Abstract
The aim of the research was to identify the effect of 4vs.4 small-sided games (SSGs) with goalkeepers (4vs.4+GK), applied twice a week, for 8 weeks, on U18 football players’ physical ability, compared to that of the athletes who performed specific aerobic endurance training. The research included 40 football players U18, divided into two groups: 20 in the experiment group (EG) aged 17.49 ± 0.61 years and 20 in the control group (CG) aged 17.66 ± 0.54 years. From the initial test (IT) to final tests (FT) performed on the parameters, maximum oxygen consumption (VO2max) and 10 m and 20 m sprint and agility with and without a ball showed a significant increase for both groups. The first and last SSG training was monitored, using total distance (TD), high-intensity distance (HSR—high-speed running) and maximum intensity distance (VHSR—very-high-speed running). Comparative analyses of EG and CG parameters at the FT shows that the differences between the means of two groups are statistically significant in favor of the experimental group in terms of all parameters, except 10 m sprint (p < 0.05). Referring to SSGs, the experimental group had a 7.78% increase rate in TD (p < 0.0005), a 30.90% (p < 0.0005) increase rate with HSR and no significant differences (p > 0.05) with VHSR. The experimental training program of 4vs.4+GK SSGs, applied to U18 football players, produced significant progress in the physical, and functional parameters.
Keywords:
small-sided games; VO2max; agility; speed; physical fitness; skills; U18 football player; training program; 4vs.4+GK 1. Introduction
Football has a complex structure that requires combined training for technical, tactical and physical skills. Studies have shown that during a match, football players actively use about 90% of their aerobic capacity at an intensity of 75% of their VO2max while the match total distance is between values. The analysis of the ways in which aerobic endurance training weeks combined with 4vs.4+GK small-sided games influence the optimization of the football players’ sporting capacity will allow the expansion of knowledge regarding specialized training [1,2,3]. Time–motion analysis indicates that the player covers an average distance of 10 to 13 km, with a distance of more than 900 m at a velocity greater than 19.8 km/h (High-speed running) and of about 250–300 m at a velocity greater than 25.2 km/h (sprinting) [2]. To cope with this type of effort, combined physical qualities such as power, explosive force, speed endurance or repeated sprint ability are required. The energy substrate is given by anaerobic alactacid and lactacid metabolism [4]. Because these efforts are repeated and last for a short duration, aerobic metabolism is predominant during a match. Therefore, aerobic capacity makes a major contribution to performance during competitions, allowing players to perform repeatedly high-intensity efforts [5,6]. Football players need training through specialized methods related to the competitive requirements of the football game [7]. Bompa and Haff [8] have proven that in high-performance sports, maximum benefits are achieved when training stimuli are similar to the requirements of those used in a competition. Over the past decade, football player monitoring has evolved through the increasing use of electronic performance and GPS tracking systems [9]. The monitoring and analysis of physical and technical parameters through modern technologies has led to the efficiency of football training due to the possibility of obtaining real-time feedback.
Specialists and researchers in the field of football are constantly concerned with identifying the possibilities of optimizing the physical and technical capacity of players, and the identification of the benefits of small-sided game (SSG) training in relation to traditional interval training falls within these trends and research directions. Small-sided games (SSGs) have become a popular method of training in both amateur and professional football clubs, being an effective drill for developing physical abilities, combining tactical technical and physical elements. SSG methods require each player to move actively and with high intensity, and reduced spaces require a high level of technical and physical skill. Planning training sessions to mimic game characteristics as closely as possible is seeing increasing importance in modern football, thus ensuring a reconciliation of technical, tactical and physical components [5,10]. Thus, small-sided games are considered to be more suitable drills for developing the specific physical characteristics required during a match, compared to traditional endurance interval training, on the standardized pitch [11,12].
SSGs, also called conditioning games, are basic in specific training based on the game model or a specific tactical concept. These games are less structured than are classic training games, but require the adaptation of players’ technical, tactical and physical abilities to the limited space and ball handling conditions, as well as to the dynamics of effort specific to these types of training [13,14,15,16]. SSGs through their specific characteristics induce in players a good ability to make quick decisions during a game with an impact on their efficiency in solving specific technical and tactical problems [17,18].
There are studies that have already investigated the effects of training with different types of small-sided games (in various forms and with the manipulation of the playing rules) on junior football players’ physical capacity and they did not find significant differences compared to traditional non-specific endurance training [19,20,21]. In terms of the aspects of functional capacity, SSG forms suggest that low-player games (two vs. two; three vs. three) are more intense, favoring the development of anaerobic endurance [22]. Souza et al. [11] rated U14 players after 20 training sessions where SSGs were used as a methodical strategy and found significant improvements in the reported tactical actions of defensive tactical principles, both in the number of actions and in tactical index performance.
There are systematic reviews related to small-sided games. The authors investigated the applications of SSGs in the sports training context with physical, physiological and tactical goals [23,24,25,26]. In the review conducted by [24], nine longitudinal research studies were found, that related to small-sided games, and in five of these, the subjects were junior football players. Most of the cross-sectional studies focused on describing differences between small-sided game protocols, while other studies focused on comparing exercise regimes in ‘interval’ and ‘continuous’ training and SSGs. Training programs based on small-sided games (two to four SSG sessions per week) show significant increases in player performance in terms of improved speed, repeated sprint ability and change in direction, along with muscular and physiological adaptation [24].
Training with small-sided games seems to be an effective strategy; variables controlled by the trainer through systematic programming adapted to training periods can influence the intensity of the exercise during a SSG [13,27,28]. Thus, small-sided game intensity can be changed according to the objectives of training, including changing several variables, such as player number, field size, game themes (number of passes, number of ball touches, etc.) or the use of a floater player [29].
In order to influence players’ physical and physiological parameters during a SSG, the number of ball touches should be limited. A smaller number of touches of the ball leads to an increase in game intensity. This seems to be the essential condition for playing elite-level football [30].
Dellal et al. [19] analyzed two vs. two, three vs. three and four vs. four SSGs with four “jolly” players on the side-lines in professional football players; the theme was to maintain possession, and the number of ball touches was limited to one to two. The authors observed increased concentrations of blood lactate, a higher rating of perceived exertion (RPE) levels, a longer total distance covered, a higher total distance covered in high-speed running (HSR) and a higher total distance covered in very-high-speed running (VHSR), under conditions limited to one or two ball touches, compared to conditions in which there were no limits to the number of ball touches. Heart rate remained constant, except in the case of a 4vs.4 small-sided game. In this case, the heart rate was higher when the number of touches was limited to one to two [19], and the number of technical errors increased. Compared to amateur players, the professional players covered greater distances at higher speeds and had fewer technical mistakes [19,31].
