Gaming Tree Based Evaluation Model for Badminton Tactic Benefit Analysis and Prediction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
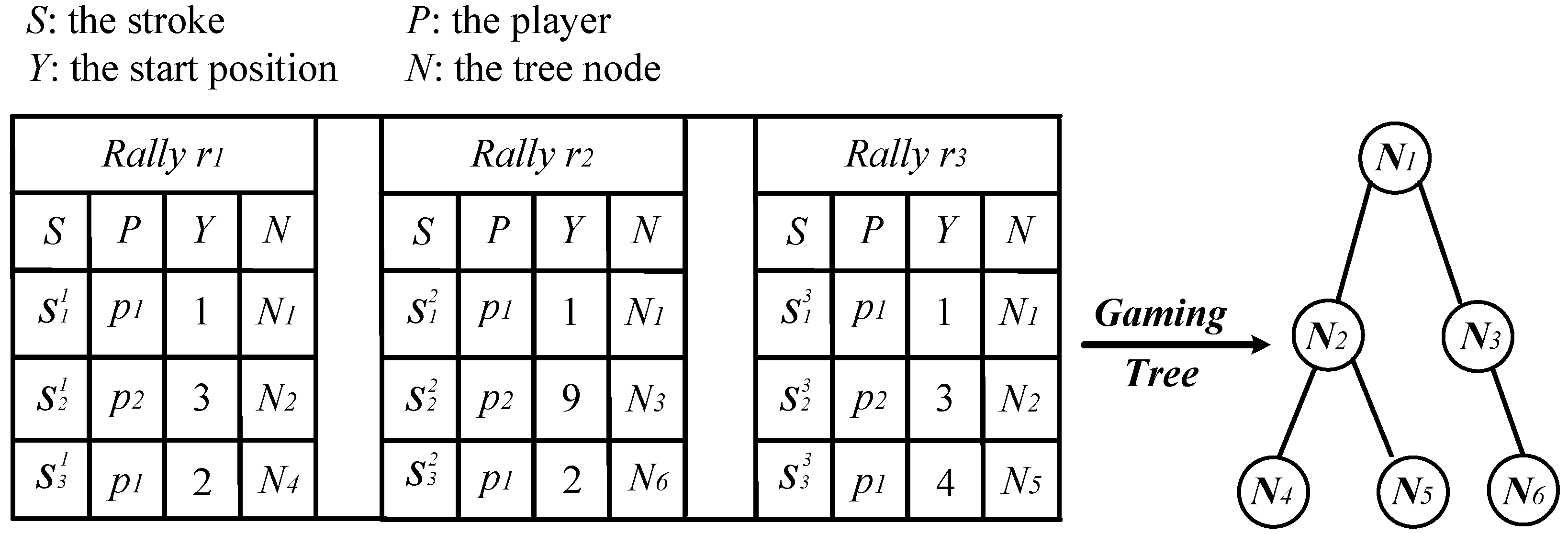
2.2. Observation Indices and Tactical Combination
- Stroke technique: Serve, including short serve and long serve; Smash, an aggressive overhead shot with a downward trajectory; Clear, an overhead shot with a flat or rising trajectory towards the back of the opponent’s court; Drop, is a smooth shot from above the head with a downward trajectory towards the front of the court; Net shot, denoting a precise shot from near the net, including the net drop, lob and kill; Drive, a powerful shot made at middle body height and in the middle of the court with a flat trajectory;
