Soft Segmentation of Terrestrial Laser Scanning Point Cloud of Forests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.1.1. Synthetic Forest Data
2.1.2. Real Forest Point Cloud
2.2. Soft Segmentation Algorithm
2.2.1. Preprocessing
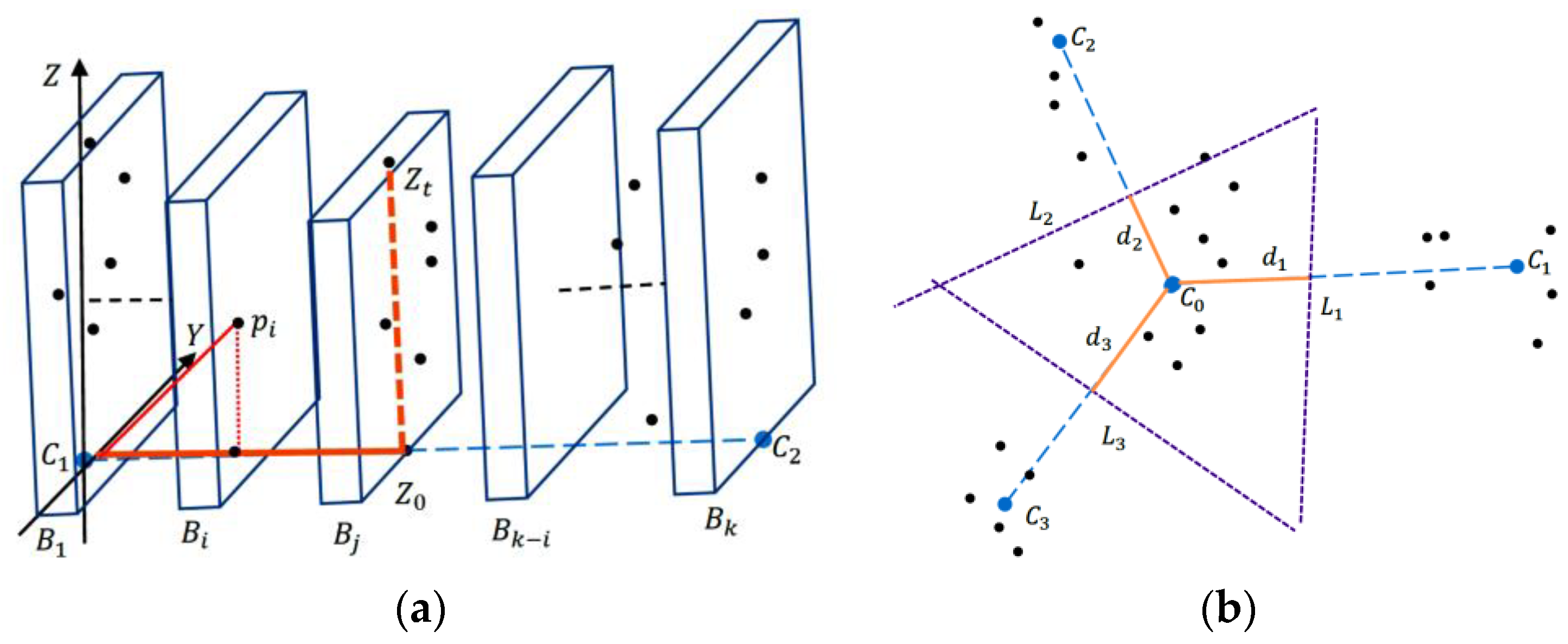
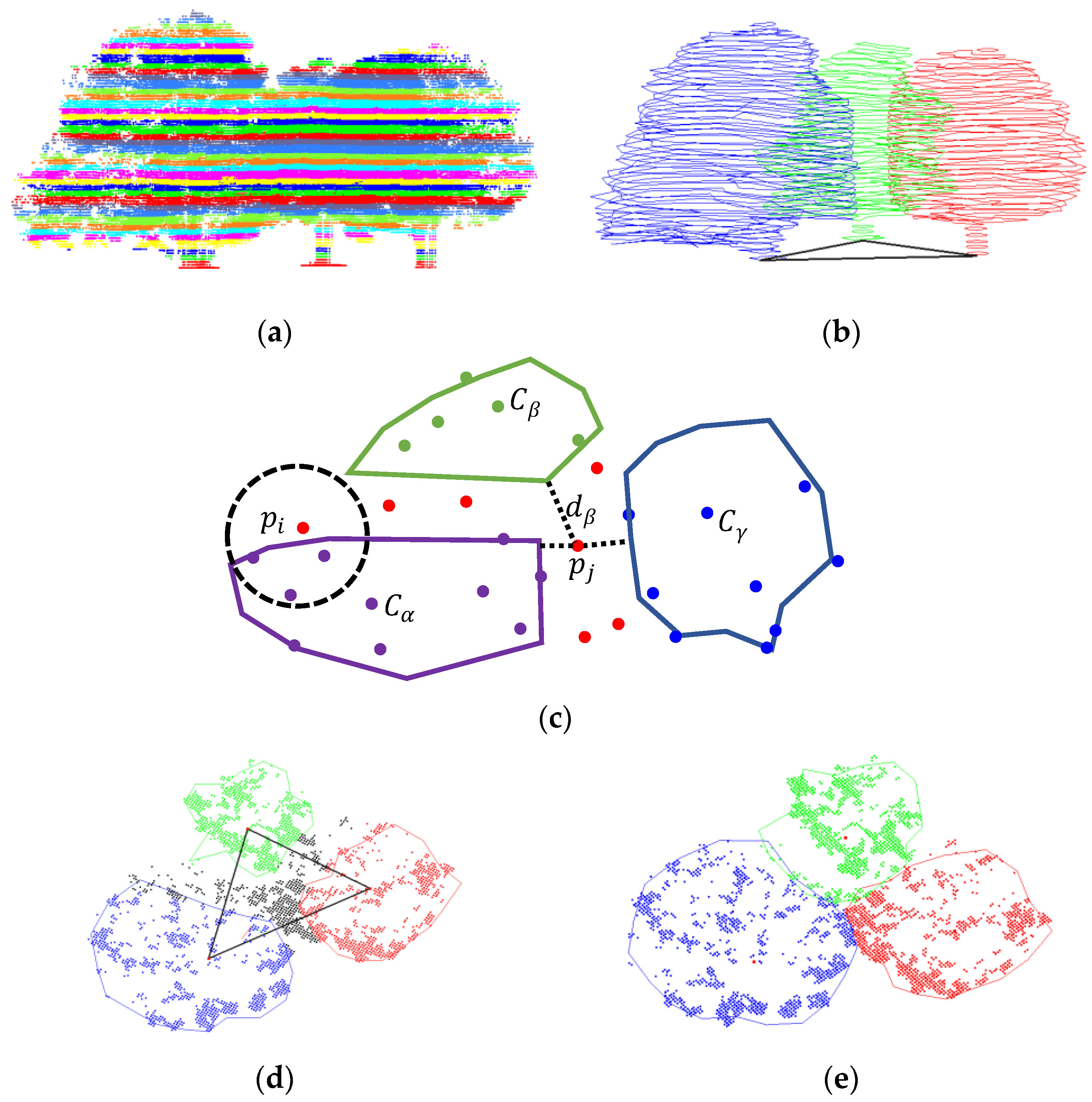
2.2.2. Partitioning with Region Growth Algorithm
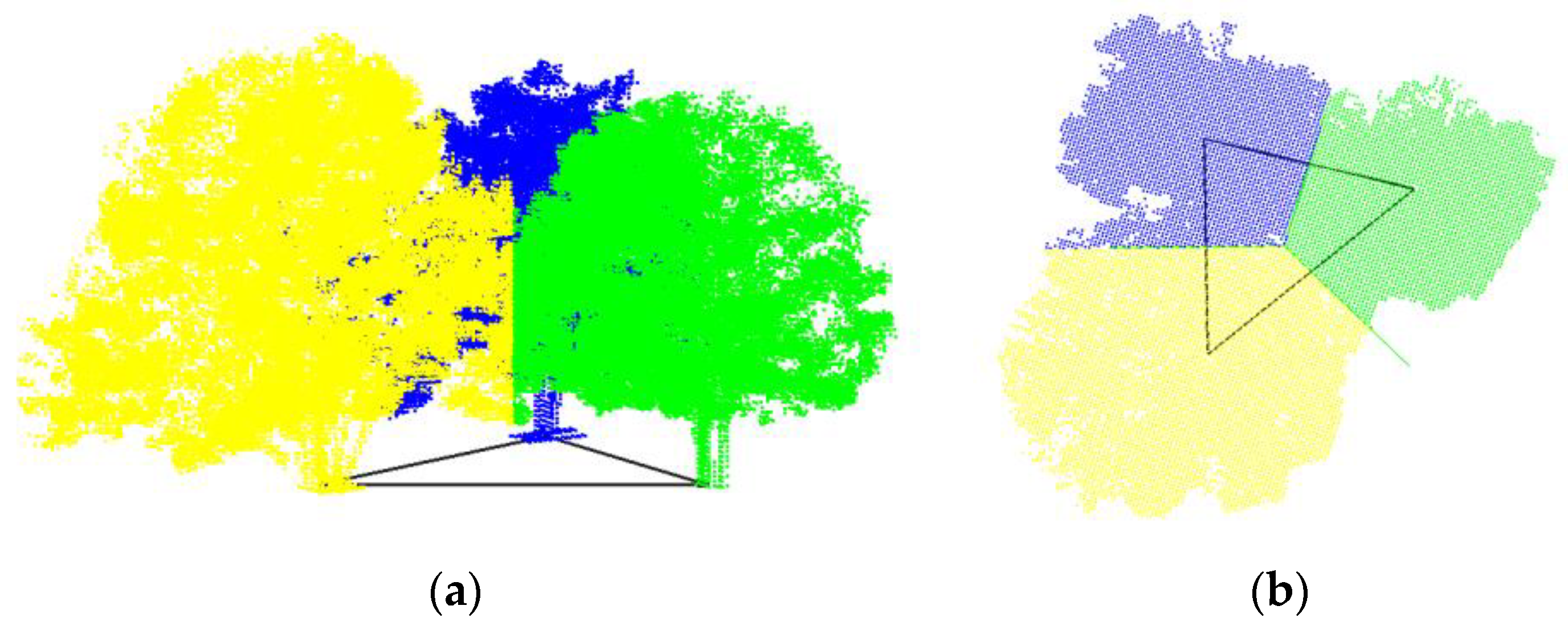
2.2.3. Modified Hard Segmentation
2.2.4. Refined by KNN and Contour Constraints
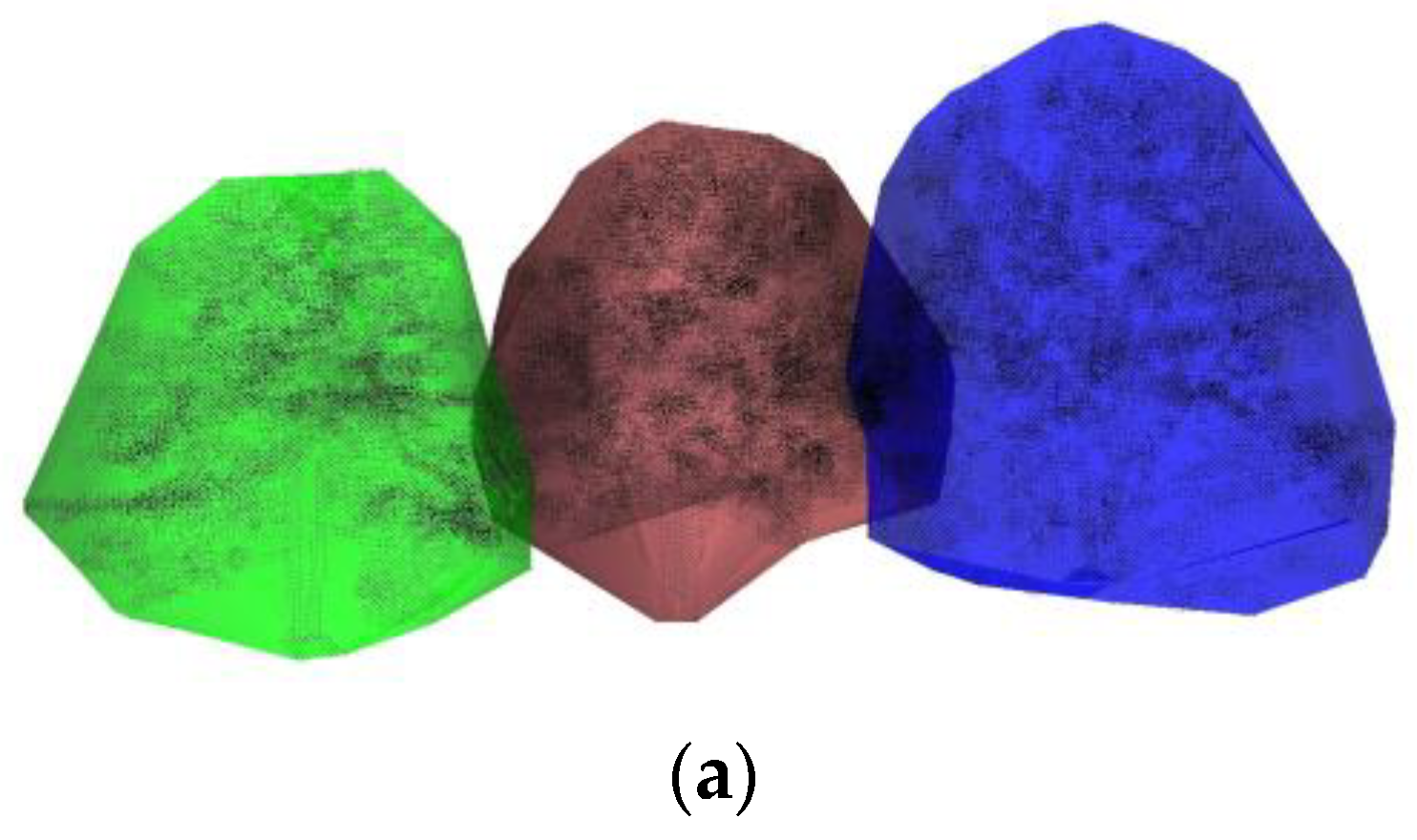
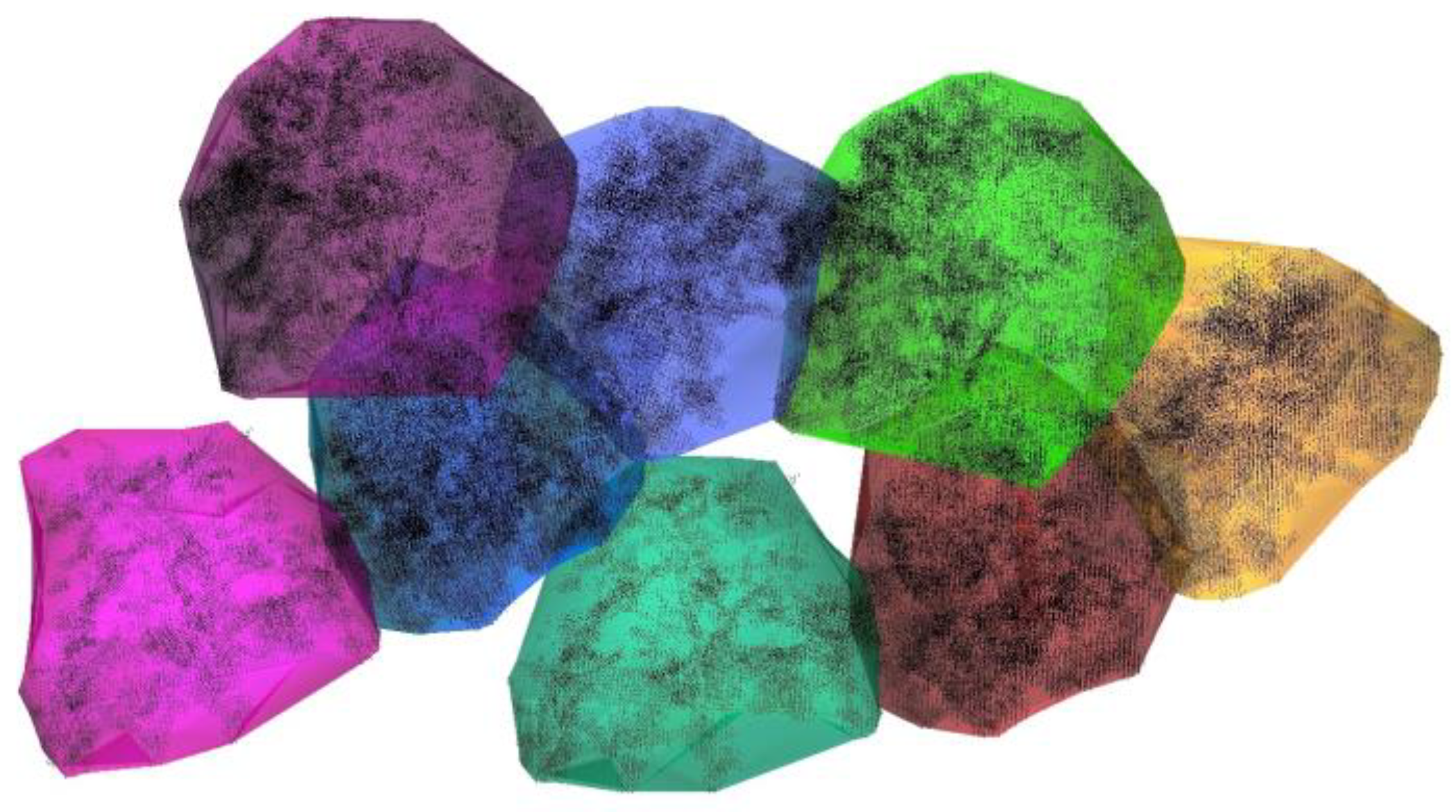
2.3. Tree Crown Silhouette Extracted and Reconstruction
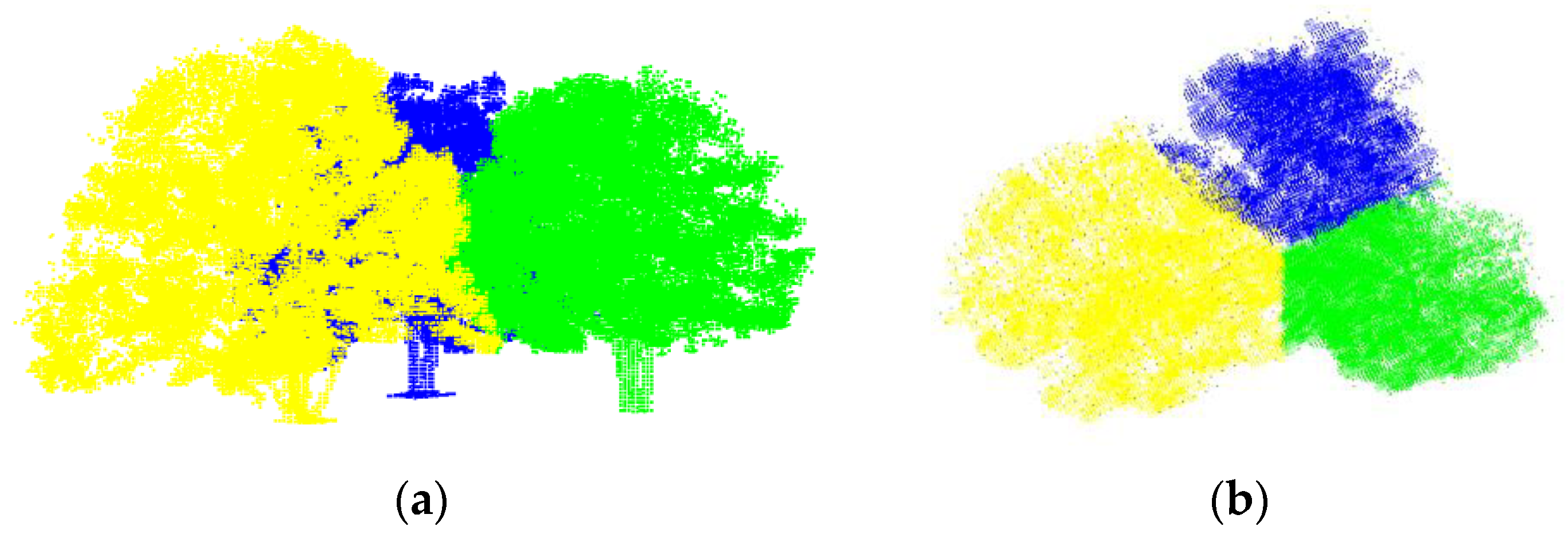
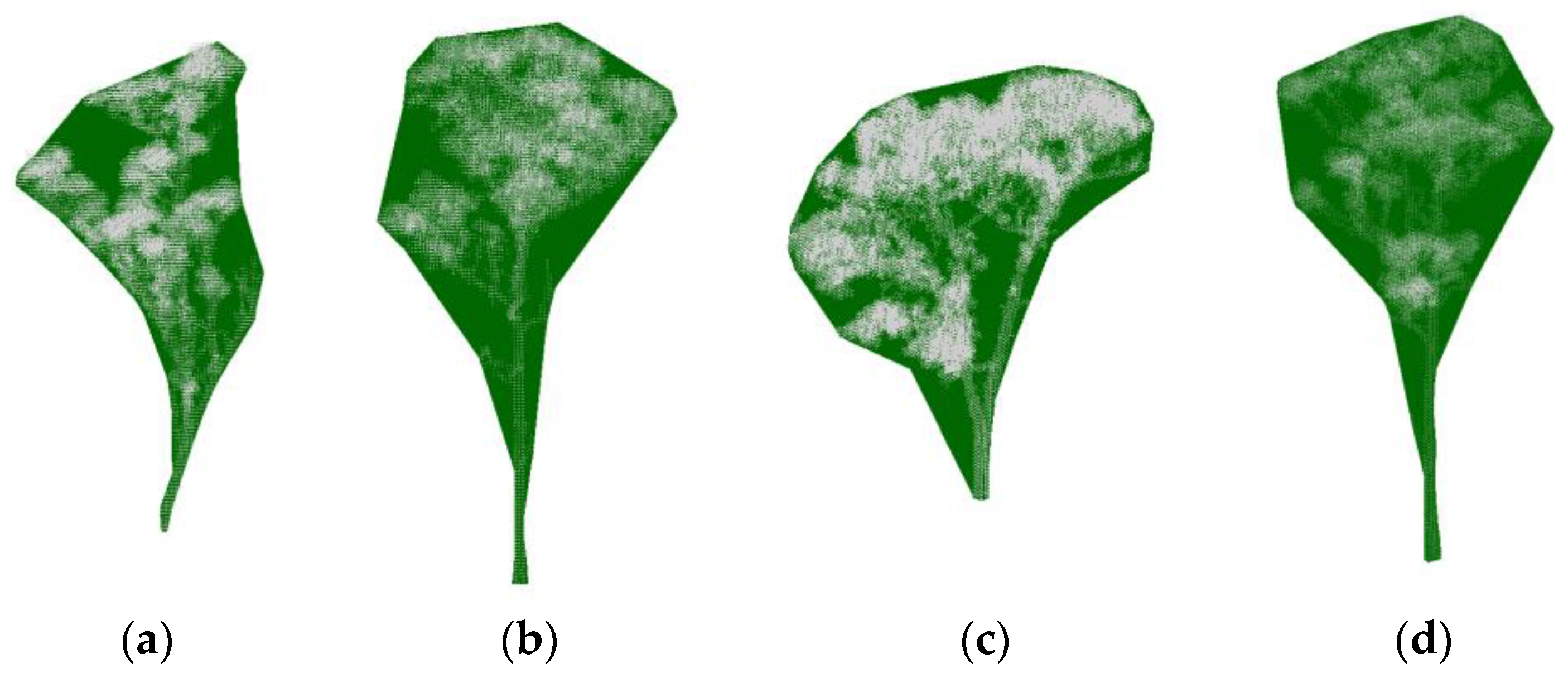
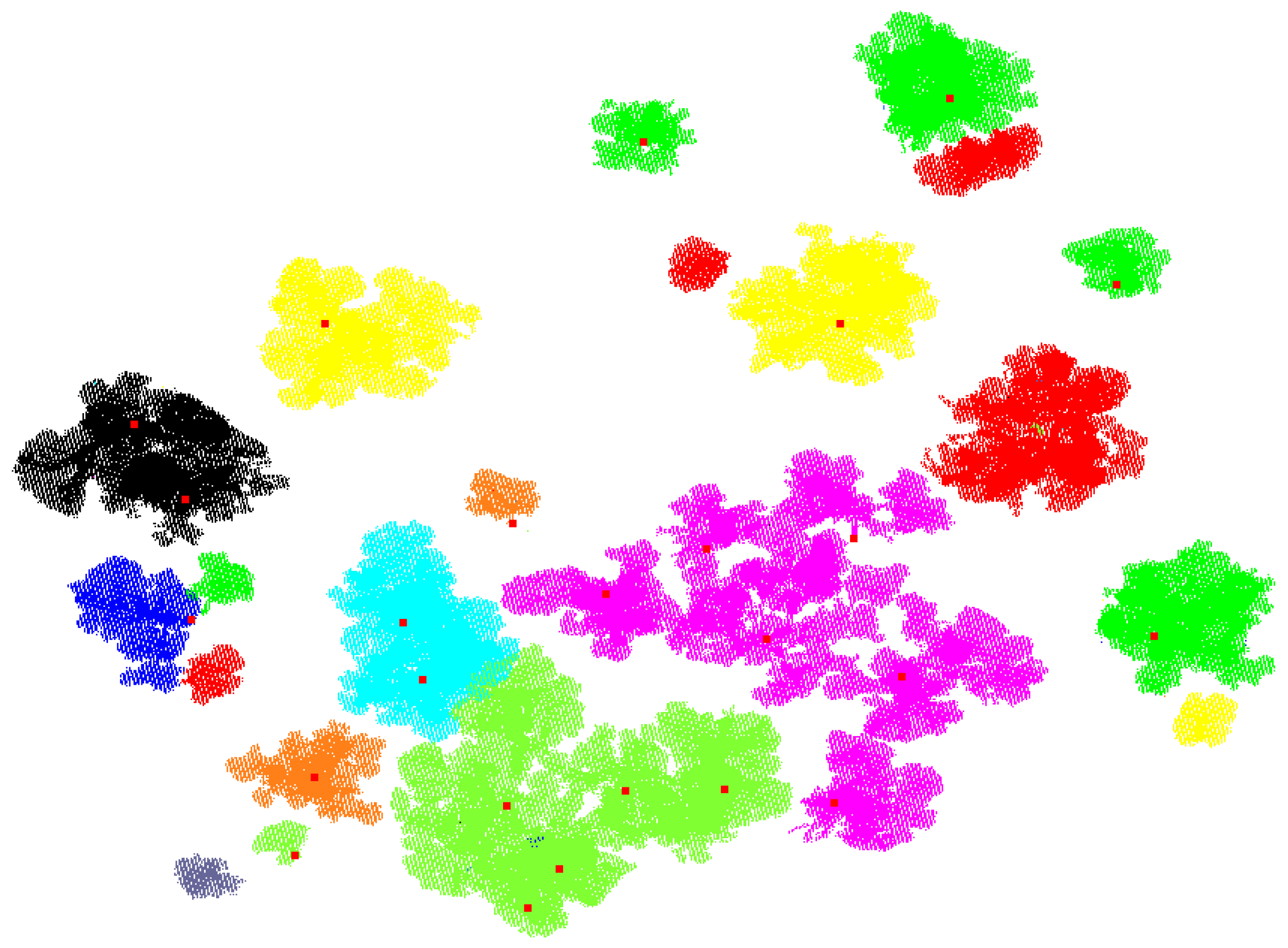
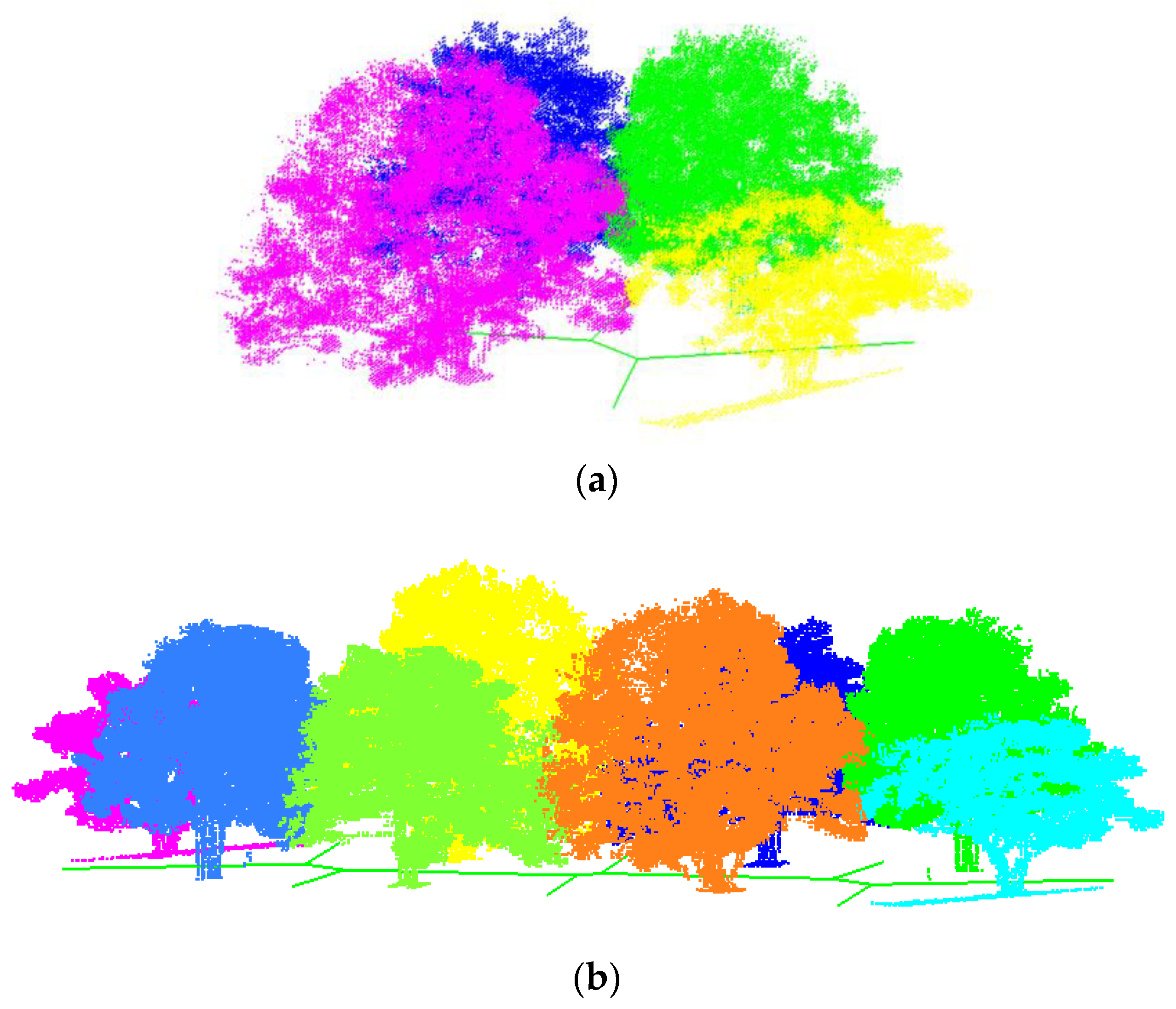
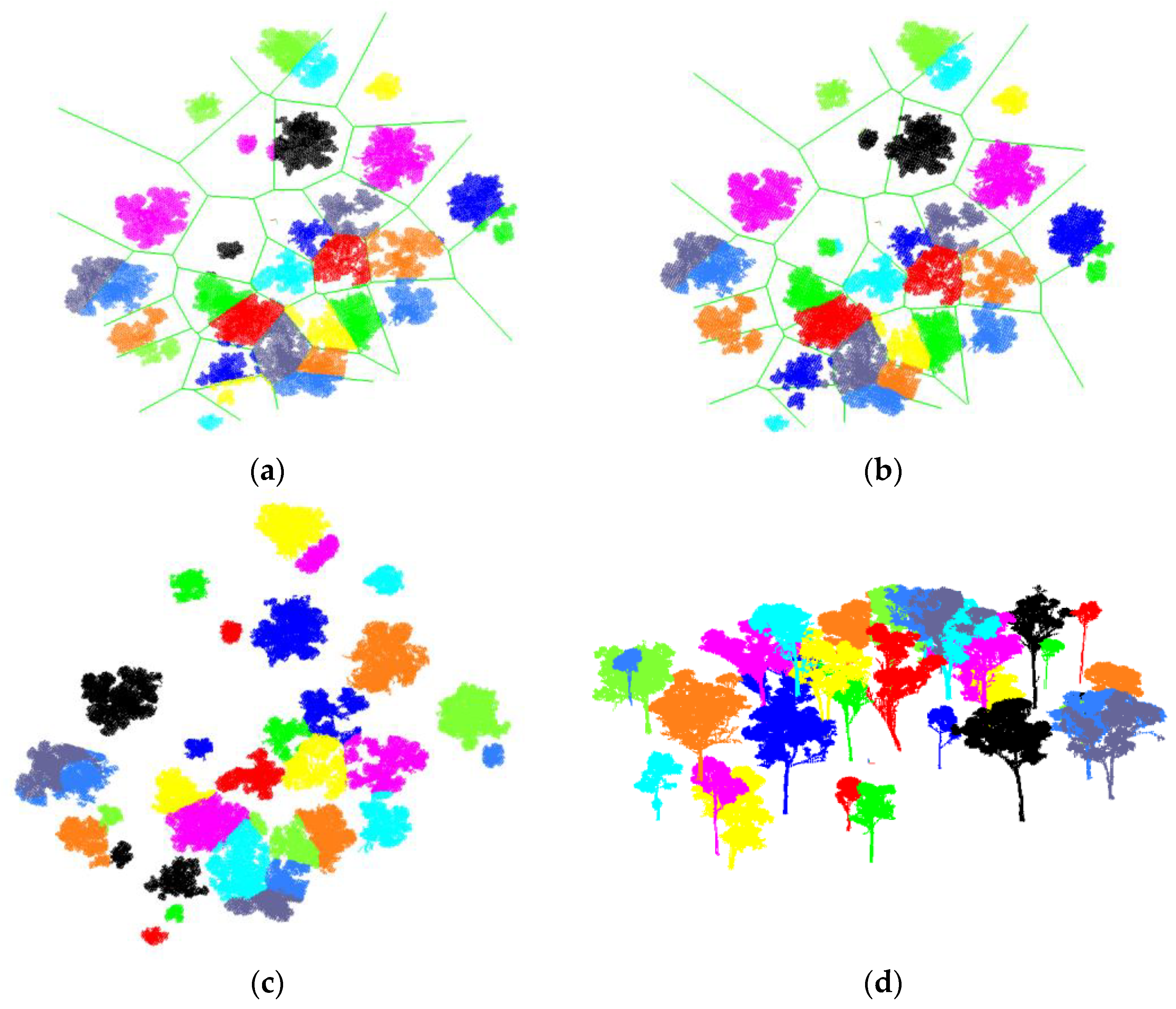
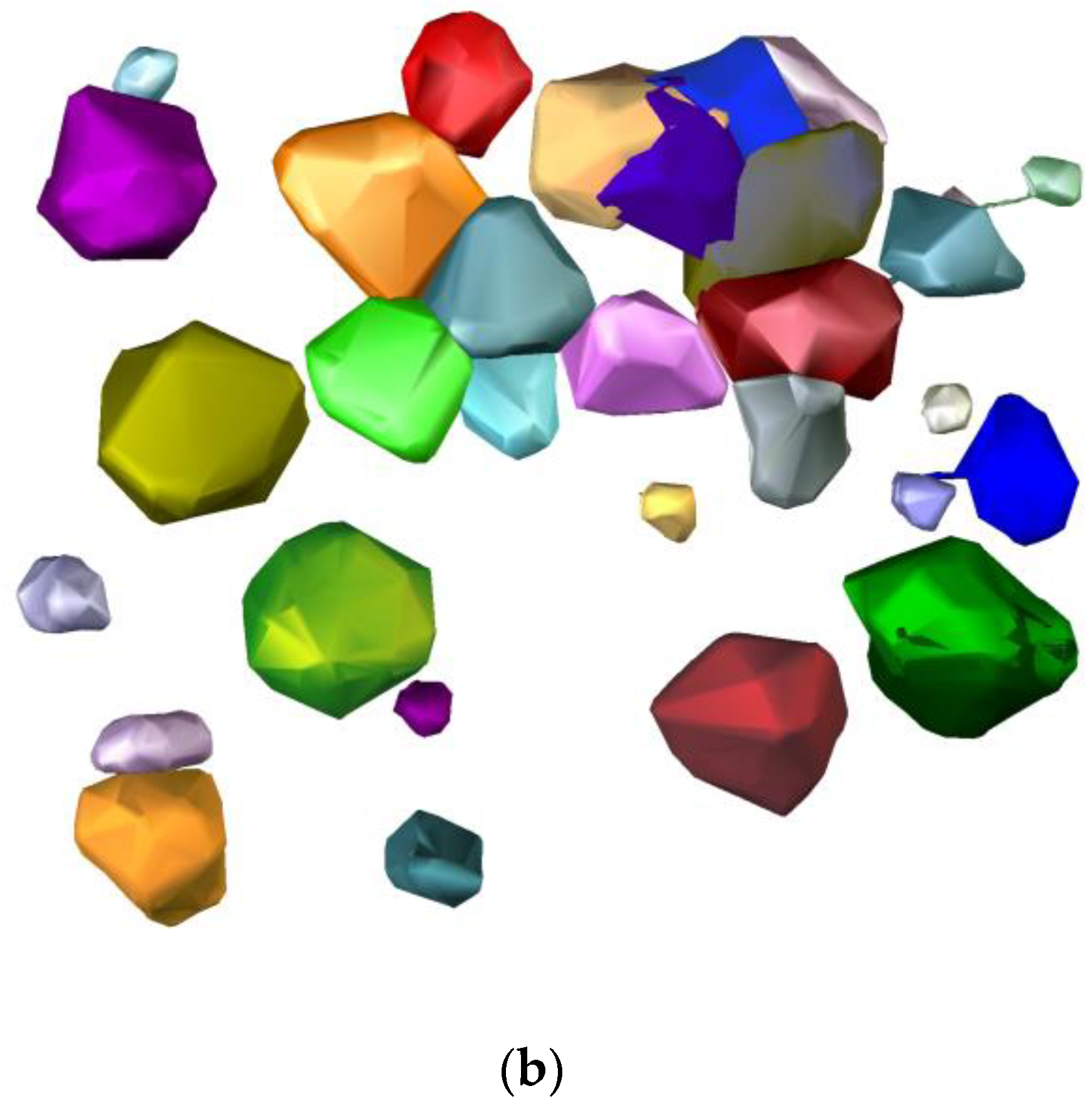
3. Results
3.1. Synthetic Forest
3.2. Real Scanning Data
3.3. Forest Reconstruction
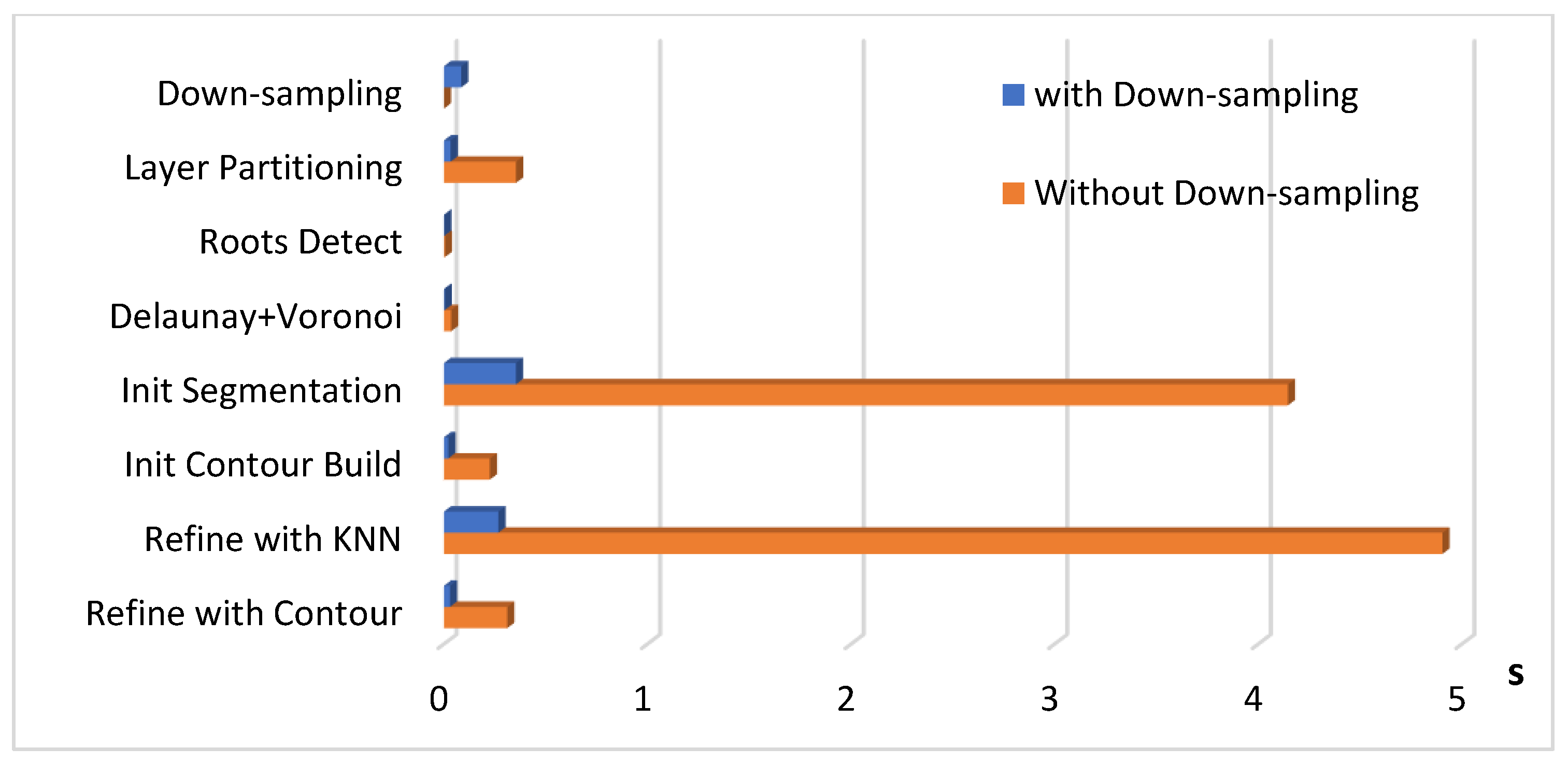
3.4. Time Efficiency
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Budei, B.C.; St-Onge, B.; Hopkinson, C.; Audet, F. Identifying the genus or species of individual trees using a three-wavelength airborne lidar system. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 632–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayrey, E.; Fraver, S.; Kershaw, J.A., Jr.; Kenefic, L.S.; Hayes, D.; Weiskittel, A.R.; Roth, B.E. Layer Stacking: A novel algorithm for individual forest tree segmentation from LiDAR point clouds. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 43, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamraz, H.; Contreras, M.A.; Zhang, J. A scalable approach for tree segmentation within small-footprint airborne LiDAR data. Comput. Geosci. 