Oliveira et al. [26] performed a critical analysis regarding the way SSGs are applied, how they are monitored and how they influence the performance of football players in the short and medium term. As a conclusion, they found that the use of small-sided games mainly in the form of three vs. three (pitch size between 20 × 25 m and 27 × 36 m) and four vs. four (pitch size between 30 × 35 m and 30 × 40 m) with three and five workouts per week, for at least one month, seems to have beneficial effects in terms of physical performance in junior footballers. Buchheit and Arslad et al. found that the role of 4vs.4 SSGs in optimizing performance in football has varied aspects; however, they are not complete, are not particular to age categories. and do not highlight the implementation periods to ensure efficiency on the physical, technical and tactical levels [32,33,34,35].
The main goal of this research was to implement an adapted training program applied two times per week including 4vs.4+GK small-sided games and to evaluate its influence on the development of VO2max parameters, physical parameters (10 m and 20 m speed) and parameters (agility with and without a ball) in U18. The secondary research aim was to compare the U18 adaptation level to that in four vs. four small-sided games with goalkeepers, applied twice a week, with conventional endurance training.
It was hypothesized that both groups would improve their physical fitness parameters, the SSG group showing an improvement in their aerobic fitness and agility and the conventional training group improving more in terms of speed.
2. Material and Method
2.1. Design of Research
The research was conducted over an eight-week period during the summer preparatory period between July and August 2022, and the monitoring of the experimental group was carried out twice a week and aimed at the implementation of the training for 4vs.4+GK SSGs. Tracking small-sided game training was performed only in the experiment group, while the control group performed interval aerobic endurance training during this time. Before and after the implementation of the experimental program, two tests were applied: initial and final.
The intervention with our proposed program in the experimental group was a four vs. four SSG with goalkeepers (GK) with an official goal, twice a week during Wednesday’s and Saturday’s training session, for eight weeks. The pitch size was 32 m long and 40 m wide. The tactical system was 1-2-1, and the number of ball touches was limited to 2 and 3 touches. The training started with a 6 min specific warm-up with technical drills; 6′ of play with 3 players vs. 1 (each player playing for 30″ as a defender in the center of the circle); 20 min of 1 vs. 1 offensive actions with dribbling and finishing (Figure 1).
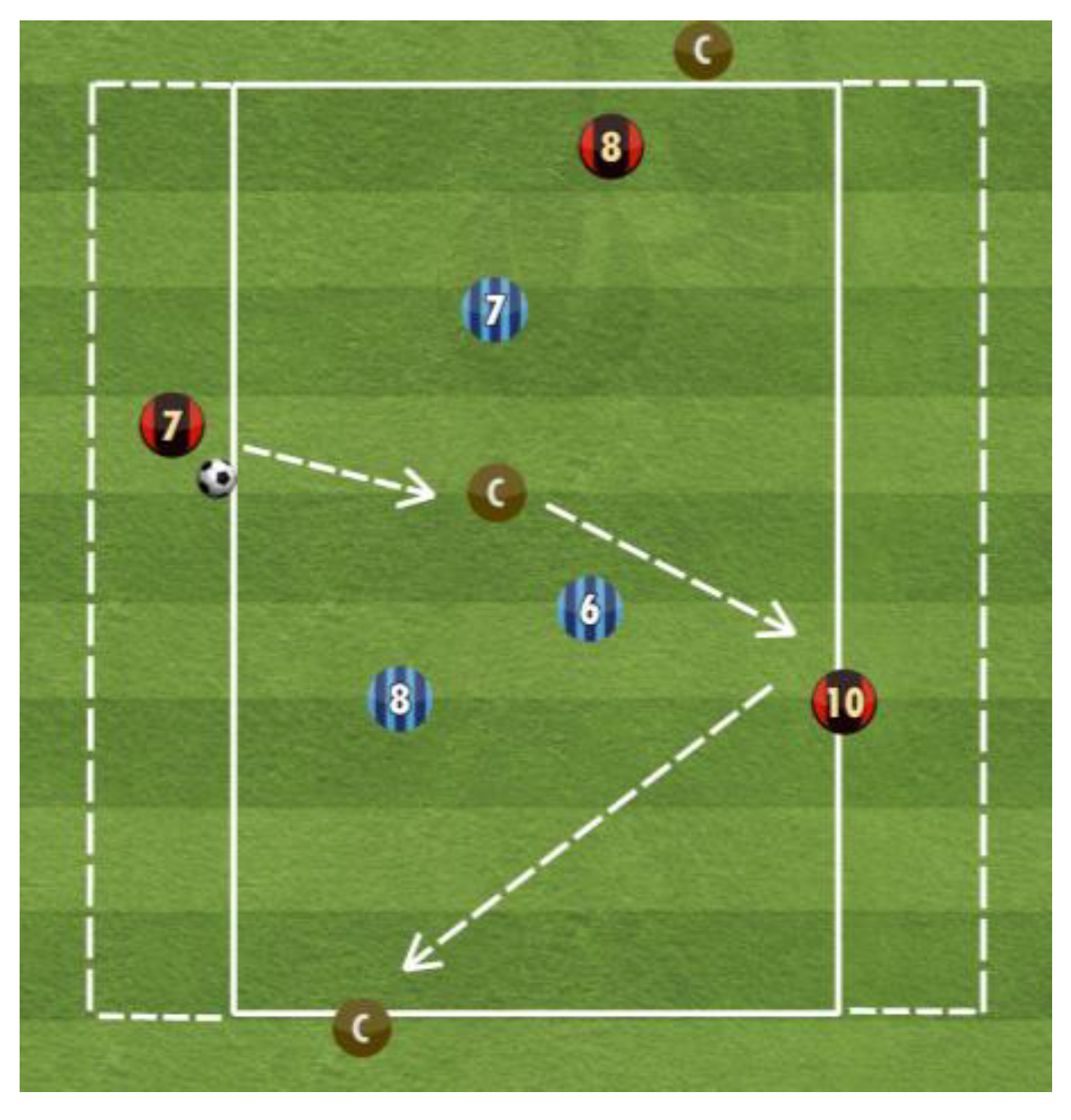
Figure 1.
Small-sided game, 3vs.3+3 jolly players (C–jolly players; the red and blue numbers correspond to the numbers on the shirts of the players of the two teams on the field)).
