Substructure Pseudo-Dynamic Test Study for a Structure Including Soil–Pile–Structure Dynamic Interaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
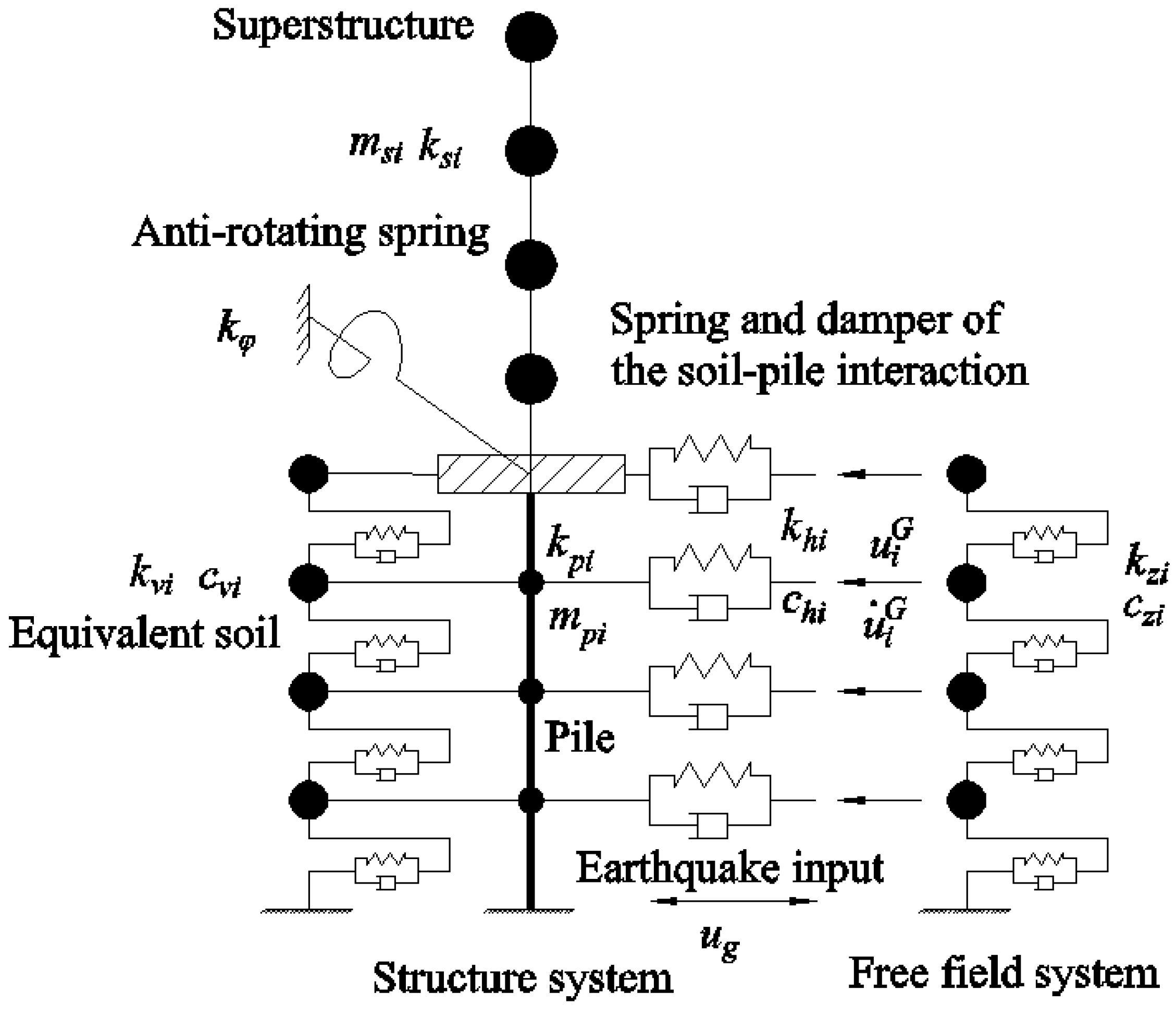
2. Improved Penzien Model
2.1. Model Details
- Only the horizontal translational degrees of the foundation soil and the free field are considered.
- Vertical and torsion effects of the structure are not considered.
- The pile foundation under the bearing pile cap maintains synchronous movement and can be combined.
