Ethyl Formate as a New Sanitary Treatment for Disinfesting the Hitchhiking Insect Pest Halyomorpha halys on Imported Nonfood Agricultural Machinery
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fumigant
2.2. Insects
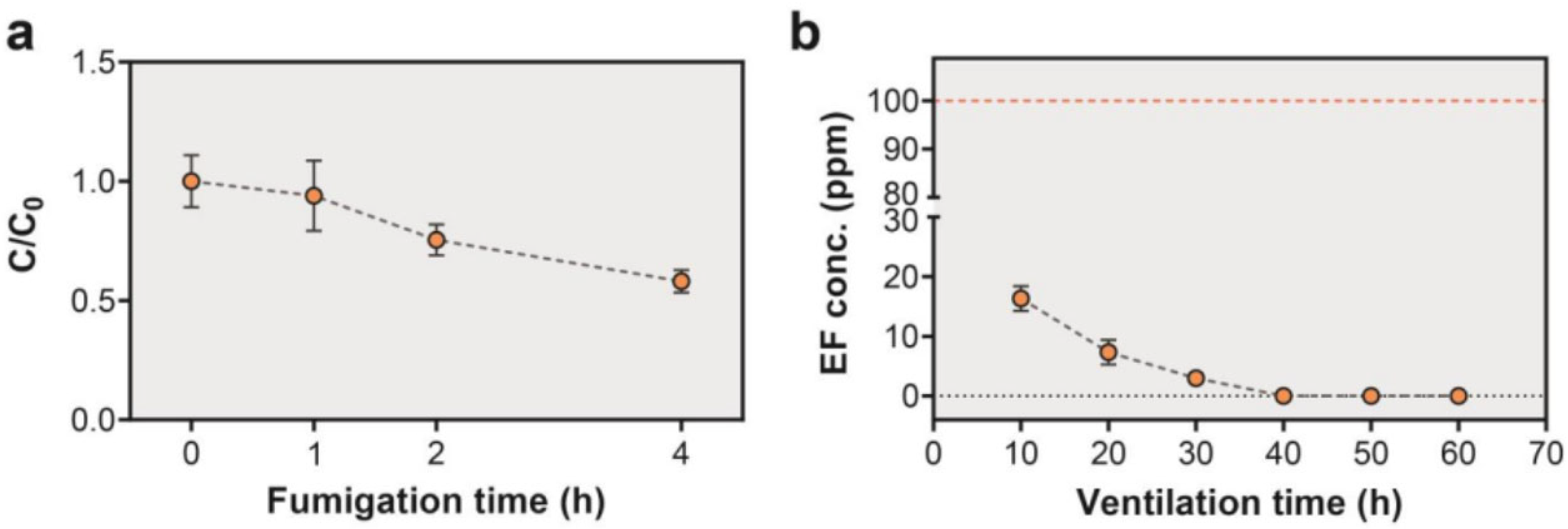
2.3. Efficacy of EF against H. Halys
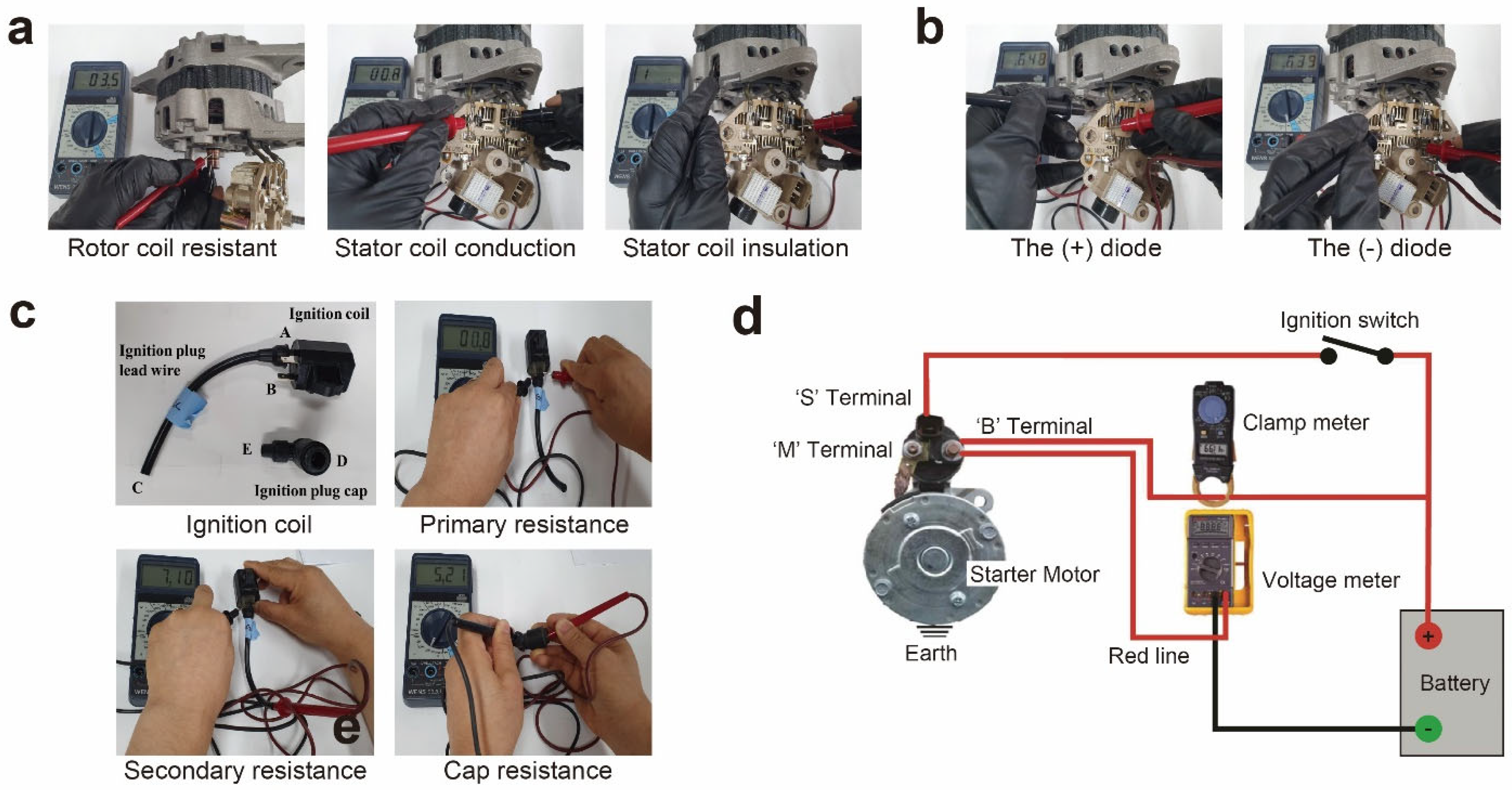
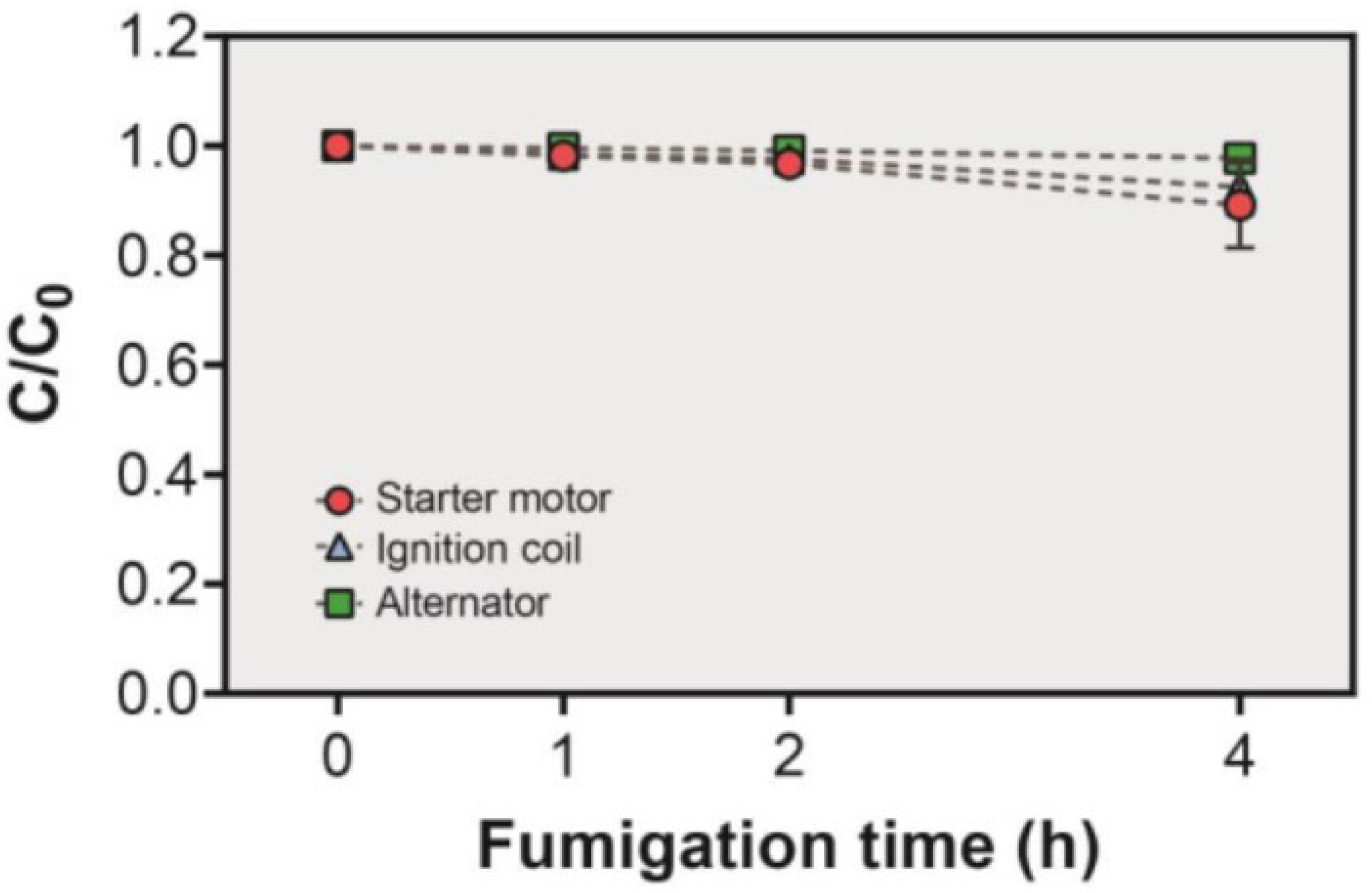
2.4. Sorption Studies of EF on Alternator, Ignition coil, and Starter Motor
2.5. Reactivity Test: Test Method for Determining the Electrical Characteristics of the Alternator
2.5.1. Rotor Coil Resistance Test
2.5.2. Stator Coil Resistance Test
2.5.3. Rectifier Conduction Test
2.6. Reactivity Test: Test Method for Determining the Electrical Characteristics of the Ignition Coil
2.6.1. Primary Ignition Coil Resistance Measurement
2.6.2. Secondary Ignition Coil Resistance Measurement
2.6.3. Ignition Pug Cap Resistance Measurement
2.7. Reactivity Test: Test Method for Determining the Electrical Characteristics of the Starter Motor
2.7.1. Starter Motor Solenoid Operation Test
2.7.2. No-Load Operation Test of the Starter Motor
