Neural Network-Based Bilingual Lexicon Induction for Indonesian Ethnic Languages
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Model a neural network-based bilingual lexicon induction between Indonesian and Minangkabau, using long short-term memory (LSTM).
- Evaluate how well the model detects the transformation rules between Indonesian and Minangkabau.
- Apply the model to Malay, Palembang, Javanese, and Sundanese languages.
2. Bilingual Lexicon Induction
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. A Neural Network Approach
3.2. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
| : at time t, output gate | |
| : at time t, input gate | |
| : output at time t | |
| : forget gate, at time t | |
| : input at time t | |
| : sigmoid function | |
| : the state of the cell at time t | |
| , , , | : weights that have been trained |
| : trained biases |
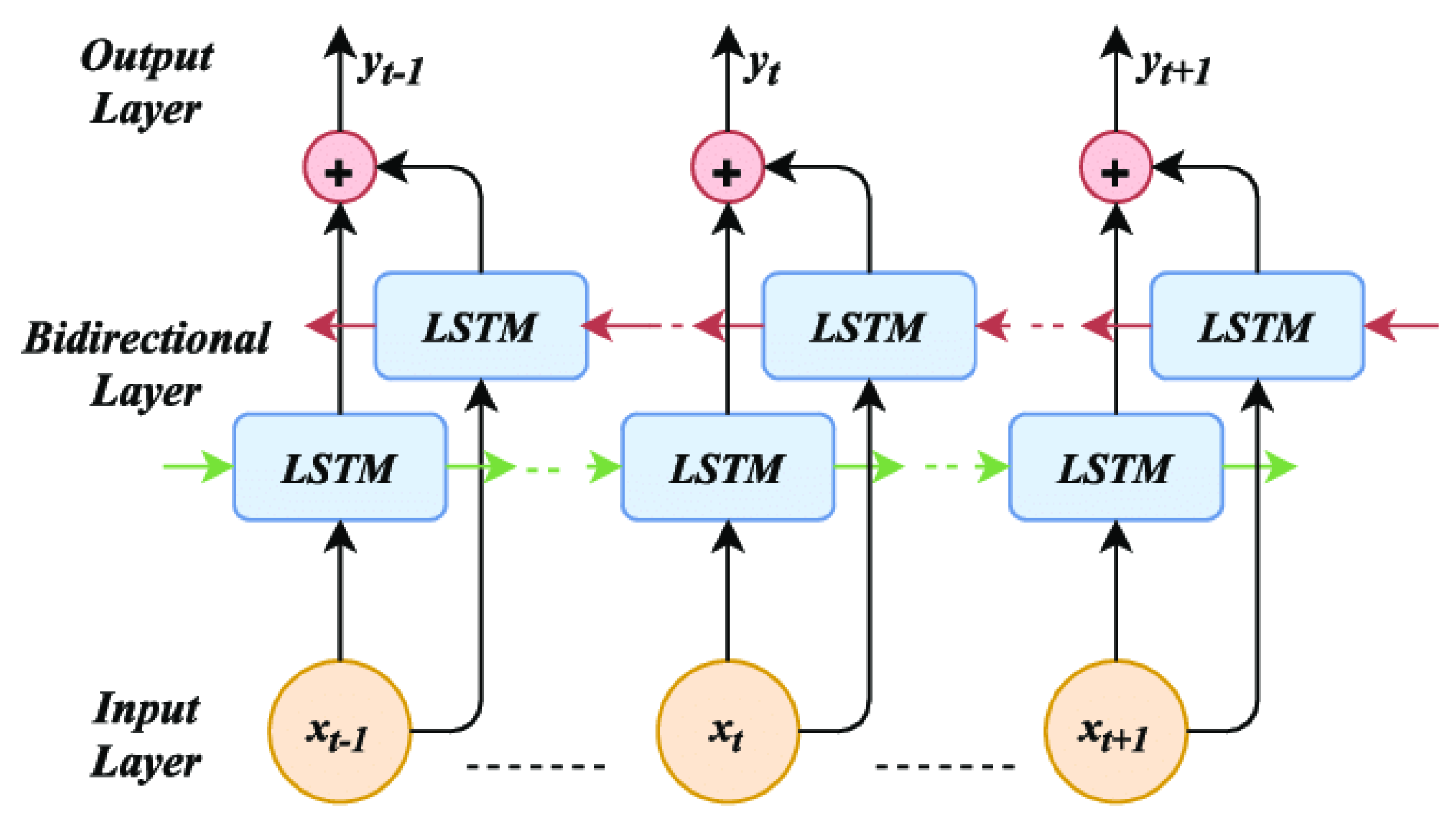
3.3. Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (Bi-LSTM)
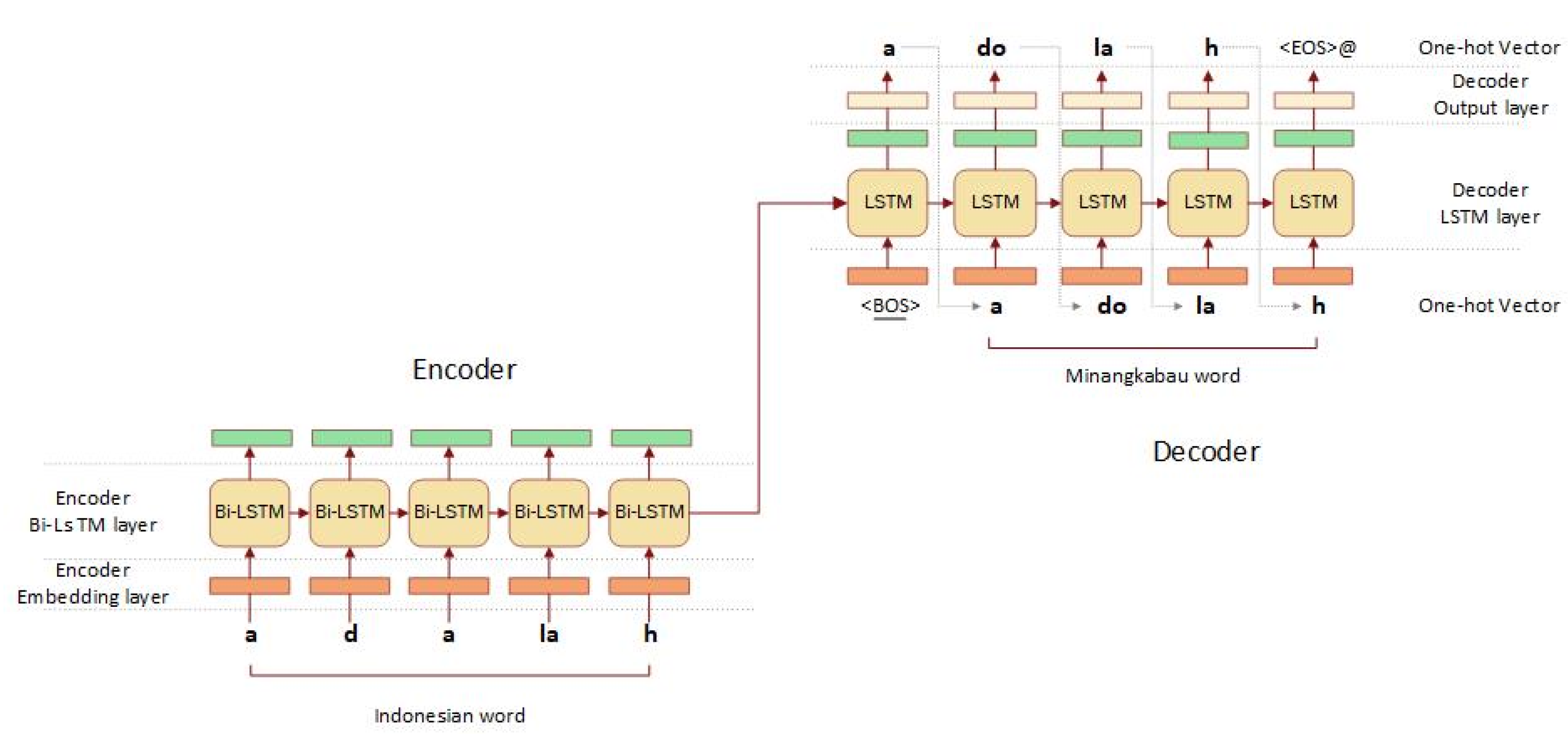
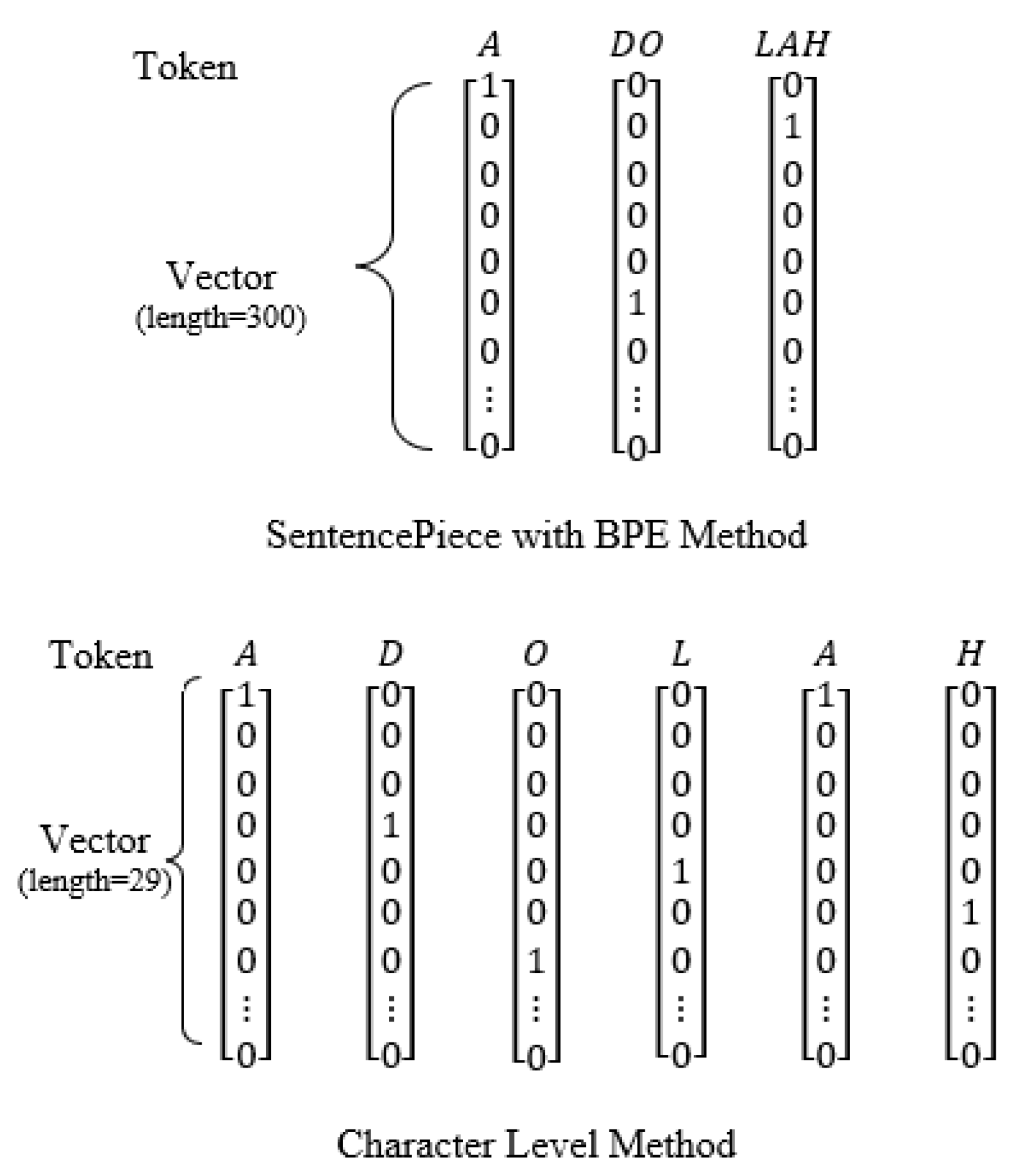
3.4. Character-Level Sequence-to-Sequence Model
3.5. SentencePiece Sequence-to-Sequence with Byte Pair Encoding (BPE)
- (1)
- Gather a huge amount of training data.
- (2)
- Determine the vocabulary size.
- (3)
- Identify the end of a word, add an identifier (</w>) to the end of each word, and then calculate the word frequency in the text.
- (4)
- Calculate the character frequency after dividing the word into characters.
- (5)
- Count the frequency of consecutive byte pairs from the character tokens for a predetermined number of rounds and combine the most frequently occurring byte pairings.
- (6)
- Repeat step 5 until the required number of merging operations has been performed or the specified vocabulary size is reached.
