The Effect of Blue Noise on the Optimization Ability of Hopfield Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Constructing Colored Noise Generators
3.2. Blue Noise Hopfield Neural Network Model
3.3. Improvement of Neural Network Model Based on Colored Noise
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Blue Noise Hopfield Neural Networks in Optimization Problems
- (1)
- The problem to be solved is described in computer language, where the output of the neural network corresponds to the solution of the problem.
- (2)
- Construct the energy function of the neural network so that its minimum value corresponds to the optimal solution of the problem.
- (3)
- The initial states of the neurons are generated, and the weights W and bias inputs I between the neurons are corrected via the output values of each iteration after noise perturbation.
- (4)
- In the case that the energy function has converged, and the output accuracy is satisfied, the steady state of its operation is the optimal solution under certain conditions.
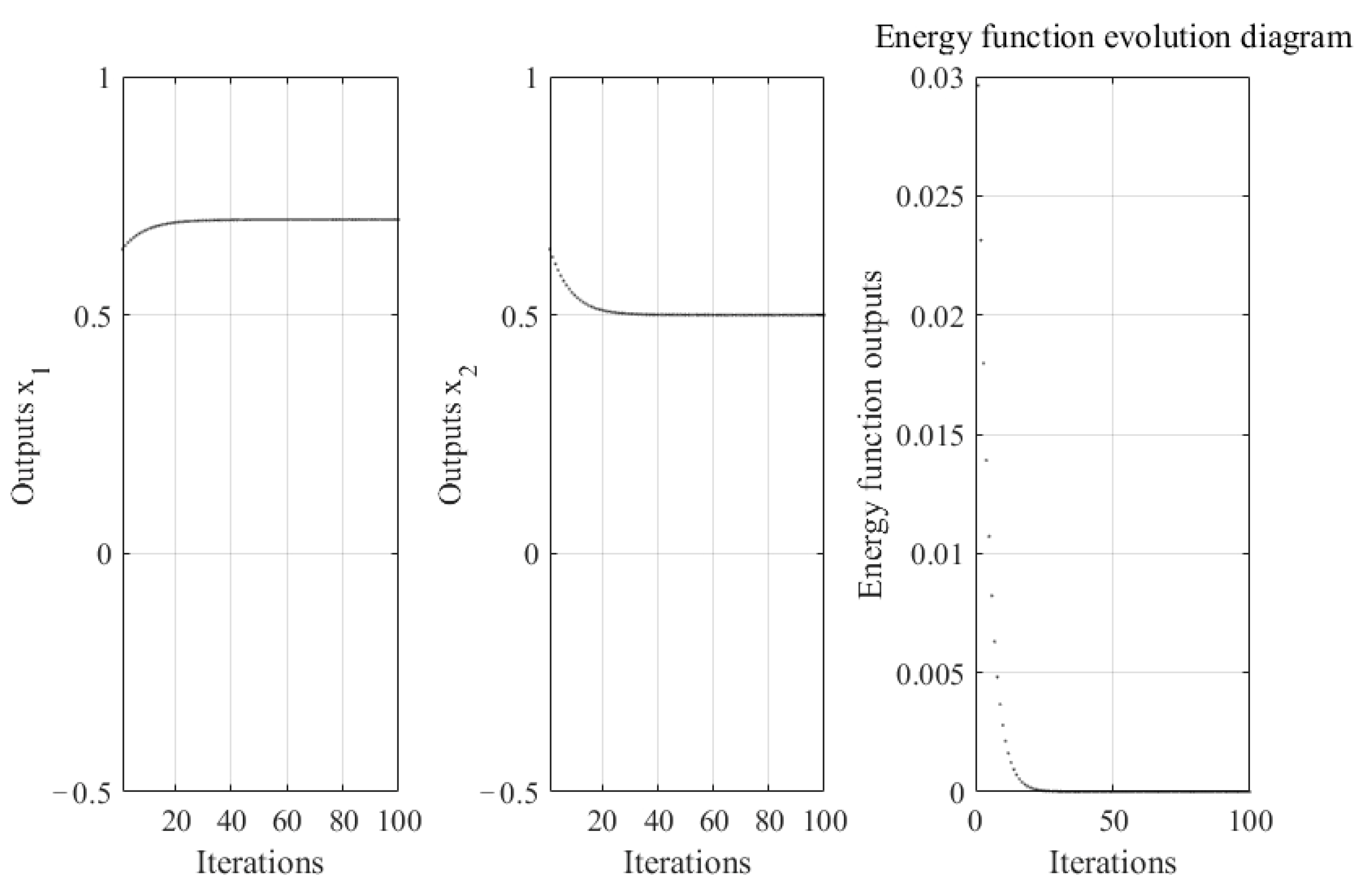
