DIVA Meets EEG: Model Validation Using Formant-Shift Reflex
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
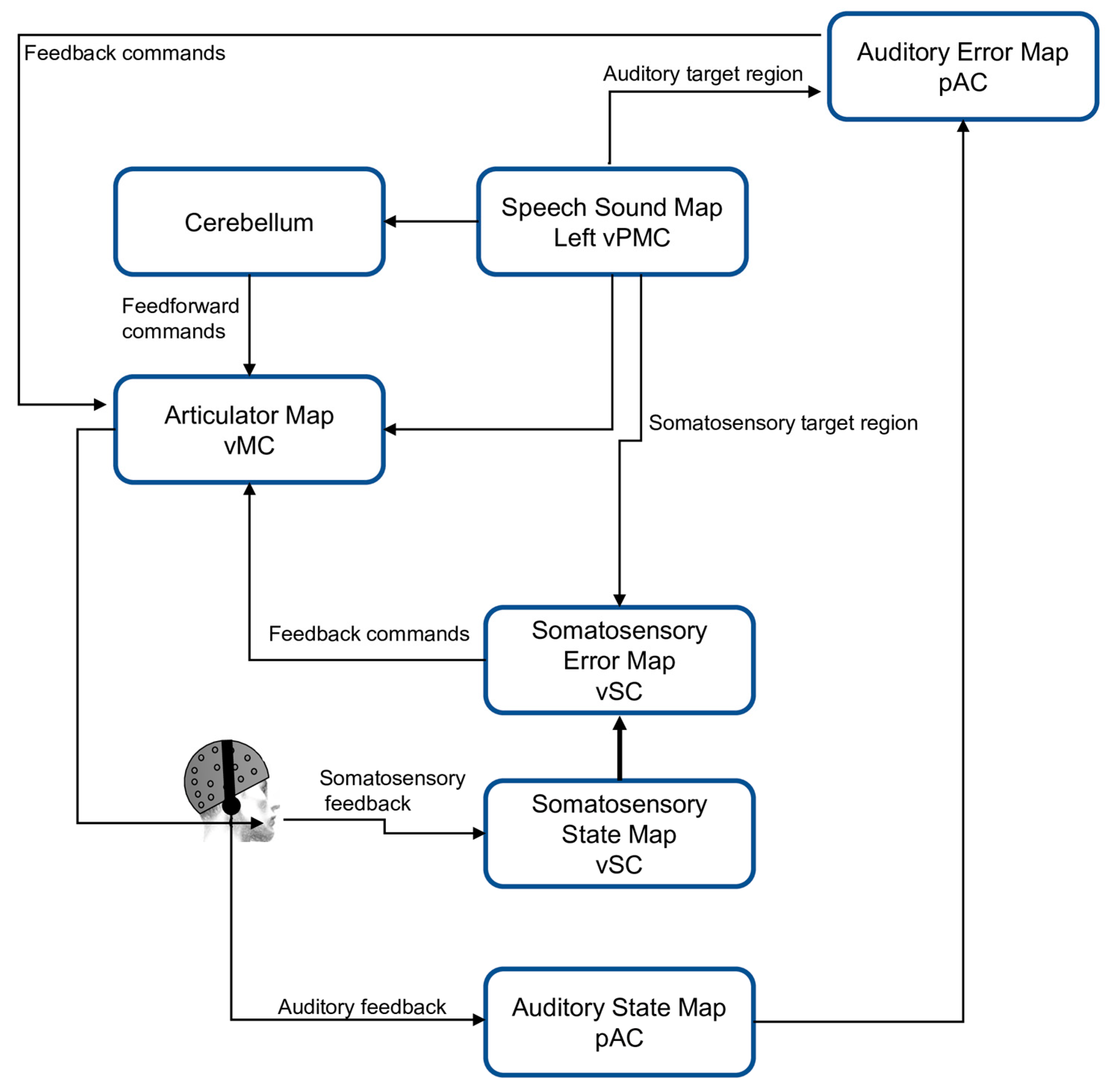
1.1. DIVA Model
1.2. Electroencephalography (EEG)
2. Materials and Methods
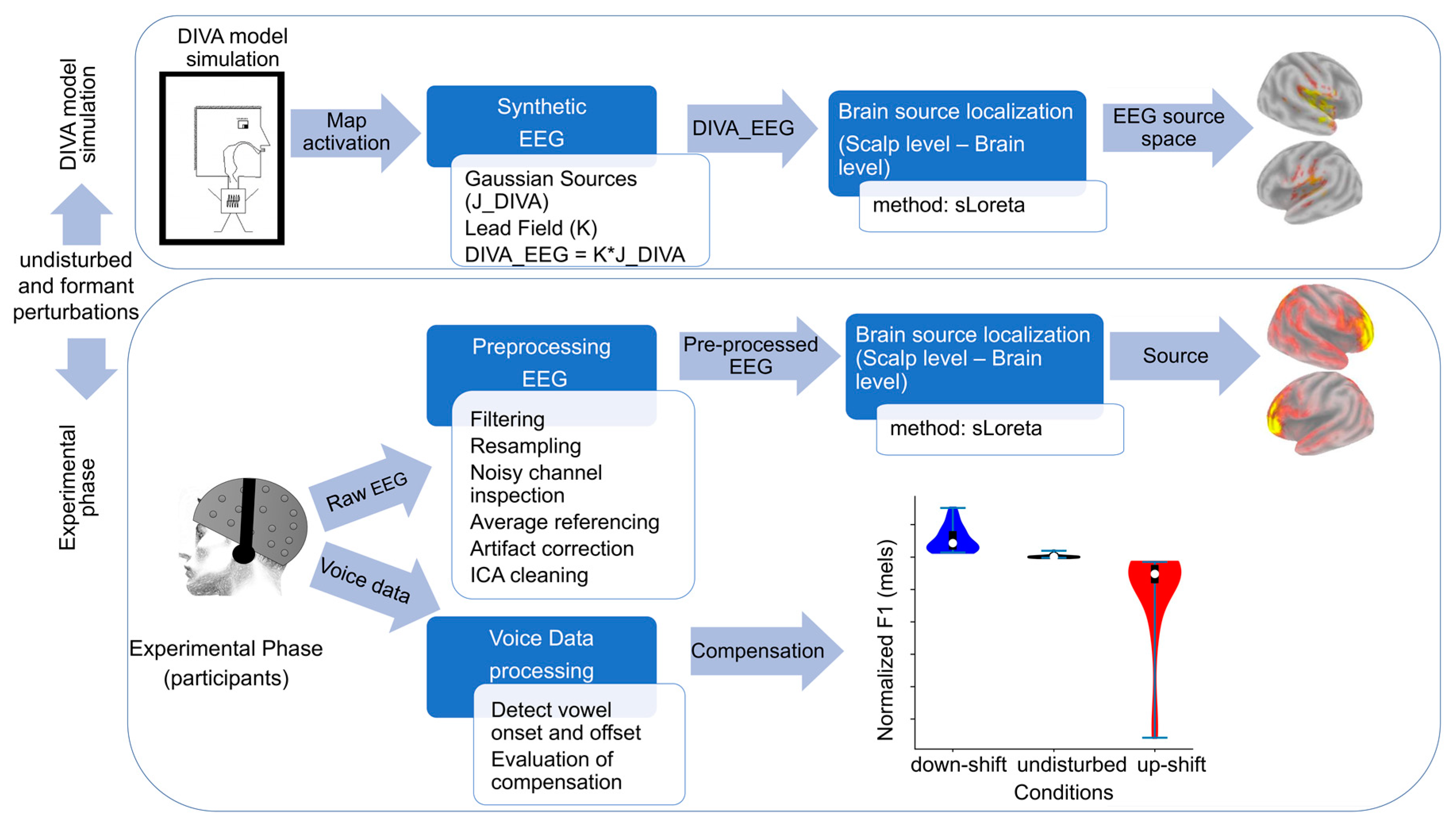
2.1. DIVA Model Simulation
2.1.1. Simulated Speech
2.1.2. Generation and Source Localization of Synthetic EEG
2.2. Experimental Phase
2.2.1. Participants
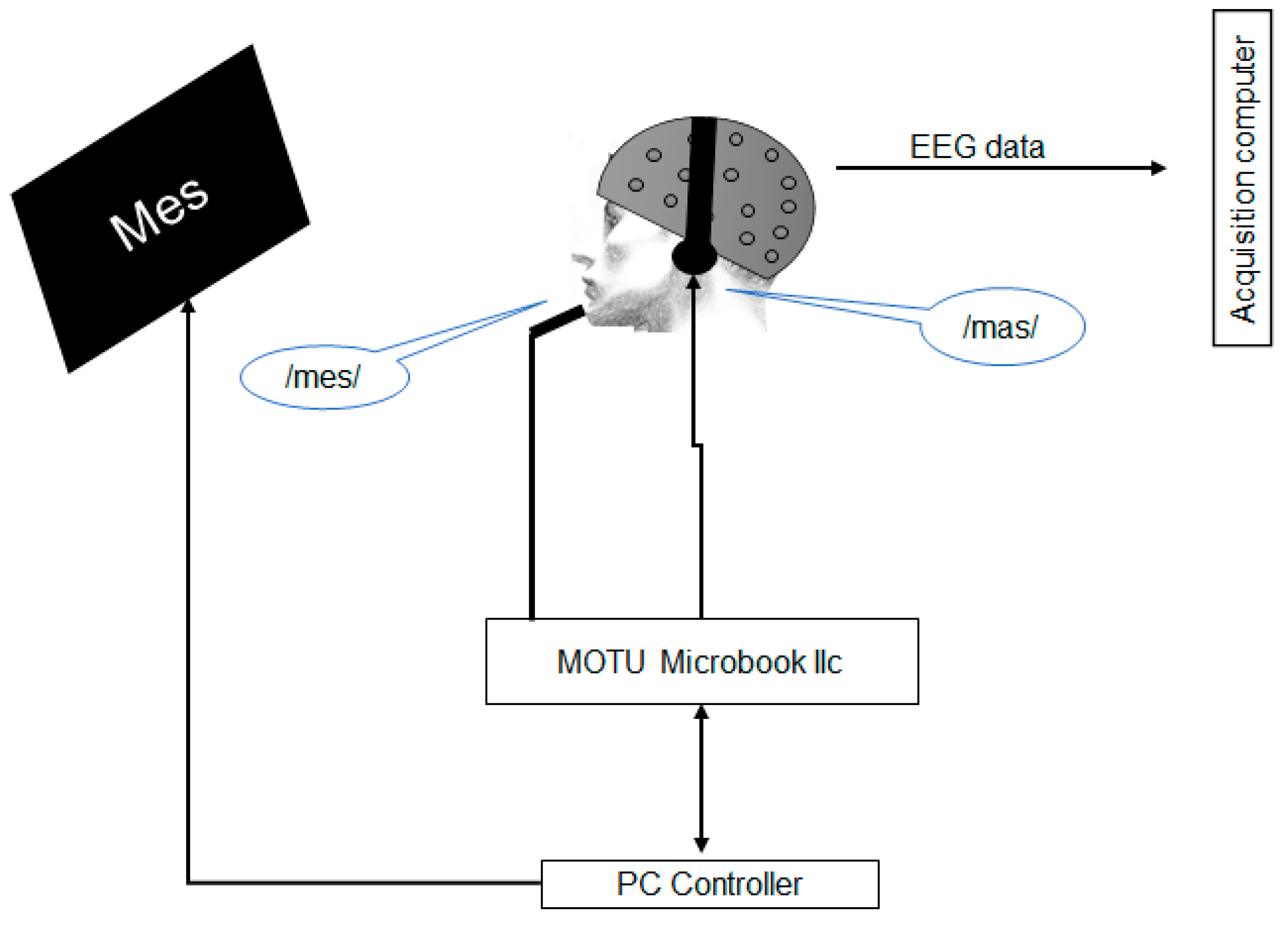
2.2.2. Experimental Setup
2.2.3. Feedback Perturbation
2.2.4. Processing of Acoustic Signals
2.2.5. EEG Acquisition and Analysis
2.2.6. ERP Source Localization
2.2.7. Match between DIVA Related (Simulated) and ERP (Real) Cortical Activation Maps
3. Results
3.1. DIVA Model Simulation
3.2. Behavioral and Physiological Data
3.3. Match between DIVA Simulations and Real EEG
4. Discussion
4.1. DIVA_EEG
4.2. Vocal Compensations
4.3. ERP Elicited by Perturbations
4.4. EEG Source Localization
4.5. Comparing Simulated and Experimentally Acquired Brain Cortical Map for Speech Motor Control
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scheerer, N.E.; Jones, J.A. The Predictability of Frequency-Altered Auditory Feedback Changes the Weighting of Feedback and Feedforward Input for Speech Motor Control. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014, 40, 3793–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrell, B.; Lammert, A.C.; Ciccarelli, G.; Quatieri, T.F. Current Models of Speech Motor Control: A Control-Theoretic Overview of Architectures and Properties. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 145, 1456–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guenther, F.H. Neural Control of Speech; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-0-262-33698-7. [Google Scholar]
- Aaron, A.S.; Abur, D.; Volk, K.P.; Noordzij, J.P.; Tracy, L.F.; Stepp, C.E. The Relationship Between Pitch Discrimination and Fundamental Frequency Variation: Effects of Singing Status and Vocal Hyperfunction. J. Voice 2023, S0892199723000103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abur, D.; Subaciute, A.; Kapsner-Smith, M.; Segina, R.K.; Tracy, L.F.; Noordzij, J.P.; Stepp, C.E. Impaired Auditory Discrimination and Auditory-Motor Integration in Hyperfunctional Voice Disorders. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Max, L.; Guenther, F.H.; Gracco, V.L.; Ghosh, S.S.; Wallace, M.E. Unstable or Insufficiently Activated Internal Models and Feedback-Biased Motor Control as Sources of Dysfluency: A Theoretical Model of Stuttering. Contemp. Issues Commun. Sci. Disord. 2004, 31, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Civier, O.; Bullock, D.; Max, L.; Guenther, F.H. Computational Modeling of Stuttering Caused by Impairments in a Basal Ganglia Thalamo-Cortical Circuit Involved in Syllable Selection and Initiation. Brain Lang. 2013, 126, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vojtech, J.M.; Stepp, C.E. Effects of Age and Parkinson’s Disease on the Relationship between Vocal Fold Abductory Kinematics and Relative Fundamental Frequency. J. Voice 2022, S0892199722000704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abur, D.; Subaciute, A.; Daliri, A.; Lester-Smith, R.A.; Lupiani, A.A.; Cilento, D.; Enos, N.M.; Weerathunge, H.R.; Tardif, M.C.; Stepp, C.E. Feedback and Feedforward Auditory-Motor Processes for Voice and Articulation in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2021, 64, 4682–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speech Production and Perception: Learning and Memory; Fuchs, S.; Cleland, J.; Rochet-Capellan, A. (Eds.) Peter Lang D: New York, NY, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-3631726914. [Google Scholar]
