Stability Improvement of the Immersed Boundary–Lattice Boltzmann Coupling Scheme by Semi-Implicit Weighting of External Force
Abstract
:1. Introduction
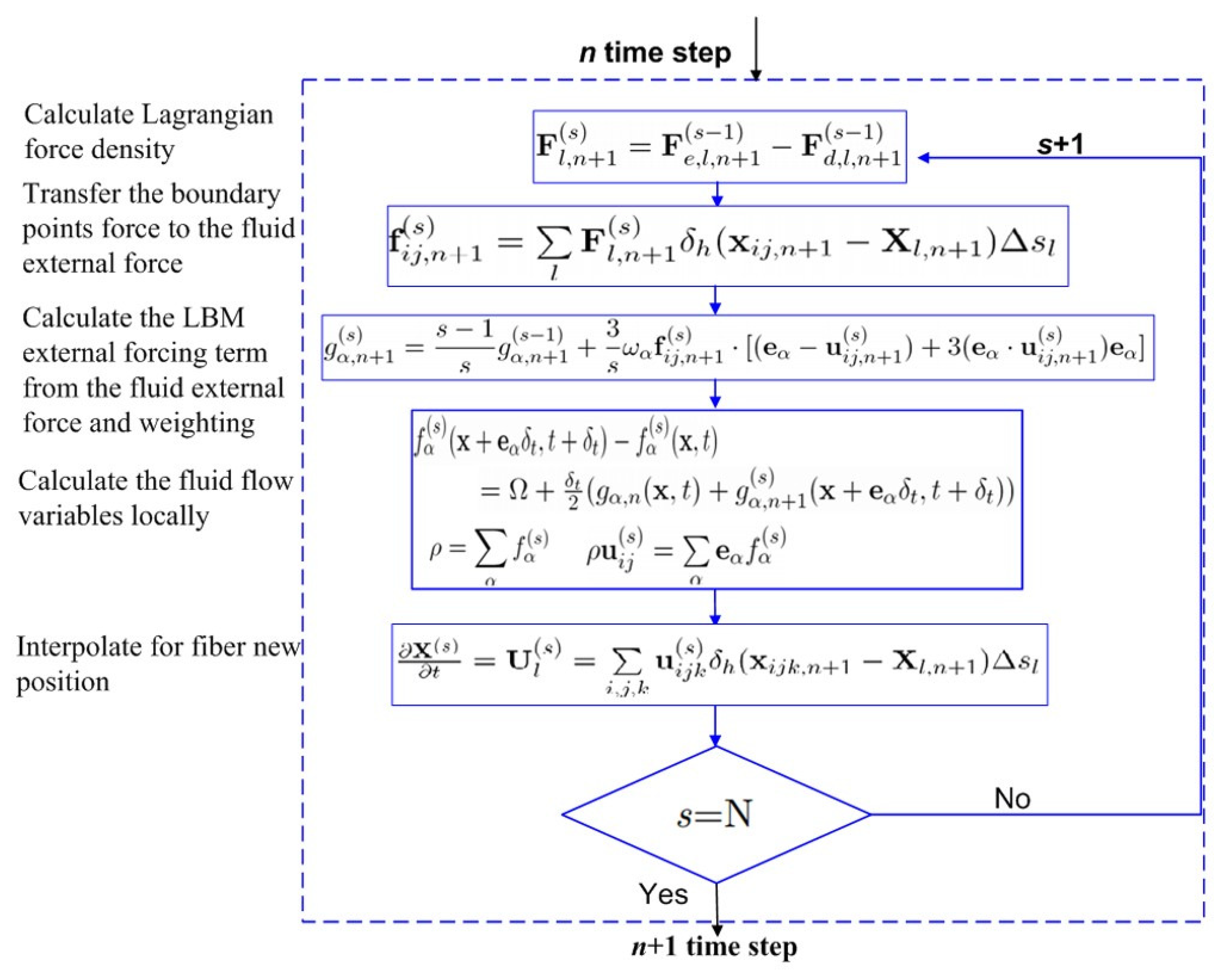
2. Immersed Boundary–Lattice Boltzmann Coupling Scheme
2.1. Immersed Boundary Method
2.2. The LB Method for the Fluid Flow
2.2.1. Basic Formulation of LBM with Multi-Relaxation-Time Collision
