Abstract
In rice paddy soil, biological nitrogen fixation is important for sustaining soil nitrogen fertility and rice growth. Anaeromyxobacter and Geobacteriaceae, iron-reducing bacteria belonging to Deltaproteobacteria, are newly discovered nitrogen-fixing bacteria dominant in paddy soils. They utilize acetate, a straw-derived major carbon compound in paddy soil, as a carbon and energy source, and ferric iron compounds as electron acceptors for anaerobic respiration. In our previous paddy field experiments, a significant increase in soil nitrogen-fixing activity was observed after the application of iron powder to straw-returned paddy field soil. In addition, combining iron application with 60–80% of the conventional nitrogen fertilizer rate could maintain rice yields similar to those with the conventional nitrogen fertilization rate. It was thus suggested that iron application to paddy soil increased the amount of nitrogen fixed in the soil by enhancing nitrogen fixation by diazotrophic iron-reducing bacteria. The present study was conducted to directly verify this suggestion by 15N-IRMS analysis combined with 15N-DNA-stable isotope probing of iron-applied and no-iron-applied plot soils in an experimental paddy field. In no-iron-applied native paddy soil, atmospheric 15N2 was incorporated into the soil by biological nitrogen fixation, in which diazotrophic iron-reducing bacteria were the most active drivers of nitrogen fixation. In iron-applied paddy soil, the amount of 15N incorporated into the soil was significantly higher due to enhanced biological nitrogen fixation, especially via diazotrophic iron-reducing bacteria, the most active drivers of nitrogen fixation in the soil. Thus, our previous suggestion was verified. This study provided a novel picture of active nitrogen-fixing microorganisms dominated by diazotrophic iron-reducing bacteria in paddy soil, and directly proved the effectiveness of iron application to enhance their nitrogen fixation and increase the incorporation of atmospheric nitrogen into soil. The enhancement of biological nitrogen fixation in paddy fields by iron application may lead to novel and unique paddy soil management strategies to increase soil nitrogen fertility and ensure rice yields with reduced nitrogen fertilizer input and lower environmental nitrogen burdens.
1. Introduction
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is one of the most important food crops and feeds more than half of the population in the world [1]. Since the green revolution in the 19th century, chemical nitrogen fertilizers have been developed and applied to rice paddy fields to increase rice yields [2]. However, long-term or excessive nitrogen fertilization leads to the release of nitrogen loads, i.e., ammonium volatilization, nitrous oxide emission, and nitrate leaching from paddy soils into the natural environment [3]. This contributes to increased environmental problems such as global warming, water eutrophication, and nitrate pollution of groundwater [4,5]. Reduced nitrogen fertilizer use is necessary for environmentally friendly and sustainable rice production.
In addition to nitrogen fertilizers, biological nitrogen fixation (BNF) can incorporate nitrogen into soil under rice paddy field conditions [6]. Flooded paddy soils possess higher nitrogen-fixing activity than upland agricultural soils, and this is important for sustainable soil nitrogen fertility and rice growth [7,8,9]. Therefore, diazotrophic bacterial communities in paddy soils have been studied for a long time. In particular, photosynthetic bacteria and cyanobacteria have been extensively studied as important diazotrophs [10]. The application of these diazotrophs as biofertilizers was also investigated with the aim of lowering the amount of nitrogen fertilizer used and reducing nitrogen pollution [11,12,13].
Our recent shotgun sequencing analysis (metagenome/metatranscriptome) of paddy soil DNA/RNA suggested that Anaeromyxobacter and Geobacter, predominant bacteria in paddy soil, are the major drivers of nitrogen fixation in paddy soils [14]. Anaeromyxobacter and Geobacter are known as metal-reducing bacteria in general [15,16] and active iron-reducing bacteria in paddy soil [17]. We confirmed the nitrogen-fixing ability of Anaeromyxobacter and Geobacter strains isolated from paddy soils by cultivation studies. They utilized acetic acid as a carbon and energy source (electron donor) and ferric iron as an electron acceptor for anaerobic respiration [18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. Based on whole-genome analysis of the isolates, the taxonomic position of bacteria belonging to the family Geobacteraceae was revised, and the conventional genus Geobacter was divided into the genera Geobacter, Geomonas, Oryzomonas, Geotalea, Geomobilimonas, Geomobilibacter, and Geoanaerobacter [20]. It was strongly suggested that in paddy soils, Anaeromyxobacter and Geobacteraceae (conventional Geobacter) grow by utilizing rice straw-derived acetic acid as an electron donor, ferric iron compounds as an electron acceptor, and nitrogen fixation.
