Sound Wave Absorption Coefficient and Sound Velocity in Thermally Modified Wood
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hill, C.A. Wood Modification: Chemical, Thermal and Other Processes; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Boonstra, M.J.; Van Acker, J.; Tjeerdsma, B.F.; Kegel, E.V. Strength Properties of Thermally Modified Softwoods and Its Relation to Polymeric Structural Wood Constituents. Ann. For. Sci. 2007, 64, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viitaniemi, P.; Jamsa, S.; Ek, P.; Viitanen, H. Method for Improving Biodegradation Resistance and Dimensional Stability of Cellulosic Products. U.S. Patent US5678324A, 21 October 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Salmén, L.; Possler, H.; Stevanic, J.S.; Stanzl-Tschegg, S.E. Analysis of Thermally Treated Wood Samples Using Dynamic FT-IR-Spectroscopy; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany/New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 62, pp. 676–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, B.M.; Pereira, H.M. Wood Modification by Heat Treatment: A Review. BioResources 2008, 4, 370–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzki, J.; Radomski, A.; Gawron, J. The Effect of Thermal Modification on Selected Physical Properties of Wood of Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris L.). Wood Res. 2013, 58, 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Bettina, G.F.; Giambra, B.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Megna, B.; Fakhrullin, R.; Akhatova, F.; Fakhrullin, R. Restoration of a XVII Century’s Predella Reliquary: From Physico-Chemical Characterization to the Conservation Process. Forests 2021, 12, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisuzzo, L.; Hueckel, T.; Cavallaro, G.; Sacanna, S.; Lazzara, G. Pickering Emulsions Based on Wax and Halloysite Nanotubes: An Ecofriendly Protocol for the Treatment of Archeological Woods. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.; Park, Y.; Yang, S.-Y.; Kim, H.; Han, Y.; Chang, Y.-S.; Yeo, H. Effect of Heat Treatment Temperature and Time on Sound Absorption Coefficient of Larix Kaempferi Wood. J. Wood Sci. 2017, 63, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk-Królak, I. Drewno Modyfikowane Termicznie. Constr. Optim. Energy Potential 2013, 1, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Mazela, B.; Zakrzewski, R.; Grześkowiak, W.; Cofta, G.; Bartkowiak, M. Resistance of Thermally Modified Wood to Basidiomycetes. Electron. J. Pol. Agric. Univ. 2004, 7, 1505-0297. [Google Scholar]