2.2.2. Introducing the External Force into the LB Model
3. Presentation of the Averagely Weighted Iteration Approach
3.1. Effectiveness of the DI Approach in Improving the Stability
- (1)
- With the explicit method, the executable program begins to run stably only at , when the membrane relaxes to a circular curve.
- (2)
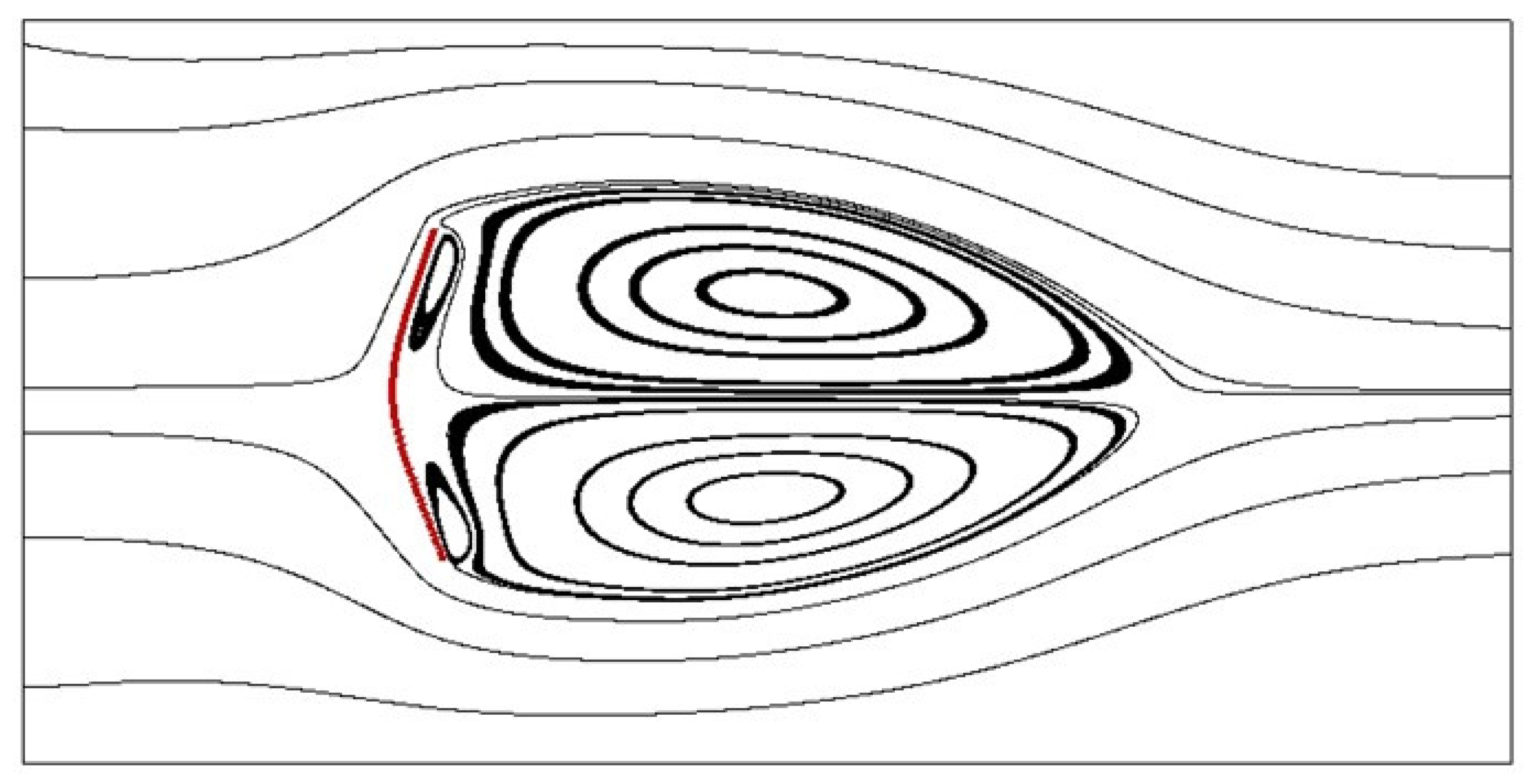
