Standardizing Criteria for Calculating Urban Storm Drainage Flow Rates Using Basin Division Based on Aerial Photogrammetry: The Case Study of Culiacan, Mexico
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methods
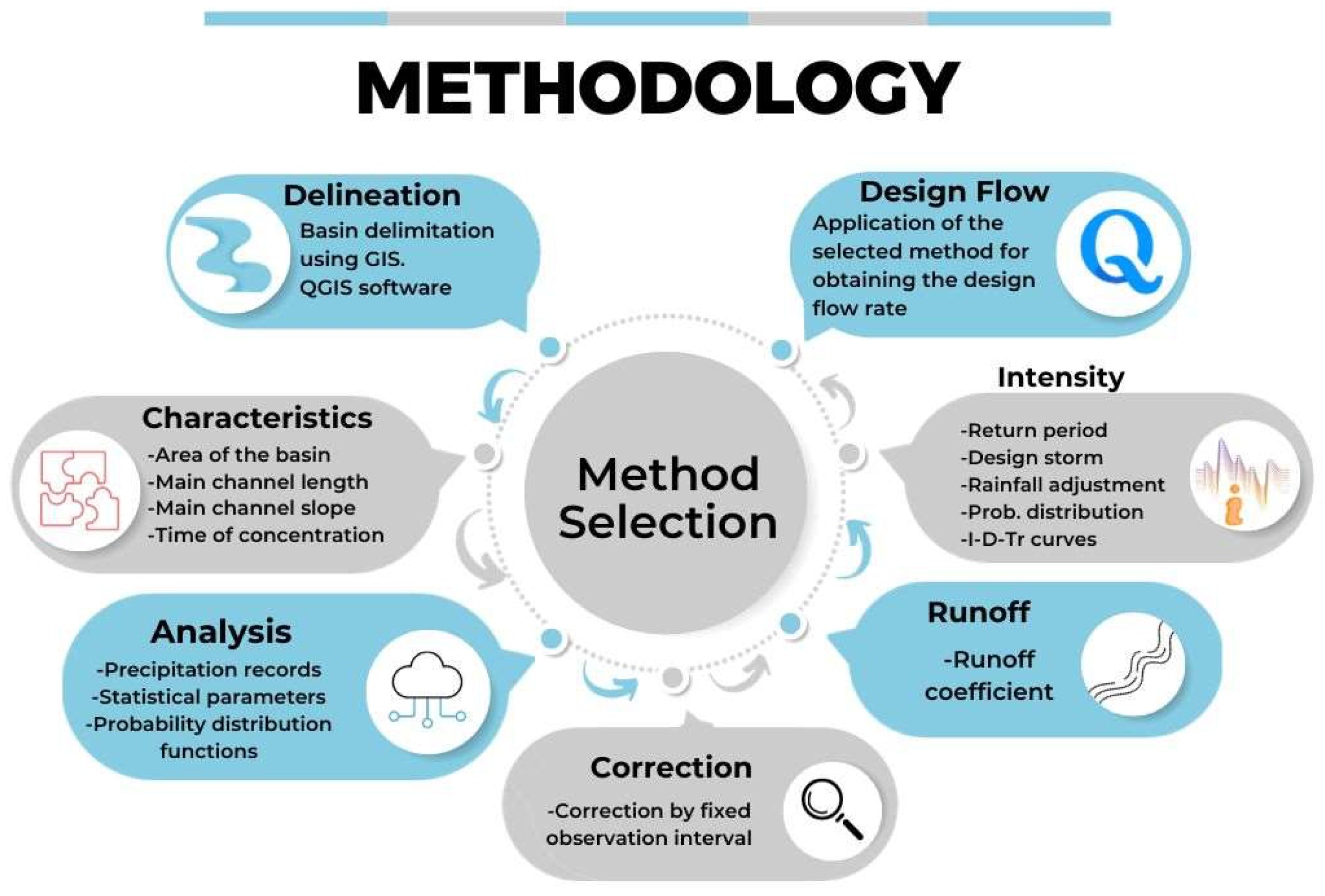
2.2.1. Methodology Overview
2.2.2. Basin Delineation Using GIS
2.2.3. Basin Morphological Characteristics
2.2.4. Analysis and Processing of Rainfall Records
2.2.5. Statistical Analysis and Probability in Hydrology
2.2.6. Correction Using Fixed Observation Interval
2.2.7. Runoff Coefficient
Intensity–Duration–Return Period (Frequency) (IDF) Curves
2.2.8. Design Flow
3. Results
3.1. Analysis and Processing of Precipitation Records
3.2. Mapping of Basin Divides and Flow Directions
3.3. Basin Delineation
3.4. Geomorphological Characterization
3.5. Determination of the Return Period
Determination of Runoff Coefficients
3.6. Estimation of IDF Curves
3.7. Determination of the Design Storm
3.8. Calculation of the Design Flow Rate
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bibi, T.S.; Reddythta, D.; Kebebew, A.S. Assessment of the Drainage Systems Performance in Response to Future Scenarios and Flood Mitigation Measures Using Stormwater Management Model. City Environ. Interact. 2023, 19, 100111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEMANAT Cuencas Hidrográficas. Fundamentos y Perspectivas Para Su Manejo y Gestión. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280938710_Cuencas_hidrograficas_Fundamentos_y_perspectivas_para_su_manejo_y_gestion (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- Diogo, A.F.; do Carmo, J.A. Peak Flows and Stormwater Networks Design—Current and Future Management of Urban Surface Watersheds. Water 2019, 11, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Muoz, M.M.; Bravo-Peia, L.C.; Aguilar-Villegas, J.M. Análisis Del Impacto de Eventos Hidrológicos Extraordinarios Mediante Modelización Hidrológica: Caso Culiacán Sinaloa; SELPER: Ciudad Juárez, Mexico, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dijk, E.; Van Der Meulen, J.; Kluck, J.; Straatman, J.H.M. Comparing Modelling Techniques for Analysing Urban Pluvial Flooding. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemczynowicz, J. Urban Hydrology and Water Management—Present and Future Challenges. Urban Water 1999, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yu, D.; Yin, Z.; Liu, M.; He, Q. Evaluating the Impact and Risk of Pluvial Flash Flood on Intra-Urban Road Network: A Case Study in the City Center of Shanghai, China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 537, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GeoEcoSphera S.C. Atlas de Peligros y/o Riesgos Del Municipio de Culiacán, Sinaloa, 1st ed.; GEOLMEX—Geología y Servicios