- Čermák, P.; Suchomelová, P.; Hess, D. Swelling Kinetics of Thermally Modified Wood. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2021, 79, 1337–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borůvka, V.; Zeidler, A.; Holeček, T. Comparison of Stiffness and Strength Properties of Untreated and Heat-Treated Wood of Douglas Fir and Alder. BioResources 2015, 10, 8281–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhta, P.; Niemz, P. Effect of High Temperature on the Change in Color, Dimensional Stability and Mechanical Properties of Spruce Wood; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, M.; Huang, X.; Jiang, M.; Yu, W.; Yu, Y. Effect of Thermo-Hydro-Mechanical Densification on Microstructure and Properties of Poplar Wood (Populus tomentosa). J. Wood Sci. 2017, 63, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smardzewski, J.; Batko, W.; Kamisiński, T.; Flach, A.; Pilch, A.; Dziurka, D.; Mirski, R.; Roszyk, E.; Majewski, A. Experimental Study of Wood Acoustic Absorption Characteristics. Holzforschung 2014, 68, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smardzewski, J.; Kamisiński, T. Właściwości Akustyczne Materiałów Stosowanych w Meblarstwie; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Przyrodniczego: Wrocław, Poland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mania, P.; Moliński, W.; Roszyk, E.; Górska, M. Optimization of Spruce (Picea abies L.) Wood Thermal Treatment Temperature