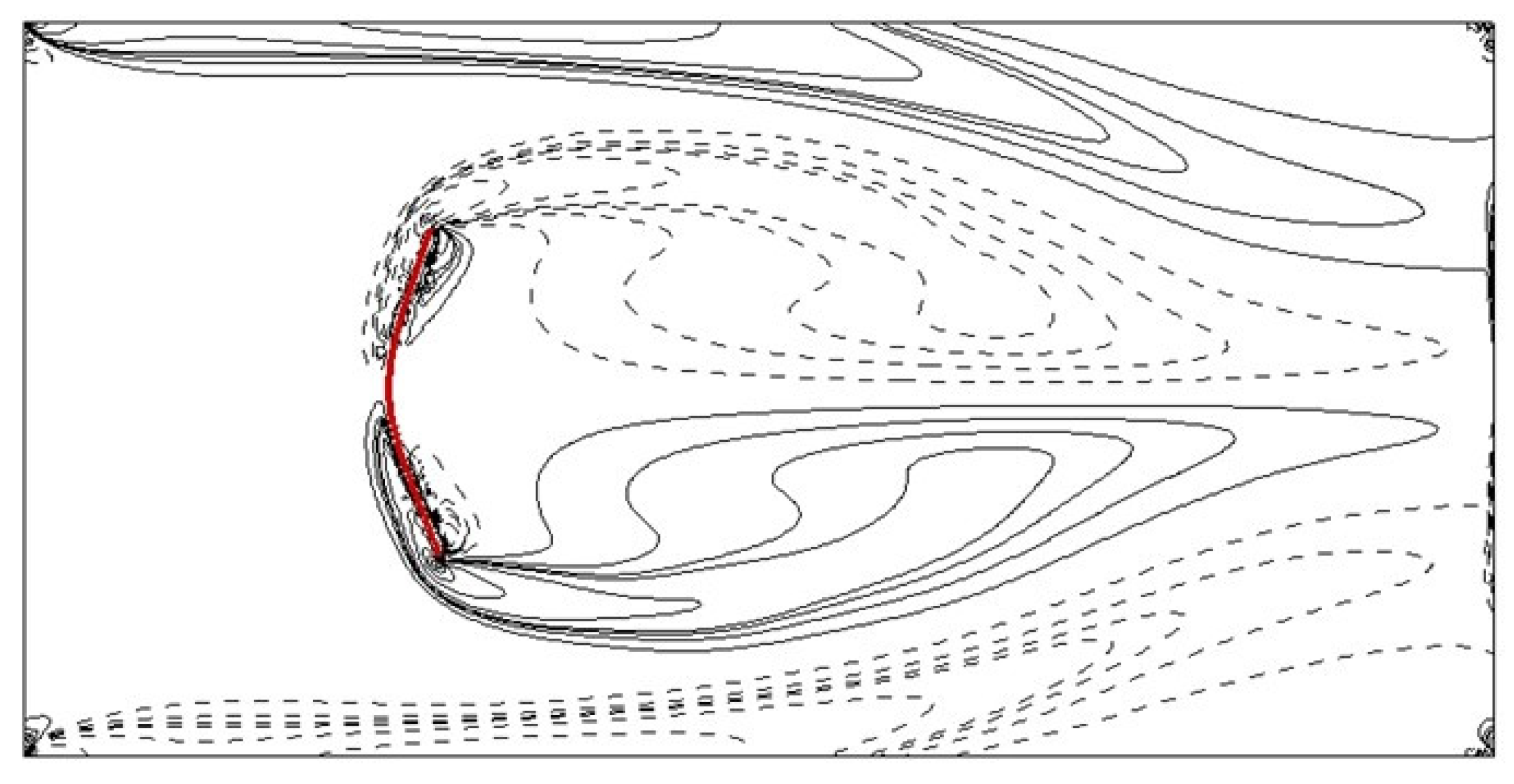
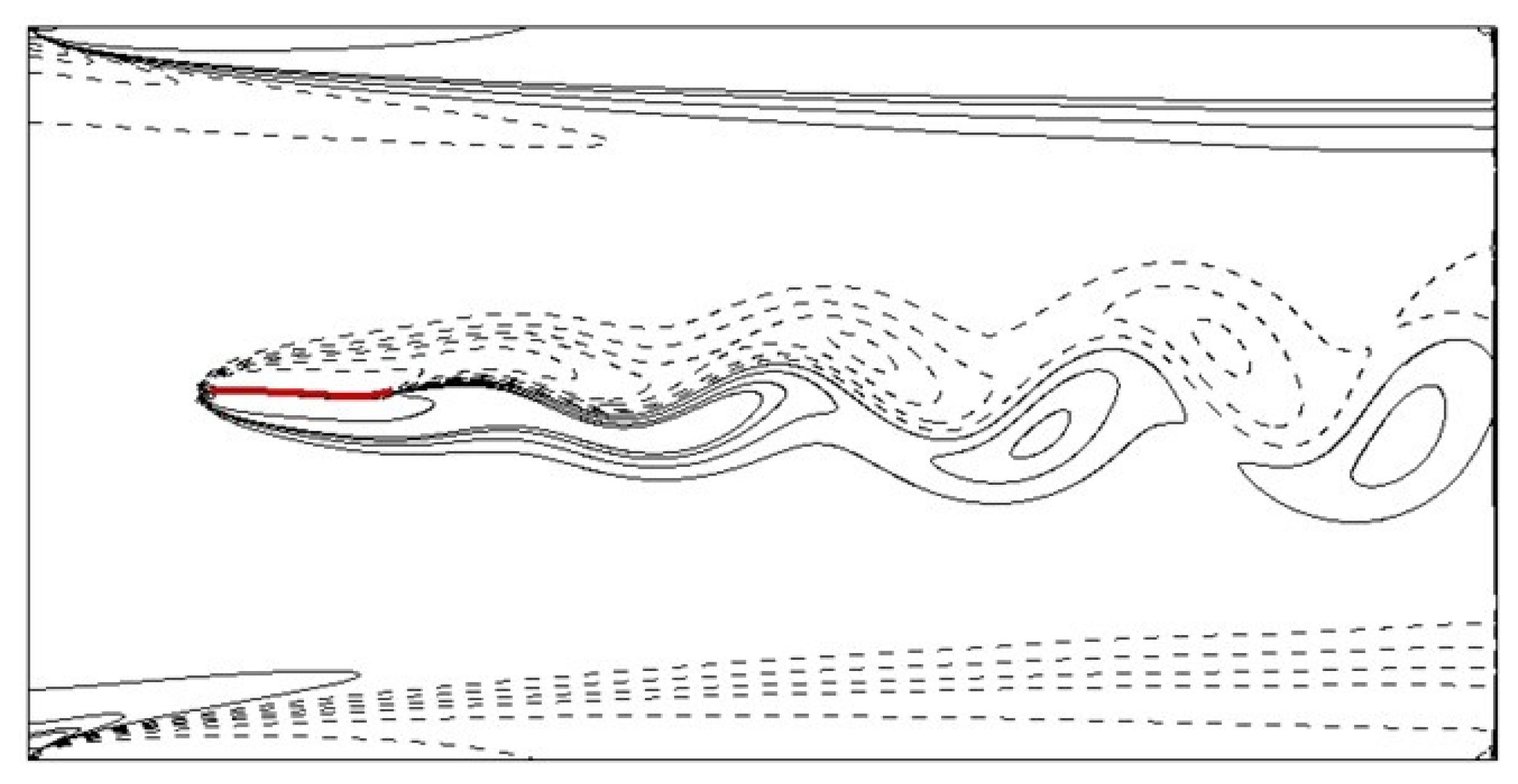
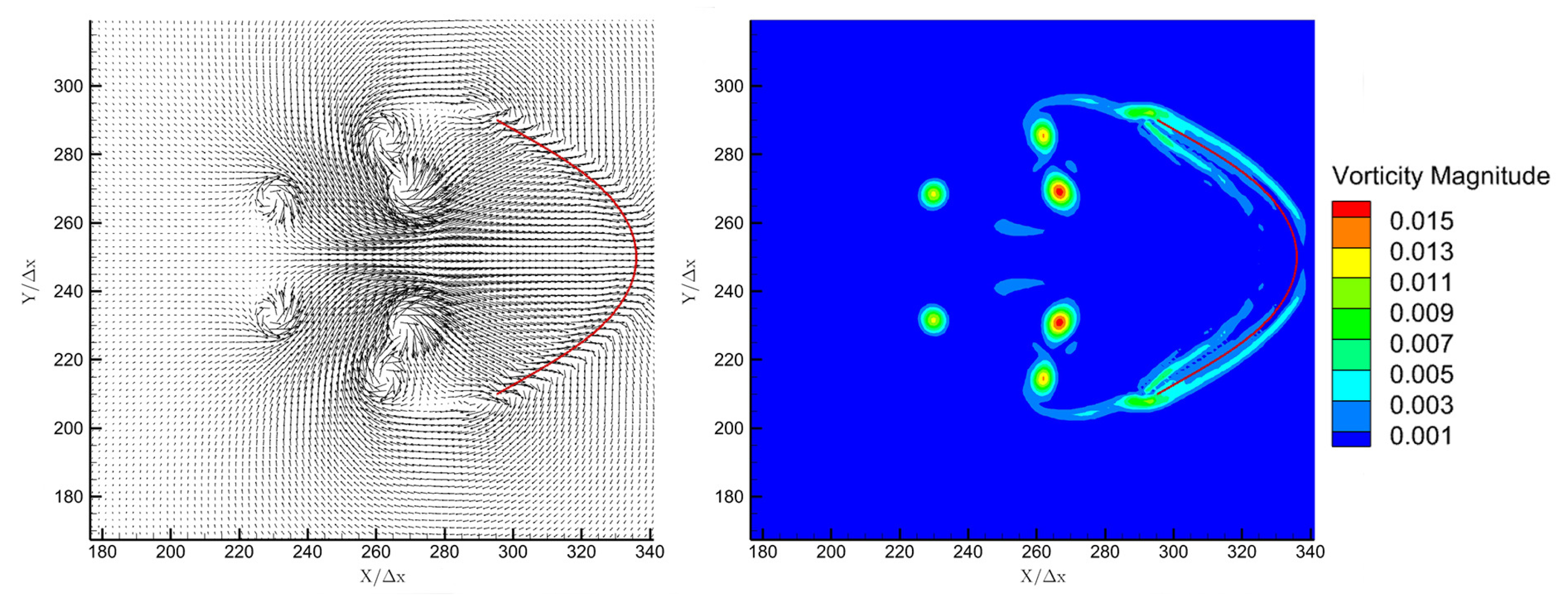
- With the DI approach (the iteration time per evolution step is set as 10), the critical value is . In addition, the stability rapidly decreases with increasing iteration time (in Figure 2 the IB knots in four diagonal regions).
