Abstract
The application range of potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) crystals can be expanded by enhancing their surface quality properties. Therefore, a method for controlling the surface-temperature field of various materials was developed to expand the plastic zone to overcome the difficulty in processing KDP crystals. The ductile/brittle transition depth of the KDP crystals was determined using a 38 nm nanoindentation experiment. The nanoscratch experiment revealed the rules of how the transformation depth of the KDP crystals changes with temperatures, and the effect of temperature on the microstructure of the KDP crystals was studied. Finally, KDP crystal surfaces were processed using a UPDFC machine at elevated temperatures. According to our experiments, the surface roughness of the KDP crystal reached 5.275 nm as temperature increased, thus enhancing its surface quality. This method could be applied to other brittle materials.
1. Introduction
KH2PO4 (KDP) crystals, which have interesting photophysical properties, such as piezoelectricity, dielectricity, and electro-optical properties, are optical materials with excellent performance. KDP crystals, which are required in inertial confinement nuclear fusion [1,2,3,4,5], can be used under a wide transmission band, large nonlinear optical coefficient, and high damage threshold (greater than 15 J/cm2, 1 ns). In addition, they can grow large-diameter crystals (Φ500–600 mm) [6,7,8]. In the 1950s, KDP, as a high-performance piezoelectric crystal material, was mainly used in the manufacturing of sonar and civilian piezoelectric transducers. In the 1960s, with the emergence of laser technology, KDP crystals were developed with a large nonlinear optical coefficient and a high laser damage threshold, and the crystals had high transmittance from the near-infrared to ultraviolet bands and a high birefringence coefficient. Thus, they were usually used in the second-, third-, and fourth-harmonic-generation devices of Nd: YAG lasers (at room temperature). At the same time, KDP is a kind of crystal material with a high electro-optic coefficient; thus, it is widely used in electro-optic modulators, Q switching, shutters for high-speed photography, and other components [9,10]. This crystal shows application prospects in major technologies such as in controlled thermonuclear reactions of high-power laser systems, nuclear explosion simulations, etc. Therefore, research on ultra-large, high-quality KDP optical crystals has attracted much attention from researchers worldwide [11,12,13].
Applying KDP crystals in high-power solid-state lasers requires higher levels of surface quality. The surface processing quality of KDP crystals affects the beam quality in laser targeting and pointing accuracy. Recently, many scholars have studied this problem considering the surface quality properties of KDP crystals. Most KDP crystal surfaces are currently processed using ultraprecision single-point diamond fly cutting (UPSDFC) technology [14,15,16]. To improve the quality of KDP crystal surfaces, Baruch A. et al. [17] studied the effect of the ultraprecision single-point diamond cutting process of KDP crystals on a PNEUMO precision machine tool. The surface quality was improved to produce a smooth surface, achieving an accuracy of 3.6 μm by changing the machining parameters and the cutting tool edge’s radius. CL Zhang et al. analyzed the influence of processing parameters on the surfaces of KDP crystals through a large number of single-point diamond-turning experiments. Based on the influence of the mechanical properties of the KDP crystals on surface quality properties, the ultrasonic-assisted cutting of KDP crystals was carried out, which improved the surface processing quality properties of the KDP crystals [18]. Q Liu et al. found that KDP crystals were difficult to machine due to their low fracture resistance, and fracture fringes were easily generated during processing. Based on material performance tests under different temperature fields, the hardness and elastic modulus properties of the KDP crystals decreased by 21.4% and 32.5% at high temperatures (160 °C), respectively [19]. Kozlowski et al. [20] reported improvements in crystal surface quality when a particular orientation was used to process the KDP crystals. The experimental results showed that the cutting state of the material’s surface in the ultraprecision cutting of KDP crystals changed with changes in the factors, such as the back-cutting tool amount, the tool cutting radius, and the crystal direction, which affected the processing quality of the KDP crystal’s surface. Pengqiang Fu et al. [21] established a model to simulate surface morphology, which included surface performance indicators, including waviness, roughness, and 3D surface morphology. After the ultraprecision fly cutting of KDP crystals, considering the tool’s thermal deformation, they demonstrated that the tool’s thermal deformation affected the surface roughness and waviness of the KDP crystals. In addition, it increased the surface slope, which affected surface precision and thus the optical performance of the KDP crystals.
