Output Feedback Tracking Control for Vessel with Collision-Avoidance and Performance Constraints
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
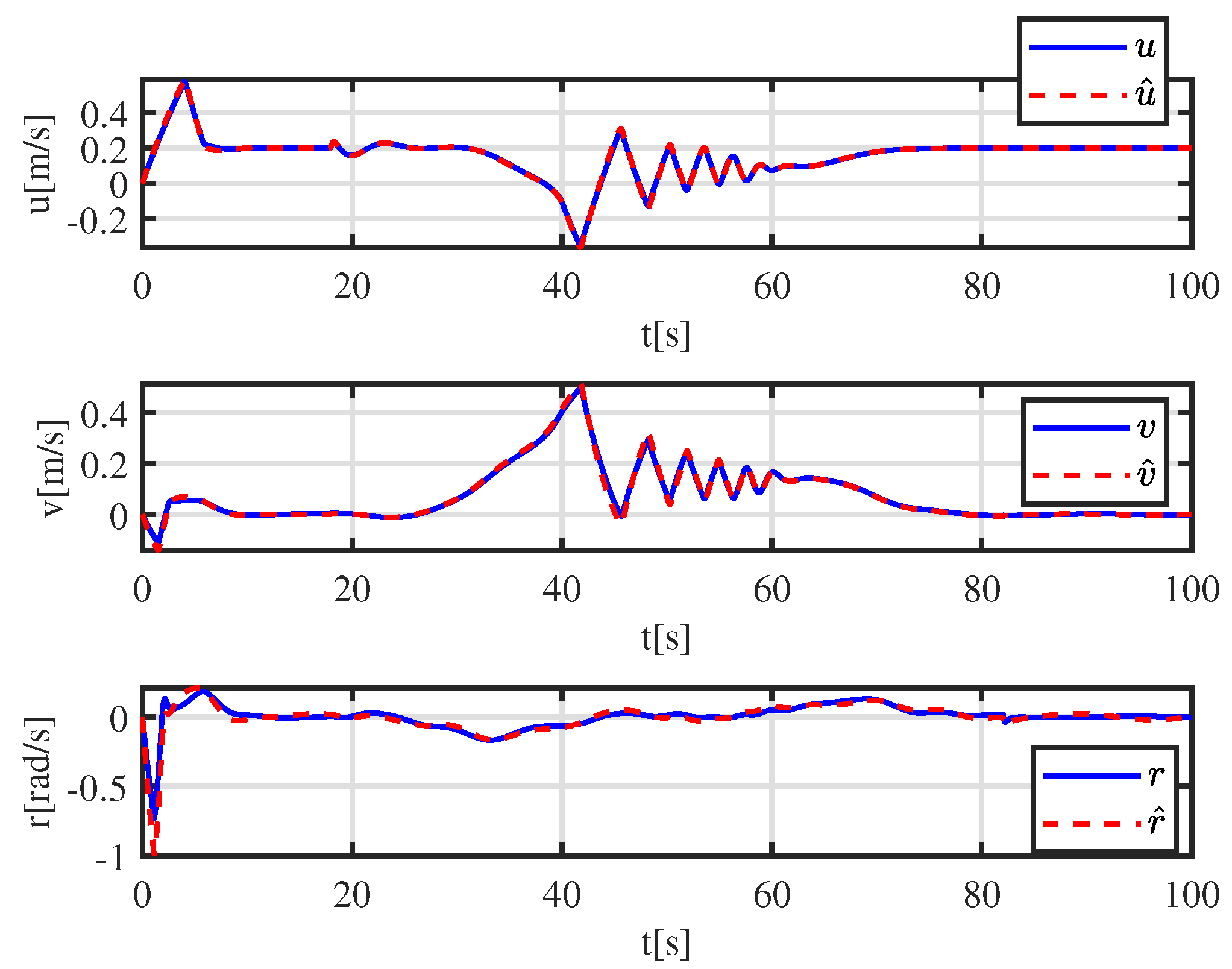
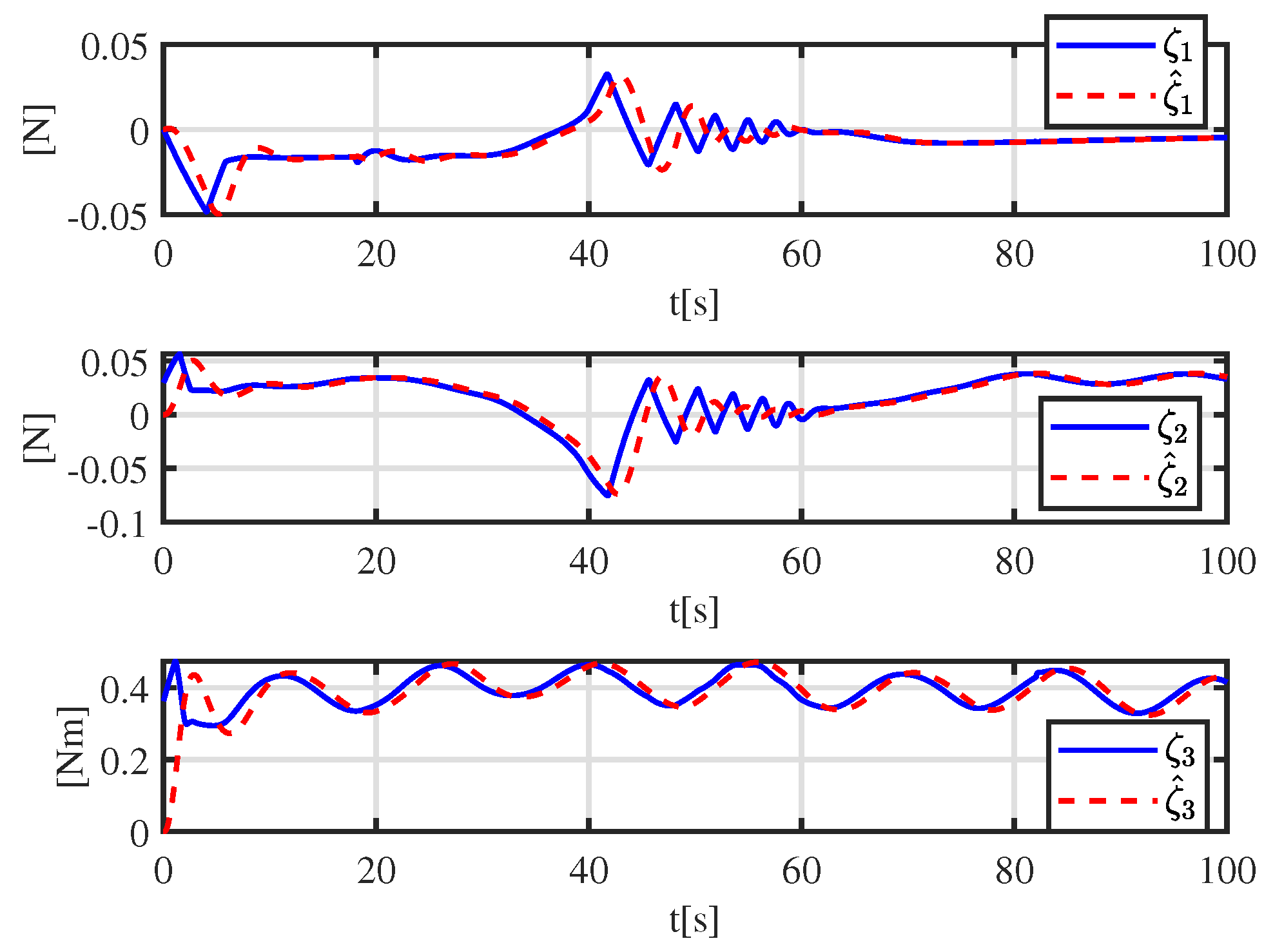
3. Observer Design
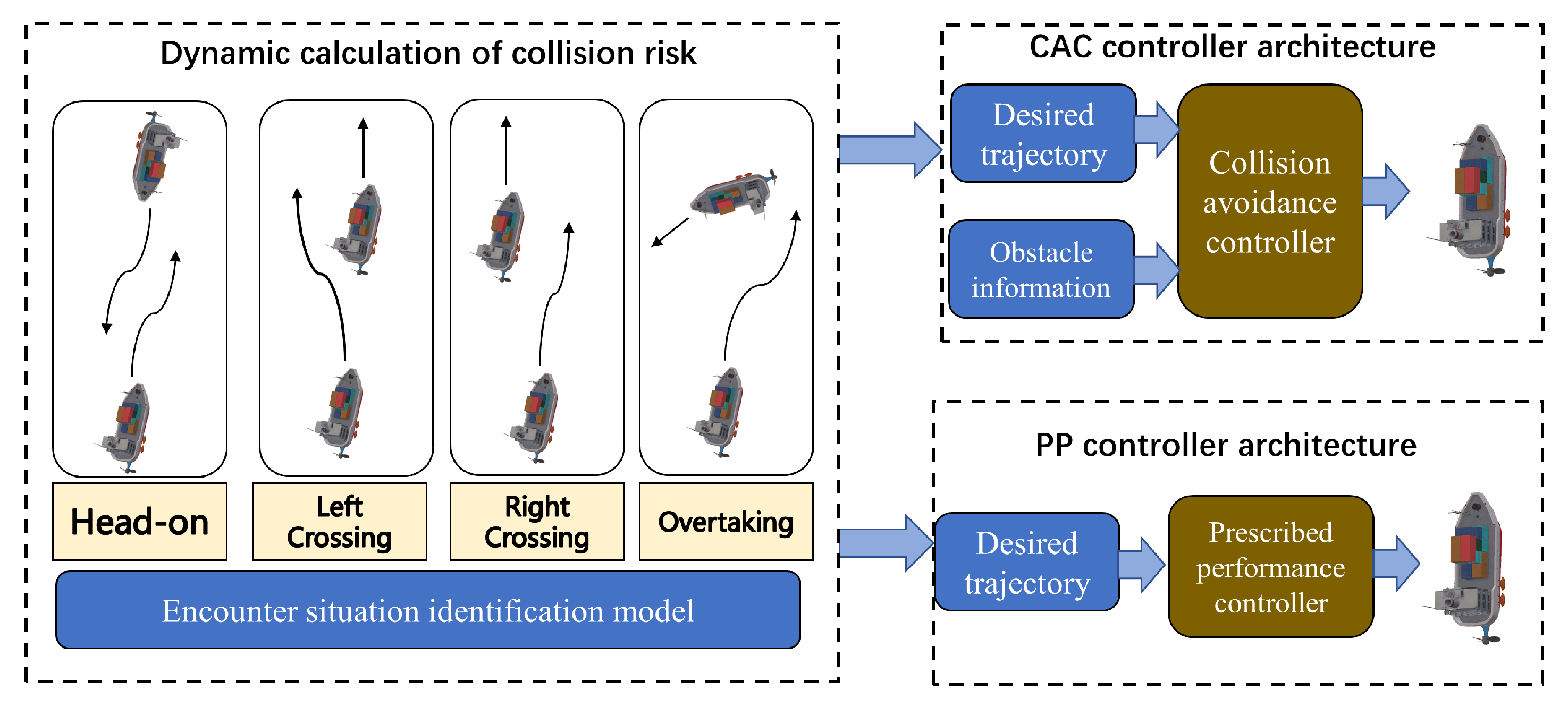
4. Collision-Avoidance Switch Control Strategy
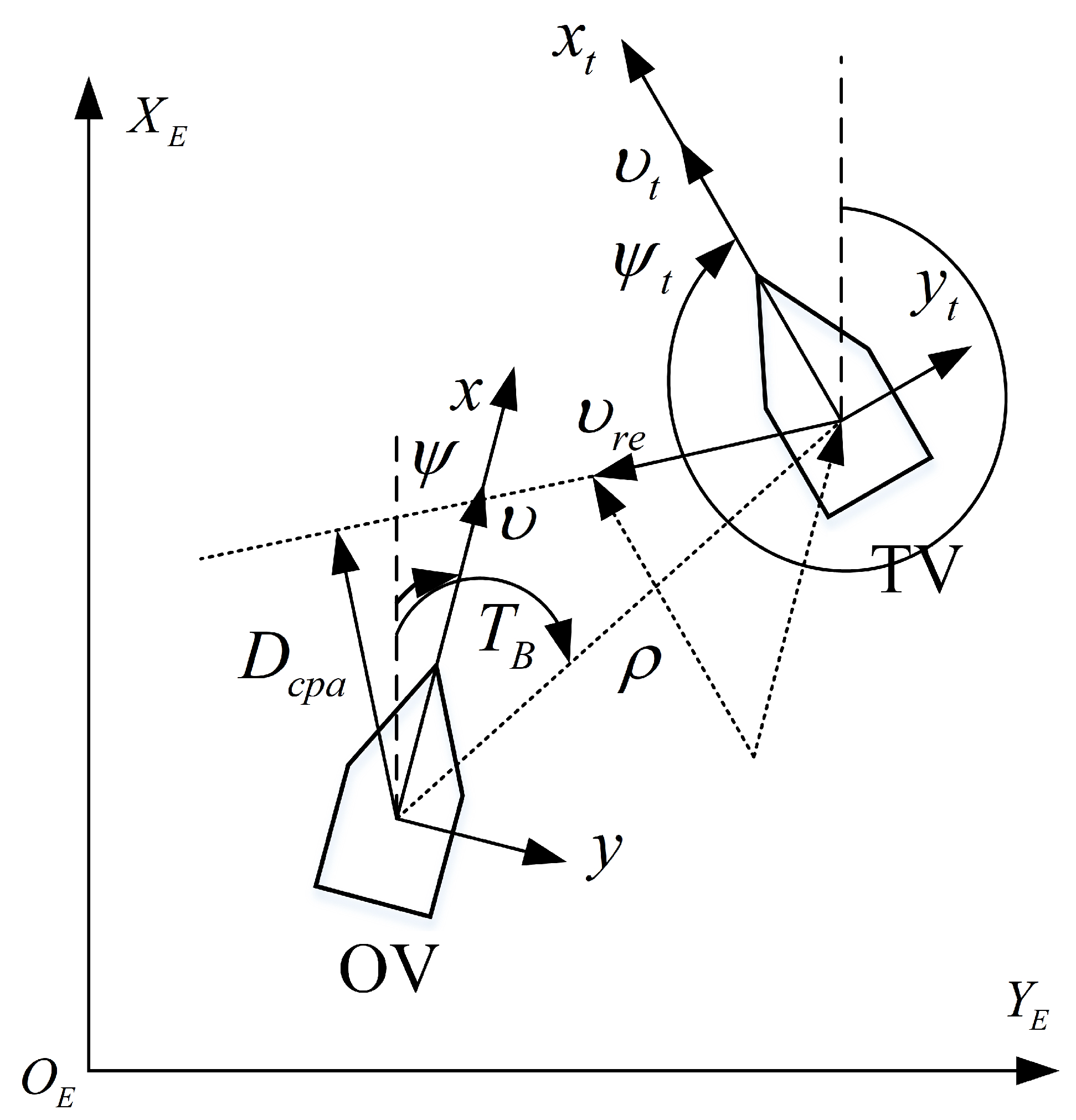
4.1. Dynamic Calculation of Collision Risk
4.2. Switching Control Strategy
4.3. Prescribed Performance Controller Design
4.4. Collision-Avoidance Controller Design
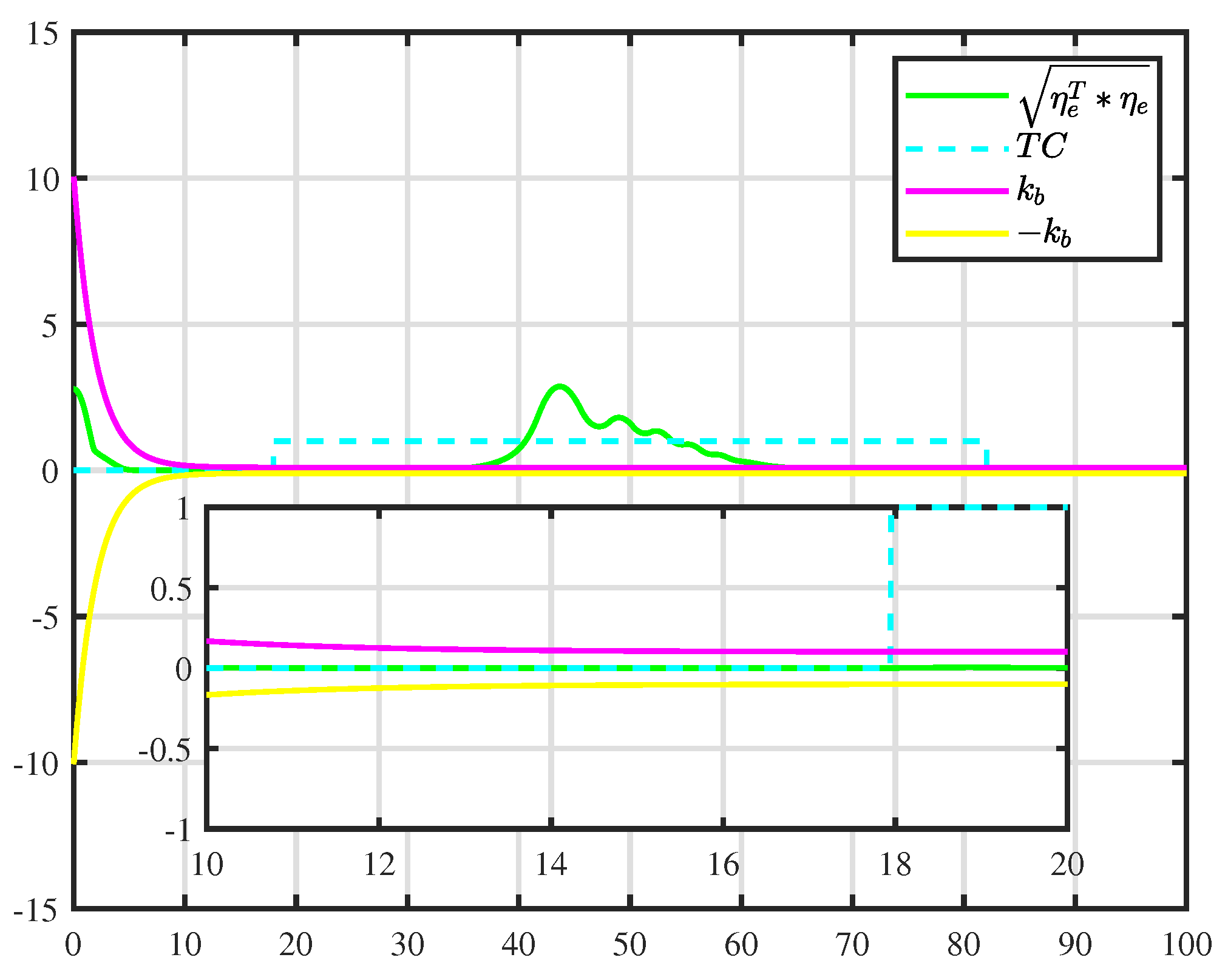
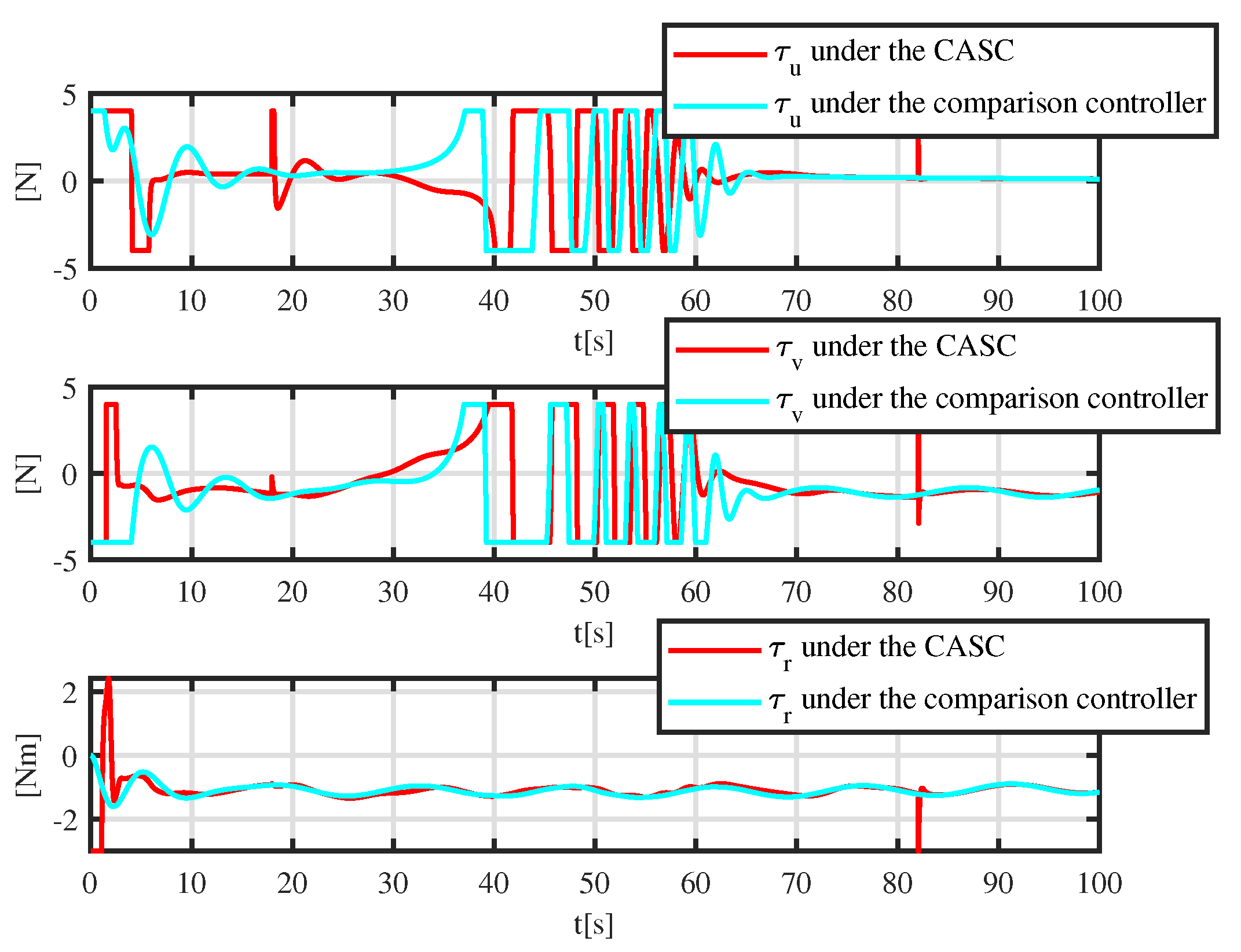
5. Simulation Results
5.1. Trajectory-Tracking-Control Results
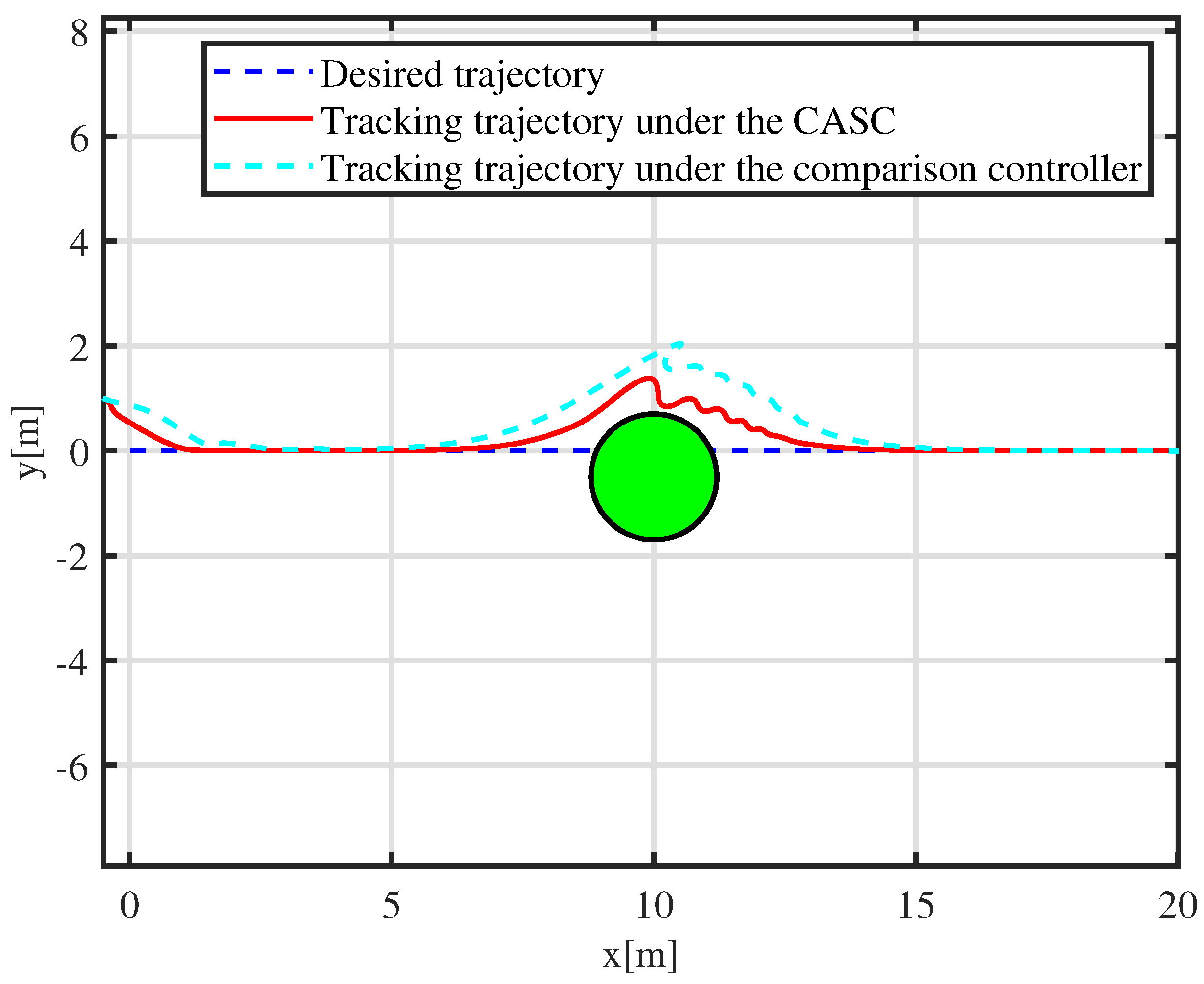
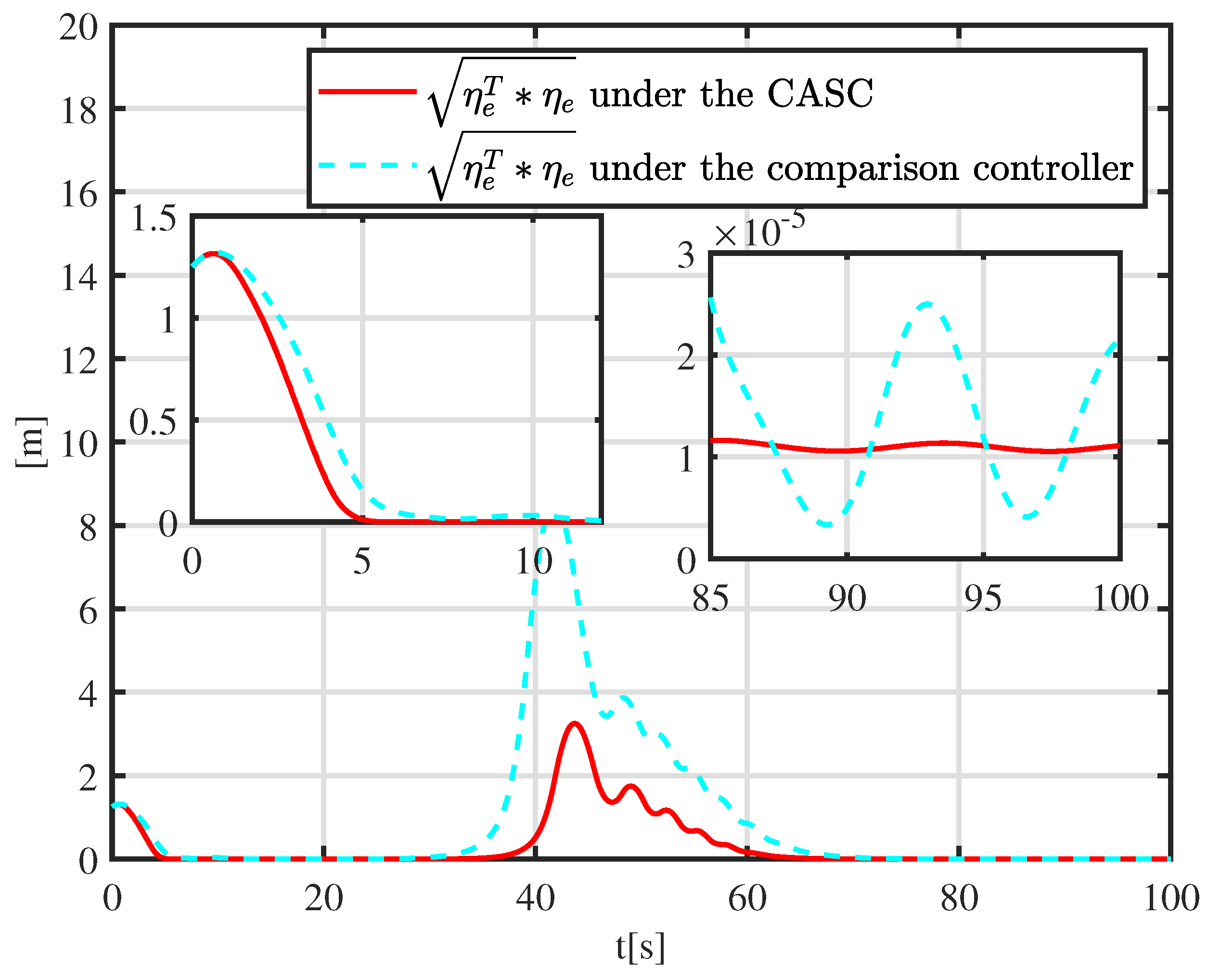
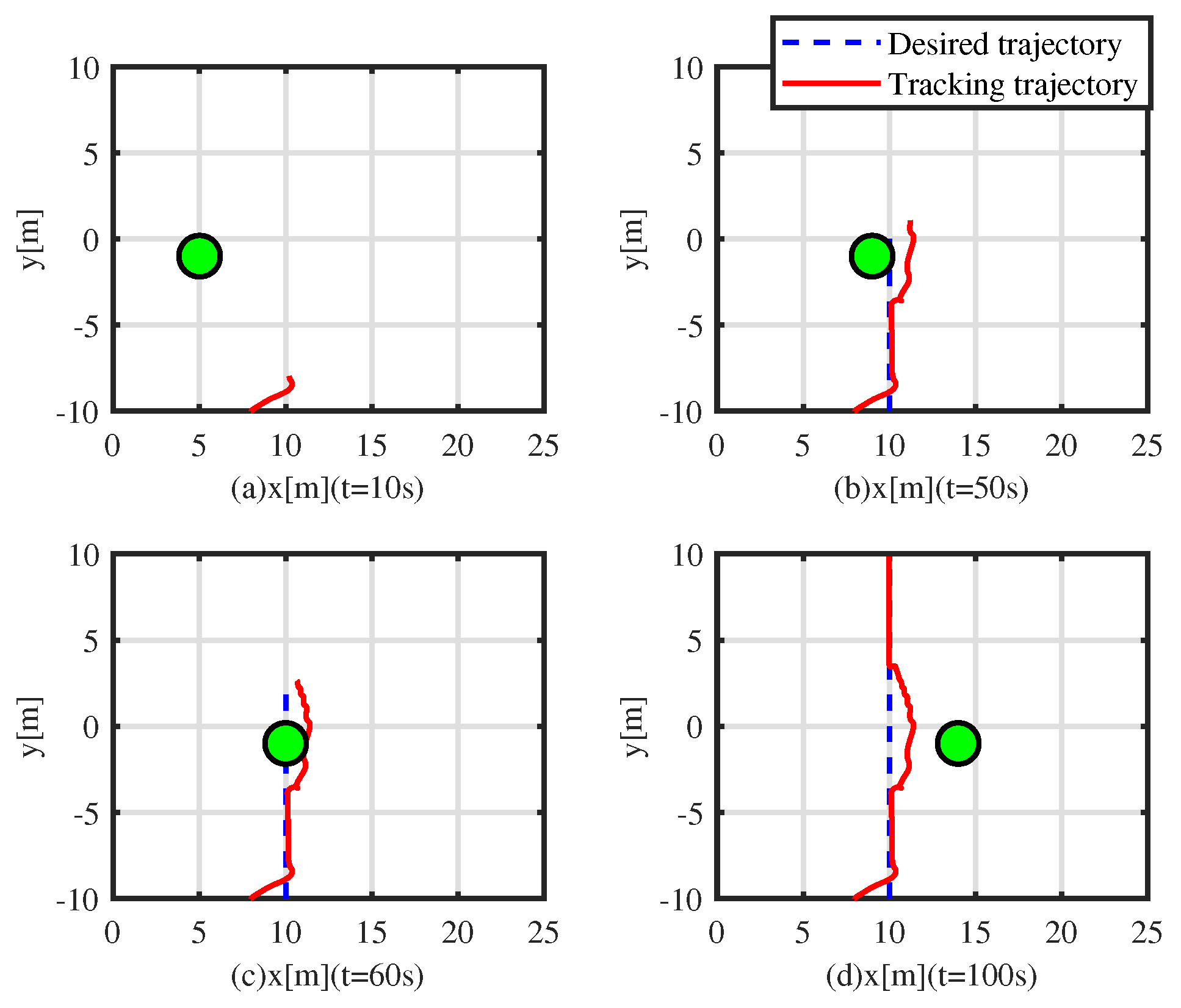
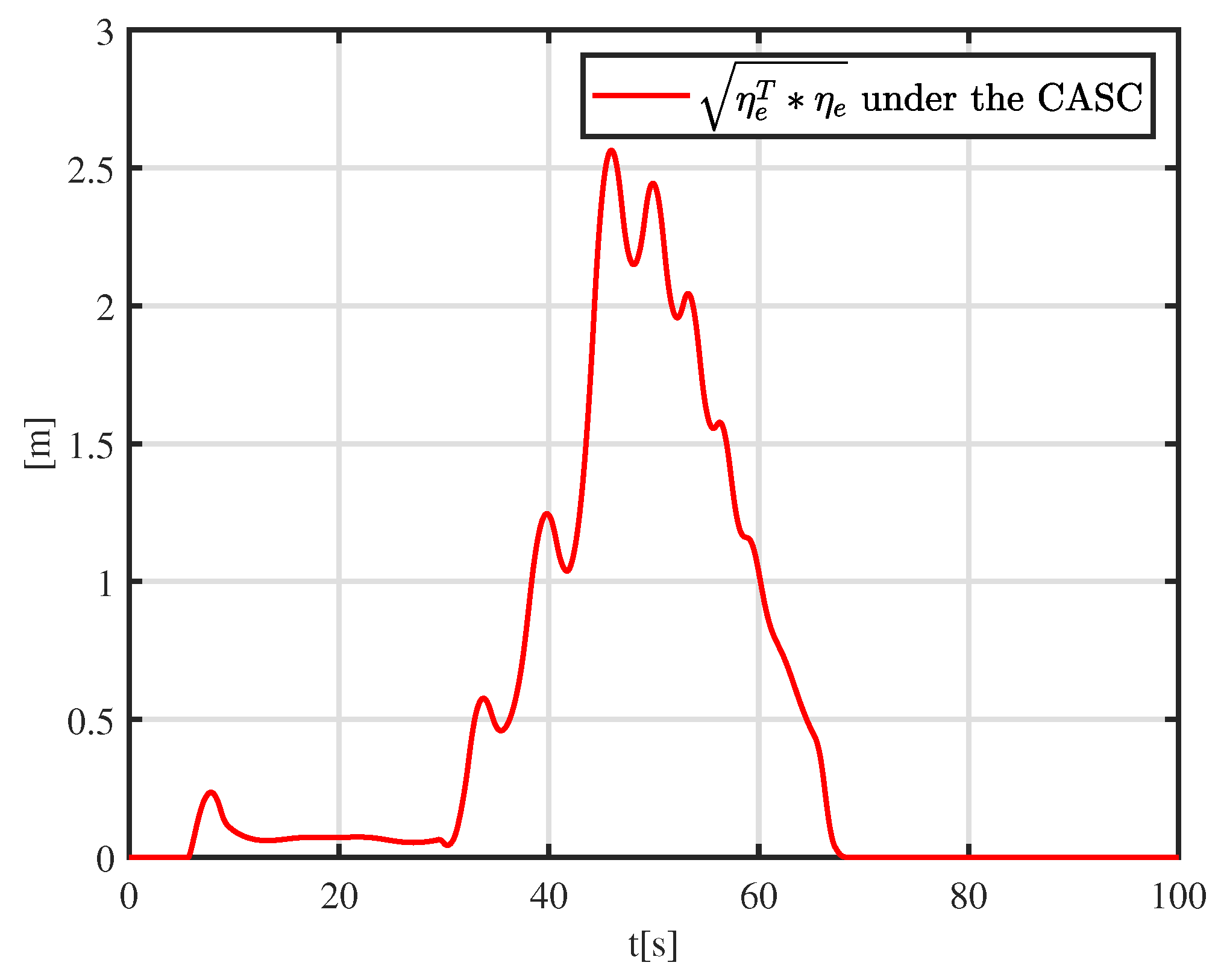
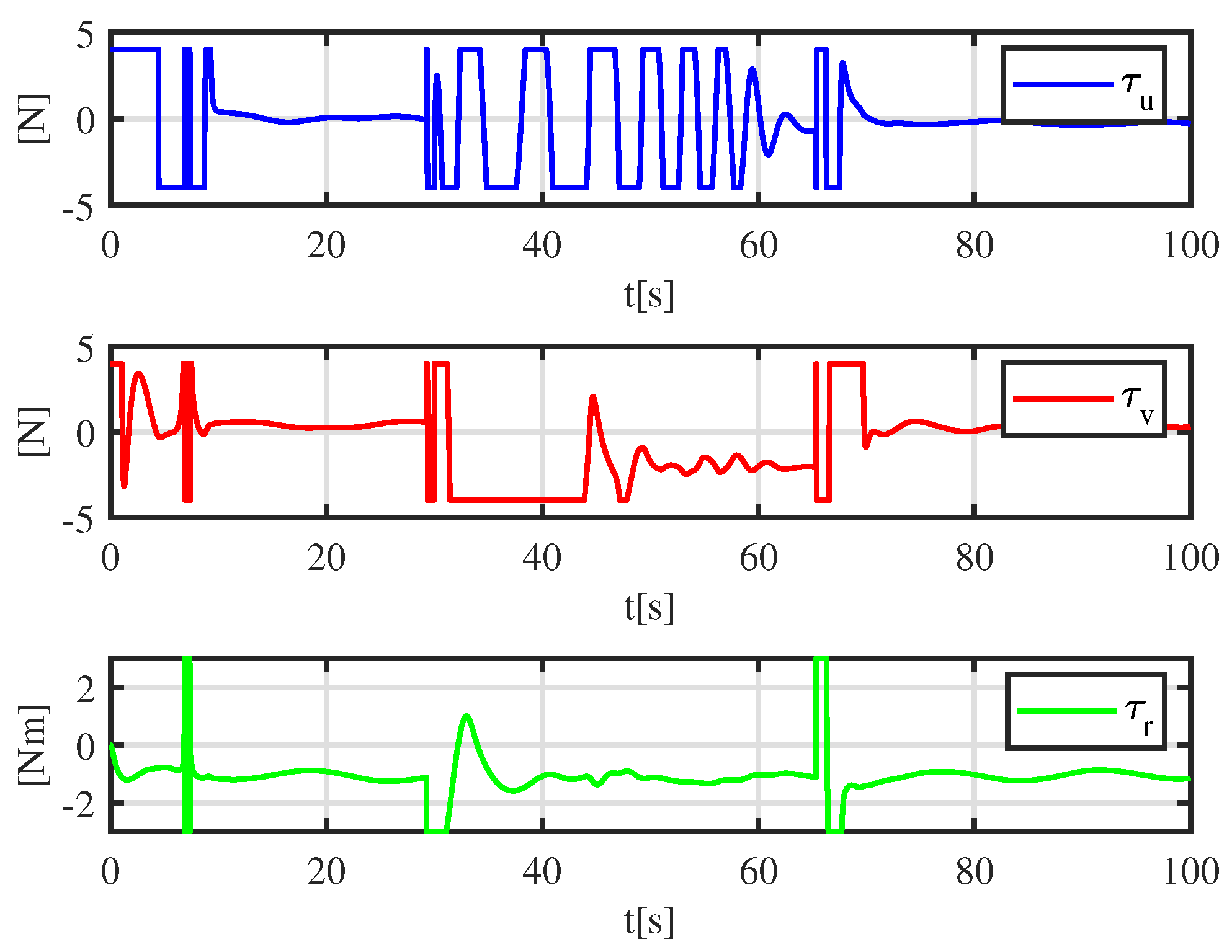
5.2. Simulation Experiment with a Moving Obstacle
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
List of Variables
| Transpose of a matrix | |
| Euclidean norm of a vector | |
| Diagonal matrix | |
| dimensional identity matrix | |
| dimensional zero matrix | |
| , | Position and yaw of dinamicaly positioned vessel |
| u, v, r | surge velocity, sway velocity and yaw rate of dinamicaly positioned vessel |
| the vector containing position and yaw angle | |
| velocity vector | |
| Input signals of vessel control system | |
| M | The positive definite inertia matrix included added mass |
