A Computational (DFT) Study on the Anti-Malarial Drug: Lumefantrine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Computational Details
- Efficiency: The 6-31G* basis set is relatively compact compared to larger basis sets such as 6-311++G** or aug-cc-pVTZ. This compactness makes calculations using the 6-31G* basis set computationally more efficient, requiring less memory and shorter computation times. It is often a good choice for preliminary calculations or screening large systems.
- Cost-effectiveness: The computational cost of calculations with the 6-31G* basis set is typically lower compared to higher-level basis sets. This makes it a cost-effective choice for routine calculations or when dealing with large-scale simulations where computational resources may be limited.
- Accuracy for organic molecules: The 6-31G* basis set has been specifically optimized for accurate calculations of organic molecules. It includes polarization functions, which allow for a better description of electron correlation effects and improved accuracy for properties, such as molecular geometries, bond lengths and vibrational frequencies.
- Transferability: The 6-31G* basis set has been extensively tested and widely used for a variety of organic systems. Its parameters have been carefully optimized to reproduce experimental data for a broad range of molecules. As a result, it can be considered a reasonably transferable basis set that provides reliable results for many chemical systems.
- Compatibility: The 6-31G* basis set is available in many popular quantum chemistry software packages, making it easily accessible for researchers. Its widespread use ensures compatibility with a range of computational tools and facilitates comparison and reproduction of results across different studies.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure of the Compound
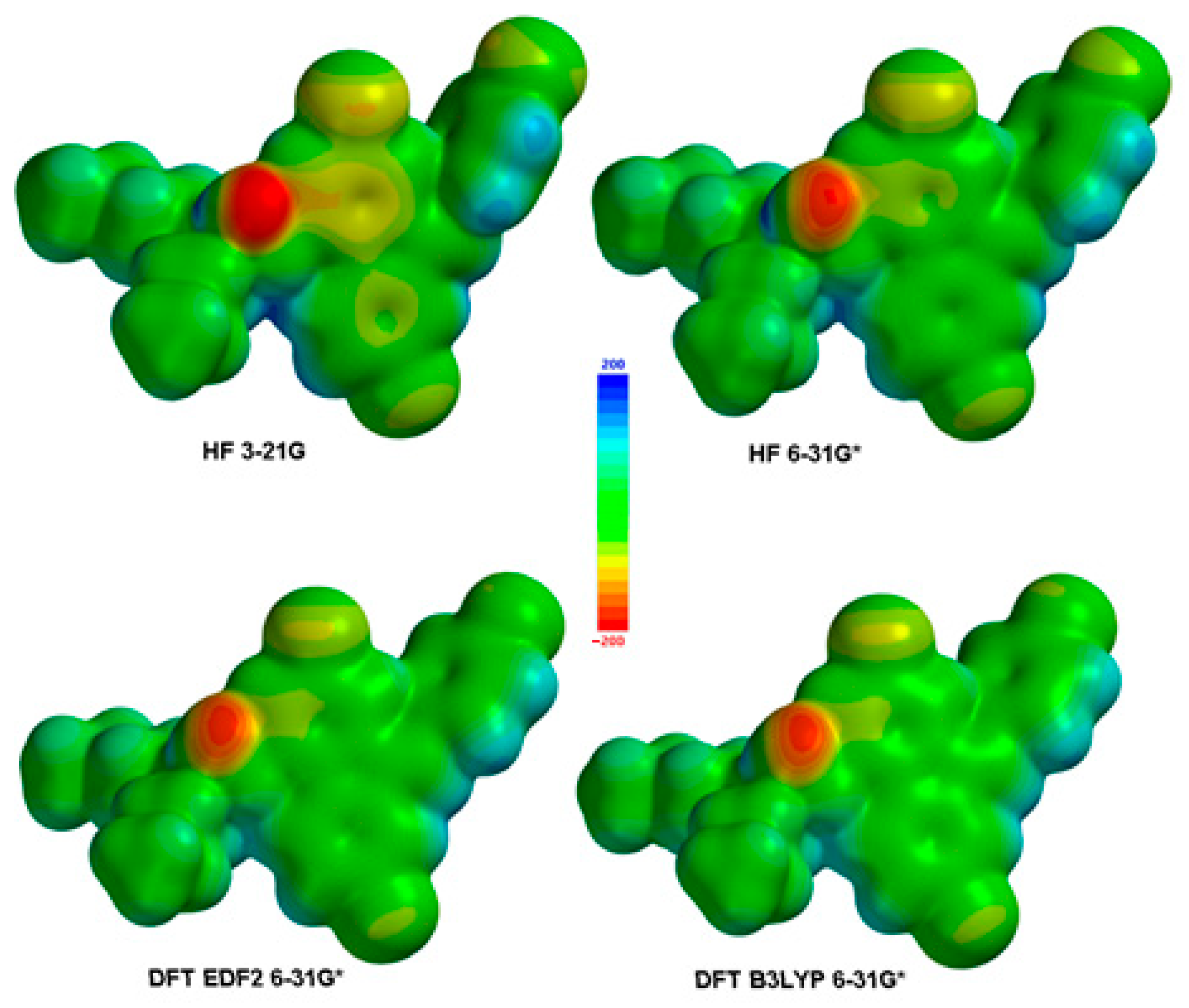
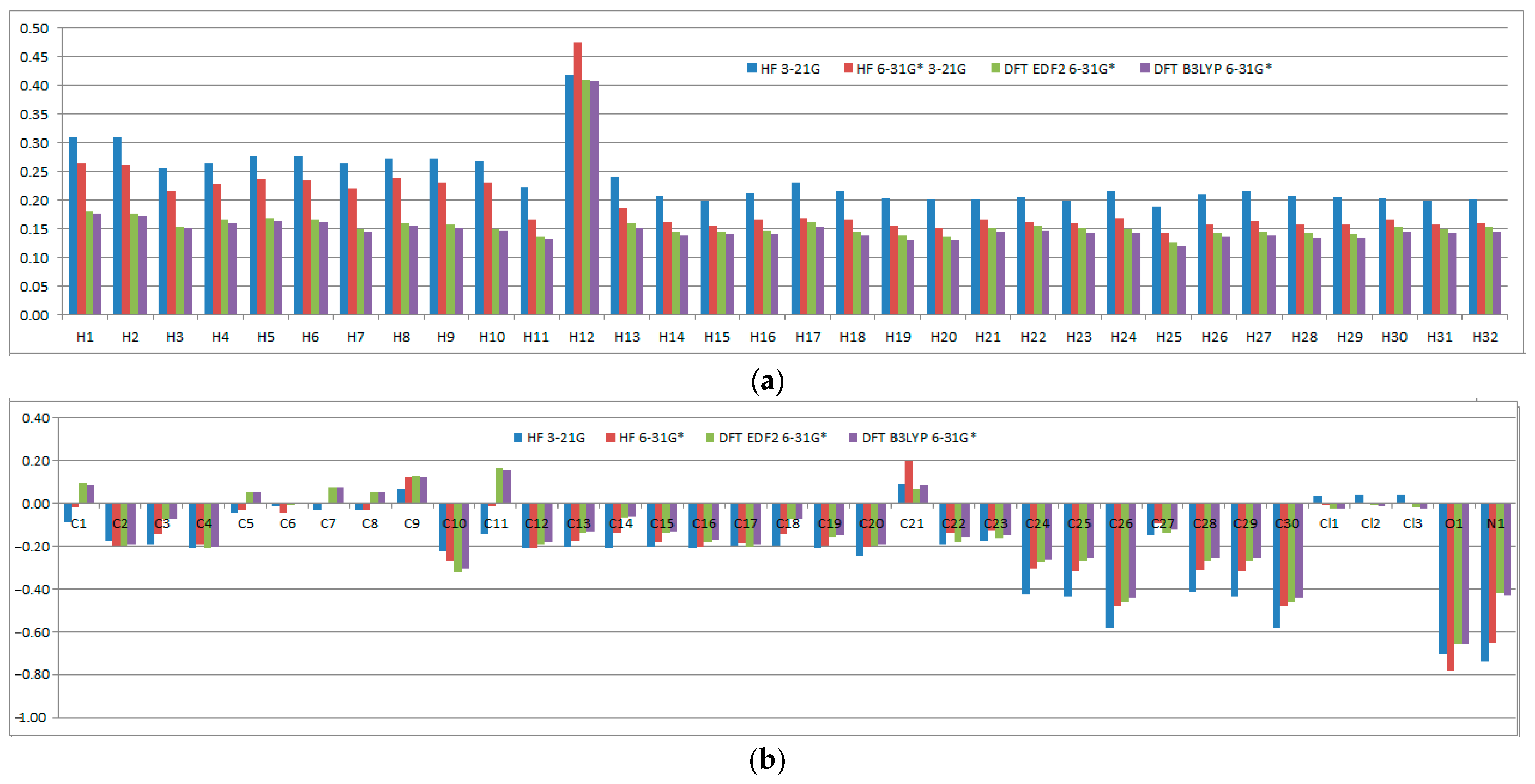
3.2. Electronic and Spectral Properties
- Molecular reactivity: The electrostatic potential is closely related to the reactivity of a molecule. It can provide insights into regions of high electron density (negative potential) that are likely to be involved in nucleophilic reactions, as well as regions of low electron density (positive potential) that are susceptible to electrophilic attacks. By examining the ESPMAP, chemists can predict sites of potential chemical reactions and understand the reactivity patterns of the molecule.