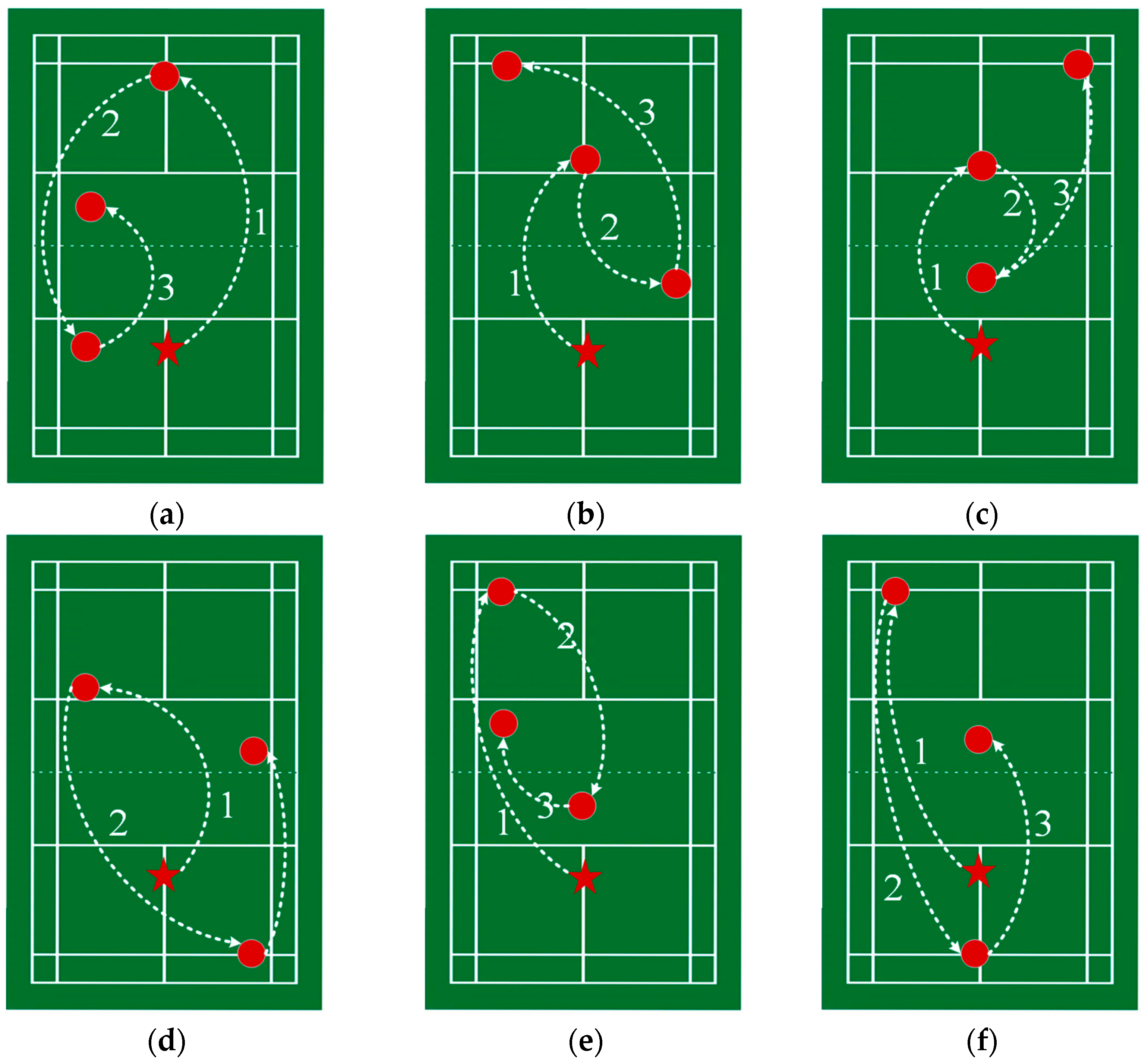
- Stroke placement: the start position and the target placement of each stroke. In this paper, the badminton court is evenly divided into 9 (3 × 3) grids, i.e., the combination of vertically three parts (front court, middle court, and back court) and horizontally three parts (left court, middle court, and right court);
- The rally results: scoring and losing.
- In fact, the speed of each stroke also contributes to the tactics. However, as the speed (including smash speed, clear shoot speed, etc.) of high-level players are almost the same (especially for Lin and Lee), the influence of the stroke speed for the rally results is not considered in this paper.