3.2. Averagely Weighted Iteration (AWI) Approach
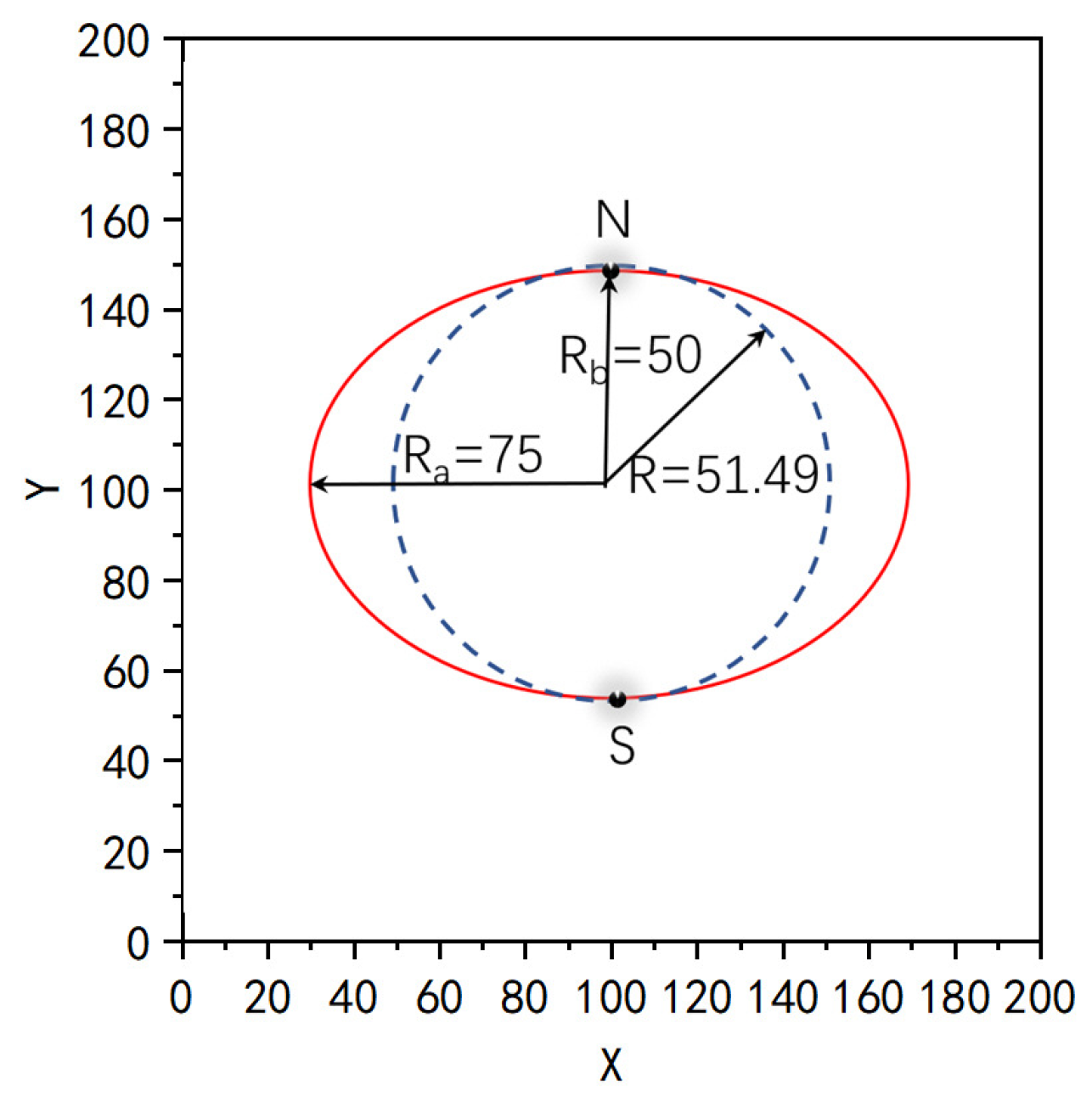
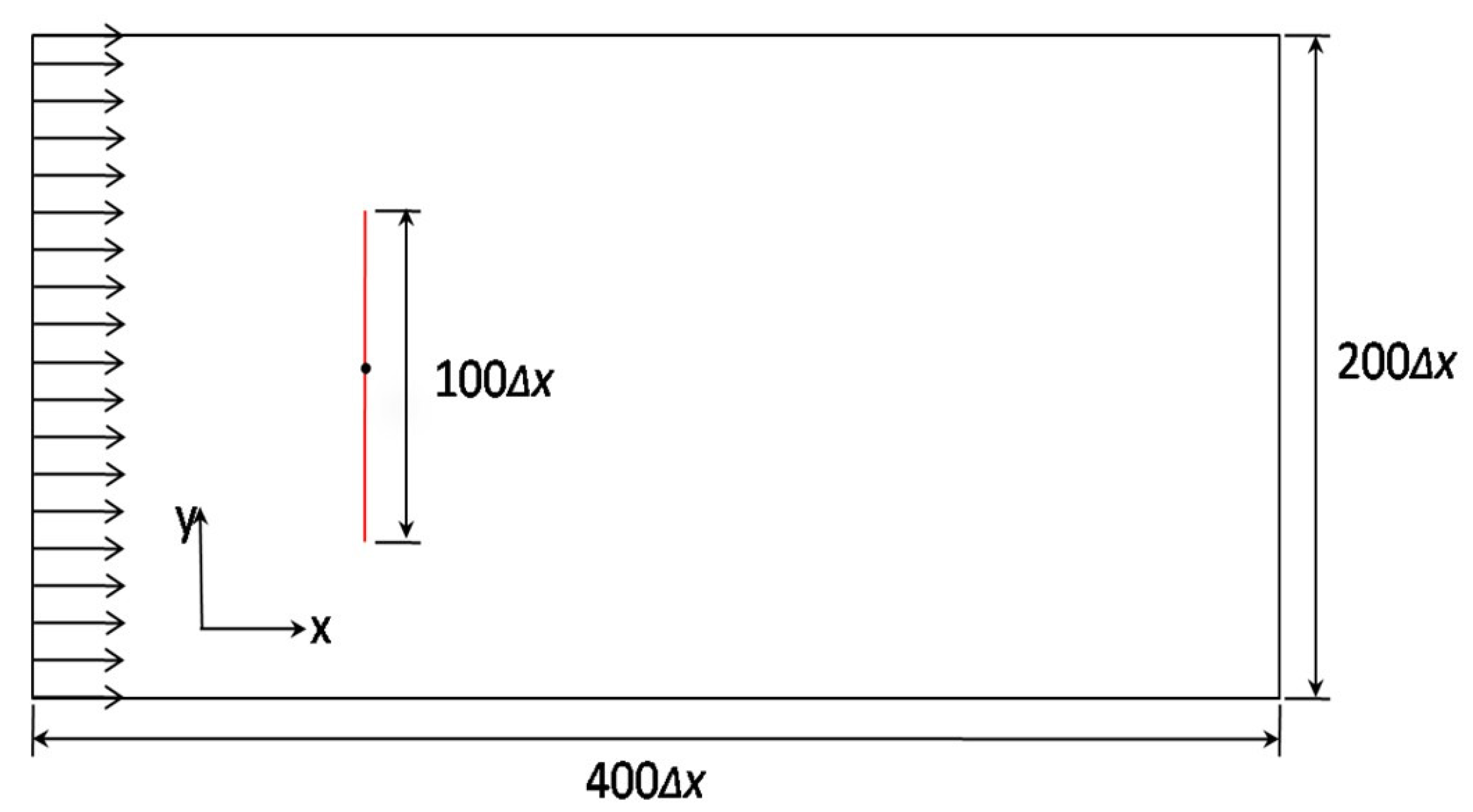
4. Verification and Validation
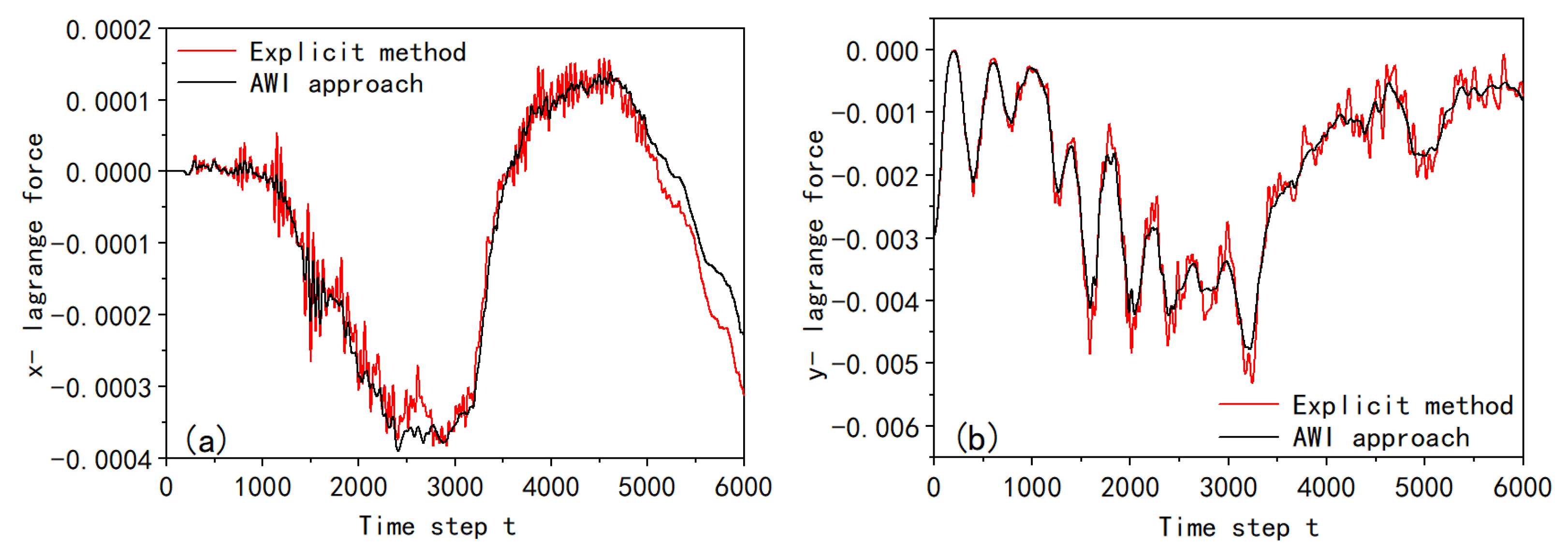
4.1. Verification of the Accuracy of the Averagely Weighted Iteration (AWI) Approach
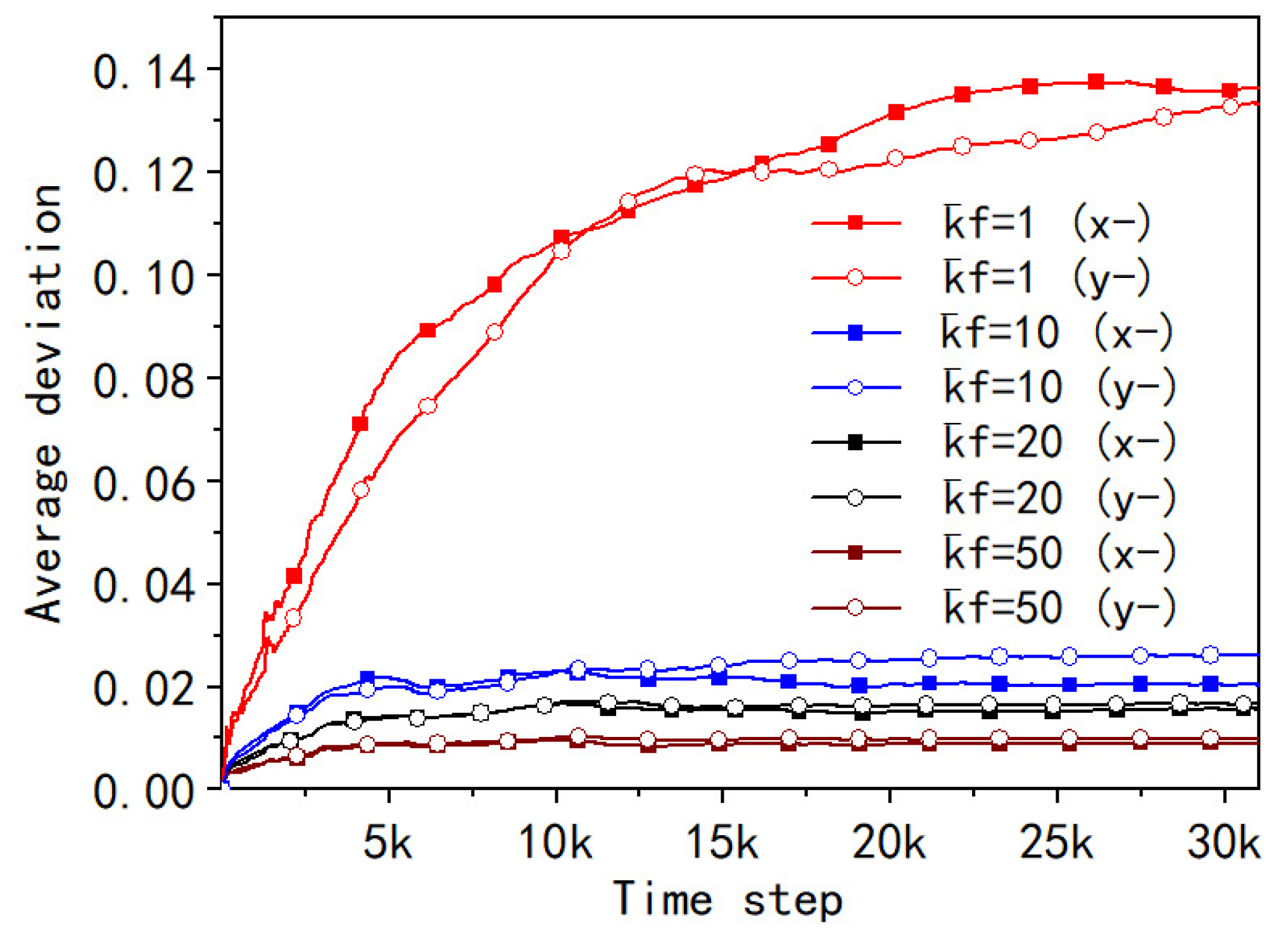
4.2. Validation of the Stability Improvement
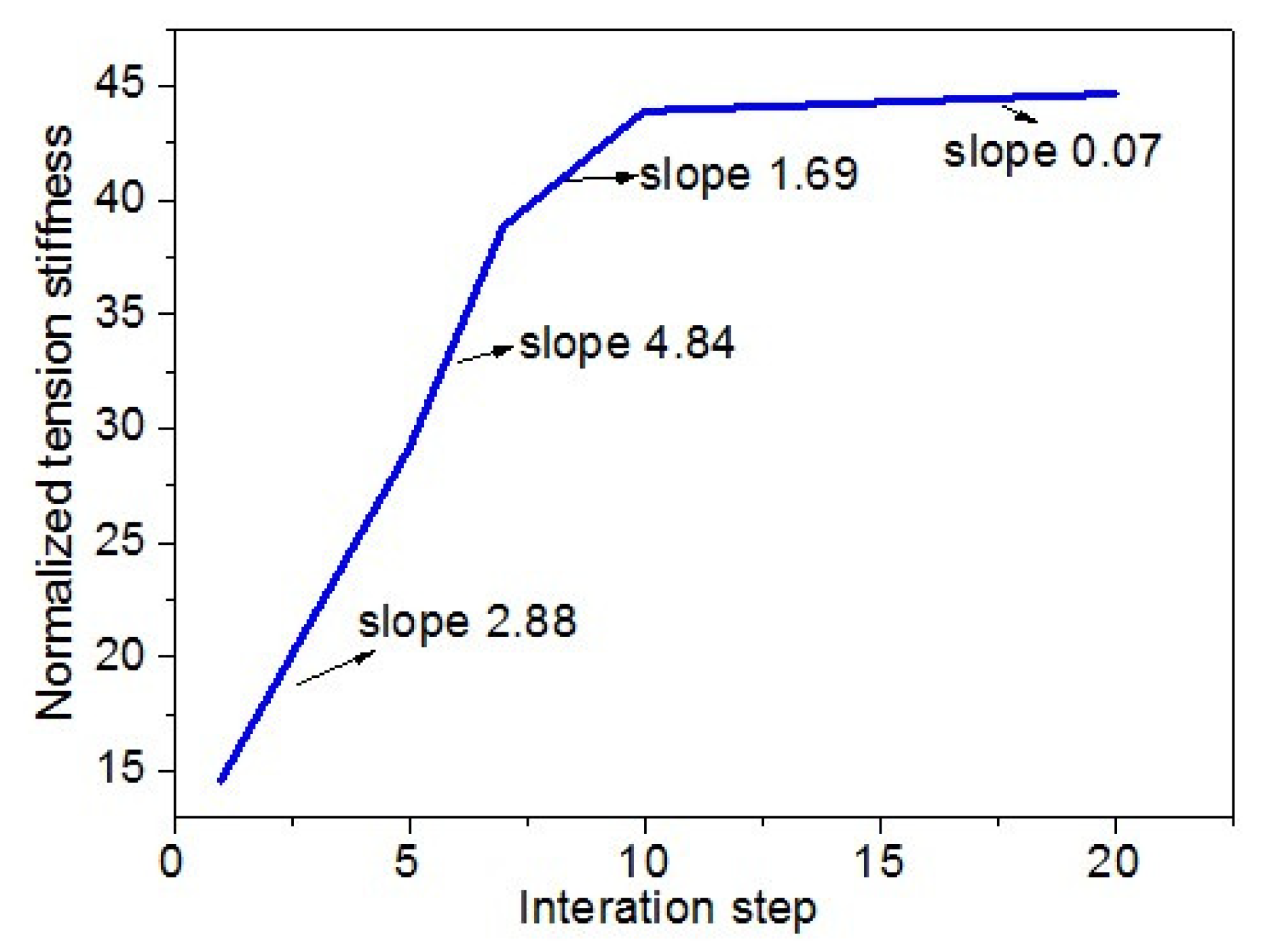
4.2.1. Tension Stiffness
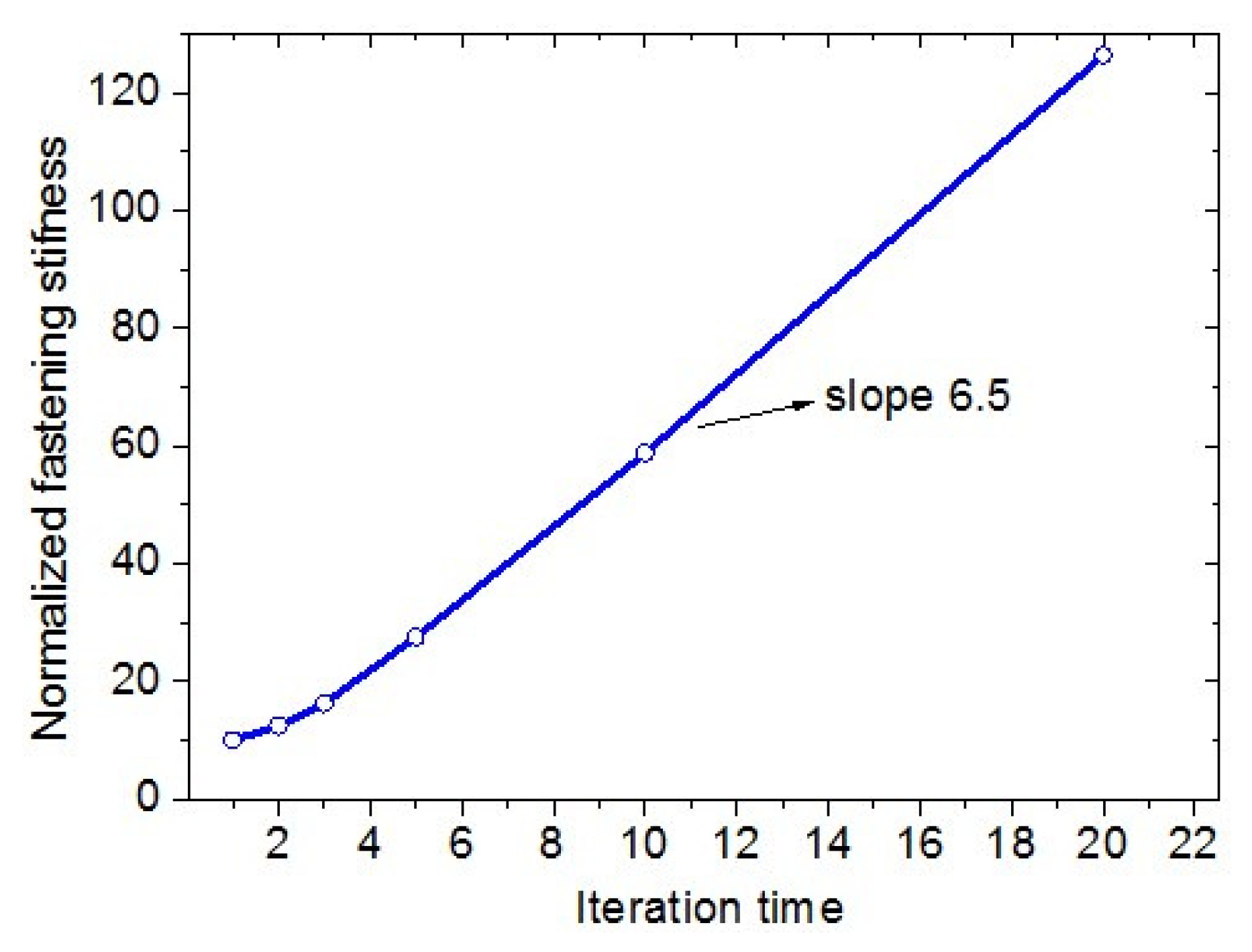
4.2.2. Fastening Stiffness
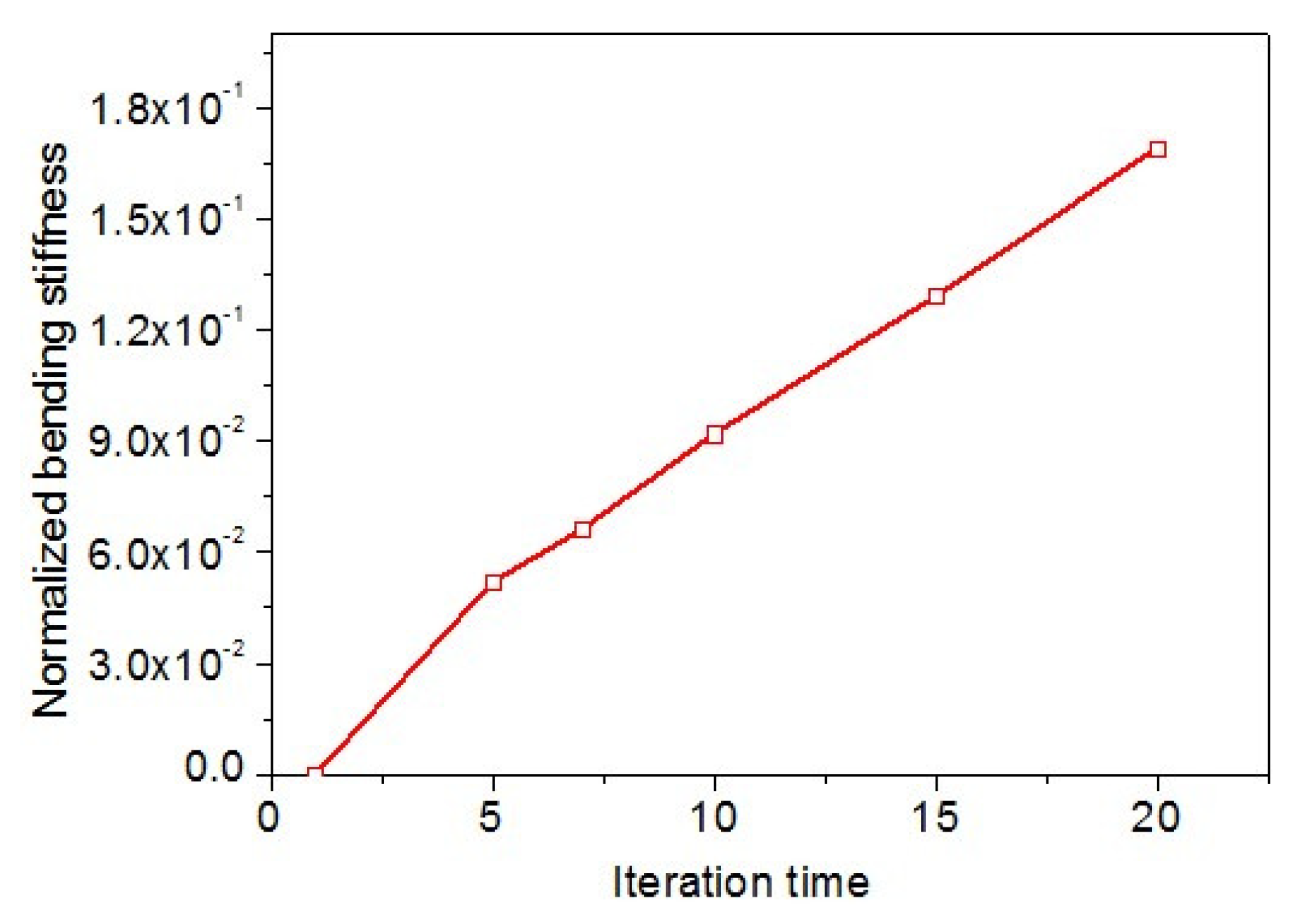
4.2.3. Bending Rigidity
4.2.4. Density of the Flexible Structure
4.2.5. Fluid Viscosity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LBM | Lattice Boltzmann method |
| IBM | Immersed boundary method |
| AWI | Averagely weighted iteration |
| DI | Directly iterative |
References
- Fauci, L.; Fogelson, A.L. Truncated Newton Methods and the Modeling of Complex Immersed Elastic Structures. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 1993, 46, 787–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeVeque, R.J.; Li, Z. Immersed Interface Methods for Stokes Flow with Elastic Boundaries or Surface Tension. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 1997, 18, 709–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roma, A.M.; Peskin, C.S.; Berger, M. An Adaptive Version of the Immersed Boundary Method. J. Comput. Phys. 1999, 153, 509–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peskin, C.S. The Immersed Boundary Method. Acta Numer. 