What followed was a 3vs.3+3 small-sided game (pitch area, 18 m long and 12 m wide plus 3 m wide side areas where the attacking players who had ball possession could enter) and 6 × 1′ rest 30″ as a transitional stage (Figure 2). The main part of the training session was 8 × 2′30″ with 2′30″ of rest, in a 4vs.4+GK small-sided game. All these variables were preserved throughout the intervention, the analysis involving entering data from the first training session (initial testing) and the last session (final testing).
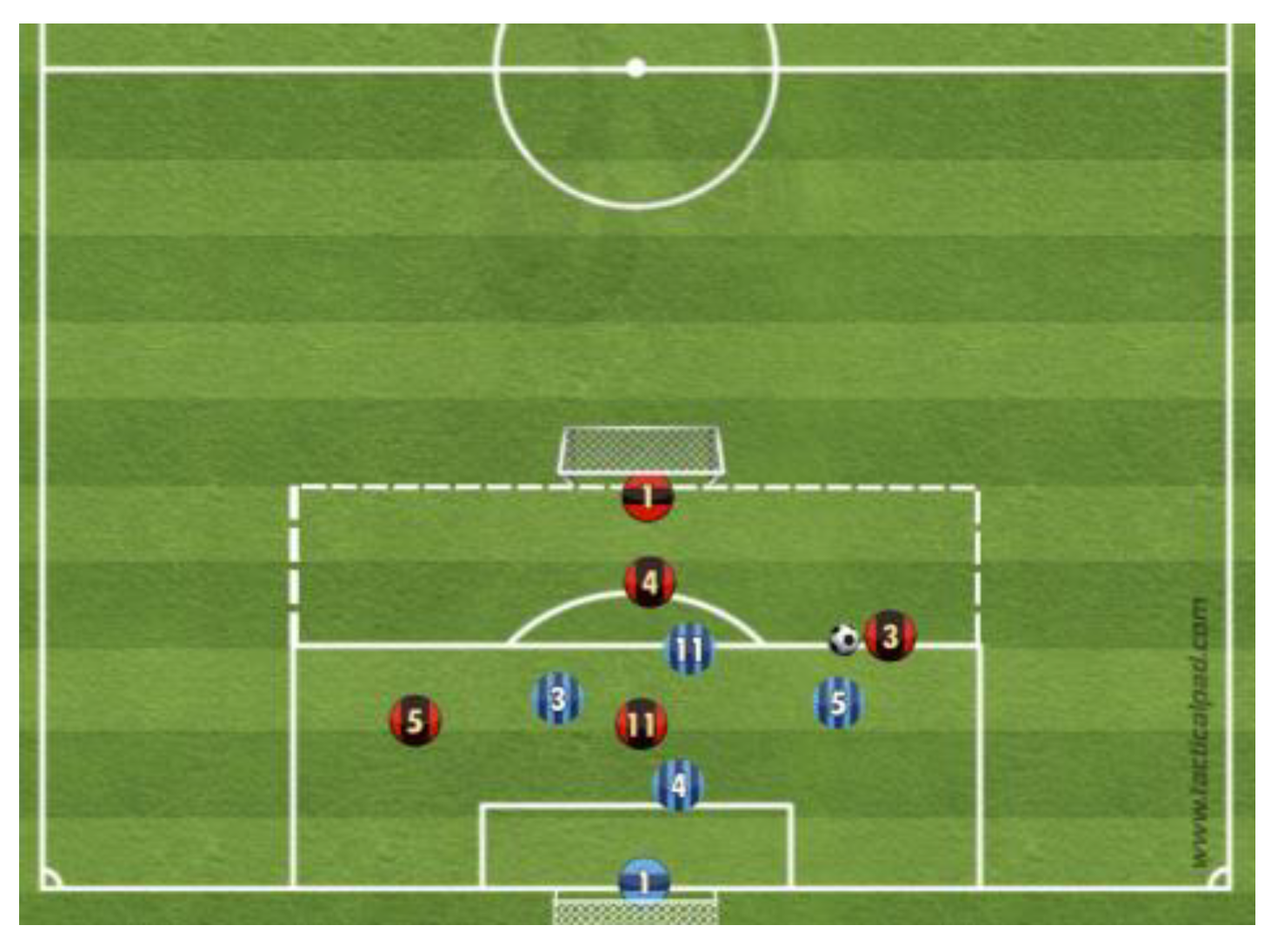
Figure 2.
Small-sided game; 4vs.4+GK game system; 1-2-1 (the red and blue numbers correspond to the numbers on the shirts of the players of the two teams on the field).
The training program of the control group was carried out every Wednesday, involving performing aerobic endurance interval training and a Saturday training game, with two 35′ halves and a 10′ break. For this article, all authors contributed equally. The research complied with the recommendations of the Helsinki Declaration and all subjects received a clear explanation of the study, including the risks and benefits of participation. Each player completed the medical examination required by the club, and read and signed the club’s consent and medical forms for participation in the U18 national championship.
2.2. Participants
In total, 43 elite football players participated in our research, and 40 players were selected and divided into two equal groups of 20 players: the experiment group and control group. The characteristics of the samples were as follows: an age of 17.49 ± 0.61 years for the experiment group and of 17.66 ± 0.54 years for the control group; a stature of 178.80 ± 9.31 cm for the experiment group and 180.80 ± 4.32 cm for the control group; a body weight of 70.74 ± 9.19 kg for the experiment group and of 76.08 ± 4.52 kg for the control group; adipose tissue coverage of 11.34 ± 2.30% for the experiment group and of 10.50 ± 1.55% for the control group). The participants were players with over 6 years of experience in football, participating regularly in over six workouts a week and a game (friendly or official, depending on the training period) and playing in the national championship Youth League U18, organized by the Romanian Football Federation. Six of them are members of the U18 Romanian football team. The inclusion criteria were as follows: participation in the training program needed to be reflected by 90% training attendance during the eight weeks of study, and participants had to be active athletes, to be of the male gender and in good health, and to have a minimum of 6 years of sports experience.
