Accurate Tracking Algorithm for Cluster Targets in Multispectral Infrared Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Fully Convolutional Neural Networks (FCNs)
- (1)
- The full connection layer is replaced with a convolution layer to achieve end-to-end convolution network training.
- (2)
- To achieve pixel-level segmentation, all pixel features in the image are classified by prediction. However, for an image with a complicated visual environment, the FCN network still adopts the simplest deconvolution method, which results in blurred contours and serious adhesion of the segmented image.
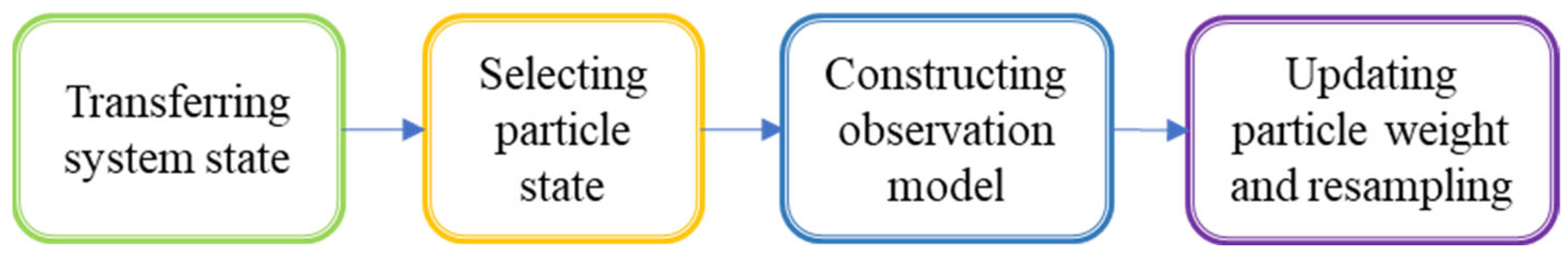
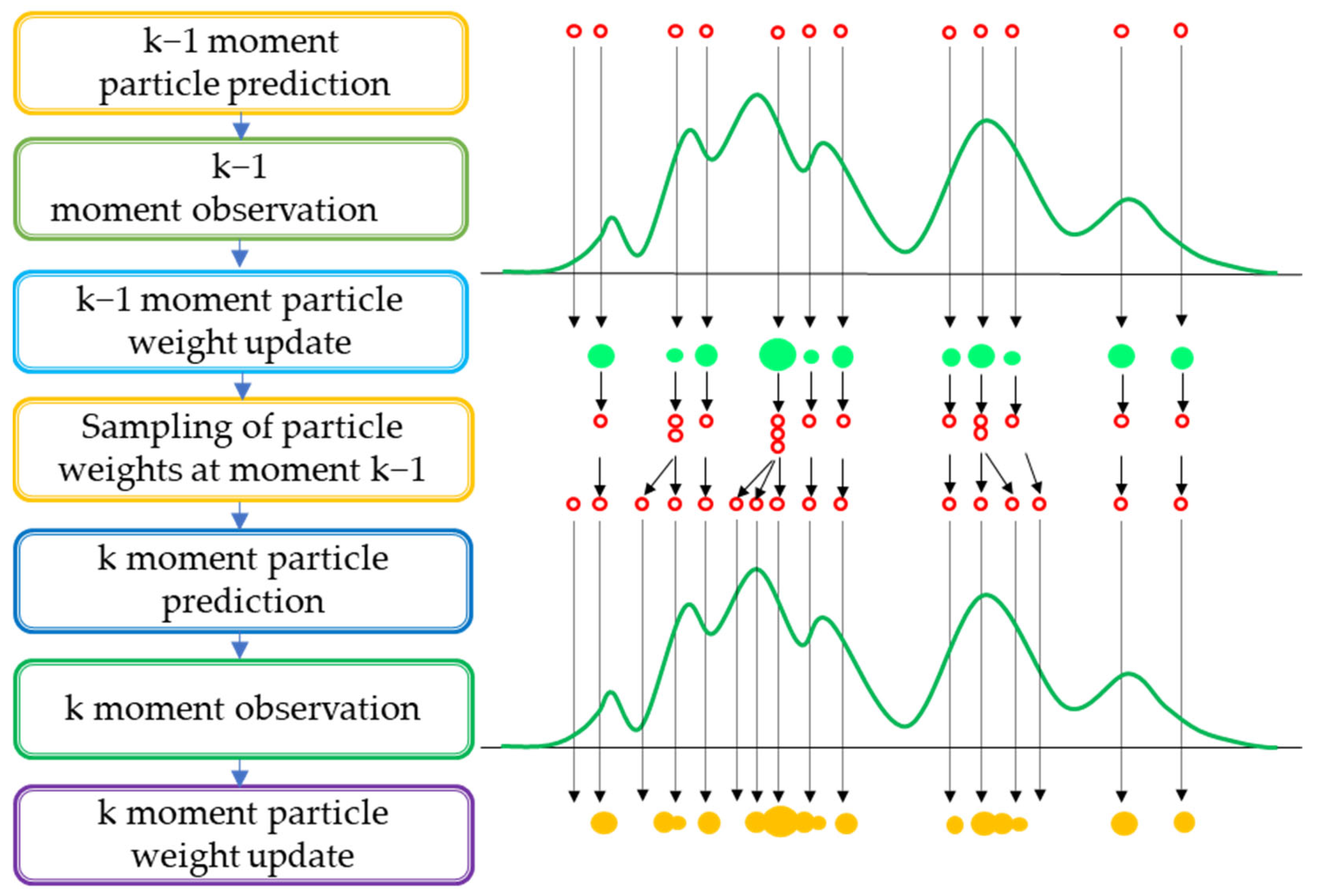
2.2. Particle Filter
2.3. Thermal Radiation Analysis
3. Methods
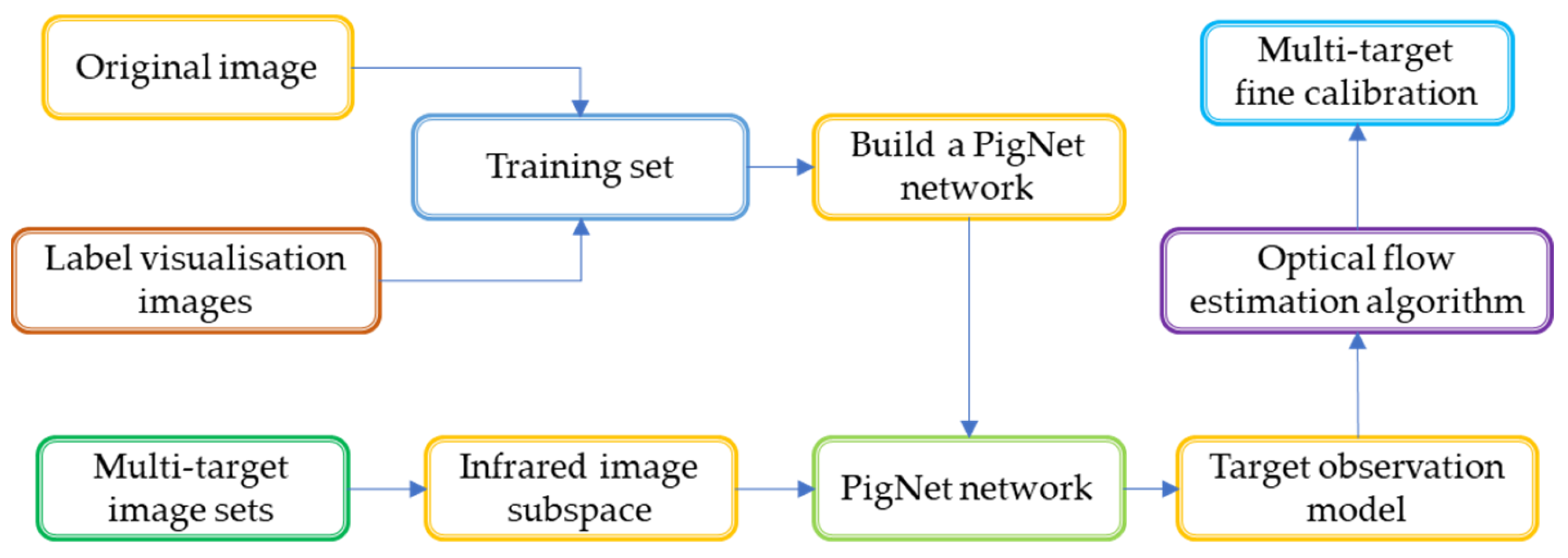