- The interactions between pile groups are ignored.
2.2. Dynamic Response of the Free Field
2.2.1. Equation of Motion
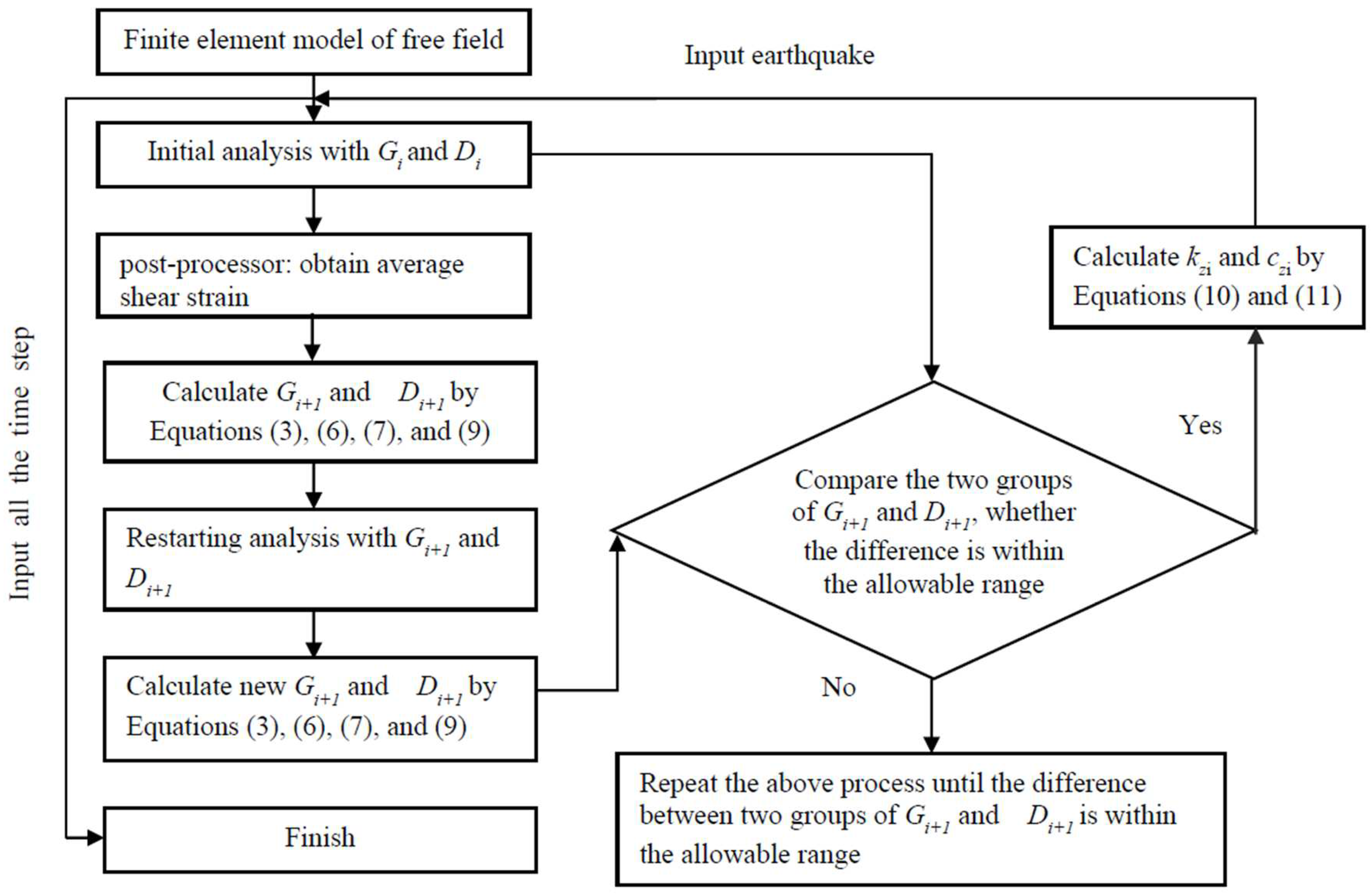
2.2.2. Dynamic Nonlinearity Model of Soil
2.2.3. Calculation Process of Soil Dynamic Nonlinearity
2.3. Parameter Determination of the Improved Penzien Model
2.3.1. Stiffness and Damping of Soil–Pile Interaction
2.3.2. Stiffness and Damping of the Equivalent Soil System
2.3.3. Bending Stiffness of Pile Cap
3. Matrix of the Improved Penzien Model
3.1. Mass and Stiffness Matrixes of Pile Group