Therefore, the surface quality of KDP crystals can be improved by optimizing the UPSDFC process. In addition, the surface morphology is affected by the temperature change in the processed surface. Thermal-assisted machining has been widely used in difficult-to-machine materials such as high-temperature alloys, but there is little research exploring whether thermal-assisted machining is helpful for the brittle surface plastic transformation of optical crystal materials and the improvements in machining surface accuracy. There are also few studies on the effect of the temperature field on the surface quality properties of the KDP crystals during processing, and the material removal mechanism is unclear. To reveal the mechanism of the ultraprecision cutting of KDP and improve the surface processing quality properties, a heat-assisted machining method was developed based on the theory of ductile/brittle transitions. The plastic region range was expanded, and the machining quality was improved by controlling the surface-temperature field of the material. The ductile/brittle transition depths of the KDP crystals were determined using nanoindentation experiments, and the mechanism of the ductile/brittle transitions of the KDP crystals was analyzed. The effects of temperature on the ductile-/brittle-transition depth and the surface morphology of KDP crystals were studied using nanoscratch experiments, and thermal field assistance was explored. The feasibility of the heating-assisted processing method was explored, and the material-removal mechanism under heat was revealed. Finally, the global machining of KDP crystals was conducted on a fly cutting machine. The effectiveness of the heating-assisted machining method in improving the surface quality of KDP crystal was verified.
2. Theory of Ductile/Brittle Transition
KDP surfaces include a plastic and a brittle zone. The plastic surface layer becomes brittle when the processing depth increases to a certain depth, known as the critical depth of ductile/brittle transition. When the processing depth is less than the critical depth, insignificant cracks or brittle collapses occur on crystal surfaces due to the plastic slip in this region. When the process depth increases beyond the critical depth, the number and severity of pits and cracks increase due to the brittle fractures in the zone. Thus, the surface quality drops [22,23,24,25,26]. By increasing the surface temperatures of the KDP crystals, the ductile zone can be expanded. Cutting in the ductile zone can reduce the surface cracks and subsurface damage in the material. The processing principle is shown in Figure 1. When the cutting depth of the tool is constant, thermal-assisted cutting causes the ductile area of the material to expand. As the temperature increases, the range of the plastic zone expands, whereas the range of the brittle zone continues to decrease. The plastic processing of the materials in the plastic area can reduce surface pits and cracks, further improving surface quality.
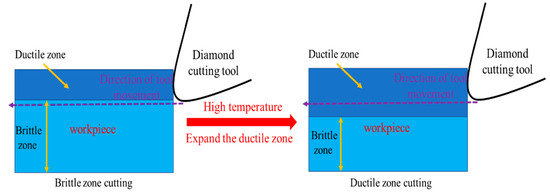
Figure 1.
High-temperature cutting principle of KDP crystal.
As a typical brittle material, the processing depth of KDP crystals occurs in the brittle region. The ultraprecision single-point diamond cutting of KDP crystals can be described as the elastic deformation changes to plastic deformation at the yield point. During the plastic deformation process, with increases in the shear stress and slip, the fracture strength is reached, and the chip is separated from the matrix. However, due to the low fracture toughness of the KDP crystal (0.74–0.8 MPam1/2), the elastic and strength limits of the material are close. Therefore, fracture failure occurs when the load on the KDP crystal exceeds its elastic limit. During the cutting process, defects such as pits, scratches, and cracks appear on the processed crystal surface. The overall fracture causes the sample to be scrapped. If the cutting depth is controlled within the critical depth of the ductile/brittle transition, the material deforms in the plastic zone via slip, improving the surface machining quality. The thermal assisted machining process method proposed in this paper provides a useful reference for the efficient and high-precision machining of similar brittle materials.
Nanoindentation experiments were used to measure the mechanical parameters of crystalline materials [27,28,29,30,31]. A diamond indenter was used in the nanoindentation experiment. The indenter acted on the sample during the indentation process, and the loading force and depth of the test sample were obtained. The Knoop hardness, critical fracture toughness, and elastic modulus of the material were calculated. Nanoindentation experiments can simulate the material removal behavior during the cutting process. The deformation of materials on both sides of the nanoscratch groove reveals effective information on material removal [32,33,34,35]. The relationship between the critical depth of the ductile/brittle transition, H; Knoop hardness, HK; material’s elastic modulus, E; and critical fracture toughness, KIC, was measured by T.G. Bifano et al. [36] via the microindentation method under static conditions. They can be expressed as
The proportional coefficient n is determined by the indenter geometry (0.15 for a diamond glass indenter). The crack was less than 10% in their experiment. The critical depth of the ductile/brittle transition of KDP crystals was calculated using Formula (1) [37,38,39].
To determine the value of the ductile/brittle transition depth of KDP crystals, we conducted nanoindentation experiments on the surfaces of KDP crystal. The experimental sample was a large KDP 80 mm × 40 mm × 5 mm crystal. As shown in Figure 2, the surface was flat without defects, such as pits or cracks.

Figure 2.
KDP crystal sized 80 mm × 40 mm × 5 mm.
