Recognizing Urban Functional Zones by GF-7 Satellite Stereo Imagery and POI Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We extract image features using a semi-transfer learning strategy and employ the LDA topic model to generate POI semantic features. These features are then fused to improve UFZ recognition.
- (2)
- We incorporate both the 2D and 3D characteristics of the study area.
- (3)
- We investigate the function of DSM generated from GF-7 images, NIR, and POI in identifying UFZs.
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. UFZs Categories
3. Methodology
3.1. Urban Functional Unit Division
3.2. Image Dataset Generation
3.3. Multimodal Data Feature Extraction and Fusion
3.3.1. Image Feature Extraction
3.3.2. Semantic Feature Extraction
3.3.3. Feature Fusion and UFZs Identification
3.4. Accuracy Evaluation
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Results
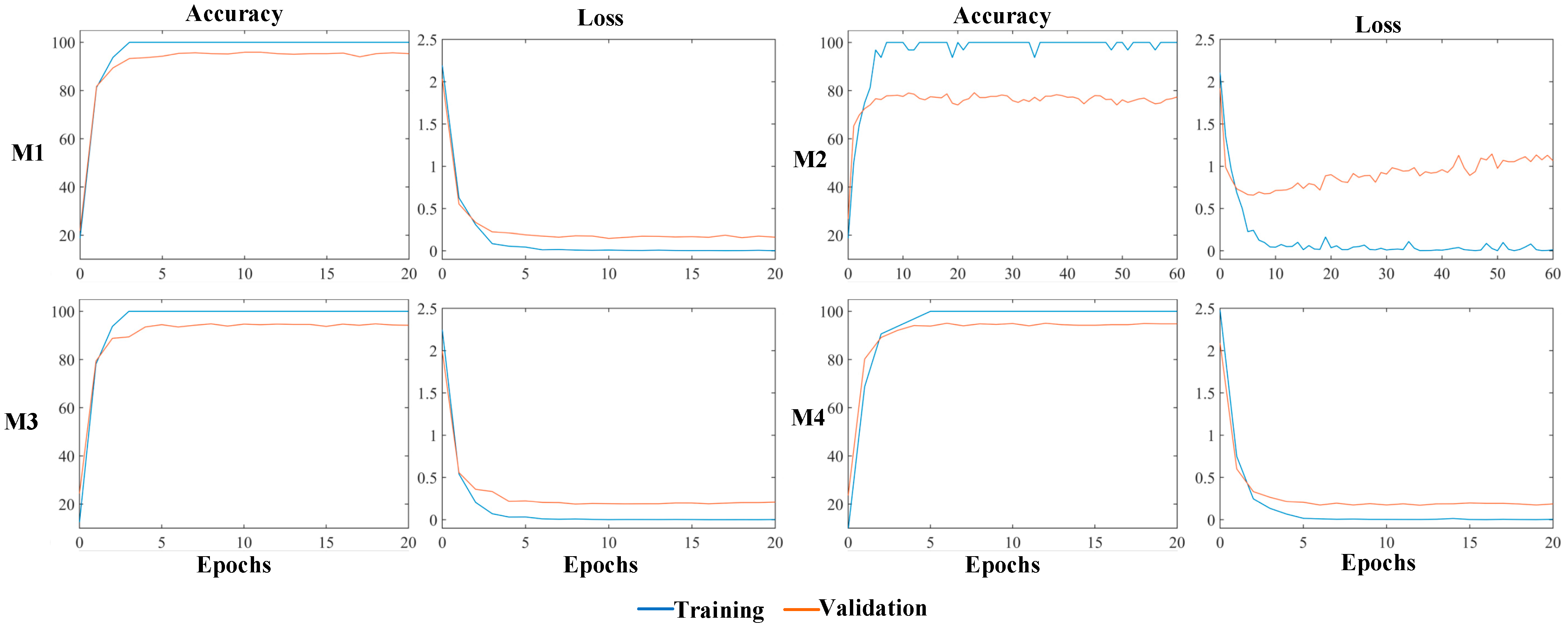
4.1.1. Experimental Setup
4.1.2. UFZs Identification Results
4.2. Discussion
4.2.1. Comparison of Different Pre-Training Models
4.2.2. Advantages of Semi-Transfer Structure
4.2.3. Contribution of Different Modality Data
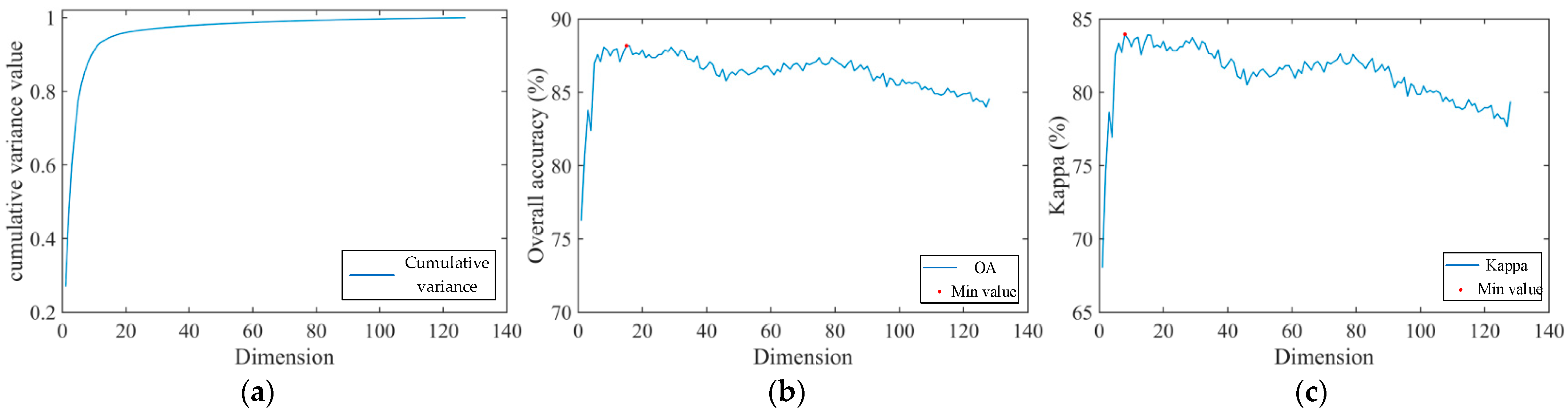
4.2.4. Impact of PCA Dimensionality Reduction on Identifying UFZs
4.2.5. Compare with Other Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, S.; Du, S.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zheng, Z.J. Large-scale urban functional zone mapping by integrating remote sensing images and open social data. Giscience Amp. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 411–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X. Mapping large-scale and fine-grained urban functional zones from VHR images using a multi-scale semantic segmentation network and object based approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 261, 11248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Du, S.; Zheng, Z. Heuristic sample learning for complex urban scenes: Application to urban functional-zone mapping with VHR images and POI data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 161, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Ming, D.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, K.; Du, S. DFCNN-Based Semantic Recognition of Urban Functional Zones by Integrating Remote Sensing Data and POI Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.; Han, Z.; Yang, J.; Yang, G.; Liu, X. Heavy metal pollution in settled dust associated with different urban functional areas in a heavily air-polluted city in North China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Publ. Health 2016, 13, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shen, Z.; Hao, X. Revealing the relationship between spatio-temporal distribution of population and urban function with social media data. GeoJournal 2016, 81, 919–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Tong, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, C.; Prishchepov, A. Monitoring finer-scale population density in urban functional zones: A remote sensing data fusion approach. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 190, 103580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.S.; Qiu, X.; Usery, E.L.; Wang, L. Using geometrical, textural, and contextual information of land parcels for classification of detailed urban land use. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2009, 99, 76–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, M.; Liu, X.; Clarke, K. Spatial metrics and image texture for mapping urban land use. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Xie, S.; Mi, J. GLC_FCS30: Global land-cover productwith fine classification system at 30 m using time-series Landsat imagery. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 2753–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, J.; Wood, E.; Pan, M.; Beck, H.E.; Coccia, G.; Serrat-Capdevila, A.; Verbist, K. Satellite Remote Sensing for Water Resources Management: Potential for Supporting Sustainable Development in Data-Poor Regions. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 9724–9758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ke, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chen, B.; Gong, H.; Lv, M.; Zhu, L.; Li, X. Multi-Scale Analysis of the Relationship between Land Subsidence and Buildings: A Case Study in an Eastern Beijing Urban Area Using the PS-InSAR Technique. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhong, Y.; Xia, G.; Zhang, L. Dirichlet-Derived Multiple Topic Scene Classification Model for High Spatial Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 5, 2108–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, D. Scene Classification Based on the Sparse Homogeneous-Heterogeneous Topic Feature Model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 2689–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L. Multi-feature probability topic scene classifier for high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 2854–2857. [Google Scholar]
- Bahmanyar, R.; Shiyong, C.; Datcu, M. A comparative study of bag-of-words and bag-of-topics models of eo image patches. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1357–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Zhu, T.; Xia, J.; Zhou, Y.; Lai, Y.; Jiang, J.; Li, Q. Portraying the spatial dynamics of urban vibrancy using multisource urban big data. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2020, 80, 101428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Hu, Z.; Li, L.; Cao, J.; Jiang, J.; Li, Q.; Li, Q. Portraying Urban Functional Zones by Coupling Remote Sensing Imagery and Human Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Huang, H.; Wu, W.; Du, X.; Wang, H. The combined use of remote sensing and social sensing data in fine-grained urban land use mapping: A case study in Beijing, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, Y.; Tang, J.; Deng, M.; Huang, J.; Yang, W.; Wu, F. Recognizing urban functional zones by a hierarchical fusion method considering landscape features and human activities. Trans. GIS 2020, 24, 1359–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Qing, L.; Han, L.; Liu, M.; Peng, Y.; Shen, L. A new remote sensing images and point-of-interest fused (rpf) model for sensing urban functional regions. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Ming, D.; Lv, X.; Zhou, K.; Bao, H.; Hong, Z. SO–CNN based urban functional zone fine division with VHR remote sensing image. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Yan, X.; Luo, P.; Liang, Y.; Ren, S.; Hu, Y.; Han, J.; Guan, Q. Classifying Land-Use Patterns by Integrating Time-Series Electricity Data and High-Spatial Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinf. 2022, 106, 102664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Tu, W.; Yang, C.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Q.; Qiu, G. Deep learning-based remote and social sensing data fusion for urban region function recognition. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 163, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Su, Y.; Wu, S.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, J.; Ma, A.; Zhu, Q.; Ye, R.; Li, X.; Pellikka, P.; et al. Open-source data-driven urban land-use mapping integrating point-line-polygon semantic objects: A case study of Chinese cities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zhao, B.; Song, Y. Urban land-use mapping using a deep convolutional neural network with high spatial resolution multispectral remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 214, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Pdf ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, S. Analyzing Urban Spatial Patterns and Functional Zones Using Sina Weibo POI Data: A Case Study of Beijing. Sustainability 2021, 13, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Bai, X.; Shi, Y.; Han, Y.; Peng, Z.R.; Gu, C. Beyond Word2vec: An approach for urban functional region extraction and identification by combining Place2vec and POIs. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 74, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, F.; Liu, R.; Du, Z. Identifying Urban Functional Zones Using Public Bicycle Rental Records and Point-of-Interest Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Luo, W.; Lin, A.; Hao, F.; Olteanu-Raimond, A.M.; Liu, L.; Li, Y. SALT: A multifeature ensemble learning framework for mapping urban functional zones from VGI data and VHR images. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2023, 100, 101921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.; Shen, Z. Discovering Functional Zones Using Bus Smart Card Data and Points of Interest in Beijing. In Geospatial Analysis to Support Urban Planning in Beijing; GeoJournal Library; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 116. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wan, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, X. An SOE-Based Learning Framework Using Multisource Big Data for Identifying Urban Functional Zones. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 7336–7348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Feng, X.; Zhang, C.; Dong, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, K. Identification of Urban Functional Areas Based on the Multimodal Deep Learning Fusion of High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images and Social Perception Data. Buildings 2022, 12, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Xing, H.; Meng, Y.; Yang, G.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y. Integrating urban morphology and land surface temperature characteristics for urban functional area classification. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, M.; Wu, C.; Zhou, W.; Chu, G. Identifying Urban Functional Regions from High-Resolution Satellite Images Using a Context-Aware Segmentation Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanlang, S.; Cao, S.; Du, M.; Mo, Y.; Chen, Q.; He, W. Integrating aerial lidar and very high-resolution images for urban functional zone mapping. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.X.; Huang, X. A deep learning method for building height estimation using high-resolution multi-view imagery over urban areas: A case study of 42 Chinese cities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 12, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Wen, D. Urban functional zone mapping by integrating high spatial resolution nighttime light and daytime multi-view imagery. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 175, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.A.; Saldaña, M.M.; Aguilar, F.J. Generation and Quality Assessment of Stereo-Extracted DSM From GeoEye-1 and WorldView-2 Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotakis, E.; Chrysoulakis, N.; Charalampopoulou, V.; Poursanidis, D.; Panagiotakis, E.; Chrysoulakis, N.; Charalampopoulou, V.; Poursanidis, D. Validation of Pleiades Tri-Stereo DSM in Urban Areas. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Yue, Q.; Gao, X. China DSM Generation and Accuracy Acessment Using ZY3 Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 23–27 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Tang, X.; Zhang, G.; Liu, B.; Hu, W. Accuracy Comparison and Assessment of DSM Derived from GFDM Satellite and GF-7 Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Jiang, S.; Jiang, W. Building Height Extraction from GF-7 Satellite Images Based on Roof Contour Constrained Stereo Matching. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Hu, X.L.; Meng, Q.Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Liu, X.C.; Zhao, M.F. Developing a Method to Extract Building 3D Information from GF-7 Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 22, 4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschmuller, H. Stereo Processing by Semiglobal Matching and Mutual Information. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 30, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, K.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y. Comparison of approaches for urban functional zones classification based on multi-source geospatial data: A case study in Yuzhong district, Chongqing, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Luo, J.; Wu, T.; Dong, W.; Zhou, N. Identification and Portrait of Urban Functional Zones Based on Multisource Heterogeneous Data and Ensemble Learning. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, P.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Mai, K. Sensing spatial distribution of urban land use by integrating points-of-interest and Google Word2Vec model. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 825–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Du, S.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X. Context-Enabled Extraction of Large-Scale Urban Functional Zones from Very-High-Resolution Images: A Multiscale Segmentation Approach. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Deng, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, J.; Liu, T. Classification schemes and identification methods for urban functional zone: A Review of Recent Papers. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Han, Y. Identification of Urban Functional Areas Based on POI Data: A Case Study of the Guangzhou Economic and Technological Development Zone. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Y. Identification of Urban Functional Areas and Their Mixing Degree Using Point of Interest Analyses. Land 2022, 11, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Xiao, C.; Rong, L. Integrating Point-of-Interest Density and Spatial Heterogeneity to Identify Urban Functional Areas. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M.; Ng, A.Y.; Jordan, M.I. Latent dirichlet allocation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 993–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, S. Identifying Urban Functional Regions by LDA Topic Model with POI Data. In Proceedings of the Big Data: 10th CCF Conference, BigData 2022, Chengdu, China, 18–20 November 2022; pp. 72–91. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Zheng, Y.; Xie, X. Discovering regions of different functions in a city using human mobility and POIs. In Proceedings of the 18th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, New York, NY, USA, 12 August 2012; pp. 186–194. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, H.; Meng, Y. Integrating Landscape Metrics and Socioeconomic Features for Urban Functional Region Classification. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2018, 72, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, E.; Lazcano, R.; López, J.; Madroñal, D.; Salvador, R.; López, S.; Juarez, E.; Guerra, R.; Sanz, C.; Sarmiento, R. Implementation of the Principal Component Analysis onto high-performance computer facilities for hyperspectral dimensionality reduction: Results and comparisons. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, A.E.; Warner, T.A.; Fang, F. Implementation of machine-learning classification in remote sensing: An applied review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 2784–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Zong, M.; Zhu, X.; Wang, R. Efficient k-NN Classification With Different Numbers of Nearest Neighbors. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 1774–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3350–3355. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Du, S.; Wang, Q. Integrating bottom-up classification and top-down feedback for improving urban land-cover and functional-zone mapping. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 212, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Du, S.; Wang, Q. Hierarchical semantic cognition for urban functional zones with vhr satellite images and poi data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 132, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Gong, P. Mapping Urban Land Use by Using Landsat Images and Open Social Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Sargent, I.; Pan, X.; Li, H.; Gardiner, A.; Hare, J.; Atkinson, P.M. An object-based convolutional neural network (OCNN) for urban land use classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Du, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, W. Multiscale geoscene segmentation for extracting urban functional zones from VHR satellite images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, P.; Biljecki, F. Knowledge and topology: A two layer spatially dependent graph neural networks to identify urban functions with time-series street view image. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 198, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