3.1. Establishment of an Infrared Image Subspace
3.2. Local Segmentation of Double-Threshold Images
- (1)
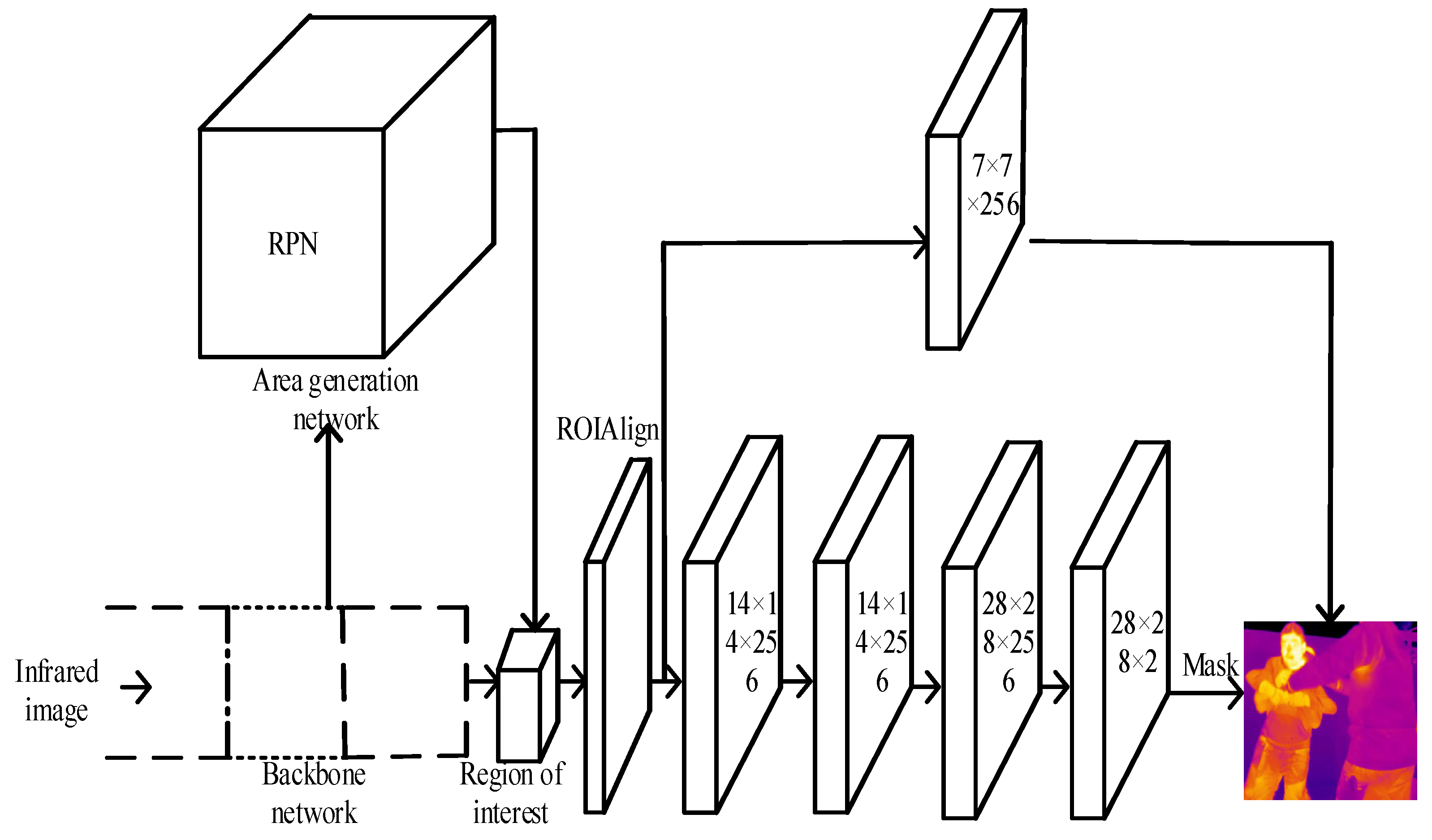
- For different target regions in the image, the Mask R-CNN network is changed from 69 convolution layers to 12 layers in the fourth stage, which can reduce the level of feature loss and the amount of convolution computation.