Six points at different positions on the surface of the KDP crystal were selected for the nanoindentation experiments. Data measurements and the related analysis are discussed in Section 5. The experimental data were recorded and averaged to obtain parameters, such as the elastic modulus, fracture toughness, and hardness of the KDP crystals. The surface morphology was checked using an atomic force microscope, and the result is presented in Figure 3.
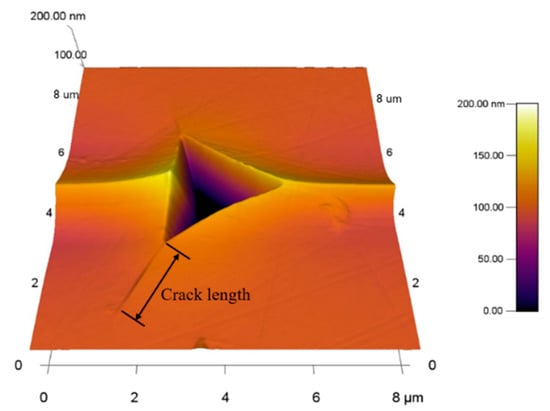
Figure 3.
Morphology of nanoindentation points on KDP crystal surfaces.
Using Formula (1), the depth, H, of the ductile/brittle transition on the test surface of the sample was obtained as 38 nm.
On the KDP crystal surface, the processing depth was controlled within 38 nm. The material was in the plastic zone; thus, the removal occurred via plastic slip, and the surface quality was high without surface defects. When the cutting depth exceeded 38 nm, the material became brittle and then was removed by brittle fracture; the surface quality was poor. The critical depth of the ductile/brittle transition of KDP crystals is small, and the cutting depth is difficult to control in the plastic region. Presently, KDP crystals are processed using ultraprecision diamond fly cutting (UPDFC) tools. During KDP crystal processing, the cutting depth of the cutter fluctuates because of the interfering environment, temperature, machine stability, etc. The cutting depth of the tool cannot be controlled in the plastic region, and brittle removal easily occurs.
The analysis of the ductile/brittle transition and the cutting process of KDP crystal demonstrates that the surface quality of KDP crystals can be enhanced by increasing the depth of the ductile/brittle transition. Therefore, a heating-assisted method was developed to reduce the strength and hardness of the cutting-layer material by introducing high-density external energy and changing the internal stress field; the cutting performance changes at high temperatures, improving the plasticity of the material. When the yield strength of the materials is reduced below the fracture strength, the material removal mode changes from brittle fracture to plastic slip, achieving a high-quality surface.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
Significant progress has been made in exploring the mechanical properties and deformation of brittle materials based on nanoindentation testing, but few have explored the impact of temperature on the properties and removal behavior of brittle materials based on nanoindentation testing [27,28,29,30]. To investigate the effectiveness of our heating-assisted machining method in improving the surface quality of KDP crystals and to reveal the mechanism of the cutting and removing of the microplastic region of materials, a high-temperature nanoscratch experiment was conducted on KDP crystal surfaces using a Hysitron Ti-950 Triboindenter. The difference in surface morphology between the plastic and brittle regions was analyzed to explore the effect of the auxiliary thermal field conditions on the mechanical properties of KDP crystals. In addition, we used a diamond fly cutting machine for processing the KDP crystal surface and confirmed that high temperatures can expand the plastic region and improve the surface quality. An 80 mm × 40 mm × 5 mm KDP crystal, having smooth surfaces without defects, was used as the experimental sample (Figure 2). After XRD analysis and detection, the [1,0,0] crystal plane of KDP was processed.
Single-point diamond fly cutting technology [40,41] is used to process infrared optical materials, such as KDP crystals; the machining contour is controlled by single-crystal and natural diamond tools, and the surface roughness is ensured using CNC schemes. As only a surface layer of the material is removed by diamond fly cutting, the surface damage can be reduced, resulting in improved surface quality. The UPDFC machine tool used in this work is shown in Figure 4. The experimental speed was 800 r/min, and the feed speed was 4 mm/min. The cutting depth was 2 μm. The arc radius of the diamond cutting tool tip was 0.5 mm, with a negative front angle of 10 degrees and a back angle of 15 degrees. The processing equipment was a self-developed flying cutting machine tool, SGDT-350.
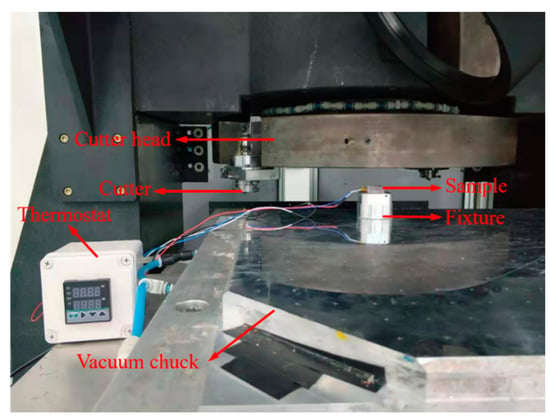
Figure 4.