- Parrell, B.; Agnew, Z.; Nagarajan, S.; Houde, J.; Ivry, R.B. Impaired Feedforward Control and Enhanced Feedback Control of Speech in Patients with Cerebellar Degeneration. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 9249–9258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, S.; Beal, D.S.; Ghosh, S.S.; Guenther, F.H.; Perkell, J.S. Impaired Timing Adjustments in Response to Time-Varying Auditory Perturbation during Connected Speech Production in Persons Who Stutter. Brain Lang. 2014, 129, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, S.; Beal, D.S.; Ghosh, S.S.; Tiede, M.K.; Guenther, F.H.; Perkell, J.S. Weak Responses to Auditory Feedback Perturbation during Articulation in Persons Who Stutter: Evidence for Abnormal Auditory-Motor Transformation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, S.; Ghosh, S.S.; Guenther, F.H.; Perkell, J.S. Focal Manipulations of Formant Trajectories Reveal a Role of Auditory Feedback in the Online Control of Both Within-Syllable and Between-Syllable Speech Timing. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 16483–16490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niziolek, C.A.; Guenther, F.H. Vowel Category Boundaries Enhance Cortical and Behavioral Responses to Speech Feedback Alterations. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 12090–12098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Purcell, D.W.; Munhall, K.G. Compensation Following Real-Time Manipulation of Formants in Isolated Vowels. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 119, 2288–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reilly, K.J.; Dougherty, K.E. The Role of Vowel Perceptual Cues in Compensatory Responses to Perturbations of Speech Auditory Feedback. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tourville, J.A.; Reilly, K.J.; Guenther, F.H. Neural Mechanisms Underlying Auditory Feedback Control of Speech. NeuroImage 2008, 39, 1429–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daliri, A.; Chao, S.-C.; Fitzgerald, L.C. Compensatory Responses to Formant Perturbations Proportionally Decrease as Perturbations Increase. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2020, 63, 3392–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franken, M.K.; Acheson, D.J.; McQueen, J.M.; Hagoort, P.; Eisner, F. Consistency Influences Altered Auditory Feedback Processing. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 2019, 72, 2371–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kearney, E.; Guenther, F.H. Articulating: The Neural Mechanisms of Speech Production. Lang. Cogn. Neurosci. 2019, 34, 1214–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourville, J.A.; Guenther, F.H. The DIVA Model: A Neural Theory of Speech Acquisition and Production. Lang. Cogn. Process. 2011, 26, 952–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, H.; Denny, M.; Guenther, F.H.; Hanson, H.M.; Marrone, N.; Matthies, M.L.; Perkell, J.S.; Stockmann, E.; Tiede, M.; Vick, J.; et al. On the Structure of Phoneme Categories in Listeners With Cochlear Implants. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2007, 50, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, E.; Nieto-Castañón, A.; Falsini, R.; Daliri, A.; Heller Murray, E.S.; Smith, D.J.; Guenther, F.H. Quantitatively Characterizing Reflexive Responses to Pitch Perturbations. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 929687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.; Prado, P.; Espinoza, V.M.; Testart, A.; Marfull, D.; Manriquez, R.; Stepp, C.E.; Mehta, D.D.; Hillman, R.E.; Zañartu, M. Lombard Effect in Individuals With Nonphonotraumatic Vocal Hyperfunction: Impact on Acoustic, Aerodynamic, and Vocal Fold Vibratory Parameters. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2022, 65, 2881–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkell, J.S.; Denny, M.; Lane, H.; Guenther, F.; Matthies, M.L.; Tiede, M.; Vick, J.; Zandipour, M.; Burton, E. Effects of Masking Noise on Vowel and Sibilant Contrasts in Normal-Hearing Speakers and Postlingually Deafened Cochlear Implant Users. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 121, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frankford, S.A.; Heller Murray, E.S.; Masapollo, M.; Cai, S.; Tourville, J.A.; Nieto-Castañón, A.; Guenther, F.H. The Neural Circuitry Underlying the “Rhythm Effect” in Stuttering. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2020, 64, 2325–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkell, J.S.; Guenther, F.H.; Lane, H.; Matthies, M.L.; Perrier, P.; Vick, J.; Wilhelms-Tricarico, R.; Zandipour, M. A Theory of Speech Motor Control and Supporting Data from Speakers with Normal Hearing and with Profound Hearing Loss. J. Phon. 2000, 28, 233–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tourville, J.T.; Cai, S.; Guenther, H. Frank Exploring Auditory-Motor Interactions in Normal and Disordered Speech. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarate, J.M. Neural Substrates Governing Audiovocal Integration for Vocal Pitch Regulation in Singing. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1060, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyomura, A.; Koyama, S.; Miyamaoto, T.; Terao, A.; Omori, T.; Murohashi, H.; Kuriki, S. Neural Correlates of Auditory Feedback Control in Human. Neuroscience 2007, 146, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaso, H.; Eisner, F.; Wise, R.J.; Scott, S.K. The Effect of Delayed Auditory Feedback on Activity in the Temporal Lobe While Speaking: A Positron Emission Tomography Study. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. JSLHR 2010, 53, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.H.Y.; Vythelingum, G.N.; Brammer, M.J.; Williams, S.C.R.; Amaro, E.; Andrew, C.M.; Yágüez, L.; Van Haren, N.E.M.; Matsumoto, K.; McGuire, P.K. An FMRI Study of Verbal Self-Monitoring: Neural Correlates of Auditory Verbal Feedback. Cereb. Cortex 2006, 16, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinks-Maldonado, T.H.; Nagarajan, S.S.; Houde, J.F. Magnetoencephalographic Evidence for a Precise Forward Model in Speech Production. NeuroReport 2006, 17, 1375–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niziolek, C.A.; Nagarajan, S.S.; Houde, J.F. What Does Motor Efference Copy Represent? Evidence from Speech Production. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 16110–16116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golfinopoulos, E.; Tourville, J.A.; Bohland, J.W.; Ghosh, S.S.; Nieto-Castanon, A.; Guenther, F.H. FMRI Investigation of Unexpected Somatosensory Feedback Perturbation during Speech. NeuroImage 2011, 55, 1324–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goriely, A.; Kuhl, E.; Bick, C. Neuronal Oscillations on Evolving Networks: Dynamics, Damage, Degradation, Decline, Dementia, and Death. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 128102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, P.M.; Di Iorio, R.; Vecchio, F.; Anfossi, M.; Babiloni, C.; Bozzali, M.; Bruni, A.C.; Cappa, S.F.; Escudero, J.; Fraga, F.J.; et al. Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease: The Role of Biomarkers Including Advanced EEG Signal Analysis. Report from the IFCN-Sponsored Panel of Experts. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 1287–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Hebert, K.; Korzyukov, O.; Larson, C.R. Effects of Sensorimotor Voice Training on Event-Related Potentials to Pitch-Shifted Auditory Feedback. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0269326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, E.Q.; Larson, C.R.; Huang, D.; Liu, H. ERP Correlates of Language-Specific Processing of Auditory Pitch Feedback during Self-Vocalization. Brain Lang. 2012, 121, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzyukov, O.; Karvelis, L.; Behroozmand, R.; Larson, C.R. ERP Correlates of Auditory Processing during Automatic Correction of Unexpected Perturbations in Voice Auditory Feedback. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2012, 83, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niedermeyer’s Electroencephalography; Schomer, D.L.; Lopes da Silva, F.H. (Eds.) Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; Volume 1, ISBN 978-0-19-022848-4. [Google Scholar]
- Blenkmann, A. Localización de Fuentes de Actividad Cerebral. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Nacional de La Plata, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sörnmo, L.; Laguna, P. Bioelectrical Signal Processing in Cardiac and Neurological Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; ISBN 978-0-12-437552-9. [Google Scholar]
- Grave de Peralta, R.; González Andino, S.; Gómez González, C.M. Bases biofísicas de la localización de los generadores cerebrales del electroencefalograma. Aplicación de un modelo de tipo distribuido a la localización de focos epilépticos. Rev. Neurol. 2004, 39, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Qin, J.; Wang, S.; Rosenberger, J.; Su, J. Supervised EEG Source Imaging with Graph Regularization in Transformed Domain. In Brain Informatics; Zeng, Y., He, Y., Kotaleski, J.H., Martone, M., Xu, B., Peng, H., Luo, Q., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 10654, pp. 59–71. ISBN 978-3-319-70771-6. [Google Scholar]
- Sanei, S.; Chambers, J.A. EEG Signal Processing: Sanei/EEG Signal Processing; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 2007; ISBN 978-0-470-51192-3. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, S.; Thakor, N.V. Quantitative EEG Analysis Methods and Clinical Applications; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-1-59693-205-0. [Google Scholar]
- Hallez, H.; Vanrumste, B.; Grech, R.; Muscat, J.; De Clercq, W.; Vergult, A.; D’Asseler, Y.; Camilleri, K.P.; Fabri, S.G.; Van Huffel, S.; et al. Review on Solving the Forward Problem in EEG Source Analysis. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2007, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Marqui, R.D. Standardized Low-Resolution Brain Electromagnetic Tomography (SLORETA): Technical Details. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 24, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Grech, R.; Cassar, T.; Muscat, J.; Camilleri, K.P.; Fabri, S.G.; Zervakis, M.; Xanthopoulos, P.; Sakkalis, V.; Vanrumste, B. Review on Solving the Inverse Problem in EEG Source Analysis. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2008, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalinowski, J.; Stuart, A.; Sark, S.; Armson, J. Stuttering Amelioration at Various Auditory Feedback Delays and Speech Rates. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 1996, 31, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Boucek, M.M.; Ghosh, S.S.; Guenther, F.H.; Perkell, J.S. A System for Online Dynamic Perturbation of Formant Trajectories and Results from Perturbations of the Mandarin Triphthong /Iau/. In Proceedings of the 8th International Seminar on Speech Production, Strasbourg, France, 8–12 December 2008; pp. 