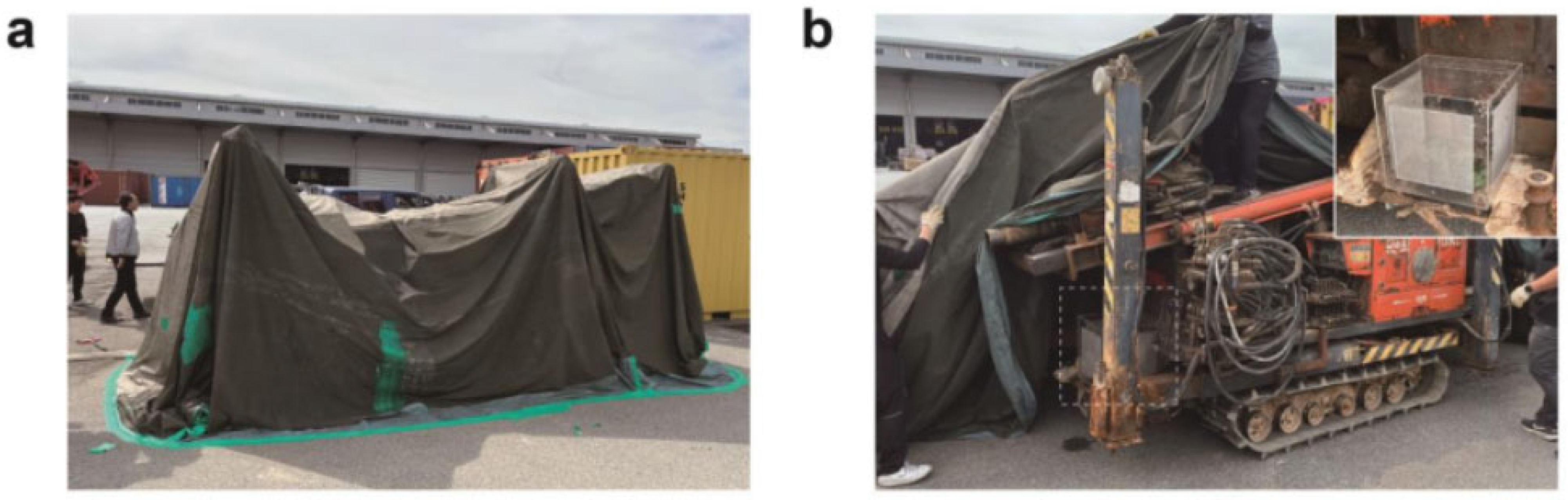
2.8. Commercial Trial with an Evaluation of Worker Safety
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Efficacy of 4 h EF Fumigation against H. Halys
3.2. Sorption Studies of EF and Reactivity Test on Alternator, Ignition Coil, and Starter Motor
3.2.1. Test Method for Determining the Electrical Characteristics of the Alternator
3.2.2. Test Method for Determining the Electrical Characteristics of the Ignition Coil
3.2.3. Test Method for Determining the Electrical Characteristics of the Starter Motor
3.3. Commercial Trial
3.4. Evaluation of Worker Safety in EF Fumigation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency (AQPA). 2023. Available online: https://okminwon.pqis.go.kr/minwon/information/statistics.html?statsType=103&frYear=2022&frMonth=01&toYear=2022&toMonth=12&trnType=IN&metType=hwa&itemCd=39009004&itemNm=%EC%A4%91%EA%B3%A0+%EB%86%8D%EA%B8%B0%EA%B3%84&x=16&y=4 (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Leskey, T.C.; Hamilton, G.C.; Nielsen, A.L.; Polk, D.F.; Rodriguez-Saona, C.; Christopher Bergh, J. Pest status of the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys in the USA. Outlooks Pest Manag. 