to Improve Its Acoustic Properties. BioResources 2020, 15, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moliński, W.; Fabisiak, E.; Szwaba, T. Properties of Thermally Modified Ash Wood (Fraxinus americana) in the Aspect of Its Affinity to Water. Ann. Wars. Univ. Life Sci.-SGGW For. Wood Technol. 2010, 72, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, E.-S. Experimental Investigation of the Sound Absorption Capability of Wood Pellets as an Eco-Friendly Material. J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol. 2022, 50, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Fang, X.; Han, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J. Effect of Coating Thickness on Sound Absorption Property of Four Wood Species Commonly Used for Piano Soundboards. Wood Fiber Sci. 2020, 52, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.-W.; Jang, E.-S.; Lee, N.-H.; Jang, S.-S.; Lee, M. Air Permeability and Sound Absorption Coefficient Changes from Ultrasonic Treatment in a Cross Section of Malas (Homalium foetidum). J. Wood Sci. 2021, 67, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubel, A.; Garoum, M.; Bousshine, S.; Bybi, A. Investigation of Loose Wood Chips and Sawdust as Alternative Sustainable Sound Absorber Materials. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 172, 107639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yazdkhasti, A.; Mao, Y.; Siciliano, A.P.; Dai, J.; Jing, S.; Xie, H.; Li, Z. A Scalable High-Porosity Wood for Sound Absorption and Thermal Insulation. Nat. Sustain. 2023, 6, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, H.; Sung, G.; Kim, J.H. Chemical Treatment of Wood Fibers to Enhance the Sound Absorption Coefficient of Flexible Polyurethane Composite Foams. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 156, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolya, H.; Kang, C.-W. Hygrothermal Treated Paulownia Hardwood Reveals Enhanced Sound Absorption Coefficient: An Effective and Facile Approach. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 174, 107758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Peng, L.; Zhu, G.; Fu, F.; Zhou, Y.; Song, B. Improving the Sound Absorption Capacity of Wood by Microwave Treatment. BioResources 2014, 9, 7504–7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, T.A.; El-Sayed, A.B.; El-Shorbagy, K.A. Sound Absorption by Wood in Relation to Anatomical and Mechanical Properties. Appl. Acoust. 1980, 13, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassilieff, C. Sound Absorption of Wood-Based Materials. Appl. Acoust. 