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Chaumon, M.; Bishop, D.V.M.; Busch, N.A. A Practical Guide to the Selection of Independent Components of the Electroencephalogram for Artifact Correction. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 250, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formant-Analyzer 2023. Available online: https://github.com/fulldecent/formant-analyzer (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Niziolek, C.A.; Parrell, B. Responses to Auditory Feedback Manipulations in Speech May Be Affected by Previous Exposure to Auditory Errors. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2021, 64, 2169–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliri, A. A Computational Model for Estimating the Speech Motor System’s Sensitivity to Auditory Prediction Errors. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2021, 64, 1841–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.L.; Neelin, P.; Peters, T.M.; Evans, A.C. Automatic 3D Intersubject Registration of MR Volumetric Data in Standardized Talairach Space. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1994, 18, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.C.; Collins, D.L.; Mills, S.R.; Brown, E.D.; Kelly, R.L.; Peters, T.M. 3D Statistical Neuroanatomical Models from 305 MRI Volumes. In Proceedings of the 1993 IEEE Conference Record Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 30 October–6 November 1993; IEEE: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 1813–1817. [Google Scholar]
- Rolls, E.T.; Joliot, M.; Tzourio-Mazoyer, N. Implementation of a New Parcellation of the Orbitofrontal Cortex in the Automated Anatomical Labeling Atlas. NeuroImage 2015, 122, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Marqui, R.D.; Michel, C.M.; Lehmann, D. Low Resolution Electromagnetic Tomography: A New Method for Localizing Electrical Activity in the Brain. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 1994, 18, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, T.E.; Holmes, A.P. Nonparametric Permutation Tests for Functional Neuroimaging: A Primer with Examples. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2002, 15, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weerathunge, H.R.; Alzamendi, G.A.; Cler, G.J.; Guenther, F.H.; Stepp, C.E.; Zañartu, M. LaDIVA: A Neurocomputational Model Providing Laryngeal Motor Control for Speech Acquisition and Production. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1010159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, E.; Nieto-Castañón, A.; Weerathunge, H.R.; Falsini, R.; Daliri, A.; Abur, D.; Ballard, K.J.; Chang, S.-E.; Chao, S.-C.; Heller Murray, E.S.; et al. A Simple 3-Parameter Model for Examining Adaptation in Speech and Voice Production. Front. Psychol. 2020, 10, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinahan, S.P.; Liss, J.M.; Berisha, V. TorchDIVA: An Extensible Computational Model of Speech Production Built on an Open-Source Machine Learning Library. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohland, J.W.; Bullock, D.; Guenther, F.H. Neural Representations and Mechanisms for the Performance of Simple Speech Sequences. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2010, 22, 1504–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Hernández, P.A.; von Ellenrieder, N.; Ojeda-Gonzalez, A.; Kochen, S.; Alemán-Gómez, Y.; Muravchik, C.; Valdés-Sosa, P.A. Approximate Average Head Models for EEG Source Imaging. J. Neurosci. Methods 2009, 185, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegaran, E.; Bosse, S.; Kohler, P.J.; Norcia, A.M. EEGSourceSim: A Framework for Realistic Simulation of EEG Scalp Data Using MRI-Based Forward Models and Biologically Plausible Signals and Noise. J. Neurosci. Methods 2019, 328, 108377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.E.; Bénar, C.G.; Quilichini, P.P.; Friston, K.J.; Jirsa, V.K.; Bernard, C. A Systematic Framework for Functional Connectivity Measures. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, P.; Birba, A.; Cruzat, J.; Santamaría-García, H.; Parra, M.; Moguilner, S.; Tagliazucchi, E.; Ibáñez, A. Dementia ConnEEGtome: Towards Multicentric Harmonization of EEG Connectivity in Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2022, 172, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, M.; Lea-Carnall, C.; Prado, P.; Escobar, M.-J.; El-Deredy, W. Modelling Neural Entrainment and Its Persistence: Influence of Frequency of Stimulation and Phase at the Stimulus Offset. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2022, 8, 045014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyafil, A.; Fontolan, L.; Kabdebon, C.; Gutkin, B.; Giraud, A.-L. Speech Encoding by Coupled Cortical Theta and Gamma Oscillations. eLife 2015, 4, e06213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.D.; Niziolek, C.A.; Duñabeitia, J.A.; Perez, A.; Hernandez, D.; Carreiras, M.; Houde, J.F. Online Adaptation to Altered Auditory Feedback Is Predicted by Auditory Acuity and Not by Domain-General Executive Control Resources. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Ghosh, S.S.; Guenther, F.H.; Perkell, J.S. Adaptive Auditory Feedback Control of the Production of Formant Trajectories in the Mandarin Triphthong /Iau/ and Its Pattern of Generalization. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 2033–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, H.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, P.; Chen, S.; Liu, H. Attention Modulates Cortical Processing of Pitch Feedback Errors in Voice Control. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behroozmand, R.; Sangtian, S.; Korzyukov, O.; Larson, C.R. A Temporal Predictive Code for Voice Motor Control: Evidence from ERP and Behavioral Responses to Pitch-Shifted Auditory Feedback. Brain Res. 2016, 1636, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Liu, P.; Huang, D.; Liu, H. Effect of Temporal Predictability on the Neural Processing of Self-Triggered Auditory Stimulation during Vocalization. BMC Neurosci. 2012, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larson, C.R.; Burnett, T.A.; Kiran, S.; Hain, T.C. Effects of Pitch-Shift Velocity on Voice F0 Responses. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2000, 107, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Larson, C.R. Effects of Perturbation Magnitude and Voice F0 Level on the Pitch-Shift Reflex. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 122, 3671–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.J.; Stepp, C.; Guenther, F.H.; Kearney, E. Contributions of Auditory and Somatosensory Feedback to Vocal Motor Control. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2020, 63, 2039–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyomura, A.; Miyashiro, D.; Kuriki, S.; Sowman, P.F. Speech-Induced Suppression for Delayed Auditory Feedback in Adults Who Do and Do Not Stutter. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behroozmand, R.; Larson, C.R. Error-Dependent Modulation of Speech-Induced Auditory Suppression for Pitch-Shifted Voice Feedback. BMC Neurosci. 