- Intermolecular interactions: The electrostatic potential plays a crucial role in intermolecular interactions, such as hydrogen bonding, van der Waals forces and solvation effects. An ESPMAP can help identify regions of positive or negative potential that are involved in these interactions. For example, the negative potential regions can indicate favorable sites for hydrogen bonding while positive potential regions can attract negatively charged species or induce dipole-dipole interactions.
- Molecular recognition: An ESPMAP is particularly useful in studying molecular recognition, such as ligand-protein interactions in drug design. By comparing the electrostatic potentials of a ligand and its target protein, researchers can identify complementary regions of positive and negative potentials that facilitate binding. Understanding the electrostatic complementarity between molecules aids in rational drug design and the development of more potent and selective compounds.
- Solvent effects: Solvent molecules can influence the electrostatic potential of a molecule, leading to changes in its properties and reactivity. An ESPMAP can help visualize how solvent molecules affect the distribution of charges and identify regions where solvation effects are significant. This knowledge is crucial in understanding the behavior of molecules in solution and predicting their behavior under different solvent conditions.
- Molecular properties: The electrostatic potential is closely related to various molecular properties, including molecular electrostatic potential (MEP), molecular dipole moment and polarizability. An ESPMAP can provide insights into these properties, allowing researchers to analyze and compare different molecular features.
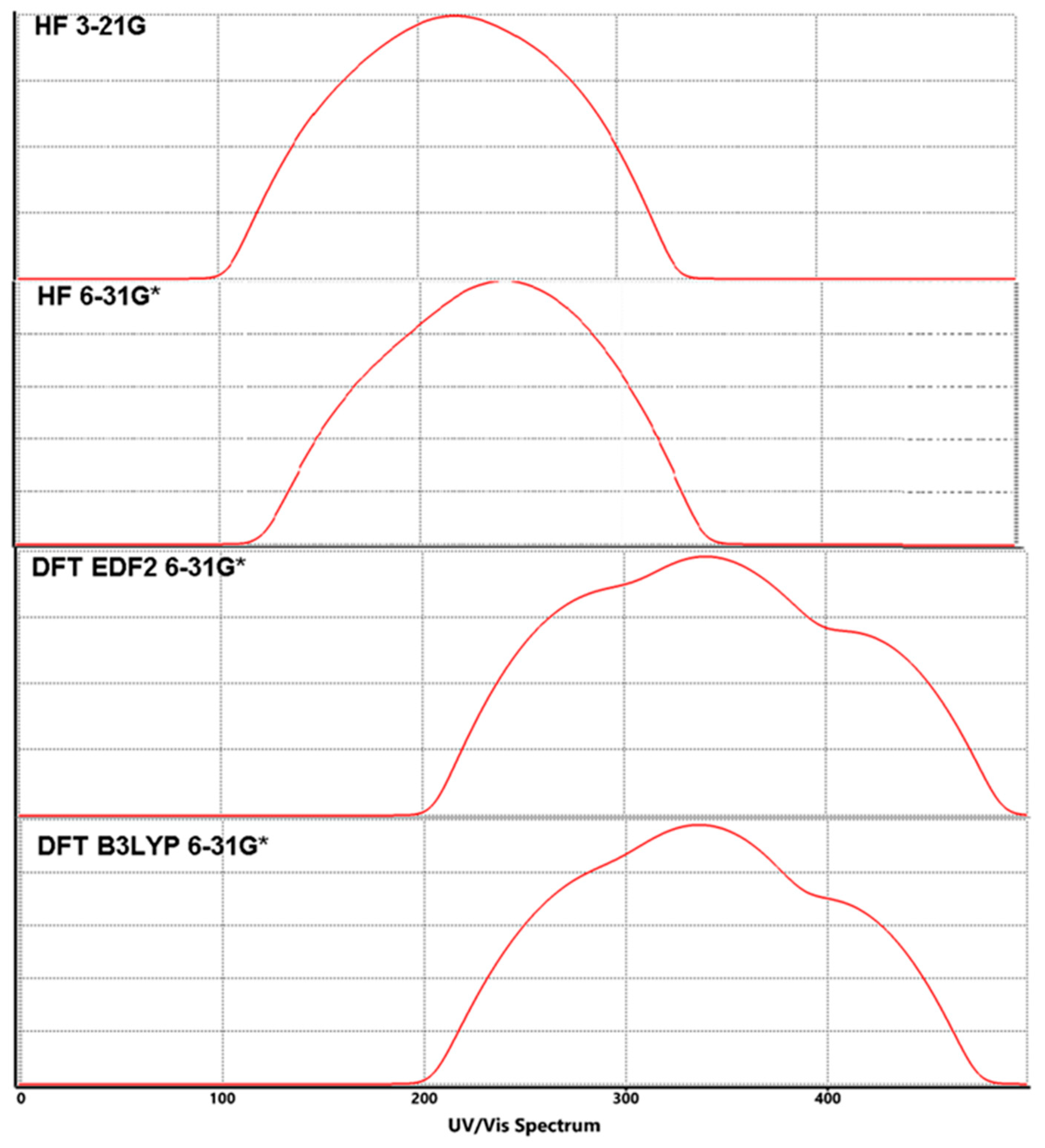
3.3. Molecular Orbitals Surfaces (HOMO-LUMO) Analysis and UV-Vis Spectra
3.4. FT-IR Vibrational Analysis
3.5. NMR Analysis
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pansuriya, P.B.; Maguire, G.E.M.; Friedrich, H.B. Structural Characterization and Thermal Properties of the Anti-malarial Drug: Lumefantrine. S. Afr. J. Chem 2019, 72, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). World Malaria Report; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gaur, D.; Chitnis, C.; Chauhan, V. Advances in Malaria Research. In The Wiley-IUBMB Series on Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 1st ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S. The Fever, How Malaria Has Ruled Humankind for 500,000 Years-Penguin Books; Penguin Random House India: Delhi, India, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, N.J.; van Vugt, M.; Ezzet, F. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics and pharmacodynamics of artemether-lumefantrine. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1999, 37, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a609024.html (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Bosaka, A.; Opsenicab, D.M.; Šinkoa, G.; Zlatarb, M.; Kovarika, Z. Structural aspects of 4-aminoquinolines as reversible inhibitors of human acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 308, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ahmary, K.M.; Alenezi, M.S.; Habeeb, M.M. Synthesis, spectroscopic and DFT theoretical studies on the hydrogen bonded charge transfer complex of 4-aminoquinoline with chloranilic acid. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 220, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaschula, C.H.; Egan, T.J.; Hunter, R.; Basilico, N.; Parapini, S.; Taramelli, D.; Pasini, E.; Monti, D. Structure-activity relationships in 4-aminoquinoline antiplasmodials. The role of the group at the 7-position. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 3531–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/4-Aminoquinoline (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Artemether (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/lumefantrine (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Lawrenson, A.S.; Cooper, D.L.; O’Neill, P.M.; Berry, N.G. Study of the antimalarial activity of 4-aminoquinoline compounds against chloroquine-sensitive and chloroquine-resistant parasite strains. J. Mol. Model. 2018, 24, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunduracioglu, A. A Novel Pyrazolium Salt with Phthalimide Functional Groups Synthesis Spectroscopic (NMR&FT-IR) and Computational Analysis. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2021, 30, 7551–7560. [Google Scholar]
- Gerbst, A.G.; Nikolaev, A.V.; Yashunsky, D.V.; Shashkov, A.S.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Nifantiev, N.E. Theoretical and NMR-based Conformational Analysis of Phos-phodiester-linked Disaccharides. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, G.; Goel, R.; Paul, K.; Luxami, V. Investigation of rotameric conformations of substituted imidazo-[1,2-a]pyrazine: Experimental and theoretical approaches†. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 9707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweckstetter, M. NMR: Prediction of molecular alignment from structure using the PALES software. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hehre, W.J. SPARTAN’14; Wavefunction, Inc.: Irvine, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hehre, W.J. SPARTAN’14: Tutorial and User’s Guide; Wavefunction, Inc.: Irvine, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kunduracioglu, A. (4-carbamoylphenyl)boronic Acid: A Dft Study On The Structural and Spectral Properties. Cauc. J. Sci. 2021, 8, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunduracioglu, A. 2-thienylboronic Acid: A DFT Study For the Spectral, Structural and Molecular Orbital Analysis. El-Cezerî J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 8, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhandapani, A.; Manivarman, S.; Subashchandrabose, S.; Saleem, H. Molecular structure and vibrational analysis on (E)-1-(3-methyl-2,6-diphenyl piperidine-4-ylidene) semicarbazide. J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1058, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://cccbdb.nist.gov/vibscalejust.asp (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Available online: https://cccbdb.nist.gov/vibnotes.asp (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Karakaş-Sarıkaya, E.; Dereli, Ö. Study on Molecular Structure and Vibrational Spectra of 5,7-Dimethoxycoumarin Using DFT: A Combined Experimental and Quantum Chemical Approach. Opt. Spectrosc. 2014, 117, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereli, Ö.; Erdoğdu, Y.; Güllüoğlu, M.T. Study on molecular structure and vibrational spectra of (triphenylphosphoranylidene) acetaldehyde using DFT: A combined experimental and quantum chemical approach. J. Mol. Struct. 2012, 1012, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarıkaya, E.K.; Dereli, Ö.; Erdoğdu, Y.; Güllüoğlu, M.T. Molecular structure and vibrational spectra of 7-Ethoxycoumarin by density functional method. J. Mol. Struct. 2013, 1049, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R.G. Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter. 1998, 37, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tormena, C.F. Conformational analysis of small molecules: NMR and quantum mechanics calculations. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2016, 96, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, R.; Kumar, A.; Kumar Awasthi, S. Practical scale up synthesis of carboxylic acids and their bioisosteres 5-substituted-1H-tetrazoles catalyzed by a graphene oxide-based solid acid carbocatalyst. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 11166–11176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemer-Kotan, G.; Yuksek, H. Experimental (FT-IR, NMR) and Theoretical (B3PW91, B3LYP, HF) Analyses of 2-(3-Ethyl-4,5-Dihydro-1H-1,2,4-Triazole-5-on-4-yl)-azomethine)-Benzoic Acid. Cauc. J. Sci. 2019, 6, 64–75. [Google Scholar]
- Turhan-Irak, Z.; Beytur, M. 4-Benzilidenamino-4,5-dihidro-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-on Türevlerinin Antioksidan Aktivitelerinin Teorik Olarak İncelenmesi [Theoretical Study on The Investigation of Antioxidant Properties of Some 4-Benzylidenamino-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-one Derivatives]. Iğdır Üniversitesi Fen Bilim. Enstitüsü Derg. 2019, 9, 512–521. [Google Scholar]
