Research on Mining Subsidence Prediction Parameter Inversion Based on Improved Modular Vector Method
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory of Parameter Inversion
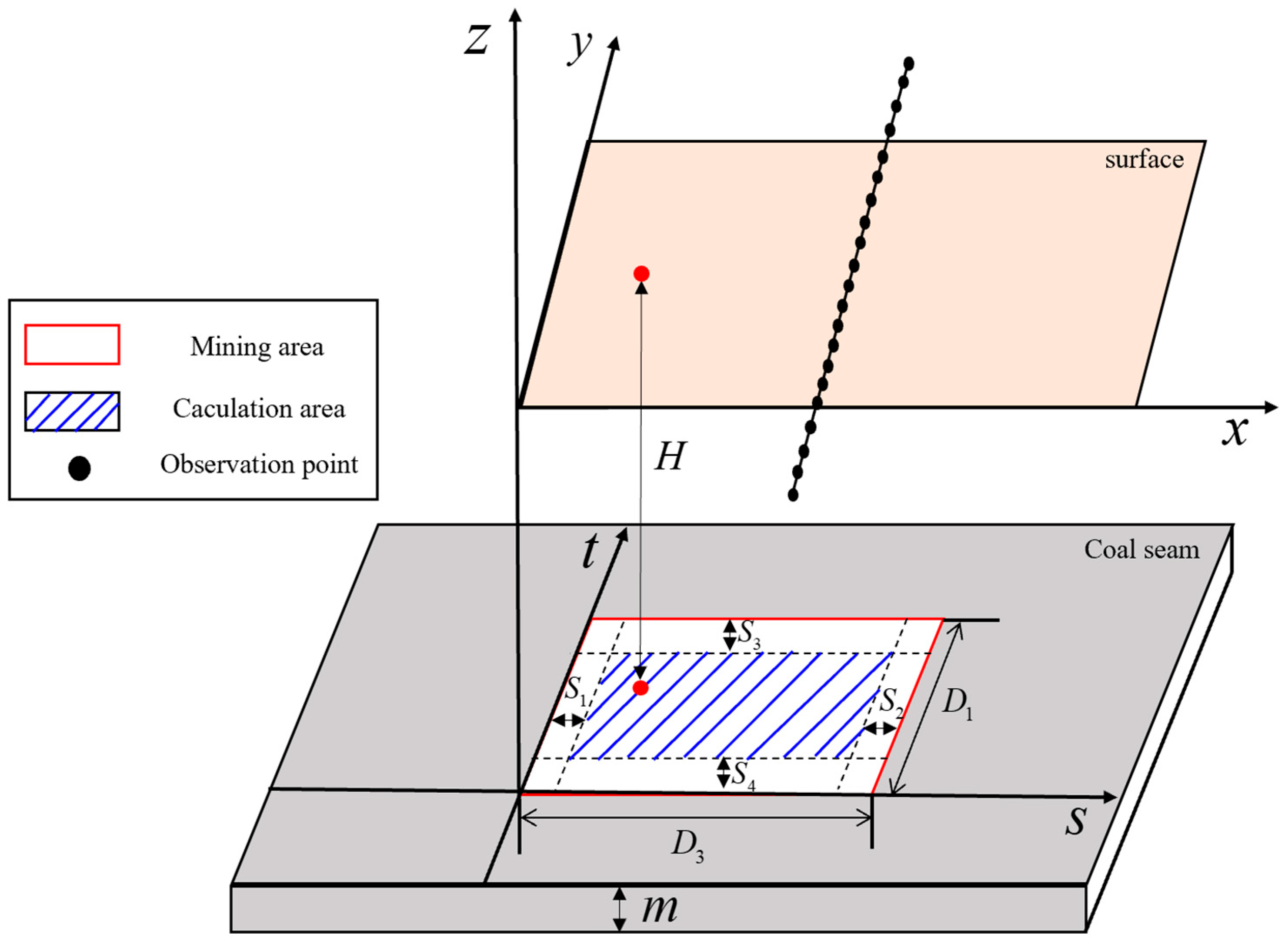
2.1. Prediction Principles of the Probability Integral Method
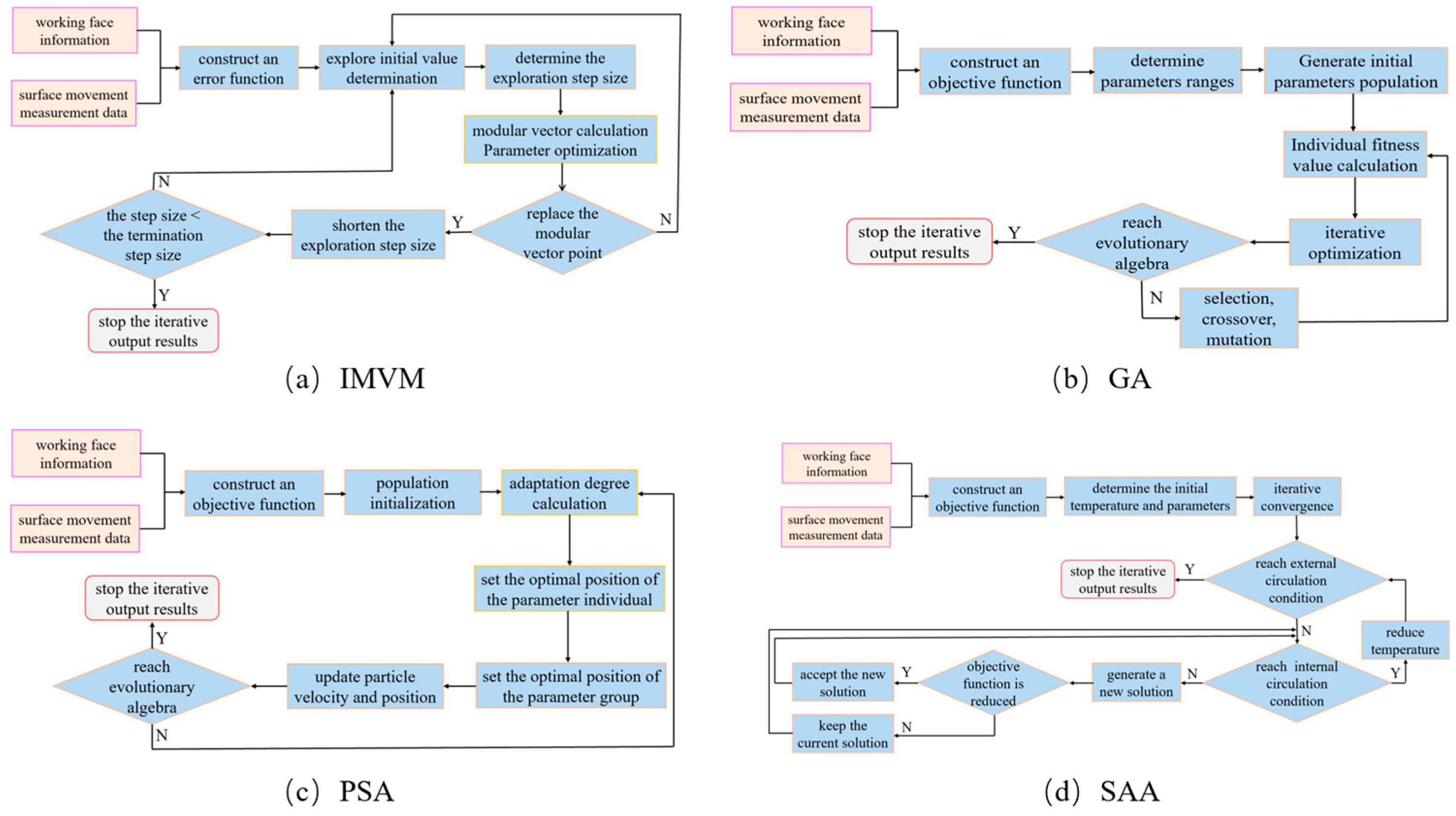
2.2. Principles and Optimization Steps of the Improved Modular Vector Method
- (1)
- Calculate the comprehensive deformation modulus of the rock mass using drilling data obtained from the specific mining area.
- (2)
- Compute the similarity criterion for the mining area in question.
- (3)
- Determine the average similarity criterion across all types of mining subsidence.
- (4)
- Calculate the proximity degree between the mining area in question and each type of mining subsidence. Following the principle of maximum proximity degree, identify the category to which the mining area belongs. Adopt the mining subsidence rock movement parameters corresponding to the determined mining subsidence category for the mining area under investigation.