Ultraprecision diamond fly cutting machine tool.
3.2. Experimental Procedures
3.2.1. Nanoscratch Experiment with Heating Assistance
The nanoscratch experiment is an important method for investigating material properties [21,36]. A nanoscratch tester was employed in our experiment. The total length of each scratch was 300 μm, the scratching was from shallow to deep; the probe moving speed was 8 μm/s; and the loading rate was 16 mN/s. The surface temperatures of the workpiece in the scratch experiment were set to 20 °C, 30 °C, 40 °C, or 50 °C; and the experimental data were recorded. The surface morphology was observed using a 3D profiler, and the rule of the change in surface morphology under different temperatures was analyzed using a scanning electron microscope.
3.2.2. Cutting Experiment with Heating Assistance
A diamond fly cutting machine tool (Figure 4) was used to conduct the heating-assisted processing experiment to reveal the effect of temperature on the surface quality of KDP crystals and to verify the feasibility of our scheme in improving surface quality. During the fly cutting experiment, the KDP crystal was placed in the fixture, and a ceramic plate was used to heat the sample. KDP is a soft and crisp material [14,15,16,17]. During the experiment, when the surface temperature of the material was above 70 °C and under continuous heating conditions, the surface of the KDP material was softened and damaged, which could lead to the inability to conduct processing experiments. Therefore, the processing temperature needed to be controlled below 70 °C. In order to distinguish the effect of temperature on the surface of the material, the temperature was lower than the soft temperature for the experimental specimen; the temperature of the control group was increased. Material softening is a process. To prevent material deformation caused by excessive temperature, the surface temperature should be below 70 degrees. The temperature of the ceramic plate was controlled using a thermostat, and this was set to 20 °C, 30 °C, 40 °C, or 50 °C. The cutter material was a high-hardness diamond tool with a 6 mm arc radius and −45° and 5° rake and relief angles, respectively. A white-light interferometer was employed to determine the surface quality of the KDP crystal.
In the heating-assisted fly cutting experiment, the thermal deformation of the material was generated when it was heated. This research aimed to increase the surface laser damage threshold of KDP crystals to meet the requirements of the advancing and developing optical components. In the process of the antilaser damage threshold test, the laser spot diameter was small, and it was insensitive to the surface shape. The surface shape accuracy could reach the micron level to meet application requirements. It was processed with a UPSDFC machine, and the surface shape accuracy could reach nanometers. Therefore, the thermal deformation during the experiment did not affect the application of KDP crystals in optical components.
During the experiment, the surface of the material was raised to a certain temperature. Temperature can change the surface properties of materials and affect surface hardness. Therefore, after multiple sets of experimental analysis, we realized that temperatures ranging from 20 °C to 50 °C were optimum. Thermal deformation did not affect the application of the KDP crystals in optical components, and the deformation was within an acceptable range.
4. Results
4.1. Heating-Assisted Nanoscratches
To investigate the effect of temperature on the surface morphology of KDP crystals, nanoscratch experiments were conducted at different temperatures. During the nanoscratch experiments, the probe scratched the surface of the material, which was observed with a three-dimensional profiler the scratch morphology is shown in Figure 5. The scratch depth continued to increase with an increase in the scratch length, which was equivalent to the probe slashing into the surface of the material; the maximum depth of the scratch was about 250 nm. The depth of the ductile/brittle transition of KDP crystals at room temperature is about 38 nm (Section 2); thus, the scratch area in the scratch experiment covered both the plastic and brittle zone, which was suitable for analyzing the ductile/brittle transition phenomenon at different temperatures.
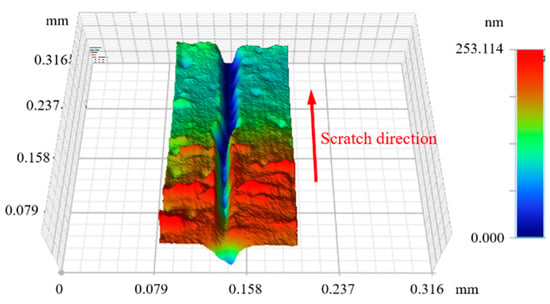
Figure 5.
Three-dimensional morphology of nanoscratch.
4.2. Results of Diamond Fly Cutting Experiment
After global cutting of the KDP crystal under heating, insignificant defects, such as pits and cracks, developed on the surface of the materials. A white-light interferometer was used to determine the surface quality of the KDP crystals. The average value of the multiple groups of a test at different temperatures was taken. Figure 6a–d show the roughness of the material surface at processing temperatures of 20 °C, 30 °C, 40 °C, and 50 °C, respectively.