We hypothesized that the addition of ferric iron compounds and rice straw could enhance the nitrogen-fixing activity of Anaeromyxobacter and Geobacteraceae in paddy soils. In fact, nitrogen-fixing activity of soil and nifD transcripts of Anaeromyxobacter and Geobacteraceae significantly increased after the addition of ferrihydrite or Fe2O3 together with rice straw to laboratory soil microcosms [25]. In our field experiment, a significant increase in soil nitrogen-fixing activity was also observed after the application of iron powder to straw-returned paddy field soil [25]. Another field experiment in China demonstrated that a combination of iron application with 60–80% of the conventional nitrogen fertilization rate could maintain rice yields similar to those of the conventional nitrogen fertilization rate while reducing critical nitrogen losses in flooded paddy fields [26]. These studies strongly suggested that iron application to paddy soil increased the amount of nitrogen fixed in the soil by enhancing nitrogen fixation by iron-reducing bacteria. However, these claims, i.e., the amount of nitrogen incorporated into soil and the incorporation of nitrogen into iron-reducing bacteria, must be demonstrated in direct ways.
Consequently, with special reference to nitrogen fixation by iron-reducing bacteria, in this study, we performed 15N-IRMS analysis together with 15N-DNA-stable isotope probing (SIP) of iron powder-applied and nonapplied (native) plot soils of the experimental paddy field mentioned above to directly (i) quantify the amount of nitrogen fixed in the soils, (ii) identify the active diazotrophs in the soils, and (iii) confirm whether iron application to paddy soil increased the amount of nitrogen fixed in the soil by enhancing nitrogen fixation by iron-reducing bacteria.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Field and Soil Sampling
Soil samples were collected from iron-applied (Fe) and no-iron-applied native (Con) plots of the experimental paddy field established in 2018 at the Niigata Agricultural Research Institute, Nagaoka, Niigata Prefecture, Japan (37°44′ N, 138°87′ E) [25]. The physicochemical properties of the field soil and field management schedule were described previously [25]. Iron application was performed as follows [25]: Prior to the initiation of waterlogging in spring 2018, iron powder for agricultural use (zero-valent iron, >92% purity; JFE Steel Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) was applied to the soil surface at 500 g/m2 and left to oxidize, which is equivalent to a 0.5% increment in the free iron oxide content of the soil (from 1.5% to 2.0%). The generation of oxidized iron compounds from the applied iron powder several days after application was visually confirmed [25]. Waterlogging, puddling, and transplanting were conventionally performed in the field plots. Iron application to paddy soil did not affect soil physicochemical properties, including soil pH [25]. The paddy soils used in this study were collected at 0–20 cm depth from the surface in Con and Fe plots in June 2020, immediately sealed into 50 mL sterile centrifuge tubes, and transported to the laboratory.
2.2. Soil Incubation
Each 4.0 g of fresh paddy soil was placed in a 20 mL glass serum vial. Each vial was sealed with a butyl rubber stopper and aluminum crimping, and the air in the bottle was exchanged with 14N2 (Nippon Sanso, Tokyo, Japan)/He (80:20, v/v) or 15N2 (98 atoms%, Isotec, Miamisburg, OH, USA)/He (80:20, v/v). Four treatments were established: (1) Con plot soil with 15N2 (15N-Con); (2) Con plot soil with 14N2 (14N-Con); (3) Fe plot soil with 15N2 (15N-Fe); and (4) Fe plot soil with 14N2 (14N-Fe). All vials were incubated at 30 °C for 6 days according to our previous soil microcosm study [25]. Soil samples were destructively collected in triplicate on Days 2, 4, and 6 and stored at −80 °C for the following experiments.
2.3. Quantification of 15N in Soil
The 15N incorporated into the incubated soil by biological nitrogen fixation was quantified using an isotope ratio mass spectrometer (IRMS). Each 2.0 g collected soil sample was freeze-dried (FDM-1000, EYELA, Tokyo, Japan) and ground with a mortar and pestle. Measurements of the N concentrations in soil samples and IRMS analysis were performed following the methods described previously [27]. In brief, the N concentrations of soil samples were determined using a CN analyzer (Elementar Analysensysteme GmbH, Hanau, Germany). Twenty-four milligrams of soil were accurately weighed and wrapped in tin foil (LUDI SWISS AG, Flawil, Switzerland), and N isotope ratios were measured by a Delta V Advantage equipped with an elemental analyzer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bremen, Germany). The amount of nitrogen introduced into the soil was calculated with the obtained values of soil N concentration and 15N/14N abundance (δ15N/δ14N [‰]).