| C | The skew-symmetric matrix of Coriolis and centripetal term |
| D | The positive definite damping matrix |
| R | The rotation matrix |
| d | The external environmental disturbances |
| The maximum constraint constraint of input signal | |
| The maximum constraint of input signal | |
| The control inputs calculated by the proposed controller | |
| The mismatch function between input without saturation and with saturation | |
| The unknown term | |
| , , | The estimates of |
| The position-heading estimation error | |
| estimation error | |
| Collision risk index | |
| The true bearing of the target vessel from the own vessel | |
| The closest point of the approach | |
| The time to the closest point of the approach | |
| The time that the vessel sail from current position to the minimum distance point | |
| The time that the vessel sail from the point of evasive actions to the closest point | |
| The control inputs of the prescribed performance controller | |
| The control inputs of the collision-avoidance controller | |
| the distance between target vessel from the own vessel | |
| the position of own vessel | |
| the center of the obstacle |
Abbreviations
| CASC | Collision-avoidance switch control |
| PPC | Prescribed performance controller |
| ADS | Auxiliary dynamic system |
| CAC | Collision-avoidance controller |
| ESO | Extended state observer |
| DCCR | Dynamic calculation of collision risk |
References
- Sørensen, A.J. A survey of dynamic positioning control systems. Annu. Rev. Control 2011, 35, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Yang, R.; Pang, C.; Zhang, Q. Observer-based adaptive robust stabilization of dynamic positioning ship with delay via Hamiltonian method. Ocean Eng. 2021, 222, 108439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Wu, D.; Liao, Y.; Hu, X. Sliding mode control unified with the uncertainty and disturbance estimator for dynamically positioned vessels subjected to uncertainties and unknown disturbances. Appl. Ocean Res. 2021, 109, 102564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Li, T.; Yuan, L.E.; Bai, W. Robust fuzzy adaptive output feedback optimal tracking control for dynamic positioning of marine vessels with unknown disturbances and uncertain dynamics. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 23, 2283–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossen, T.I. Guidance and Control of Ocean Vehicles; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Wu, H.T.; Liu, W.X. Effects of mooring line hydrodynamic coefficients and wave parameters on the floating production storage and offloading motions. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 239, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Miao, Q.; Wang, X.; Xu, S.; Fan, H. A novel numerical method for the hydrodynamic analysis of floating bodies over a sloping bottom. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2021, 26, 1198–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Yang, Z.; Yang, T. Leader–Follower Formation Tracking Control of Underactuated Surface Vehicles Based on Event-Trigged Control. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, T.; Chen, C.P. Finite-time control for USV path tracking under input saturation with random disturbances. Appl. Ocean Res. 2023, 138, 103628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, M.; Do, V.T.; Khyam, M.O.; Do, X.P. Tracking control of uncertain surface vessels with global finite-time convergence. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 241, 109974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D. Optimal Jamming Strategy Against Two-state Switched System. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 13, 2283–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Xue, J.J. Nonlinear vector model control of underactuated air cushion vehicle based on parameter reduction algorithm. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2021, 43, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. Polynomial regressors based data-driven control for autonomous underwater vehicles. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 2020, 13, 1767–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, K.D. Global robust and adaptive output feedback dynamic positioning of surface ships. J. Mar. Sci. Appl. 2011, 10, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossen, T.I.; Strand, J.P. Passive nonlinear observer design for ships using Lyapunov methods: Full-scale experiments with a supply vessel. Automatica 1999, 35, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Xia, C.; Sun, C. Distributed formation tracking control of underactuated surface vehicles based on event-trigged control. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Lin, X.G.; Liang, K. Robust tracking control for dynamic positioning ships subject to dynamic safety constraints. Ocean Eng. 2022, 266, 112710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Du, J.L.; Hu, X. Robust adaptive prescribed performance control for dynamic positioning of ships under unknown disturbances and input constraints. Ocean Eng. 2020, 206, 107254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Du, J. Global Robust Adaptive Trajectory Tracking Control for Surface Ships Under Input Saturation. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2020, 45, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Du, Y.; Deng, Z. Finite-time trajectory tracking control of unmanned surface vessel with error constraints and input saturations. J. Frankl. Inst. 2020, 357, 11472–11495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.L.; Hu, X.; Krstic, M.; Sun, Y.Q. Robust dynamic positioning of ships with disturbances under input saturation. Automatica 2016, 73, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.D.; Li, C.P.; Sun, Y.C.; Wang, N. Adaptive trajectory tracking algorithm of unmanned dinamicaly positioned vessel