2.3. Test Applied
The tests were divided into three categories: anthropometric tests (height, body weight and adipose tissue) performed in the medical office of the club; speed tests (10 m sprint; 20 m sprint) and agility tests (Illinois agility test; short dribbling test; and a multistage 20 m fitness test (beep test) performed on a synthetic-surface field. The analyzed parameters were the following: subjects’ age, stature (cm), body weight (kg), fat percentage (%), maximum oxygen consumption—VO2max (mL/kg/min)—with the multistage 20 m fitness test (beep test), 10 m and 20 m sprint times (s), agility without the ball in the Illinois test(s), and agility with the ball in the short dribbling Test(s), and among the experiment group they were total distance covered (TD), distance covered in high-speed running (HSR) (19.2–25.2 km/h) and distance covered in very-high-speed running (VHSR) > (25.2 km/h) during a 4vs.4+GK SSG. Both groups were tested under the same conditions, after a specific warm-up. No training was scheduled on the testing day. Anthropometric testing was performed with a Tanita Mc-780ma weight scale and speed and agility tests were conducted with a Microgate Witty Timing electronic timer. The 20 m fitness multistage test was performed with the app Beep Test (Enterprises) on an android device, the test starting at level 1 at a speed of 8.0 km/h, and with a 20 m lap distance. Player tracking during small-sided game training was recorded with the Polar Team pro GPS tracking system (© Polar Electro 2023, Singapore).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The statistical data analysis was performed in IBM SPSS Statistics 26. The statistical parameters analyzed were as follows: arithmetic mean (M), standard deviation (SD), coefficient of variability (CV), median, asymmetry coefficient “β” representing the difference between the mean and median, dependent Student “t” test, Cohen’s effect size (d)—method of estimating the extent to which a cause influences the effect (representing the standardized difference between averages), ω2 estimation of the importance of a cause (the independent variable) on the effect (effect is the difference between the experiment group and the control group in the final test, after the application of the independent variable), the independent Student “t” test and the correlation coefficient “r”—Pearson. ω2 estimation of the cause importance (independent variable), on the effects (differences between the means of the independent t final test) between the experimental group and the control group after the final tests was performed. For the interpretation of the asymmetry coefficient, β—±0.3 < β < ±0.5 indicated notable asymmetry; ±0.5 < β < ±3 indicated high asymmetry. For the interpretation of the effect size, >0.8 indicated that it was very large; 0.8–05 indicated that it was large; 05–0.3 indicated that it was medium; <0.2 indicated that it was small.
3. Results
3.1. VO2max
The data from the initial and final tests were analyzed statistically and a significance level of less than 5% was used as the criterion for statistical significance. Thus, we have in Table 1 the statistical analysis of the dependent “t” Student test for VO2max.

Table 1.
Statistical description of VO2max; experimental group and control group.
The maximum oxygen consumption (VO2max) analyzed shows that from the IT to FT, the experimental group had an increase in parameters of 10.34%, the difference between the averages values being statistically significant (p < 0.0005). The parameters present high homogeneity (CV = 7.87%, for the initial test; CV = 4.33% for the final test) and notable asymmetry. For the control group, the difference between the average values in the two tests (initial and final) being statistically insignificant (p > 0.05), the increase in maximum oxygen consumption was 0.30%; the values for the coefficient of variability show us good homogeneity and notable asymmetry (Table 1).
3.2. Tests of 10 m Sprint and 20 m Sprint
In Table 2, the results for the IT and FT for both samples in the 10 m sprint reflected good homogeneity and notable asymmetry. The increase in the 10 m sprint performance was 6.70%, which was statistically significant at p < 0.0005 for the experimental group, and 6.40%, which was statistically significant at p < 0.025 for the 20 m sprint. The performance for the control group in the 10 m sprint was improved by 4.52%, and was statistically significant (p < 0.0005), and in the 20 m sprint, the players improved their parameters by only 2.60%, which was statistically significant (p < 0.005). For both parameters and both groups, the values of CV% show high homogeneity and notable asymmetry.

Table 2.
Statistical descriptions of 10 m and 20 m sprint tests; experimental group and control group.
3.3. Agility Tests
Analysis of the results of the agility tests with and without the ball obtained by the players in the experimental group during the initial and final tests are remarkable. For the Illinois agility test at the IT the result was 15.72 ± 0.36 s. The values are homogeneous (CV = 2.27%) and the asymmetry is notable (β = −0.23). At the FT, the result was 15.04 ± 0.18 s and the level of asymmetry between homogenous values (CV = 1.18%) was good (β = −0.03). The difference between averages is statistically significant, with a 4.52% increase, (p < 0.0005). In the short dribbling test, the players of the experimental group had at the IT a result of 11.87 ± 0.47 s. The values are homogeneous (CV = 3.94%) and have notable asymmetry (β = 0.02). At the FT, the result was 11.30 ± 0.55 s, with homogeneous values (CV = 4.84%) and notable asymmetry (β = −0.10). The increase rate in the ball agility performance of the players from the experimental group was 5.05%, which was statistically significant (p < 0.0005). The players of the control group, in agility performance without the ball, had the result at the IT of 15.71 ± 0.41 s, with homogeneous values (CV = 2.59%) and notable asymmetry (−0.46), and at the FT the result was 15.67 ± 0.43 s; the values are homogeneous (CV = 2.75%) and have notable asymmetry (β = −0.32). The rate of increase in the ball-free agility performance of the control group players was 0.26%, which was statistically significant (p < 0.025) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Statistical description of the agility tests (Illinois agility test and short dribbling test) in the experiment and control group.
3.4. Tests of Total Distance, High-Speed Running and Very-High-Speed Running Recorded during a Small-Sided Game
Table 4 shows the physical parameters during 4vs.4+GK SSG training, with eight reps of 2′30″, the pitch size being 40 m wide by 32 m long, with two large (official) goals. The total distance covered in the eight bouts in the first training session, which was considered the IT, was 2201.65 ± 121.57 m, the values being homogeneous (CV = 5.52%) and having pronounced asymmetry (β = −118.00). The average total distance covered in the FT was 2373.15 ± 104.79 m, the values being homogeneous (CV = 4.42%) with notable asymmetry (β = 0.23). We can see an increase in the total distance covered by the experimental group of 7.78%, which is statistically significant (p < 0.0005). For HSR, the total distance covered in this speed range (19.2–25.2 km/h) during the first monitorized training session was 146.60 ± 29.33 m; here, the values are non-homogeneous (CV = 20.00%) and the asymmetry is notable (β = 0.21). In the last monitored training session, the distance travelled in the HSR range was 191.90 ± 37.14 m; the values are non-homogeneous (CV = 19.36%) and the asymmetry is notable β = −0.10). By analyzing the results, we note a statistically significant increase in the total distance covered in the VHSR speed range of 30.90% (p < 0.0005). During the first SSG training procedure, the subjects of the experimental group covered in the VHSR speed range a total distance of 4.25 ± 6.81 m; the values are not homogeneous (CV = 160.12%) and the asymmetry is pronounced (β = 0.63). During the last monitorized training they covered an average of 5.25 ± 5.96 m; these values are also non-homogeneous (CV = 113.60%) and have notable asymmetry (β = 0.46). Between the first monitored SSG training procedure and the last training procedure, there was an increase in the distance travelled at speeds above 25.2 km/h, but this was statistically insignificant (p > 0.05).

