Research on Multi-Robot Formation Control Based on MATD3 Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
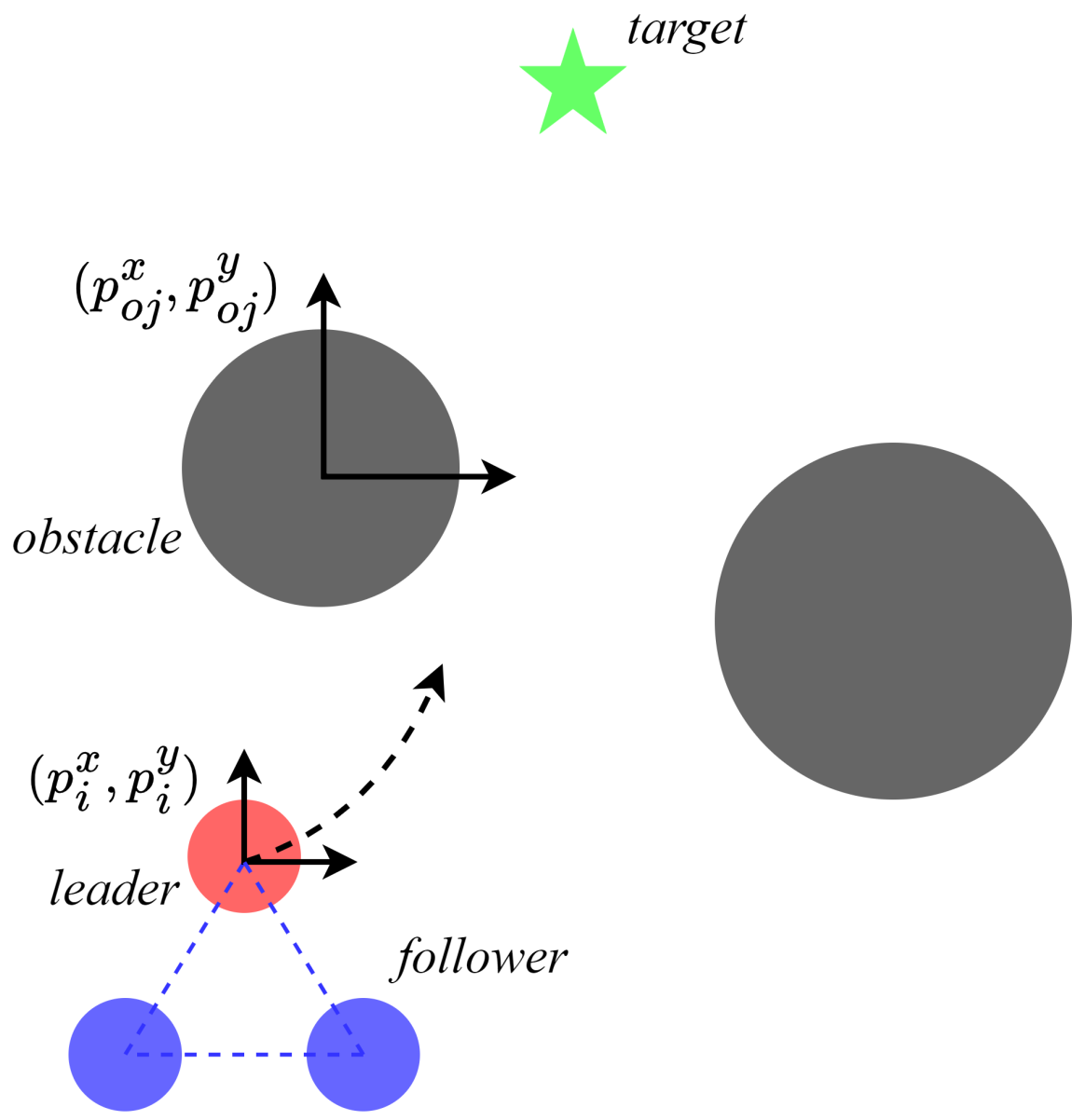
2. Problem Description and Modeling
2.1. System Model
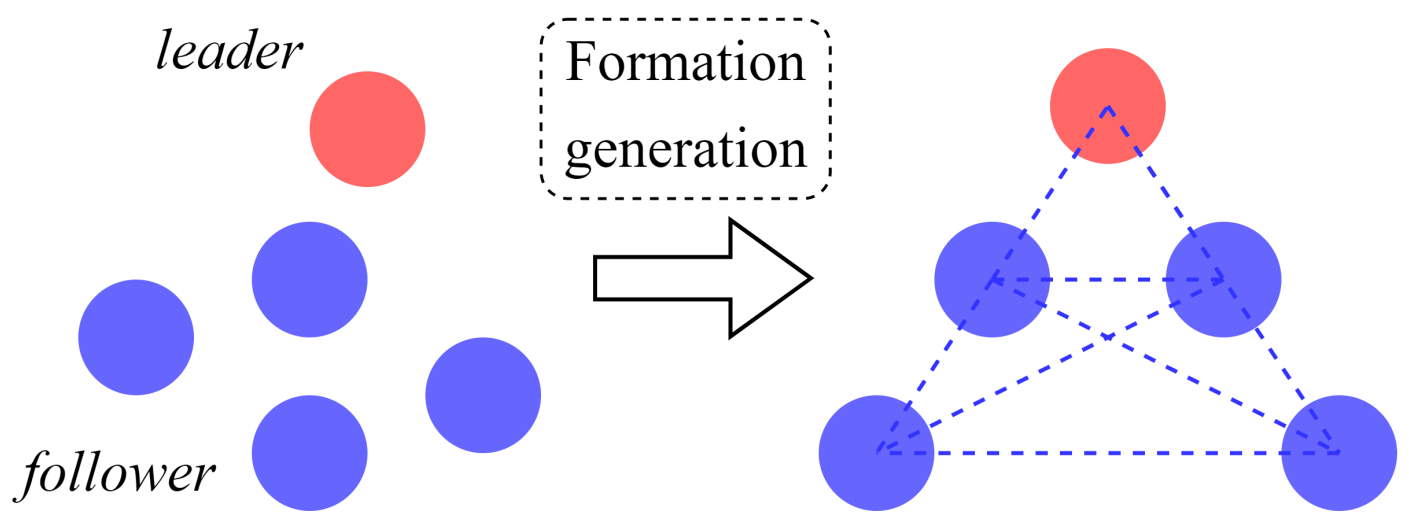
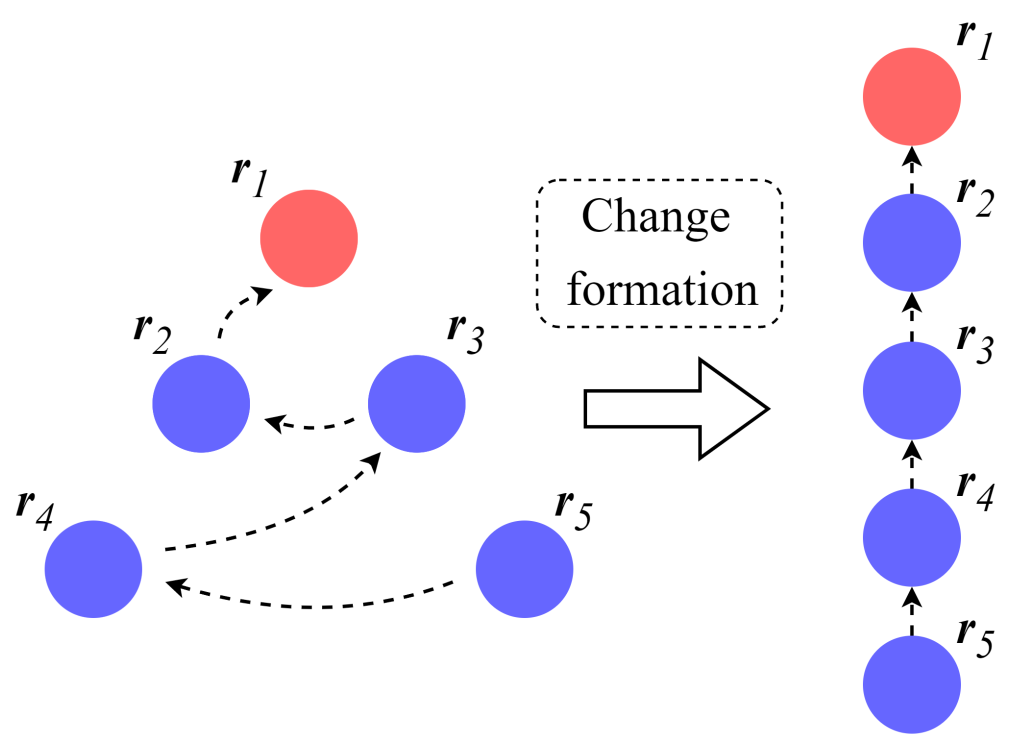
2.2. Formation Problem Description
3. Multi-Robot Formation Control Based on Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
3.1. Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
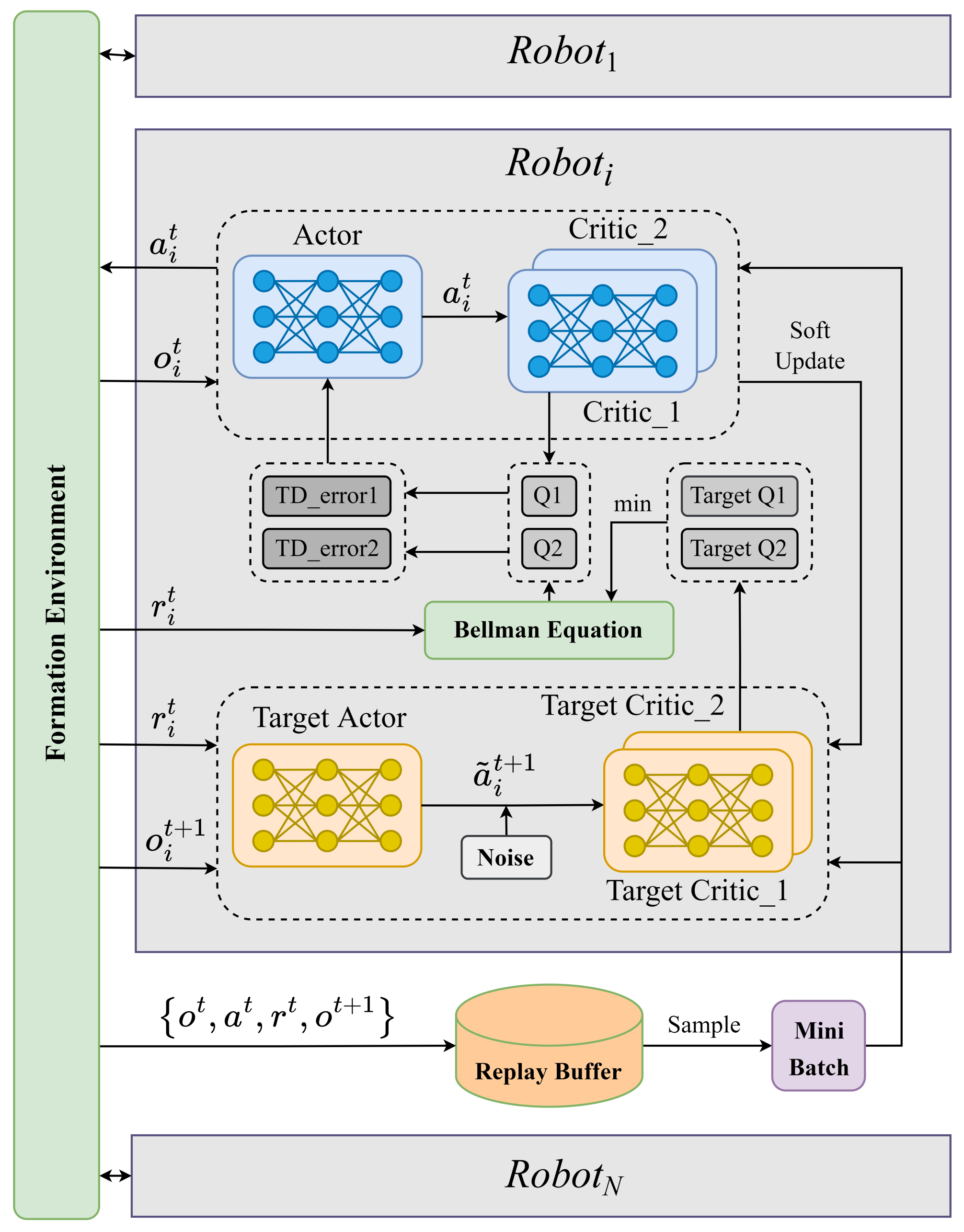
3.2. MATD3
3.3. Combining Prioritized Experience Replay
| Algorithm 1 MATD3 with prioritized experience replay. |
|
4. Multi-Robot Formation Strategy Design Based on Improved MATD3
4.1. Robot Formation MDP Design
4.2. State and Action Space Design
4.3. Reward Function Design
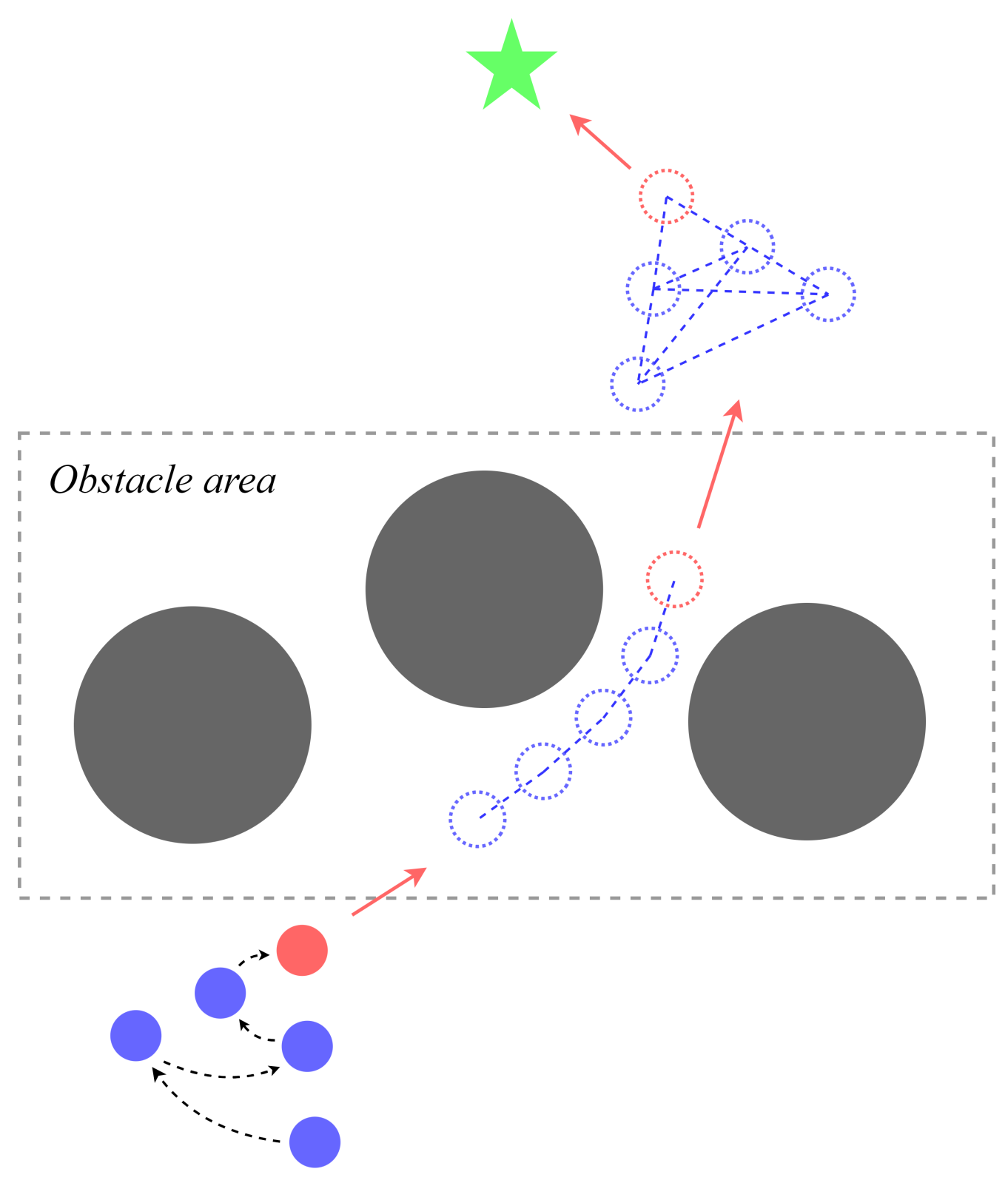
5. Simulation Experiments
5.1. Experimental Environment Setup
5.2. Training Parameters’ Setting
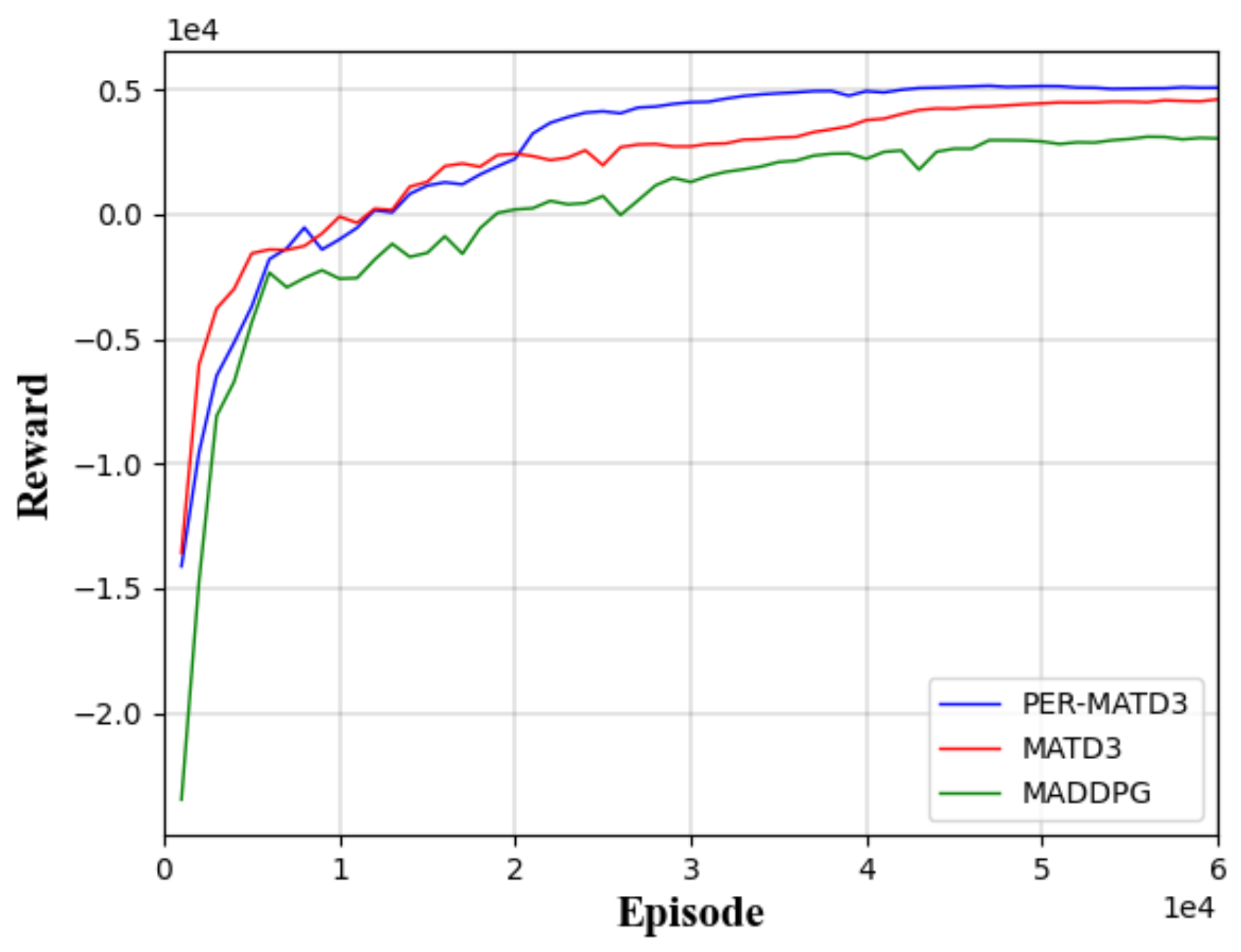
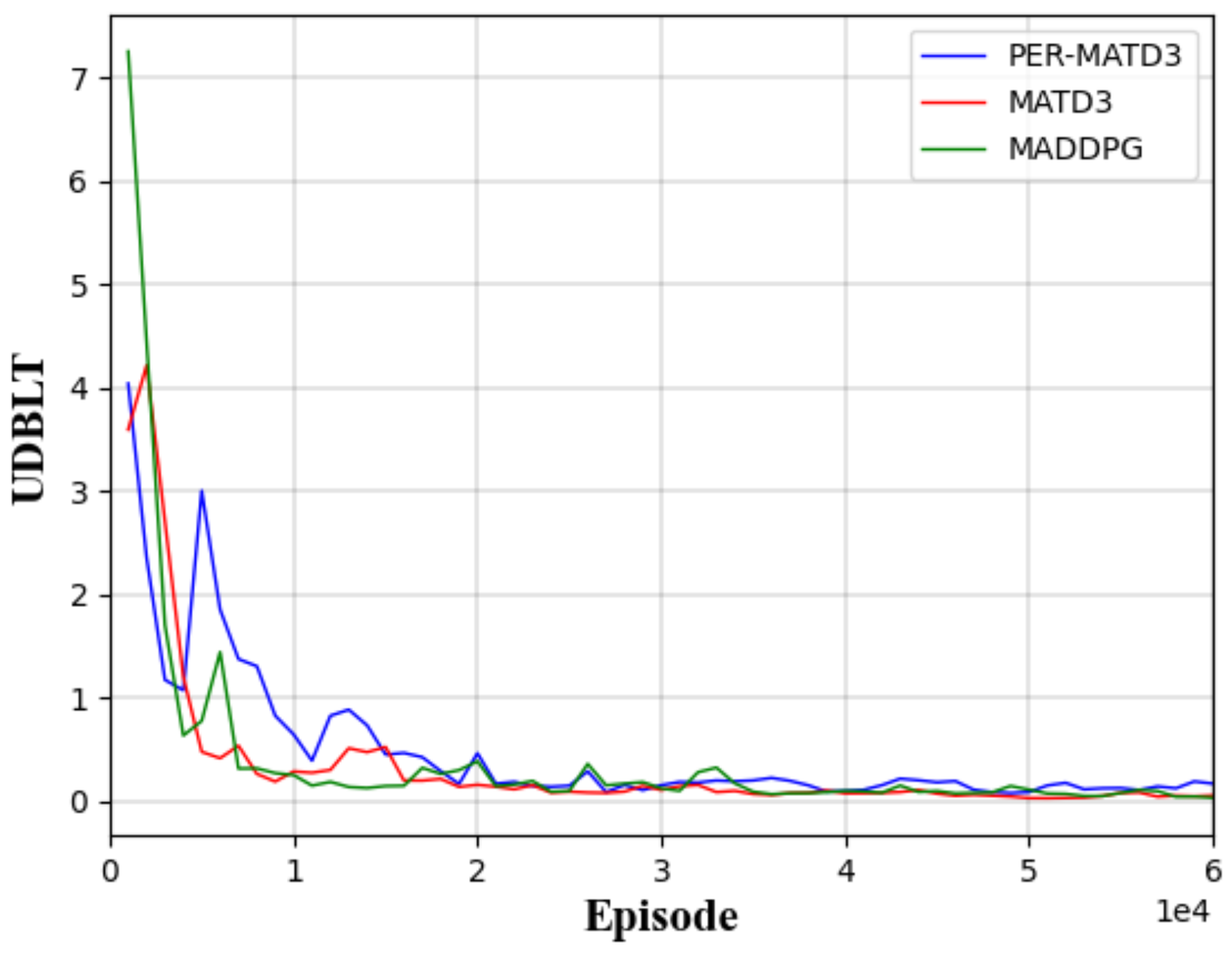
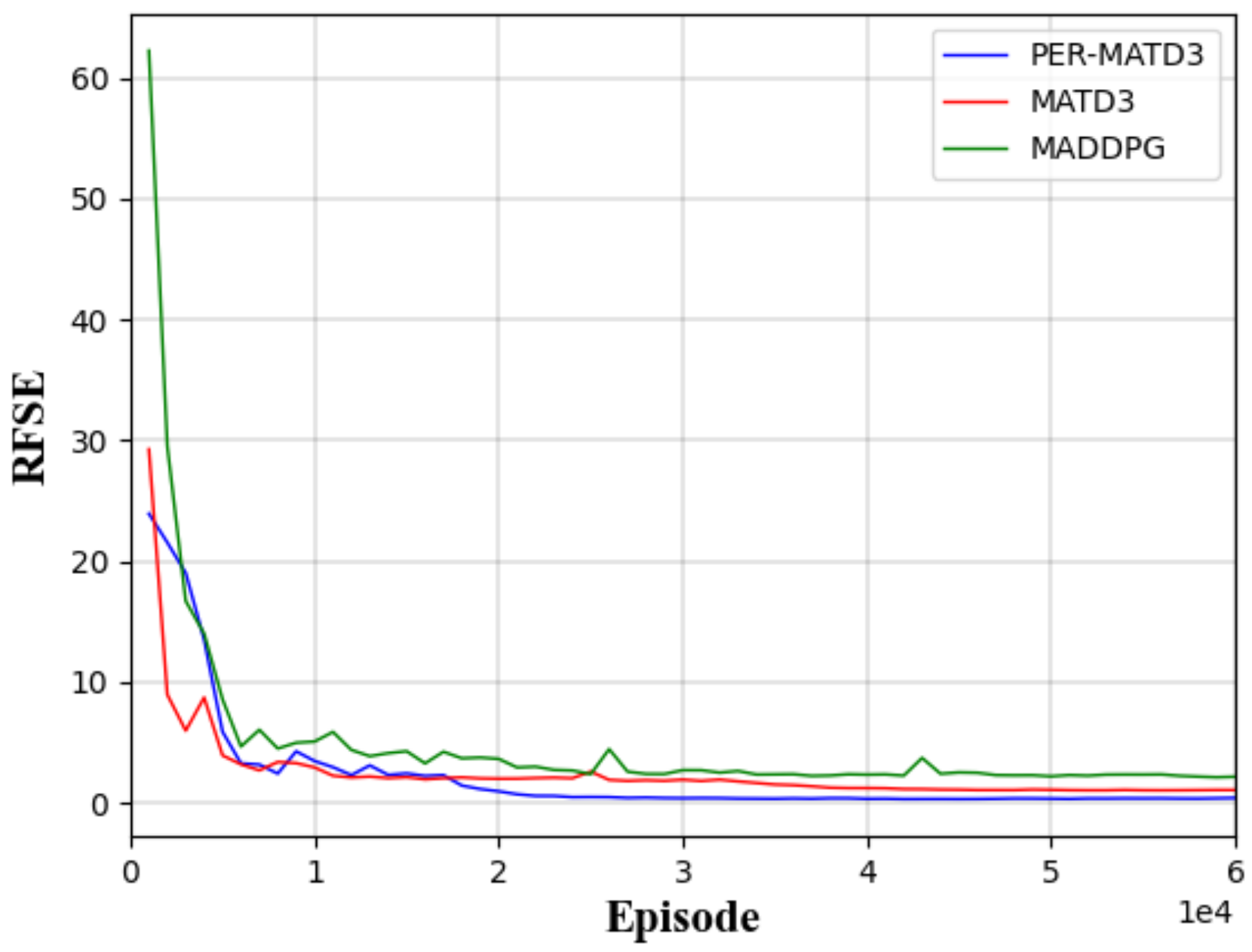
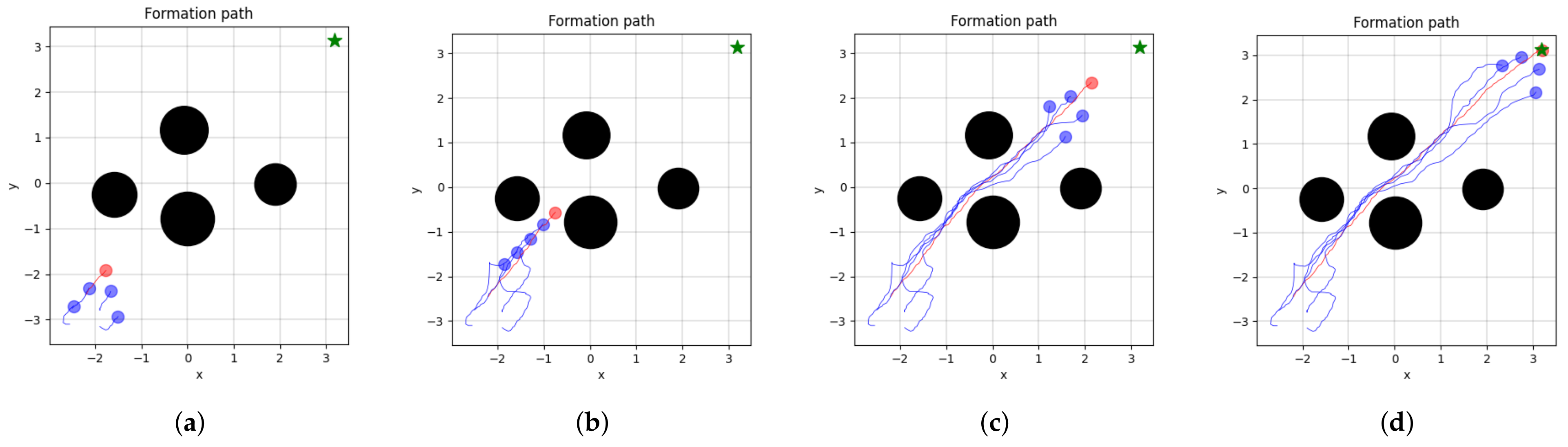
5.3. Experimental Results and Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dorri, A.; Kanhere, S.S.; Jurdak, R. Multi-agent systems: A survey. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 28573–28593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Mora, J.; Baker, S.; Rus, D. Multi-robot formation control and object transport in dynamic environments via constrained optimization. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2017, 36, 1000–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macwan, A.; Vilela, J.; Nejat, G.; Benhabib, B. A multirobot path-planning strategy for autonomous wilderness search and rescue. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2014, 45, 1784–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, K.; Matsunaga, N.; Murata, K. Formation path learning for cooperative transportation of multiple robots using MADDPG. In Proceedings of the 2021 21st International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 12–15 October 2021; pp. 1619–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasik, A.; Pereira, J.N.; Ventura, R.; Lima, P.U.; Martinoli, A. Graph-based distributed control for adaptive multi-robot patrolling through local formation transformation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.J. Unmanned aerial vehicle formation inspired by bird flocking and foraging behavior. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 2018, 15, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.P. Formation control of leader–follower mobile robots’ systems using model predictive control based on neural-dynamic optimization. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 5752–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defoort, M.; Floquet, T.; Kokosy, A.; Perruquetti, W. Sliding-mode formation control for cooperative autonomous mobile robots. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 3944–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Wang, M.; Dai, S.L.; Luo, F. Leader–follower formation control of USVs with prescribed performance and collision avoidance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 15, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.A.; Tan, K.H. High precision formation control of mobile robots using virtual structures. Auton. Robot. 1997, 4, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balch, T.; Arkin, R.C. Behavior-based formation control for multirobot teams. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1998, 14, 926–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Mora, J.; Montijano, E.; Schwager, M.; Rus, D. Distributed multi-robot formation control among obstacles: A geometric and optimization approach with consensus. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 5356–5363. [Google Scholar]