- Kunduracioglu, A. Tautomeric Forms of 2–Amino–5–Bromobenzoic Acid: A DFT Study for Structural and Molecular Orbital Analysis. Open J. Nano (OJN) 2021, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, F. Introduction to Computational Chemistry; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Webster, F.X.; Kiemle, D.J. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds, 7th ed.; John Wiley Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, K.I.; Deepa, G.; Namboori, K. Computational Chemistry and Molecular Modeling: Principles and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
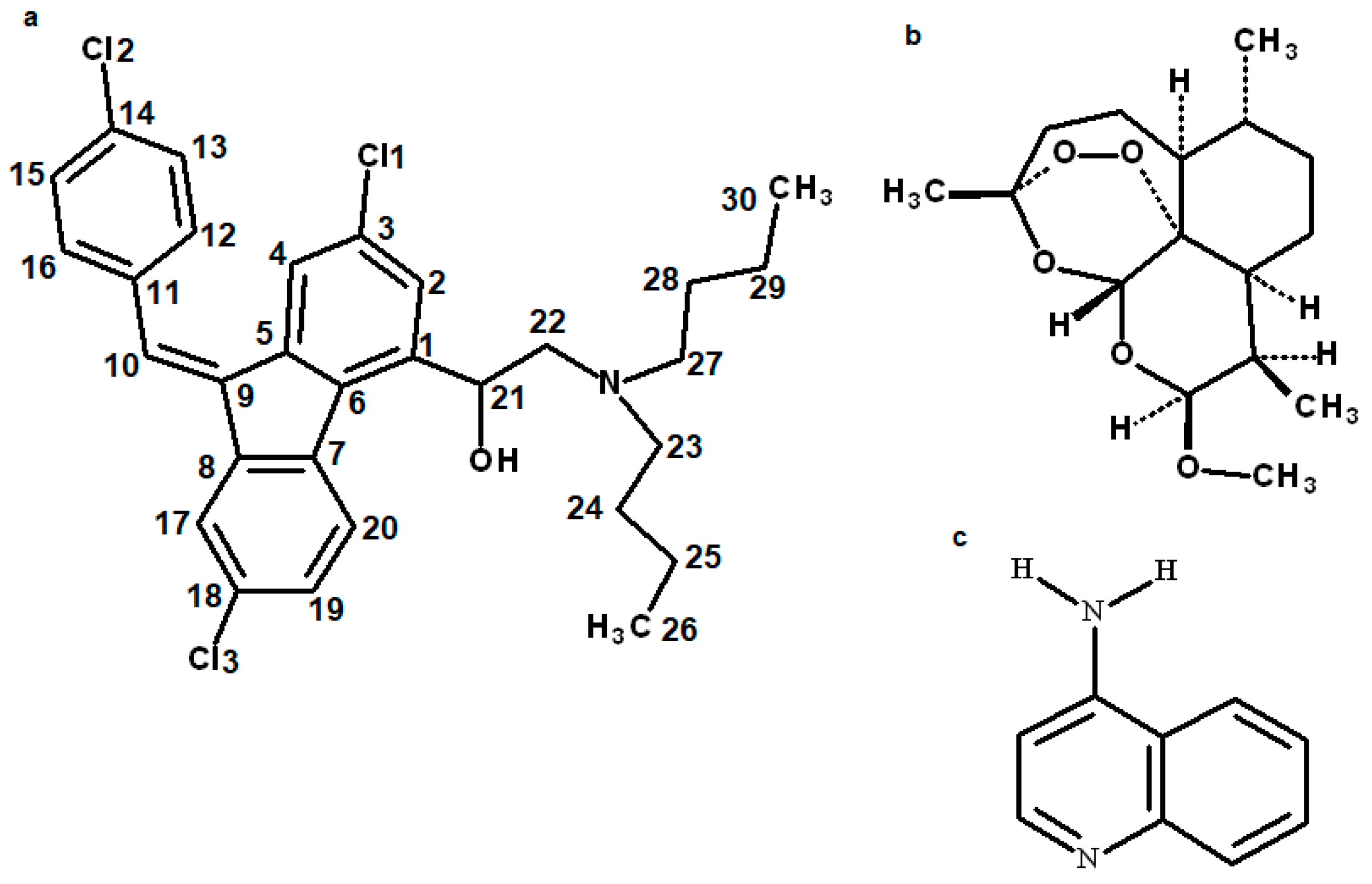

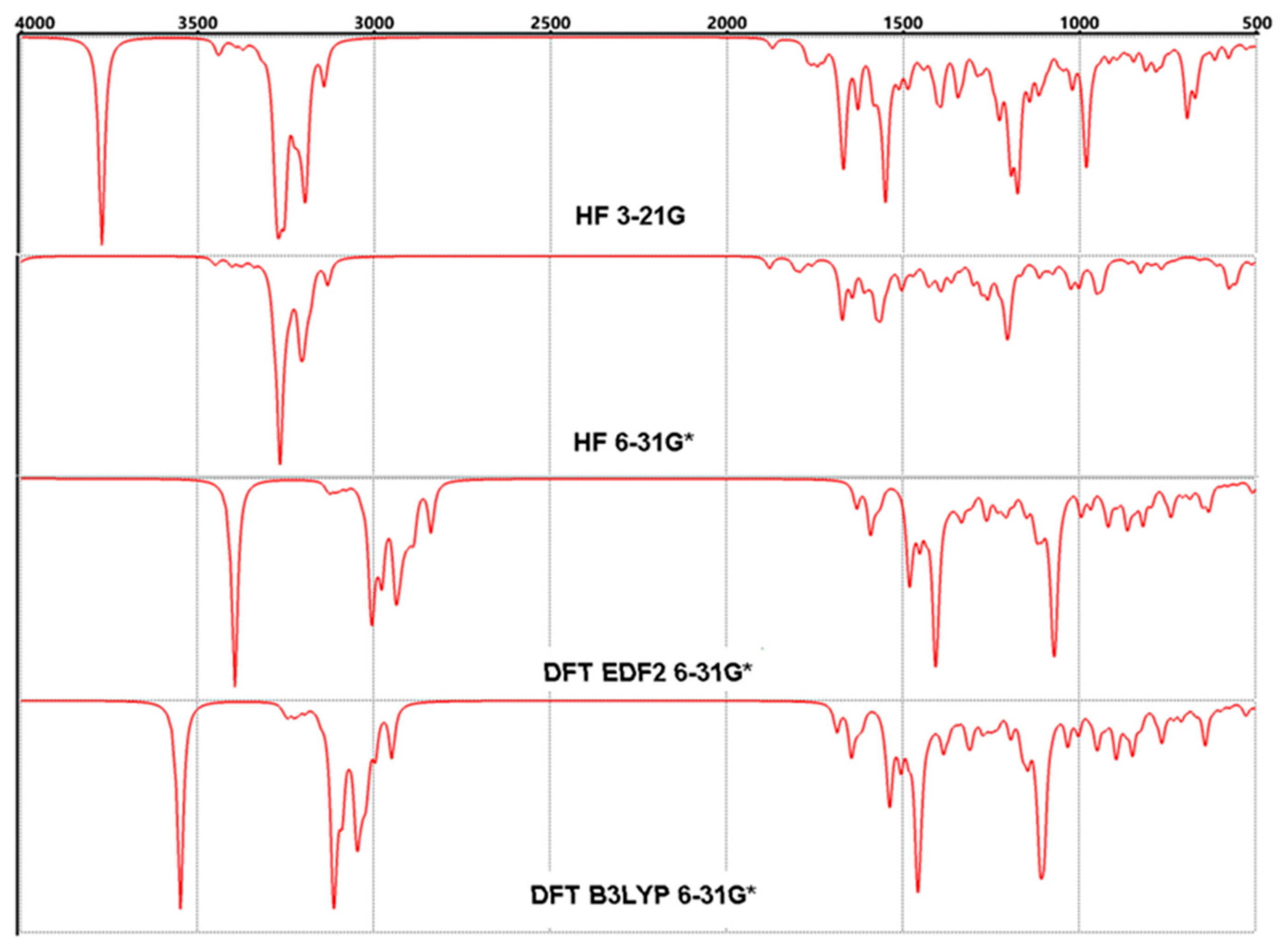
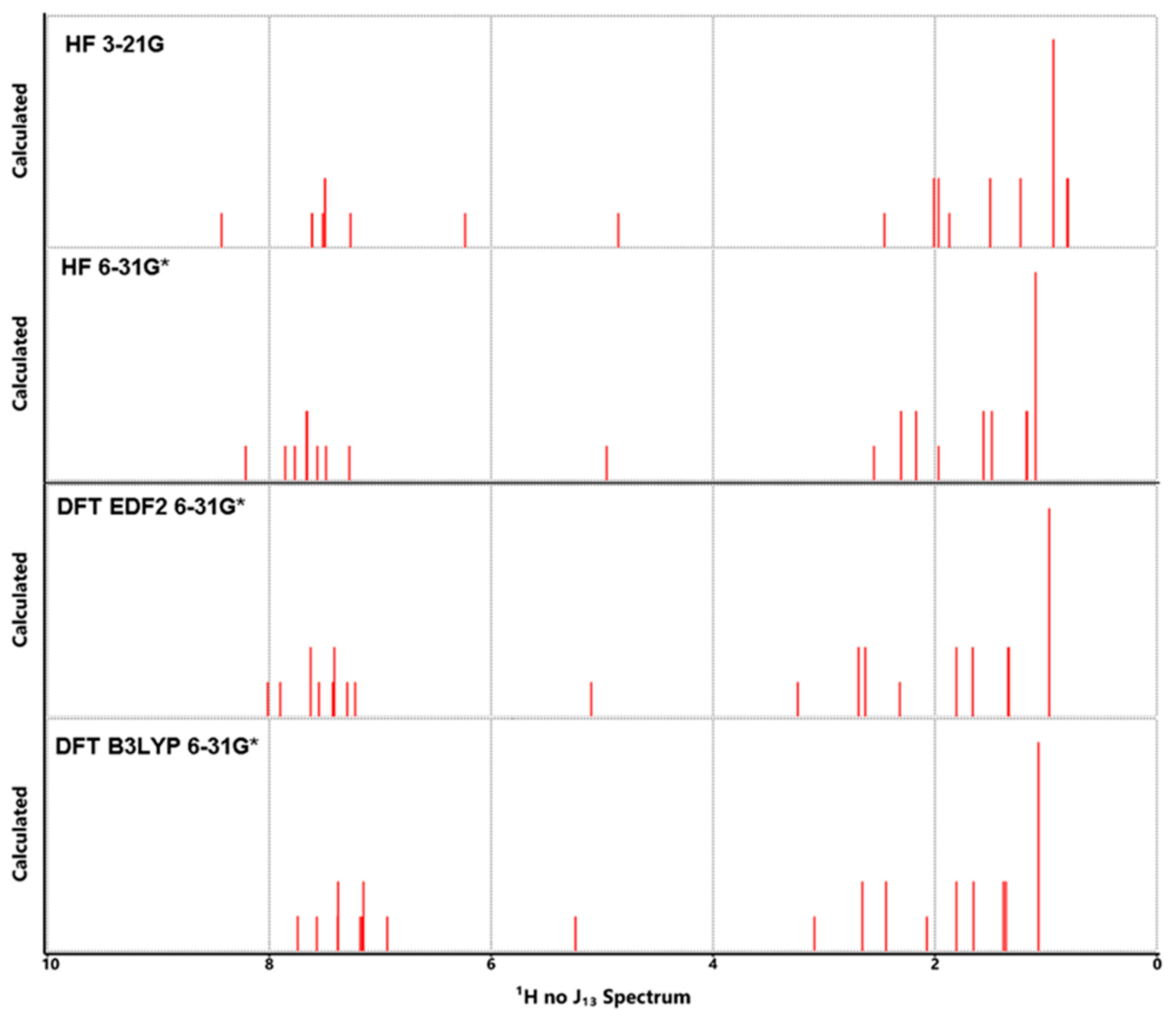
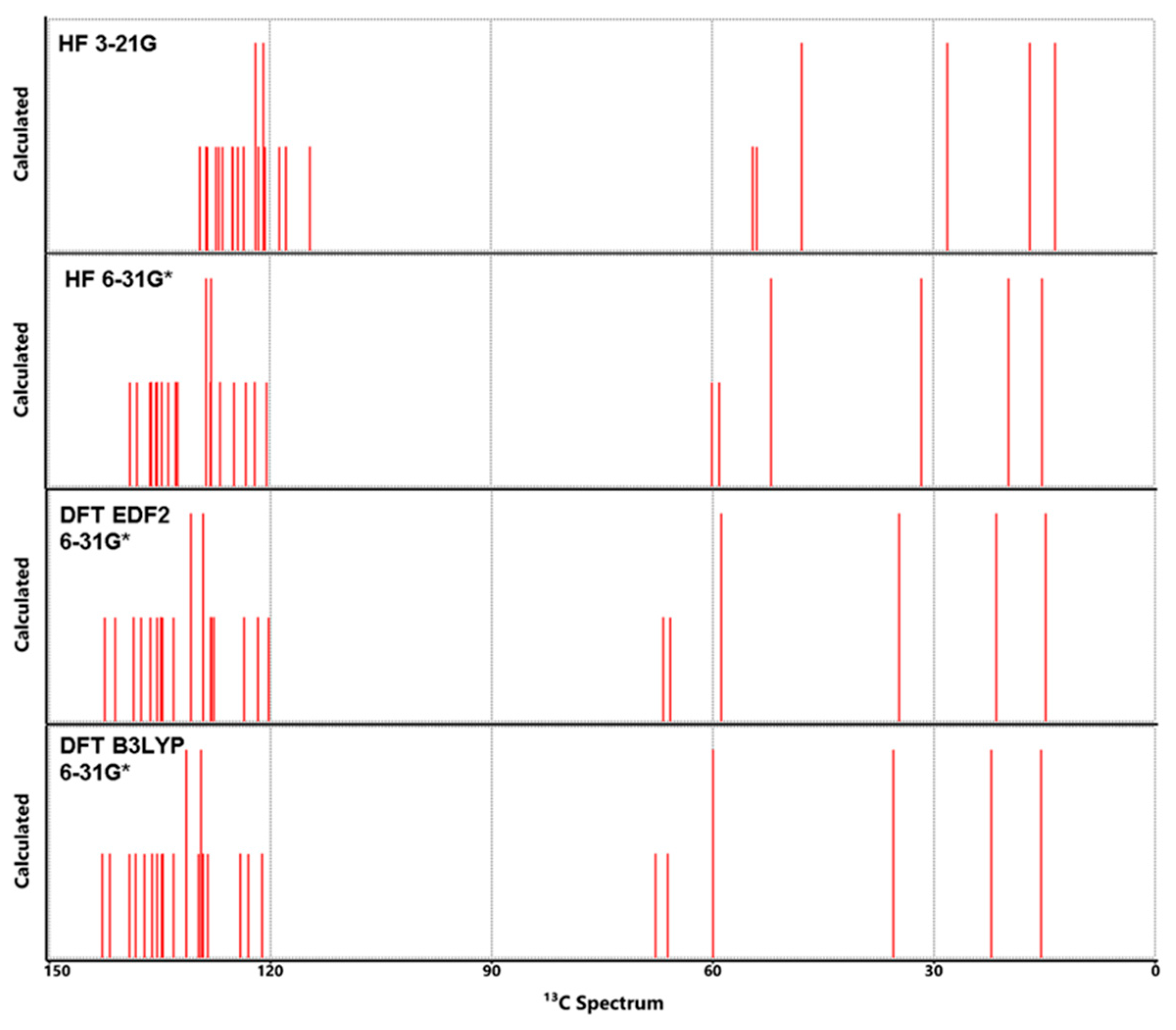
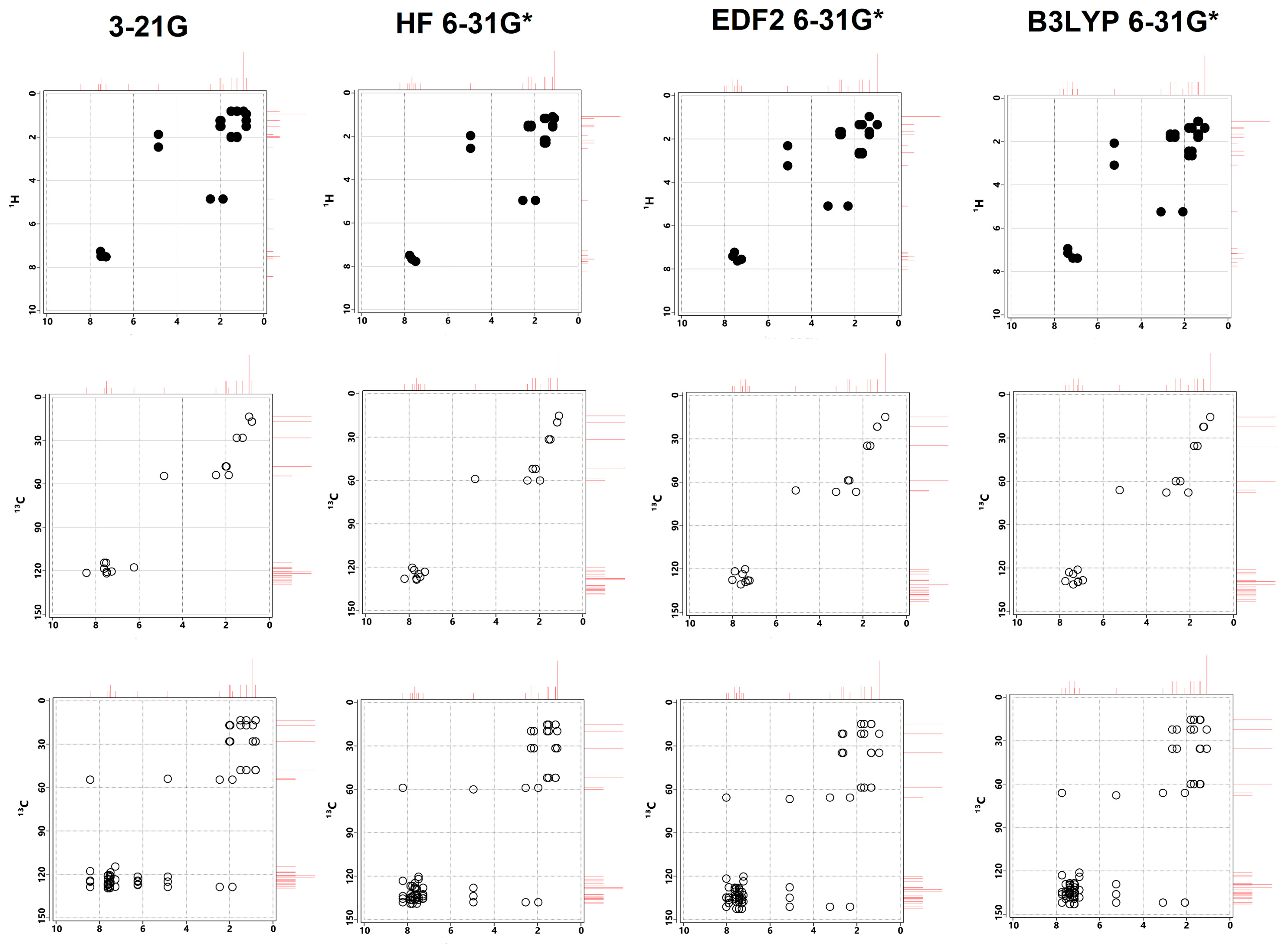

| Properties | Lumefantrine | Artemeter | 4-Aminoquinoline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Formulae | C30H32Cl3NO | C16H26O5 | C9H8N2 |
| Molecular weight (amu) | 528.9 | 298.37 | 144.17 |
| Physical State/Color | Yellow Solid Powder | White to pale yellow crystals or powder | Powder to crystalline, White/Yellow/Orange |
| Density (g/cm3) | 1.252 | 1.0733 | 1.1148 |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 23.5 Å2 | 46.2 Å2 | 38.9 Å2 |
| Melting Point (°C) | 128 °C–131 °C | 86–90 °C | 151.0–155.0 °C |
| Boiling Point (°C) | 642.5 °C | 359.79 °C | 312.78 °C |
| Refractive Index | 1.633 | 1.518 | 1.708 |
| Solubility | DMF, Chloroform Ethyl Acetate | 12 mg/L (in water) | Slightly soluble in water |
| Lipophilicity (logP) | 9.19 | 3.48 | 2.0–2.5 |
| Atom | HF | DFT EDF2 | DFT B3LYP | Atom | HF | DFT EDF2 | DFT B3LYP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-21G | 6-31G* | 6-31G* | 6-31G* | 3-21G | 6-31G* | 6-31G* | 6-31G* | ||
| C1 | −0.087 | −0.019 | 0.093 | 0.083 | H1 | 0.310 | 0.265 | 0.181 | 0.177 |
| C2 | −0.178 | −0.195 | −0.199 | −0.190 | H2 | 0.310 | 0.261 | 0.176 | 0.172 |
| C3 | −0.194 | −0.142 | −0.075 | −0.071 | H3 | 0.255 | 0.217 | 0.154 | 0.151 |
| C4 | −0.209 | −0.190 | −0.208 | −0.202 | H4 | 0.263 | 0.229 | 0.167 | 0.160 |
| C5 | −0.047 | −0.029 | 0.054 | 0.051 | H5 | 0.276 | 0.236 | 0.169 | 0.164 |
| C6 | −0.012 | −0.044 | −0.001 | 0.001 | H6 | 0.277 | 0.235 | 0.166 | 0.161 |
| C7 | −0.030 | 0.006 | 0.075 | 0.072 | H7 | 0.264 | 0.221 | 0.150 | 0.145 |
| C8 | −0.031 | −0.031 | 0.051 | 0.051 | H8 | 0.273 | 0.238 | 0.160 | 0.156 |
| C9 | 0.067 | 0.121 | 0.126 | 0.124 | H9 | 0.273 | 0.231 | 0.157 | 0.152 |