3.1.1. Mass Matrix of Pile Group
3.1.2. Stiffness Matrix of Pile Group
3.2. Mass and Stiffness Matrixes of the Superstructure
3.3. Mass and Stiffness Matrixes of the Equivalent Soil System
3.4. Damping Matrix of Structure System
4. Substructure Pseudo-Dynamic Test of Soil–Pile–Structure İnteraction
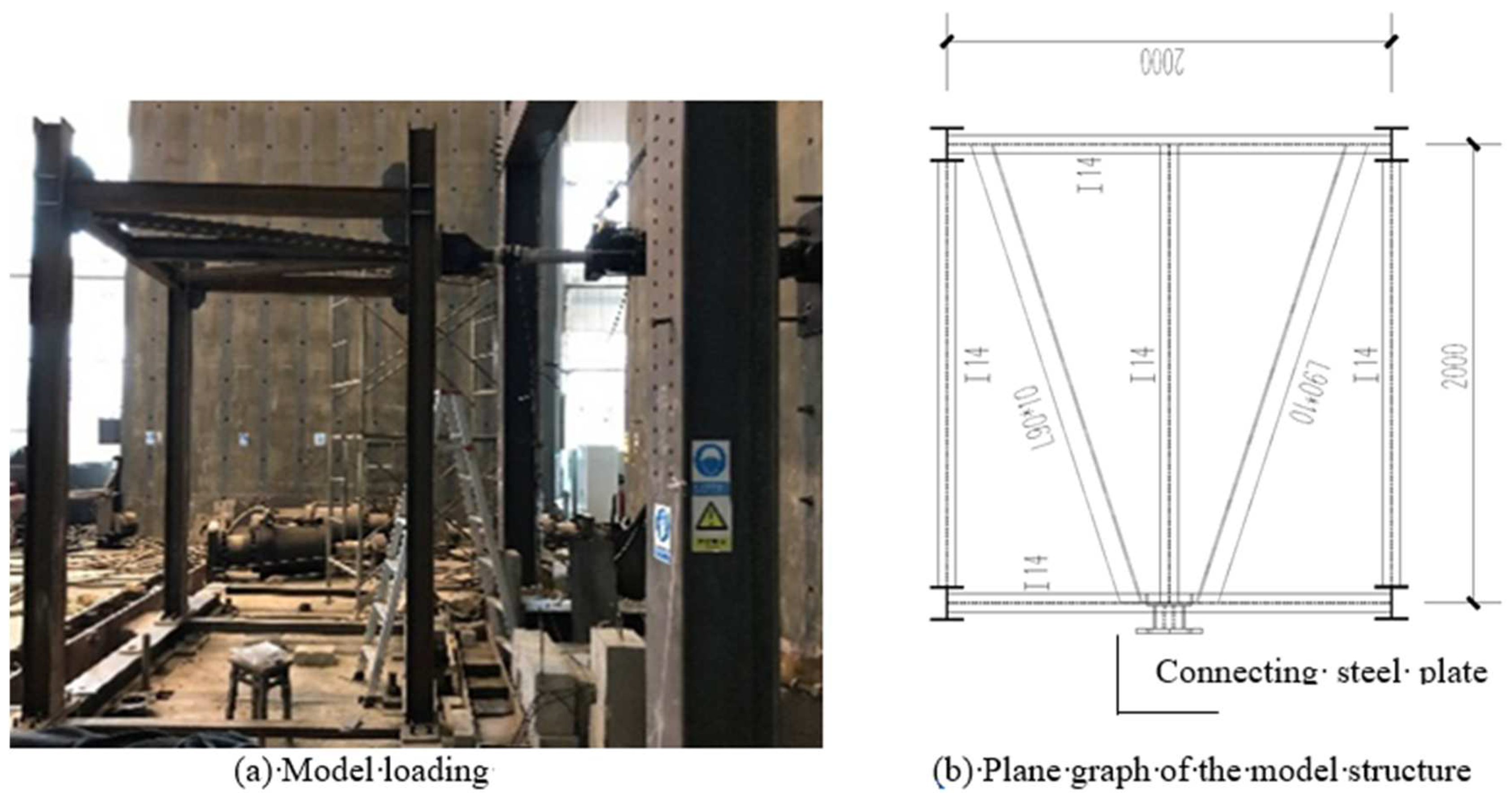
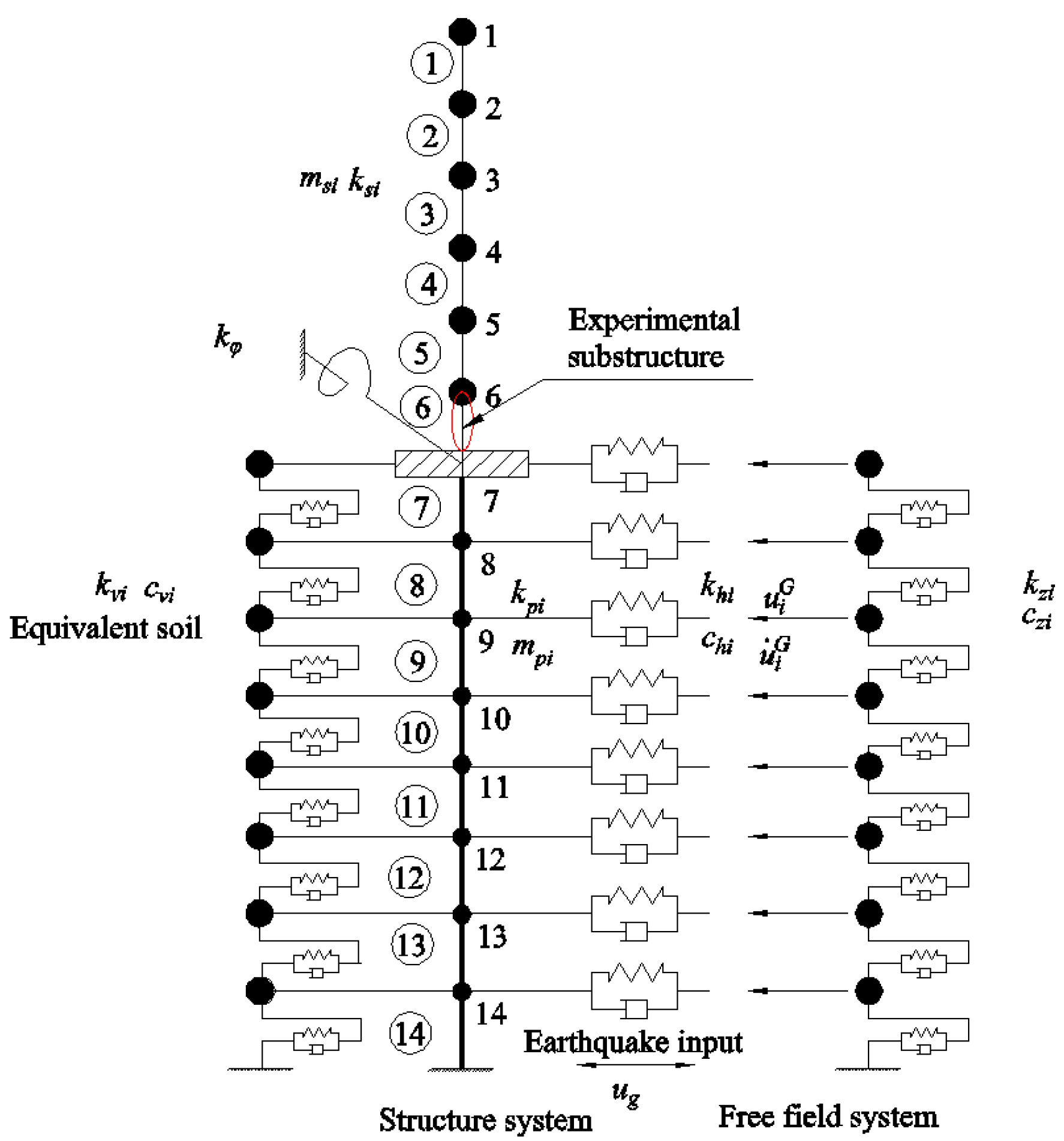
4.1. Experimental Substructure
4.2. Numerical Substructure
4.2.1. Soil Parameters
4.2.2. Details of the Numerical Substructure Model
4.3. Results