2002, 11, 479–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, R.; Minion, M.L. The Blob Projection Method for Immersed Boundary Problems. J. Comput. Phys. 2000, 161, 428–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, M.; Peskin, C.S. An Analysis of the Numerical Stability of the Immersed Boundary Method. J. Comput. Phys. 2021, 467, 111435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peskin, C.S.; Printz, B.F. Improved Volume Conservation in the Computation of Flows with Immersed Elastic Boundaries. J. Comput. Phys. 1993, 105, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockburn, B.; Shu, C.W.; Johnson, C.; Tadmor, E.; Shu, C.W. Essentially Non-Oscillatory and Weighted Essentially Non-Oscillatory Schemes for Hyperbolic Conservation Laws; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Connell, B.S.H.; Yue, D.K.P. Flapping Dynamics of a Flag in a Uniform Stream. J. Fluid Mech. 2007, 581, 33–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.X.; Sung, H.J. Three-Dimensional Simulation of a Flapping Flag in a Uniform Flow. J. Fluid Mech. 2010, 653, 301–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Luo, H. Effect of Wing Inertia on Hovering Performance of Flexible Flapping Wings. Phys. Fluids 2010, 22, 111902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxian, O.; Peskin, C.S. An Immersed Boundary Method with Subgrid Resolution and Improved Numerical Stability Applied to Slender Bodies in Stokes Flow. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2020, 42, B847–B868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newren, E.P.; Fogelson, A.L.; Guy, R.D.; Guy, R.D.; Kirby, R.M. Unconditionally Stable Discretizations of the Immersed Boundary Equations. J. Comput. Phys. 2007, 222, 702–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.B.; Luo, H.; Zhu, L.; Liao, J.C.; Lu, X.Y. An Efficient Immersed Boundary-Lattice Boltzmann Method for the Hydrodynamic Interaction of Elastic Filaments. J. Comput. Phys. 2011, 230, 7266–7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Zhu, L. A lattice Boltzmann based implicit immersed boundary method for fluid-structure interaction. Comput. Math. Appl. 2010, 59, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Diao, W. Simulating Vortex Induced Vibration of an Impulsively Started Flexible Filament by an Implicit IB–LB Coupling Scheme. Comput. Math. Appl. 2017, 79, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Zhan, J.; Zhao, N.; Wang, T. A Robust Immersed Boundary-Lattice Boltzmann Method for Simulation of Fluid-Structure Interaction Problems. Commun. Comput. Phys. 2016, 20, 156–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C. Numerical Study of Stability and Accuracy of the Immersed Boundary Method Coupled to the Lattice Boltzmann BGK Model. Commun. Comput. Phys. 2014, 16, 136–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; He, G.; Wang, S.; Miller, L.A.