3. Accuracy and Robustness Simulation of the Improved Modular Vector Method
3.1. Simulation Scheme
3.2. Accuracy Analysis of Parameter Inversion
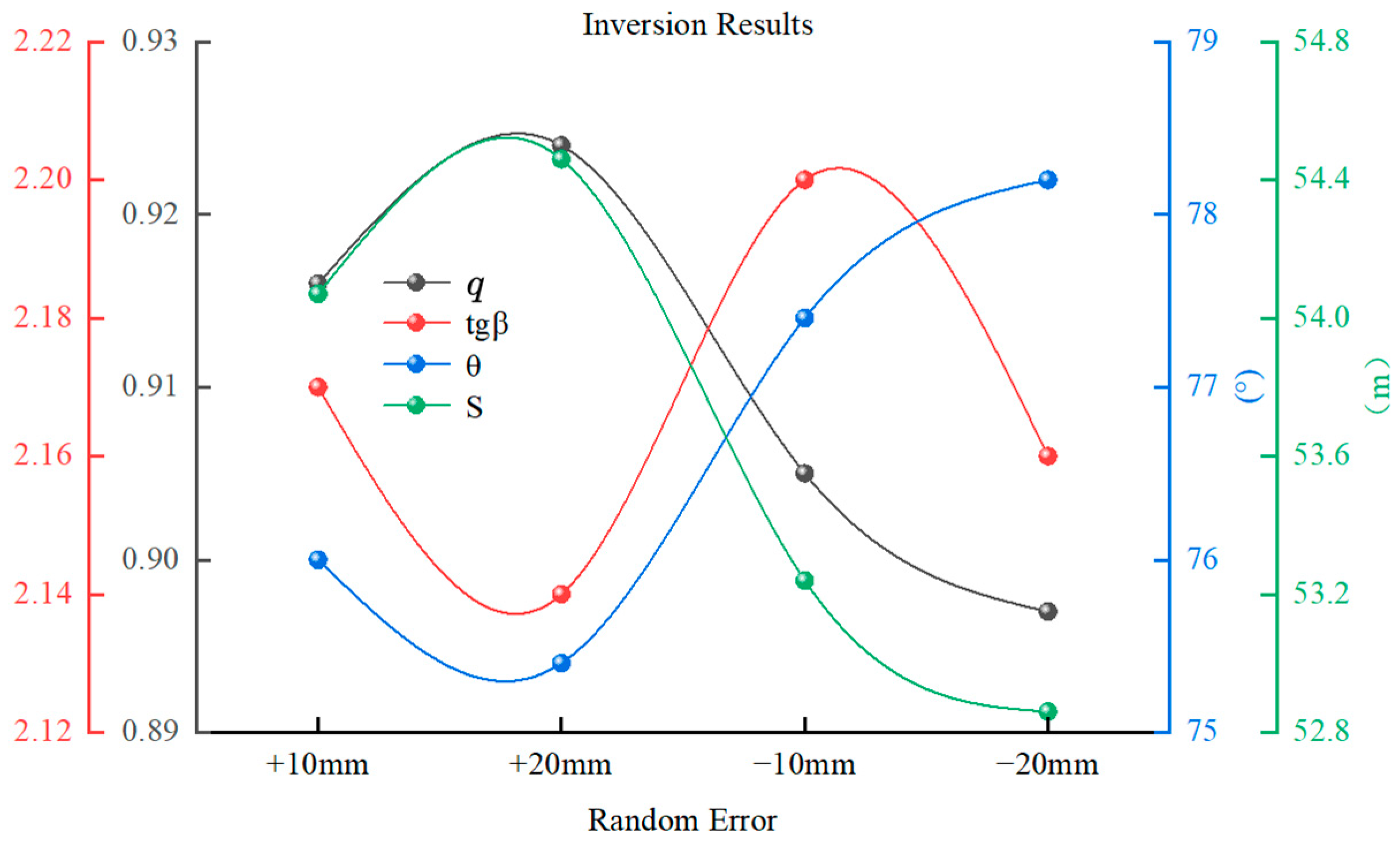
3.3. Analysis of Anti-Random-Error Interference Ability
3.4. Analysis of Anti-Gross-Error Interference Ability
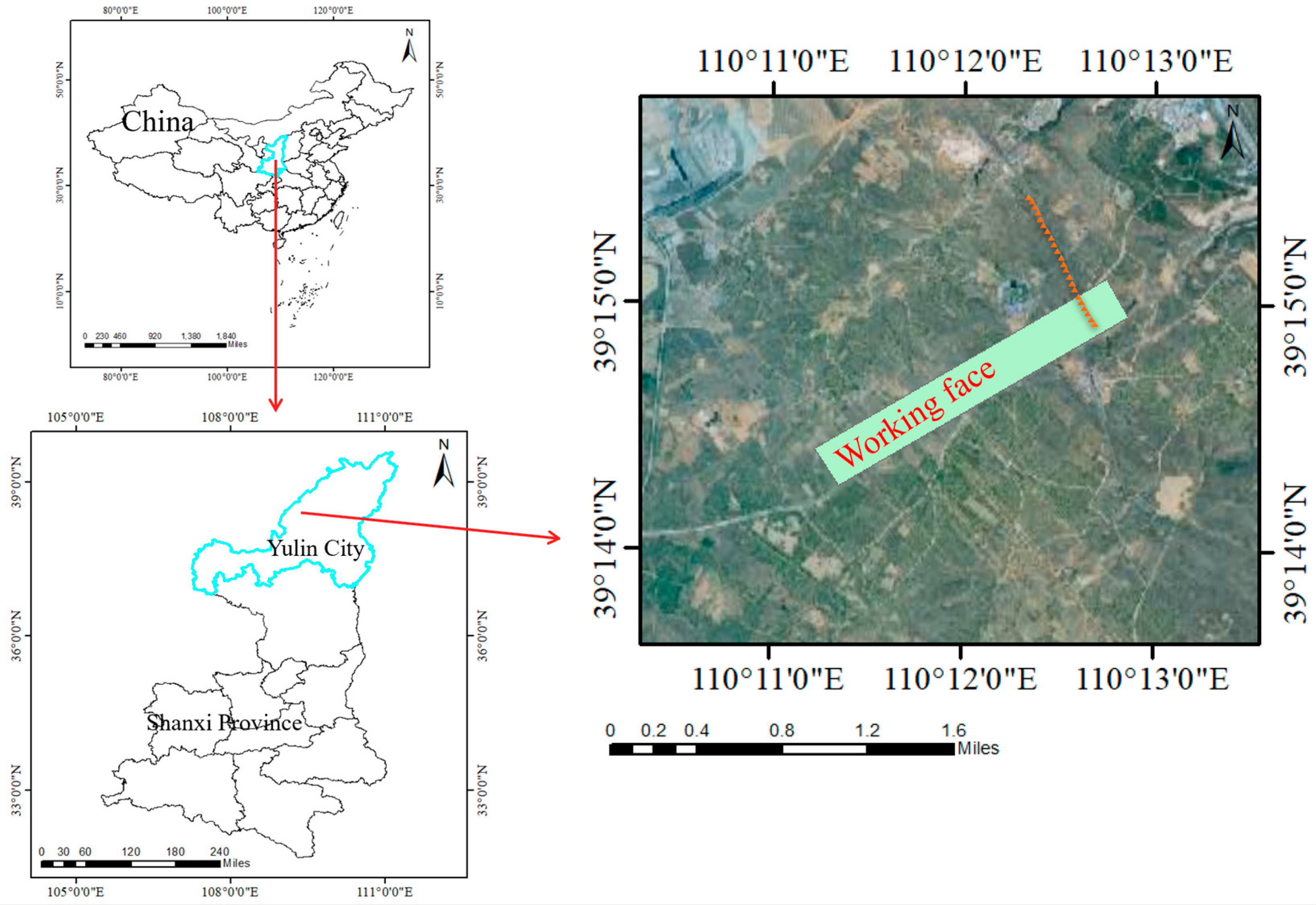
4. Engineering Example
4.1. Geological and Mining Conditions of the Working Face and Initial Exploration Value Acquisition for Parameter Inversion
4.2. Program Design for Parameter Inversion Algorithm
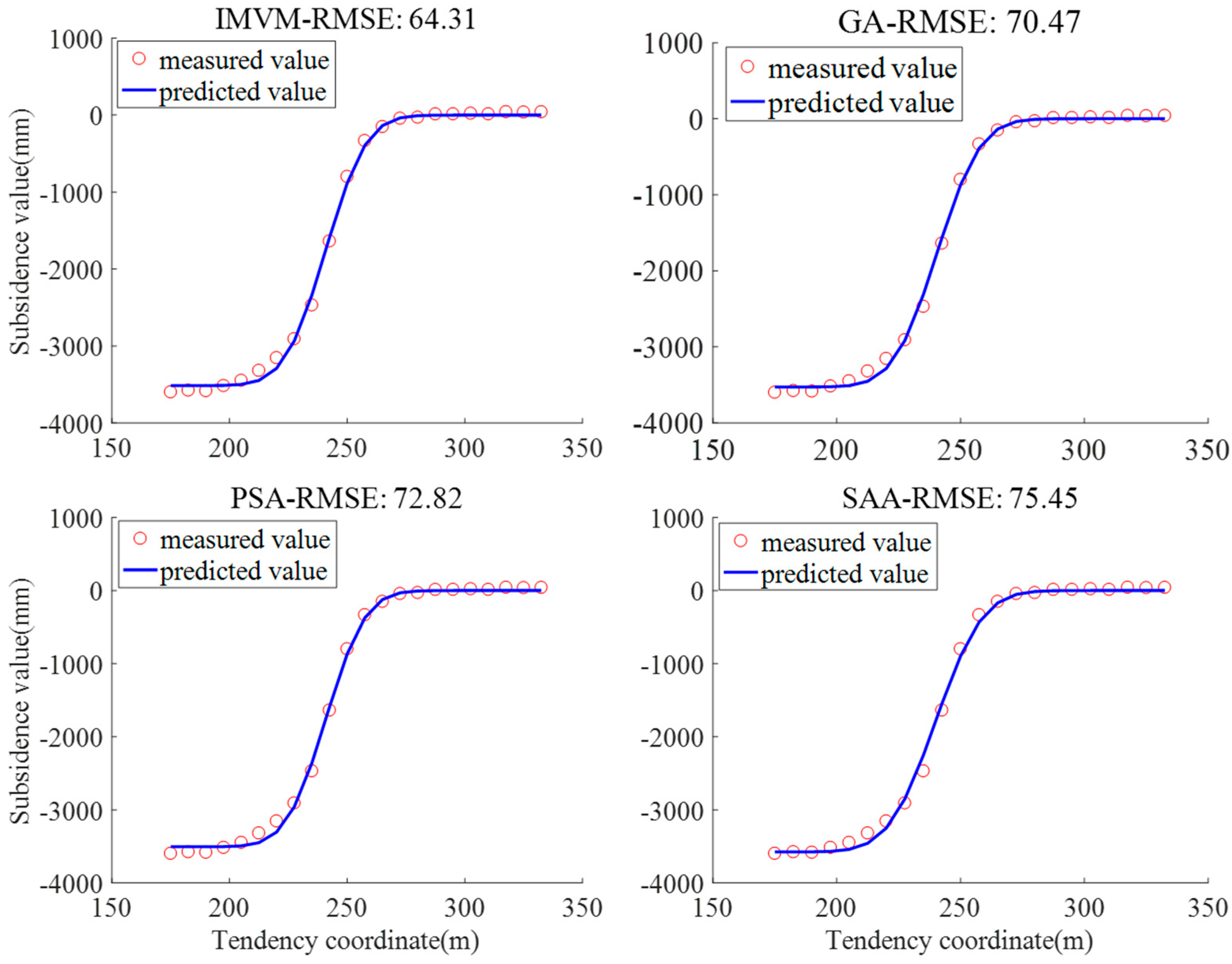
4.3. Accuracy Analysis of the Algorithms
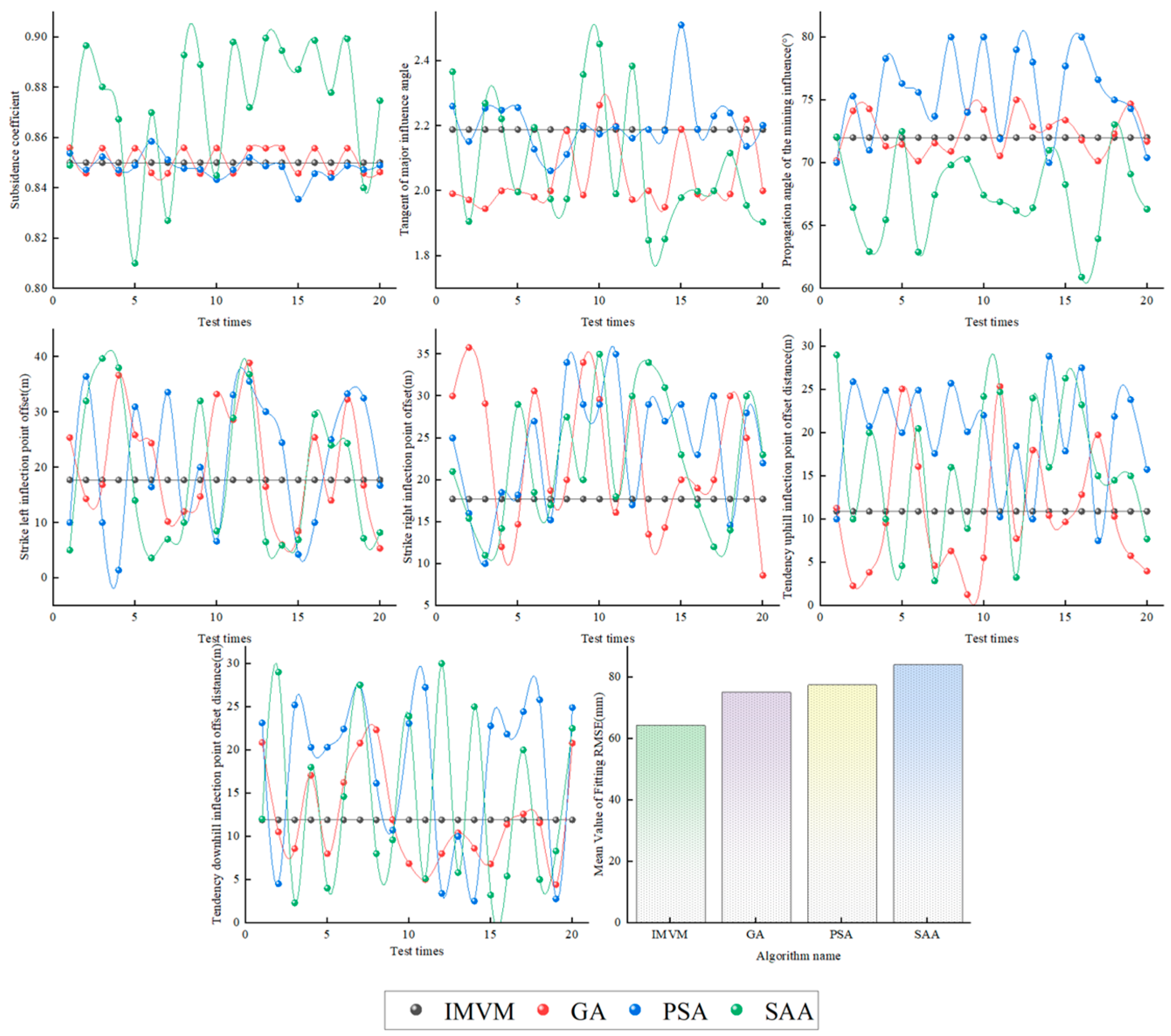
4.4. Stability Analysis of the Algorithm
4.5. Analysis of Algorithm Dependence on the Number of Measured Values
5. Discussion
5.1. Analysis of Simulation Test Results
5.2. Engineering Example Analysis
5.3. Influence of Parameter Selection
5.4. Stability and Reliability of Results
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The improved modular vector method, which incorporates pattern recognition techniques for initial parameter estimation, demonstrated superior accuracy and reliability compared to other intelligent algorithms, such as GA, PSA, and SAA. The root mean square error of the improved method was only 1.79% of the measured maximum subsidence value, validating its accuracy.
- (2)
- The algorithm exhibited robustness against both random and gross error in the measured data. Even in the presence of significant errors, the relative errors of the inverted parameters remained within acceptable limits, highlighting the method’s ability to mitigate data-related uncertainties.
- (3)
- The stability analysis revealed that the improved modular vector method maintained consistent parameter inversion results across multiple experiments, in contrast to other algorithms, which exhibited more significant fluctuations. This stability enhances the method’s reliability and practicality in real-world applications.
- (4)
- The method displayed reduced sensitivity to the number of measured values, making it less dependent on data availability. This characteristic allows for the reduction in observation points in challenging field conditions without sacrificing accuracy, thereby lowering the workload and maintaining result accuracy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bian, Z.; Miao, X.; Lei, S.; Chen, S.-E.; Wang, W.; Struthers, S. The Challenges of Reusing Mining and Mineral-Processing Wastes. Science 2012, 337, 702–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rošer, J.; Potočnik, D.; Vulić, M. Analysis of Dynamic Surface Subsidence at the Underground Coal Mining Site in Velenje, Slovenia through Modified Sigmoidal Function. Minerals 2018, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamich, D.; Marschalko, M.; Yilmaz, I.; Bednářová, P.; Niemiec, D.; Kubečka, K.; Mikulenka, V. Subsidence measurements in roads and implementation in land use plan optimisation in areas affected by deep coal mining. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 75, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Guo, G.; Zha, J.; Chen, T.; Fang, Q.; Yang, X. Surface dynamic subsidence prediction model of solid backfill mining. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.Q.; Yang, L. Mining Subsidence; China University of Mining and Technology Press: Xuzhou, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.C.; Dai, H.Y. Research Development and Origin of Probability Integral Method. J. Min. Strat. Control Eng. 2016, 21, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, G.L.; Wang, Y.J. Study of Robust Determining Parameters Model for Probability integral Method and its Application. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2000, 29, 162–165+171. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; Xu, L.J.; Liu, Z.; Qin, C.C. Calculating on the Prediction Parameters of Mining Subsidence with Probability Integral Method Based on Matlab. Met. Mine 2015, 9, 170–174. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.X.; Liu, C.; Feng, X.; Lu, Q.; Wang, D. Comparisons and analyses of several optimization methods in the application of frequency-domain full waveform inversion. Prog. Geophys. 2013, 28, 2060–2068. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.G.; Liu, J.X.; Li, G.; Liu, P.M. One-dimentional inversion of marine controlled-source electromagnetic fields. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2013, 23, 2551–2556. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, J.F.; Jia, X.G.; Guo, G.L. Uniform Design Method for Initial Value Selection in Parameter Determination by Probability-Integral Method. Met. Mine 2006, 11, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, J.F.; Feng, W.K.; Zhu, X.J. Reseash on Parameters Inversion in Probability Integral Method by Genetic Algorithm. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2011, 28, 655–659. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, D.; Wu, J. Application of Pattern Search Method in Deterning Surface Movement Parameters of Thick Loose Bed. Surv. Mapp. Geol. Miner. Resour. 2014, 30, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, H.Z.; Tan, X.F.; Song, B.Z.; Li, C.X.; Sun, L.L. Inversion of parameters of probability integral method based on the combination of genetic algorithm and pattern search. China Min. Mag. 2020, 29, 151–155+160. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, L.; Wei, T.; Chi, S.S.; Fang, S.Y.; Guo, Q.B. Identification Method of the Goaf’s Parameters in Guqiao Mine Based on Pattern Search Method. Met. Mine 2018, 8, 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Aivaliotis-Apostolopoulos, P.; Loukidis, D. Swarming genetic algorithm: A nested fully coupled hybrid of genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.Q.; Zha, J.F.; Li, H.Z. Parameters Inversion in Probability Integral Method by Particle Swarm Optimization. Coal Eng. 2015, 47, 117–119+123. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhang, L.Y.; Chen, H. Parameter Inversion of Probability Integral Method Based on P-SA-PSO Algorithm. Geomat. Spat. Inf. Technol. 2023, 46, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Zhang, H.; Fan, H.; Zheng, C.; Liu, J. Position Inversion of Goafs in Deep Coal Seams Based on DS-InSAR Data and the Probability Integral Methods. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, N.; Zhang, X.N.; Wei, T.; Chen, Y.F.; Zha, J.F. Full parameters inversion model for mining subsidence prediction using simulated annealing based on single line of sight D-InSAR. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Guo, G.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y. Fusing Minimal Unit Probability Integration Method and Optimized Quantum Annealing for Spatial Location of Coal Goafs. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2022, 26, 2381–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, C.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y. The invasive weed optimization–based inversion of parameters in probability integral model. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, K.; Wei, T.; Jiang, C.; Zha, J.; Chi, S. Estimation of parameters of probability integral method model based on improved fireworks algorithm. Surv. Rev. 2020, 53, 366–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, T.; Chen, L.; Liao, W.; Shi, Y.; Xu, D.; Jung, H.-S. Probability Integral Method Parameter Determination by SBAS-InSAR Technology and GWO Algorithm. J. Sens. 2021, 2021, 9376711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Zhu, X.J. Mining Subsidence Prediction Parameter Inversion Based on Robust Genetic Algorithm. Met. Mine 2023, 8, 237–244. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, W.; Xu, L.J.; Zhang, K. SAAFC Model for Probability-integral Method Parameters Inversion. Met. Mine 2021, 4, 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.; Song, B.; Bo, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Lu, G. Extraction of Irregularly Shaped Coal Mining Area Induced Ground Subsidence Prediction Based on Probability Integral Method. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Chen, B.Q.; Wang, Z.S.; Gao, J.; Yu, H. Comparative Study on the Parameters of the Inversion Probability Integral Method with Different Intelligent Optimization Algorithms. Met. Mine 2021, 5, 149–159. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, H.B.; Zou, Y.F.; Guo, W.B. Determination of mining subsidence predicting parameters using fuzzy pattern recognition. J. China Coal Soc. 2005, 30, 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, F.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, H.; Xu, M.; Jan, N. Prediction Model of Mining Subsidence Parameters Based on Fuzzy Clustering. J. Math. 2022, 2022, 7827104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Kong, D.; Liu, Q.; Cai, H.; Chen, L. Study on law and prediction of surface movement and deformation in mountain area under repeated mining of shallow coal seam. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, R.; Wu, L.; Wu, H. Research on the Prediction Model of Mine Subsidence Based on Object-Oriented and Probability Integration Method. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 8107024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Guo, G.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Q.; Jiang, C. A novel probability integral method segmental modified model for subsidence prediction applicable to thick loose layer mining areas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 52049–52061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-J.; Kang, H.; Lee, K.; Kwon, S. A Pattern Search Method to Optimize Mars Exploration Trajectories. Aerospace 2023, 10, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, W.; Li, H.; Guo, G.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y. Surface Subsidence Prediction Method for Backfill Mining in Shallow Coal Seams with Hard Roofs for Building Protection. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Wang, M.; Zhu, W.; Fan, J.; Liu, M. Study on Height Development Characteristics of Water-Conducting Fracture Zone in Fully Mechanized Mining of Shallow Thick Coal Seam under Water. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Guo, G.L.; He, G.Q. The Influence of Missing Measuring Points on the Determination of Surface Movement Parameters. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 1995, 24, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.N.; Chen, Y.F.; Zha, J.F. Method of mining subsidence prediction parameters inversion based on D-InSAR LOS deformation. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2017, 46, 1159–1165+1180. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.W.; Peng, X.Q.; Ge, X. Probabilistic integral estimation parametekgr solution based on mould vector method. J. Heilongjiang Inst. Technol. 