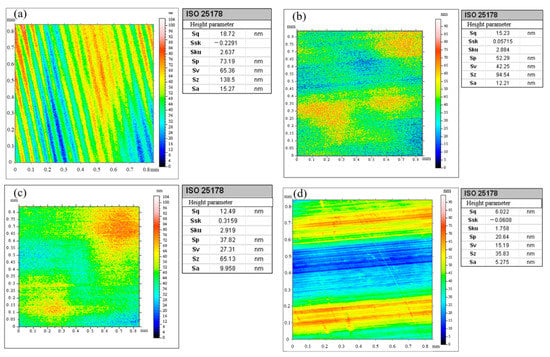
Figure 6.
Roughness of machined KDP crystal surface at (a) 20 °C, (b) 30 °C, (c) 40 °C, and (d) 50 °C.
5. Discussion
5.1. Effect of Heating on Cutting Performance of KDP Crystals
The method commonly used for judging the brittle–plastic transition is based on the surface topography. Energy detection needs to take into account the dissipation of energy. The whole experiment takes a long time, and there are problems such as large energy loss and the environment can easily interference. Therefore, the detection results are usually inaccurate. The scratches on the KDP crystal surfaces were observed via scanning electron microscopy, as shown in Figure 7a: toward the direction of the scratch, the scratch depth increases with the increase in the scratch length. In the initial stage of the nanoscratch, the scratch depth is low, and the scratches are in the plastic region, as shown in Figure 7b. As removing the KDP crystal surface by plastic slip had little effect on the surface morphology, the surface had no evident defects. As the scratch depth increased, the surface of the material became brittle (Figure 7c). The surface of the material was removed by brittle fracturing, and massive chips and pits appeared on the surface of the scratch, which affected the surface quality. The critical depth of the ductile/brittle transition is where the material transforms from the plastic to brittle region. When the scratch depth is lower than the critical depth, the surface is removed by plastic slip, without significant surface defects.
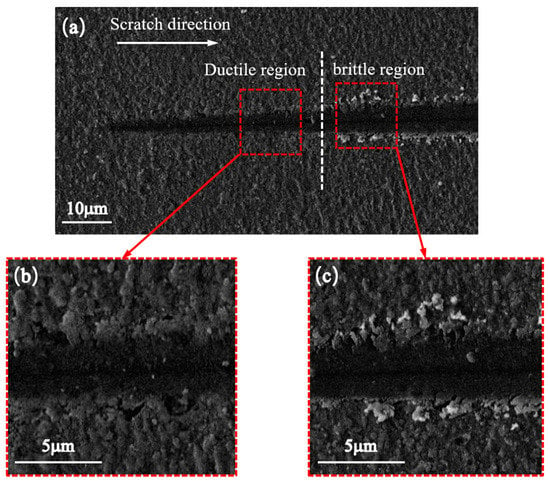
Figure 7.
Surface morphology of nanoscratch. (a) Overall morphology of nanoscratch. (b) Plastic region. (c) Brittle region.
The effect of temperature on the toughness/brittle transition depth of KDP crystals is explained by Formula (1). An increase in temperature leads to a decrease in the hardness HK of KDP crystals, which leads to an increase in the depth H of the ductile/brittle transition. To study the effect of temperature on the depth of the ductile/brittle transition of KDP crystals, the surface morphology of scratches at 20 °C, 30 °C, 40 °C, and 50 °C was recorded using a scanning electron microscope, and the results are presented in Figure 8a–d, respectively. The scratch surface changed from the plastic to the brittle zone as the scratch length and depth increased. When the scratch depth exceeded the critical depth of the ductile/brittle transition, the material removal mode was brittle fracture, and block chips appeared. The first position where block cutting occurred was the critical position of the ductile/brittle transition. As shown in Figure 8a–d, the locations of brittle–plastic transformation corresponding to 20 °C, 30 °C, 40 °C, and 50 °C were sections A–A, B–B, C–C, and D–D, respectively.
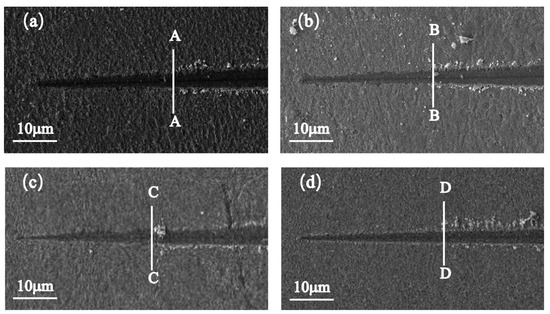
Figure 8.
Surface morphology of nanoscratch at (a) 20 °C, (b) 30 °C, (c) 40 °C, and (d) 50 °C.