| C10 | −0.226 | −0.266 | −0.319 | −0.307 | H10 | 0.268 | 0.230 | 0.149 | 0.147 |
| C11 | −0.142 | −0.014 | 0.166 | 0.154 | H11 | 0.223 | 0.165 | 0.137 | 0.132 |
| C12 | −0.206 | −0.208 | −0.192 | −0.182 | H12 | 0.418 | 0.474 | 0.410 | 0.408 |
| C13 | −0.203 | −0.177 | −0.136 | −0.130 | H13 | 0.242 | 0.186 | 0.159 | 0.152 |
| C14 | −0.207 | −0.135 | −0.066 | −0.064 | H14 | 0.208 | 0.162 | 0.145 | 0.138 |
| C15 | −0.203 | −0.179 | −0.138 | −0.131 | H15 | 0.200 | 0.156 | 0.146 | 0.140 |
| C16 | −0.207 | −0.202 | −0.180 | −0.172 | H16 | 0.211 | 0.167 | 0.148 | 0.141 |
| C17 | −0.197 | −0.184 | −0.201 | −0.194 | H17 | 0.230 | 0.168 | 0.161 | 0.153 |
| C18 | −0.199 | −0.145 | −0.072 | −0.070 | H18 | 0.215 | 0.165 | 0.145 | 0.139 |
| C19 | −0.206 | −0.196 | −0.158 | −0.149 | H19 | 0.203 | 0.155 | 0.138 | 0.131 |
| C20 | −0.245 | −0.203 | −0.195 | −0.193 | H20 | 0.201 | 0.151 | 0.137 | 0.130 |
| C21 | 0.092 | 0.200 | 0.068 | 0.085 | H21 | 0.202 | 0.165 | 0.152 | 0.145 |
| C22 | −0.194 | −0.140 | −0.180 | −0.161 | H22 | 0.205 | 0.162 | 0.156 | 0.148 |
| C23 | −0.173 | −0.124 | −0.166 | −0.148 | H23 | 0.200 | 0.159 | 0.151 | 0.144 |
| C24 | −0.423 | −0.307 | −0.273 | −0.260 | H24 | 0.216 | 0.168 | 0.149 | 0.142 |
| C25 | −0.436 | −0.316 | −0.268 | −0.255 | H25 | 0.188 | 0.142 | 0.127 | 0.121 |
| C26 | −0.580 | −0.479 | −0.463 | −0.442 | H26 | 0.210 | 0.158 | 0.142 | 0.136 |
| C27 | −0.148 | −0.096 | −0.140 | −0.123 | H27 | 0.215 | 0.164 | 0.146 | 0.139 |
| C28 | −0.416 | −0.311 | −0.270 | −0.256 | H28 | 0.208 | 0.158 | 0.143 | 0.135 |
| C29 | −0.434 | −0.314 | −0.267 | −0.254 | H29 | 0.206 | 0.157 | 0.141 | 0.134 |
| C30 | −0.581 | −0.479 | −0.464 | −0.442 | H30 | 0.204 | 0.166 | 0.154 | 0.146 |
| Cl1 | 0.038 | −0.002 | −0.021 | −0.026 | H31 | 0.199 | 0.158 | 0.150 | 0.143 |
| Cl2 | 0.044 | 0.003 | −0.008 | −0.013 | H32 | 0.202 | 0.160 | 0.153 | 0.146 |
| Cl3 | 0.042 | 0.000 | −0.020 | −0.025 | |||||
| O1 | −0.708 | −0.783 | −0.656 | −0.659 | |||||
| N1 | −0.737 | −0.650 | −0.417 | −0.430 | |||||
| MOs | HF | DFT | Average | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 321G | 6-31G* | EDF2 6-31G* | B3LYP 6-31G* | ||
| LUMO{+1} | 2.5 | 2.4 | −1.2 | −1.1 | 0.7 |
| LUMO | 1.6 | 1.5 | −2.3 | −2.2 | −0.4 |
| HOMO | −8.3 | −8.1 | −5.8 | −5.9 | −7.0 |
| HOMO{−1} | −8.7 | −8.3 | −5.9 | −6.0 | −7.2 |
| HOMO{−2} | −9.4 | −9.4 | −6.1 | −6.3 | −7.8 |
| HOMO{−3} | −9.6 | −9.5 | −6.9 | −7.0 | −8.3 |
| HOMO{−4} | −9.9 | −9.7 | −7.2 | −7.3 | −8.5 |
| HOMO{−5} | −10.0 | −10.0 | −7.2 | −7.4 | −8.7 |
| HOMO{−6} | −10.4 | −10.2 | −7.3 | −7.4 | −8.8 |
| HOMO{−7} | −11.6 | −11.6 | −7.3 | −7.5 | −9.5 |
| HOMO{−8} | −12.1 | −12.1 | −8.2 | −8.4 | −10.2 |