1996, 48, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Peña, M.M.; Hale, M.D.C. Colour in Thermally Modified Wood of Beech, Norway Spruce and Scots Pine. Part 2: Property Predictions from Colour Changes; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 63, pp. 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN ISO 10534-2; Determination of Sound Absorption Coefficient and Acoustic Impedance with the Interferometer. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001.
- Bucur, V. Acoustics of Wood; Springer Series in Wood Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; ISBN 978-3-540-26123-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wagenführ, R. Holzatlas; Fachbuchverlag Leipzig: Leipzig, Germany, 2000; ISBN 978-3-446-21390-6. [Google Scholar]
- Helbin, J. Środowiskowe Czynniki Fizyczne Wpływające na Organizm Człowieka; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Jagiellońskiego: Kraków, Poland, 2008; ISBN 978-83-233-2467-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, C.; Kang, W.; Chung, W.; Matsumura, J.; Oda, K. Changes in Anatomical Features, Air Permeability and Sound Absorption Capability of Wood Induced by Delignification Treatment. J. Fac. Agric. Kyushu Univ. 2008, 53, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
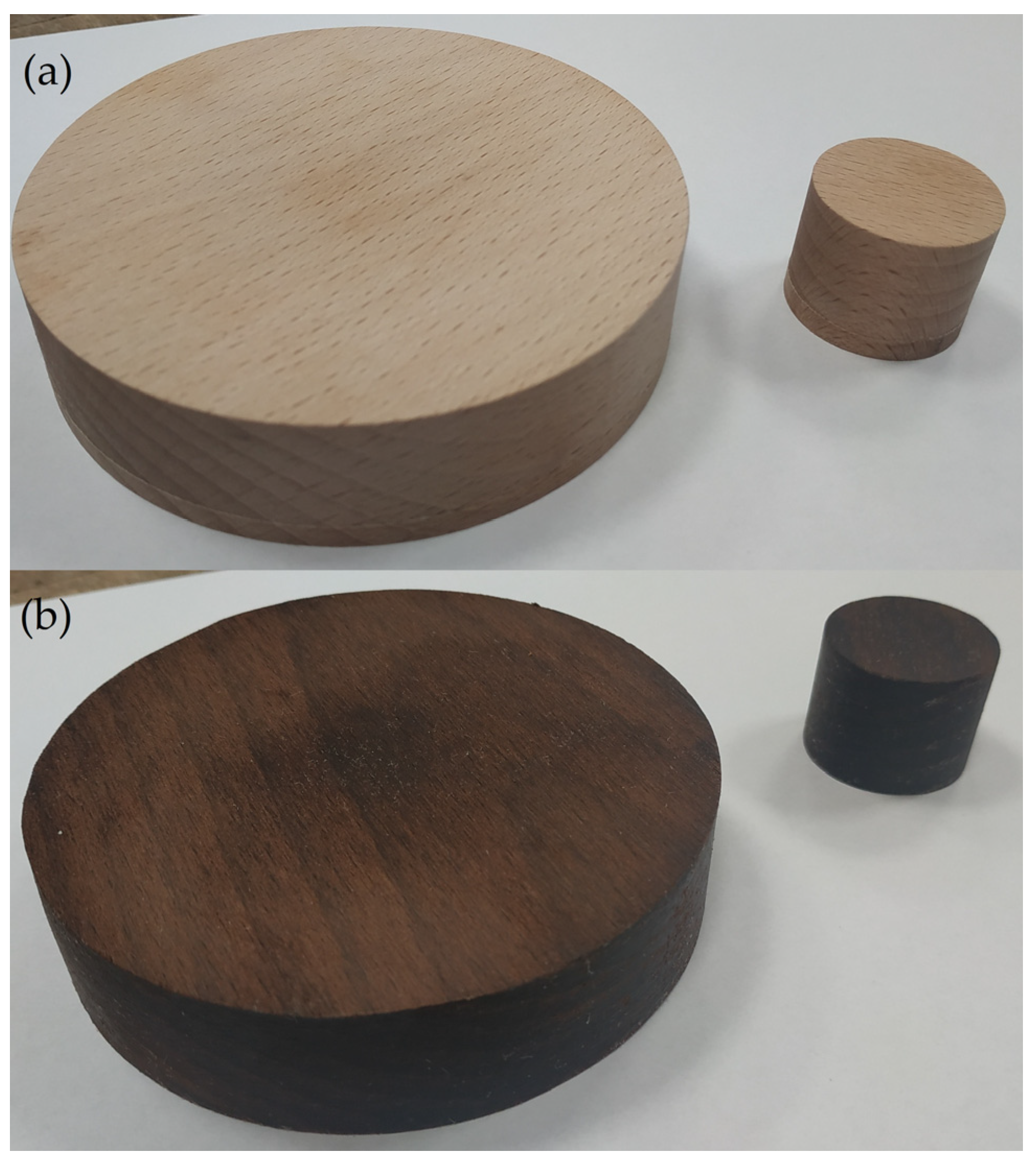
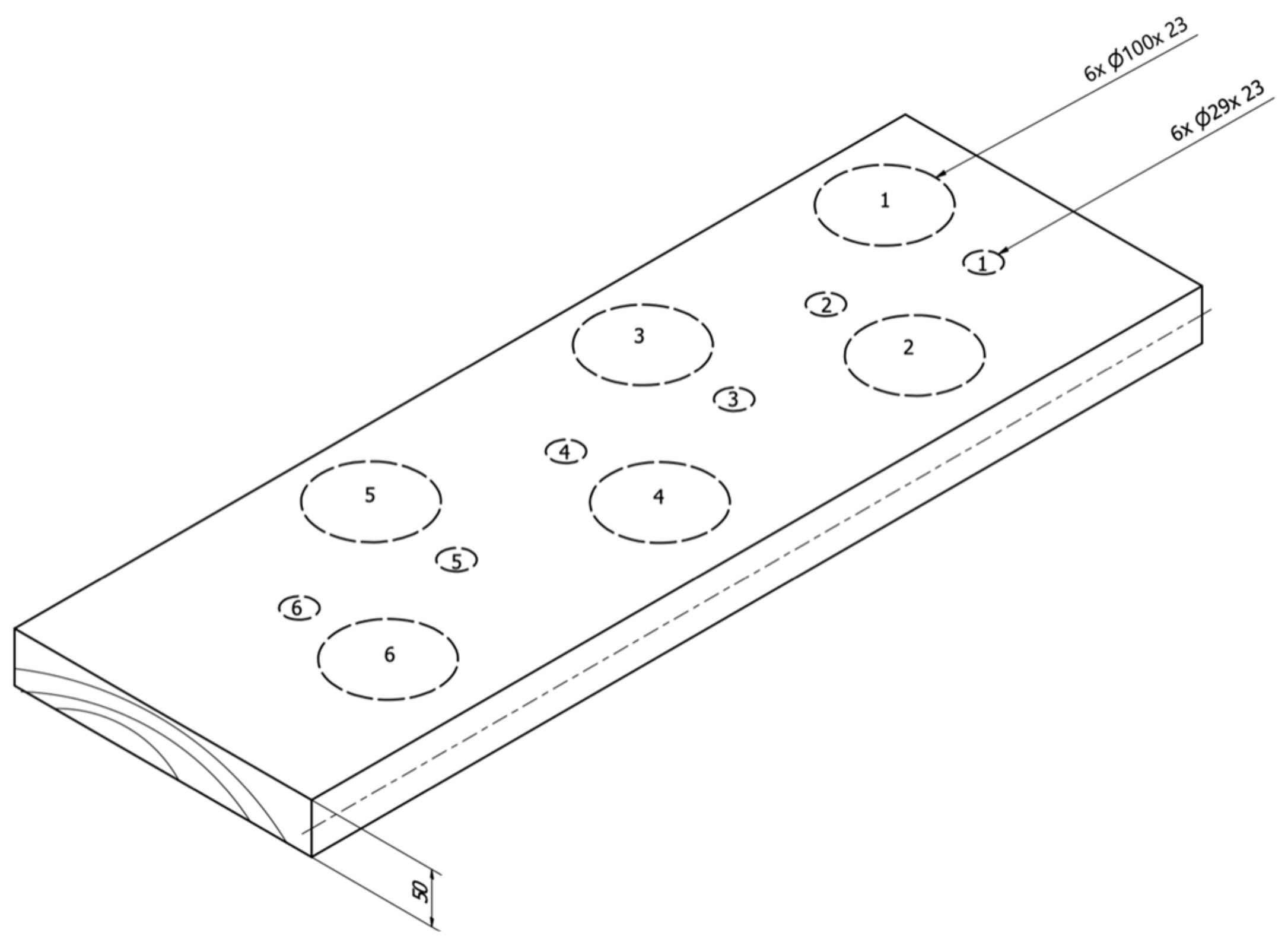
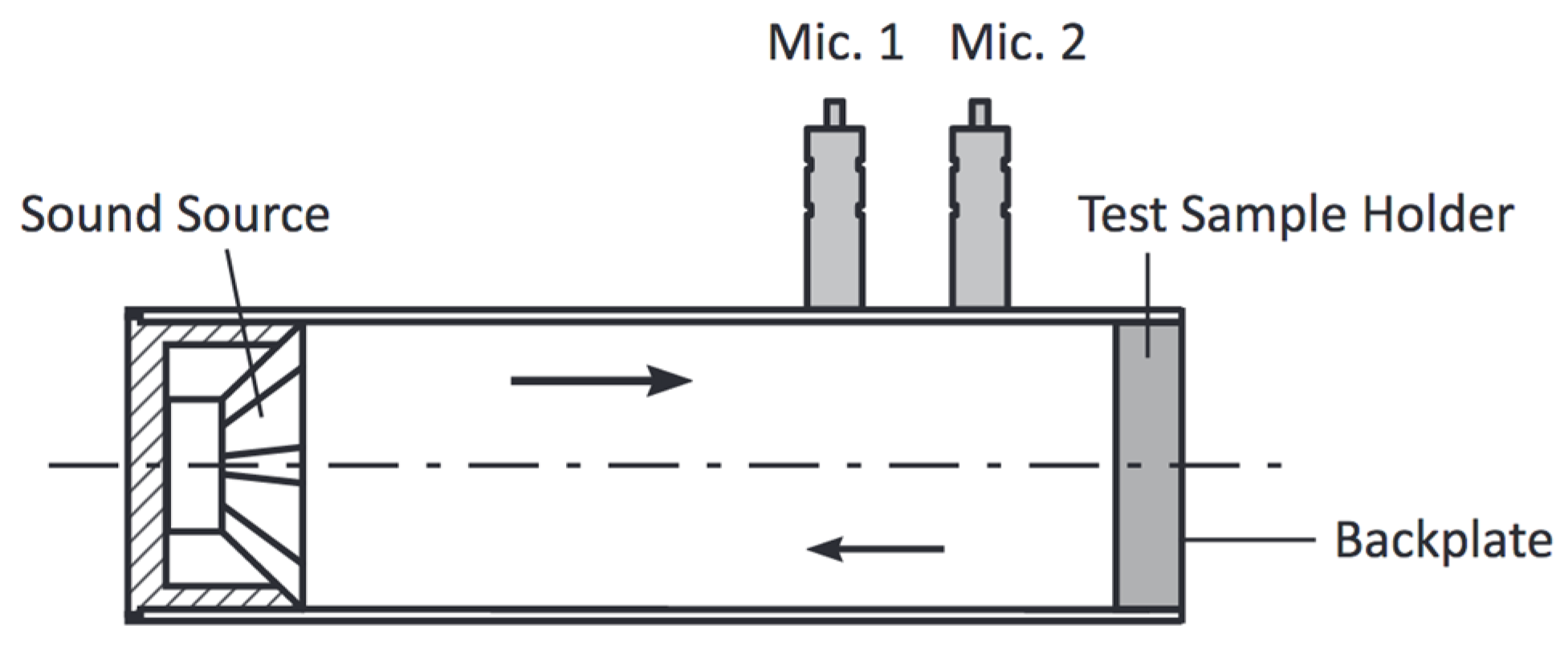
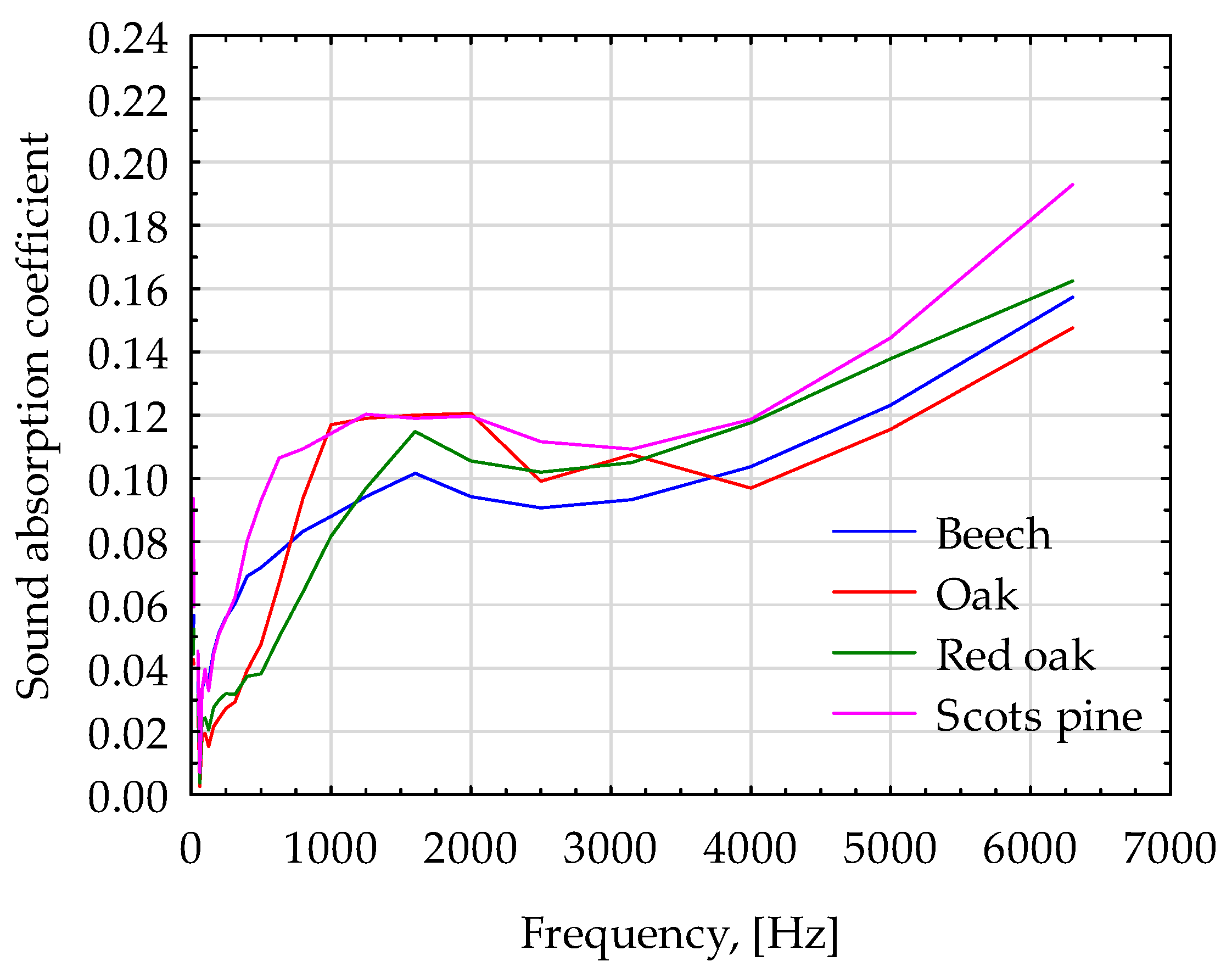