2012, 23, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, A.E.; Kawagoe, J.C.; Najar-Rodriguez, A.; Walse, S.S. Sulfuryl fluoride fumigation to control brown marmorated stinkbug (Hempitera: Pentatomidae). Postharvest. Biol. Technol. 2020, 163, 111111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Cullum, J.P.; Anderson, J.L.; Daugherty, J.L.; Beckett, L.M.; Leskey, T.C. Characterization of overwintering sites of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug in natural landscapes using human surveyors and detector canines. PLoS ONE 2012, 9, e91575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inkley, D.B. Characteristics of home invasion by the brown marmorated stink bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). J. Entomol. Sci. 2012, 47, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.L.; Hamilton, G.C. Life history of the invasive species Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in northeastern United States. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2009, 102, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.L.; Hamilton, G.C. Seasonal occurrence and impact of Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in tree fruit. Econ. Entomol. 2009, 102, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskey, T.C.; Short, B.D.; Butler, B.B.; Wright, S.E. Impact of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stal) in mid-Atlantic tree fruit orchards in the United States: Case studies of commercial management. Psyche 2012, 2012, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Department of Agriculture and Water Resources (DAWR). Draft Pest. Risk Analysis for Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (Halyomorpha halys); Department of Agriculture and Water Resources: Canberra, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Leskey, T.; Hamilton, G.C. Brown Marmorated Stink Bug Working Group Meeting. 2010. Available online: http://projects.ipmcenters.org/Northeastern/FundedProjects/ReportFiles/Pship2010/Pship2010-Leskey-ProgressReport-237195-Meeting-2010_11_17.pdf (accessed on 22 March 2023).