2019, 33, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Peng, D.; Tan, Z.; Deng, K. Study of probability integration method parameter inversion by the genetic algorithm. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2017, 27, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, W.; Ma, S.; Zhao, B. Inversion of Fracture Parameters in Anisotropic Coal Seam. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 660, 012102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.F.; Liu, K. A Novel Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Global Optimization. Comput Intell Neurosci 2016, 2016, 9482073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Tan, D.; Liu, L. Particle swarm optimization algorithm: An overview. Soft Comput. 2017, 22, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Guo, G. Multiple-Try Simulated Annealing Algorithm for Global Optimization. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 9248318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.R.; Dorea, C.C.Y. Simple conditions for the convergence of simulated annealing type algorithms. J. Appl. Probab. 2016, 35, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Category | (°) | /m | /m | /m | /m | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Empirical value | 0.90 | 2.14 | 78 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 |
| Initial exploration value | 0.85 | 2.00 | 75 | 15.5 | 15.5 | 15.5 | 15.5 |
| Exploration step size | 0.10 | 0.10 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Termination step size | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Category | (°) | /m | /m | /m | /m | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Empirical value | 0.90 | 2.14 | 78.0 | 14.00 | 14.00 | 14.00 | 14.00 |
| Inversion value | 0.91 | 2.18 | 76.7 | 13.75 | 13.75 | 13.25 | 12.90 |
| Relative error/% | 1.11 | 1.87 | 1.67 | 1.79 | 1.79 | 5.36 | 7.86 |
| Overlying Strata | Layer Thickness/m | Stability Coefficient | Delamination Deformation Modulus/MPa | Layered Mass Density /(g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loose layer | 12 | 0.7 | 360 | 1.80 |
| Fine sandstone | 8 | 4.5 | 2721 | 2.56 |
| Medium stone | 14 | 5.0 | 3095 | 2.59 |
| Silty sandstone | 10 | 7.8 | 5571 | 2.62 |
| Fine sandstone | 10 | 4.5 | 2721 | 2.56 |
| Silty sandstone | 8 | 7.8 | 5571 | 2.62 |
| Fine sandstone | 12 | 4.5 | 2721 | 2.56 |
| Medium stone | 14 | 5.0 | 3095 | 2.59 |
| Grit sandstone | 18 | 6.0 | 3900 | 2.63 |
| Silty sandstone | 4 | 7.8 | 5571 | 2.62 |
| upper coal | 3 | 2.0 | 1100 | 1.44 |
| Fine sandstone | 12 | 4.5 | 2721 | 2.56 |
| Medium stone | 12 | 5.0 | 3095 | 2.59 |