| HOMO{−9} | −12.2 | −12.2 | −8.4 | −8.5 | −10.3 |
| Method & Basis Set | HOMO-1 | HOMO | LUMO | LUMO+1 | Energy Diff. (ΔE) | λmax | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔE1 | ΔE2 | ΔE3 | Calculated (Vac.) | ||||||||
| HF | 3-21G | −8.7 | −8.3 | 1.6 | 2.5 | 10.3 | 9.9 | 10.8 | 120.47 | 125.34 | 114.89 |
| 6-31G* | −8.3 | −8.1 | 1.5 | 2.4 | 9.8 | 9.6 | 10.5 | 126.61 | 129.25 | 118.17 | |
| DFT | EDF2 6-31G* | −5.9 | −5.8 | −2.3 | −1.2 | 3.6 | 3.5 | 4.6 | 344.67 | 354.52 | 269.74 |
| B3LYP 6-31G* | −6.0 | −5.9 | −2.2 | −1.1 | 3.8 | 3.7 | 4.8 | 326.53 | 335.36 | 258.50 | |
| 321G | 6-31G* | EDF2 631G* | B3LYP 631G* | 321G | 6-31G* | EDF2 631G* | B3LYP 631G* | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 493 | 490 | 456 | 456 | 11 | 1434 | 1439 | 1333 | 1331 |
| 2 | 616 | 588 | 560 | 558 | 12 | 1494 | 1507 | 1396 | 1392 |
| 3 | 663 | 630 | 596 | 595 | 13 | 1607 | 1582 | 1470 | 1474 |
| 4 | 700 | 670 | 607 | 621 | 14 | 1678 | 1710 | 1570 | 1561 |
| 5 | 783 | 767 | 731 | 732 | 15 | 1801 | 1806 | 1631 | 1622 |
| 6 | 983 | 974 | 886 | 882 | 16 | 3023 | 3010 | 2837 | 2836 |
| 7 | 1296 | 1304 | 1230 | 1226 | 17 | 3088 | 3083 | 2929 | 2926 |
| 8 | 1179 | 1180 | 1100 | 1098 | 18 | 3142 | 3141 | 3003 | 2994 |
| 9 | 1296 | 1304 | 1230 | 1226 | 19 | 3313 | 3316 | 3131 | 3130 |
| 10 | 1352 | 1344 | 1259 | 1261 | 20 | 3629 | 3884 | 3393 | 3124 |
| Atom | HF | DFT | DFT | Exp ** | Atom | HF | DFT | DFT | Exp ** | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-21G | 6-31G* | EDF2 6-31G* | B3LYP 6-31G* | 3-21G | 6-31G* | EDF2 6-31G* | B3LYP 6-31G* | ||||
| C1 | 128.66 | 137.99 | 141.12 | 135.18 | 141.7 | H1 | 8.43 | 8.21 | 8.02 | 7.74 | 7.58 |
| C2 | 121.57 | 128.09 | 127.69 | 122.43 | 124.1 | H2 | 6.24 | 7.28 | 7.90 | 7.57 | 7.58 |
| C3 | 124.34 | 135.48 | 134.71 | 136.72 | 133.3 | H3 | 7.62 | 7.57 | 7.30 | 7.16 | 7.31 |
| C4 | 117.79 | 123.27 | 121.72 | 116.39 | 127.8 | H4 | 7.49 | 7.66 | 7.63 | 7.67 | 7.44 |
| C5 | 126.93 | 135.30 | 138.57 | 132.56 | 140.0 | H5 | 7.50 | 7.67 | 7.41 | 7.12 | 7.44 |
| C6 | 125.01 | 133.79 | 134.90 | 129.57 | 133.0 | H6 | 7.50 | 7.67 | 7.41 | 7.18 | 7.44 |
| C7 | 128.51 | 136.27 | 137.52 | 131.71 | 136.6 | H7 | 7.49 | 7.60 | 7.63 | 7.09 | 7.44 |
| C8 | 129.51 | 138.94 | 142.48 | 136.16 | 138.4 | H8 | 7.61 | 7.86 | 7.43 | 7.18 | 7.67 |
| C9 | 127.29 | 132.49 | 136.33 | 131.10 | 135.1 | H9 | 7.27 | 7.49 | 7.23 | 6.94 | 7.44 |
| C10 | 118.67 | 124.84 | 128.04 | 123.58 | 128.5 | H10 | 7.52 | 7.77 | 7.55 | 7.38 | 7.71 |
| C11 | 126.38 | 132.76 | 134.66 | 128.27 | 135.1 | H11 | 4.85 | 4.96 | 5.10 | 5.24 | 5.35 |
| C12 | 120.90 | 128.68 | 130.80 | 124.41 | 130.7 | H12 | 3.83 | 3.06 | 4.16 | 3.95 | - |