de Ingeniería, Ed.; Gobierno de Culiacán: Culiacán, México, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Sun, Y.; Wendi, D.; Jiang, Z.; Liong, S.Y.; Gourbesville, P. Flood Modelling Framework for Kuching City, Malaysia: Overcoming the Lack of Data. Springer Water 2018, 1, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowska, J.; Menéndez Orellana, A.E.; Kilian, W.; Moryl, A.; Cielecka, N.; Michałowska, K.; Policht-Latawiec, A.; Michalski, A.; Bednarek, A.; Włóka, A. Between Flood and Drought: How Cities Are Facing Water Surplus and Scarcity. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UAS Estación Climatológica de la Facultad de Biología. Available online: https://www.uas.edu.mx/servicios/clima/ (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- Culiacán, A. Reglamento de Construcciones Para El Municipio de Culiacán, Sinaloa. Periodico Oficial del Estado de Sinaloa, 10 February 2021; 121. [Google Scholar]
- INEGI Hidrografía. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/temas/hidrografia/ (accessed on 27 May 2022).
- El Clima En Culiacán, El Tiempo Por Mes, Temperatura Promedio (México)—Weather Spark. Available online: https://es.weatherspark.com/y/3157/Clima-promedio-en-Culiac%C3%A1n-M%C3%A9xico-durante-todo-el-a%C3%B1o (accessed on 16 May 2023).
- SMN Resúmenes Mensuales de Temperaturas y Lluvia. Available online: https://smn.conagua.gob.mx/es/climatologia/temperaturas-y-lluvias/resumenes-mensuales-de-temperaturas-y-lluvias (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- GS Atlas de Riesgos Del Estado de Sinaloa. Available online: http://www.atlasnacionalderiesgos.gob.mx/AtlasEstatales/?&NOM_ENT=Sinaloa&CVE_ENT=25 (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- OMM. International Glossary of Hydrology Glossaire Intenational D’Hydrologie MEЖДУHAPOДHЫЙ ГИДPOЛOГИЧECKИЙ CЛOBAPЬ Glosario Hidrológico Internacional, 3rd ed.; Jarraud, M., Ed.; World Meteorological Organization (WMO): Geneve, Switzerland, 2012; ISBN 978-92-63-03385-8. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera Buelna, A. Delimitación de Una Cuenca Urbana Mediante Metodología Basada en Fotogrametría. Caso Cuenca en la Ciudad de Culiacán, Sinaloa, México. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Sinaloa, Culiacán, Sinaloa, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Aranda, D.F.C. Introducción a La Hidrología Urbana; Printego: San Luis Potosí, Mexico, 2010; ISBN 9709511815. [Google Scholar]
- CENAPRED. Guía Básica Para Elaboración de Atlas Estatales y Municipales de Peligros y Riesgos: Conceptos Básicos Sobre Peligros, Riesgos y Su Representación Geográfica, 1st ed.; Ramos Radilla, V., Ed.; Secretaría de Seguridad y Protección Ciudadana: Ciudad de México, México, 2006; ISBN 970-628-904-6.