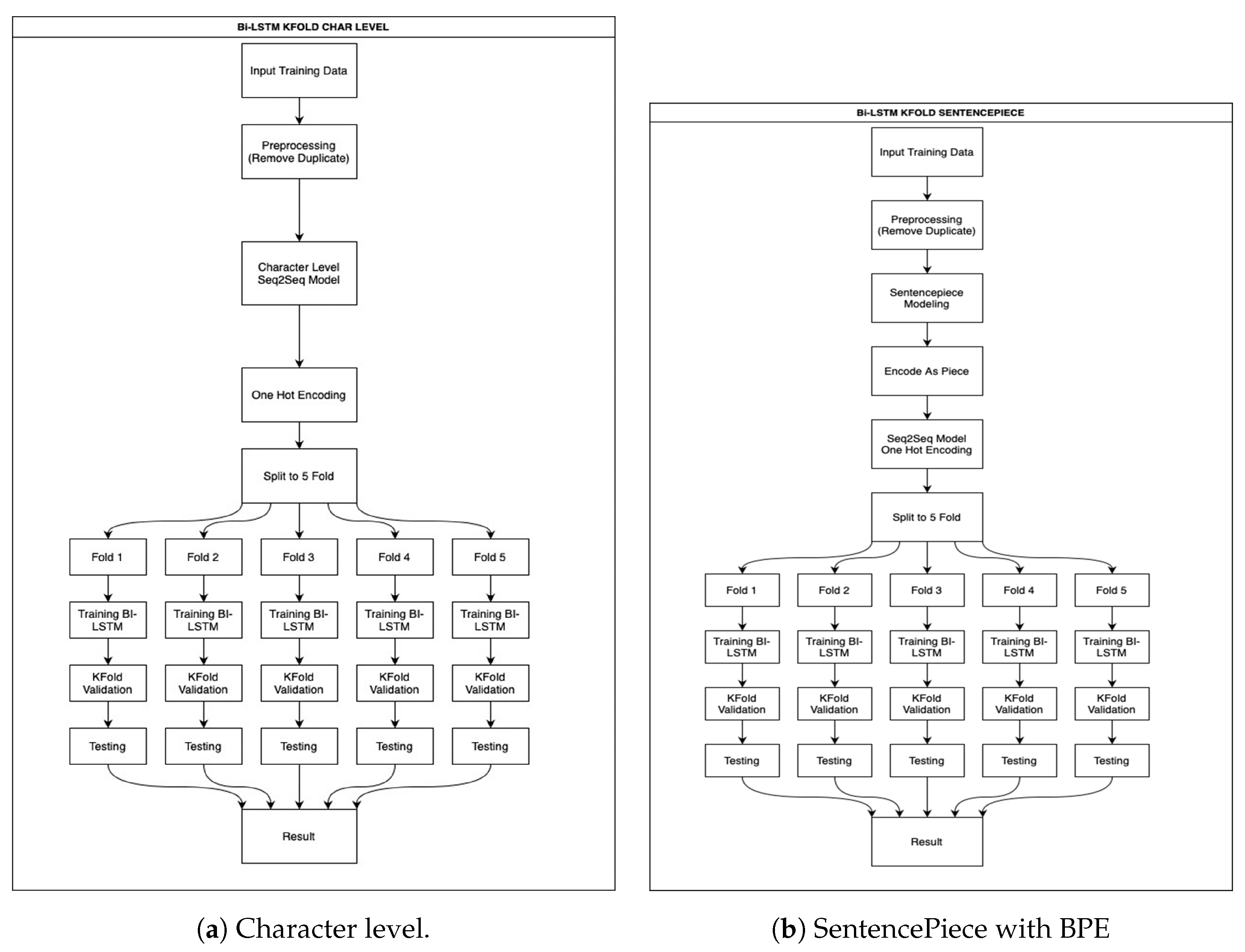
3.6. Experiment Design
4. Results
4.1. Neural Network Performance
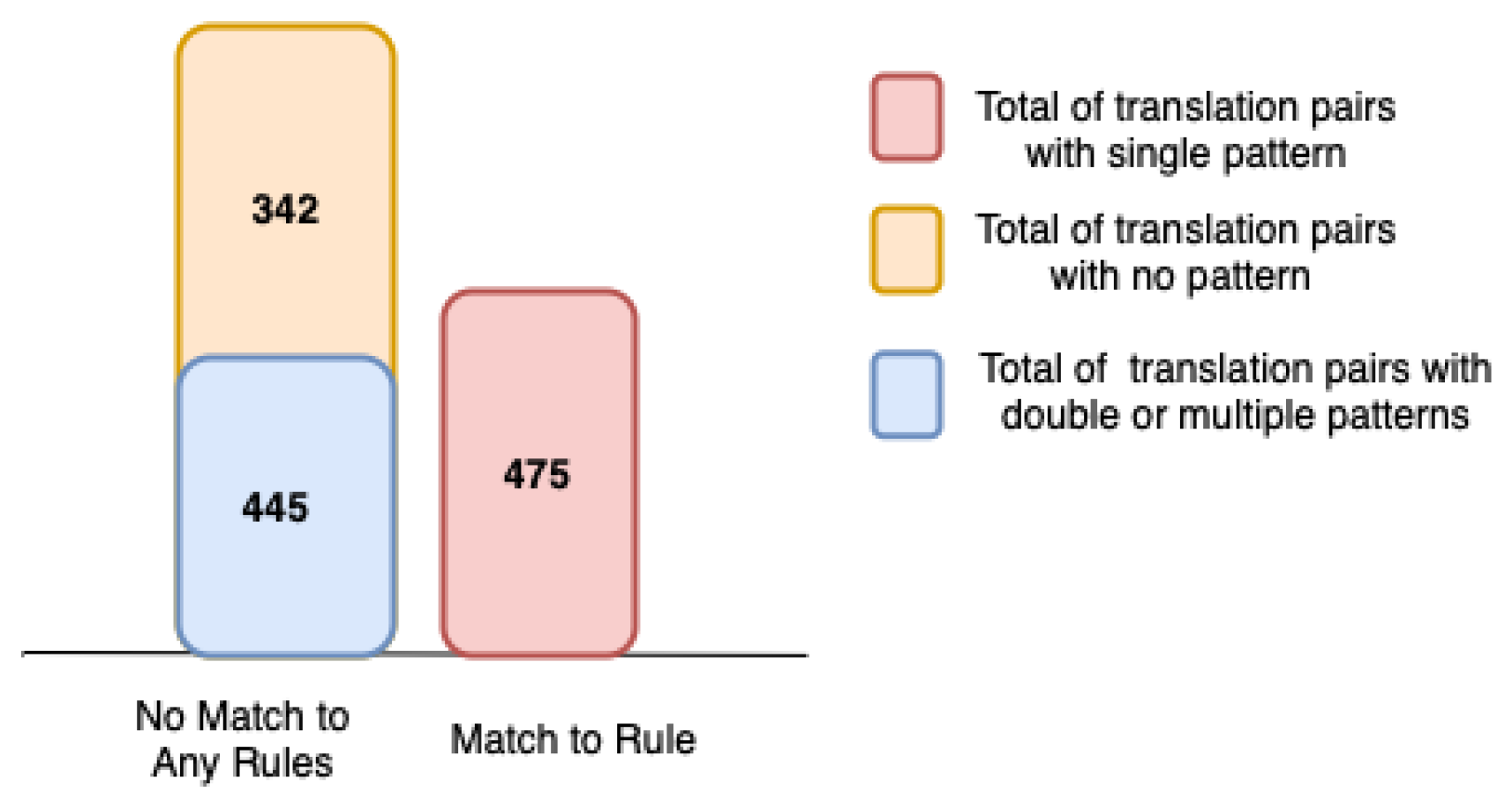
4.2. Pattern Recall
- (1)
- Remove the translation pairs, where the source word and the target word are identical from the 2056 translation pair candidates, making 1262 translation pairs.
- (2)
- Following the transformation pattern from the expert, define the transformation rules by regular expressions.
- (3)
- Use the transformation rules that have been determined with all source words and replace rule matches with a string.