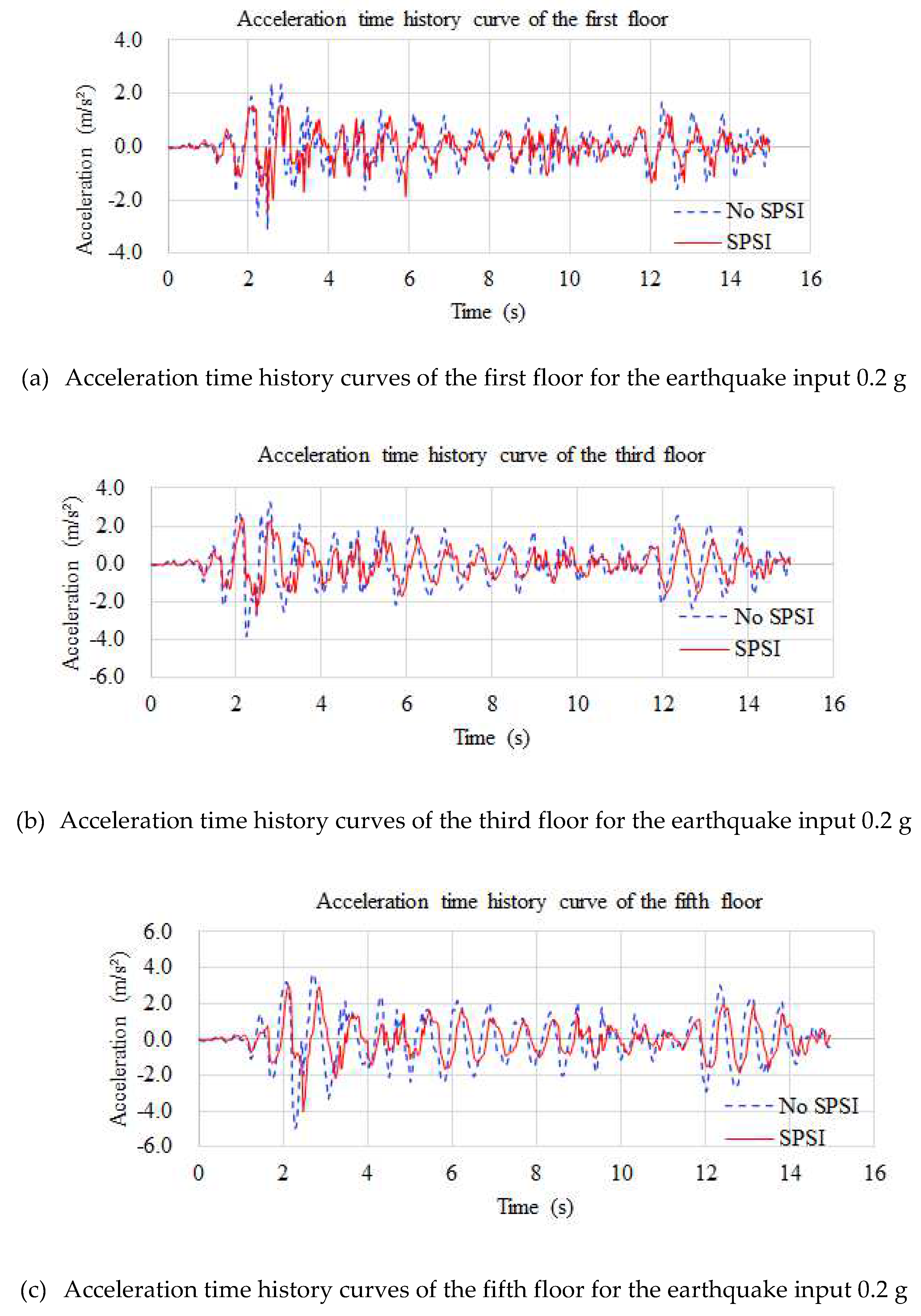
4.3.1. Acceleration Time History
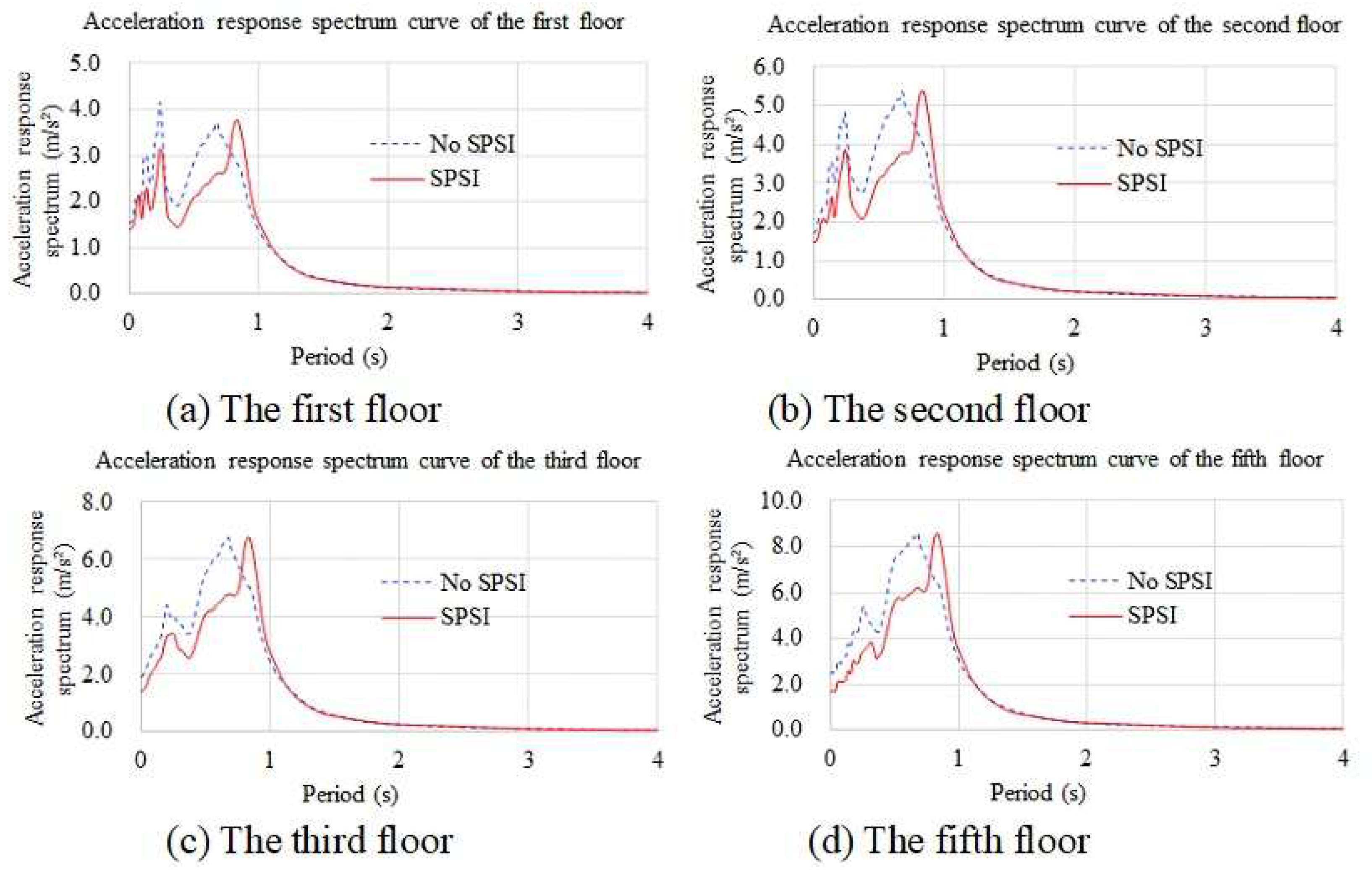
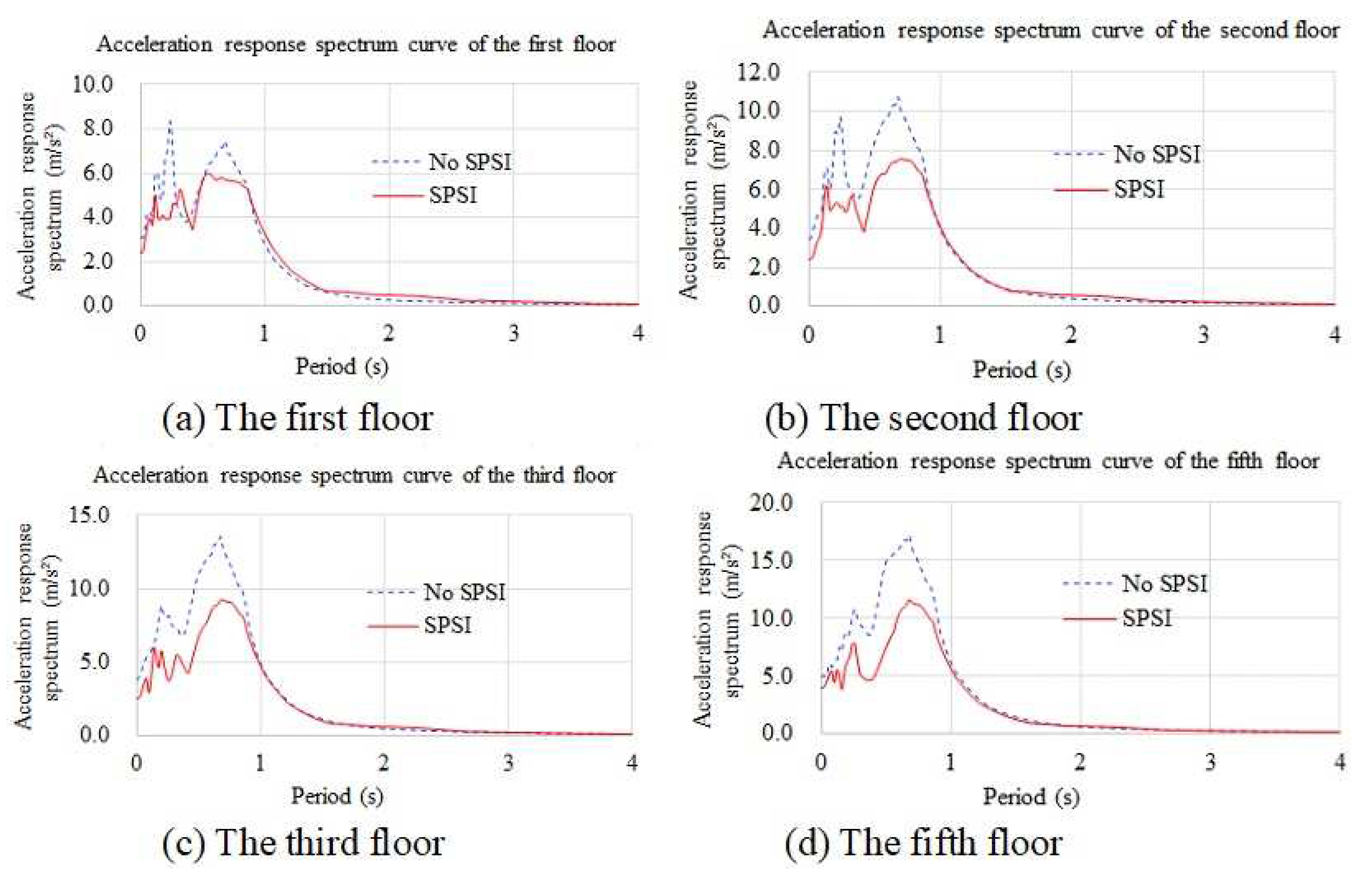
4.3.2. Acceleration Response Spectra
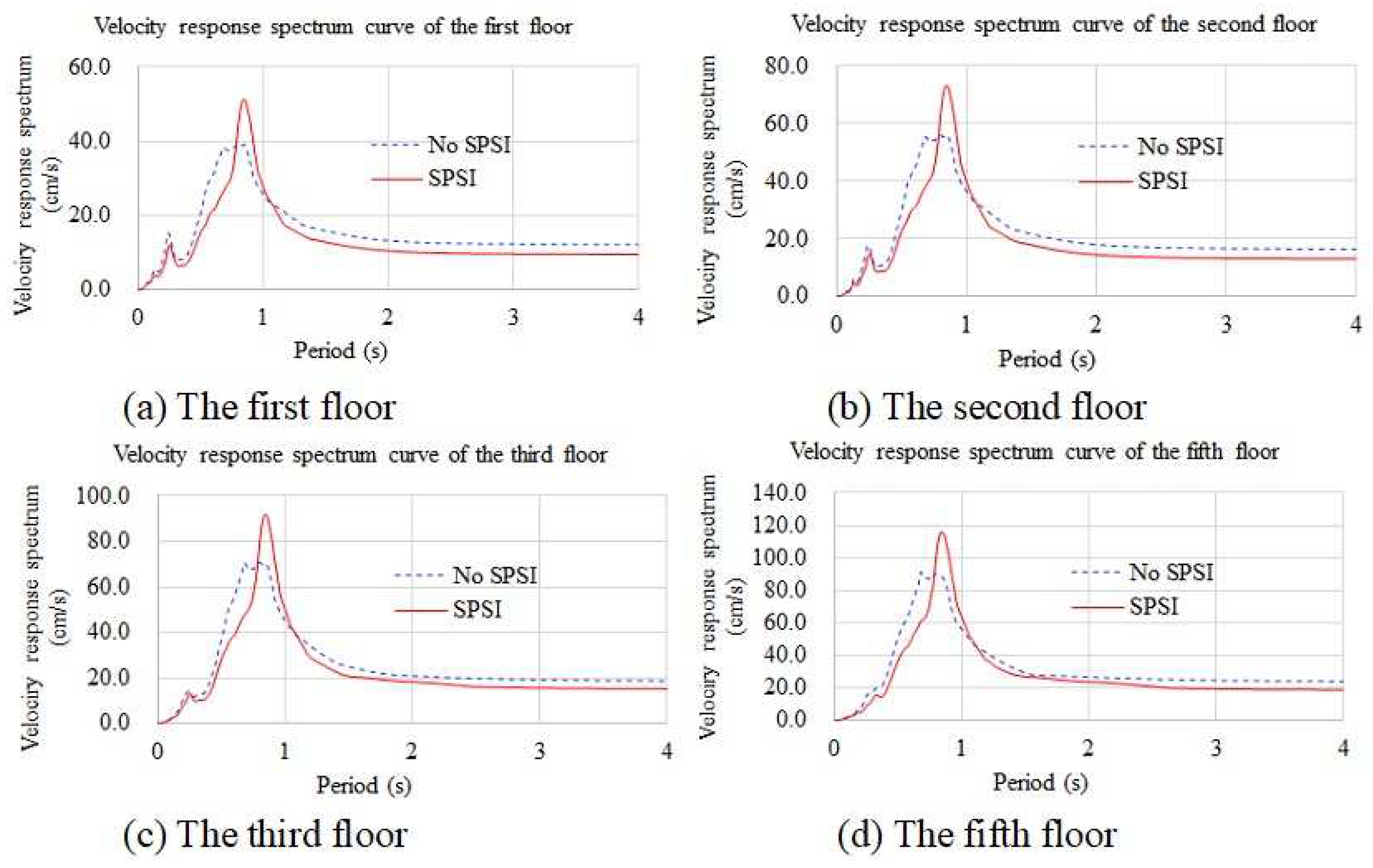
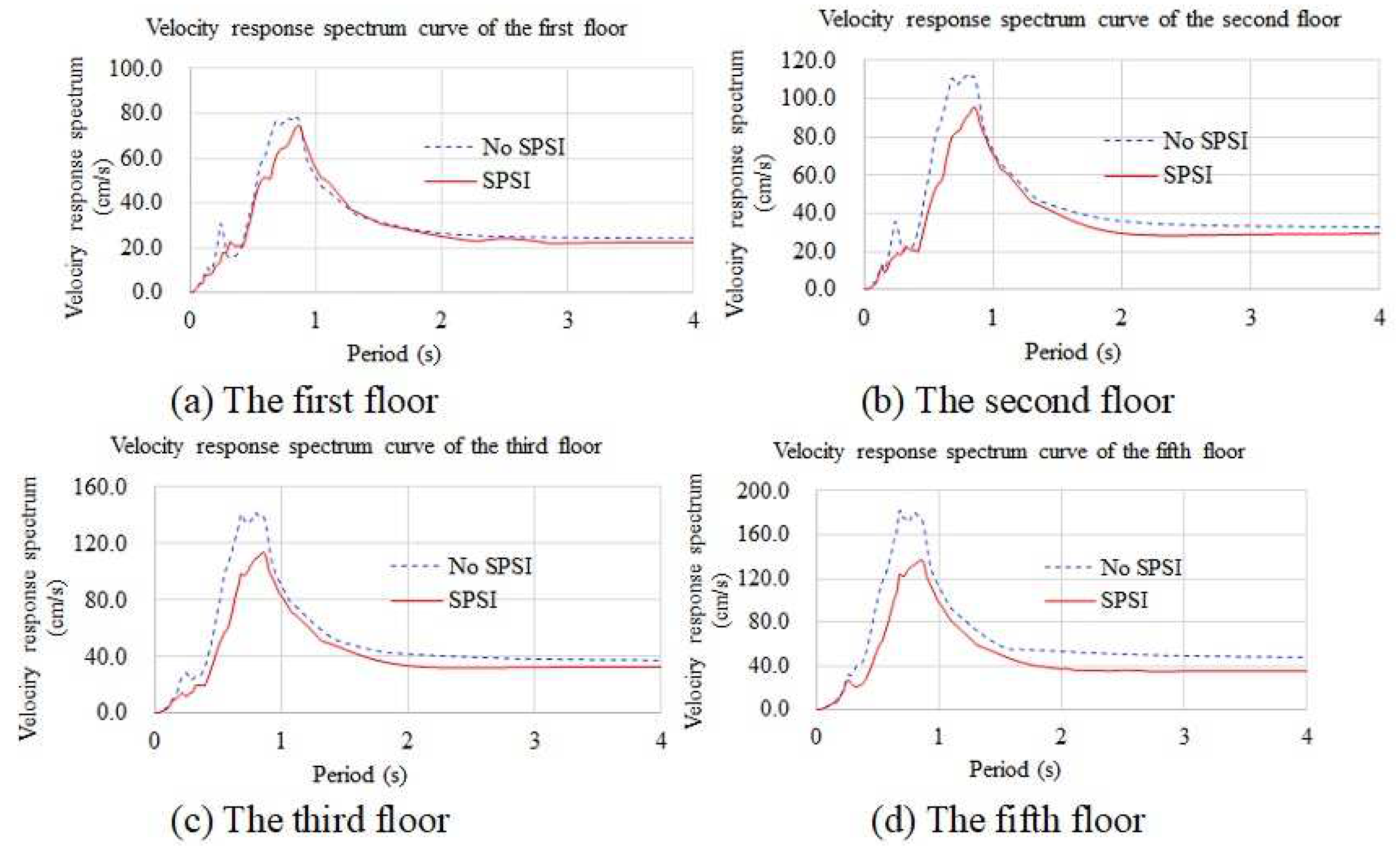
4.3.3. Velocity Response Spectra
4.3.4. Displacement Response Spectra
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NIST GCR 12-917-21; Soil-Structure Interaction for Building Structures. NEHRP Consultants Joint Venture: Gaithersburg, MA, USA, 2012.