| C13 | 121.93 | 127.96 | 129.17 | 122.37 | 129.2 | H13 | 1.87 | 1.97 | 2.31 | 2.07 | 2.44 |
| C14 | 125.05 | 136.10 | 135.43 | 137.50 | 134.8 | H14 | 2.45 | 2.55 | 3.24 | 3.09 | 2.87 |
| C15 | 121.93 | 127.96 | 129.17 | 122.99 | 129.2 | H15 | 1.97 | 2.30 | 2.69 | 2.58 | 2.59 |
| C16 | 120.90 | 128.68 | 130.80 | 124.88 | 130.7 | H16 | 2.01 | 2.17 | 2.63 | 2.57 | 2.59 |
| C17 | 114.58 | 120.41 | 120.28 | 114.59 | 126.5 | H17 | 1.50 | 1.56 | 1.80 | 2.00 | 1.49 |
| C18 | 123.53 | 134.68 | 133.14 | 135.27 | 134.3 | H18 | 1.23 | 1.49 | 1.66 | 1.64 | 1.49 |
| C19 | 120.67 | 126.74 | 128.14 | 121.79 | 130.7 | H19 | 0.81 | 1.17 | 1.33 | 1.38 | 1.36 |
| C20 | 114.60 | 122.07 | 123.59 | 117.46 | 120.8 | H20 | 0.80 | 1.18 | 1.34 | 1.42 | 1.36 |
| C21 | 54.52 | 58.98 | 65.74 | 65.49 | 65.6 | H21 | 0.93 | 1.09 | 0.97 | 1.19 | 0.96 |
| C22 | 53.92 | 60.05 | 66.73 | 65.96 | 60.1 | H22 | 0.93 | 1.09 | 0.97 | 1.06 | 0.96 |
| C23 | 47.89 | 52.00 | 58.82 | 56.47 | 53.5 | H23 | 0.93 | 1.09 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.96 |
| C24 | 28.11 | 31.58 | 34.76 | 36.97 | 29.2 | H24 | 2.01 | 2.17 | 2.63 | 2.31 | 2.59 |
| C25 | 16.90 | 19.79 | 21.57 | 23.31 | 20.7 | H25 | 1.97 | 2.30 | 2.69 | 2.73 | 2.59 |
| C26 | 13.48 | 15.27 | 14.86 | 15.78 | 14.2 | H26 | 1.50 | 1.56 | 1.80 | 1.61 | 1.49 |
| C27 | 47.89 | 52.00 | 58.82 | 60.59 | 53.5 | H27 | 1.23 | 1.49 | 1.66 | 1.66 | 1.49 |
| C28 | 28.11 | 31.58 | 34.76 | 34.67 | 29.2 | H28 | 0.81 | 1.17 | 1.33 | 1.34 | 1.36 |
| C29 | 16.90 | 19.79 | 21.57 | 23.05 | 20.7 | H29 | 0.80 | 1.18 | 1.34 | 1.34 | 1.36 |
| C30 | 13.48 | 15.27 | 14.86 | 15.89 | 14.2 | H30 | 0.93 | 1.09 | 0.97 | 1.17 | 0.96 |
| H31 | 0.93 | 1.09 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.96 | ||||||
| H32 | 0.93 | 1.09 | 0.97 | 1.03 | 0.96 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kunduracioglu, A. A Computational (DFT) Study on the Anti-Malarial Drug: Lumefantrine. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9219. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169219
Kunduracioglu A. A Computational (DFT) Study on the Anti-Malarial Drug: Lumefantrine. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(16):9219. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169219
Chicago/Turabian StyleKunduracioglu, Ahmet. 2023. "A Computational (DFT) Study on the Anti-Malarial Drug: Lumefantrine" Applied Sciences 13, no. 16: 9219. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169219
APA StyleKunduracioglu, A. (2023). A Computational (DFT) Study on the Anti-Malarial Drug: Lumefantrine. Applied Sciences, 13(16), 9219. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169219







