Femtosecond Pulsed Laser Irradiation of Zirconia for Embedding Silver Nanoparticles in Surface Nanopores
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
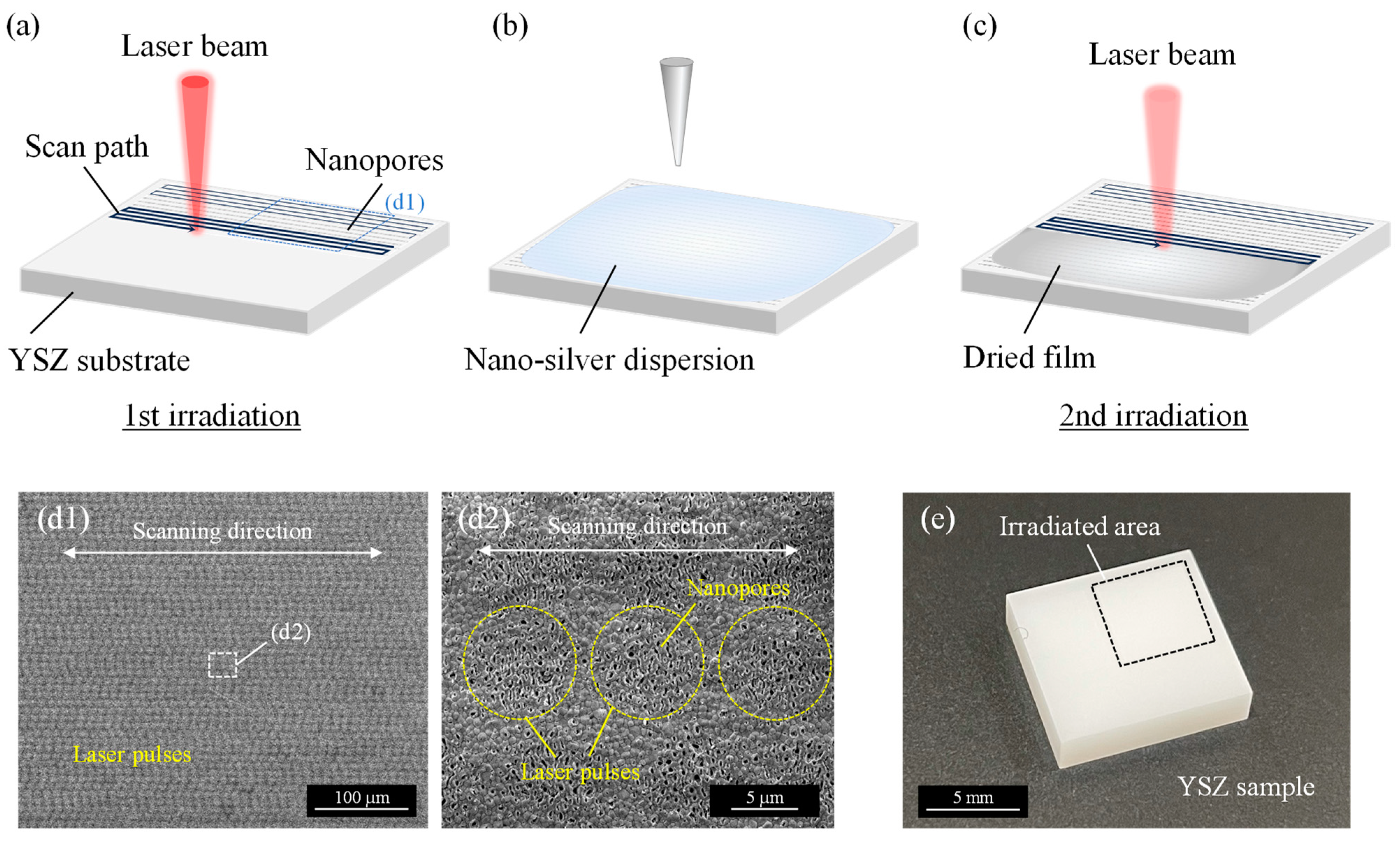