- FEMA P-58; Development of Next Generation Performance-Based Seismic Design Procedures for New and Existing Buildings. Federal Emergency Management Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- Chopra, A.K.; Gutierrez, J.A. Earthquake response analysis of multistory buildings including foundation interaction. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1974, 3, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghannad, M.A.; Jahankhah, H. Site-dependent strength reduction factors for soil–structure systems. Soil. Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2007, 27, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnoudian, F.; Ahmadi, E.; Nik, F.A. Inelastic displacement ratios for soil–structure systems. Eng. Struct. 2013, 57, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharad, A.M.; Sonparote, R.S. Study of direct finite element method of analysing soil-structure interaction in a simply supported railway bridge subjected to resonance. IJST-T. Civ. Eng. 2019, 43, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veletsos, A.S.; Verbic, B. Vibration of viscoelastic foundations. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1973, 2, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mita, A.; Yoshida, K.; Kumagai, S.; Shioya, K. Soil structure interaction experiment using impulse-response. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1989, 18, 727–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veletsos, A.S.; Verbic, B. Basic response functions for elastic foundations. J. Eng. Mech. Div.-ASCE 1974, 100, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylonakis, G.; Nikolaou, S.; Gazetas, G. Footings under seismic loading: Analysis and design issues with emphasis on bridge foundations. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2006, 26, 824–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi-Ghoozhdi, H.; Attarnejad, R. The effect of nonlinear soil-structure interaction on the ductility and strength demands of vertically irregular structures. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 18, 1209–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.M.; Ghanbari, A.; Derakhshandi, M. Analytical model for natural frequency of SDOF system considering soil-pile-structure interaction. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 16, 1399–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casciati, S.; Borja, R.L. Dynamic FE analysis of South Memnon Colossus including 3D soil-foundation-structure interaction. Comput. Struct. 2004, 82, 1719–1736. [Google Scholar]
- Amorosi, A.; Boldini, D.; di Lerniac, A. Dynamic soil-structure interaction: A three-dimensional numerical approach and its application to the Lotung case study. Comput. Geotech. 2017, 90, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, P.; Romero, A. A 3D time domain numerical model based on half-space Green’s function for soil-structure interaction analysis. Comput. Mech. 2014, 53, 1073–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.Y.; Du, C.B.; Sun, L.G. Numerical analysis of sheet pile wall structure considering Soil–structure interaction. Geomech. Geoengin. 2018, 16, 309–320. [Google Scholar]
- Sarlak, A.; Saeedmonir, H.; Gheyratmand, C. Numerical and experimental study of soil–structure interaction in structures resting on loose soil using laminar shear box. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2017, 30, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar]
- Kildashti, K.; Dolatshahi, K.M.; Mirghaderi, R. A case study on the soil–pile–structure interaction of a long span arched structure. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2016, 12, 1614–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.S.; Shi, J.Y.; Wu, Y.Y. Numerical damage localisation for building systems including dynamic soil–structure interaction. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2019, 15, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.Z.; Yang, J.P.; Lu, Z. Shaking table test and theoretical analysis of the pile–soil–structure interaction at a liquefiable site. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2018, 27, e1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldimashki, M.M.; Brownjohn, J.M.W.; Bhattacharya, S. Experimental and analytical study of seismic soil–pile–structure interaction in layered soil half-space. J. Earthq. Eng. 2014, 18, 655–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, K.T.; Shen, C.Y.; Guo, X. Nonlinear seismic soil–pile–structure interactions: Shaking table tests and FEM analyses. Soil. Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2009, 29, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martakis, P.; Taeseri, D.; Chatzi, E.; Laue, J. A centrifuge-based experimental verification of Soil–structure Interaction effects. Soil. Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2017, 103, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Trombetta, N.W.; Mason, H.B.; Hutchinson, T.C.; Zupan, J.D.; Bray, J.D.; Kutter, B.L. Nonlinear soil–foundation–structure and structure–soil–structure interaction: Centrifuge test observations. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. 2014, 140, 04013057. [Google Scholar]