4.3. Neural Network Performances for Other Ethnic Languages
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASJP | Automated Similarity Judgment Program |
| Bi-LSTM | bidirectional long short-term memory |
| BPE | byte pair encoding |
| LSTM | long short-term memory |
| RNN | recurrent neural network |
| seq2seq | sequence-to-sequence |
References
- Paauw, S. One land, one nation, one language: An analysis of Indonesia’s national language policy. Univ. Rochester Work. Pap. Lang. Sci. 2009, 5, 2–16. [Google Scholar]
- Nasution, A.H.; Murakami, Y.; Ishida, T. Generating similarity cluster of Indonesian languages with semi-supervised clustering. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. (IJECE) 2019, 9, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y. Indonesia Language Sphere: An ecosystem for dictionary development for low-resource languages. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1192, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasution, A.H.; Syafitri, N.; Setiawan, P.R.; Suryani, D. Pivot-based hybrid machine translation to support multilingual communication. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Culture and Computing (Culture and Computing), Kyoto, Japan, 10–12 September 2017; pp. 147–148. [Google Scholar]
- Nasution, A.H. Pivot-based hybrid machine translation to support multilingual communication for closely related languages. World Trans. Eng. Technol. Educ. 2018, 16, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Nasution, A.H.; Murakami, Y.; Ishida, T. Plan Optimization to Bilingual Dictionary Induction for Low-resource Language Families. Trans. Asian Low-Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. 2021, 20, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasution, A.H.; Murakami, Y.; Ishida, T. Constraint-based bilingual lexicon induction for closely related languages. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’16), Portorož, Slovenia, 23–28 May 2016; pp. 3291–3298. [Google Scholar]
- Nasution, A.H.; Murakami, Y.; Ishida, T. A generalized constraint approach to bilingual dictionary induction for low-resource language families. ACM Trans. Asian Low-Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. (TALLIP) 2017, 17, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Nasution, A.H.; Murakami, Y.; Ishida, T. Plan optimization for creating bilingual dictionaries of low-resource languages. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Culture and Computing (Culture and Computing), Kyoto, Japan, 10–12 September 2017; pp. 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Heyman, G.; Vulić, I.; Moens, M.F. A deep learning approach to bilingual lexicon induction in the biomedical domain. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Ji, Y.; Yue, H. A character-level sequence-to-sequence method for subtitle learning. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 14th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Poitiers, France, 19–21 July 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Cao, H.; Zhao, T.; Wang, W.; Peng, W. Cross-lingual Feature Extraction from Monolingual Corpora for Low-resource Unsupervised Bilingual Lexicon Induction. In Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Gyeongju, Republic of Korea, 12–17 October 2022; pp. 5278–5287. [Google Scholar]
- Aysa, A.; Ablimit, M.; Yilahun, H.; Hamdulla, A. Chinese-Uyghur Bilingual Lexicon Induction Based on Morpheme Sequence and Weak Supervision. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning (PRML), Chengdu, China, 22–24 July 2022; pp. 357–363. [Google Scholar]
- Aysa, A.; Ablimit, M.; Yilahun, H.; Hamdulla, A. Sub-word based unsupervised bilingual dictionary induction for Chinese-Uyghur. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Asian Language Processing (IALP), Singapore, 27–28 October 2022; pp. 476–481. [Google Scholar]