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
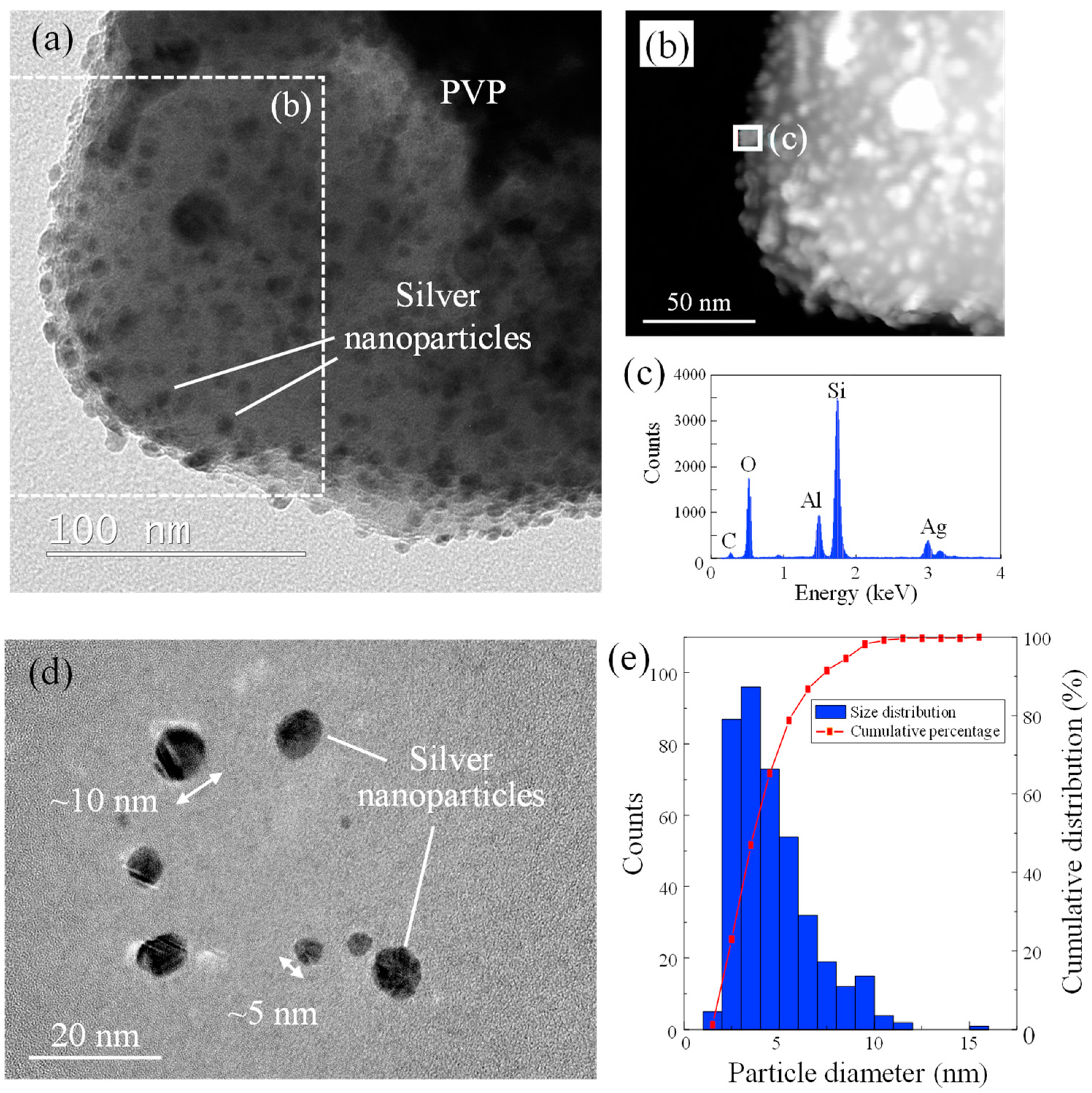
3.1. Characteristics of Nano-Silver Dispersion
3.2. Surface Morphology
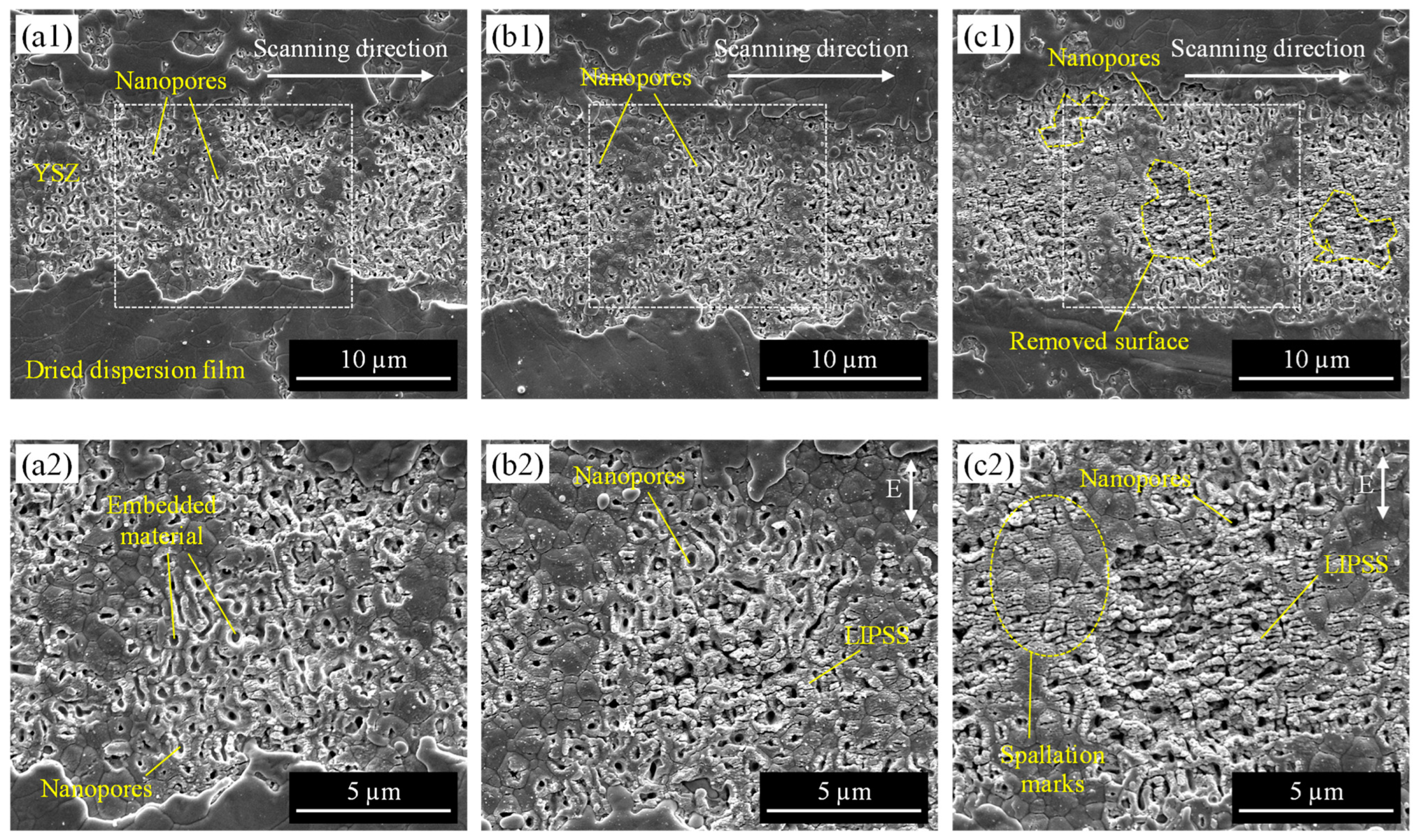
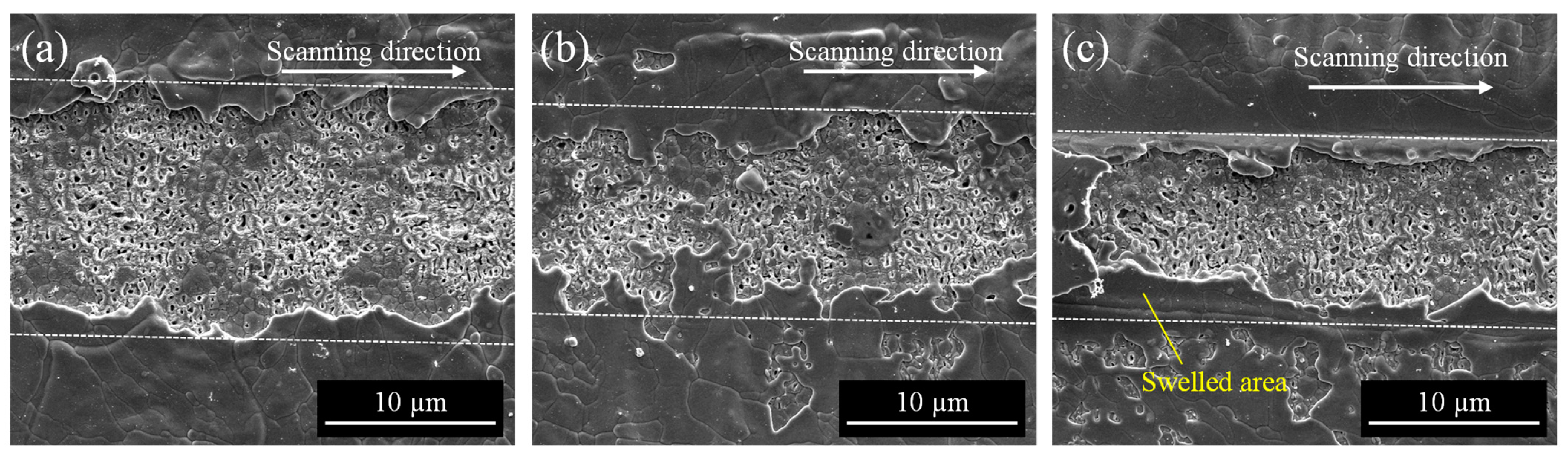
