A Non-Linear Non-Planar Coupling Mechanism of Suspended Cables in Thermal Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
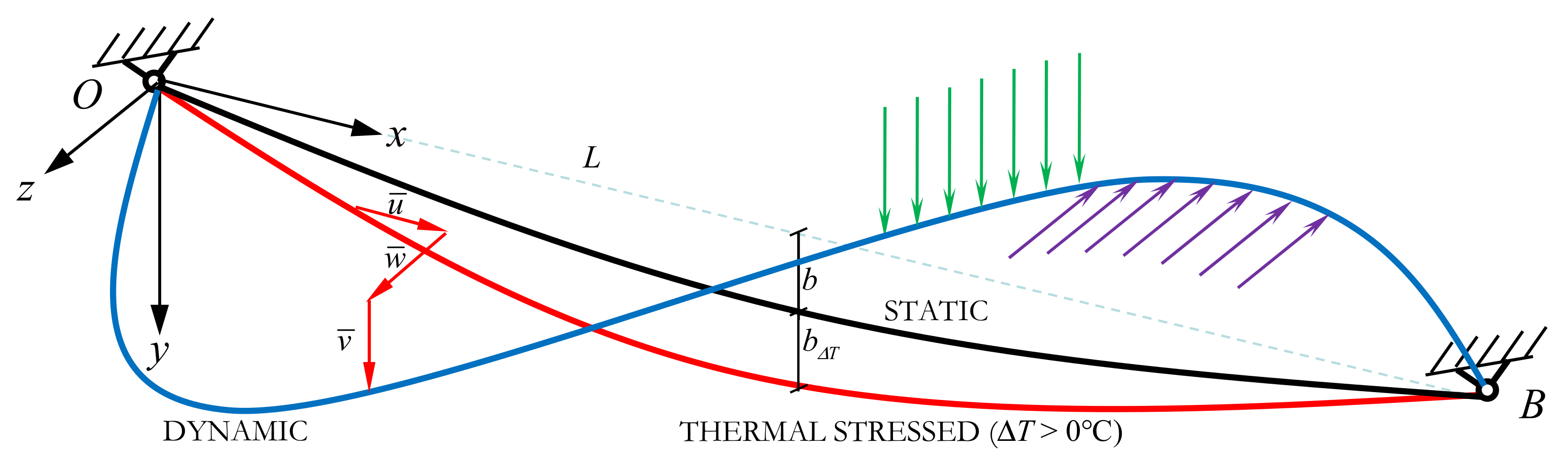
2. Mathematical Modeling and Equations
3. Perturbation Analysis and Modulation Equations
4. Numerical Examples and Illustrations
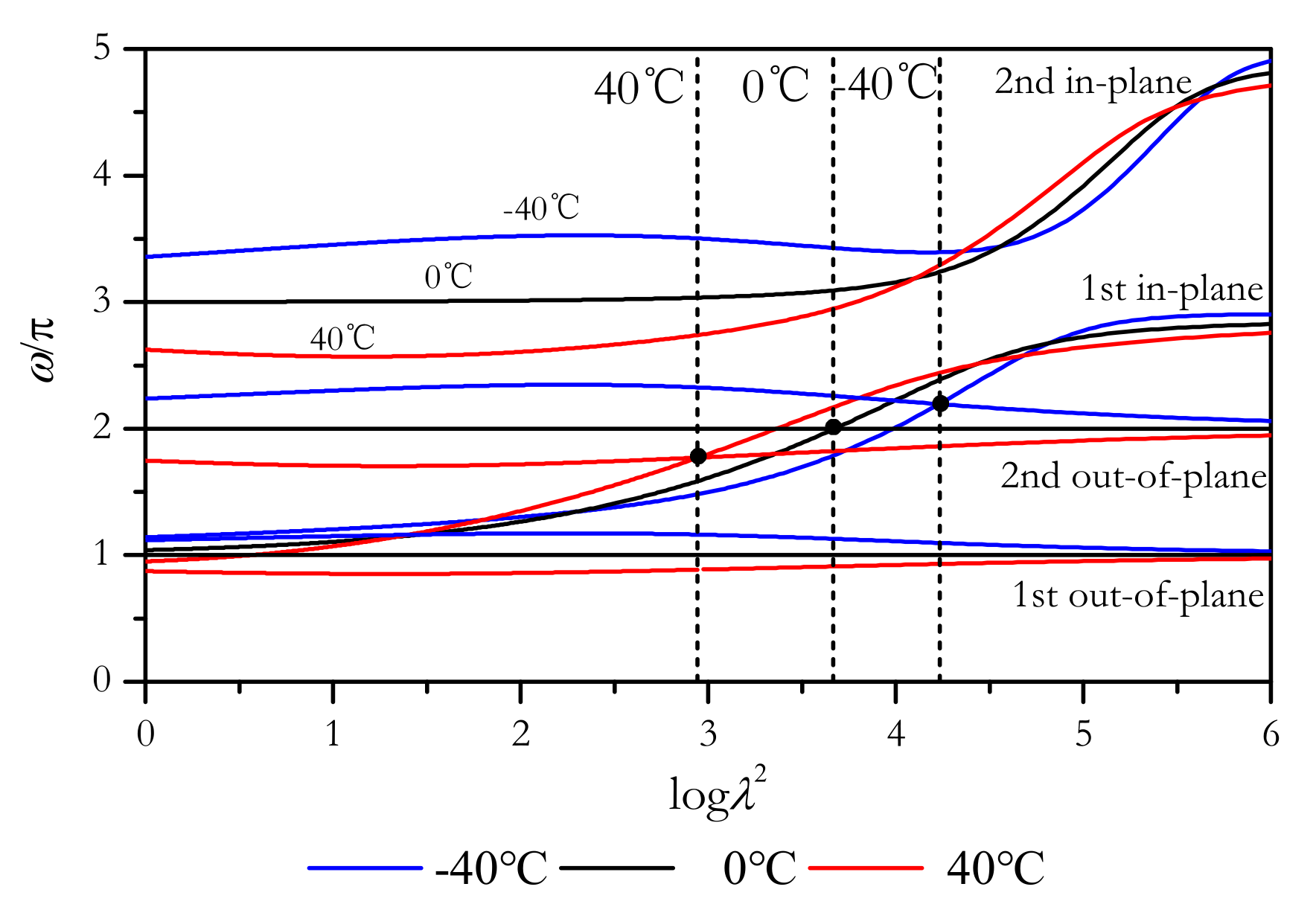
4.1. Parameters and Coefficients
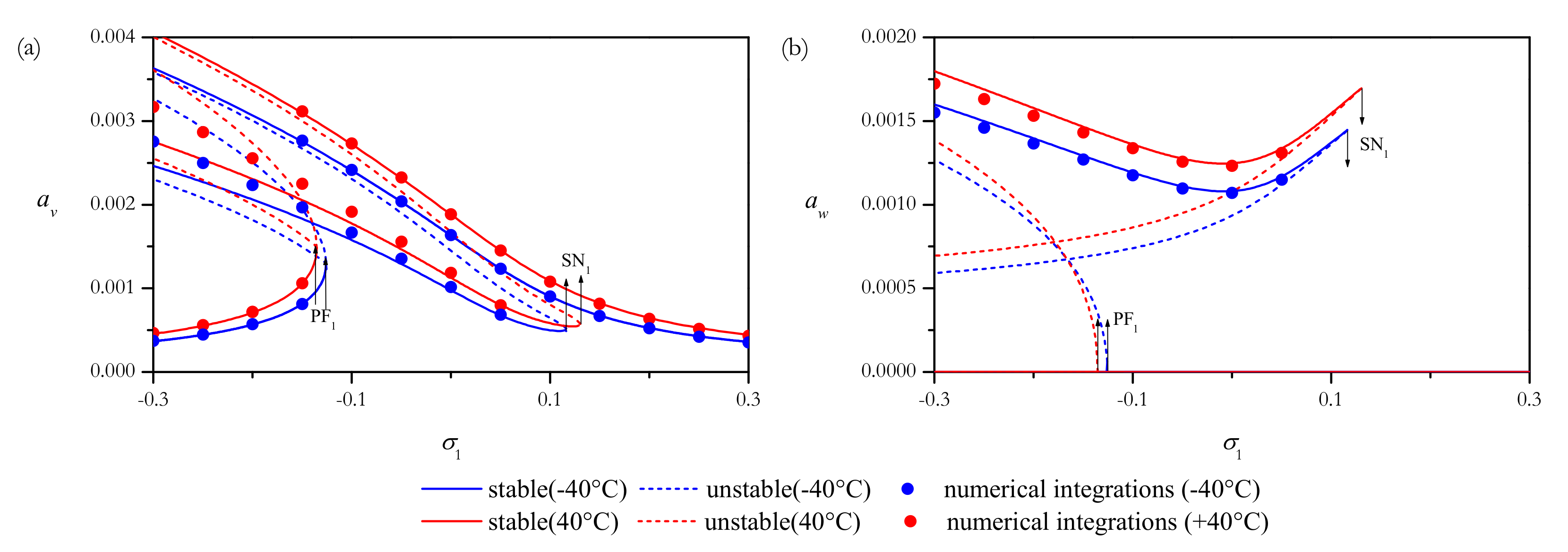
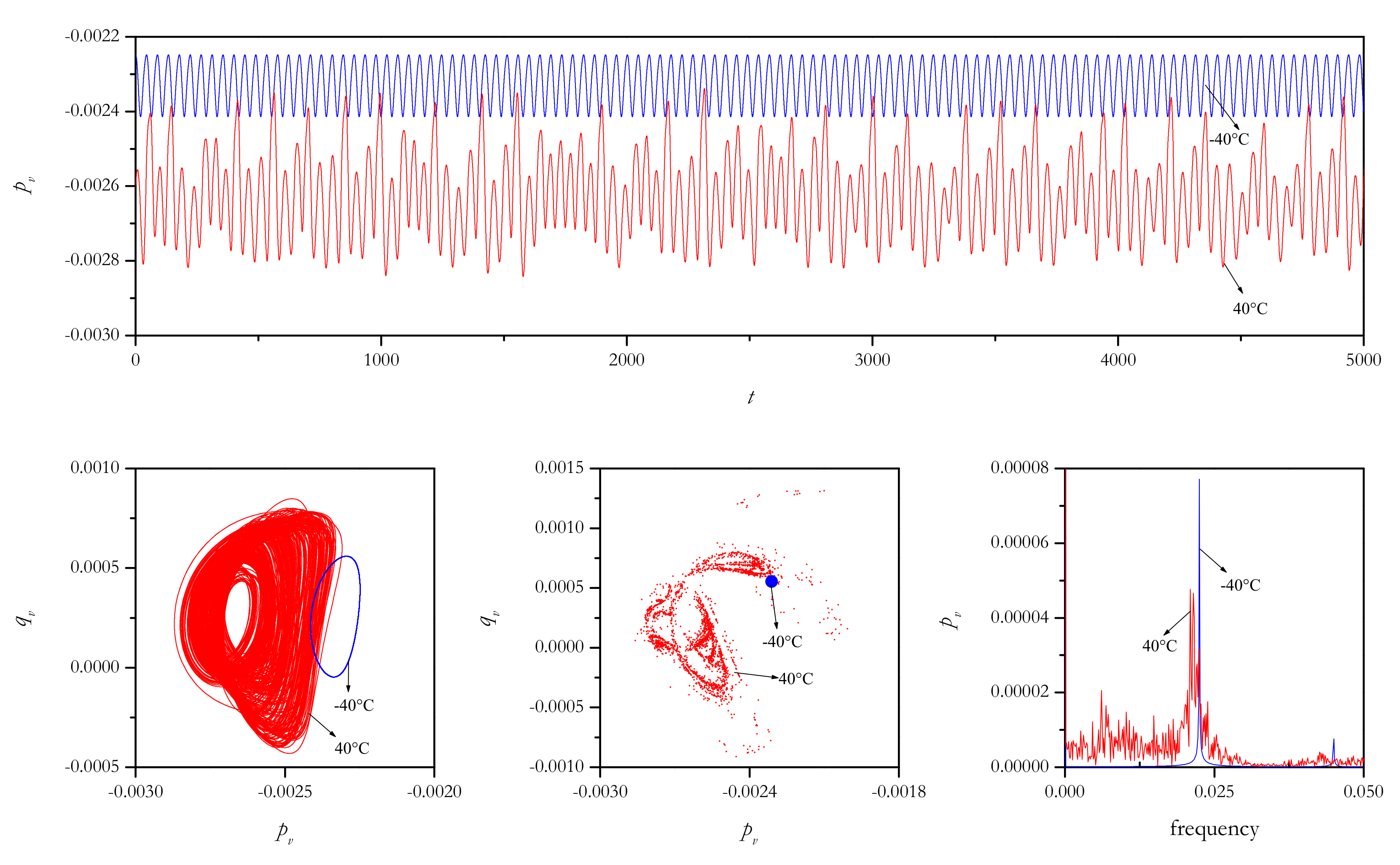
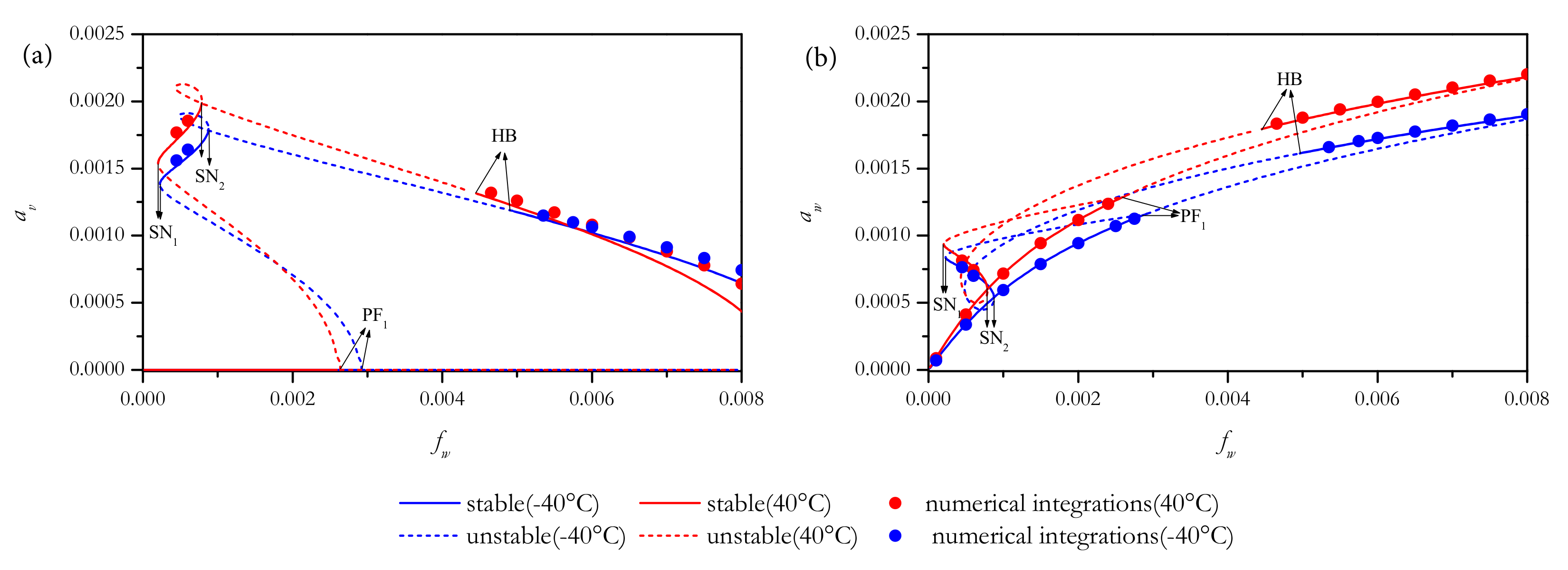
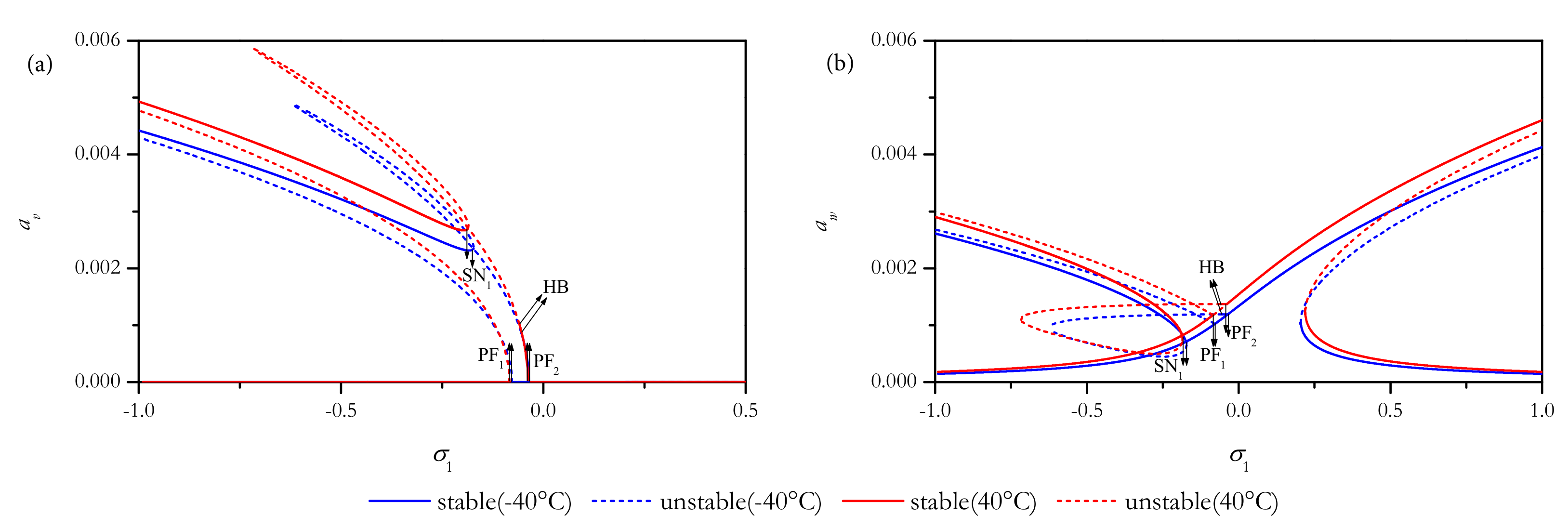
4.2. Bifurcation and Stability Analysis
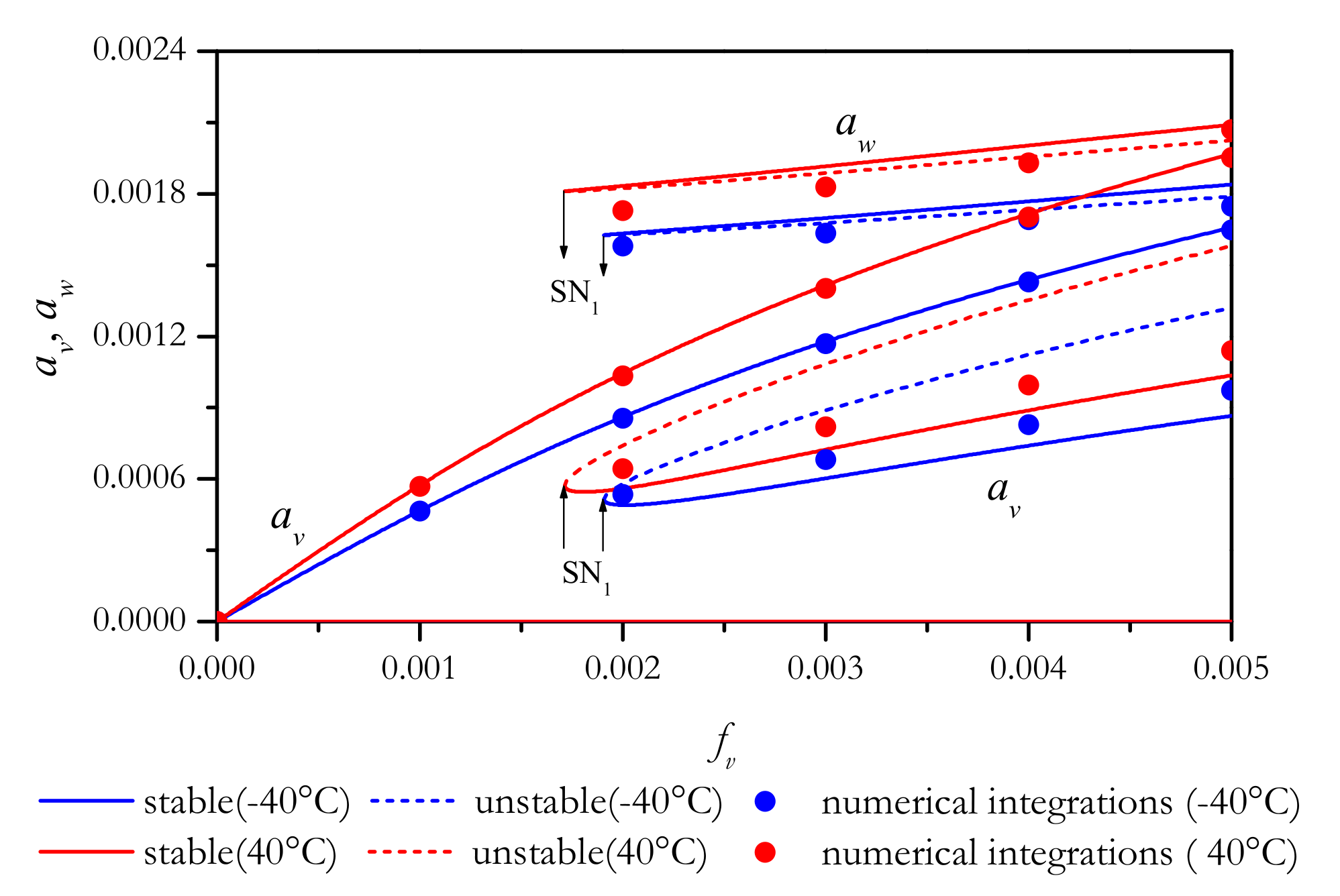
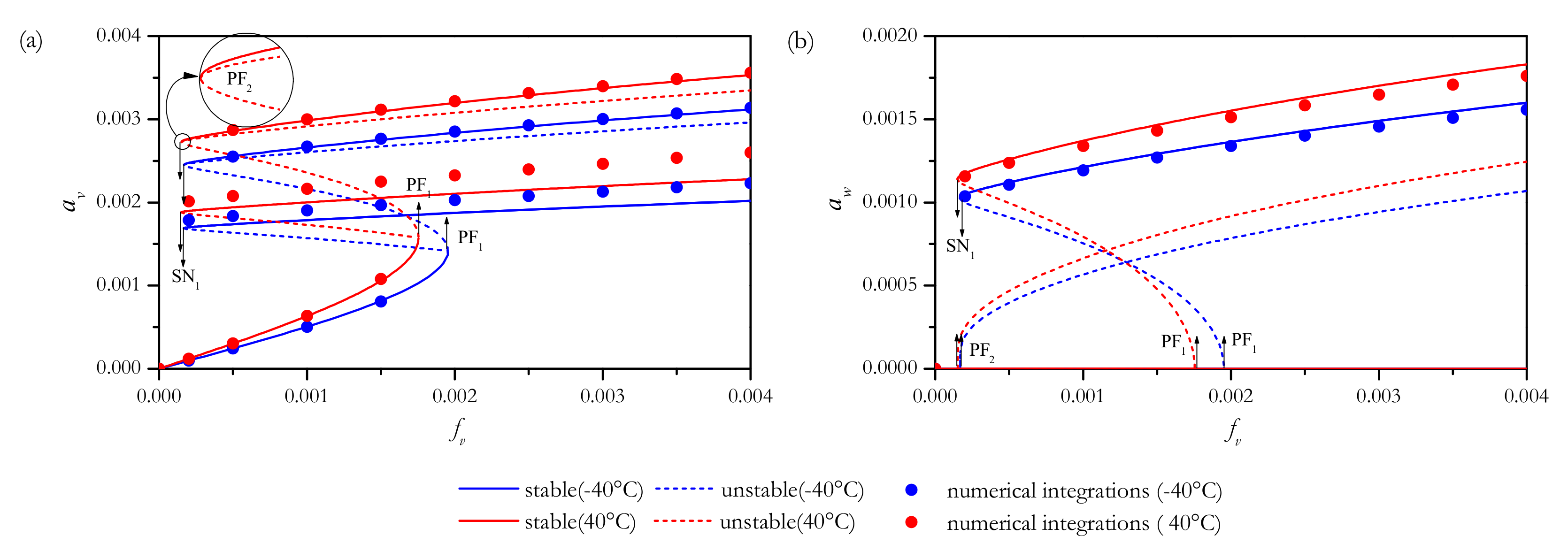
4.2.1. In-Plane Excitations
4.2.2. Out-of-Plane Excitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
Appendix C
References
- Warminski, J.; Zulli, D. Revisited modelling and multimodal non-linear oscillations of a sagged cable under support motion. Meccanica 2016, 51, 2541–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z. Stanciulescu I. Non-linear normal modes of a shallow arch with elastic constraints for two-to-one internal resonances. Non-Linear Dyn. 2016, 83, 1577–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Guo, T.; Kang, H.; Zhao, Y. An asymptotic study of non-linear coupled vibration of arch-foundation structural system. Eur. J. Mech. Solid. 