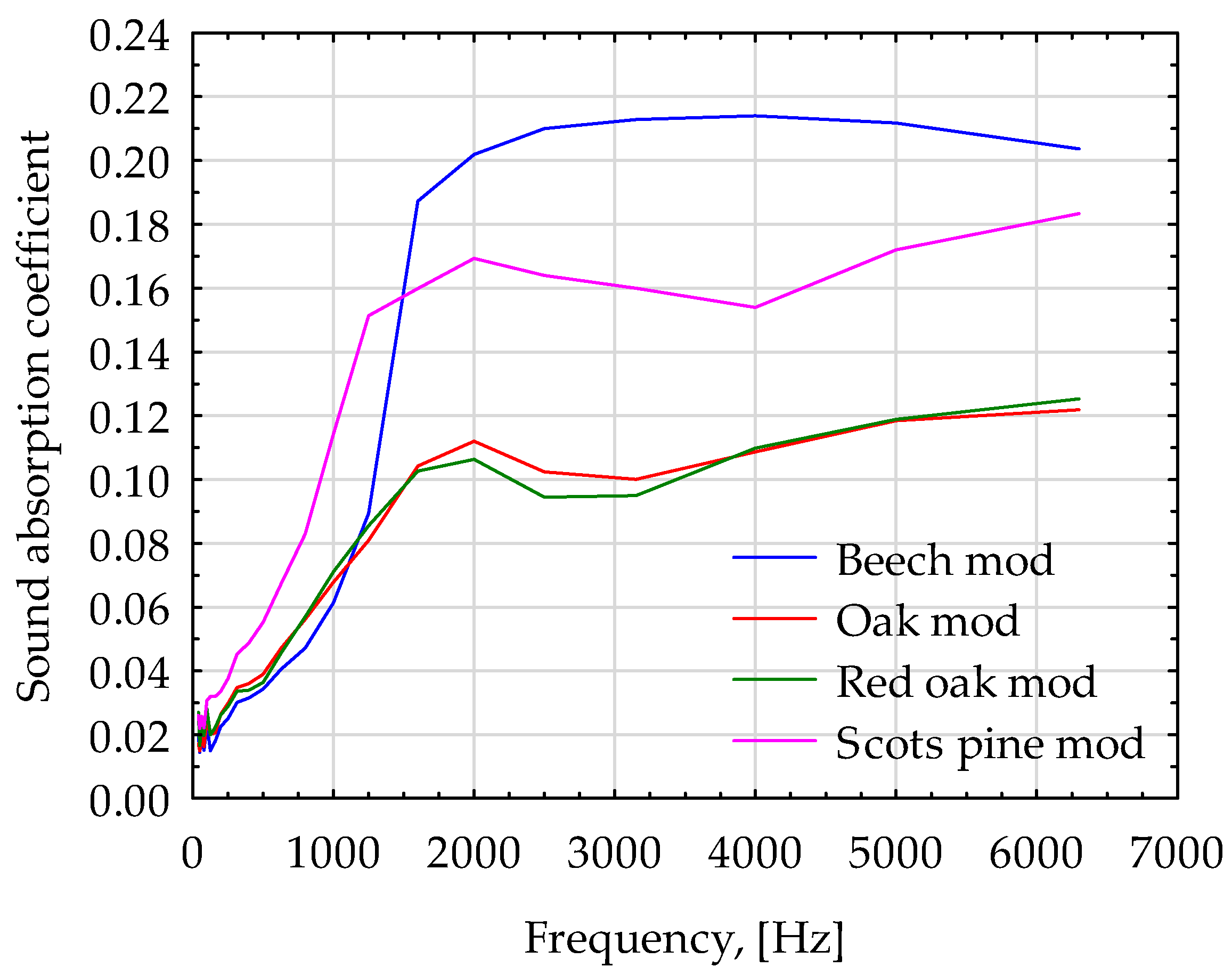
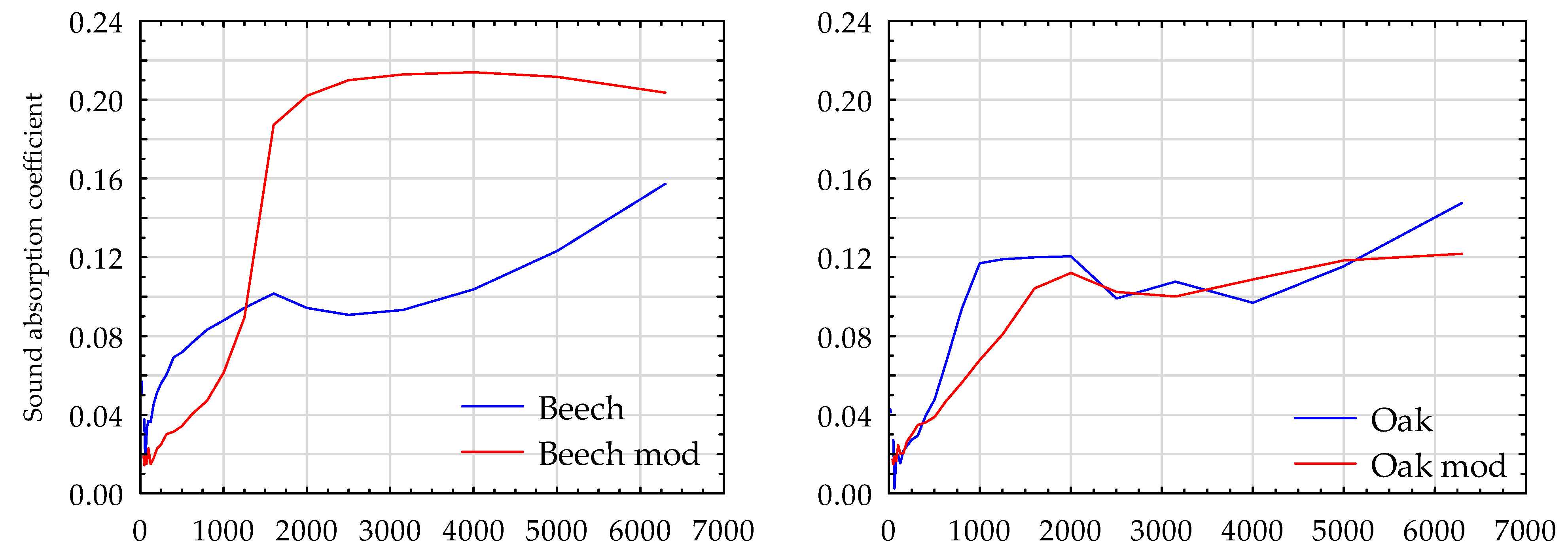
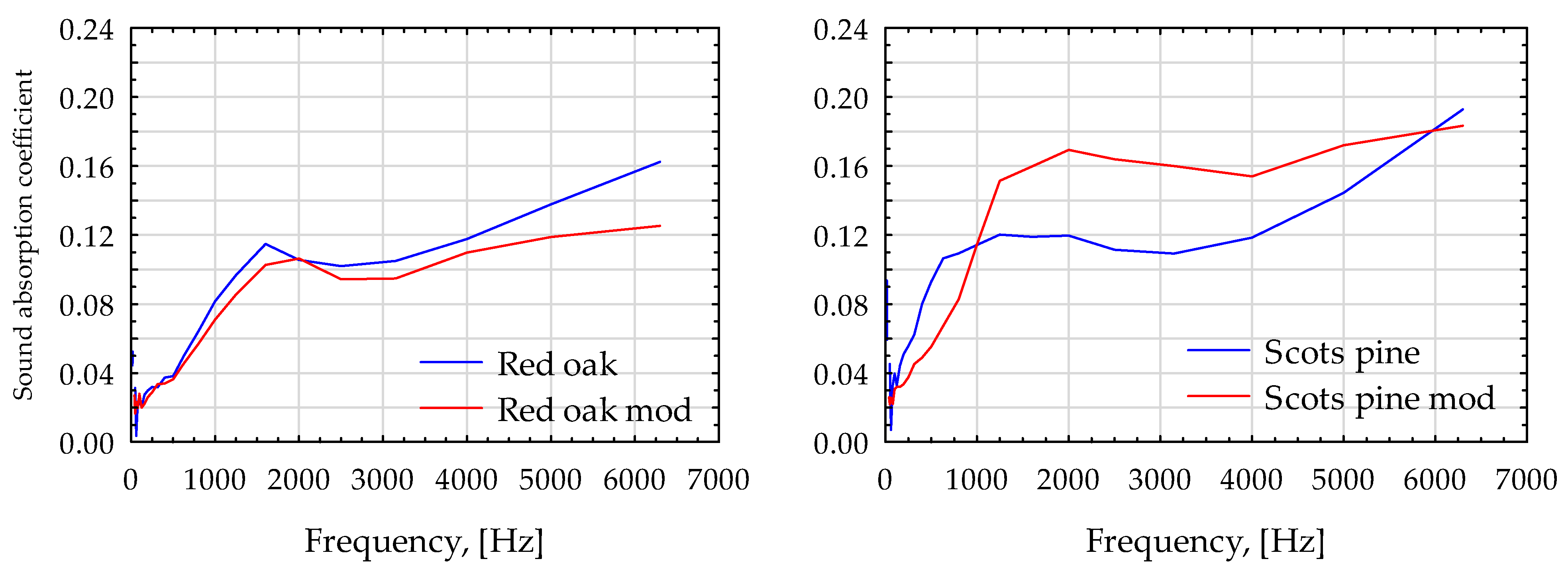
| Wood Species | Oven Dry | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (kg·m−3) | (%) | ||
| Beech | 743 ± 32.6 | 579 ± 38.0 | −22.1 ± 1.02 |
| Oak | 686 ± 41.5 | 573 ± 46.1 | −16.5 ± 0.94 |
| Red oak | 679 ± 49.1 | 601 ± 50.7 | −11.5 ± 0.92 |
| Scots pine | 641 ± 43.5 | 564 ± 38.3 | −12.0 ± 0.98 |
| Wood Species | 29 mm | 100 mm | Average | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VRR | VLL | VTT | VRR | VLL | VTT | VRR | VLL | VTT | |
| [m/s] | |||||||||
| Beech | 2439 | 5331 | 1457 | 2274 | 4831 | 1354 | 2356 | 5081 | 1405 |
| Oak | 2203 | 5458 | 1219 | 2115 | 5178 | 1355 | 2159 | 5318 | 1287 |
| Red oak | 2516 | 5247 | 1228 | 2025 | 4257 | 1268 | 2271 | 4752 | 1248 |
| Scots pine | 1865 | 6094 | 901 | 2172 | 6430 | 1060 | 2019 | 6262 | 981 |
| Wood Species | 29 mm | 100 mm | Average | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VRR | VLL | VTT | VRR | VLL | VTT | VRR | VLL | VTT | |
| [m/s] | |||||||||
| Beech | 1951 | 5365 | 1066 | 1522 | 5708 | 1302 | 1737 | 5536 | 1184 |
| Oak | 2368 | 5283 | 1149 | 2345 | 5206 | 1321 | 2230 | 5244 | 1235 |
| Red oak | 2650 | 5455 | 1044 | 2230 | 5629 | 1266 | 2440 | 5542 | 1155 |
| Scots pine | 1820 | 6364 | 885 | 2062 | 6495 | 811 | 1991 | 6430 | 848 |