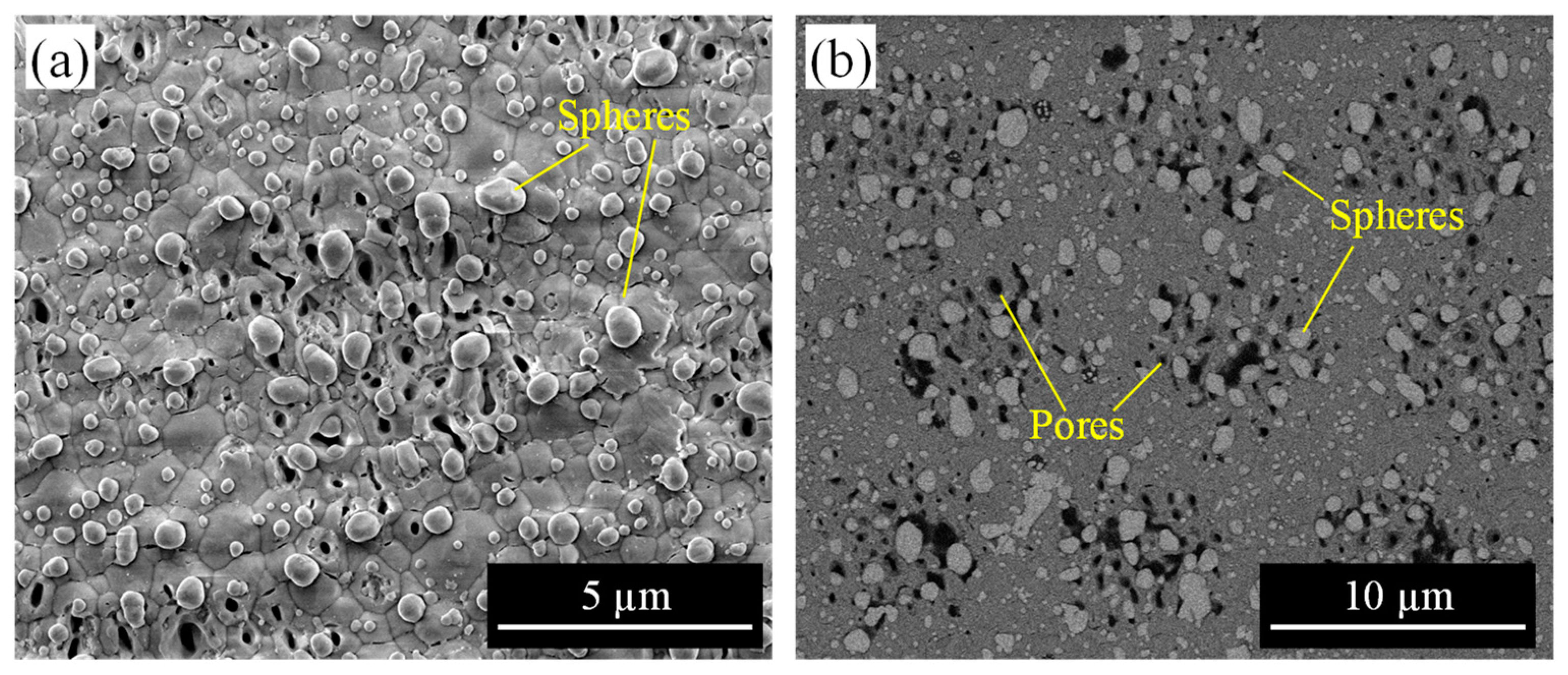
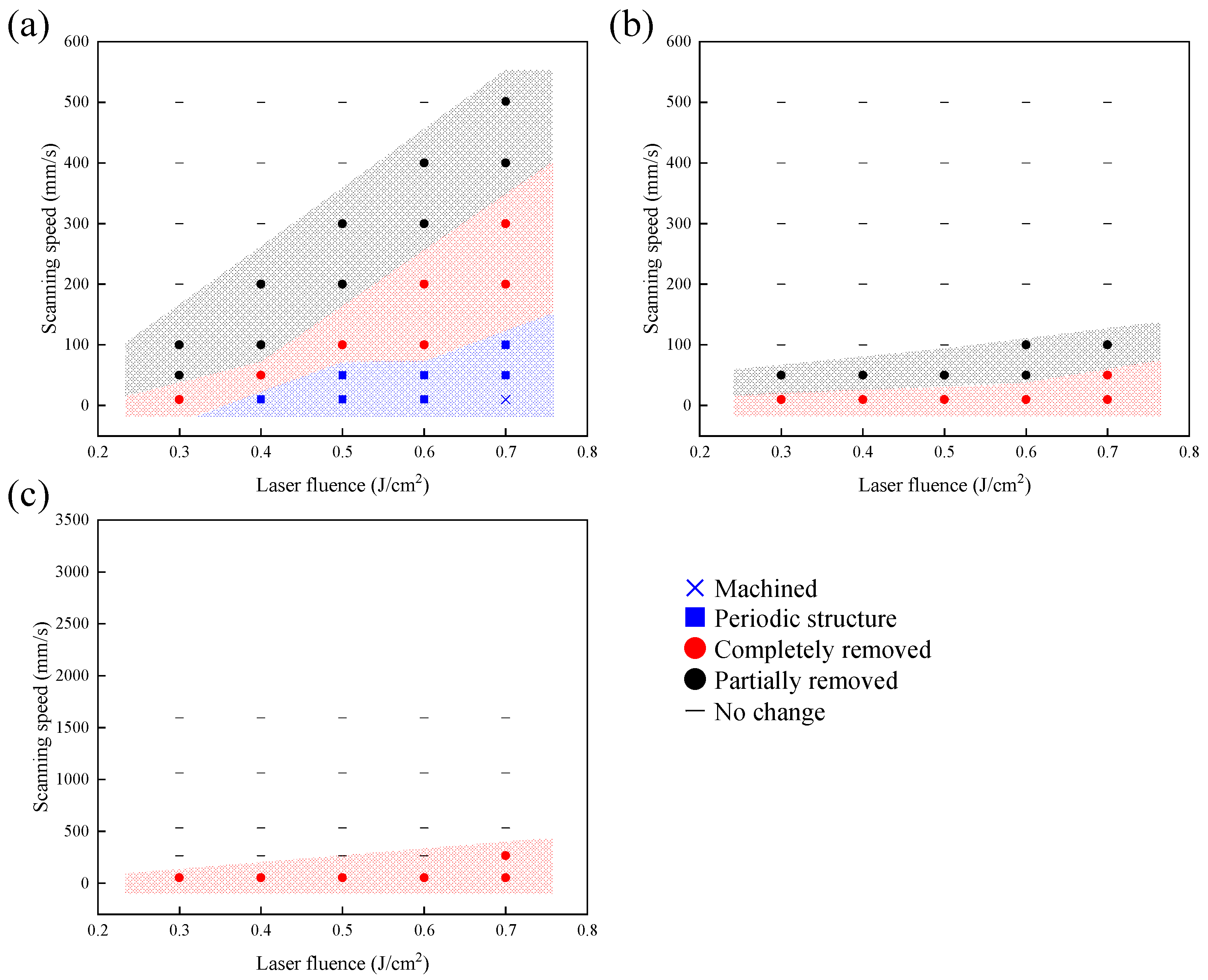
3.2.1. Effect of Laser Fluence and Scanning Speed
3.2.2. Effect of Pulse Width
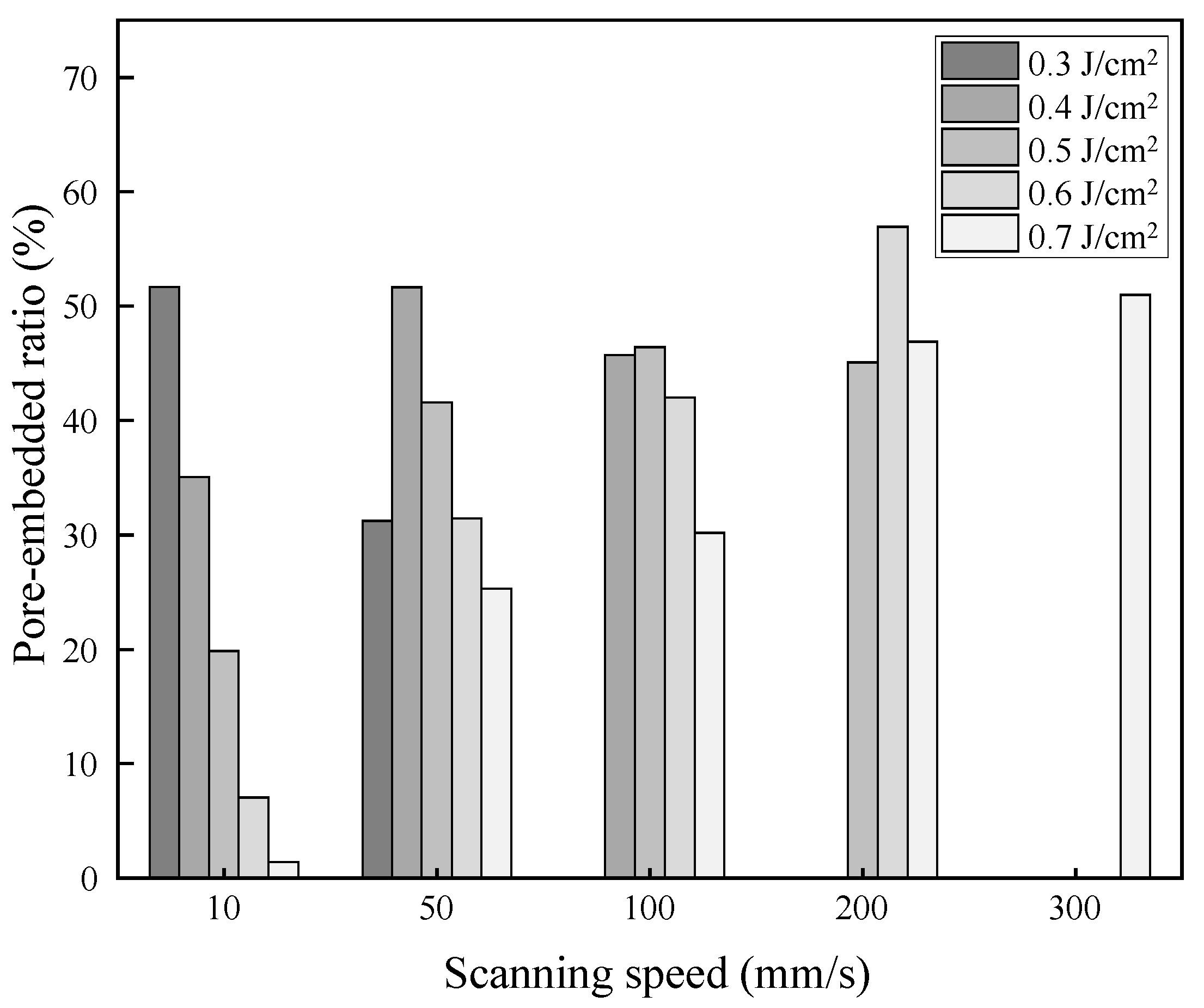