2.4. Soil DNA Extraction for SIP Analysis
Soil DNA was extracted from each incubated soil (2 days, 4 days, and 6 days) following a method described previously [28], with some modifications. Each 0.4 g soil sample was placed in a 2 mL tube and mixed with 1.0 g zirconia/silica beads (0.1 mm, Biospec, Bartlesville, OK, USA), 375 μL phosphate buffer (PB), 500 μL phenol/chloroform/isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1), and 125 μL Tris-sodium chloride/sodium dodecyl sulfate buffer (TNS) and then homogenized using a cell destroyer (PS2000, Bio Medical Science, Tokyo, Japan) for 30 s at a frequency of 6.5 m/s. After repeating this process twice, the collected supernatant was treated with 1 volume of phenol/chloroform/isoamyl alcohol and then 1 volume of chloroform/isoamyl alcohol for purification. One microliter of aqueous glycogen solution (20 mg/mL) and 1 mL of polyethylene glycol solution were used for nucleic acid precipitation. The raw nucleic acids were washed using 75% ethanol and resuspended in 100 μL TE buffer. The collected nucleic acid solution was purified to remove the PCR inhibitors using a OneStep PCR inhibitor Removal kit (Zymo Research, Orange, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. RNA removal was carried out using 10 μL RNase I (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) in 100 μL extract under an incubation temperature of 37.8 °C for 1 h. The RNA-free DNA solution was then obtained using a QIAquick PCR Purification Kit (Qiagen, Venlo, The Netherlands) and quantified using a NanoDrop One (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
2.5. SIP Gradient Fractionation
Isopycnic gradient centrifugation and fractionation were performed according to a previously reported method [29]. The extracted DNA solution containing 2.4 µg DNA was mixed with the CsCl and gradient buffer in an OptiSeal polyallomer tube (Beckman Coulter, Indianapolis, IN, USA) with a final density of 1.69 g/mL. The mixture was then ultracentrifuged at 55,000 rpm for 66 h using an Optima MAX-TL Ultracentrifuge (Beckman Coulter) equipped with a TLA 110 rotor. The resulting DNA gradient solutions were fractionated into 15 fractions with equal volumes. The buoyant density (BD) value of each fraction was measured by a digital refractometer (LLG-Labware, Meckenheim, Germany). The DNA recovered from each fraction corresponding to densities between 1.695 and 1.739 g mL−1 was precipitated using a polyethylene glycol solution (30% PEG, 1.6 M NaCl) with 20 µg glycogen and then resuspended in 30 μL TE buffer (pH 8.0).
2.6. qPCR of 16S rRNA and nifD Gene in SIP Gradient Fractions
Quantitative PCR (qPCR) targeting the bacterial 16S rRNA gene, the nifD gene of the genus Anaeromyxobacter and the family Geobacteraceae (A&G_nifD), for each SIP gradient fraction was performed using the StepOnePlus System (Applied Biosystems, Foster city, CA, USA) with TB Green Premix Ex Taq (Takara Bio, Shiga, Japan). The specific primer sets, details of the PCR conditions, and the standard curve for each target gene were the same as those described previously [25].
2.7. 16S rRNA Amplicon Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
Based on the qPCR results, the fractions with the first and second highest relative abundance in 14N2-treatment (light fraction 1; L1, light fraction 2; L2) and 15N2-treatment (heavy fraction 1; H1, and heavy fraction 2; H2) from the Con and Fe plot samples (2-day, 4-day, and 6-day) were selected and subjected to amplicon sequencing targeting the V3–V4 region of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene as follows. The first-step PCR amplification was performed using a 20 µL mixture: 10× Ex buffer, 2.0 µL; dNTPs (each 2.5 mM), 1.6 µL; forward and reverse primers (10 µM), each 0.5 µL; DNA template, 1 µL; Ex Taq (5 units/µL), 0.2 µL; Milli-Q water, 13.2 µL. The amplification program was initial denaturation at 94 °C for 2 min, followed by 25 cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, 55 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s, and a final elongation step at 72 °C for 5 min. The second-step PCR was conducted with primers 2ndF/2ndR [30] under the following amplification program: 94 °C for 2 min, followed by 10 cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, 60 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s, with a final extension at 72 °C for 5 min. Sequencing was performed using the Illumina MiSeq platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) for a 2 × 300 paired-end (PE) configuration at Bioengineering Lab. Co. (Kanagawa, Japan). All raw sequence data were cleaned in QIIME 2 (ver. 2021.2) using DADA2 to remove low-quality sequence reads before regenerating the operational taxonomic unit (OTU) tables. The erroneous molecular OTUs were removed using LULU [31]. With a cutoff value of 97%, the clustered sequences corresponding to OTUs were annotated against the Greengenes database (ver. 13_8). Notably, the genus Geobacter annotated by the public database is paraphyletic in taxonomy and contains species currently belonging to several genera in the order Geobacterales [20,32]. Several novel Anaeromyxobacter strains were isolated from the environment and genome-sequenced [21,23]. Thus, the sequences in the Geobacter and Anaeromyxobacter-related OTUs were reannotated against the NCBI-nr database. The 16S rRNA relative abundances for each bacterial genus in the 15N-labeled DNA combined fraction (H1 and H2) and the 14N-labeled DNA combined fraction (L1 and L2) were calculated by normalizing the number of amplicon sequence reads using the copy numbers of 16S rRNA genes obtained by qPCR. Genera with higher relative abundances in 15N-labeled DNA than in 14N-labeled DNA were selected, and a heatmap depicting the transitions of bacterial community composition incorporating 15N was generated using the Pheatmap package in R-version 4.2.1 [33].