2017, 102, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Zaforemska, A.; Smigaj, M.; Wang, Y.; Gaulton, R. Mean shift segmentation assessment for individual forest tree delineation from airborne lidar data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Pang, Y.; Wang, D.; Liang, X.; Chen, B.; Lu, H.; Weinackerm, H.; Koch, B. Individual tree crown segmentation of a larch plantation using airborne laser scanning data based on region growing and canopy morphology features. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ma, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, D.; Wang, J. Point-cloud segmentation of individual trees in complex natural forest scenes based on a trunk-growth method. J. For. Res. 2021, 32, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liang, X.; Mofack, G.I.; Martin-Ducup, O. Individual tree extraction from terrestrial laser scanning data via graph pathing. For. Ecosyst. 2021, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Guo, Q.; Li, W.; Flanagan, J. A bottom-up approach to segment individual deciduous trees using leaf-off LiDAR point cloud data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 94, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, X.; Hang, M.; Li, J. Research on the improvement of single tree segmentation algorithm based on airborne LiDAR point cloud. Open Geosci. 2021, 13, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comesaña-Cebral, L.; Martínez-Sánchez, J.; Lorenzo, H.; Arias, P. Individual tree segmentation method based on mobile backpack LiDAR point clouds. Sensors 2021, 21, 6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dersch, S.; Heurich, M.; Krueger, N.; Krzystek, P. Combining graph-cut clustering with object-based stem detection for tree segmentation in highly dense airborne lidar point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2021, 172, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Jaeger, M.; Constant, T. Segmentation of forest terrain laser scan data. In Proceedings of the 9th ACM SIGGRAPH Conference on Virtual-Reality Continuum and Its Applications in Industry, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 12–13 December 2010; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J. Segmentation of tree crown model with complex structure from airborne LiDAR data. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Nanjing, China, 25–27 May 2007; Volume 6752. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Xing, Y.; Wang, C.; Xi, X. A graph cut-based approach for individual tree detection using airborne LiDAR data. J. Univ. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2019, 36, 385–391. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, W.; Xu, S.; Elberink, S.O.; Vosselman, G. Individual tree crown modeling and change detection from airborne LiDAR data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 3467–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, M.; Jakub, L.; Theodora, L. Automatic tree crown extraction from uas multispectral imagery for the detection of bark beetle disturbance in mixed forests. Remote Sens. 2020, 24, 4081. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, K.; Xiong, Y.; Jiang, F.; Chen, S.; Sun, H. A novel vegetation point cloud density tree-segmentation model for overlapping crowns using uav LiDAR. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, M.; Schmitt, M.; Zhu, X.X. Segmentation and crown parameter extraction of indiviudal trees in an airborne TomoSAR point cloud. In Proceedings of the Copernicus Publications, PIA15+HRIGI15—Joint ISPRS Conference, Munich, Germany, 25–27 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, T.; Zhang, X.; Ding, Z.; Fan, J. Multi-layered tree crown extraction from LiDAR data using graph-based segmentation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 170, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotn, J. Tree crown delineation using region growing and active contour: Approach introduction. Mendel 2014, 2014, 213–216. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Z.; Zhao, D.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, B.; Zhu, J. Assessing and correcting topographic effects on forest canopy height retrieval using airborne LiDAR data. Sensors 2015, 15, 12133–12155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strîmbu, V.F.; Strîmbu, B.M. A graph-based segmentation algorithm for tree crown extraction using airborne LiDAR data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 104, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry-Kientz, M.; Laybros, A.; Weinstein, B.; Ball, J.G.; Jackson, T.; Coomes, D.; Vincent, G. Multi-sensor data fusion for improved segmentation of individual tree crowns in dense tropical forests. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 3927–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janoutová, R.; Homolová, L.; Novotný, J.; Navrátilová, B.; Pikl, M.; Malenovský, Z. Detailed reconstruction of trees from terrestrial laser scans for remote sensing and radiative transfer modelling applications. Silico Plants 2021, 3, diab026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyysalo, U.; Hyyppa, H. Reconstructing tree crowns from laser scanner data for feature extraction. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Commission III, Symposium 2002, Graz, Austria, 9–13 September 2002. 4p. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Hu, B.; Jaeger, M. Reconstruction of Tree Crown Shape from Scanned Data. In Proceedings of the Technologies for E-Learning and Digital Entertainment, Third International Conference, Edutainment 2008, Nanjing, China, 25–27 June 2008; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Hyyppa, J. Multiecho-recording mobile laser scanning for enhancing individual tree crown reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 4323–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Moskal, L.M.; Schiess, P.; Swanson, M.E.; Calhoun, D.; Stuetzle, W. Capturing tree crown formation through implicit surface reconstruction using airborne LiDAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 113, 1148–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calders, K. Terrestrial Laser Scans—Riegl VZ400, Individual Tree Point Clouds and Cylinder Models, Rushworth Forest; Version 1; Terrestrial Ecosystem Research Network (Dataset): Indooroopilly, QLD, Australia, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Li, H. Counting of plantation trees based on line detection of point cloud data. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 22 July 2022, pp. 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, H. Registration of 3D point clouds based on voxelization simplify and accelerated iterative closest point algorithm. In Artificial Intelligence—CICAI 2021; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; LNAI 13069; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rawabdeh, A.; He, F.; Habib, A. Automated feature-based down-sampling approaches for fine registration of irregular point clouds. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.; Jiang, K.; Li, G.; Eichhorn, M.P.; Fan, J.; Liu, F.; Chen, B.; An, F.; Cao, L. Individual tree crown segmentation from airborne LiDAR data using a novel Gaussian filter and energy function minimization-based approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 256, 112307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, E.; Ernst, P.M. Three-dimensional alpha shapes. ACM Trans. Graph. 1994, 13, 43–72. [Google Scholar]
- Sunil, A.; Theocharis, M.; David, M. Space-time tradeoffs for approximate nearest neighbor searching. J. ACM 2009, 57, 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, H. Surface reconstruction algorithm using self-adaptive step alpha-shape. J. Data Acquis. Process. 2019, 34, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; del Rey Castillo, E.; Zou, Y.; Wotherspoon, L.; Tan, Y. Automated semantic segmentation of bridge components from large-scale point clouds using a weighted superpoint graph. Autom. Constr. 2022, 142, 104519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
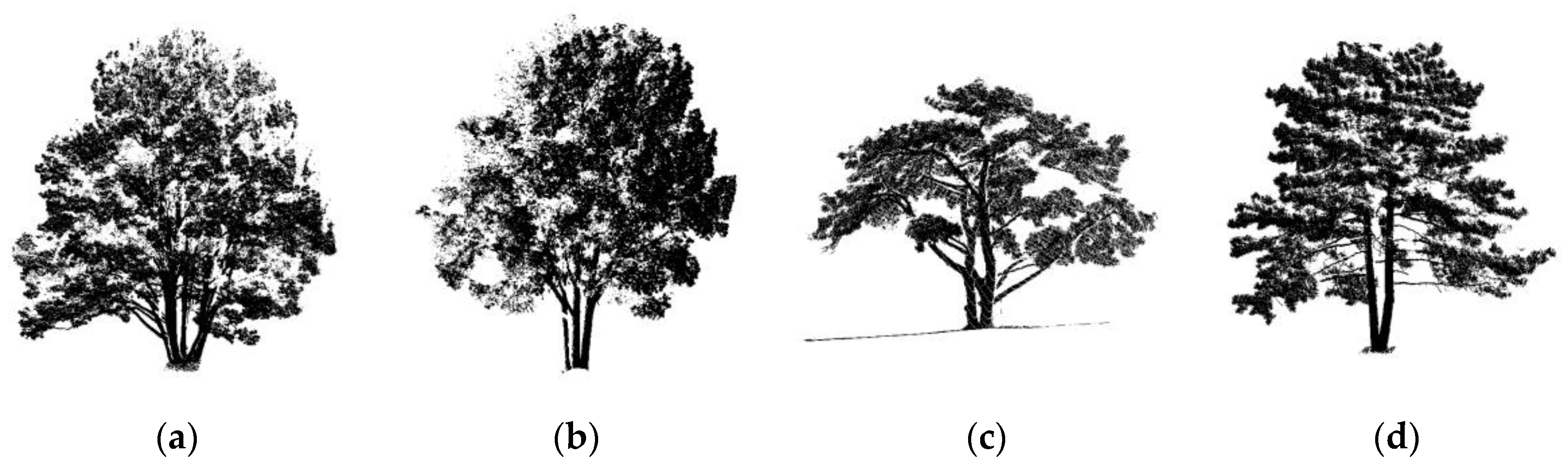
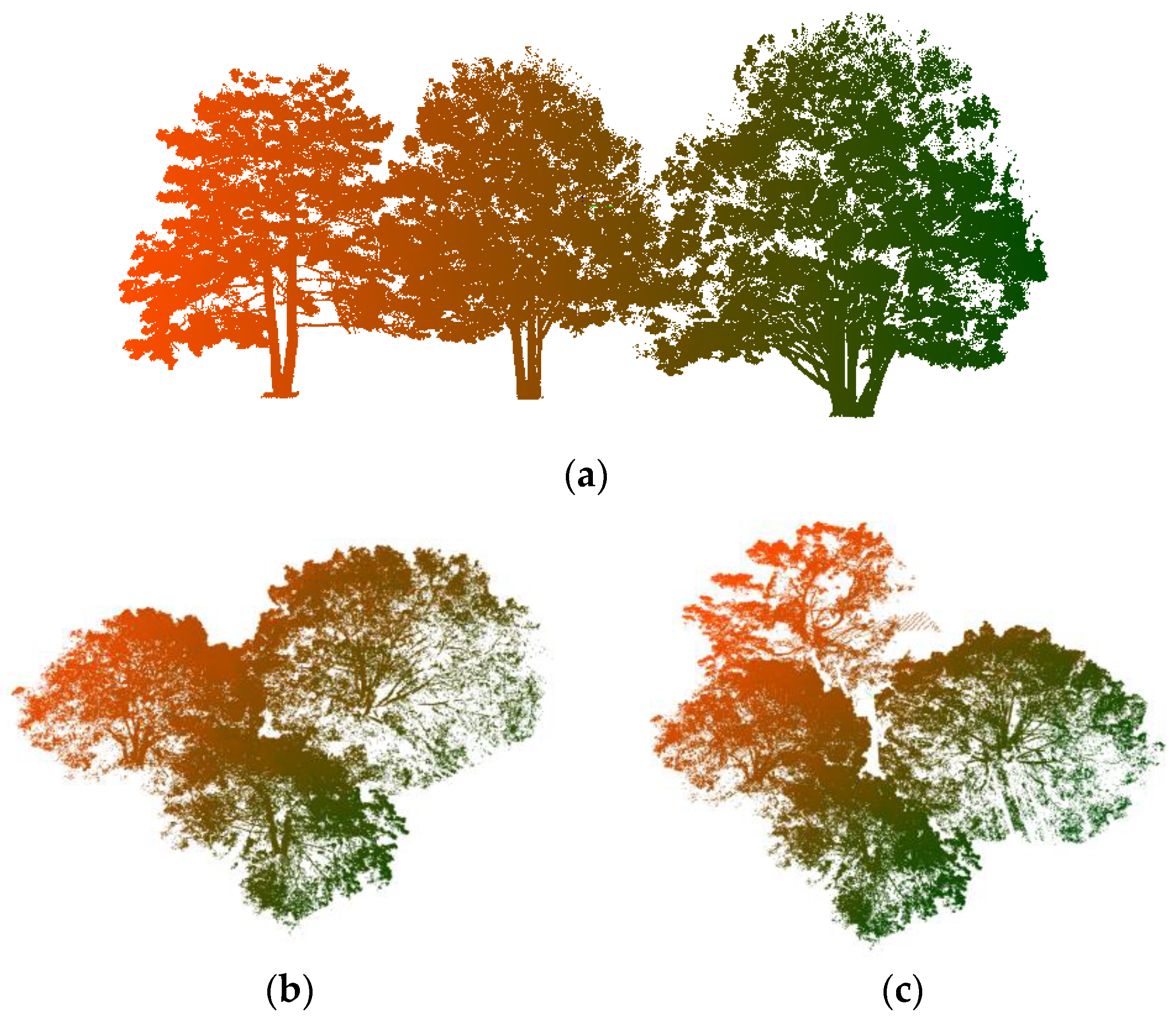
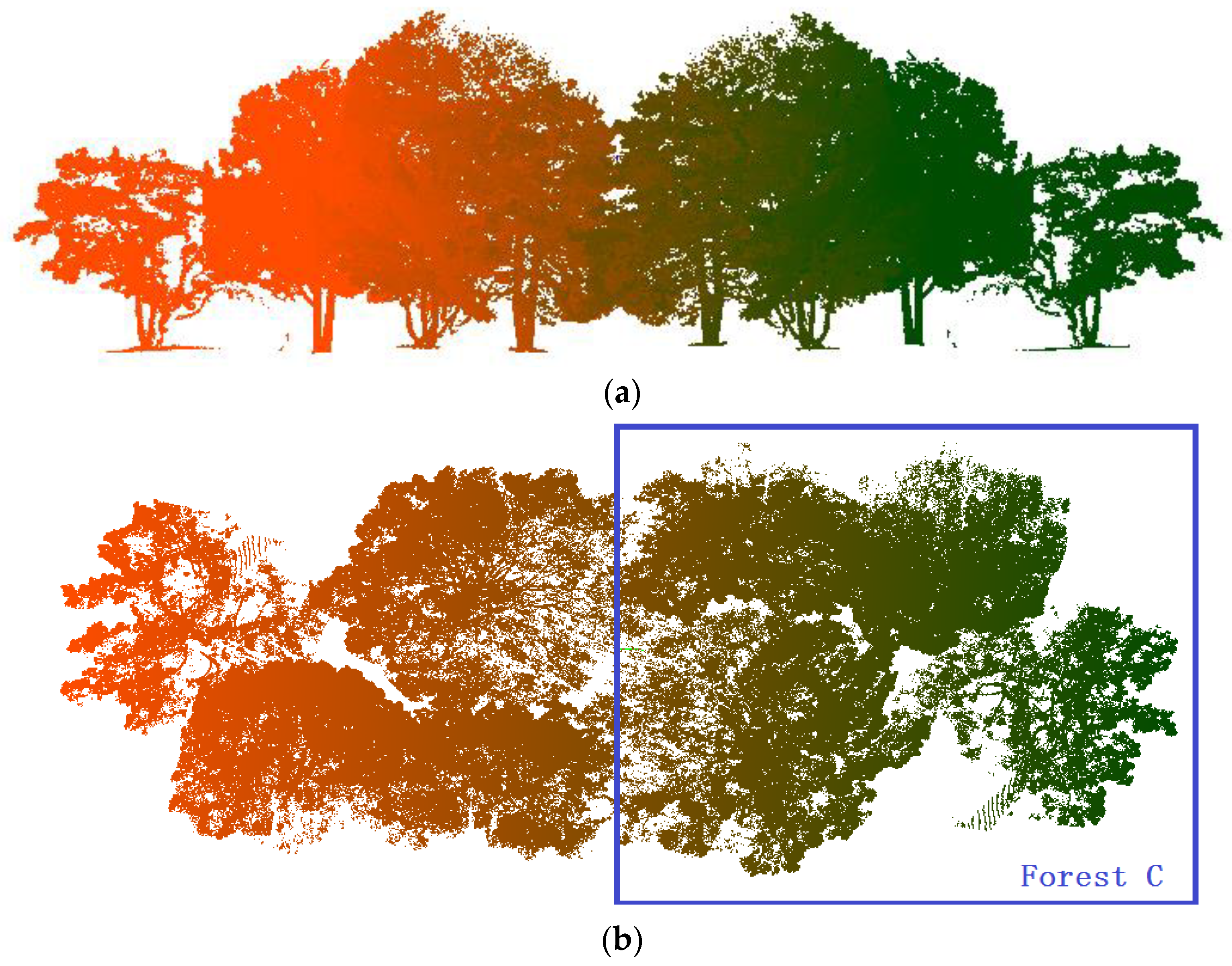

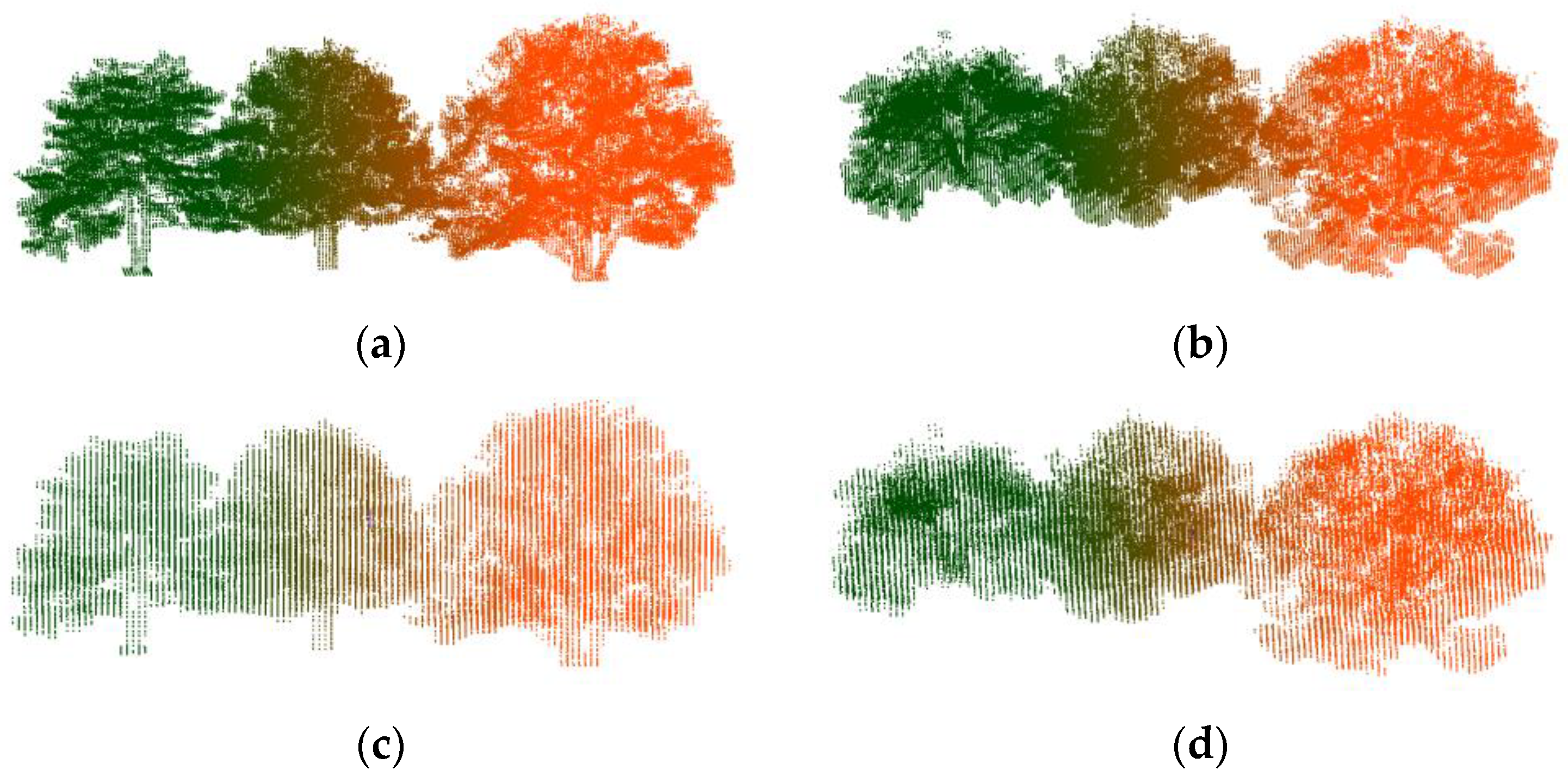






| Pine Na | Point N | Scene L | Scene W | Scene H |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pine A | 311,505 | 12.648 | 13.841 | 13.686 |
| Pine B | 487,555 | 10.182 | 9.306 | 11.932 |
| Pine C | 116,940 | 10.308 | 12.254 | 8.241 |
| Pine D | 269,366 | 8.469 | 11.188 | 11.113 |
| Forest Na | Tree N | Point N | Scene L | Scene W | Scene H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest A | 3 | 1,068,426 | 13.017 | 29.802 | 13.686 |
| Forest B | 3 | 1,068,426 | 21.072 | 17.680 | 13.686 |
| Forest C | 4 | 1,185,366 | 21.087 | 23.774 | 13.686 |
| Forest D | 8 | 2,370,732 | 21.587 | 44.774 | 13.686 |
| Forest Na | Tree N | Point N | Scene L | Scene L | Scene L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUSH06 | 34 | 14,500,905 | 82.259 | 76.570 | 25.164 |
| Method | Hard Segmentation | Soft Segmentation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | mAcc | mIoU | Acc | mAcc | mIoU | |
| Forest A | 0.9801 | 0.9815 | 0.9622 | 0.9827 | 0.9845 | 0.9672 |
| Forest B | 0.9563 | 0.9624 | 0.9172 | 0.9639 | 0.9691 | 0.9318 |
| Forest C | 0.9595 | 0.9679 | 0.9319 | 0.9672 | 0.9749 | 0.9456 |
| Forest D | 0.9463 | 0.9556 | 0.9066 | 0.9575 | 0.9652 | 0.9262 |
| Average (%) | 0.9606 | 0.9669 | 0.9295 | 0.9678 | 0.9734 | 0.9427 |
| Method | Acc | mAcc | mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hard Seg. | 0.859 | 0.8791 | 0.7279 |
| Soft Seg. without RG | 0.8587 | 0.8205 | 0.6826 |
| Soft Seg. with RG | 0.9516 | 0.9632 | 0.9272 |