- Buenker, J.M.; Brandenberg, S.J.; Stewart, J.P. Centrifuge testing of soil-structure interaction effects on cyclic failure potential of fine-grained soil. Earthq. Spectra 2021, 37, 1177–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisa, M.S.; Salih, T.; Michael, J.G.; George, M.; Jonathan, P.S. Evaluation of soil–structure interaction effects from system identification of structures subject to forced vibration tests. Soil. Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 116, 747–760. [Google Scholar]
- Zangeneh, A.; Svedholm, C.; Andersso, A.; Pacoste, C.; Karoumi, R. Identification of soil–structure interaction effect in a portal frame railway bridge through full-scale dynamic testing. Eng. Struct. 2018, 159, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisa, M.S.; Michael, J.G.; Robert, L.N.; Jonathan, P.S. Field-testing of structure on shallow foundation to evaluate soil–structure interaction effects. Earthq. Spectra 2015, 31, 2511–2534. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.S.; Yun, C.B.; Kim, J.M. Earthquake response analysis of the Hualien soil–structure interaction system based on updated soil properties using forced vibration test data. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2001, 30, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, Y.; Uetake, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Yamaya, H. Forced vibration test of the Hualien large scale soil structure interaction model (part 2). Nucl. Eng. Des. 1997, 172, 273–280. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.B.; Zhao, D.D.; Zhang, X.B.; Wang, W.H. Dynamic centrifuge model tests on an unconfined soil foundation. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2013, 35, 980–987. [Google Scholar]
- Luco, J.E.; Wong, H.L. Forced vibration of the Lotung containment model: Theory and observations. J. Eng. Mech. 1990, 116, 845–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.P.; Fenves, G.L.; Seed, R.B. Seismic soil-structure interaction in buildings II: Empirical findings. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. 1999, 125, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, M.; Takai, H. Use of Substructures in Pseudo Dynamic Testing; Building Research Institute of Japan, Ministry of Construction: Tsukuba, Japan, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Pauschke, J.; Anderson, T.L.; Goldstein, S.N. Construction status of the George E. Brown, Jr. Network for earthquake engineering simulation. In Proceedings of the 7th US National Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Boston, MA, USA, 21–25 July 2002; pp. 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Stojadinovic, B.; Mosqueda, G.; Mahin, S.A. Event-driven control system for geographically distributed hybrid simulation. J. Struct. Eng. 2006, 132, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, K.; Nagata, N.; Suzuka, Y. Internet related structural testing. In Proceedings of the Eighth KKNN Seminar on Civil Engineering, Singapore, 30 November–1 December 1998; pp. 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Takashi, Y.; Kazutoshi, N.; Eiichi, W. International collaborative pseudo dynamic testing method for continuous elevated bridges by using Internet. Adv. Exp. Struct. Eng. 2005, 18, 371–376. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.S.; Wang, K.J.; Wang, S.J.; Hsu, C.W.; Tsai, K.C.; Hsien, S.H. Networked pseudo-dynamic testing part I: Database approach. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2007, 36, 2291–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Wang, K.J.; Yang, Y.S.; Cheng, W.C.; Yeh, C.C.; Tsai, K.C. Networked pseudo-dynamic testing part II: Application protocol Approach. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2007, 36, 2307–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.S.; Wang, S.J.; Wang, K.J.; Tsai, K.C.; Hsien, S.H. ISEE: Internet-based Simulations for earthquake engineering, Part I: The database approach. In Proceeding of the 13th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1–6 August 2004; p. 1910. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.J.; Wang, S.J.; Yang, Y.S.; Cheng, W.C.; Tsai, K.C. ISEE: Internet-based simulations for earthquake engineering, Part II: The application protocol approach. In Proceeding of the 13th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1–6 August 2004; p. 1548. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Hu, Q.; Guo, Y.R.; Yi, W.J.; Zhu, P.S. A network platform for remote pseudo-dynamic testing. J. Build. Struct. 2005, 2, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.R.; Zeng, D.; Xiao, Y. Development of a remotely collaborative pseudo-dynamic testing platform for bridge structures. J. Hunan Univ. Nat. Sci. 2009, 36, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kohh, H.H.; Tsai, K.C.; Tsai, C.Y.; Tsai, C.Y.; Wang, K.J. Bidirectional substructure pseudo-dynamic tests and analysis of a full-scale two-story buckling-restrained braced frame. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2016, 45, 1085–1107. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.X.; Xu, G.S.; Wu, B.; Sun, Y.T.; Wang, H.D.; Wang, F.L. Equivalent force control method for substructure pseudo-dynamic test of a full-scale masonry structure. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2014, 43, 969–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.S.; Elnashai, A.S.; Spencer, B.F. A framework for distributed analytical and hybrid simulations. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2008, 30, 331–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Kim, J.K. Pseudo-dynamic test for soil–structure interaction analysis using shake tables. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 23, 2313–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lysmer, J.; Westman, R.A. Dynamic response of footing to vertical loading. J. Soil Mech. Found. Div. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1996, 92, 1965–1991. [Google Scholar]
- McClelland, B.; Focht, J.A.J. Soil modulus for laterally loaded piles. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1958, 123, 1049–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penzien, J.; Scheffy, C. Seismic analysis of bridge on long piles. J. Eng. Mech. 1964, 90, 223–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.H.; Huang, K.; Wang, L.Y. Vibration control of adjacent buildings considering pile-soil-structure interaction. J. Vib. Control 2011, 18, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.H.; Fang, L.K.; Huang, K.; Wang, L.Y. Vibration Control of Soil-structure Systems and Pile-soil-structure Systems. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2012, 16, 794–802. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, L.; Zhao, R.X. Analysis of Long-period Seismic Response of Long-span Cable-stayed Bridge Considering Soil-structure Interaction. J. Highw. Transp. Res. Dev. 2012, 9, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Clough, R.W.; Penzien, J. Dynamics of Structures; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, S.L.; Dai, G.L.; Yu, Z.W.; Chen, F.; He, X.H. Interaction between continuous welded rail and long-span steel truss arch bridge of a high-speed railway under seismic action. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2018, 14, 1051–1064. [Google Scholar]
- Idriss, I.M.; Sun, I.J. User’s Manual for SHAKE91: A Computer Program for Conducting Equivalent Linear Seismic Response Analyses of Horizontally Layered Soil Deposits; Center for Geotechnical Modeling, Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering, University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.Y. Theoretical Model Study and Parameter Analysis of Pile-Soil-Structure Dynamic Interaction; Tongji University: Shanghai, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Q.; Xiong, F.; Xie, L.W.; Chen, J.; Yu, M.J. Dynamic interaction of soil-structure cluster. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 123, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Xiong, F.; Chen, J.; Yao, Z.Y. Effects of soil–structure cluster interactions on ground motions. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2020, 29, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idriss, I.M.; Seed, H.B. Seismic response of horizontal soil layers. Am. Soc. Civil Engr. J. Soil Mech. 1968, 94, 1003–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed, H.B.; Idriss, I.M. Soil Moduli and Damping Factors for Dynamic Response Analysis; Report No. EERC70-10; Earthquake Engineering Research Center, University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Hardin, B.O.; Drnevich, V.P. Shear modulus and damping in soils: Design equations and curves. J. Soil Mech. Found. Div. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1972, 98, 667–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.P. Nonlinear Method for Dynamic Analysis of Ground Response. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, P.P.; Seed, H.B. One-dimensional dynamic ground response analyses. ASCE J. Soil Mech. Found. Div. 1982, 108, 935–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Lv, X.L.; Li, P.Z.; Chen, Y.Q. Modelling of dynamic Soil–structure interaction by ANSYS program. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 2002, 22, 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Q.; Xiong, F.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J. Shaking table test of dynamic interaction of soil–high-rise buildings. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2017, 21, 249–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.X.; Liu, X.Z. Experimental study on dynamic shear modulus and damping ratio of recently deposited soils in Nanjing and its neighboring areas. J. Disaster Prev. Mitig. 2014, 24, 168–176. [Google Scholar]