- Pfeiffer, D.G.; Leskey, T.C.; Burrack, H.J. Threatening the harvest: The threat from three invasive insects in late season vineyards. In Arthropod Management in Vineyards: Pests, Approaches and Future Directions; Bostanian, N.J., Vincent, C., Isaacs, R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment (DAWE). 2020. Available online: www.agriculture.gov.au/import/ (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Bond, E.J. Manual of Fumigation for Insect Control: FAO Plant Production and Protection Paper; IPPC, FAO: Rome, Italy, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Production and Consumption of Ozone Depleting Substances under the Montreal Protocol 1986–2004; Ozone Secretariat, United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, C.H. Fumigation in the 21st century. Crop Prot. 2000, 19, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambeau, M.B.; Benitez, D.P.; Dupuis, S.; Ducom, P. Hydrogen cyanide as an immediate alternative to methyl bromide for structural fumigations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Controlled Atmosphere and Fumigation in Stored Products, Fresno, CA, USA, 29 October–3 November 2000; Donahaye, E.J., Navarro, S., Leesch, J.G., Eds.; Executive Printing Services: Clovis, CA, USA, 2001; pp. 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.F.; Toews, M.D.; Arthur, F.H.; Arbogast, R.T. Long-term monitoring of Tribolium castaneum in two flour mills: Seasonal patterns and impact of fumigation. J. Econ. Entomol. 2010, 103, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherdán, K.; Weiszburg, T.G.; Bendő, Z.; Kristály, F.; Váczi, T.; Zajzon, N. Phosphine fumigation damage: Corrosion of metal and metal-texile composite museum objects. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Non-destructive Investigations and Microanalysis for Diagnostics and Conservation of Cultural and Environmental Heritage, Florence, Italy, 13–15 April 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.G.; Lee, B.H.; Yang, J.O.; Kim, B.S.; Roh, G.H.; Kendra, P.E.; Cha, D.H. Ethyl formate as a methyl bromide alternative for fumigation of citrus: Efficacy, fruit quality, and workplace safety. J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 2290–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kim, C.; Kwon, T.H.; Jeon, H.J.; Kim, Y.; Cho, Y.; Kim, D.; Lee, Y.; Kim, D.; Lee, B.H.; et al. Optimizing Ethyl Formate Fumigation in Greenhouse Cucurbit Crops for Efficient Control of Major Agricultural Pests, Myzus persicae and Thrips palmi. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2023, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, T.; Bikoba, V.; Tipping, C.; Mitcham, E.J. Ethyl formate as a postharvest fumigant for selected pests of table grapes. J. Econ. Entomol. 2007, 100, 1084–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misumi, T.; Ogawa, N.; Yamada, K.; Shukuya, T. Susceptibilities of five species of scales (Diaspididae and Coccidae) and mealybugs (Pseudococcidae) to fumigation with a gas mixture of ethyl formate and carbon dioxide under normal atmospheric pressure or vacuum. Bull. Plant Prot. Jpn. 2013, 49, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, M.J.; Jamieson, L.E.; Chhagan, A.; Page-Weir, N.E.M.; Poulton, J.; Davis, V.A.; Zulhendri, F.; Connolly, P.G. The potential of ethyl formate + carbon dioxide to control a range of horticultural pests. NZ Plant Prot. 2013, 66, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, M.; Ren, Y.; Newman, J.; Learmonth, S. Ethyl formate: A potential disinfestation treatment of Eucalyptus weevil (Gonipterus platensis) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in apples. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 2566–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyung, Y.J.; Kim, H.K.; Cho, S.W.; Kim, B.S.; Yang, J.O.; Koo, H.N.; Kim, G.H. Comparison of the efficacy and phytotoxicity of phosphine and ethyl formate for controlling Pseudococcus longispinus (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) and Pseudococcus orchidicola in imported foliage nursery plants. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 2149–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.B.; Kim, K.W.; Park, M.G.; Roh, G.H.; Cha, D.H.; Lee, B.H. New feasible quarantine disinfestation using ethyl formte for termites and ants on imported lumber. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2021, 24, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.B.; Kwon, T.H.; Park, M.G.; Kim, K.W.; Cha, D.H.; Lee, B.H. Ethyl formate-based quarantine treatment for exotic ants and termites in imported rubber plants and stone products. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.L.; Lee, B.H.; Padovan, B. Penetration of methyl bromide, sulfuryl fluoride, ethanedinitrile and phosphine into timber blocks and the sorption rate of the fumigants. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2011, 47, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawagoe, J.C.; Abrams, A.E.; Lourie, A.P.; Walse, S.S. Ethyl formate dilution in carbon dioxide for fumigation control of the brown marmorated stink bug Halyomorpha halys, Stål (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 3090–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKirdy, H.L.R. Efficacy and Suitability of Liquid Ethyl Formate for Insect Pest Management; Colleage of Science, Health, Engineering and Education Food Futures Institute, Murdoch University: Perth, Australia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.O.; Park, Y.R.; Hyun, I.H.; Kim, G.H.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, B.H.; Ren, Y.L. A combination treatment using ethyl formate and phosphine to control Planococcus citri (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) on pineapples. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 2355–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.K.; Kyung, Y.J.; Park, G.H.; Lee, B.H.; Yang, J.O.; Koo, H.N.; Kim, G.H. Fumigation activity of ethyl formate and phosphine against Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae) on imported sweet pumpkin. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 114, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrion, A.C.; Scheffrahn, R.H.; Serre, S.; Lee, S.D. Impact of sporicidal fumigation with methyl bromide or methyl iodide on electronic equipment. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Park, M.Y.; Fraser, P.J.; Park, H.; Muhle, J.; Kim, J.; Porter, I.; Salameh, P.K.; Harth, C.M.; Dunse, B.L.; et al. Top-down and bottom-up estimates of anthropogenic methyl bromide emissions from eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 5157–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.H.; Park, C.G.; Lee, B.H.; Jeong, I.H.; Lee, S.E. A new approach: Ethyl formate fumigation to control Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) in a yellow melon vinyl house. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, E.M.; Newman, J.; Coupland, G.T.; Thomas, M.; van der Merwe, J.; Ren, Y.; McKirdy, S.J. Commercial trials evaluating the novel use of ethyl formate for in-transit fumigation of shipping containers. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2019, 54, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Temp. (°C) | 1 LCt50 (95% CL 2, g h/m3) | LCt99 (95% CL, g h/m3) | Slope ± SE | df | X2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23 | 15.88 (15.09–16.69) | 31.51 (28.20–36.77) | 7.82 ± 0.7 | 16 | 8.93 |
| Fumigation Items | Measured Value | Judgment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 (Control) | Rotor coil | Resistance test | 3.5 ± 0.1 [Ω] | Conduction | ☑ Normal, □ Faulty |
| Stator coil | Conduction test | ☑ Conduction,□Insulation | 0.7 ± 0.1 [Ω] | ||
| Insulation test | □ Conduction, ☑ Insulation | “1” = ∞ [Ω] | |||
| Rectifier check | (+) Diode | ☑ Normal, □ Faulty | 0.648 ± 0.01 [Ω] | ||
| (−) Diode | ☑ Normal, □ Faulty | 0.639 ± 0.01 [Ω | |||
| Sample 2 (EF 35 g/m3) | Rotor coil | Resistance test | 3.5 ± 0.1 [Ω] | Conduction | ☑ Normal, □ Faulty |
| Stator coil | Conduction test | ☑ Conduction, □ Insulation | 0.8 ± 0.1 [Ω] | ||
| Insulation test | □ Conduction, ☑ Insulation | “1” = ∞ [Ω] | |||
| Rectifier check | (+) Diode | ☑ Normal, □ Faulty | 0.626 ± 0.01 [Ω] | ||
| (−) Diode | ☑ Normal, □ Faulty | 0.637 ± 0.01 [Ω] | |||
| Sample 3 (EF 70 g/m3) | Rotor coil | Resistance test | 3.4 [Ω] | Conduction | ☑ Normal, □ Faulty |