2.8. Statistics
To compare the differences in incorporated 15N in paddy soils, a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s test was used.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influence of Fe Application on the Amount of Fixed Nitrogen in Soil
The cumulative amount of incorporated 15N in soil collected from the Con plot on Days 2, 4, and 6 of incubation was 0.14 ± 0.01, 0.22 ± 0.01, and 0.53 ± 0.01 μg/g-dry soil, while that in soil collected from the Fe plot was 0.28 ± 0.01, 0.81 ± 0.10, and 1.32 ± 0.07, respectively (Figure 1). The amount of fixed nitrogen in paddy soils with 50% and 75% water content was reported to be 0.00714 and 0.171 (μg/g-dry soil) per day, respectively [34]. Given that the water content of the soils in this study was approximately 65%, the average amount of incorporated 15N in the Con plot soil (0.08 μg/g-dry soil/day) seems reasonable. On all days examined, the amount of incorporated 15N in the Fe plot soil was significantly higher (2–3.7 times) than that in the Con plot soil. Since biological nitrogen fixation is the only way atmospheric nitrogen can be incorporated into soil, these results indicate the occurrence of biological nitrogen fixation in native (Con plot) soil and increased biological nitrogen fixation in iron-applied (Fe plot) soil. In our previous study on the same experimental paddy field, enhanced nitrogen-fixing activity, examined by acetylene reduction assay, of Fe plot soil compared with Con plot soil was observed [25]. This study, supplementing the results of the previous study, clearly demonstrates an increased amount of fixed nitrogen in Fe plot soil compared with Con plot soil upon iron application.
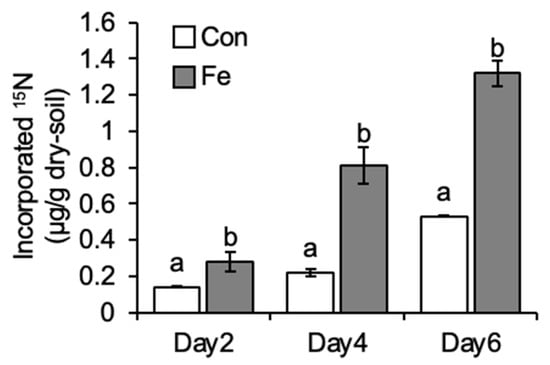
Figure 1.
The amount of 15N incorporated in iron-applied (Fe) and non-applied native (Con) plot paddy soils. Data are presented as means ± standard deviations (SD) from triplicate tests. A different letter above the bar indicates a significant difference.
3.2. Influence of Fe Application on the Quantity of 16S rRNA and nifD Genes in Fractionated DNA
In the soil incubated with 15N2, nitrogen-fixing microorganisms incorporate 15N, and their 15N-labeled DNA becomes heavier than 14N-(15N-unlabeled) DNA. CsCl gradient ultracentrifugation was used to separate 15N-labeled heavy DNA from 14N-labeled light DNA based on their different densities.
In the analysis of Con plot soil DNA, the relative abundance of the 16S rRNA gene for the 14N2-treated samples reached its maximum value at a density of around 1.71, while for the 15N2-treated samples, apparent peak shifts toward heavier densities were observed at all incubation periods (Figure 2a–c), indicating that atmospheric nitrogen was incorporated by bacteria. To confirm whether the genus Anaeromyxobacter and family Geobacteraceae (A&G) were involved in 15N incorporation, qPCR was performed targeting the nitrogen fixation genes (nifD) derived from these bacteria in each fraction. Due to the large amount of pseudo-nifH present in soil environments [35], the nifD gene, a more reliable marker than the nifH gene, was used in this study. The relative abundances of the A&G nifD showed a peak shift similar to that of the 16S rRNA gene in all samples (Figure 2d–f), suggesting the incorporation of 15N by bacteria belonging to the genus Anaeromyxobacter and family Geobacteraceae in native (Con plot) paddy soils.