- (2)
- The number of classes in the last convolution layer of the mask branch of the Mask R-CNN network is optimized and adjusted to the PigNet class and background class. The structure is shown in Figure 1.
3.3. Construction of the Target Observation Model
3.4. Target Analysis and Tracking of Infrared Dim and Small Images Based on the Optical Flow Estimation Model
4. Experimental Procedure
4.1. Experimental Equipment and Environment
4.2. Experimental Materials
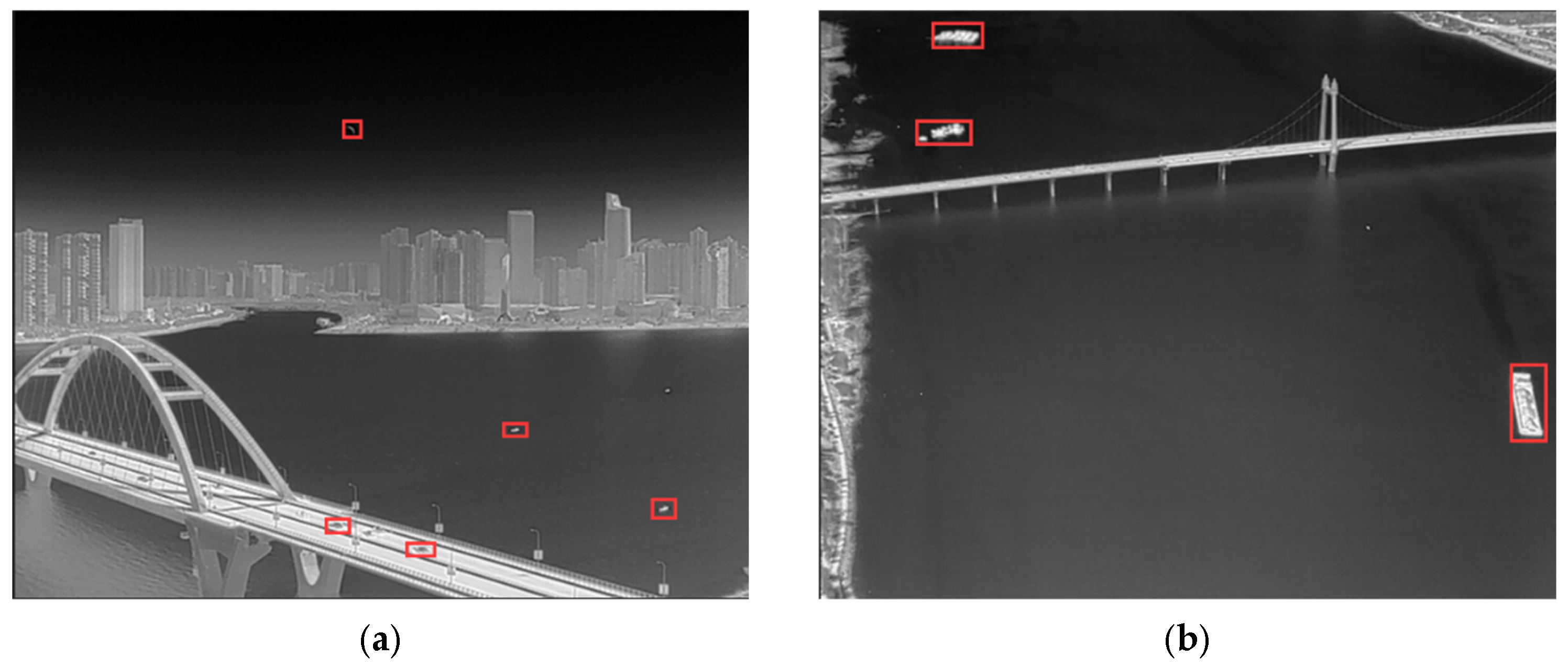
4.3. Analysis of the Experimental Results
4.4. Comparison to State-of-the-Art Methods
4.5. Performance Evaluation Indicators
4.6. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Komagata, H.; Kakinuma, E.; Ishikawa, M.; Shinoda, K.; Kobayashi, N. Semi-Automatic Calibration Method for a Bed-Monitoring System Using Infrared Image Depth Sensors. Sensors 2019, 19, 4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, R.; Li, S. Residual Depth Feature-Extraction Network for Infrared Small-Target Detection. Electronics 2023, 12, 2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liang, C. A Survey on One-Shot Multi-Object Tracking Algorithm. J. Univ. Electron. Sci. Technol. China 2022, 51, 736. [Google Scholar]
- Yousefi, B.; Ibarra-Castanedo, C.; Chamberland, M.; Maldague, X.P.V.; Beaudoin, G. Unsupervised Identification of Targeted Spectra Applying Rank1-NMF and FCC Algorithms in Long-Wave Hyperspectral Infrared Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jin, B.; Zhou, X.; Fu, J.; Wang, X.Y.; Guo, Z.Q.; Niu, Y. Correlation filter target tracking algorithm based on feature fusion and adaptive model updating. CAAI Trans. Intell. Syst. 2020, 15, 714–721. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.L.; Zhang, L.X.; Xiao, M.S.; Zuo, G.C. Target tracking by deep fusion of fast multi-domain convolutional neural network and optical flow method. Comput. Eng. Sci. 2020, 42, 2217–2222. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.W.; Xu, C.X.; Liu, Y. Kernelized correlation filter for target tracking with multi-feature fusion. Comput. Eng. Des. 2019, 40, 3463–3468. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yun, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, S. Adaptive Strategy Fusion Target Tracking Based on Multi-layer Convolutional Features. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2019, 41, 2464–2470. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Fang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.; Xie, Y.; Song, H. Improved RT-MDNet for panoramic video target tracking. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2020, 52, 152–160+174. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Pang, Y.; Han, J.; Mou, E.; Cao, E. An Infrared Small Target Detection Method Based on a Weighted Human Visual Comparison Mechanism for Safety Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, S.S.; Singh, S.; Alotaibi, Y.; Alghamdi, S.; Kumar, G. Infrared Target-Background Separation Based on Weighted Nuclear Norm Minimization and Robust Principal Component Analysis. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Ding, Y.D. Color Transfer Algorithm between Images Based on a Two-Stage Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors 2022, 22, 7779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Rubio, V.; Rodrigo Ferran, J.A.; Menendez Garcia, J.M.; Sanchez Almodovar, N.; Lalueza Mayordomo, J.M.; Álvarez, F. Automatic Change Detection System over Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Video Sequences Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. Sensors 2019, 19, 4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.R.; Cong, B.; Zhang, H.P. Multi-objective Cross-sectional Projection Image Feature Segmentation Based on Visual Dictionary. Comput. Simul. 2020, 37, 347–351. [Google Scholar]