- Flowers-Cano, R.S.; Ortiz-Gómez, R.; Burgos-Flores, D.; León-Jiménez, J.E.; Balladares-Sánchez, M.Á. Comparación de Cuatro Técnicas Para Seleccionar La Distribución de Probabilidad de Mejor Ajuste Para El Análisis de Datos de Precipitación Máxima Anual En México. J. Energy Eng. Optim. Sustain. 2017, 1, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parece, T.E.; Campbell, J.B. Identifying Urban Watershed Boundaries and Area, Fairfax County, Virginia. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2015, 81, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, F.; Andrieu, H.; Morena, F. A Distributed Hydrological Model for Urbanized Areas—Model Development and Application to Case Studies. J. Hydrol. 2008, 351, 268–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, P.V.N.; Amaro, V.E.; Silva, R.M.; Lopes, A.B. Delimitation of Flood Areas Based on a Calibrated a DEM and Geoprocessing: Case Study on the Uruguay River, Itaqui, Southern Brazil. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 19, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanhouse-García, A.J.; Gabriel Rangel-Peraza, J.; Rentería-Guevara, S.A.; Bustos-Terrones, Y.A.; Mora-Félix, Z.D.; Plata-Rocha, W.; Alberto Monjardin-Armenta, S. Flood-Prone Area Delineation in Urban Subbasins Based on Stream Ordering: Culiacan Urban Basin as a Study Case. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusineri, G.; Pedraza, R.; Lozeco, C. Uso de Modelos Digitales de Elevación y de Sistemas de Información Geográfica En La Modelación Hidrológica. Geog. Digit. 2005, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentería-Guevara, S.A.; Rangel-Peraza, J.G.; Rodríguez-Mata, A.E.; Amábilis-Sosa, L.E.; Sanhouse-García, A.J.; Uriarte-Aceves, P.M. Effect of Agricultural and Urban Infrastructure on River Basin Delineation and Surface Water Availability: Case of the Culiacan River Basin. Hydrology 2019, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentería-Guevara, S.A.; Rangel-Peraza, J.G.; Bustos-Terrones, Y.A.; Amábilis-Sosa, L.E.; Rodríguez-Mata, A.E. Hydrological Basins in Mexico: Divisions and Legal Definition; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 17–43. [Google Scholar]
- INEGI Hidrología. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/temas/hidrologia/#Mapa (accessed on 19 May 2023).
- Cisneros, S.; García, É.; Montoya, K.; Sinde, Í. Estudio de Las Configuraciones de Puntos de Control Terrestre Para Fotogrametría Con Drone. Rev. Geoespacial 2019, 16, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Felix, Z.D.; Sanhouse-Garcia, A.J.; Bustos-Terrones, Y.A.; Loaiza, J.G.; Monjardin-Armenta, S.A.; Rangel-Peraza, J.G. Effect of Photogrammetric RPAS Flight Parameters on Plani-Altimetric Accuracy of DTM. Open Geosci. 2020, 12, 1017–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robredo Sánchez, J.C.; Mintegui Aguirre, J.Á. Diseño de Un Modelo Distribuido Elemental Para El Análisis Del Comportamiento Hidrológico de Una Cuenca Vertiente. Ing. Agua 1994, 1, 79–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aparicio Mijares, F.J. Fundamentos de Hidrología de Superficie, 1st ed.; Editorial Limusa: México City, México, 2008; ISBN 139789681830144. [Google Scholar]
- Campos-Aranda, D.F. Calibración Del Método Del Coeficiente de Escurrimiento Para Estimación de La Disponibilidad Anual En Dos Zonas Geográficas de México. Ing. Hidráulica México 2009, 24, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, D.F. Identificación Del Número N Con Base En El Método Del HUT, En Quince Cuencas Rurales de Dos Zonas Geográficas de México. Agrociencia 2009, 43, 763–775. [Google Scholar]
- Mejía Marcacuzco, J.A. Probabilidad y Estadística En Hidrología, 1st ed.; Mejía Marcacuzco, J.A., Ed.; Universidad Nacional Agraria la Molina: Lima, Peru, 2017; Volume 1, ISBN 9786124147913. [Google Scholar]
- US COE 33 CFR § 222.6—National Program for Inspection of Non-Federal Dams. Electronic Code of Federal Regulations (e-CFR)|US Law|LII/Legal Information Institute. Available online: https://www.law.cornell.edu/cfr/text/33/222.6 (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- Weiss, L.L. Ratio of True to Fixed-Interval Maximum Rainfall. J. Hydraul. Div. 1964, 90, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMO. Manual on Estimation of Probable Maximum Precipitation (PMP): WMO-No. 1045, 2nd ed.; Stewart, B., Ed.; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009; Volume 1, ISBN 978-92-63-11045-9. [Google Scholar]
- Llabrés-Brustenga, A.; Rius, A.; Rodríguez-Solà, R.; Casas-Castillo, M.C. Influence of Regional and Seasonal Rainfall Patterns on the Ratio between Fixed and Unrestricted Measured Intervals of Rainfall Amounts. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2020, 140, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONAGUA Manual de Agua Potable, Alcantarillado y Saneamiento. Drenaje Pluvial Urbano, 1st ed.; Agua Potable, S.G., Ed.; CONAGUA: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2019; Volume 1, ISBN 978-607-626-019-7.