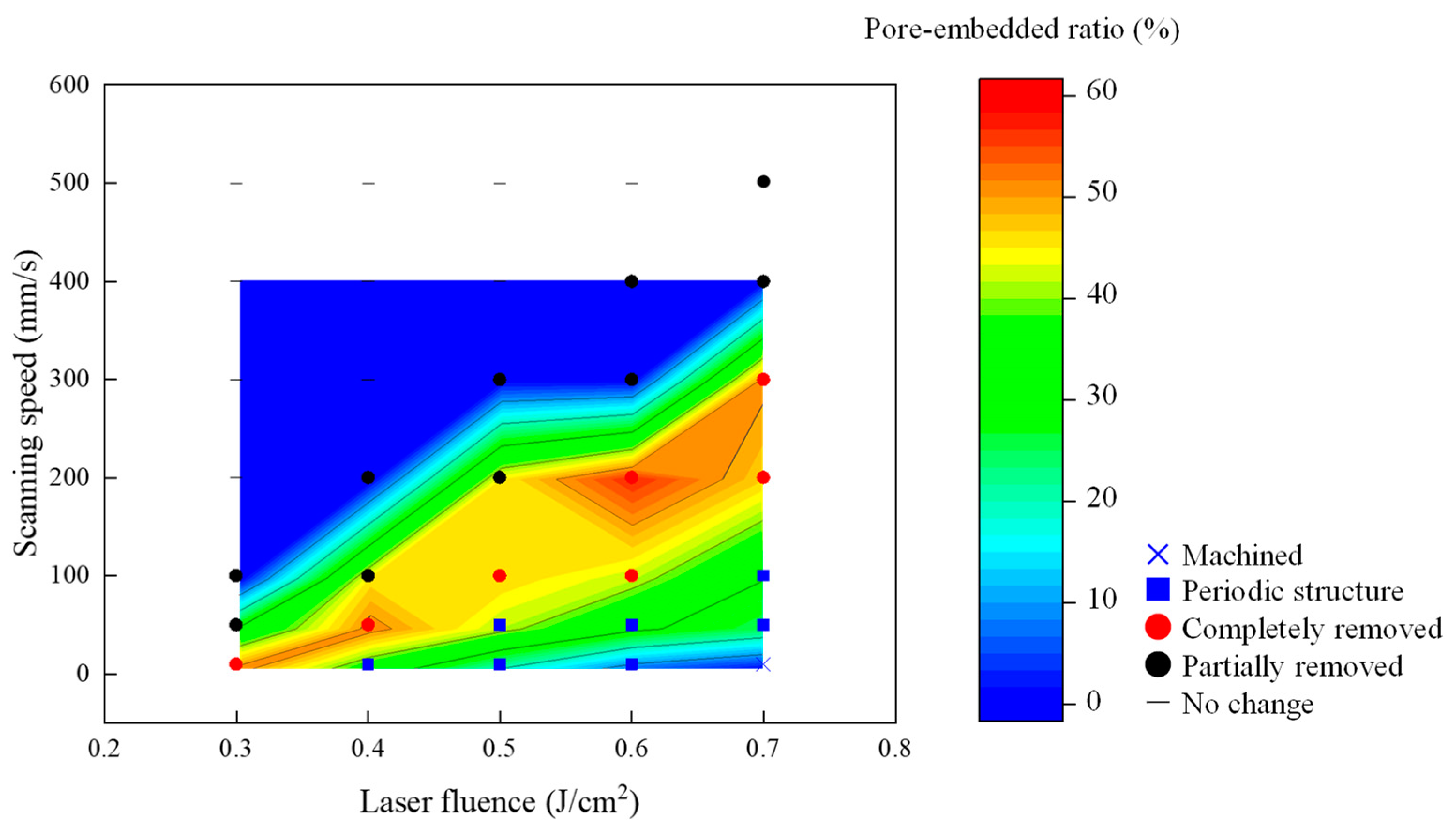
3.3. Pore-Embedded Ratio
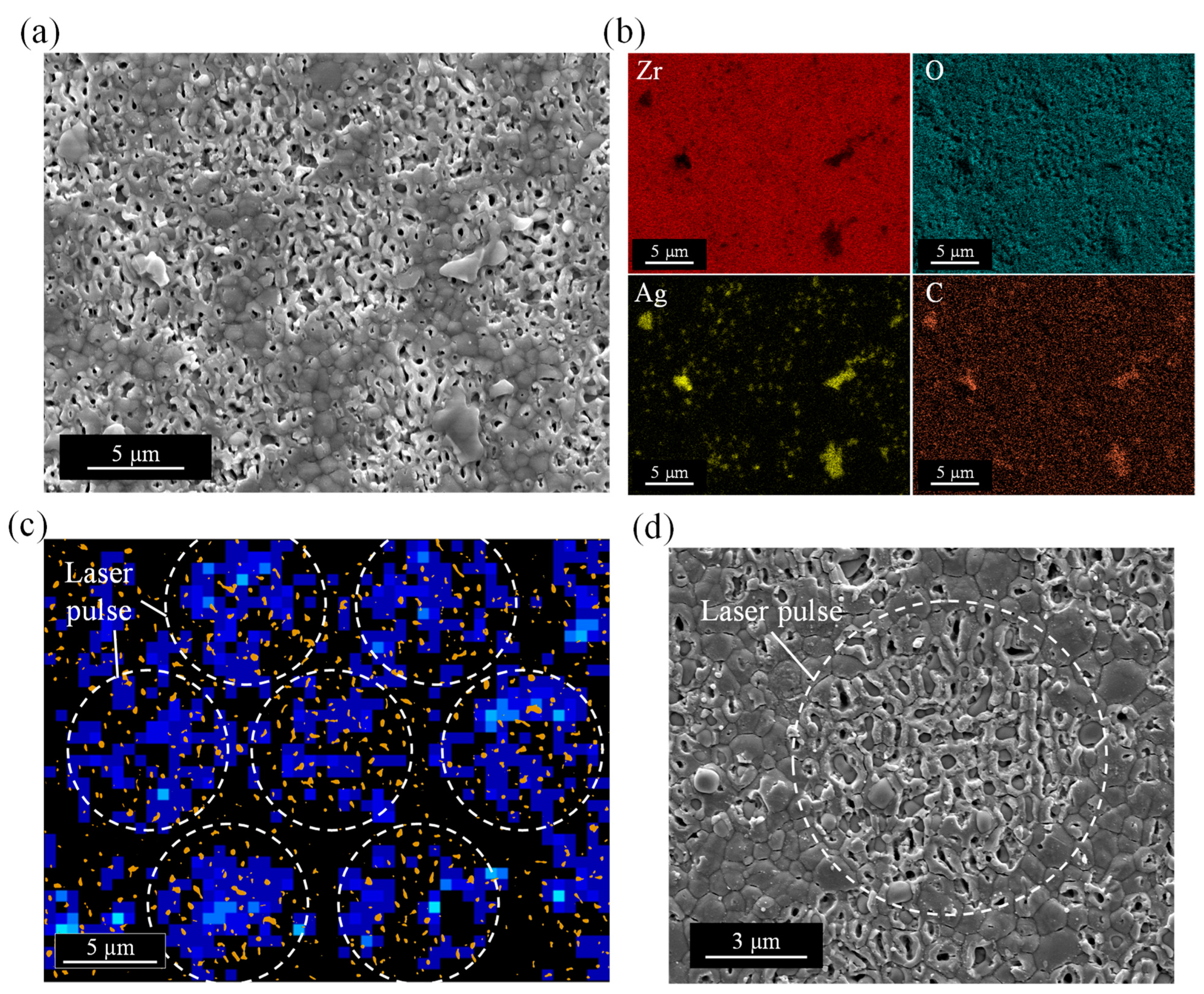
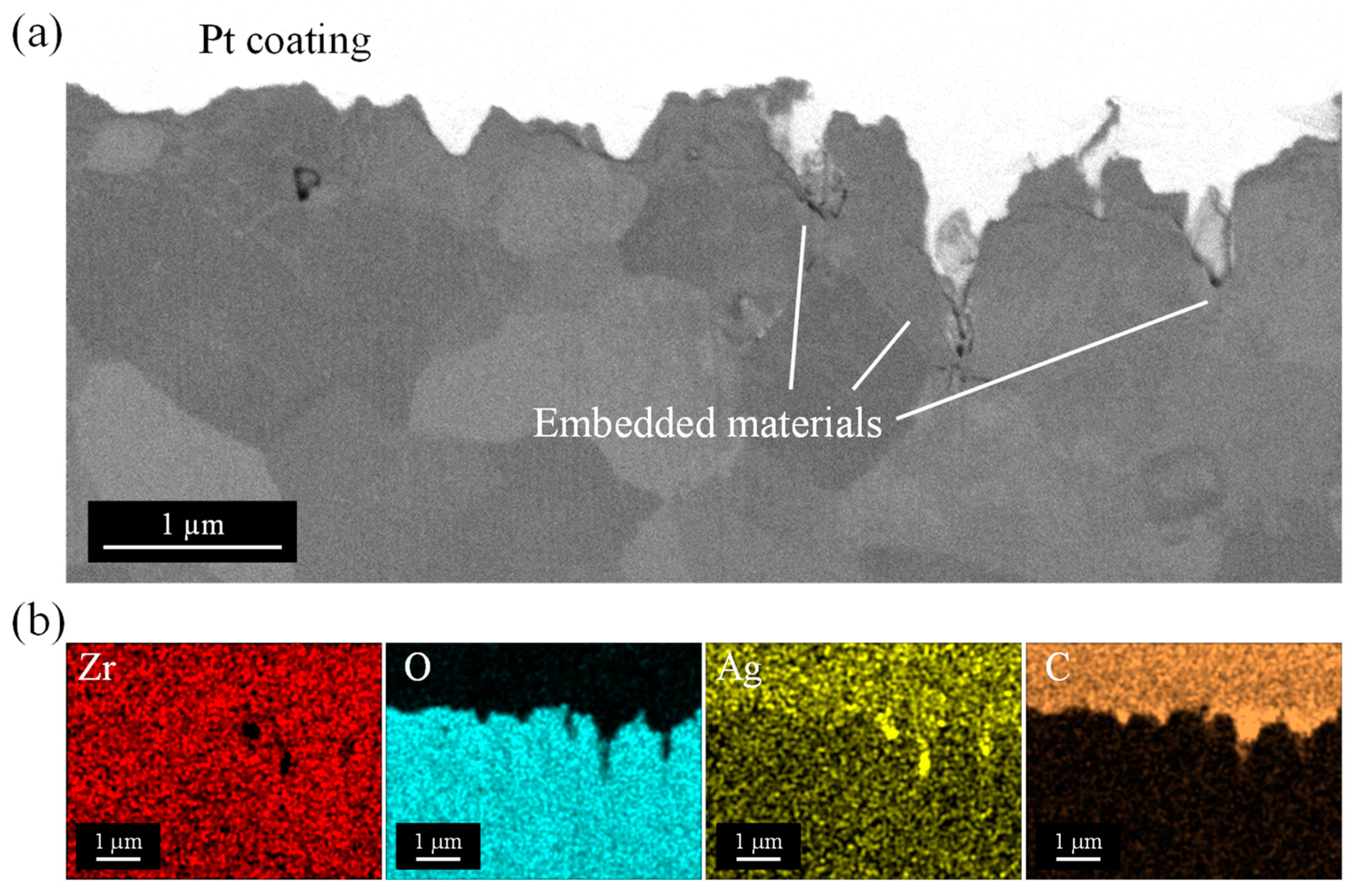
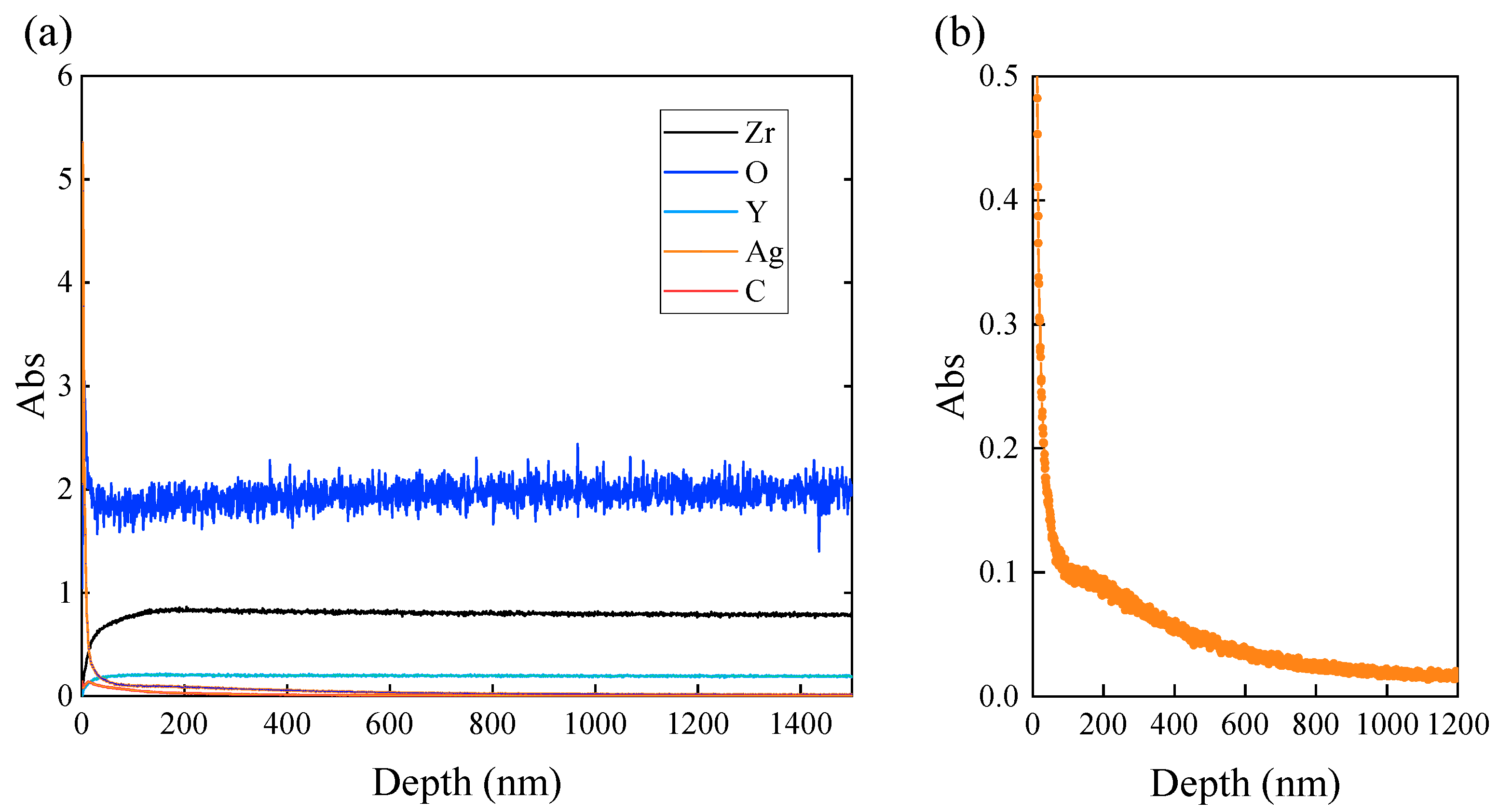
3.4. Cross-Sectional Structures