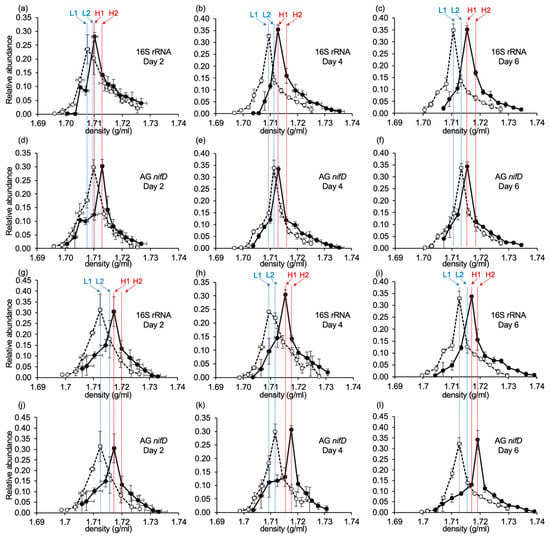
Figure 2.
Relative abundance of the 16S rRNA gene (a–c,g–i) and A&G (Anaeromyxobacter and Geobacteraceae) nifD (d–f,j–l) in fractionated DNA derived from non-applied native (Con) plot paddy soils (14N-Con and 15N-Con) on day 2 (a,d), day 4 (b,e), and day 6 (c,f) and iron-applied (Fe) plot paddy soils (14N-Fe and 15N-Fe) on day 2 (g,j), day 4 (h,k), and day 6 (i,l) of soil incubation. The open and closed circles show 14N-treated and 15N-treated samples, respectively. L1, L2, H1, and H2 indicate the samples chosen for amplicon sequencing. Data are shown in triplicate.
In the analysis of Fe plot soil DNA, peak shifts of the relative 16S rRNA gene (Figure 2g–i) and A&G nifD (Figure 2j–l) abundance toward heavier fractions were also observed in all 15N2-treated samples compared to corresponding 14N2-treated samples. These results indicate atmospheric nitrogen fixation by bacteria, including those in the genus Anaeromyxobacter and the family Geobacteraceae, in the Fe plot soil as well. Peak shifts in both the 16S rRNA gene and A&G nifD qPCR were greater in Fe plot soil DNA analysis than in Con plot soil DNA analysis, suggesting increased nitrogen fixation by bacteria, particularly by the genus Anaeromyxobacter and the family Geobacteraceae in iron-applied (Fe plot) paddy soil.
3.3. Influence of Fe Application on the Diazotrophic Communities in Soil
Amplicon sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene in the L1,2 and H1,2 fractions was performed to clarify the active nitrogen fixing bacteria in native (Con plot) and iron-applied (Fe plot) paddy soils, particularly to confirm whether the bacteria belonging to the genus Anaeromyxobacter and the family Geobacteraceae were the most active diazotrophs. Soil samples collected on days 2, 4, and 6 were subjected to this analysis to cover a wide variety of diazotrophic bacterial communities containing bacteria with different growth rates. In some cases of qPCR targeting A&G nifD (Figure 2d,k,l), 15N-incorporated Anaeromyxobacter/Geobacteraceae DNA was present in heavier fractions than top-peak fractions of the 16S rRNA gene. Therefore, in addition to using the highest peaks of the 16S rRNA gene (L1 and H1), we performed amplicon sequencing of the L2 and H2 fractions (Figure 2). Bacteria with increased relative abundance in the 15N treatments compared to the 14N treatments are shown as a heatmap (Figure 3).
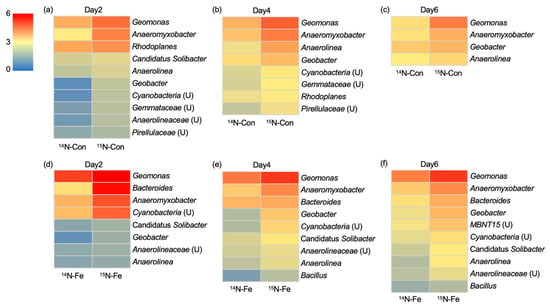
Figure 3.
Bacterial community composition based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing at the genera with higher relative abundances in 15N-labelled DNA(15N-Con and 15N-Fe) than in 14N-labelled DNA (14N -Con and 14N-Fe) of non-applied native (Con; a–c) and iron-applied (Fe; d–f) plot samples on day 2 (a,d), day 4 (b,e) and day 6 (c,f) of soil incubation. (U) indicates unclassified bacteria. Data are shown as the average of triplicates.