- Lysmer, J.; Udaka, T.; Tsai, C.F. A Computer Program for Approximate 3-D Analysis of Soil-Structure Interaction Problems; Report No. EERC 75-30; Earthquake Engineering Research Center, College of Engineering, University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.C.; Du, Y.P. Seismic response analysis of TV tower-pile-soil interaction system. China Civ. Eng. J. 1991, 24, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, A.K. Dynamics of Structures: Theory and Applications to Earthquake Engineering, 4th ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- GB50010-2010; Code for Seismic Design of Buildings (2016 Version). China Architecture and Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2010.
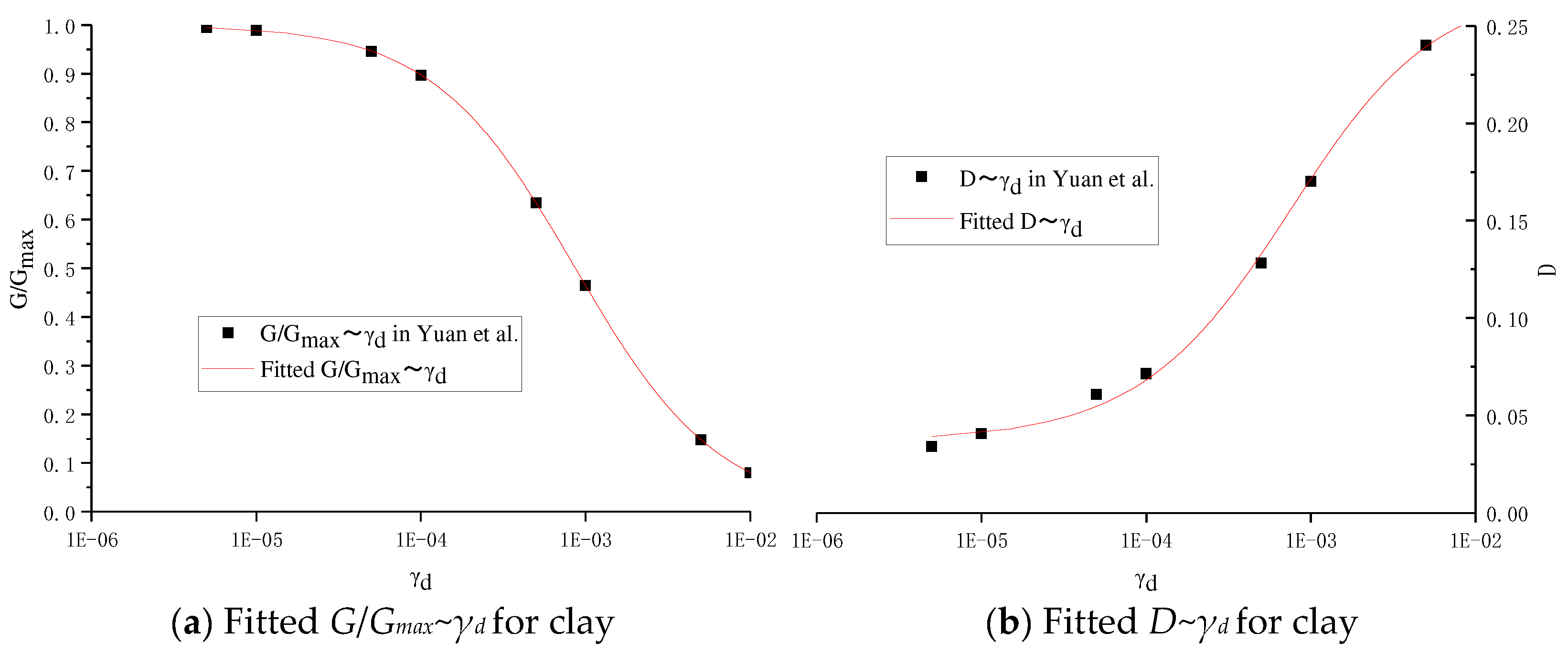
- Yuan, X.M.; Sun, R.; Sun, J.; Meng, S.J.; Shi, Z.J. Laboratory experimental study on dynamic shear modulus ratio and damping ratio of soils. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 2000, 20, 133–139. [Google Scholar]


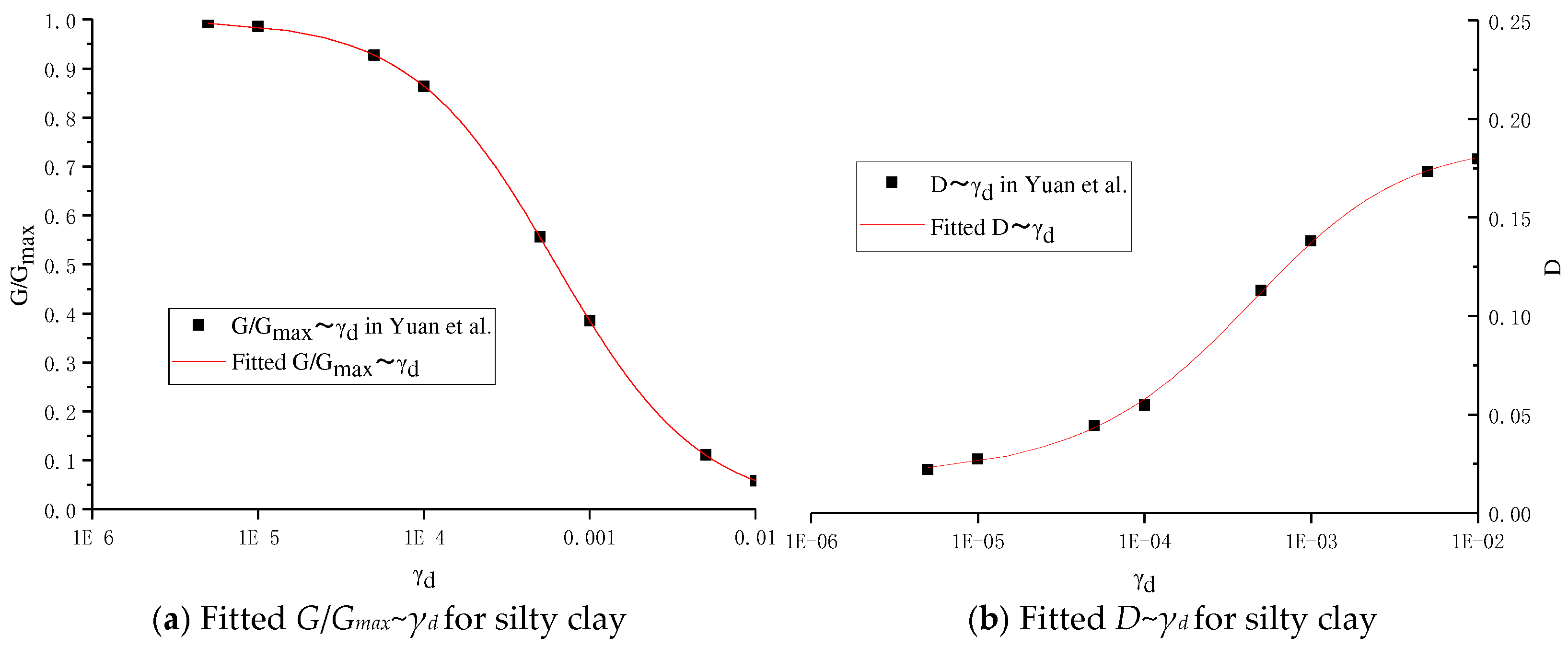
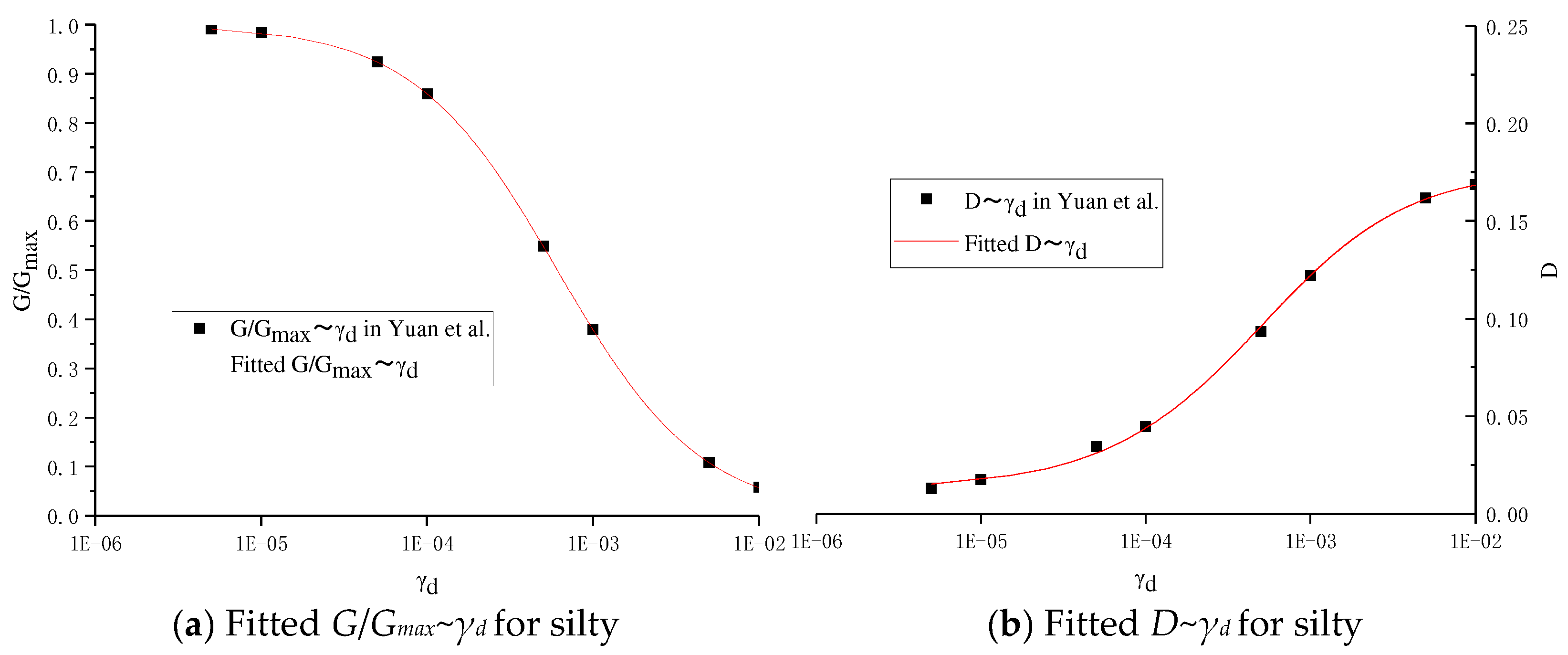

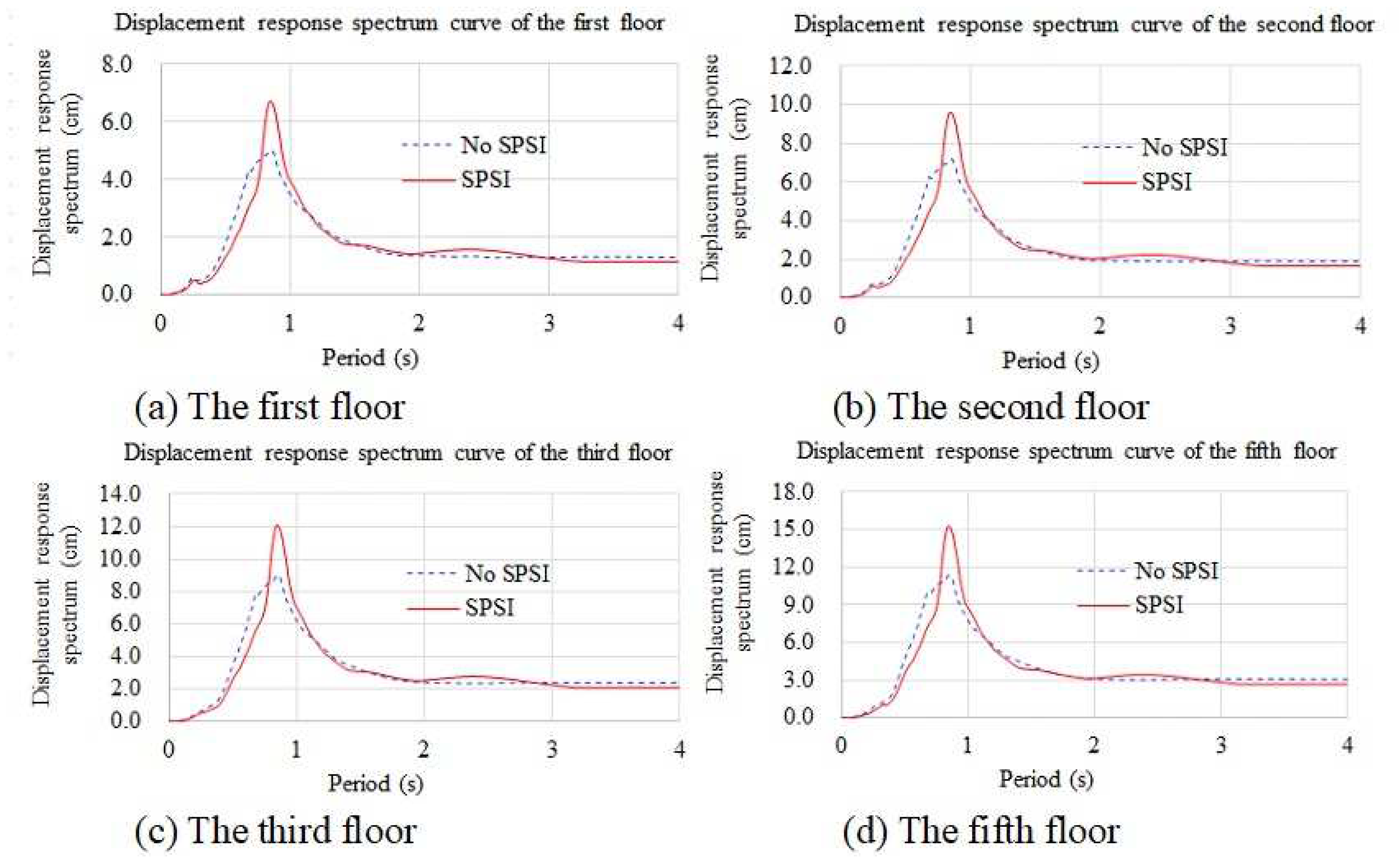
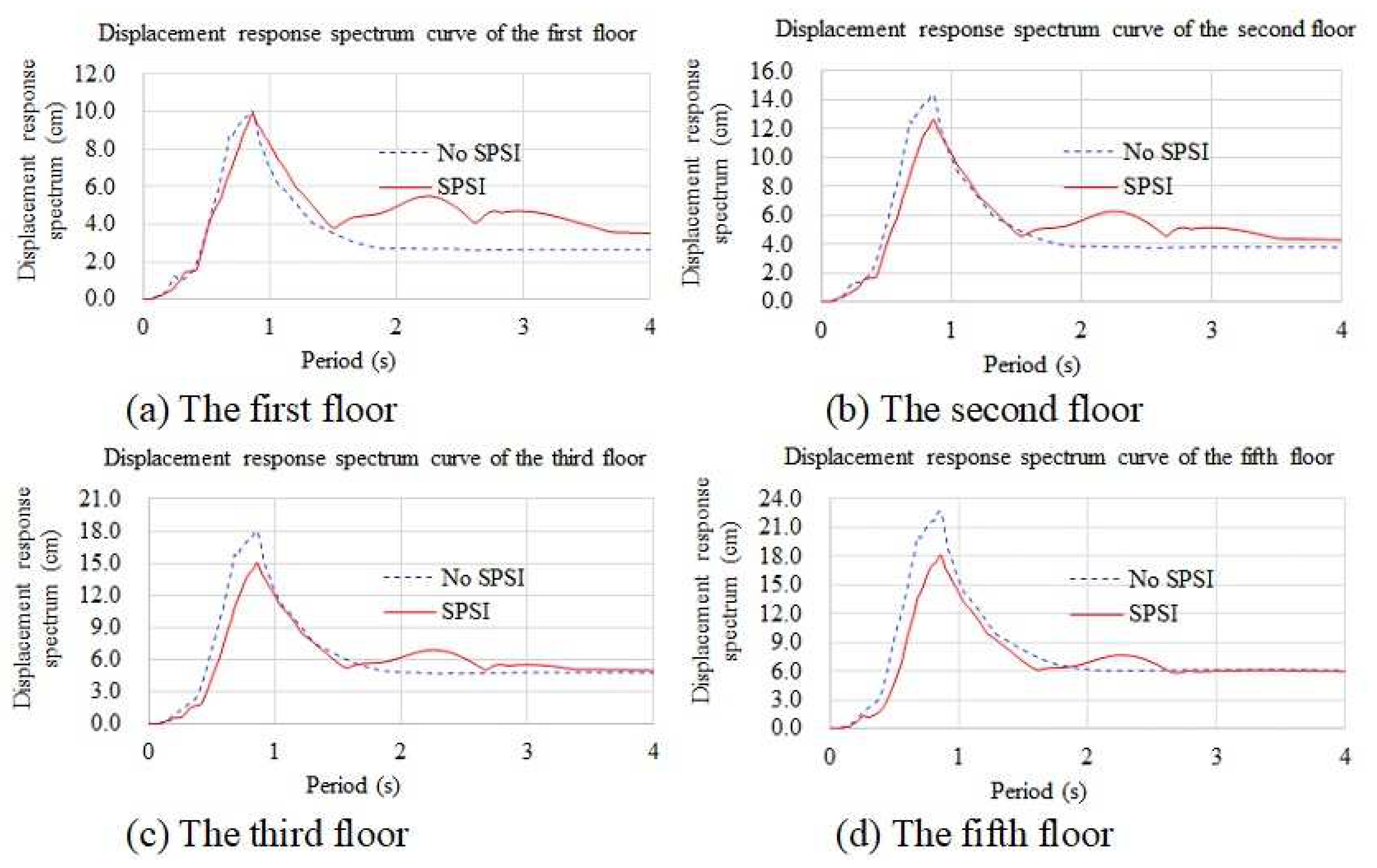
| Soil Type | Height (m) | Shear Wave Velocity m/s | Density (kg/m3) | Poisson’s Ratio | Damping Ratio | Shear Modulus (MPa) | Elasticity Modulus (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clay | 4 | 135 | 1980 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 20 | 48.8 |
| Silty clay | 4 | 210 | 2010 | 0.24 | 0.01 | 39 | 96.7 |
| Silty | 8 | 330 | 2010 | 0.26 | 0.01 | 56 | 141.1 |
| Soil Type | Parameter | Shear Strain γ (10−4) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 1 | 5 | 10 | 50 | 100 | ||
| Clay | G/Gmax | 0.9954 | 0.9897 | 0.9465 | 0.8975 | 0.6347 | 0.4647 | 0.1478 | 0.0798 |
| D | 0.0342 | 0.0408 | 0.0608 | 0.0716 | 0.1284 | 0.1703 | 0.2402 | 0.2543 | |
| Silty clay | G/Gmax | 0.9936 | 0.9858 | 0.9274 | 0.8634 | 0.5563 | 0.3851 | 0.1112 | 0.0589 |
| D | 0.0223 | 0.0276 | 0.0447 | 0.0549 | 0.1131 | 0.1383 | 0.1735 | 0.1798 | |
| Silty | G/Gmax | 0.9919 | 0.9839 | 0.9242 | 0.8591 | 0.5495 | 0.3788 | 0.1087 | 0.0575 |
| D | 0.0129 | 0.0174 | 0.0342 | 0.0445 | 0.0934 | 0.1220 | 0.1620 | 0.1689 | |
| Soil Type | A | B | γ | Dmin | D0 | β |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clay | 1.01712 | 0.49852 | 8.47 × 10−4 | 0.03699 | 0.23288 | 0.88074 |
| Silty clay | 1.02237 | 0.49812 | 6.07 × 10−4 | 0.01833 | 0.16941 | 0.72872 |
| Silty | 1.00003 | 0.49998 | 6.10 × 10−4 | 0.01235 | 0.16416 | 0.84408 |
| Floor | Acceleration (m/s2) (for Input 0.1 g) | Difference (%) | Acceleration (m/s2) (for Input 0.2 g) | Difference (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPSI | No SPSI | SPSI | No SPSI | |||
| 6 | 1.823 | 2.657 | −31 | 4.453 | 5.319 | −16 |
| 5 | 1.686 | 2.466 | −32 | 3.978 | 4.933 | −19 |
| 4 | 1.551 | 2.214 | −30 | 3.214 | 4.427 | −27 |
| 3 | 1.402 | 1.914 | −27 | 2.554 | 3.833 | −33 |
| 2 | 1.470 | 1.722 | −15 | 2.406 | 3.446 | −30 |
| 1 | 1.399 | 1.539 | −9 | 2.412 | 3.080 | −22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, Q.; Zheng, T.; Xiong, F.; Ran, M.; Chen, J.; Lu, Y. Substructure Pseudo-Dynamic Test Study for a Structure Including Soil–Pile–Structure Dynamic Interaction. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116709
Ge Q, Zheng T, Xiong F, Ran M, Chen J, Lu Y. Substructure Pseudo-Dynamic Test Study for a Structure Including Soil–Pile–Structure Dynamic Interaction. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(11):6709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116709
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Qi, Tiancai Zheng, Feng Xiong, Mingming Ran, Jiang Chen, and Yang Lu. 2023. "Substructure Pseudo-Dynamic Test Study for a Structure Including Soil–Pile–Structure Dynamic Interaction" Applied Sciences 13, no. 11: 6709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116709
APA StyleGe, Q., Zheng, T., Xiong, F., Ran, M., Chen, J., & Lu, Y. (2023). Substructure Pseudo-Dynamic Test Study for a Structure Including Soil–Pile–Structure Dynamic Interaction. Applied Sciences, 13(11), 6709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116709