| Stator coil | Conduction test | ☑ Conduction, □ Insulation | 0.8 ± 0.1 [Ω] | ||
| Insulation test | □ Conduction, ☑ Insulation | “1” = ∞ [Ω] | |||
| Rectifier check | (+) Diode | ☑ Normal, □ Faulty | 0.627 ± 0.1 [Ω] | ||
| (−) Diode | ☑ Normal, □ Faulty | 0.619 ± 0.1 [Ω] | |||
| Fumigation Items | Measured Value | Reference Value | Judgment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 (Control) | Ignition coil primary resistance | 0.8 ± 0.1 [Ω] | 0.7~1.2 [Ω] | ☑ Normal, □ Faulty |
| Ignition coil secondary resistance | 7.10 ± 0.1 [kΩ] | 5.0~10.0 [kΩ] | ||
| Ignition plug cap resistance | 5.21 ± 0.1 [kΩ] | 3.0~6.0 [kΩ] | ||
| Sample 2 (EF 35 g/m3) | Ignition coil primary resistance | 0.9 ± 0.1 [Ω] | 0.7~1.2 [Ω] | ☑ Normal, □ Faulty |
| Ignition coil secondary resistance | 7.0 ± 0.1 [kΩ] | 5.0~10.0 [kΩ] | ||
| Ignition plug cap resistance | 4.74 ± 0.1 [kΩ] | 3.0~6.0 [kΩ] | ||
| Sample 3 (EF 70 g/m3) | Ignition coil primary resistance | 0.8 ± 0.1 [Ω] | 0.7~1.2 [Ω] | ☑ Normal, □ Faulty |
| Ignition coil secondary resistance | 6.78 ± 0.1 [kΩ] | 5.0~10.0 [kΩ] | ||
| Ignition plug cap resistance | 4.71 ± 0.1 [kΩ] | 3.0~6.0 [kΩ] | ||
| Solenoid Operation Test | Test Results | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 (Control) | Selonoid switch | PULL-IN | Pinion advance |
| HOLD-IN | Keep pinion forward | ||
| RETURN | Return to original position | ||
| Sample 2 (EF 35 g/m3) | Selonoid switch | PULL-IN | Pinion advance |
| HOLD-IN | Keep pinion forward | ||
| RETURN | Return to original position | ||
| Sample 3 (EF 70 g/m3) | Selonoid switch | PULL-IN | Pinion advance |
| HOLD-IN | Keep pinion forward | ||
| RETURN | Return to original position | ||
| Fumigated Items | Measured Value | Reference Value | Judgment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 (Control) | Voltage drop | 11.45 ± 0.1 [V] | >10.8 [V] | ☑ Normal, □ Faulty |
| Consumption current | 100.2 ± 0.1 [A] | 90~110 [A] | ||
| Sample 2 (EF 35 g/m3) | Voltage drop | 11.38 ± 0.1 [V] | >10.8 [V] | ☑ Normal, □ Faulty |
| Consumption current | 102.9 ± 0.1 [A] | 90~110 [A] | ||
| Sample 3 (EF 70 g/m3) | Voltage drop | 11.49 ± 0.1 [V] | >10.8 [V] | ☑ Normal, □ Faulty |
| Consumption current | 104.9 ± 0.1 [A] | 90~110 [A] | ||
| Applied Dose (g/m3) | Fumigation Time (h) | EF Concentration (g/m3) | Mortality (Mean ± SE, %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Front | Middle | Rear | |||
| 0 | - | - | - | - | 2.5 ± 0.5 |
| 35 | 0.1 | 35.3 ± 0.5 | 29.1 ± 0.6 | 29.6 ± 0.5 | 100 ± 0.0 |
| 1.0 | 34.7 ± 0.5 | 26.5 ± 0.8 | 27.0 ± 0.8 | ||
| 2.0 | 21.5 ± 0.6 | 25.5 ± 0.5 | 23.9 ± 0.7 | ||
| 4.0 | 16.4 ± 0.6 | 19.0 ± 0.6 | 19.0 ± 0.6 | ||
| Ct products (g h/m3) | 99.7 ± 0.9 | 97.7 ± 0.6 | 96.1 ± 2.1 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.; Kim, D.; Lee, B.-H.; Roh, G.H.; Kim, K.W.; Jeon, H.-Y.; Lee, S.-E. Ethyl Formate as a New Sanitary Treatment for Disinfesting the Hitchhiking Insect Pest Halyomorpha halys on Imported Nonfood Agricultural Machinery. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11764. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132111764
Kim K, Kim D, Lee B-H, Roh GH, Kim KW, Jeon H-Y, Lee S-E. Ethyl Formate as a New Sanitary Treatment for Disinfesting the Hitchhiking Insect Pest Halyomorpha halys on Imported Nonfood Agricultural Machinery. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(21):11764. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132111764
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Kyeongnam, Dongbin Kim, Byung-Ho Lee, Gwang Hyun Roh, Kyung Won Kim, Hwan-Young Jeon, and Sung-Eun Lee. 2023. "Ethyl Formate as a New Sanitary Treatment for Disinfesting the Hitchhiking Insect Pest Halyomorpha halys on Imported Nonfood Agricultural Machinery" Applied Sciences 13, no. 21: 11764. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132111764
APA StyleKim, K., Kim, D., Lee, B.-H., Roh, G. H., Kim, K. W., Jeon, H.-Y., & Lee, S.-E. (2023). Ethyl Formate as a New Sanitary Treatment for Disinfesting the Hitchhiking Insect Pest Halyomorpha halys on Imported Nonfood Agricultural Machinery. Applied Sciences, 13(21), 11764. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132111764