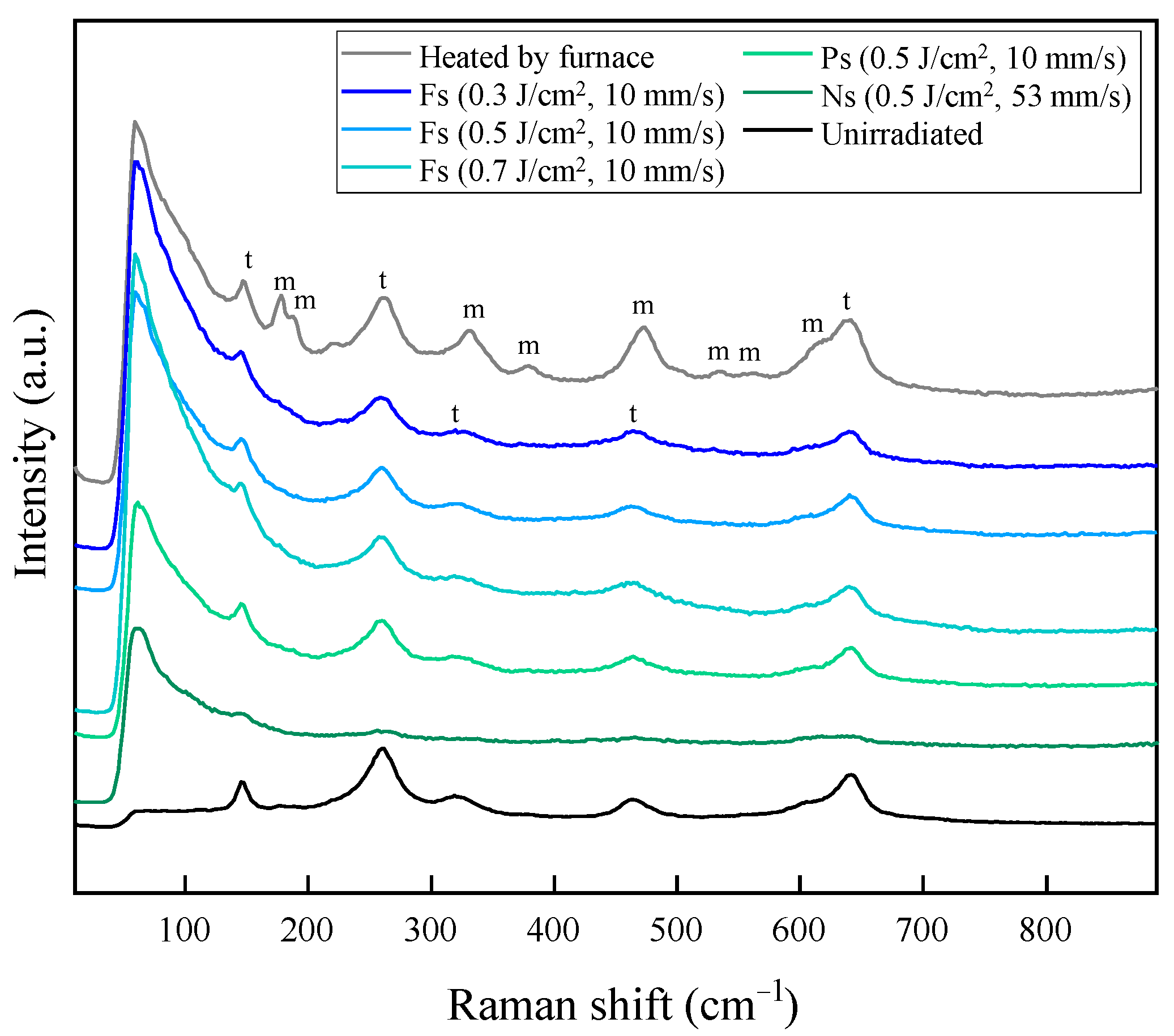
3.5. Material Phase Analysis
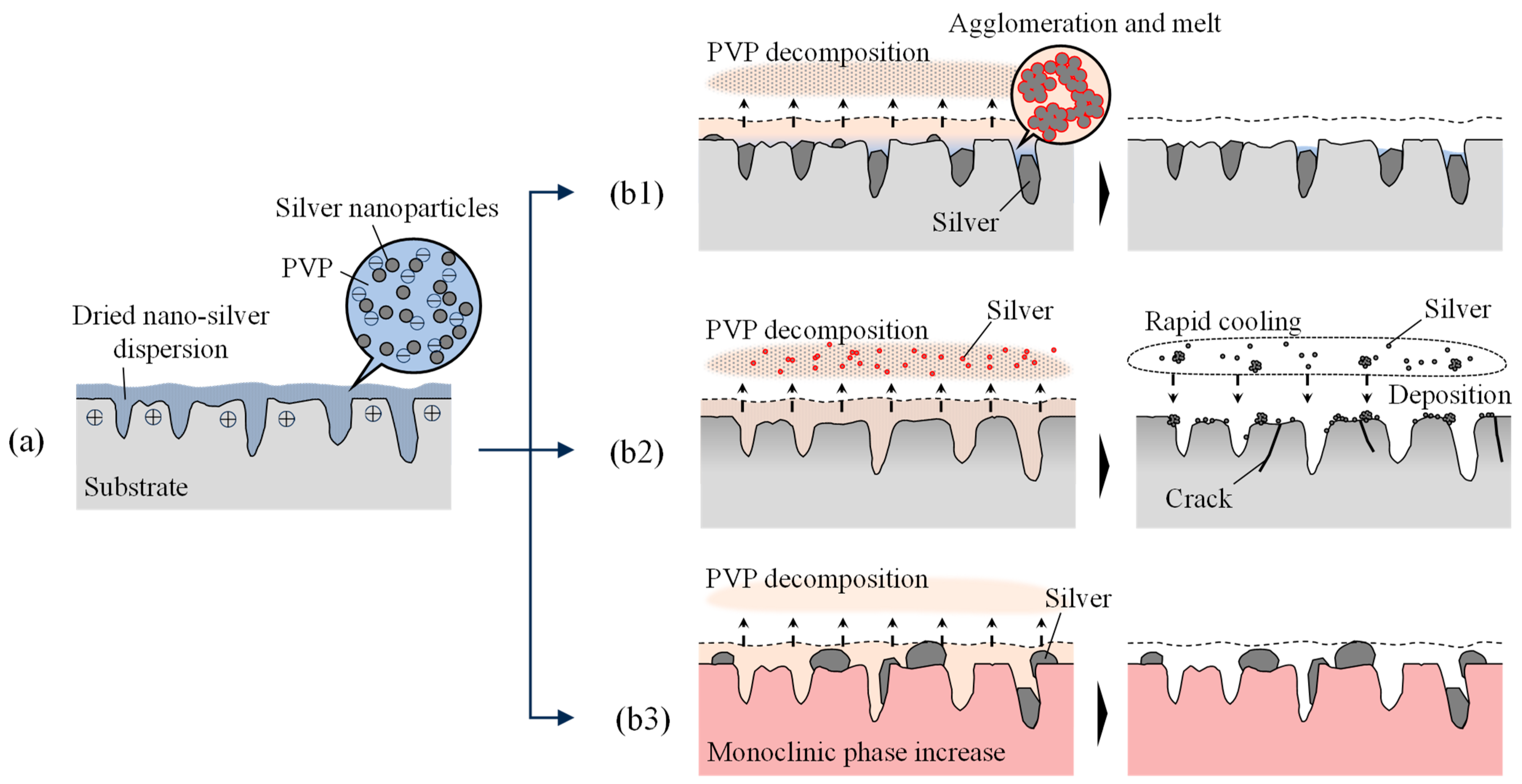
3.6. Mechanism of Silver Implantation
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Silver nanoparticles were successfully embedded in nanopores generated by irradiating a YSZ substrate with a femtosecond pulsed laser, by dropping a commercially available nano-silver dispersion into the pores and re-irradiating the laser.