Table 4.
Statistical description of total distance, high-speed running (19.2–25.2 km/h) and very-high-speed running (>25.2 km/h) recorded during a small-sided game of 4 vs. 4 players, with 8 reps of 2′30″ and a field that was 40 m wide × 32 m long, in the experiment group.
3.5. Independent Comparative Statistical Analysis
The comparative analysis between the experimental group and the control group, after final tests, for the beep test, 20 m sprint, Illinois agility test and short dribbling test parameters shows statistically significant progress in favor of the experimental group (respectively: p < 0.0005, p < 0.025, p < 0.0005 and p < 0.005). We note for the 10 m sprint, that there was no difference between the average values of the two groups (p > 0.05) and an explanation for this could be, that over short distances which are characteristic of SSGs, players cannot develop high running speeds (Table 5).

Table 5.
Independent comparative statistical analysis of the results obtained in the initial and final tests; experiment and control group.
4. Discussion
The hypothesis of this research presumed that a 8-week training program that included a SSG twice a week, 4vs.4+GK would improve the VO2max level, and 10 m and 20 m sprint and agility with and without a ball, for U18 football players. Our findings showed that the SSG group has a greater improvement in aerobic fitness and agility than the conventional training group which further improves the speed indicators.
There is research in which it is shown that the level of the effort capacity of football players can be correlated with their physical performance during a match, including parameters such as total distance, accelerations, decelerations and total distance in high-speed running and very-high-speed running [36,37]. However, only few papers analyze the correlation between the physical condition of players and their physical and technical performance in SSGs. The findings of these studies are important for coaches because the “training load” of the training session should be designed individually to improve performance and avoid excess fatigue and overtraining.
In the research of Campos Rebelo et al. [38], they compared the physical requirements of two SSG formats: 4vs.4+GK (goalkeeper) and 8vs.8+GK. It has been shown that 4vs.4+GK is more demanding in relation to repetitions and fatigue, the development of actions being based on muscle strength having as a substrate the anaerobic energy path, the perceived effort and the number of technical actions, while during 8vs.8+GK games players run more at a high intensity. In addition, the performance of repeated jump tests appears to correlate with distances covered at high intensities in 4vs.4+GK games. It is therefore possible to use 4vs.4+GK games to develop the football skills of players. The results of our study on the influence of a 4vs.4+GK SGG on VO2max optimization align with the results of previous studies that aimed to optimize the functional capacity of soccer players by testing with SGGs and different training variations depending on the type of effort. For the players from the experimental group after implementing the 4vs.4+GK SGG twice a week, on Wednesday and Saturday, the VO2max values showed an increase of 10.34%, reaching 61.44 ± 2.66 mL/kg/min, with the increase being statistically significant (p < 0.0005). At the same time, the control group that followed a training program based on aerobic endurance interval training on Wednesday and a match on Saturday had an increase in the VO2max value with only a 0.30% progress rate being considered statistically unsignificant (p > 0.05). The results shows that elite junior football players are more motivated during SSGs to exert aerobic efforts under game-specific conditions, compared to when undergoing interval training. We believe this may be due to the fact that the effort and type of activity in SSGs is very close to that encountered during a match. This can motivate players to obtained a better experience, sensations and feelings, compared to those obtained via interval training [22,39]. It can be observed that after four weeks of training with SSGs, the VO2max level of elite junior soccer players increased from 55.6 ± 3.4 mL/kg/min initial testing to 59.7 ± 4.1 mL/kg/min during final testing.
The results of the 10 m sprint tests reveal that the experimental group’s performance increased significantly (6.70%) (p < 0.0005), and the control group’s performance also increased significantly (p < 0.0005), but at a slower rate (only 4.52%), compared to the experimental group. At the end of the exam, there was no significant difference between the two groups (p > 0.05). However, the difference between the two groups at the final test was small (p > 0.05) and the estimated cause importance to the effect was −0.8%. The last test for the 20 m sprint revealed significant differences between the two groups (p = 0.005), with the cause’s impact being 7.7%. Initially, the experimental group recorded lower values at certain parameters, compared to the control group. However, the players in the experimental group improved their sprint and VO2max performance, and in the final test they recorded higher values than did the control group. In our paper, we have shown that the two training methods (SSGs and traditional training) are equally effective in the physical training of junior football players, but the SSG method brings more technical–tactical advantages.
Our findings are consistent with those of previous research that examined the impact of small-sided games on improving physical fitness [40,41], technical–tactical skills [42,43,44], functional capacity [27,45,46], psychological and behavioral characteristics of players [47,48] and the monitoring of football performances [49,50].
Our findings correlate with those of previous research that examined the impact of small-sided games on improving physical fitness [40,41], technical–tactical skills [42,43,44]. functional capacity [27,45,46], psychological and behavioral characteristics of players [47,48] and the monitoring of football players’ performances [49,50].
For football players, the ability to quickly change direction depending on different stimuli (visual, kinesthetic or auditory) is often the difference between success and failure. Football, through its specific techniques, requires players to accelerate, decelerate or change direction quickly and instantly in response to game situations. which has shown that in most team sports, the ability to change quickly the direction with agility is more important than is the maximum sprint speed in a straight line [49]. For this reason, many coaches and athletes are interested in finding effective ways to improve agility and speed. In terms of agility without the ball, the differences between the two groups at the final tests were statistically significant, the experimental group having significantly better results. The impact of the experimental SSG program on agility without the ball was significant, having an increased effect on the ability to change direction and on agility with and without the ball. The results of our study highlight that the impact of SSGs in the experimental group was a significant increase in the total distance covered and the total distance covered in HSR by the EG players.
In terms of physical training, both methods are suitable for improving motor skills; however, the specifics of the game are included in SSGs. Thus, in addition to developing physical qualities, SSGs increase engagement, therefore influencing the relationship between players adapted to the demands of the game. This leads to the emergence of a learning environment via the stimulation of the ability to make decisions, according to the individual and collective behaviors inherent in the game, with possibilities of increasing exploratory behavior, which is fundamental for the development of creativity and thus ensures a transfer (adaptation, accommodation and understanding) of technical and tactical behaviors at the most contextually relevant level possible, i.e., in the game [51,52,53]. After 4 weeks of study, Impellizzeri et al. [12] determined that the training method using SSGs was as effective as was interval training at improving aerobic capacity in junior soccer players, especially in terms of aerobic power.