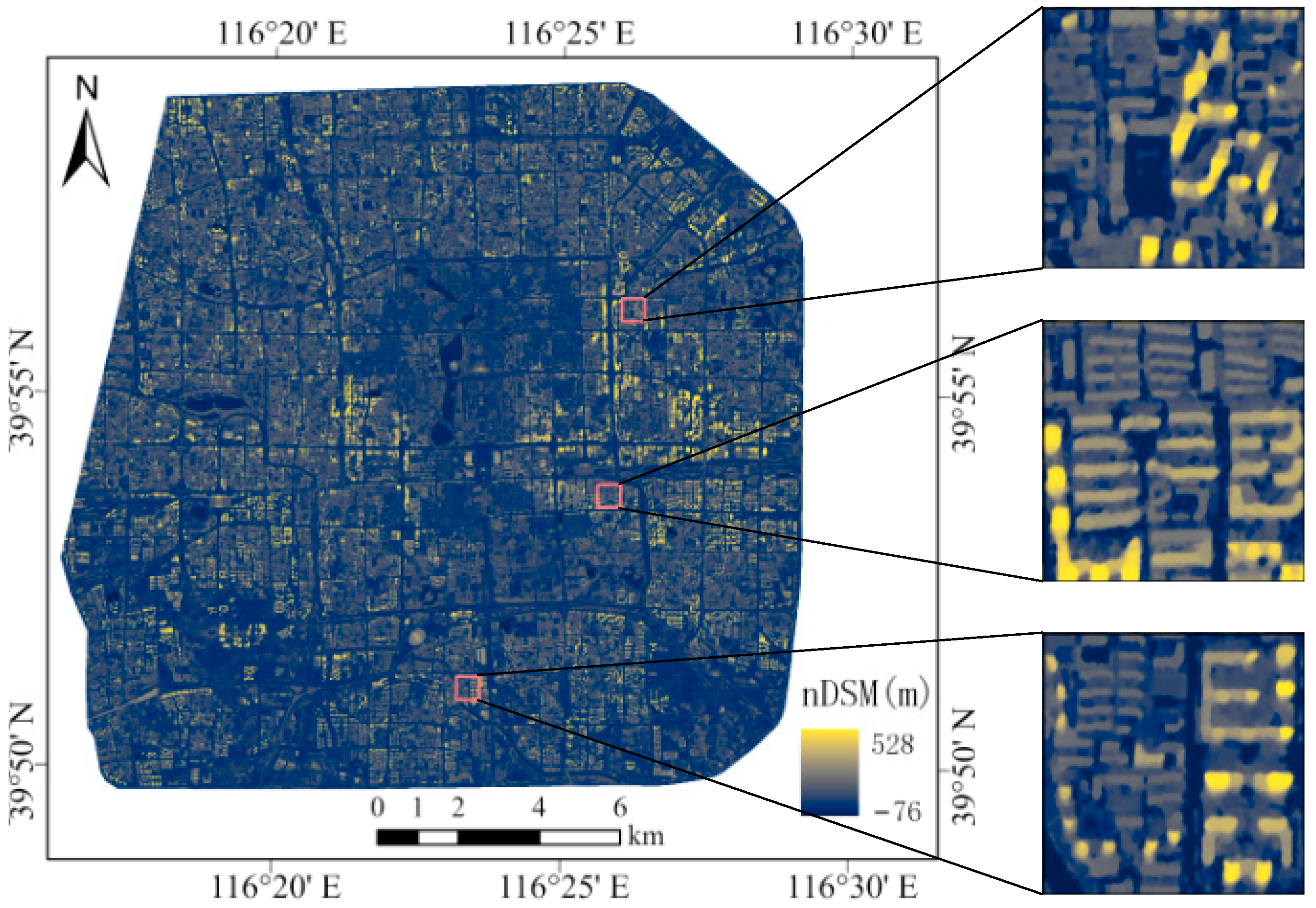


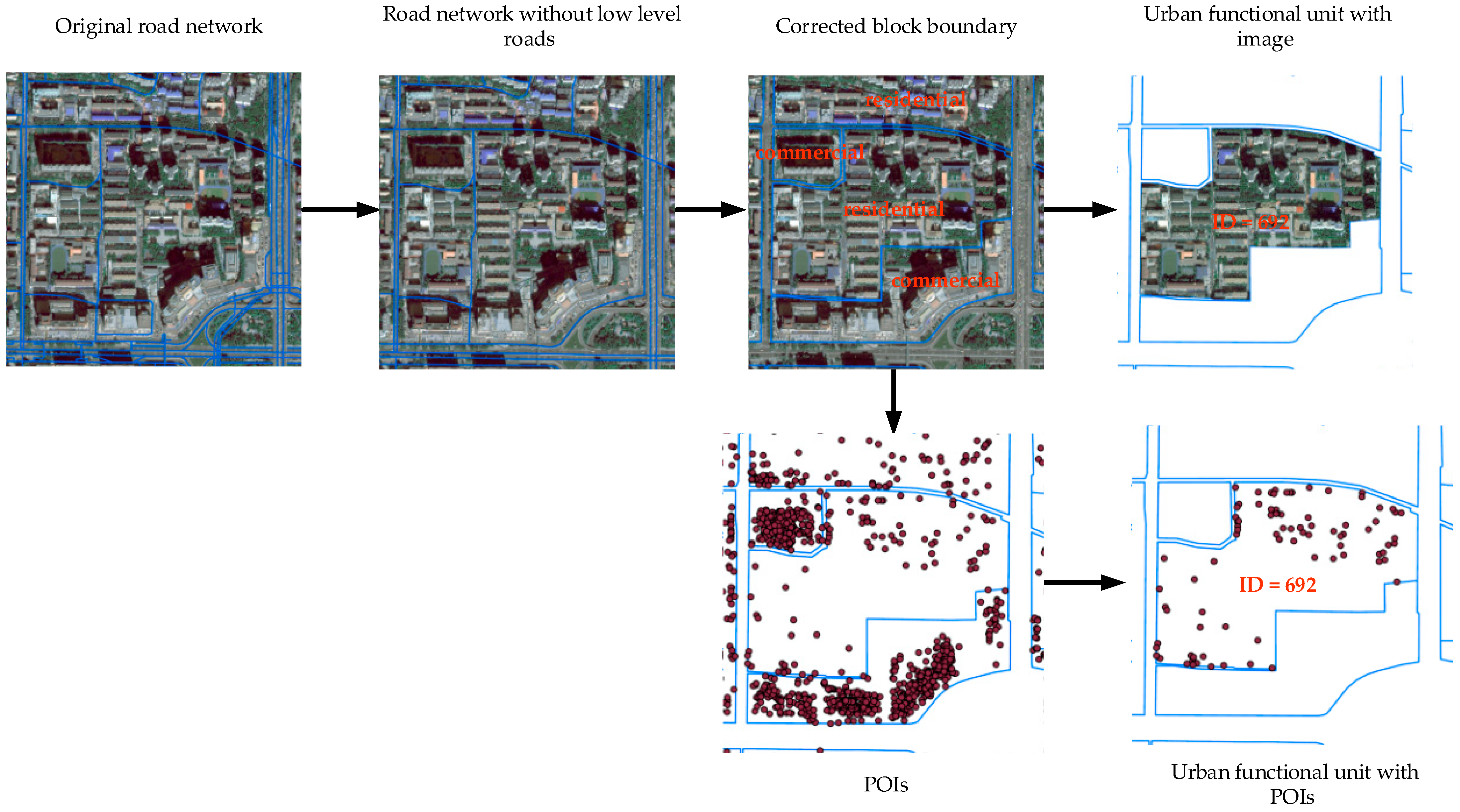

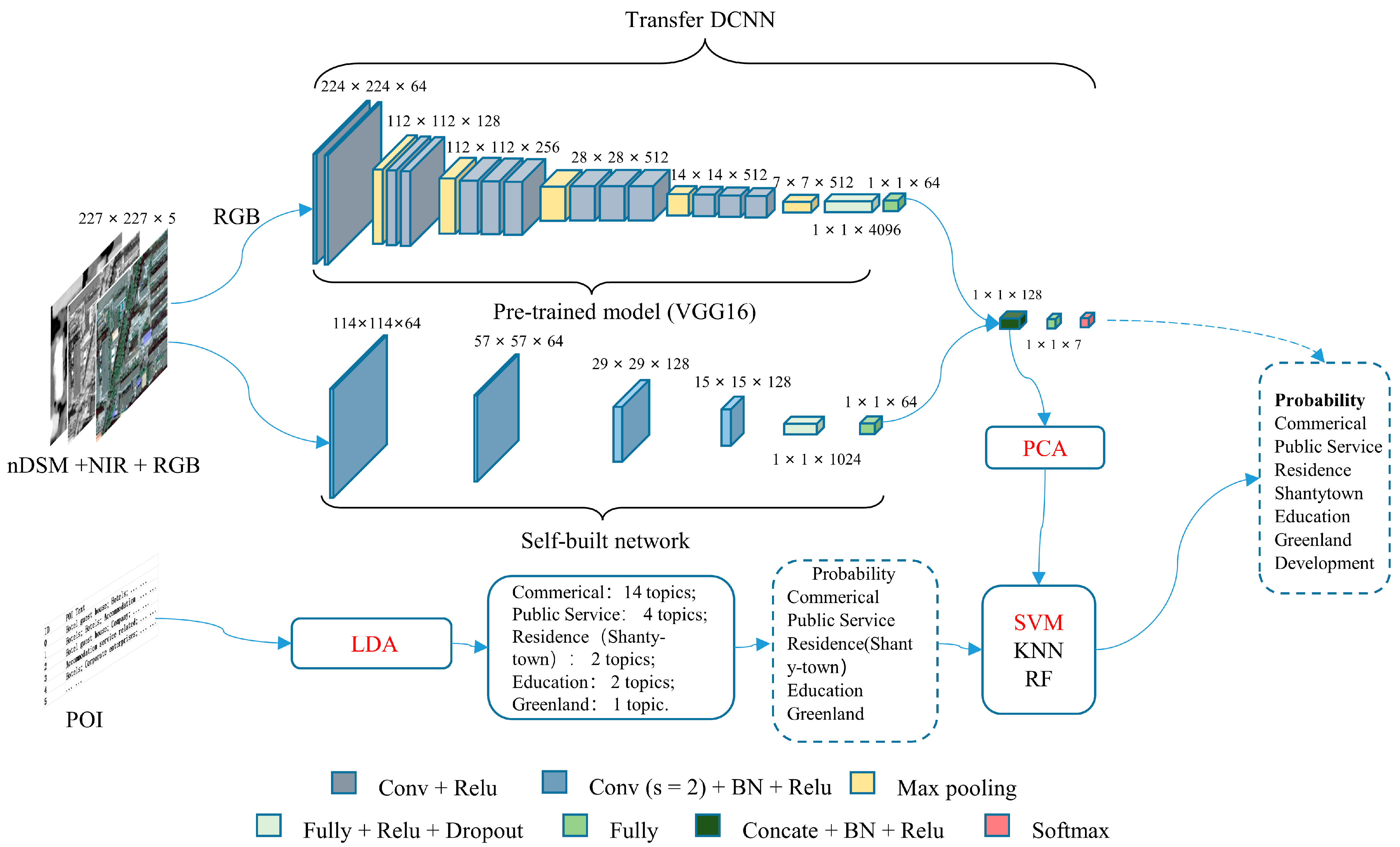



| Spectral Band | Wavelength (μm) | Spatial Resolution (m) | Swath Width (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Front-view Pan | 0.45–0.90 | 0.8 | ≥20 |
| Rear-view Pan | 0.45–0.90 | 0.65 | |
| Blue | 0.45–0.52 | 2.6 | |
| Green | 0.52–0.59 | ||
| Red | 0.63–0.69 | ||
| NIR | 0.77–0.89 |
| Category | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Residential zones | Regular, well-equipped communities, such as apartments and high-rise residential areas |
| Commercial zones | Commercial retail, restaurants, financial, and media places, such as office buildings and malls |
| Shantytown | Dilapidated, old low-rise communities, such as villages within cities |
| Public service | Administrative, medical, sport, and cultural places, such as government, hospitals, and libraries |
| Development | A place to be developed or under construction |
| Education | Education and research places, such as schools, universities, and institutes |
| Green land | Park and greenspace places, such as parks, greenbelts, and water |
| Residence | Commercial | Shantytown | Public Service | Development | Education | Green Land | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training set | 360 | 230 | 90 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 45 | 965 |
| Training set 1 | 720 | 690 | 720 | 600 | 560 | 500 | 450 | 4240 |
| Test set | 417 | 239 | 102 | 56 | 74 | 101 | 17 | 1006 |
| SVM (%) | KNN (%) | RF (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residential zone | 94.00 | 94.72 | 91.61 |
| Commercial zone | 83.68 | 85.36 | 87.45 |
| Shantytown | 92.16 | 87.25 | 90.20 |
| Public service | 55.41 | 47.30 | 47.30 |
| Development | 96.43 | 94.64 | 98.21 |
| Education | 64.71 | 70.59 | 47.06 |
| Green land | 94.06 | 96.04 | 95.05 |
| OA | 88.17 | 87.97 | 87.18 |
| Kappa coefficient | 83.91 | 83.60 | 82.65 |
| Model | Network | Input | OA (%) | Kappa Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | Pre-trained VGG16 | RGB | 81.71 | 75.56 |
| M2 | Self-built CNN | RGB + NIR + nDSM | 75.84 | 67.92 |
| M3 | ST-CNN | RGB | 82.01 | 75.94 |
| M4 | ST-CNN | RGB + NIR + nDSM | 84.00 | 78.41 |
| RGB | RGB + N | RGB + D | RGB + N + D | RGB + N + D + P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residential zones | 86.81 | 89.69 | 89.93 | 90.41 | 94.00 |