In the 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis of Con plot soil, Geomonas, Anaeromyxobacter, and Geobacter, all of which are iron-reducing bacteria, were most frequently detected in 15N treatments with higher abundance than in 14N treatments (Figure 3a–c). This result suggests that Geobacteraceae and Anaeromyxobacter are the primary drivers of nitrogen fixation in the native (Con plot) paddy soil. Anaerolinea (days 2, 4, and 6), Cyanobacteria (days 2 and 4), and Rhodoplanes (days 2 and 4) were also frequently detected, suggesting that they are active nitrogen fixers as well. Cyanobacteria are well-known nitrogen-fixing bacteria in paddy soils [6]. Within the genus Rhodoplanes, some strains, e.g., R. roseus, R. piscinae, and R. elegans, possess a nitrogenase gene cluster in their genome, while R. sp. Z2-YC6860 does not (NPEX01000005.1, NPEW01000030.1, NPEU01000442.1, and NZ_CP007440.1). Thus, some bacteria belonging to Rhodoplanes likely have nitrogen-fixing abilities. On the other hand, bacteria belonging to the genus Anaerolinea have rarely been isolated, and only genomic information on Anaerolinea thermophila, which does not possess nitrogenase genes, is available in the NCBI database “https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 14 June 2023)”. Given the presence of a partial nitrogenase gene in the genome of Anaerolineae bacterium isolate ANRL2 (CAG0970598.1), Anaerolinea harboring nitrogenase may be found as the number of isolates increases.
In the 16S rRNA gene analysis of Fe plot soil, Geomonas, Anaeromyxobacter, and Geobacter were most frequently detected, indicating that these iron-reducing bacteria are primary drivers of nitrogen fixation in the iron-applied (Fe plot) paddy soil as well (Figure 3d–f). In addition to these bacteria, Bacteroides spp., which were not detected in Con plot soil, were frequently detected, indicating that they are another primary driver of nitrogen fixation in iron-applied paddy soil. Although the nitrogen-fixing ability of Bacteroides spp. has not been verified, nitrogenase gene clusters are present on the genomes of Bacteroides graminisolvens (BAJS01000002.1), Bacteroides reticulotermitis (NZ_BAIV01000007.1), and B. luti (FQTV01000005.1), suggesting diazotrophic ability in some Bacteroides spp. Bacteriodes were only detected in Fe plot soil, which suggests their nitrogen fixation was enhanced by iron application, i.e., they are iron-reducing bacteria. Bacteoides strains harboring iron-reducing abilities were reported [36]. Cyanobacteria (days 2, 4, and 6) and Anaerolinea (days 2, 4, and 6) were also frequently detected in the Fe-applied soil as well as in the Con plot soil. Since the iron-reducing ability of these bacteria has not been reported thus far, they are likely to be active nitrogen fixers in both plot soils, irrespective of iron application. Candidatus Solibacter was detected on all the days examined, as well as on day 2 in the Con plot soil. Although there are no nif genes registered in the NCBI database, it is strongly suggested that they are active nitrogen fixers in soils.
Overall, 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequence analysis revealed that iron-reducing bacteria belonging to the genera Anaeromyxobacter, Geomonas, and Geobacter are the most active diazotrophs in native and iron-applied paddy soils. In addition to these bacteria, Bacteroides, most likely consisting of iron-reducing bacteria, are active diazotrophs in iron-applied paddy soil. Iron application to the soil might stimulate the nitrogen-fixing activity of these iron-reducing diazotrophs and lead to increased nitrogen incorporation into the soil. Anaerolinea, Cyanobacteria, and Candidatus Solibacter are active nitrogen fixers in paddy soils, irrespective of iron application.
4. Conclusions
Overall, the IRMS and DNA-SIP analyses clearly demonstrated the predominance of iron-reducing bacteria as the primary drivers of nitrogen fixation in native paddy soil and the enhancement of their nitrogen fixation by iron application. To be specific, (1) in native paddy soil, atmospheric nitrogen was incorporated into the soil primarily by diazotrophic iron-reducing bacteria belonging to Geomonas, Anaeromyxobacter, and Geobacter. (2) In the paddy soil treated with iron, the amount of nitrogen incorporated into the soil increased as a result of enhanced biological nitrogen fixation. (3) Nitrogen fixation by iron-reducing bacteria belonging to Geomonas, Anaeromyxobacter, and Geobacter and possibly by iron-reducing Bacteroides was enhanced by iron application, and these bacteria were the primary drivers of nitrogen fixation in iron-applied paddy soil. (4) In addition to these iron-reducing bacteria, Anaerolinea, Cyanobacteria, and Candidatus Solibacter are active nitrogen fixers in paddy soil. This study provided a novel picture of active nitrogen-fixing microorganisms dominated by diazotrophic iron-reducing bacteria in paddy soil, and directly proved the effectiveness of iron application to enhance their nitrogen fixation and to increase the incorporation of atmospheric nitrogen into soil. The enhancement of biological nitrogen fixation in paddy fields by iron application may lead to novel and unique paddy soil management strategies to increase soil nitrogen fertility and ensure rice yields with reduced nitrogen fertilizer input and lower environmental nitrogen burdens. To achieve this, further studies are necessary to clarify the effects of iron application on rice growth and yields and the possible reduction of nitrogen fertilizer in paddy fields with different types of soil and environmental conditions. It will also be important to investigate the persistence of the effects of iron applied to soil.