- (2)
- By irradiating at the fluence in a limited range much lower than the ablation threshold, the polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) polymer dispersant remaining on the outer surface of the nanopores was selectively decomposed and removed. On the other hand, increasing the fluence at low scanning speeds caused delamination of the YSZ substrate surface and the formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures. Laser fluence and scanning speed interacted to embed silver in the pores while maintaining the grain shape of the substrate surface. The best conditions in this study were laser fluence of 0.6 J/cm2 and scanning speed of 200 mm/s, at which the silver implantation rate reached about 60%.
- (3)
- When the pulse width was increased, the substrate surface melted and a crack occurred due to the thermal effect. At the same time, not only the PVP but also silver was removed from both the surface and inside the pores, indicating that ultrashort pulses are suitable for maintaining the substrate surface morphology and silver loading.
- (4)
- The silver nanoparticles melted and agglomerated, forming large agglomerates inside the nanopores by laser irradiation while separated from the dispersant PVP. The silver was embedded to the bottom of the elongated pore, reaching a depth of approximately 600 nm from the surface.
- (5)
- The thermally induced tetragonal–to–monoclinic phase transformation was suppressed on the YSZ surface after embedding silver nanoparticles in the nanopore by using low laser fluence under the ablation threshold, indicating no thermal damage to the bulk.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garvie, R.C.; Hannink, R.H.; Pascoe, R.T. Ceramic Steel? Nature 1975, 258, 703–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Q.; Yong, J.; Du, G.; Si, J.; Yun, F.; Hou, X. Bioinspired Wetting Surface via Laser Microfabrication. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 6777–6792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; He, J. Recent Progress in Antireflection and Self-Cleaning Technology—From Surface Engineering to Functional Surfaces. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 94–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.J.; Ou, K.L.; Wang, C.C.; Huang, C.F.; Ruslin, M.; Sugiatno, E.; Yang, T.S.; Chou, H.H. Hybrid Micro/Nanostructural Surface Offering Improved Stress Distribution and Enhanced Osseointegration Properties of the Biomedical Titanium Implant. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 79, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schünemann, F.H.; Galárraga-Vinueza, M.E.; Magini, R.; Fredel, M.; Silva, F.; Souza, J.C.M.; Zhang, Y.; Henriques, B. Zirconia Surface Modifications for Implant Dentistry. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 1294–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, M.; Xu, J.; Chen, M.; El Mansori, M. Enhanced Hydrophilicity and Tribological Behavior of Dental Zirconia Ceramics Based on Picosecond Laser Surface Texturing. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 7161–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancy, P.; Jose, J.; Joy, N.; Valluvadasan, S.; Philip, R.; Antoine, R.; Thomas, S.; Kalarikkal, N. Fabrication of Silver-Decorated Graphene Oxide Nanohybrids via Pulsed Laser Ablation with Excellent Antimicrobial and Optical Limiting Performance. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furutani, M.; Fujii, E.; Ogura, K. Immobilization of Silver Nanoparticles on the Surface of Cellulose Nanofibers Using High-Pressure Wet-Type Jet Mill. J. Soc. Mater. Sci. 2021, 70, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Setyawati, M.I.; Leong, D.T.; Xie, J. Antimicrobial Silver Nanomaterials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 357, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachman, A.L.; Hofmeister, L.H.; Costa, L.; Boire, T.C.; Hwang, Y.S.; Hofmeister, W.H.; Sung, H.J. Femtosecond Laser-Patterned Nanopore Arrays for Surface-Mediated Peptide Treatment. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2014, 10, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losic, D.; Simovic, S. Self-Ordered Nanopore and Nanotube Platforms for Drug Delivery Applications. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 1363–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smielak, B.; Klimek, L. Effect of Hydrofluoric Acid Concentration and Etching Duration on Select Surface Roughness Parameters for Zirconia. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2015, 113, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriamporn, T.; Thamrongananskul, N.; Busabok, C.; Poolthong, S.; Uo, M.; Tagami, J. Dental Zirconia Can Be Etched by Hydrofluoric Acid. Dent. Mater. J. 2014, 33, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, H.G. Phase Relationships in the Zirconia-Yttria System. J. Mater. Sci. 1975, 10, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, T.K.; Lange, F.F.; Bechtold, J.H. Effect of Stress-Induced Phase Transformation on the Properties of Polycrystalline Zirconia Containing Metastable Tetragonal Phase. J. Mater. Sci. 1978, 13, 1464–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmač, T.; Oblak, Č.; Marion, L. The Effects of Dental Grinding and Sandblasting on Ageing and Fatigue Behavior of Dental Zirconia (Y-TZP) Ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigore, A.; Spallek, S.; Petschelt, A.; Butz, B.; Spiecker, E.; Lohbauer, U. Microstructure of Veneered Zirconia after Surface Treatments: A TEM Study. Dent. Mater. 2013, 29, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkar, S.; Pantawane, M.V.; Gu, J.J.; Ghoshal, A.; Walock, M.; Murugan, M.; Young, M.L.; Dahotre, N.; Berman, D.; Aouadi, S.M. Laser Surface Modification of Porous Yttria Stabilized Zirconia against CMAS Degradation. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 6038–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wei, J.; Ma, Z.; Song, P.; Ma, J.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yang, F.; Wang, X. The Fabrication of Micro/Nano Structures by Laser Machining. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, Y.V.; Li, X.; Sikorski, Z.; Davis, L.M.; Hofmeister, W. Single-Pulse Ultrafast-Laser Machining of High Aspect Nano-Holes at the Surface of SiO2. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 14411–14420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Kai, L.; Yang, Q.; Du, G.; Hou, X.; Chen, F. Laser Fabrication of Nanoholes on Silica through Surface Window Assisted Nano-Drilling (Swan). Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, D.; Crowder, S.W.; Hofmeister, L.; Costa, L.; Sung, H.J.; Hofmeister, W. Cell Interaction Study Method Using Novel 3D Silica Nanoneedle Gradient Arrays. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zamfirescu, M.; Ulmeanu, M.; Jipa, F.; Anghel, I.; Simion, S.; Dabu, R.; Ionita, I. Laser Processing and Characterization with Femtosecond Laser Pulses. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2010, 62, 594–609. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, T.; Yan, J. Generating Nanodot Structures on Stainless-Steel Surfaces by Cross Scanning of a Picosecond Pulsed Laser. Nanomanufacturing Metrol. 2020, 3, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaue, K.; Motoyama, H.; Hayashi, R.; Iwasaki, A.; Mimura, H.; Yamanouchi, K.; Shibuya, T.; Ishino, M.; Dinh, T.-H.; Ogawa, H.; et al. Surface Processing of PMMA and Metal Nano-Particle Resist by Sub-Micrometer Focusing of Coherent Extreme Ultraviolet High-Order Harmonics Pulses. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamuro, Y.; Shimoyama, T.; Yamashita, I.; Yan, J. Multiscale Surface Patterning of Zirconia by Picosecond Pulsed Laser Irradiation. J. Micro Nano-Manuf. 