- García Páez, F.; Rentería Guevara, S.A. Evaluación de Riesgo Por Inundaciones En Cuencas Urbanas Con Base En Caracterización Morfométrica y Análisis de La Dirección Del Flujo de Agua Superficial. Caso de Estudio: Cuenca En Culiacán, Sinaloa, 1st ed.; Universidad Autónoma de Sinaloa: Culiacán, México, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Maidment, D.R. Handbook of Hydrology, 1st ed.; Maidment, D.R., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1993; ISBN 0070397325/9780070397323. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, F.C. Generalized Rainfall-Duration-Frequency Relationship Applicability in Different Climatic Regions of Argentina. J. Hydrol. Eng. 1969, 9, 311–327. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C. Rainfall Intensity-Duration-Frequency Formulas. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1983, 109, 1603–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, A.K. Impact of Urbanization on the Hydrology of Ganga Basin (India). Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, H. Extending the Rational Method for Assessing and Developing Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems. Water Res. 2018, 144, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, M.P.; Yadav, S.M.; Manekar, V.L. Assessment of the Empirical Methods for the Development of the Synthetic Unit Hydrograph: A Case Study of a Semi-Arid River Basin. Water Pract. Technol. 2022, 17, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.N. Analysis of Surface Runoff Potential in Ungauged Basin Using Basin Parameters and SCS-CN Method. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, D.; Tsunekawa, A.; Tsubo, M.; Haregeweyn, N.; Adgo, E.; Meshesha, D.T.; Fenta, A.A.; Ebabu, K.; Berihun, M.L.; Setargie, T.A. Evaluation of Lag Time and Time of Concentration Estimation Methods in Small Tropical Watersheds in Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 40, 101025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapides, D.A.; Sytsma, A.; Thompson, S. Implications of Distinct Methodological Interpretations and Runoff Coefficient Usage for Rational Method Predictions. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2021, 57, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, W.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X. Application of HEC-HMS Parameter Regionalization in Small Watershed of Hilly Area. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 1961–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Xiong, L.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; Cai, X.; Chen, K.; Wu, J. Runoff Simulation of Two Typical Urban Green Land Types with the Stormwater Management Model (SWMM): Sensitivity Analysis and Calibration of Runoff Parameters. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, A.; Hassan, S.S.; Khan, G.D.; Goheer, M.A.; Khan, A.A.; Sheraz, K.; Salman, A.; Hassan, S.S.; Khan, G.D.; Goheer, M.A.; et al. HEC-RAS and GIS-Based Flood Plain Mapping: A Case Study of Narai Drain Peshawar. Acta Geophys. 2021, 69, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Bourke, R. Urbanization Impacts on Flood Risks Based on Urban Growth Data and Coupled Flood Models. Nat. Hazards 2021, 106, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos Aranda, D.F. Intensidades Máximas de Lluvia Para Diseño Hidrológico Urbano En La República Mexicana. Available online: https://www.scielo.org.mx/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1405-77432010000200005 (accessed on 30 September 2023).