The cross-sectional view of the ductile/brittle transition position at different temperature points was obtained via atomic force microscope observation, as shown in Figure 9. When the scratch temperature of the KDP crystal surface was 20 °C, 30 °C, 40 °C, and 50 °C, the KDP crystal ductile/brittle transition depth values were 40 nm, 49 nm, 71 nm, and 89 nm, respectively. The surface ductile/brittle transition depth value continued to increase as the surface temperature of KDP crystals increased, which verifies the effectiveness of the heating-assisted processing in improving the processing performance of KDP crystals and increasing the ductile/brittle transition depth. If the machining depth remains unchanged, the heating-assisted method can effectively improve the ductile/brittle transition depth; therefore, the cutting process changes from the brittle to the plastic zone, resulting in reduced pits and cracks caused by brittle fracture and improving surface quality.
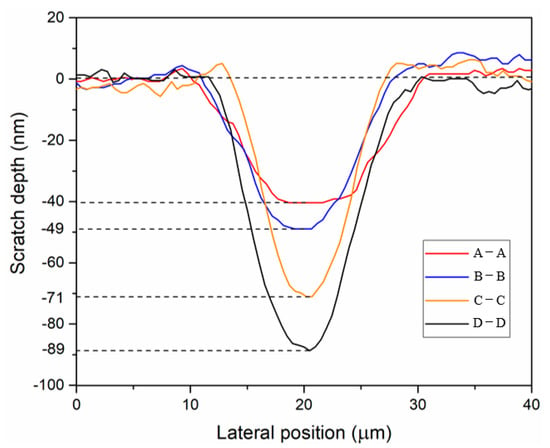
Figure 9.
Section depth of ductile/brittle transition position.
5.2. Impact of Heating-Assistance on the Surface Quality of KDP Crystals
The surface roughness Sa was 15.270 nm, 12.210 nm, 9.958 nm, and 5.275 nm ta cutting temperatures of 20 °C, 30 °C, 40 °C, and 50 °C, respectively, as shown in Figure 10. The surface roughness gradually decreased as the surface temperature increased. Multiple groups of surface roughness values were recorded, the average value was taken, and error bars were added. Combined with the result of the nanoscratch experiments, this finding can be explained by the theory of ductile/brittle transition. When temperature increases, the plastic zone of the KDP crystal surface expands, the depth of the ductile/brittle transition increases, and the material removal mode transforms from brittle fracture to plastic slip, resulting in reduced surface defects, e.g., pits and cracks and improved surface quality.
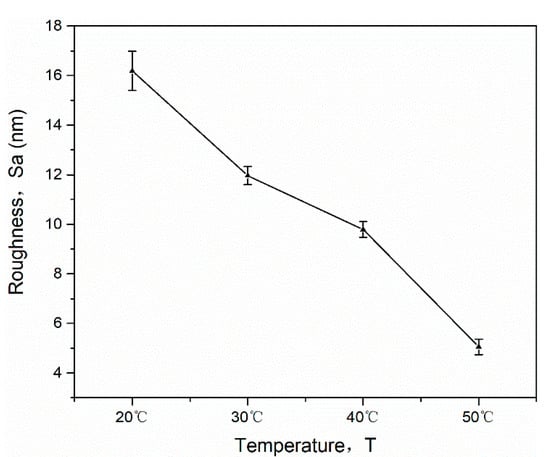
Figure 10.
Surface roughness versus temperature of KDP crystal.
The heating-assisted fly cutting experiment of KDP crystals verified that our heating-assisted processing method can effectively improve surface quality. Increasing the surface temperature during the processing of KDP crystals can effectively expand the range of the surface plasticity and increase the depth of the ductile/brittle transition. The removal changes from the brittle zone to the plastic zone in the material. The tool remains in the plastic region during the cutting process to remove material via plastic slip; therefore, the defects, e.g., pits and cracks, caused by brittle removal are reduced, and the surface quality is significantly improved.
6. Conclusions
In this work, we studied the impact of heating assistance on the surface quality in the processing of KDP crystals.
- A processing method was developed to improve the surface quality of KDP crystals on the basis of the theory of ductile/brittle transition, wherein the surface temperature of KDP crystals is increased to enlarge the plastic zone. Several nanoindentation experiments were conducted on KDP crystals, and the critical depth of the ductile/brittle transition of KDP crystals was about 38 nm.
- Nanoscratch experiments were performed on KDP crystal surfaces under heat. With the increase in the scratch length, the surface scratch changed from the plastic to the brittle zone, and the surface removal mode transformed from plastic slip to brittle fracture. The ductile/brittle transition depth of KDP crystals increased with increasing temperature. The surface morphology was affected by temperature, verifying the effectiveness of the heating-assisted method in improving the cutting performance of KDP crystal.