| 4 | 2.0 | 1100 | 1.44 | |
| Fine sandstone | 4 | 4.5 | 2721 | 2.56 |
| Category | I | II-1 | II-2 | II-3 | II-4 | II-5 | II-6 | III |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness degree | 0.562 | 0.702 | 0.783 | 0.948 | 0.946 | 0.859 | 0.745 | 0.838 |
| Category | (°) | /m | /m | /m | /m | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial exploration value | 0.85 | 2.00 | 75 | 20 | 20 | 15 | 15 |
| Exploration step size | 0.10 | 0.10 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Termination step size | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Category | (°) | /m | /m | /m | /m | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower limit of value | 0.50 | 1.00 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Upper limit of value | 1.00 | 3.00 | 90 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| Category | (°) | /m | /m | /m | /m | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower limit of value | 0.50 | 1.00 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Upper limit of value | 1.00 | 3.00 | 90 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| Max flight speed | 0.1 | 0.1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Category | (°) | /m | /m | /m | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial exploration value | 0.85 | 2.00 | 75 | 20 | 20 | 15 | 15 |
| Inversion value | 0.85 | 2.18 | 72 | 17.7 | 17.7 | 10.9 | 11.9 |
| Relative error/% | 0.00 | 9.00 | 4.00 | 11.5 | 11.5 | 27.3 | 20.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chai, H.; Xu, M.; Guan, P.; Ding, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhao, Y. Research on Mining Subsidence Prediction Parameter Inversion Based on Improved Modular Vector Method. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 13272. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132413272
Chai H, Xu M, Guan P, Ding Y, Xu H, Zhao Y. Research on Mining Subsidence Prediction Parameter Inversion Based on Improved Modular Vector Method. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(24):13272. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132413272
Chicago/Turabian StyleChai, Huabin, Mingtao Xu, Pengju Guan, Yahui Ding, Hui Xu, and Yuqiao Zhao. 2023. "Research on Mining Subsidence Prediction Parameter Inversion Based on Improved Modular Vector Method" Applied Sciences 13, no. 24: 13272. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132413272
APA StyleChai, H., Xu, M., Guan, P., Ding, Y., Xu, H., & Zhao, Y. (2023). Research on Mining Subsidence Prediction Parameter Inversion Based on Improved Modular Vector Method. Applied Sciences, 13(24), 13272. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132413272