| Steps | Forest A | Forest B | Forest C | Forest D | RUSH06 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Down-sampling | 0.0434 | 0.0376 | 0.0479 | 0.0851 | 0.7864 |
| Region Growing | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.5919 |
| Layer Partitioning | 0.031 | 0.0378 | 0.0394 | 0.033 | 0.1098 |
| Roots Detect | 0.0036 | 0.0041 | 0.0049 | 0.0018 | 0.014 |
| Delaunay + Voronoi | 0.0024 | 0.0022 | 0.0029 | 0.0037 | 0.0176 |
| Init Segmentation | 0.0295 | 0.0279 | 0.0534 | 0.3537 | 0.6606 |
| Init Contour Build | 0.0111 | 0.0108 | 0.012 | 0.0214 | 0.0436 |
| Refine with KNN | 0.0777 | 0.0895 | 0.1076 | 0.2674 | 1.083 |
| Refine with Contour | 0.0119 | 0.0128 | 0.014 | 0.0298 | 0.0697 |
| Total | 0.2106 | 0.2227 | 0.2821 | 0.7959 | 6.3766 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, M.; Li, G. Soft Segmentation of Terrestrial Laser Scanning Point Cloud of Forests. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6228. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106228
Dai M, Li G. Soft Segmentation of Terrestrial Laser Scanning Point Cloud of Forests. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(10):6228. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106228
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Mingrui, and Guohua Li. 2023. "Soft Segmentation of Terrestrial Laser Scanning Point Cloud of Forests" Applied Sciences 13, no. 10: 6228. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106228
APA StyleDai, M., & Li, G. (2023). Soft Segmentation of Terrestrial Laser Scanning Point Cloud of Forests. Applied Sciences, 13(10), 6228. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106228