2.3. Tactical Frequency and Scoring Rate Algorithm
2.4. Evaluation Model of Tactical Benefit
2.4.1. Tactical Benefit
2.4.2. Evaluation Model
3. Results
3.1. Basic Data
3.2. General Analysis
3.3. Analysis for Different Periods
3.4. Prediction Using Top-k Benefits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lees, A. Science and the major racket sports: A review. J. Sports Sci. 2003, 21, 707–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phomsoupha, M.; Laffaye, G. The science of badminton: Game characteristics, anthropometry, physiology, visual fitness and biomechanics. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 473–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G. Technology and badminton. Br. J. Sports Med. 2010, 44, i51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabello, M.D.; González-Badillo, J.J. Analysis of the characteristics of competitive badminton. Br. J. Sports Med. 2003, 37, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonoda, T.; Tashiro, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Kajiwara, Y.; Zeidan, H.; Yokota, Y.; Aoyama, T. Relationship between agility and lower limb muscle strength, targeting university badminton players. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2018, 30, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, I.; Ramamurthy, S.R.; Chakma, A.; Roy, N. DeCoach: Deep Learning-Based Coaching for Badminton Player Assessment. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2022, 83, 101608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillot, A.; Nadrowska, E.; Collet, C. Using Motor Imagery to Learn Tactical Movements in Basketball. J. Sport Behav. 2009, 32, 189. [Google Scholar]
- Figueira, B.; Mateus, N.; Esteves, P.; Dadelienė, R.; Paulauskas, R. Physiological responses and technical-tactical performance of youth basketball players: A brief comparison between 3 × 3 and 5 × 5 basketball. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2022, 21, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, F.A.; Martins, L.E.B.; Cunha, S.A. Analysis of football game-related statistics using multivariate techniques. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 1881–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, H.; Clemente, F.M.; Araújo, D.; Davids, K.; McRobert, A.; Figueiredo, A. What performance analysts need to know about research trends in association football (2012–2016): A systematic review. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 799–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Gallego, R.; Salvador, S.M.; Luján, J.F.G.; Reid, M.; Ramón-Llin, J.; Crespo, M. Challenging serve myths in doubles tennis. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach. 2021, 16, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, D.; Guo, Z.; Xu, Q.; Wu, Y. TacticFlow: Visual analytics of ever-changing tactics in racket sports. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2021, 28, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Cao, A.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y. Tac-miner: Visual tactic mining for multiple table tennis matches. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2021, 27, 2770–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Liang, M.; Xiao, D.; Hao, W. A systematic and comparative study on the line-changing strategies in top-level table tennis players. Int. J. Perform. Anal. Sport 2020, 20, 1018–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Luque, G.; Blanca-Torres, J.C.; Giménez-Egido, J.M.; Cabello-Manrique, D.; Ortega-Toro, E. Design, validation, and reliability of an observational instrument for technical and tactical actions in singles badminton. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 582693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carboch, J.; Smocek, P. Serve and Return in Badminton: Gender Differences of Elite Badminton Players. Int. J. Phys. Educ. Fit. Sports 2020, 9, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y. Sports decision-making model based on data mining and neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 3911–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Bai, B.; Zhao, Y. Variation Factors and Dynamic Modeling Analysis of Tennis Players’ Competitive Ability Based on Big Data Mining Algorithm. J. Sens. 2022, 2022, 3880527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabtah, F.; Zhang, L.; Abdelhamid, N. NBA game result prediction using feature analysis and machine learning. Ann. Data Sci. 2019, 6, 103–116. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, N.; Wadhwa, H. Applications of Modern Classification Techniques to Predict the Outcome of ODI Cricket. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 87, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valero, C.S. Predicting Win-Loss outcomes in MLB regular season games-A comparative study using data mining methods. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Sport 2016, 15, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Razali, N.; Mustapha, A.; Yatim, F.A.; Ab Aziz, R. Predicting football matches results using bayesian networks for English Premier League (EPL). In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, International Research and Innovation Summit (IRIS2017), Melaka, Malaysia, 6–7 May 2017; Volume 226, p. 012099. [Google Scholar]
- Karlis, D.; Ntzoufras, I. Analysis of sports data using bivariate Poisson models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. D Stat. 2003, 52, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunado, I.T. An overview to game theory, physical education and sports, its thirteen essentials and categories. Educ. J. 2016, 5, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kao, C.C. Development of team cohesion and sustained collaboration skills with the sport education model. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sindik, J.; Vidak, N. Application of game theory in describing efficacy of decision making in sportsman’s tactical performance in team sports. Interdiscip. Descr. Complex Syst. INDECS 2008, 6, 53–66. [Google Scholar]
- Tuyls, K.; Omidshafiei, S.; Muller, P.; Wang, Z.; Connor, J.; Hennes, D.; Hassabis, D. Game Plan: What AI can do for Football, and What Football can do for AI. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2021, 71, 41–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orugun, J.; Nafiu, A.; Aduku, D.J. Strategy implementation and its effect on superior performance and competitive advantage of SMEs in Kogi State, Nigeria. Asian J. Econ. Bus. Account. 2017, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, D.A.; Turner, J.D.; Johnstone, A.J. Coaches’ perceptions of the potential use of performance analysis in badminton. Int. J. Perform. Anal. Sport 2012, 12, 452–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Peng, Y.; Shen, Z.; Chen, H.; Peng, B.; Yan, X. Application of tactics in technical and tactical analysis of table tennis mixed doubles based on artificial intelligence graph theory model. J. Environ. Public Health 2022, 2022, 6543953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abián-Vicén, J.; Sánchez, L.; Abián, P. Performance structure analysis of the men’s and women’s badminton doubles matches in the Olympic Games from 2008 to 2016 during playoffs stage. Int. J. Perform. Anal. Sport 2018, 18, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, H. Stroke performance relevance model for elite table tennis matches. Int. J. Perform. Anal. Sport 2022, 22, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H. A visible analysis approach for table tennis tactical benefit. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2022, 21, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iizuka, T.; Hirano, K.; Atomi, T.; Shimizu, M.; Atomi, Y. Changes in duration and intensity of the world’s top-level badminton matches: A consideration of the increased acute injuries among elite women’s singles players. Sports 2020, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barreira, J.; Chiminazzo, J.G.C.; Fernandes, P.T. Analysis of point difference established by winners and losers in games of badminton. Int. J. Perform. Anal. Sport 2016, 16, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’donoghue, P.G. The most important points in grand slam singles tennis. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2001, 72, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Xie, X.; Ye, S.; Lu, H.; Xiao, H.; Yuan, Z.; Wu, Y. TIVEE: Visual exploration and explanation of badminton tactics in immersive visualizations. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2021, 28, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, C.; Karlsen, A.; Nybo, L. Novel speed test for evaluation of badminton-specific movements. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Jie, Y. Analysis of Badminton Technical Movement Scoring Rate in International Competitions with the Help of Computer. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1992, 022039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Gonzalez, C.; del Corral, J. Professional tennis in the twenty-first century: Hawk-Eye on competitive balance. In Outcome Uncertainty in Sporting Events; Edward Elgar Publishing: Gloucestershire, UK, 2020; pp. 27–43. [Google Scholar]