based on 269 anti-windup compensator with full-state constraints. Ocean Eng. 2020, 200, 106906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Gong, C.; Zhang, D.; Hu, X. Simple Dynamic Positioning Control Design for Surface Vessels with Input Saturation and External Disturbances. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2023, 70, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechlioulis, C.P.; Rovithakis, G.A. Robust adaptive control of feedback linearizable MIMO nonlinear systems with prescribed performance. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2008, 53, 2090–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Yin, X.H.; Shen, F. Disturbance observer based adaptive neural prescribed performance control for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems with unknown backlash-like hysteresis. Neurocomputing 2018, 299, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.Q.; Zhang, B.W. Finite-Time Control of dinamicaly positioned vessel Based on Disturbance Observer. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 9262457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.K.; Bucknall, R. Cooperative path planning algorithm for marine dinamicaly positioned vessels. Ocean Eng. 2013, 57, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, T.; Han, M. Output-Feedback Cooperative Formation Maneuvering of Autonomous dynamic positioning 273 Vehicles With Connectivity Preservation and Collision Avoidance. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 50, 2527–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.S.; Yoo, S.J. An error transformation approach for connectivity-preserving and collision-avoiding formation tracking of networked uncertain underactuated surface vessels. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 49, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.S.; Yoo, S.J. Distributed dynamic obstacle avoidance design to connectivity-preserving formation control of uncertain underactuated surface vehicles under a directed network. Ocean Eng. 2023, 273, 113872. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.W.; Xia, G.Q. Output Feedback Tracking Control with Collision Avoidance for Dynamic Positioning Vessel under Input Constraint. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Huang, L.; He, Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, X. A real-time multi-ship collision avoidance decision-making system for autonomous ships considering ship motion uncertainty. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 278, 114205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Y.A.; Hannan, M.A.; Oraby, M.Y.; Maimun, A. COLREGs compliant Fuzzy-Based collision avoidance system for multiple ship encounters. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, H.T.L.; Tapia, L. COLREG-RRT: An RRT-based COLREGS-compliant motion planner for surface vehicle navigation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 2024–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Jin, Y.; Huang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, P.; Mou, J. Quantitative analysis of COLREG rules and seamanship for autonomous collision avoidance at open sea. Ocean Eng. 2017, 140, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjetne, R.; Fossen, T.I.; Kokotovi, P.V. Adaptive maneuvering, with experiments, for a model ship in a marine control laboratory. Automatica 2005, 41, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Xia, G. Output Feedback Tracking Control for Vessel with Collision-Avoidance and Performance Constraints. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11285. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011285
Zhang B, Xia G. Output Feedback Tracking Control for Vessel with Collision-Avoidance and Performance Constraints. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(20):11285. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011285
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Benwei, and Guoqing Xia. 2023. "Output Feedback Tracking Control for Vessel with Collision-Avoidance and Performance Constraints" Applied Sciences 13, no. 20: 11285. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011285
APA StyleZhang, B., & Xia, G. (2023). Output Feedback Tracking Control for Vessel with Collision-Avoidance and Performance Constraints. Applied Sciences, 13(20), 11285. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011285