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhang, X.; You, Q.; Fang, S. An Immersed Boundary Method Based on the Lattice Boltzmann Approach in Three Dimensions, with Application. Comput. Math. Appl. 2011, 61, 3506–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Humières, D.; Ginzburg, I.; Krafczyk, M.; Lallemand, P.; Luo, L.S. Multiple-Relaxation-Time Lattice Boltzmann Models in Three Dimensions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2002, 360, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, J. Introducing Unsteady Non-Uniform Source Terms into the Lattice Boltzmann Model. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2008, 56, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H. Immersed Boundary Method and Lattice Boltzmann Method Coupled FSI Simulation of Mitral Leaflet Flow. Comput. Fluids 2010, 39, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Niu, X.D.; Shu, S.; Li, M.; Yamaguchi, H.; Yamaguchi, H. A Momentum Exchange-Based Immersed Boundary-Lattice Boltzmann Method for Simulating a Flexible Filament in an Incompressible Flow. Comput. Math. Appl. 2014, 67, 1039–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


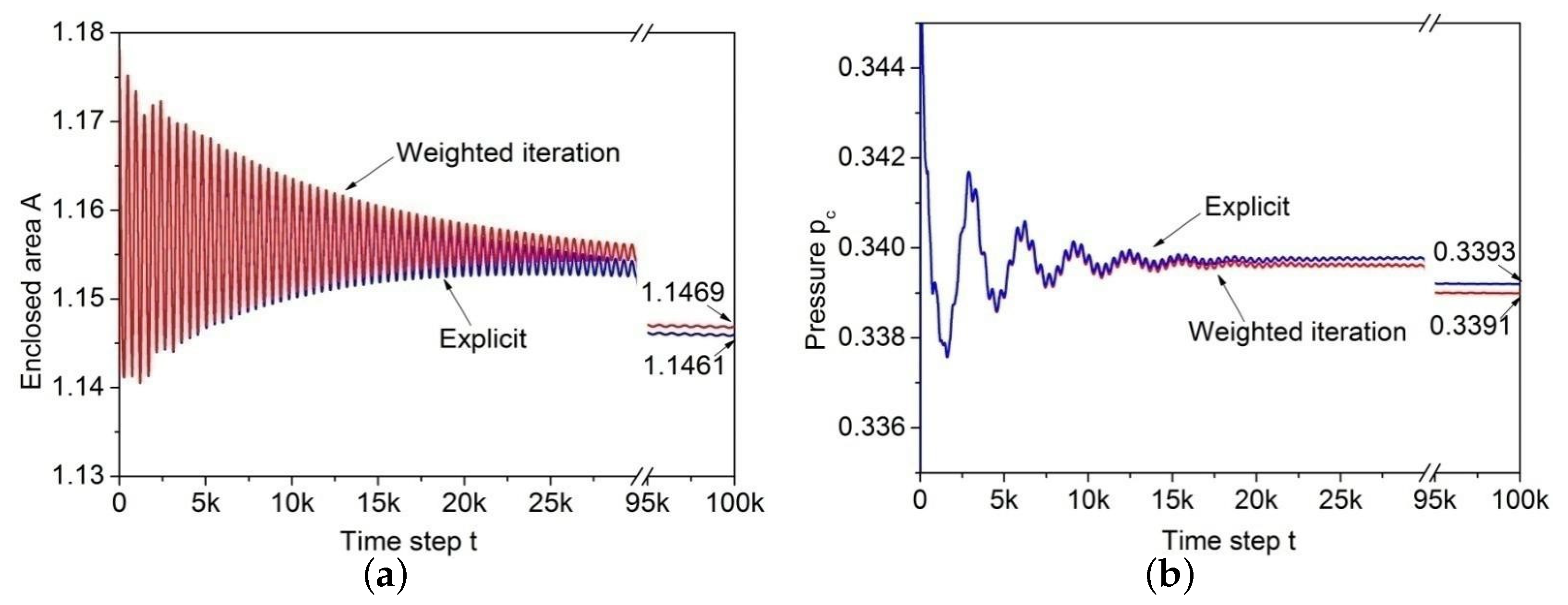
| Parameters | Enclosed Area, A | Pressure Jump, Δp | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t = 30,000 | t = 100,000 | t = 30,000 | t = 100,000 | ||
| Simulated | (Explicit) | 1.1532 | 1.1461 | 0.00607 | 0.00596 |
| (AWI) | 1.1544 | 1.1469 | 0.00601 | 0.00581 | |
