285.4 | 284.8 | 405.0 | 399.4 | 398.4 |
| Area (%) | 2.01 | 67.90 | 9.43 | 2.54 | 18.12 | 3.41 | 52.59 | 44.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.; Kim, S.; Park, Y.; Kim, T.-H.; Hwang, Y. Aminated Covalent Organic Polymers for Anionic Dye Adsorption in Aqueous Systems. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13042043
Park J, Kim S, Park Y, Kim T-H, Hwang Y. Aminated Covalent Organic Polymers for Anionic Dye Adsorption in Aqueous Systems. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(4):2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13042043
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jooeun, Soyeon Kim, Yuri Park, Tae-Hyun Kim, and Yuhoon Hwang. 2023. "Aminated Covalent Organic Polymers for Anionic Dye Adsorption in Aqueous Systems" Applied Sciences 13, no. 4: 2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13042043
APA StylePark, J., Kim, S., Park, Y., Kim, T.-H., & Hwang, Y. (2023). Aminated Covalent Organic Polymers for Anionic Dye Adsorption in Aqueous Systems. Applied Sciences, 13(4), 2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13042043