| Commercial zones | 78.66 | 79.50 | 80.75 | 79.92 | 83.68 |
| Shantytown | 90.20 | 88.24 | 91.18 | 92.16 | 92.16 |
| Public service | 40.54 | 31.08 | 29.73 | 37.84 | 55.41 |
| Development | 91.07 | 94.64 | 91.07 | 94.64 | 96.43 |
| Education | 35.29 | 41.18 | 47.06 | 47.06 | 64.71 |
| Green land | 95.05 | 95.05 | 92.08 | 93.07 | 94.06 |
| OA | 82.01 | 82.80 | 83.00 | 84.00 | 88.17 |
| Kappa coefficient | 75.94 | 76.82 | 77.03 | 78.41 | 83.91 |
| Method | Data Source | Study Area | Spatial | OA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Integrating bottom-up classification and top-down feedback [66] | WorldView-II image | Beijing, China (67.1 km2) | Residential, commercial, shantytown, industrial, campuses, park | 84% |
| Hierarchical semantic cognition [67] | QuickBird image; POIs | Beijing, China (67.1 km2) | Residential, commercial, shantytown, industrial, campuses, park | 90.8% |
| Similarity measures and threshold [68] | Landsat8 image; POIs | Beijing, China (16,808 km2) | Level I classes: agriculture, green space, waterbody, undeveloped, residential, commercial, industrial, institutional | 81.0% |
| Integrating high spatial resolution nighttime light and daytime multi-view imagery based on B-OVW model [69] | Ziyuan3 (ZY3-01) im-age Jilin1-07 (JL1-07) im-age | Beijing, China (300 km2) | Residential, commercial, shantytown, industrial, campuses, park, and green space | 89.6% |
| Our method | GF-7 image; POIs | Beijing, China (300 km2) | Residential, commercial, shantytown, public service, development, education, green land | 88.2% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Li, P.; Wang, D.; Meng, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhai, W. Recognizing Urban Functional Zones by GF-7 Satellite Stereo Imagery and POI Data. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6300. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106300
Sun Z, Li P, Wang D, Meng Q, Sun Y, Zhai W. Recognizing Urban Functional Zones by GF-7 Satellite Stereo Imagery and POI Data. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(10):6300. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106300
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zhenhui, Peihang Li, Dongchuan Wang, Qingyan Meng, Yunxiao Sun, and Weifeng Zhai. 2023. "Recognizing Urban Functional Zones by GF-7 Satellite Stereo Imagery and POI Data" Applied Sciences 13, no. 10: 6300. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106300
APA StyleSun, Z., Li, P., Wang, D., Meng, Q., Sun, Y., & Zhai, W. (2023). Recognizing Urban Functional Zones by GF-7 Satellite Stereo Imagery and POI Data. Applied Sciences, 13(10), 6300. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106300