- Resiandi, K.; Murakami, Y.; Nasution, A.H. A Neural Network Approach to Create Minangkabau-Indonesia Bilingual Dictionary. In Proceedings of the the 1st Annual Meeting of the ELRA/ISCA Special Interest Group on Under-Resourced Languages, Marseille, France, 24–25 June 2022; European Language Resources Association: Marseille, France, 2022; pp. 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Koto, F.; Koto, I. Towards Computational Linguistics in Minangkabau Language: Studies on Sentiment Analysis and Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 34th Pacific Asia Conference on Language, Information and Computation, Hanoi, Vietnam, 24–26 October 2020; pp. 138–148. [Google Scholar]
- Baidalina, A.R.; Boranbayev, S.A. Programming date structure algorithm in Python. Bull. Ser. Phys. Math. Sci. 2021, 73, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, M.; Paliwal, K. Bidirectional recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulita, I.N.; Fanany, M.I.; Arymuthy, A.M. Bi-directional Long Short-Term Memory using Quantized data of Deep Belief Networks for Sleep Stage Classification. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 116, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O.; Le, Q.V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.3215. [Google Scholar]
- Kudo, T. Subword Regularization: Improving Neural Network Translation Models with Multiple Subword Candidates. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.10959. [Google Scholar]
- Sennrich, R.; Haddow, B.; Birch, A. Neural Machine Translation of Rare Words with Subword Units. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1508.07909. [Google Scholar]
- Ranaldi, L.; Pucci, G. Knowing knowledge: Epistemological study of knowledge in transformers. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Language | Vocab Size = 40 | Vocab Size = 100 |
|---|---|---|
| Indonesian | an, ng, nya, ta, kan, _di, _men, | an, ng, kan, ta, _di, la, nya, ra, da, si, _ke, _ber, ti, ba, li, ga, ri, ja, er, tu, bu, _se, at, in, _men, ma, sa, _per, ka, en, di, wa, ku, _meng, ya, na, _me, _pen, te, mp, ca, _p, _ter, ru, du, _mem, de, pa, or,un, ar, ju, is, _ka, bi, _ko, _ma, re, on, _ba, _pe, _pem, tan, pu, gu, al, ran, asi |
| Minangkabau | an, ang, _pa, _di, _ma, _ba, ng | an, ng, _di, _ba, ra, si, la,_pa, nyo, _ka, ta, da, ang, _ma, ik, kan, li, ri, ti, ak, tu, ka, _sa, _man, ja, ah, _ta, bu, ga, ek, in, ba, ku, sa, ma, su, di, ru, ya, _a, mp, _pan, to, wa, pa, ca, ran, du, ro, lu, tan, lo, mba, angan, ju, bi, pu, re, han, en, te, do, de, ko, gu, gi, _mam |
| Vocab Size = 40 | Vocab Size = 100 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Indonesian | Minangkabau | Indonesian | Minangkabau |
| _,y,a,ng | _,n,an,‘\n’ | _,ya,ng | _,n,an,‘\n’ |
| _,p,a,d,a | _,pa,d,o,‘\n’ | _pa,da | _,pa,do,‘\n’ |
| _a,d,a,la,h | _a,d,o,l,a,h,‘\n’ | _a,da,la,h | _a,do,la,h,‘\n’ |
| _,s,e,g,e,ra | _,s,a,g,i,r,o,‘\n’ | _,se,ge,ra | _,se,ge,ra,‘\n’ |
| _,d,a,s,a,r,nya | _,d,a,s,a,n,y,o,‘\n’ | _,da,sa,r,nya | _,da,sa,nyo,‘\n’ |
| Character Level and SentencePiece with BPE | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Bi-LSTM | LSTM |
| Embedding Size | 512 | 512 |
| Epoch | 120 | 120 |
| Batch Size | 64 | 64 |
| Method | K-Fold Cross-Validation Indonesian–Minangkabau | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K = 1 | K = 2 | K = 3 | K = 4 | K = 5 | Average Precision | |
| Bi-LSTM (encoder), LSTM (decoder) | 84.72 | 83.70 | 83.31 | 83.60 | 84.30 | 83.92 |
| LSTM (encoder–decoder) | 76.79 | 74.56 | 77.82 | 78.21 | 75.87 | 76.65 |
| Vocab Size | K-Fold Cross-Validation Indonesian–Minangkabau | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K = 1 | K = 2 | K = 3 | K = 4 | K = 5 | Average Precision | |
| 33 | 79.96 | 76.55 | 78.84 | 81.71 | 80.78 | 79.56 |
| 35 | 76.11 | 76.89 | 79.42 | 74.31 | 80.73 | 77.49 |
| 40 | 72.12 | 72.88 | 75.23 | 75.99 | 71.64 | 73.59 |
| 50 | 67.12 | 62.15 | 66.97 | 67.41 | 64.29 | 65.58 |
| 80 | 58.73 | 59.32 | 53.35 | 54.12 | 56.47 | 56.39 |
| 100 | 49.36 | 48.24 | 49.46 | 49.70 | 48.78 | 49.10 |
| 300 | 34.85 | 34.93 | 30.31 | 35.76 | 36.19 | 34.40 |
| Pattern | Indonesian | Minangkabau | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ending uk to uak | Rusuk | Rusuak |
| 2 | Ending a to o | Sama | Samo |
| 3 | Ending ik to iak | Batik | Batiak |
| 4 | Ending ing to iang | Baling | Baliang |