- Finally, with heating, KDP crystal surfaces were processed using a UPDFC machine. The results showed that the surface roughness value of the material reached 5.275 nm as the surface temperature increased to 50 °C, indicating the superior surface quality compared with that at room temperature. These results verified the effectiveness of the heating-assisted machining method in improving the surface quality. As a typically brittle material, the processing of KDP crystals is a challenge. We proposed a heating-assisted method to improve surface quality, which provides a useful reference for the processing of other soft and brittle materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Y., S.F., M.H., and Z.J.; formal analysis, S.F., B.W., and G.Y.; investigation, Z.C., M.H., B.W., and G.Y.; methodology, S.F., H.Y., M.H., Z.C., and Z.J.; project administration, Z.J., H.Y., and G.Y.; resources, H.Y., G.Y., and Z.J.; software, S.F., Z.C., and B.W.; validation, H.Y. and Z.J.; visualization, S.F., H.Y., and B.W.; writing—original draft, S.F., Z.C., and G.Y.; writing—review and editing, H.Y., M.H., and Z.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financed the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51305413, 52105490, and 51905507; funder: Hong Yang, Zhong Jiang, Guangwei Yang.), Sichuan International Science and Technology Innovation Cooperation Project (Nos. 2020YFH0006 and 2020YJ0031; funder: Guangwei Yang, Zhong Jiang).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful for the support from the Institute of Machinery Manufacturing Technology, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mian-yang 621900, Sichuan Province, China.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Su, G.; Zeng, J.; He, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, B.; Jang, R. Application of large section KDP crystals in the study of laser fusion. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 1997, 25, 717–719. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.; Yang, H.; Zeng, X.; Wu, B.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Duan, J. Study on mechanics and key technologies of laser nondestructive mirror-separation for KDP crystal. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2015, 94, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Deng, L.; Duan, J.; Wu, B.; Zeng, X.; Shangguan, Y.; Wang, X. A study on laser multi-focus separation technology of thick KDP crystal. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2017, 118, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, F. A two-parameter model for predicting thermal contact resistance between crystal and aluminum alloy based on turning morphology. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2022, 236, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Q.; Kuang, L.; Xu, Y.; Dai, X. Study on the extraction and reconstruction of arbitrary frequency topography from precision machined surfaces. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2019, 233, 1772–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.-M.; Li, X.-Z.; Zheng, B.; Yang, L.-L. Progress in the Research of KDP(KH2PO4) Crystals. Hebei J. Ind. Sci. Technol. 2006, 2006, 377–380. [Google Scholar]
- Pritula, I.M.; Salo, V.I.; Kolybayeva, M.I. Optical and structural characteristics of oriented rapidly grown KDP single crystals. In Proceedings of the Operational Characteristics and Crystal Growth of Nonlinear Optical Materials, Denver, CO, USA, 19–20 July 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, V.T.; Do, T.T.; Ho, T.M.; Nguyen, D.T.; Van Le, B.; Le, A.T.; Van Le, N.; Huynh, D.T. Some structural, linear and nonlinear optical characteristics of single KDP crystals influenced by EDTA additive. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2018, 50, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, S.; Ramkumaar, G.R. Analysis on suitability of pure and α-Histidine doped KDP crystals in high speed applications. Indian J. Phys. 2009, 83, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hébert, D.; Hallo, L.; Voisin, L.; Desanlis, T.; Galtié, A.; Bicrel, B.; Maunier, C.; Mercier, P.; Duchateau, G. A KDP equation of state for laser-induced damage applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 123527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Shao, Z.; Wang, S.; Gao, Z. Optical characteristics of H3BO3-doped KDP crystals. Acta Opt. Sin. 2001, 21, 1396–1399. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Wang, Z.P.; Wang, S.L.; Gu, Q.T.; Xu, X.G.; Li, Y.P.; Fang, C.S. Origin and relation of three kinds of scatter centers in KDP and DKDP crystals. Cryst. Res. Technol. J. Exp. Ind. Crystallogr. 2004, 39, 796–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Q.; Kuang, L.; Xu, Y. The influence of cutting parameters on micro-topography of frequency features extracted from the machined KH2PO4 surfaces. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2020, 234, 1762–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Zeng, W.; Yang, N.; Tang, B.; Liu, Q.-J. The micro-wear mechanism of diamond during diamond tool fly-cutting KDP (KH2PO4) from first principle calculations. J. Mol. Model. 2020, 26, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Hu, D. Surface quality of large KDP crystal fabricated by single-point diamond turning. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Advanced Optical Manufacturing and Testing Technologies: Advanced Optical Manufacturing Technologies 2006, Xi’an, China, 2–5 December 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, X.Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.F.; Zhang, J.F.; Su, W.H.; Zhang, L.P.; An, C.H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.H.; Liu, M.C.; et al. Influence of the arrangement of vacuum chuck holes on the transmittance wavefront of large-aperture KDP in single-point diamond turning. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 3619–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, B.A.; Hed, P.P.; Baker, P.C. Fine diamond turning of KDP crystals. Appl. Opt. 1986, 25, 1733–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, M.; Liao, Z.; Feng, J.; Xu, D.; Cheng, J. On the improvement of the ductile removal ability of brittle KDP crystal via temperature effect. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 33127–33139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Feng, P.F.; Wu, Z.J.; Yu, D.W. Experimental Investigation on Surface Roughness of KDP Crystal Processed with Rotary Ultrasonic Face Milling. Key Eng. Mater. 2012, 499, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, M.R.; Thomas, I.; Edwards, G.; Stanion, K.; Fuchs, B.; Latanich, L. Influence of diamond turning and surface cleaning processes on the degradation of KDP crystal surfaces. In Proceedings of the Inorganic Crystals for Optics, Electro-Optics, and Frequency Conversion 1991, San Diego, CA, USA, 25 July 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, P.; Xue, J.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Lan, Z.; Zhan, L.; Zhang, F. Influence of the heat deformation of ultra-precision fly cutting tools on KDP crystal surface microstructure. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.; Zhang, X.; Fang, F.; Bi, M. Effects of crystallographic orientation and negative rake angle on the brittle-ductile transition and subsurface deformation in machining of monocrystalline germanium. Precis. Eng. 2019, 56, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-L.; Chen, H.-R.; Yuan, S.-S.; Zhu, Q.-Z. Experimental investigation and micromechanical modeling of the brittle-ductile transition behaviors in low-porosity sandstone. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 179, 105654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, R.; Chen, D.; Su, Y.; Ding, H.; Guo, J.; Fu, H. The characteristics and mechanisms of creep brittle-ductile transition in TiAl alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 767, 138393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, S.; Wan, F. Competition mechanism of brittle–ductile transition of metals under tensile condition. Mech. Mater. 2019, 137, 103138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, C.; Wang, J. Removal mechanism and surface quality of crystal semiconductor materials in scratching tests with Berkovich indenter. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 105, 104746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Song, H.; Xie, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, C.; Luo, H.; Niu, R. Fabrication and nanoindentation characterization of MgAlON transparent ceramics. Opt. Mater. 2018, 84, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Luo, Q.; Xu, X.; Huang, H.; Jiang, F. Removal mechanism of 4 h- and 6 h-sic substrates (0001 and 0001) in mechanical planarization machining. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2019, 233, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Ming, L.; Zhou, Z.; Hui, Y.; Shi, X. Comparison of nano-indentation hardness to microhardness. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 195, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zhao, D.; Tian, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J. Study on the deformation mechanism of spherical diamond indenter and its influence on 3C-SiC sample during nanoindentation process via molecular dynamics simulation. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2019, 90, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszalski, J.; Sankowska, I.; Kucharski, S. Nanoindentation of GaAs/AlAs distributed bragg reflector grown on GaAs substrate. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 109, 104912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Guo, X.; Zhai, R.; Luo, X.; Kang, R.; Jin, Z.; Guo, D. Study on the subsurface damage mechanism of optical quartz glass during single grain scratching. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 7683–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Z. An investigation on the nano-abrasion wear mechanisms of KDP crystals. Wear 2021, 476, 203692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, X.; Zhang, F.; Lu, Y.; Luo, X.; Chen, F. Surface and subsurface damage of reaction-bonded silicon carbide induced by electrical discharge diamond grinding. Int. J. Mach. Tool Manuf. 2020, 154, 103564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bifano, T.G.; Dow, T.A.; Scattergood, R.O. Ductile-regime grinding—A new technology for machining brittle materials. J. Eng. Ind.-Trans. ASME 1991, 113, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebisu, T.; Horibe, S. Analysis of the indentation size effect in brittle materials from nanoindentation load–displacement curve. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 30, 2419–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Luo, X.; Comley, P.; Reuben, R.L.; Cox, A. Brittle–ductile transition during diamond turning of single crystal silicon carbide. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2013, 65, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.G.; Shen, Y.G.; Lu, C. Nanoscale elastic–plastic deformation and stress distributions of the C plane of sapphire single crystal during nanoindentation. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 1865–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayomoh, M.K.O.; Abouelhossein, K.A.; Olufayo, O.A. Model for cutting force prediction in high precision single-point diamond turning of optical silicon. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. Innov. Dev. 2017, 9, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Suet, T.; Yin, Z.; Liu, J. Modeling and prediction of surface topography with three tool-work vibration components in single-point diamond turning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 98, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, M.; Zhu, H.; Huang, C.; Liu, A.; Bi, W. Investigation on critical crack-free cutting depth for single crystal silicon slicing with fixed abrasive wire saw based on the scratching machining experiments. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2018, 74, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).