- Hafez, A.; Givigi, S. Formation reconfiguration of cooperative UAVs via Learning Based Model Predictive Control in an obstacle-loaded environment. In Proceedings of the 2016 Annual IEEE Systems Conference (SysCon), Orlando, FL, USA, 18–21 April 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kiumarsi, B.; Vamvoudakis, K.G.; Modares, H.; Lewis, F.L. Optimal and autonomous control using reinforcement learning: A survey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2017, 29, 2042–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopp, M.; Aykın, C.; Feldmaier, J.; Shen, H. Formation control using GQ (λ) reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 26th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Lisbon, Portugal, 28–31 August 2017; pp. 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Chen, C.P.; Feng, J.; Zhou, N. Optimized multi-agent formation control based on an identifier–actor–critic reinforcement learning algorithm. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 26, 2719–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhou, R.; Liu, Y.; Luo, J.; Xie, S.; Peng, Y.; Pu, H. Reinforcement-learning-based asynchronous formation control scheme for multiple unmanned surface vehicles. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Hu, S. USV formation and path-following control via deep reinforcement learning with random braking. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 5468–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Ye, Q.; Wang, C.; Xie, G. Decentralized Circle Formation Control for Fish-like Robots in the Real-world via Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 8814–8820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, O.; Sun, G.; Wu, C.; Yao, W. Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Multiple Omnidirectional Mobile Robots Control. In Proceedings of the 2021 China Automation Congress (CAC), Beijing, China, 22–24 October 2021; pp. 7226–7231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Meng, P.; Yin, W.; Liu, H. A neural network method for time-dependent inverse source problem with limited-aperture data. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2023, 421, 114842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. On local and global structures of transmission eigenfunctions and beyond. J. Inverse Ill-Posed Probl. 2022, 30, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K. On an artificial neural network for inverse scattering problems. J. Comput. Phys. 2022, 448, 110771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Yang, W.; Liu, H. A neural network scheme for recovering scattering obstacles with limited phaseless far-field data. J. Comput. Phys. 2020, 417, 109594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillicrap, T.P.; Hunt, J.J.; Pritzel, A.; Heess, N.; Erez, T.; Tassa, Y.; Silver, D.; Wierstra, D. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1509.02971. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Rusu, A.A.; Veness, J.; Bellemare, M.G.; Graves, A.; Riedmiller, M.; Fidjeland, A.K.; Ostrovski, G.; et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, S.; Hoof, H.; Meger, D. Addressing function approximation error in actor–critic methods. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 1587–1596. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, R.; Wu, Y.I.; Tamar, A.; Harb, J.; Pieter Abbeel, O.; Mordatch, I. Multi-agent actor–critic for mixed cooperative-competitive environments. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 6379–6390. [Google Scholar]
- Schaul, T.; Quan, J.; Antonoglou, I.; Silver, D. Prioritized experience replay. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.05952. [Google Scholar]
- Otterlo, M.v.; Wiering, M. Reinforcement learning and markov decision processes. In Reinforcement Learning; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hasselt, H.; Guez, A.; Silver, D. Deep reinforcement learning with double q-learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 12–17 February 2016; Volume 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zou, J. Uniqueness in an inverse acoustic obstacle scattering problem for both sound-hard and sound-soft polyhedral scatterers. Inverse Probl. 2006, 22, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Zou, J. Strengthened linear sampling method with a reference ball. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2010, 31, 4013–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Zou, J. Locating multiple multiscale acoustic scatterers. Multiscale Model. Simul. 2014, 12, 927–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Yin, W.; Meng, P.; Liu, H. On a hybrid approach for recovering multiple obstacles. Commun. Comput. Phys. 2022, 31, 869–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tsou, C.H. Stable determination by a single measurement, scattering bound and regularity of transmission eigenfunctions. Calc. Var. Partial Differ. Equ. 2022, 61, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, Y.T.; Deng, Y.; He, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, X. Surface-localized transmission eigenstates, super-resolution imaging, and pseudo surface plasmon modes. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2021, 14, 946–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blåsten, E.L.; Liu, H. Scattering by curvatures, radiationless sources, transmission eigenfunctions, and inverse scattering problems. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 2021, 53, 3801–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, H.; Cao, X.; Liu, H. On the geometric structures of transmission eigenfunctions with a conductive boundary condition and applications. Commun. Partial Differ. Equ. 2021, 46, 630–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Algorithm | CBRO (%) | UDBLT | RFSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| MADDPG | 3.72 | 0.15 | 2.28 |
| MATD3 | 4.29 | 0.05 | 1.09 |
| PER-MATD3 | 2.37 | 0.08 | 0.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, C.; Li, J.; Shi, Y.; Lin, Z. Research on Multi-Robot Formation Control Based on MATD3 Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031874
Zhou C, Li J, Shi Y, Lin Z. Research on Multi-Robot Formation Control Based on MATD3 Algorithm. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(3):1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031874
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Conghang, Jianxing Li, Yujing Shi, and Zhirui Lin. 2023. "Research on Multi-Robot Formation Control Based on MATD3 Algorithm" Applied Sciences 13, no. 3: 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031874
APA StyleZhou, C., Li, J., Shi, Y., & Lin, Z. (2023). Research on Multi-Robot Formation Control Based on MATD3 Algorithm. Applied Sciences, 13(3), 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031874