| Year | DMP (mm) | Year | DMP (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 250.3 | 2009 | 69.9 |
| 1996 | 224 | 2010 | 69.9 |
| 1997 | 157.7 | 2011 | 67 |
| 1998 | 152.8 | 2012 | 67 |
| 1999 | 111.3 | 2013 | 60.8 |
| 2000 | 103 | 2014 | 60.2 |
| 2001 | 101.4 | 2015 | 59.5 |
| 2002 | 87.7 | 2016 | 58.3 |
| 2003 | 84.3 | 2017 | 58.2 |
| 2004 | 84 | 2018 | 55.4 |
| 2005 | 80.3 | 2019 | 54.5 |
| 2006 | 77.4 | 2020 | 51.6 |
| 2007 | 72.9 | 2021 | 39.7 |
| 2008 | 71 |
| Return Period (Years) | Precipitation Height (mm) |
|---|---|
| 2 | 79.439 |
| 5 | 127.69 |
| 10 | 185.32 |
| 20 | 232.78 |
| 25 | 246.34 |
| 50 | 284.76 |
| 100 | 317.53 |
| Area (ha) | Perimeter (m) | Length of Main Stream (m) | Slope | Tc (h) | Tc (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21.271 | 2849 | 568 | 0.0202 | 0.193 | 11.56 |
| Surfaces | Area (km2) | C-TR-2 | C-TR-5 | C-TR-10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land without vegetation | 0.769 | 0.1 | 0.25 | 0.35 |
| Roof | 1.331 | 0.8 | 0.85 | 0.9 |
| Inclined roof | 9.674 | 0.8 | 0.85 | 0.9 |
| Sidewalk | 0.633 | 0.1 | 0.25 | 0.35 |
| Concrete street | 5.583 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.9 |
| Asphalt | 1.360 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.9 |
| Landscaped area | 1.791 | 0.1 | 0.25 | 0.35 |
| Total area | 21.14 | 0.72 | 0.77 | 0.82 |
| Tr (Years) | Duration (min) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 45 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 120 | 1440 | |
| 2 | 115.85 | 89.26 | 73.91 | 63.74 | 50.90 | 40.01 | 33.49 | 27.90 | 24.15 | 21.44 | 3.99 |
| 5 | 181.45 | 139.80 | 115.76 | 99.84 | 79.72 | 62.67 | 52.45 | 43.70 | 37.83 | 33.58 | 6.25 |
| 10 | 231.08 | 178.03 | 147.42 | 127.15 | 101.52 | 79.81 | 66.80 | 55.65 | 48.18 | 42.77 | 7.96 |
| 25 | 296.68 | 228.57 | 189.27 | 163.24 | 130.34 | 102.47 | 85.76 | 71.45 | 61.86 | 54.91 | 10.23 |
| 50 | 346.30 | 266.81 | 220.93 | 190.55 | 152.14 | 119.61 | 100.11 | 83.40 | 72.21 | 64.10 | 11.94 |
| 100 | 395.93 | 305.04 | 252.59 | 217.85 | 173.94 | 136.75 | 114.45 | 95.35 | 82.55 | 73.28 | 13.65 |
| Rational Method | Chow Method | SCS Method | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrograph of Direct Runoff | Triangular Unit Hydrograph | ||
| 8.07 | 4.569 | 6.371 | 2.964 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez-Núñez, G.Y.; Rentería-Guevara, S.A.; Rangel-Peraza, J.G.; Monjardín-Armenta, S.A.; Sanhouse-García, A.J.; Mora-Felix, Z.D. Standardizing Criteria for Calculating Urban Storm Drainage Flow Rates Using Basin Division Based on Aerial Photogrammetry: The Case Study of Culiacan, Mexico. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12334. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132212334
Sánchez-Núñez GY, Rentería-Guevara SA, Rangel-Peraza JG, Monjardín-Armenta SA, Sanhouse-García AJ, Mora-Felix ZD. Standardizing Criteria for Calculating Urban Storm Drainage Flow Rates Using Basin Division Based on Aerial Photogrammetry: The Case Study of Culiacan, Mexico. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(22):12334. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132212334
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez-Núñez, Guadalupe Yuceli, Sergio Arturo Rentería-Guevara, Jesús Gabriel Rangel-Peraza, Sergio Alberto Monjardín-Armenta, Antonio Jesús Sanhouse-García, and Zuriel Dathan Mora-Felix. 2023. "Standardizing Criteria for Calculating Urban Storm Drainage Flow Rates Using Basin Division Based on Aerial Photogrammetry: The Case Study of Culiacan, Mexico" Applied Sciences 13, no. 22: 12334. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132212334
APA StyleSánchez-Núñez, G. Y., Rentería-Guevara, S. A., Rangel-Peraza, J. G., Monjardín-Armenta, S. A., Sanhouse-García, A. J., & Mora-Felix, Z. D. (2023). Standardizing Criteria for Calculating Urban Storm Drainage Flow Rates Using Basin Division Based on Aerial Photogrammetry: The Case Study of Culiacan, Mexico. Applied Sciences, 13(22), 12334. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132212334