2022, 96, 104711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Xiang, M.; Wang, L.; Xie, X.; Sun, H.; Yu, J. Non-linear primary resonance in vibration control of cable-stayed beam with time delay feedback. Mech. Sys. Sig. Proc. 2020, 137, 106488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.; Kang, H.; Yan, G.; Guo, T. Modeling, dynamics, and parametric studies of a multi-cable-stayed beam model. Acta Mech. 2020, 231, 4947–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattulli, V.; Lepidi, M.; Potenza, F.; Sabatino, U.D. Modal interactions in the non-linear dynamics of a beam-cable-beam. Non-Linear Dyn. 2019, 96, 2547–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Jiao, D.; Lin, J.; Li, C.; Tan, C. Modal characteristics of sagged-cable-crosstie systems. Part 1: Modeling and validation. Appl. Math. Model. 2023, 119, 698–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, W.; Jiao, D.; Li, C. Modal characteristics of sagged-cable-crosstie systems. Part 2: Parametric analysis. Appl. Math. Model. 2023, 119, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, T.; Yao, S. Non-linear dynamic analysis of space cable net structures with one to one internal resonances. Non-Linear Dyn. 2014, 78, 1461–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rega, G. Non-linear vibrations of suspended cables Part I: Modeling and analysis. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2004, 57, 443–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinil, N.; Rega, G.; Chucheepsakul, S. Large amplitude three-dimensional free vibrations of inclined sagged elastic cables. Non-Linear Dyn. 2003, 33, 129–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rega, G. Non-linear vibrations of suspended cables, Part II: Deterministic phenomena. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2004, 57, 479–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, N.C. Modal interactions in the non-linear response of elastic cables under parametric/external excitation. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 1992, 27, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedettini, F.; Rega, G.; Alaggio, R. Non-linear oscillations of a four-degree-of-freedom model of a suspended cable under multiple internal resonance conditions. J. Sound Vib. 1995, 182, 775–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakdemirli, M.; Nayfeh, S.A.; Nayfeh, A.H. Analysis of one-to-one autoparametric resonances in cables—Discretization vs. direct treatment. Non-Linear Dyn. 1995, 8, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Perkins, N.C. Three-dimensional oscillations of suspended cables involving simultaneous internal resonances. Non-Linear Dyn. 1995, 8, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rega, G.; Lacarbonara, W.; Nayfeh, A.H.; Chin, C.M. Multiple resonances in suspended cables: Direct versus reduced-order models. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 1999, 34, 901–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayfeh, A.H.; Chin, C.M.; Lacarbonara, W. Multimode interactions in suspended cables. J. Vib. Control 2002, 8, 337–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattulli, V.; Martinelli, L.; Perotti, F.; Vestroni, F. Non-linear oscillations of cables under harmonic loading using analytical and finite element models. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2004, 193, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlioz, A.; Lamarque, C.-H. A non-linear model for the dynamics of an inclined cable. J. Sound Vib. 2005, 279, 619–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinil, N.; Rega, G. The effects of kinematic condensation on internally resonant forced vibrations of shallow horizontal cables. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2007, 42, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Buelga, A.; Neild, S.A.; Wagg, D.J.; Macdonald, J.H.G. Modal stability of inclined cables subjected to vertical support excitation. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 318, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, A. Validity and accuracy of solutions for non-linear vibration analyses of suspended cables with one-to-one internal resonance. Non-Linear Anal. Real World Appl. 2010, 11, 2594–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luongo, A.; Zulli, D. Dynamic instability of inclined cables under combined wind flow and support motion. Non-Linear Dyn. 2012, 67, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Kang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y. Cable’s non-planar coupled vibrations under asynchronous out-of-plane support motions: Travelling wave effect. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2016, 86, 1647–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, J.H.G. Multi-modal vibration amplitudes of taut inclined cables due to direct and/or parametric excitation. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 363, 473–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulli, D.; Piccardo, G.; Luongo, A. On the non-linear effects of the mean wind force on the galloping onset in shallow cables. Non-Linear Dyn. 2021, 103, 3127–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayfeh, A.H. Non-linear Interactions: Analytical, Computational, and Experimental Method; Wiley Series in Non-linear Science; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Manevich, A.I.; Manevich, L.I. The Mechanics of Non-linear Systems with Internal Resonances; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Chen, B.; Weng, S.; Ni, Y.Q.; Xu, Y.L. Temperature effect on the vibration properties of civil structures: A literature review and case studies. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2012, 2, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treyssède, F. Finite element modeling of temperature load effects on the vibration of local modes in multi-cable structures. J. Sound Vib. 2018, 413, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ni, Y.Q.; Ko, J.M. Eliminating temperature effect in vibration-based structural damage detection. J. Eng. Mech. 2011, 137, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Xu, H.; Munkhbaatar, T.; Li, S. An accurate frequency-based method for identifying cable tension while considering environmental temperature variation. J. Sound Vib. 2021, 490, 115693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montassar, S.; Mekki, O.B.; Vairo, G. On the effects of uniform temperature variations on stay cables. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2015, 5, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepidi, M.; Gattulli, V. Static and dynamic response of elastic suspended cables with thermal effects. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2012, 49, 1103–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaanani, N.; Marcuzzi, P. Finite difference thermoelastic analysis of suspended cables including extensibility and large sag effects. J. Therm. Stress. 2011, 34, 18–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treyssède, F. Free linear vibrations of cables under thermal stress. J. Sound Vib. 2009, 327, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L. Effects of temperature variations on non-linear planar free and forced oscillations at primary resonances of suspended cables. Non-Linear Dyn. 2017, 89, 2815–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, L.; Peng, J. Non-linear vibration behaviors of suspended cables under two-frequency excitation with temperature effects. J. Sound Vib. 2018, 416, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, L. Non-linear planar secondary resonance analyses of suspended cables with thermal effects. J. Therm. Stress. 2019, 42, 1515–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zheng, P. Parameter analyses of suspended cables subjected to simultaneous combination, super and sub-harmonic excitations. Steel Compos. Struct. 2021, 40, 203–216. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, P.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, L. Revisited modeling and non-linear oscillation behaviors of multi-segment damaged suspended cables in thermal environments. Meccanica 2022, 57, 1831–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zheng, P.; Lin, H.; Chen, L. Non-linear coupled dynamics of suspended cables due to crossover points shifting and symmetry breaking. Eur. J. Mech. A-Solid. 2023, 99, 104921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lin, H. Non-linear dynamics of suspended cables in thermal environments under periodic excitation: Two-to-one internal resonance. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos. 2021, 31, 2150153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacarbonara, W.; Rega, G.; Nayfeh, A.H. Resonant nonliear normal modes. Part I: Analytical treatment for structural one-dimensional systems. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2003, 38, 851–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacarbonara, W.; Rega, G. Resonant nonliear normal modes. Part II: Activation/orthogonality conditions for shallow structural systems. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2003, 38, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermentrout, B. Simulating, Analyzing, and Animating Dynamical Systems: A Guide to XPPAUT fro Researchers and Students; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]

| Parameter (Unit) | Value |
|---|---|
| Density (kg/m) | 7800 |
| Area of cross-section A (m) | |
| Young’s modulus E (Pa) | |
| Thermal expansion coefficient (1/C) | |
| Cable span L (m) | 200 |
| Damping ratio / (1) | 0.005/0.006 |
| Temperature variations (C) | ±40 |
| C | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −40 | −5295 | −196,781 | −590,337 | −10,590 | −590,337 | −1,770,990 | |||
| 0 | −4402 | −4402 | −163,579 | −490,736 | −8803 | −490,736 | −1,472,200 | ||
| 40 | −3452 | −3452 | −128,293 | −384,875 | −6904 | −384,875 | −1,154,610 |
| C | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | |||||
| 40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Z.; Lin, H.; Ni, W.; Zhao, Y. A Non-Linear Non-Planar Coupling Mechanism of Suspended Cables in Thermal Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6646. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116646
Guo Z, Lin H, Ni W, Zhao Y. A Non-Linear Non-Planar Coupling Mechanism of Suspended Cables in Thermal Conditions. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(11):6646. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116646
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Zhirui, Henghui Lin, Weilong Ni, and Yaobing Zhao. 2023. "A Non-Linear Non-Planar Coupling Mechanism of Suspended Cables in Thermal Conditions" Applied Sciences 13, no. 11: 6646. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116646
APA StyleGuo, Z., Lin, H., Ni, W., & Zhao, Y. (2023). A Non-Linear Non-Planar Coupling Mechanism of Suspended Cables in Thermal Conditions. Applied Sciences, 13(11), 6646. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116646