The results of our study on physical capacity contribute to the specialized literature based on previous studies. Bujalance-Moreno et al. [24], monitored external training load and physiological parameters, performing initial and final tests to assess physical capacities. They observed a statistically significant difference in the 20 m sprint between initial and final testing (+1.3%). In another study, Runacres et al. [34] found that the maximum oxygen consumption (VO2max) in the HIIT group was significantly higher than that in the control group. All groups showed a similar magnitude of change in performance during the three-month training period (p > 0.05). Thus, the authors concluded that HIIT is not superior to constant intensity endurance training (CIET) in improving aerobic or anaerobic parameters in adolescents. The research regarding the importance of SSG on the optimization of sports performance in sports games in general [54,55,56,57,58], and in football in particular, is numerous, as is made evident by their positive impact on psychological, physical, tactical and technical skills in the sports training process and in competitive games, for all age groups [59,60,61,62,63,64,65].
The importance of our research lies in the design conception and implementation of a specific training program with SGGs (4vs.4+GK) adapted to U18 footballers; the application period of the experimental training program was over 8 weeks with two training sessions per week. Several functional and proprioceptive parameters were tested. However, some limitations of the research should be pointed out, regarding the lack of data on the technical performance of the players, which could have contributed useful information regarding this training method.
5. Conclusions
The research’s results contributed to highlighting the positive impact that the implementation of an experimental training program had for U18 footballers with 4vs.4+GK SSGs; in the 1-2-1 system, twice a week for 8 weeks, during the preparatory period, it showed significant progress in the physical, functional and proprioceptive parameters. Comparatively analyzing the progress in EG and CG, between the initial and final testing, EG showed superior progress compared to that in CG, as a result of the implementation of the program of 4vs.4+GK SSGs. (i) VO2max caused a significant increase in EG between trials and greater progress compared to that in CG; (ii) 10 m and 20 m running speeds were increased statistically significantly, and the comparative analysis between groups shows that the differences between the averages are statistically insignificant at the 10 m distance, while only for the 20 m distance are they statistically significant; (iii) VHSR during SSGs was not influenced. The differences are insignificant, and the conclusion is that the pitch size did not allow players to reach speeds higher than 25.2 km/h and thus, this type of exercise is not suitable for maximum speed training; (iv) SSGs influenced agility with and without the ball, thus having a positive impact on the ability to change running directions both with and without the ball. Future research should focus on highlighting the relationships between the impact of SGGs on the physical and technical capacity of different categories of football players.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.Z., D.B., V.T., R.C., A.G., M.D., L.G., C.D., V.E.U., R.G.R., I.T.H., I.S. and C.T.; methodology, G.Z., D.B., V.T., R.C., A.G., M.D., L.G., C.D., V.E.U., R.G.R., I.T.H., I.S. and C.T.; validation, G.Z., D.B., V.T., R.C., A.G., M.D., L.G., C.D., V.E.U., R.G.R., I.T.H., I.S. and C.T.; formal analysis, G.Z., D.B., V.T., R.C., A.G., M.D., L.G., C.D., V.E.U., R.G.R., I.T.H., I.S. and C.T.; data curation, G.Z., D.B., V.T., R.C., A.G., M.D., L.G., C.D., V.E.U., R.G.R., I.T.H., I.S. and C.T.; writing—original draft preparation, G.Z., D.B., V.T., R.C., A.G., M.D., L.G., C.D., V.E.U., R.G.R., I.T.H., I.S. and C.T.; writing—review and editing, G.Z., D.B., V.T., R.C., A.G., M.D., L.G., C.D., V.E.U., R.G.R., I.T.H., I.S. and C.T.; visualization, G.Z., D.B., V.T., R.C., A.G., M.D., L.G., C.D., V.E.U., R.G.R., I.T.H., I.S. and C.T.; supervision, G.Z., D.B., V.T., R.C., A.G., M.D., L.G., C.D., V.E.U., R.G.R., I.T.H., I.S. and C.T. All authors contributed equally for this manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by funded by the Human Capital Operational Program 2014–2020 (POCU), Romania; the project “Proinvent”, contract no. 62487/03.06.2022—POCU/993/6/13—code 153299.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of the National University of Physical Education and Sports In Bucharest, Romania (2020/ID: 745).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Acknowledgments
The contributions of Gabriel Zaharia and Raluca Costache were supported by the project “Proinvent”, contract no. 62487/03.06.2022—POCU/993/6/13—code 153299, financed by the Human Capital Operational Programme 2014–2020 (POCU), Romania.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Edis, Ç.; Vural, F.; Vurgun, H. The Importance of Postural Control in Relation to Technical Abilities in Small-Sided Soccer Games. J. Hum. Kinet. 2016, 53, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire, L.A.; de Brito, M.A.; Esteves, N.S.; Tannure, M.; Slimani, M.; Znazen, H.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Brito, C.J.; Soto, D.A.S.; Gonçalves, D.; et al. Running Performance of High-Level Soccer Player Positions Induces Significant Muscle Damage and Fatigue Up to 24 h Postgame. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 708725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellal, A.; Varliette, C.; Owen, A.; Chirico, E.N.; Pialoux, V. Small-sided games versus interval training in amateur soccer players: Effects on the aerobic capacity and the ability to perform intermittent exercises with changes of direction. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 2712–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, A.; Roqueta, E.; Tarrago, J.R.; Seirullo, F.; Cos, F. Training in team sports: Coadjuvant training in the FCB. Apunts. Educ. Fis. Y Deporte 2019, 138, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, P.; Engel, F.A.; Holmberg, H.C.; Sperlich, B. A Meta-Comparison of the Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training to Those of Small-Sided Games and Other Training Protocols on Parameters Related to the Physiology and Performance of Youth Soccer Players. Sports Med. Open 2019, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massamba, A.; Dufour, S.P.; Favret, F.; Hureau, T.J. Small-Sided Games Are Not as Effective as Intermittent Running to Stimulate Aerobic Metabolism in Prepubertal Soccer Players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2021, 16, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rodenas, J.; Calabuig, F.; Aranda, R. Effect of the Game Design, the Goal Type and the Number of Players on Intensity of Play in Small-Sided Soccer Games in Youth Elite Players. J. Hum. Kinet. 2015, 49, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bompa, T.O.; Buzzichelli, C. Periodization: Theory and Methodology of Training; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pino-Ortega, J.; Oliva-Lozano, J.M.; Rico-González, M. Comparison of the validity and reliability of local positioning systems against other tracking technologies in team sport: A systematic review. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part P. J. Sports Eng. Technol. 