Author Contributions
Y.M., Z.X., Y.S., H.O. and K.S. designed the experiment. Z.Z. performed most of the laboratory work and the data analysis. Z.Z. and Y.M. wrote the manuscript. Z.X. and K.S. edited the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers JP20H05679, JP20H00409, JP20K15423, JP18K19165, JP18K14366, and JP17H01464 Japan, the Canon Foundation, and JST (Japan Science and Technology Agency)—Mirai Program Grant Number JPMJMI20E5. Z. Zhang thanks the financial support from the China Scholarship Council (CSC).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The nucleotide sequences generated by amplicon sequencing in this study have been deposited in SRA (Bioproject: PRJNA881308).
Acknowledgments
We greatly appreciate the technical staff at Niigata Agricultural Research Institute working on field management. The measurement by the IRMS was performed by Mariko Norisada, Center for Asian Bioresources and Environment, the University of Tokyo.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Gross, B.L.; Zhao, Z. Archaeological and genetic insights into the origins of domesticated rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6190–6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, J.; Hirose, M.; Tanaka, S.; Sakamoto, K.; Nakao, A.; Dejbhimon, K.; Lattirasuvan, T.; Abe, S. Changes in paddy soil fertility in Thailand due to the Green Revolution during the last 50 years. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 66, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Yang, J. Nitrogen (N) transformation in paddy rice field: Its effect on N uptake and relation to improved N management. Crop Environ. 2022, 1, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainju, U.M.; Ghimire, R.; Pradhan, G.P. Nitrogen fertilization I: Impact on crop, soil, and environment. In Nitrogen Fixation; Rigobelo, E.C., Serra, A.P., Eds.; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; and Zhang, F. Nitrogen fertilizer induced greenhouse gas emissions in China. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2011, 3, 407–413. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, S.; Ikeda, S.; Minamisawa, K.; Senoo, K. Nitrogen cycling in rice paddy environments: Past achievements and future challenges. Microbes Environ. 2011, 26, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, T. Rice production in unfertilized paddy field—Mechanism of grain production as estimated from nitrogen economy. Plant Prod. Sci. 2002, 5, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Ancajas, R.R. Nitrogen-fixing activity in upland and flooded rice fields. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1973, 37, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladha, J.K.; Tirol-Padre, A.; Reddy, C.K.; Cassman, K.G.; Verma, S.; Powlson, D.S.; van Kessel, C.; de Richter, D.B.; Chakraborty, D.; Pathak, H. Global nitrogen budgets in cereals: A 50-year assessment for maize, rice, and wheat production systems. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.L.; Zhang, M.; Tian, Y.H.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, B.W.; Zeng, K.; Zhao, M.; Yin, B. Urea deep placement in combination with Azolla for reducing nitrogen loss and improving fertilizer nitrogen recovery in rice field. Field Crops Res. 2018, 218, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, P.A.; Ladha, J.K. Biological N2 fixation in wetland rice fields: Estimation and contribution to nitrogen balance. Plant Soil. 1992, 141, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, C.; Bogusz, D.; Franche, C. Biological nitrogen fixation in non-legume plants. Ann. Bot. 2013, 111, 743–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Menge, D.N.L.; Reed, S.C.; Cleveland, C.C. Biological nitrogen fixation: Rates, patterns and ecological controls in terrestrial ecosystems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20130119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, Y.; Itoh, H.; Shiratori, Y.; Isobe, K.; Otsuka, S.; Senoo, K. Predominant but previously-overlooked prokaryotic drivers of reductive nitrogen transformation in paddy soils, revealed by metatranscriptomics. Microbes Environ. 2017, 32, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovley, D.R.; Ueki, T.; Zhang, T.; Malvankar, N.S.; Shrestha, P.M.; Flanagan, K.A.; Aklujkar, M.; Butler, J.E.; Giloteaux, L.; Rotaru, A.E.; et al. Geobacter: The microbe electric’s physiology, ecology, and practical applications. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2011, 59, 1–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Sanford, R.A.; Löffler, F.E. Uranium(VI) reduction by Anaeromyxobacter dehalogenans strain 2CP-C. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 3608–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, T.; Müller, A.; Igarashi, Y.; Conrad, R.; Friedrich, M.W. Identification of iron-reducing microorganisms in anoxic rice paddy soil by 13C-acetate probing. ISME J. 2010, 4, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Masuda, Y.; Hayakawa, C.; Ushijima, N.; Kawano, K.; Shiratori, Y.; Senoo, K.; Itoh, H. Description of three novel members in the family Geobacteraceae, Oryzomonas japonicum gen. nov., sp. nov., Oryzomonas sagensis sp. nov., and Oryzomonas ruber sp. nov. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Masuda, Y.; Itoh, H.; Ushijima, N.; Shiratori, Y.; Senoo, K. Geomonas oryzae gen. nov., sp. nov., Geomonas edaphica sp. nov., Geomonas ferrireducens sp. nov., Geomonas terrae sp. nov., Four ferric-reducing bacteria isolated from paddy soil, and reclassification of three species of the genus Geobacter as members of the genus Geomonas gen. nov. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2201. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Masuda, Y.; Wang, X.; Ushijima, N.; Shiratori, Y.; Senoo, K.; Itoh, H. Genome-based taxonomic rearrangement of the order Geobacterales including the description of Geomonas azotofigens sp. nov. and Geomonas diazotrophica sp. nov. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 737531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, Y.; Yamanaka, H.; Xu, Z.; Shiratori, Y.; Aono, T.; Amachi, S.; Senoo, K.; Itoh, H. Diazotrophic Anaeromyxobacter isolates from soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00956-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, H.; Xu, Z.; Masuda, Y.; Ushijima, N.; Hayakawa, C.; Shiratori, Y.; Senoo, K. Geomonas silvestris sp. nov., Geomonas paludis sp. nov. and Geomonas limicola sp. nov., isolated from terrestrial environments, and emended description of the genus Geomonas. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 004607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, H.; Xu, Z.; Mise, K.; Masuda, Y.; Ushijima, N.; Hayakawa, C.; Shiratori, Y.; Senoo, K. Anaeromyxobacter oryzae sp. nov., Anaeromyxobacter diazotrophicus sp. nov. and Anaeromyxobacter paludicola sp. nov., isolated from paddy soils. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 005546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Masuda, Y.; Wang, X.; Ushijima, N.; Shiratori, Y.; Senoo, K.; Itoh, H. Geomesophilobacter sediminis gen. nov., sp. nov., Geomonas propionica sp. nov. and Geomonas anaerohicana sp. nov., three novel members in the family Geobacterecace isolated from river sediment and paddy soil. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 44, 126233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, Y.; Shiratori, Y.; Ohba, H.; Ishida, T.; Takano, R.; Satoh, S.; Shen, W.; Gao, N.; Itoh, H.; Senoo, K. Enhancement of the nitrogen-fixing activity of paddy soils owing to iron application. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 67, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Long, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Gao, N.; Masuda, Y.; Itoh, H.; Senoo, K. Investigation of rice yields and critical N losses from paddy soil under different N fertilization rates with iron application. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaario, L.M.; Sah, S.P.; Norisada, M.; Narimatsu, M.; Matsushita, N. Tricholoma matsutake may take more nitrogen in the organic form than other ectomycorrhizal fungi for its sporocarp development: The isotopic evidence. Mycorrhiza 2019, 29, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, R.; Claus, P.; Conrad, R. Methanogenic archaea are globally ubiquitous in aerated soils and become active under wet anoxic conditions. ISME J. 2012, 6, 847–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, R.; Panhölzl, C.; Gabriel, R.; Herbold, C.; Wanek, W.; Richter, A.; Eichorst, S.A.; Woebken, D. Application of stable-isotope labeling techniques for the detection of active diazotrophs. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, D.; Fujiyoshi, S.; Maruyama, F.; Goto, M.; Koyama, S.; Kanatani, J.-I.; Isobe, J.; Watahiki, M.; Sakatoku, A.; Kagaya, S.; et al. Size resolved characteristics of urban and suburban bacterial bioaerosols in Japan as assessed by 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frøslev, T.G.; Kjøller, R.; Bruun, H.H.; Ejrnæs, R.; Brunbjerg, A.K.; Pietroni, C.; Hansen, A.J. Algorithm for post-clustering curation of DNA amplicon data yields reliable biodiversity estimates. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, D.W.; Chuvochina, M.; Pelikan, C.; Parks, D.H.; Yilmaz, P.; Wagner, M.; Loy, A.; Naganuma, T.; Nakai, R.; Whitman, B.W.; et al. Proposal to reclassify the proteobacterial classes Deltaproteobacteria and Oligoflexia, and the phylum Thermodesulfobacteria into four phyla reflecting major functional capabilities. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 5972–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolde, R. pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps, R Package Version 1.0.8. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=pheatmap (accessed on 15 February 2022).
- Kondo, M.; Yasuda, M. Effects of temperature, water regime, light, and soil properties on 15N2 fixation associated with decomposition of organic matter in paddy soils. JARQ-Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2003, 37, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mise, K.; Masuda, Y.; Senoo, K.; Itoh, H. Undervalued Pseudo-nifH sequences in public databases distort metagenomic insights into biological nitrogen fixers. Msphere 2021, 6, e0078521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Liu, L.; Sun, D.; Ren, N.; Lee, D.J. Isolation of Fe(III)-reducing fermentative bacterium Bacteroides sp. W7 in the anode suspension of a microbial electrolysis cell (MEC). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 3178–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).