2020, 8, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, W.; Millon, E.; Vulliet, J.; Tabbal, M.; Thomann, A.; Semmar, N. Applied Surface Science Nano-Squares and Regular LIPSS on YSZ Coating by Picosecond UV Laser Beam: Thin Film Mediated and Direct Texturing. Appl. Surf. Sci. J. 2023, 623, 157110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakehata, M.; Yashiro, H.; Oyane, A.; Ito, A.; Torizuka, K. Pulsewidth Dependence of Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structure Formed on Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia Polycrystal. In Proceedings of the Frontiers in Ultrafast Optics: Biomedical, Scientific, and Industrial Applications XVI, San Francisco, CA, USA, 9 March 2016; Heisterkamp, A., Herman, P.R., Meunier, M., Nolte, S., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9740, p. 97401G. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamuro, Y.; Shimoyama, T.; Yan, J. Generation of Nanopore Structures in Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia by Femtosecond Pulsed Laser Irradiation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 1155–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijnendonckx, K.; Leys, N.; Mahillon, J.; Silver, S.; Van Houdt, R. Antimicrobial Silver: Uses, Toxicity and Potential for Resistance. Biometals 2013, 26, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Yang, L.; Cui, Y. Microneedles: Materials, Fabrication, and Biomedical Applications. Biomed. Microdevices 2023, 25, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turon-Vinas, M.; Anglada, M. Strength and Fracture Toughness of Zirconia Dental Ceramics. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Hohm, S.; Kirner, S.V.; Rosenfeld, A.; Kruger, J. Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures-A Scientific Evergreen. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2017, 23, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Kirner, S.V.; Höhm, S.; Epperlein, N.; Spaltmann, D.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J. Applications of Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures (LIPSS). In Proceedings of the Laser-based Micro- and Nanoprocessing XI, San Francisco, CA, USA, 17 February 2017; Klotzbach, U., Washio, K., Kling, R., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; Volume 10092, pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Bonse, J.; Gräf, S. Ten Open Questions about Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, A.; Yan, J. Response of Resin Coating Films Containing Fine Metal Particles to Ultrashort Laser Pulses. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2022, 23, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, D.; Liu, Q. The Influence of Nanosecond Laser Pulse Energy Density for Paint Removal. Optik 2018, 156, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzotti, G.; Porporati, A.A. Raman Spectroscopic Analysis of Phase-Transformation and Stress Patterns in Zirconia Hip Joints. J. Biomed. Opt. 2004, 9, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz Tabares, J.A.; Anglada, M.J. Quantitative Analysis of Monoclinic Phase in 3Y-TZP by Raman Spectroscopy. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 93, 1790–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, A.; Nagaki, Y.; Yoneyama, Y. Solvent Washing and Calcination for Effective PVP-Cap Removal on Pt Nanoparticles. Annu. Rep. Hydrog. Isot. Res. Cent. Univ. Toyama 2014, 34, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Rioux, R.M.; Song, H.; Grass, M.; Habas, S.; Niesz, K.; Hoefelmeyer, J.D.; Yang, P.; Somorjai, G.A. Monodisperse Platinum Nanoparticles of Well-Defined Shape: Synthesis, Characterization, Catalytic Properties and Future Prospects. Top. Catal. 2006, 39, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston-Thomas, H. The International Temperature Scale of 1990 (ITS-90). Metrologia 1990, 27, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Feng, Y.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G. Melting Behavior of Ag Nanoparticles and Their Clusters. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 111, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, T.; Hauer, M.; Phipps, C.R.; Wokaun, A. Fundamentals and Applications of Polymers Designed for Laser Ablation. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2003, 77, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Rong, M.Z.; Zhang, M.Q.; Liang, H.C.; Zeng, H.M. Laser Ablation of Polymer-Based Silver Nanocomposites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 187, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.C.; Qiao, Y.L.; Zhang, Q.; Du, X.; Zang, Y.; Liu, X.T.; Han, B.Y. Study on the Characteristics and Mechanism of Pulsed Laser Cleaning of Polyacrylate Resin Coating on Aluminum Alloy Substrates. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, F.; Busse, C.A.; Loehrke, R.I. The Vapor Pressure of Indium, Silver, Gallium, Copper, Tin, and Gold Between 0.1 and 3.0 Bar. Int. J. Thermophys. 1987, 8, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancy, P.; James, J.; Valluvadasan, S.; Kumar, R.A.V.; Kalarikkal, N. Laser–Plasma Driven Green Synthesis of Size Controlled Silver Nanoparticles in Ambient Liquid. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2018, 16, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, L.; Zhimin, Z.; Anchun, M.; Lei, L.; Jingchao, Z. Deposition of Silver Nanoparticles on Titanium Surface for Antibacterial Effect. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | (a) Nanopore Generation | (b) Fixation of Nanoparticles | (c) Fixation of Nanoparticles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser medium | Yb:KGW | Yb:KGW | Nd:YVO4 |
| Wavelength: λ [nm] | 1028 | 1028 | 532 |
| Spot size [μm] | 16 | 16 | 85 |
| Pulse width | 256 fs | 256 fs, 10 ps | 26 ns |
| Repetition frequency: f [kHz] | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Scanning speed: v [mm/s] | 1000 | 10~500 | 53~1593 |
| Laser power: E [mW] | 450 | 60~140 | 1.7 × 103~4.0 × 103 |
| Laser fluence: F [J/cm2] | 2.2 | 0.3~0.7 | 0.3~0.7 |
| Number of scans: N | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Atmosphere | Air | Air | Air |
| Parameters | (a) 0.4 J/cm2 | (b) 0.5 J/cm2 | (c) 0.7 J/cm2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average pore diameter [nm] | 125 ± 21 | 122 ± 16 | 128 ± 20 |
| Substrate Material | Substrate Structure | Embedding Material | Embedding Method | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | Cellulose nanofiber (CNF) | Nanofiber | Ag nanoparticle | High-pressure wet-type jet mill | [8] |
| (b) | Graphene oxide (GO) | Nanosheet | Ag nanoparticle | Laser ablation in GO suspension | [7] |
| (c) | Titanium | Polished flat surface | Ag nanoparticle | Deposition in silver nanoparticle solution | [49] |
| (d) | Fused silica | Nanopore arrays | Peptide | Adsorption | [10] |
| (e) | Yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) | Nanopores | Ag nanoparticle | Laser irradiation | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamamuro, Y.; Shimoyama, T.; Nagata, H.; Yan, J. Femtosecond Pulsed Laser Irradiation of Zirconia for Embedding Silver Nanoparticles in Surface Nanopores. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 13108. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132413108
Yamamuro Y, Shimoyama T, Nagata H, Yan J. Femtosecond Pulsed Laser Irradiation of Zirconia for Embedding Silver Nanoparticles in Surface Nanopores. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(24):13108. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132413108
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamamuro, Yuka, Tomotaka Shimoyama, Hiroya Nagata, and Jiwang Yan. 2023. "Femtosecond Pulsed Laser Irradiation of Zirconia for Embedding Silver Nanoparticles in Surface Nanopores" Applied Sciences 13, no. 24: 13108. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132413108
APA StyleYamamuro, Y., Shimoyama, T., Nagata, H., & Yan, J. (2023). Femtosecond Pulsed Laser Irradiation of Zirconia for Embedding Silver Nanoparticles in Surface Nanopores. Applied Sciences, 13(24), 13108. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132413108