- Balakrishnan, H.N.; Kathpalia, A.; Saha, S.; Nagaraj, N. A Chaos-based Artificial Neural Network Architecture for Classification. Chaos 2019, 29, 113125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaranageswarao, G.; Deivalakshmi, S.; Ko, S.B. Residual learning based densely connected deep dilated network for joint deblocking and super resolution. Appl. Intell. 2020, 50, 2177–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, R.; Garcés, Y.; Torres, E.; Sossa, H.; Tovar, R. A vision from a physical point of view and the information theory on the image segmentation. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 37, 2835–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.; Wang, X.; Meng, F.; Zhu, J.; Wang, D.; Dai, J. Improved Faster R-CNN Traffic Sign Detection Based on a Second Region of Interest and Highly Possible Regions Proposal Network. Sensors 2019, 19, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abarca, M.; Sanchez, G.; Garcia, L.; Avalos, J.G.; Frias, T.; Toscano, K.; Perez-Meana, H. A Scalable Neuromorphic Architecture to Efficiently Compute Spatial Image Filtering of High Image Resolution and Size. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2019, 18, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, S.; Kaushik, P. Gradient nuclear norm minimization-based image filter. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2019, 33, 1950214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Du, J.; Zhang, Z. Testing linearity in partial functional linear quantile regression model based on regression rank scores. J. Korean Stat. Soc. 2021, 50, 214–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hait, E.; Gilboa, G. Spectral Total-Variation Local Scale Signatures for Image Manipulation and Fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 880–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.Y.; Li, S.H. Multi-Object Tracking Algorithm Based on AttentionEnhancementand Feature Selection. J. Shenyang Ligong Univ. 2022, 41, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Ma, X.H. Anti-Occlusion Infrared Target Tracking Algorithm Based on Fusion of Discriminant and Fine-Grained Features. Infrared Technol. 2022, 44, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.J.; Song, X.N. Dual-Stream Object TrackingAlgorithm Based on Vision Transformer. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2022, 58, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P.; Chen, B.; Liu, B.; Qi, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, L. Object Dctection for Hazardous Material Vehicles Based on Improved YOLOv5 Algorithm. Electronics 2023, 12, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Yang, S. Infrared small object tracking based on Att-Siam network. IEEE Access 2022, 12, 133766–133777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisi, F.; Amato, E. Characterization of Volcanic Cloud Components Using Machine Learning Techniques and SEVIRI Infrared Images. Sensors 2022, 22, 7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, S.A.; Cowen, E.A. Instantaneous River-Wide Water Surface Velocity Field Measurements at Centimeter Scales Using Infrared Quantitative Image Velocimetry. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, 1266–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Su, S.; Wu, P.; Guo, R.; Wei, J.; Zuo, Z.; Sun, B. MSAFFNet: A Multiscale Label-Supervised Attention Feature Fusion Network for Infrared Small Target Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Tang, J.; Fu, X.; Geng, Y.; Su, J. Detection of infrared small target based on background subtraction local contrast measure and Gaussian structural similarity. Heliyon 2023, 7, e16998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Configuration Types | Specific Configuration | Configuration Data |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware | CPU | Intel (R) Core (TM) i7-8565U |
| Frequency | 1.8 GHz | |
| RAM | 40 G | |
| Software | Operating system | Win 10 |
| Development tools | 2020 vs. platform | |
| Cameras | Operating bands | 8~14 μm |
| Pixel resolution | 640 × 512 | |
| Pixel spacing | 17 μm | |
| NETD | ≤60 mK@25 °C, F#1.0 (8) | |
| Frame rate | 50 Hz | |
| Focal length | 20 mm | |
| Field of view | 30° | |
| Spatial resolution | 0.6 mrad |
| Configuration | Set-Up |
|---|---|
| Coding class | High class |
| Image fine-tracking size | 4 CIF, CIF |
| Encoding bandwidth (k) | 2048, 1024, 768, 384 |
| Coding format | 8 MPEG |
| Reference code | XVID V2.1 reference software |
| Encoding specific bit rate | 2048 |
| Encoding specific frame rate | 36 frames per second |
| Configuration | Set-Up |
|---|---|
| Color space configuration | HSV space |
| Component configuration | H component |
| Quantitative processing series | 64 |
| Kernel function | Epanachnekov |
| Algorithm | MOTA | IDF1 | ML | MT | IDs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ours | 79.7 | 77.5 | 25.4% | 51.6% | 1876 | 42.3 |
| CenterTrack | 66.7 | 63.7 | 25.5% | 34.7% | 3042 | 22.7 |
| CSTrack | 65.4 | 66.5 | 25.1% | 33.1% | 2998 | 20.6 |
| MOT | 75.4 | 73.2 | 19.2% | 49.2% | 2082 | 30.4 |
| SiamFC | 77.1 | 74.8 | 25.1% | 49.8% | 3845 | 38.5 |
| MDNef | 63.4 | 61.7 | 18.4% | 37.1% | 2978 | 30.7 |
| TrSiam | 70.2 | 72.4 | 19.7% | 42.5% | 3058 | 28.5 |
| TrDiMP | 76.3 | 71.9 | 21.3% | 36.7% | 3176 | 25.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Zou, Z.; Li, Y.; Shi, H.; Fu, Q. Accurate Tracking Algorithm for Cluster Targets in Multispectral Infrared Images. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7931. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137931
Yang S, Zou Z, Li Y, Shi H, Fu Q. Accurate Tracking Algorithm for Cluster Targets in Multispectral Infrared Images. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(13):7931. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137931
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shuai, Zhihui Zou, Yingchao Li, Haodong Shi, and Qiang Fu. 2023. "Accurate Tracking Algorithm for Cluster Targets in Multispectral Infrared Images" Applied Sciences 13, no. 13: 7931. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137931
APA StyleYang, S., Zou, Z., Li, Y., Shi, H., & Fu, Q. (2023). Accurate Tracking Algorithm for Cluster Targets in Multispectral Infrared Images. Applied Sciences, 13(13), 7931. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137931