- Jayalath, L. Hawk Eye technology used in cricket. South Asian Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2021, 3, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Win/ Lose | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Odd/Even | Situation | ||
| Odd Stroke | Leaf node, and the is positive | Win | 1 |
| Leaf node, and the is negative | Lose | −1 | |
| Leaf node, and the is 0 | - | 0 | |
| Non-leaf, > 0 | Win | 1 | |
| Non-leaf, < 0 | Lose | −1 | |
| Non-leaf, = 0 | - | 0 | |
| Even Stroke | Leaf node, and the is positive | Win | 1 |
| Leaf node, and the is negative | Lose | −1 | |
| Leaf node, and the is 0 | - | 0 | |
| Non-leaf, > 0 | Win | 1 | |
| Non-leaf, < 0 | Lose | −1 | |
| Non-leaf, = 0 | - | 0 | |
| No. | Year | Tournament | Match | Round | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2006 | Hong Kong Open | Super Series | Final | Lin |
| 2 | 2007 | Sudirman Cup | BWF tournaments | Group stage | Lee |
| 3 | 2007 | China Masters | Super Series | Semi-finals | Lin |
| 4 | 2007 | Japan Open | Super Series | Semi-finals | Lee |
| 5 | 2007 | Hong Kong Open | Super Series | Final | Lin |
| 6 | 2008 | Swiss Open | Super Series | Final | Lin |
| 7 | 2008 | Thomas Cup | BWF tournaments | Semi-finals | Lee |
| 8 | 2008 | Olympic Games | Multi-sport events | Final | Lin |
| 9 | 2008 | China Open | Super Series | Final | Lin |
| 10 | 2009 | All England Open | Super Series | Final | Lin |
| 11 | 2009 | Swiss Open | Super Series | Final | Lee |
| 12 | 2009 | Sudirman Cup | BWF tournaments | Semi-finals | Lin |
| 13 | 2010 | Thomas Cup | BWF tournaments | Semi-finals | Lin |
| 14 | 2010 | Japan Open | Super Series | Final | Lee |
| 15 | 2010 | Asian Games | Multi-sport events | Final | Lin |
| 16 | 2011 | All England Open | Super Series Premier | Final | Lee |
| 17 | 2011 | BWF World Championships | BWF tournaments | Final | Lin |
| 18 | 2011 | China Open | Super Series Premier | Semi-finals | Lin |
| 19 | 2012 | Korea Open | Super Series Premier | Final | Lee |
| 20 | 2012 | Olympic Games | Multi-sport events | Final | Lin |
| 21 | 2013 | BWF World Championships | BWF tournaments | Final | Lin |
| 22 | 2014 | Asian Games | Multi-sport events | Semi-finals | Lin |
| 23 | 2015 | Japan Open | Super Series | Last 16 | Lin |
| 24 | 2015 | China Open | Super Series Premier | Semi-finals | Lee |
| 25 | 2016 | Badminton Asia Championships | BAC tournaments | Semi-finals | Lee |
| 26 | 2016 | Olympic Games | Multi-sport events | Semi-finals | Lee |
| 27 | 2017 | Malaysia Open | Super Series Premier | Final | Lin |
| 28 | 2017 | Badminton Asia Championships | BAC tournaments | Semi-finals | Lin |
| 29 | 2018 | All England Open | Super 1000 | Quarter-finals | Lin |
| First 3 Beats | First 5 Beats | First 7 Beats | First 9 Beats | All Beats | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Win | Lose | Win | Lose | Win | Lose | Win | Lose | Win | Lose | |
| Lin | 122 | 114 | 487 | 550 | 830 | 984 | 906 | 1066 | 910 | 1071 |
| Lee | 102 | 119 | 433 | 539 | 769 | 925 | 841 | 999 | 846 | 1005 |
| Win–Loss Ratio | ||||||||||
| Lin | 0.517 | 0.47 | 0.458 | 0.459 | 0.459 | |||||
| Lee | 0.462 | 0.445 | 0.454 | 0.457 | 0.457 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, W.; Wang, X.; Yu, S. Gaming Tree Based Evaluation Model for Badminton Tactic Benefit Analysis and Prediction. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7380. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137380
Liu W, Zhu Y, Guo W, Wang X, Yu S. Gaming Tree Based Evaluation Model for Badminton Tactic Benefit Analysis and Prediction. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(13):7380. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137380
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wenming, Yifan Zhu, Wenxia Guo, Xinyuan Wang, and Songkun Yu. 2023. "Gaming Tree Based Evaluation Model for Badminton Tactic Benefit Analysis and Prediction" Applied Sciences 13, no. 13: 7380. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137380
APA StyleLiu, W., Zhu, Y., Guo, W., Wang, X., & Yu, S. (2023). Gaming Tree Based Evaluation Model for Badminton Tactic Benefit Analysis and Prediction. Applied Sciences, 13(13), 7380. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137380