| Wood Species | Oven Dry | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (MPa) | (%) | ||
| Beech | 19,182 ± 1922 | 17,745 ± 2089 | −7.5 ± 0.42 |
| Oak | 19,401 ± 1935 | 15,757 ± 2416 | −18.8 ± 0.68 |
| Red oak | 15,333 ± 1757 | 18,459 ± 2332 | +20.4 ± 1.72 |
| Scots pine | 25,135 ± 2134 | 23,318 ± 2688 | −7.2 ± 0.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mania, P.; Flach, A.; Pilarska, M. Sound Wave Absorption Coefficient and Sound Velocity in Thermally Modified Wood. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8136. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148136
Mania P, Flach A, Pilarska M. Sound Wave Absorption Coefficient and Sound Velocity in Thermally Modified Wood. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(14):8136. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148136
Chicago/Turabian StyleMania, Przemysław, Artur Flach, and Marta Pilarska. 2023. "Sound Wave Absorption Coefficient and Sound Velocity in Thermally Modified Wood" Applied Sciences 13, no. 14: 8136. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148136
APA StyleMania, P., Flach, A., & Pilarska, M. (2023). Sound Wave Absorption Coefficient and Sound Velocity in Thermally Modified Wood. Applied Sciences, 13(14), 8136. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148136