| 5 | Remove last character | Tukar | Tuka |
| 6 | Ending as to eh | Panas | Paneh |
| 7 | Ending uh to uah | Penuh | Penuah |
| 8 | Ending ut to uik | Laut | Lauik |
| 9 | Ending ung to uang | Patung | Patuang |
| 10 | Ending ap to ok | Atap | Atok |
| 11 | Ending it to ik | Kulit | Kulik |
| 12 | Ending is to ih | Lapis | Lapih |
| 13 | Ending up to uik | Hidup | Hiduik |
| 14 | Ending ul to ua | Pukul | Pukua |
| 15 | Ending kan to an | Arahkan | arahan |
| 16 | Ending a to ok | Jika | Jikok |
| 17 | Ending ur to ua | Kabur | Kabua |
| 18 | Ending t to ik | Giat | Giaik |
| 19 | Beginning meng to ma | Mengadu | Maadu |
| 20 | Beginning meng to mang | Mengaku | Mangaku |
| 21 | Beginning Ber to Ba | Berlari | Balari |
| 22 | Beginning Per to Pa | Perjalanan | Pajalanan |
| 23 | Beginning Pe to Pa | Penyabar | Panyaba |
| 24 | Beginning Se to Sa | Seirama | Sairama |
| 25 | Beginning Re to Ra | Retak | Ratak |
| 26 | Beginning Te to Ta | Tepian | Tapian |
| 27 | Beginning Ter to Ta | Termakan | Tamakan |
| 28 | Ending ir to ia | Kincir | Kincia |
| 29 | Ending at to ek | Keringat | Keringek |
| 30 | Ending d to ik | Jasad | Jasaik |
| 31 | Ending id to ik | Murid | Murik |
| 32 | Ending ih to iah | Gigih | Gigiah |
| 33 | Ending us to uih | Arus | Aruih |
| 34 | Ending il to ia | Hasil | Hasia |
| Pattern | Indonesian | Minangkabau | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Me to ma, kan to an | Meresmikan | Maresmian |
| 2 | Pe to Pa, ih to iah | Pemilih | Pamiliah |
| 3 | Ke to Ka, Ing to Iang, Kan to An | Keringkan | Kariangan |
| Method | Result | Neural | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Correct | Wrong | ||
| Rule | Correct | 414 | 61 |
| Wrong | 603 | 184 | |
| Language Pair | #Translation Pair | #Training Set | #Test Set |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indonesian–Minangkabau | 13,761 | 11,008 | 2753 |
| Indonesian–Malay | 5229 | 4183 | 1046 |
| Indonesian–Palembang | 5098 | 4078 | 1020 |
| Indonesian–Javanese | 4778 | 3822 | 956 |
| Indonesian–Sundanese | 5045 | 4036 | 1009 |
| Method | K-Fold Cross-Validation Indonesian–Malay | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K = 1 | K = 2 | K = 3 | K = 4 | K = 5 | Average Precision | |
| Bi-LSTM (encoder), LSTM (decoder) | 64.72 | 66.15 | 65.20 | 65.96 | 63.38 | 65.08 |
| Method | K-Fold Cross-Validation Indonesian–Palembang | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K = 1 | K = 2 | K = 3 | K = 4 | K = 5 | Average Precision | |
| Bi-LSTM (encoder), LSTM (decoder) | 63.82 | 62.45 | 63.23 | 60.29 | 62.84 | 62.52 |
| Method | K-Fold Cross-Validation Indonesian–Javanese | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K = 1 | K = 2 | K = 3 | K = 4 | K = 5 | Average Precision | |
| Bi-LSTM (encoder), LSTM (decoder) | 62.02 | 59.30 | 59.62 | 55.34 | 61.08 | 59.69 |
| Method | K-Fold Cross-Validation Indonesian–Sundanese | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K = 1 | K = 2 | K = 3 | K = 4 | K = 5 | Average Precision | |
| Bi-LSTM (encoder), LSTM (decoder) | 57.77 | 58.47 | 59.36 | 59.26 | 57.48 | 58.46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Resiandi, K.; Murakami, Y.; Nasution, A.H. Neural Network-Based Bilingual Lexicon Induction for Indonesian Ethnic Languages. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8666. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13158666
Resiandi K, Murakami Y, Nasution AH. Neural Network-Based Bilingual Lexicon Induction for Indonesian Ethnic Languages. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(15):8666. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13158666
Chicago/Turabian StyleResiandi, Kartika, Yohei Murakami, and Arbi Haza Nasution. 2023. "Neural Network-Based Bilingual Lexicon Induction for Indonesian Ethnic Languages" Applied Sciences 13, no. 15: 8666. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13158666
APA StyleResiandi, K., Murakami, Y., & Nasution, A. H. (2023). Neural Network-Based Bilingual Lexicon Induction for Indonesian Ethnic Languages. Applied Sciences, 13(15), 8666. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13158666