2022, 236, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, K.; Araújo, D.; Correia, V.; Vilar, L. How small-sided and conditioned games enhance acquisition of movement and decision-making skills. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2013, 41, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, H.; Gouveia, É.R.; Marques, A.; Sarmento, H.; Pestana, M.; Quintal, T.; Lopes, H.; Ihle, A. The Influence of Small-Sided Football Games with Numerical Variability in External Training Load. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impellizzeri, F.M.; Marcora, S.M.; Castagna, C.; Reilly, T.; Sassi, A.; Iaia, F.M.; Rampinini, E. Physiological and performance effects of generic versus specific aerobic training in soccer players. Int. J. Sports Med. 2006, 27, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill-Haas, S.V.; Dawson, B.; Impellizzeri, F.M.; Coutts, A.J. Physiology of small-sided games training in football: A systematic review. Sports Med. 2011, 41, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köklü, Y.; Cihan, H.; Alemdaroğlu, U.; Dellal, A.; Wong, D.P. Acute effects of small-sided games combined with running drills on internal and external loads in young soccer players. Biol. Sport 2020, 37, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouertatani, Z.; Selmi, O.; Marsigliante, S.; Aydi, B.; Hammami, N.; Muscella, A. Comparison of the Physical, Physiological, and Psychological Responses of the High-Intensity Interval (HIIT) and Small-Sided Games (SSG) Training Programs in Young Elite Soccer Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olthof, S.B.H.; Frencken, W.G.P.; Lemmink, K.A. A Match-Derived Relative Pitch Area Facilitates the Tactical Representativeness of Small-Sided Games for the Official Soccer Match. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, S.; Jiménez, S.; Sampaio, J.; Leite, N. Effects of the Skills4Genius sports-based training program in creative behavior. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, G.; Da Costa, I.T. TacticUP Video Test for Soccer: Development and Validation. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellal, A.; Chamari, K.; Owen, A.L.; Wong, D.P. Influence of technical instructions on the physiological and physical demands of small-sided soccer games. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2011, 11, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellal, A.; da Silva, C.D.; Hill-Haas, S.; del Wong, P.; Natali, A.J.; De Lima, J.R.; Bara Filho, M.G.; Marins, J.J.; Garcia, E.S.; Chamari, K. Heart rate monitoring in soccer: Interest and limits during competitive match play and training, practical application. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 2890–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellal, A.; Hill-Haas, S.; Lago-Penas, C.; Chamari, K. Small-sided games in soccer: Amateur vs. professional players’ physiological responses, physical, and technical activities. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 2371–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köklü, Y.; Aşçi, A.; Koçak, F.U.; Alemdaroğlu, U.; Dündar, U. Comparison of the physiological responses to different small-sided games in elite young soccer players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 1522–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Dios-Álvarez, V.; Lorenzo-Martínez, M.; Padrón-Cabo, A.; Rey, E. Small-sided games in female soccer players: A systematic review. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2022, 62, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujalance-Moreno, P.; Latorre-Román, P.Á.; García-Pinillos, F. A systematic review on small-sided games in football players: Acute and chronic adaptations. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 921–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, F.M.; Sarmento, H. Combining small-sided soccer games and running-based methods: A systematic review. Biol. Sport 2021, 38, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, J.; Hofman, B.N.; Pasquarelli, B.N.; Leonardi, T.J. Proposals and effects of training using small-sided games for young soccer players: A narrative review. Motriz. Rev. De Educ. Física 2022, 28, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, F.M.; Silva, A.F.; Kawczyński, A.; Yıldız, M.; Chen, Y.S.; Birlik, S.; Nobari, H.; Akyildiz, Z. Physiological and locomotor demands during small-sided games are related to match demands and physical fitness? A study conducted on youth soccer players. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 14, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, F.M.; Soylu, Y.; Arslan, E.; Kilit, B.; Garrett, J.; van den Hoek, D.; Badicu, G.; Filipa Silva, A. Can high-intensity interval training and small-sided games be effective for improving physical fitness after detraining? A parallel study design in youth male soccer players. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguiar, M.V.; Botelho, G.M.; Gonçalves, B.S.; Sampaio, J.E. Physiological responses and activity profiles of football small-sided games. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Quintana, J.S.; Casamichana, D.; Castellano, J.; Calleja-González, J.; Jukić, I.; Ostojić, S.M. The influence of ball-touches number on physical. Kinesiology 2013, 45, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Nayıroğlu, S.; Yılmaz, A.K.; Silva, A.F.; Silva, R.; Nobari, H.; Clemente, F.M. Effects of small-sided games and running-based high-intensity interval training on body composition and physical fitness in under-19 female soccer players. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 14, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, E.; Orer, G.E.; Clemente, F.M. Running-based high-intensity interval training vs. small-sided game training programs: Effects on the physical performance, psychophysiological responses and technical skills in young soccer players. Biol. Sport 2020, 37, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faude, O.; Steffen, A.; Kellmann, M.; Meyer, T. The effect of short-term interval training during the competitive season on physical fitness and signs of fatigue: A crossover trial in high-level youth football players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runacres, A.; Mackintosh, K.A.; McNarry, M.A. The effect of constant-intensity endurance training and high-intensity interval training on aerobic and anaerobic parameters in youth. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 2492–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchheit, M.J.S.P.S.R. Managing high-speed running load in professional soccer players: The benefit of high-intensity interval training supplementation. Sport Perform. Sci. Rep. 2019, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Manzi, V.; Impellizzeri, F.; Castagna, C. Aerobic fitness ecological validity in elite soccer players: A metabolic power approach. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dello Iacono, A.; McLaren, S.J.; Macpherson, T.W.; Beato, M.; Weston, M.; Unnithan, V.B.; Shushan, T. Quantifying Exposure and Intra-Individual Reliability of High-Speed and Sprint Running During Sided-Games Training in Soccer Players: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2023, 53, 371–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos Rebelo, A.N.; Silva, P.; Rago, V.; Barreira, D.; Krustrup, P. Differences in strength and speed demands between 4v4 and 8v8 small-sided football games. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 34, 2246–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los Arcos, A.; Vázquez, J.S.; Martin, J.; Lerga, J.; Sánchez, F.; Villagra, F.; Zulueta, J.J. Effects of Small-Sided Games vs. Interval Training in Aerobic Fitness and Physical Enjoyment in Young Elite Soccer Players. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.F.; Oliveira, R.; Ceylan, H.I.; Akyildiz, Z.; González-Fernández, F.T.; Nobari, H.; Yıldız, M.; Birlik, S.; Clemente, F.M. Effects of a small-sided games training program in youth male soccer players: Variations of the locomotor profile while interacting with baseline level and with the accumulated load. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makar, P.; Praça, G.; Kawczyński, A.; Akyildiz, Z.; Yıldız, M.; Aquino, R.; Clemente, F.M. Testing the effects of 4-week training programs based on extreme and medium-sided soccer games: A study focusing on change-of-direction, vertical jump height and locomotor profile. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 14, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, F.M.; Praça, G.M.; Aquino, R.; Castillo, D.; Raya-González, J.; Rico-González, M.; Afonso, J.; Sarmento, H.; Silva, A.F.; Silva, R.; et al. Effects of pitch size on soccer players’ physiological, physical, technical, and tactical responses during small-sided games: A meta-analytical comparison. Biol. Sport 2023, 40, 111–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, F.M.; Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Sarmento, H.; Praça, G.M.; Afonso, J.; Silva, A.F.; Rosemann, T.; Knechtle, B. Effects of Small-Sided Game Interventions on the Technical Execution and Tactical Behaviors of Young and Youth Team Sports Players: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 667041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, C.H.; Hwang-Bo, K.; Jee, H. Technical and Physical Activities of Small-Sided Games in Young Korean Soccer Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 2164–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.F.; González-Fernández, F.T.; Aquino, R.; Akyildiz, Z.; Vieira, L.P.; Yıldız, M.; Birlik, S.; Nobari, H.; Praça, G.; Clemente, F.M. Analyzing the within and between Players Variability of Heart Rate and Locomotor Responses in Small-Sided Soccer Games Performed Repeatedly over a Week. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gantois, P.; Piqueras-Sanchiz, F.; Cid, M.J.F.A.; Pino-Ortega, J.; Castillo, D.; Nakamura, F.Y. The effects of different small-sided games configurations on heart rate, rating of perceived exertion, and running demands in professional soccer players. Eur. J. Sport. Sci. 2022, 8, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mara, J.K.; Thompson, K.G.; Pumpa, K.L. Physical and Physiological Characteristics of Various-Sided Games in Elite Women’s Soccer. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2016, 11, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trecroci, A.; Boccolini, G.; Duca, M.; Formenti, D.; Alberti, G. Mental fatigue impairs physical activity, technical and decision-making performance during small-sided games. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, C.; Akenhead, R.; Thomas, K. Time-motion analysis of acceleration demands of 4v4 small-sided soccer games played on different pitch sizes. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2014, 33, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparkes, W.; Turner, A.; Weston, M.; Russell, M.; Johnston, M.; Kilduff, L. Neuromuscular, Biochemical, Endocrine, and Mood Responses to Small-Sided Games’ Training in Professional Soccer. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 2569–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ric, A.; Hristovski, R.; Gonçalves, B.; Torres, L.; Sampaio, J.; Torrents, C. Timescales for exploratory tactical behaviour in football small-sided games. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 34, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, R.; Gonçalves, B.; Coutinho, D.; Oliveira, R.; Travassos, B.; Sampaio, J.; Marques, M.C. Effects of Knowing the Task’s Duration on Soccer Players’ Positioning and Pacing Behaviour during Small-Sided Games. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, J.; Travassos, B.; Gonçalves, B.; Mourão, P.; Viana, J.L.; Sampaio, J. Exploring the Effects of Playing Formations on Tactical Behavior and External Workload During Football Small-Sided Games. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 2024–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muntianu, V.-A.; Abalașei, B.-A.; Nichifor, F.; Dumitru, I.-M. The Correlation between Psychological Characteristics and Psychomotor Abilities of Junior Handball Players. Children 2022, 9, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusa, F.S.; Badau, A.; Badau, D.; Trambitas, C.; Brinzaniuc, K. Investigating the deformation parameters of PVC fitness balls in relation to the height and body mass index of the users. Mater. Plast. 2017, 54, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantau, C.; Nae, C.; Hantau, C.; Neagu, N. Formation Strategy for the Young Handball Players. Procedia Social. Behav. Sci. 2013, 93, 1936–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hantau, C.; Hatzimanouil, D.; Giannakos, A. The Impact of Dynamic Games on the Coordination Development. Marathon 2015, 7, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Gherghel, A.; Badau, D.; Badau, A.; Moraru, L.; Manolache, G.M.; Oancea, B.M.; Tifrea, C.; Tudor, V.; Costache, R.M. Optimizing the Explosive Force of the Elite Level Football-Tennis Players through Plyometric and Specific Exercises. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, A.L.; Newton, M.; Shovlin, A.; Malone, S. The Use of Small-Sided Games as an Aerobic Fitness Assessment Supplement Within Elite Level Professional Soccer. J. Hum. Kinet. 2020, 71, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riboli, A.; Esposito, F.; Coratella, G. Small-Sided Games in Elite Football: Practical Solutions to Replicate the 4-min Match-Derived Maximal Intensities. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2023, 37, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryanoosh, F.; Alishavandi, H.; Nemati, J.; Basereh, A.; Jowhari, A.; Asad-Manesh, E.; Oliveira, R.; Brito, J.P.; Prieto-González, P.; García-Calvo, T.; et al. Effect of interval and continuous small-sided games training on the bio-motor abilities of young soccer players: A comparative study. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čaušević, D.; Rani, B.; Gasibat, Q.; Čović, N.; Alexe, C.I.; Pavel, S.I.; Burchel, L.O.; Alexe, D.I. Maturity-Related Variations in Morphology, Body Composition, and Somatotype Features among Young Male Football Players. Children 2023, 10, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albina, A.M.; Buga, A.A.M.; Ion, L.; Burchel, L.O. How introducing isoinertial exercises using a flywheel can improve the training of athletes: A systematic review. Bull. Transilv. Univ. Braşov Ser. IX Sci. Hum. Kinet. 2023, 16, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riboli, A.; Dellal, A.; Esposito, F.; Coratella, G. Can small-sided games assess the training-induced aerobic adaptations in elite football players? J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2022, 62, 1313–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalen, T.; Sandmæl, S.; Stevens, T.G.A.; Hjelde, G.H.; Kjøsnes, T.N.; Wisløff, U. Differences in Acceleration and High-Intensity Activities Between Small-Sided Games and Peak Periods of Official Matches in Elite Soccer Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2021, 35, 2018–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).