| Analytical | 1.1576 | 1.1576 | 0.00589 | 0.00589 | |
| Relative error (%) | (Explicit) | 0.38 | 0.99 | 3.1 | 1.2 |
| (AWI) | 0.28 | 0.92 | 2 | 1.4 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Li, T.; Hou, J.; Zhou, Q.; Meng, W.; Ma, Q.; Peng, P. Stability Improvement of the Immersed Boundary–Lattice Boltzmann Coupling Scheme by Semi-Implicit Weighting of External Force. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9995. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13189995
Zhang C, Li T, Hou J, Zhou Q, Meng W, Ma Q, Peng P. Stability Improvement of the Immersed Boundary–Lattice Boltzmann Coupling Scheme by Semi-Implicit Weighting of External Force. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(18):9995. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13189995
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chunze, Tao Li, Ji Hou, Qin Zhou, Wanwan Meng, Qian Ma, and Peiyi Peng. 2023. "Stability Improvement of the Immersed Boundary–Lattice Boltzmann Coupling Scheme by Semi-Implicit Weighting of External Force" Applied Sciences 13, no. 18: 9995. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13189995
APA StyleZhang, C., Li, T., Hou, J., Zhou, Q., Meng, W., Ma, Q., & Peng, P. (2023). Stability Improvement of the Immersed Boundary–Lattice Boltzmann Coupling Scheme by Semi-Implicit Weighting of External Force. Applied Sciences, 13(18), 9995. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13189995