2011, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behroozmand, R.; Oya, H.; Nourski, K.V.; Kawasaki, H.; Larson, C.R.; Brugge, J.F.; Howard, M.A.; Greenlee, J.D.W. Neural Correlates of Vocal Production and Motor Control in Human Heschl’s Gyrus. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 2302–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butler, B.E.; Trainor, L.J. Sequencing the Cortical Processing of Pitch-Evoking Stimuli Using EEG Analysis and Source Estimation. Front. Psychol. 2012, 3, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Mathalon, D.H.; Roach, B.J.; Reilly, J.; Keedy, S.K.; Sweeney, J.A.; Ford, J.M. Action Planning and Predictive Coding When Speaking. NeuroImage 2014, 91, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behroozmand, R.; Shebek, R.; Hansen, D.R.; Oya, H.; Robin, D.A.; Howard, M.A.; Greenlee, J.D.W. Sensory–Motor Networks Involved in Speech Production and Motor Control: An FMRI Study. NeuroImage 2015, 109, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parkinson, A.L.; Flagmeier, S.G.; Manes, J.L.; Larson, C.R.; Rogers, B.; Robin, D.A. Understanding the Neural Mechanisms Involved in Sensory Control of Voice Production. NeuroImage 2012, 61, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guenther, F.H.; Ghosh, S.S.; Tourville, J.A. Neural Modeling and Imaging of the Cortical Interactions Underlying Syllable Production. Brain Lang. 2006, 96, 280–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houde, J.F.; Nagarajan, S.S. Speech Production as State Feedback Control. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houde, J.F.; Chang, E.F. The Cortical Computations Underlying Feedback Control in Vocal Production. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2015, 33, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ford, J.M.; Gray, M.; Faustman, W.O.; Roach, B.J.; Mathalon, D.H. Dissecting Corollary Discharge Dysfunction in Schizophrenia. Psychophysiology 2007, 44, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendixen, A.; SanMiguel, I.; Schröger, E. Early Electrophysiological Indicators for Predictive Processing in Audition: A Review. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2012, 83, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Meshman, M.; Behroozmand, R.; Larson, C.R. Differential Effects of Perturbation Direction and Magnitude on the Neural Processing of Voice Pitch Feedback. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 122, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korzyukov, O.; Sattler, L.; Behroozmand, R.; Larson, C.R. Neuronal Mechanisms of Voice Control Are Affected by Implicit Expectancy of Externally Triggered Perturbations in Auditory Feedback. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behroozmand, R.; Sangtian, S. Neural Bases of Sensorimotor Adaptation in the Vocal Motor System. Exp. Brain Res. 2018, 236, 1881–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Chen, M.; Chen, X.; Guo, Z.; Li, T.; Jones, J.A.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Liu, P.; Liu, H.; et al. A Causal Link between Left Supplementary Motor Area and Auditory-Motor Control of Vocal Production: Evidence by Continuous Theta Burst Stimulation. NeuroImage 2022, 264, 119767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shum, M.; Shiller, D.M.; Baum, S.R.; Gracco, V.L. Sensorimotor Integration for Speech Motor Learning Involves the Inferior Parietal Cortex: Speech Motor Adaptation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 1817–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venezia, J.H.; Richards, V.M.; Hickok, G. Speech-Driven Spectrotemporal Receptive Fields Beyond the Auditory Cortex. Hear. Res. 2021, 408, 108307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeriani, D.; Simonyan, K. The Dynamic Connectome of Speech Control. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 376, 20200256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallgatter, A.J.; Bartsch, A.J.; Zielasek, J.; Herrmann, M.J. Brain Electrical Dysfunction of the Anterior Cingulate in Schizophrenic Patients. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2003, 124, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, G.E.; Peterson, S.D.; Erath, B.D.; Castro, C.; Hillman, R.E.; Zañartu, M. Modeling the Pathophysiology of Phonotraumatic Vocal Hyperfunction With a Triangular Glottal Model of the Vocal Folds. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2017, 60, 2452–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manriquez, R.; Peterson, S.D.; Prado, P.; Orio, P.; Galindo, G.E.; Zañartu, M. Neurophysiological Muscle Activation Scheme for Controlling Vocal Fold Models. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado-Gutierrez, P.; Martínez-Montes, E.; Weinstein, A.; Zañartu, M. Estimation of Auditory Steady-State Responses Based on the Averaging of Independent EEG Epochs. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0206018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prado-Gutierrez, P.; Castro-Fariñas, A.; Morgado-Rodriguez, L.; Velarde-Reyes, E.; Martínez, A.D.; Martínez-Montes, E. Habituation of Auditory Steady State Responses Evoked by Amplitudemodulated Acoustic Signals in Rats. Audiol. Res. 2015, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Brain Lobe | AAL Region | Hemisphere |
|---|---|---|
| Frontal | Precentral | (bilateral) |
| Frontal_Inf_Oper | (right) | |
| Rolandic_Oper | (bilateral) | |
| Limbic | Insula | (bilateral) |
| Cingulum_Mid | (bilateral) | |
| Cingulum_Post | (right) | |
| Hippocampus | (left) | |
| ParaHippocampal | (bilateral) | |
| Temporal | Heschl | (bilateral) |
| Temporal_Sup | (bilateral) | |
| Temporal_Pole_Sup | (bilateral) | |
| Temporal_Mid | (bilateral) | |
| Temporal_Pole_Mid | (left) | |
| Parietal | Postcentral | (bilateral) |
| Parietal_Sup | (bilateral) | |
| Parietal_Inf | (right) | |
| SupraMarginal | (bilateral) | |
| Paracentral | (right) | |
| Occipital | Lingual | (bilateral) |
| Fusiform | (bilateral) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cuadros, J.; Z-Rivera, L.; Castro, C.; Whitaker, G.; Otero, M.; Weinstein, A.; Martínez-Montes, E.; Prado, P.; Zañartu, M. DIVA Meets EEG: Model Validation Using Formant-Shift Reflex. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7512. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137512
Cuadros J, Z-Rivera L, Castro C, Whitaker G, Otero M, Weinstein A, Martínez-Montes E, Prado P, Zañartu M. DIVA Meets EEG: Model Validation Using Formant-Shift Reflex. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(13):7512. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137512
Chicago/Turabian StyleCuadros, Jhosmary, Lucía Z-Rivera, Christian Castro, Grace Whitaker, Mónica Otero, Alejandro Weinstein, Eduardo Martínez-Montes, Pavel Prado, and Matías Zañartu. 2023. "DIVA Meets EEG: Model Validation Using Formant-Shift Reflex" Applied Sciences 13, no. 13: 7512. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137512
APA StyleCuadros, J., Z-Rivera, L., Castro, C., Whitaker, G., Otero, M., Weinstein, A., Martínez-Montes, E., Prado, P., & Zañartu, M. (2023). DIVA Meets EEG: Model Validation Using Formant-Shift Reflex. Applied Sciences, 13(13), 7512. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137512