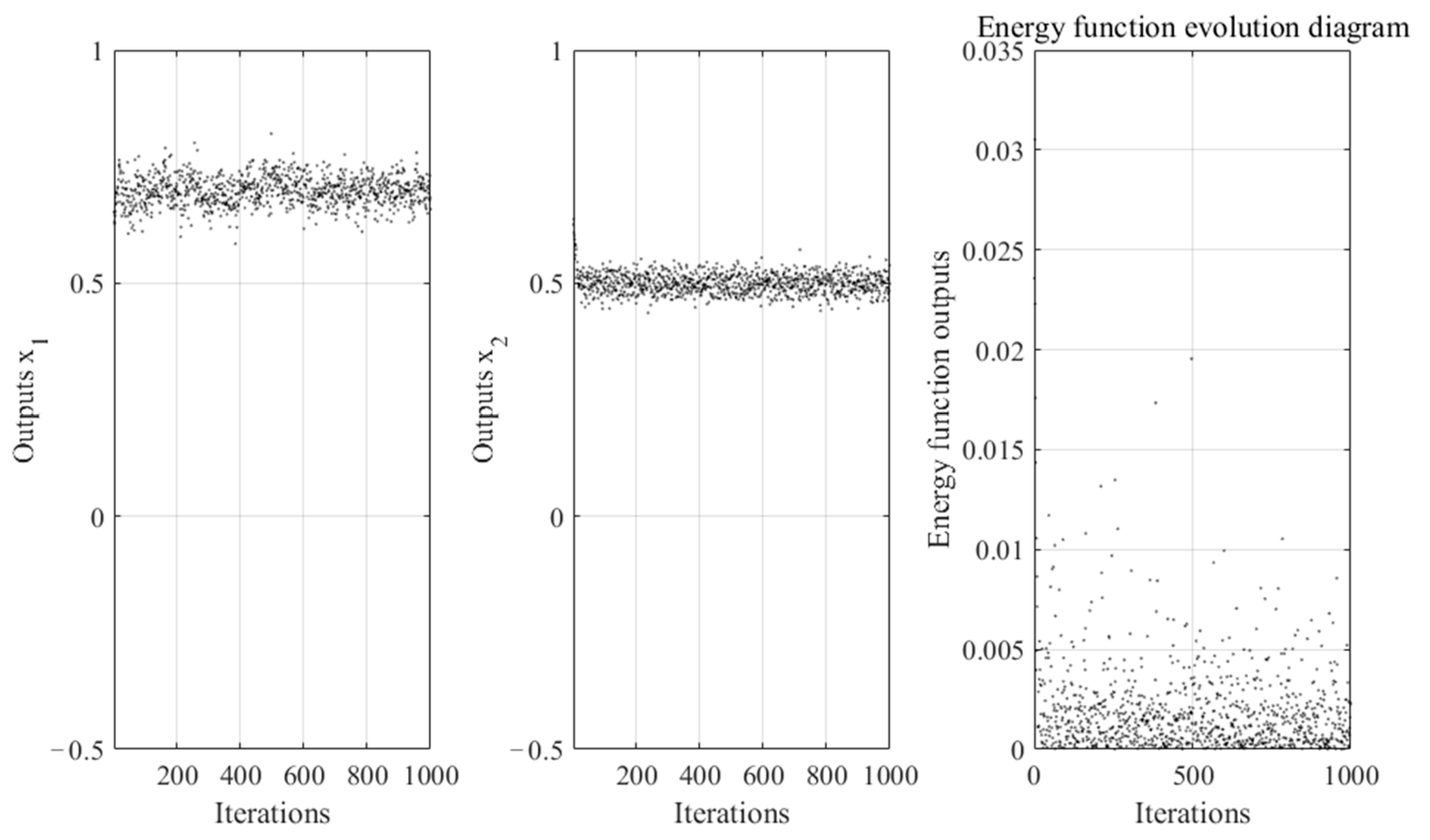
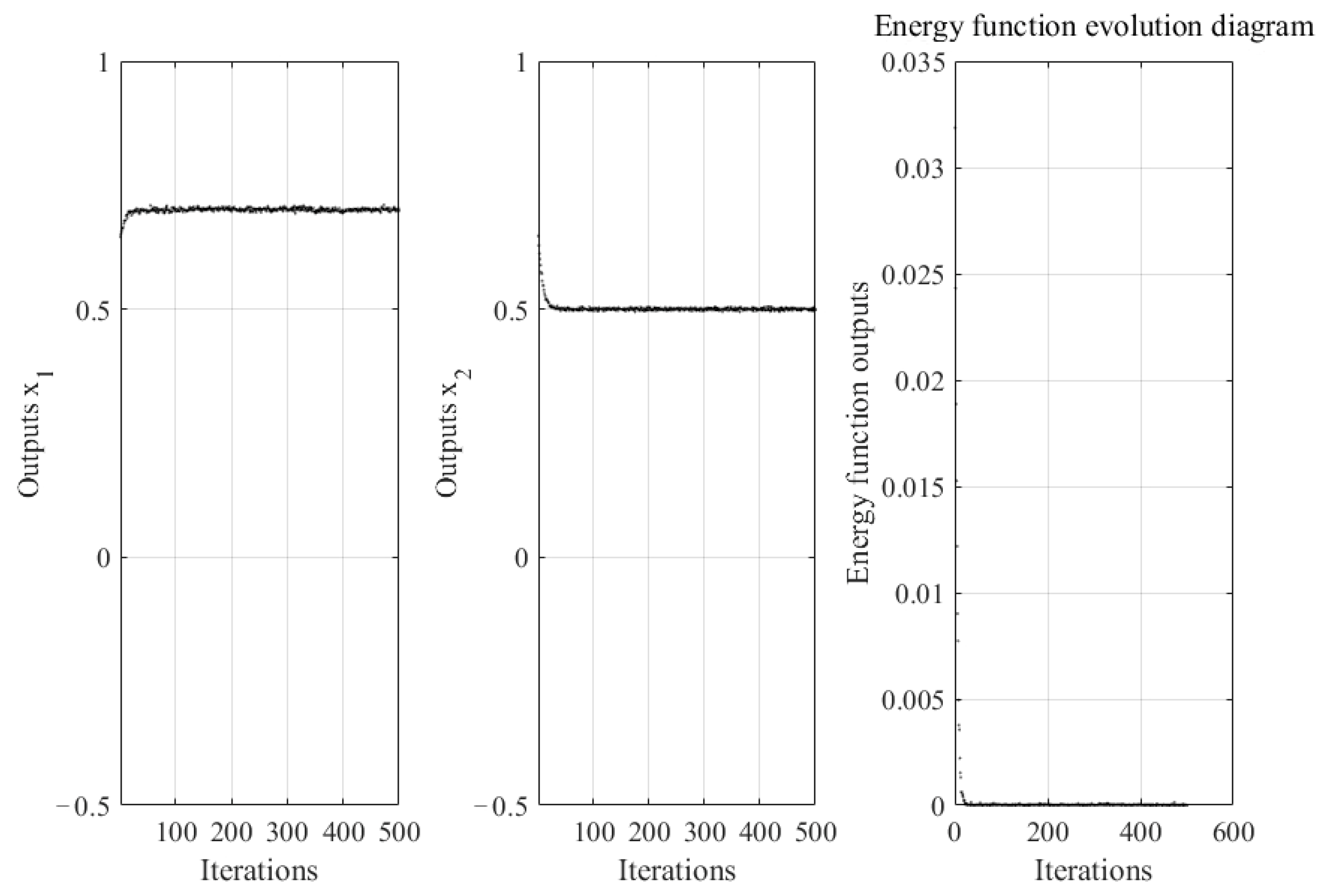
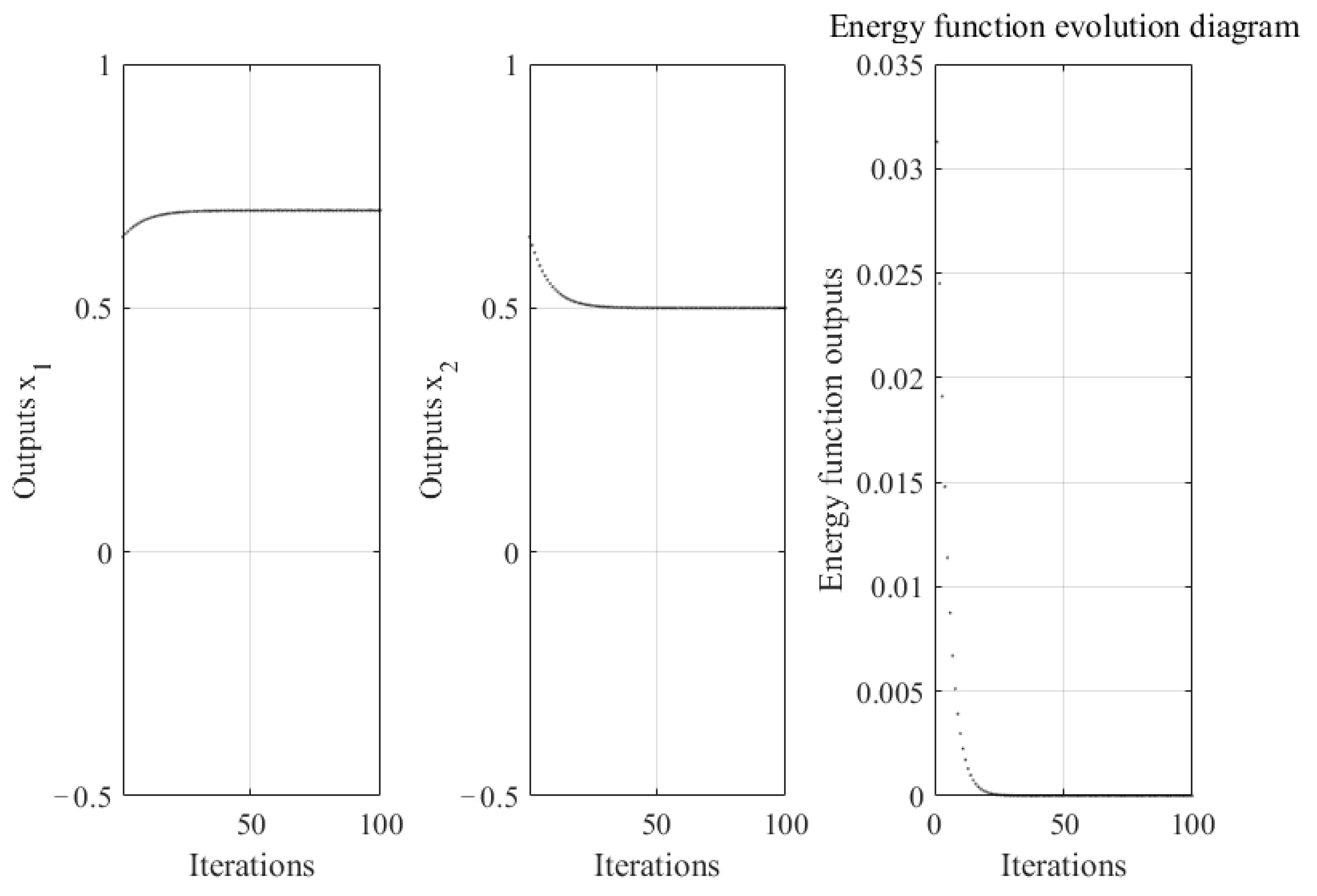
4.1.1. The Effect of Blue Noise on the Ability of Neural Networks to Optimize Continuous Functions
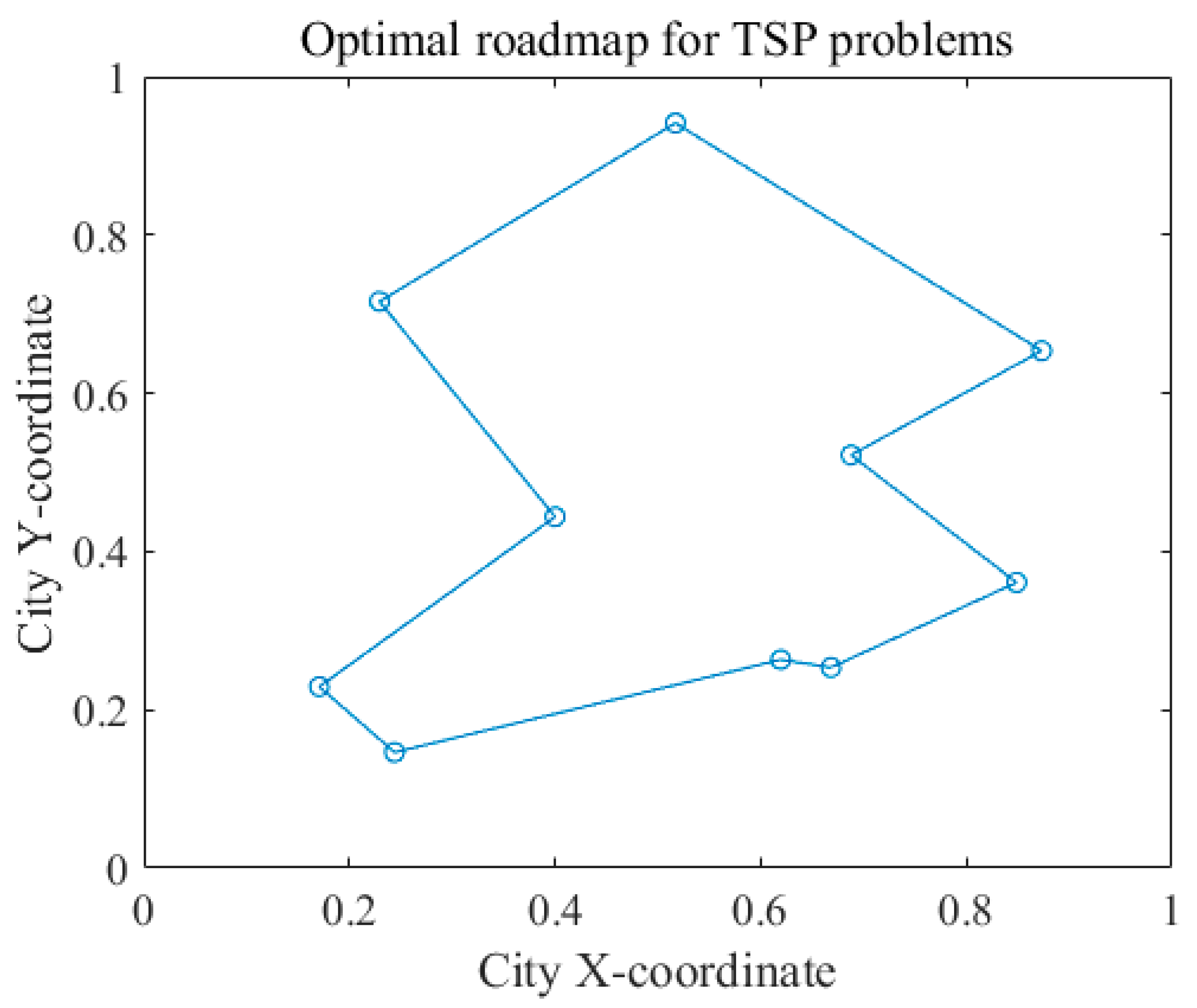
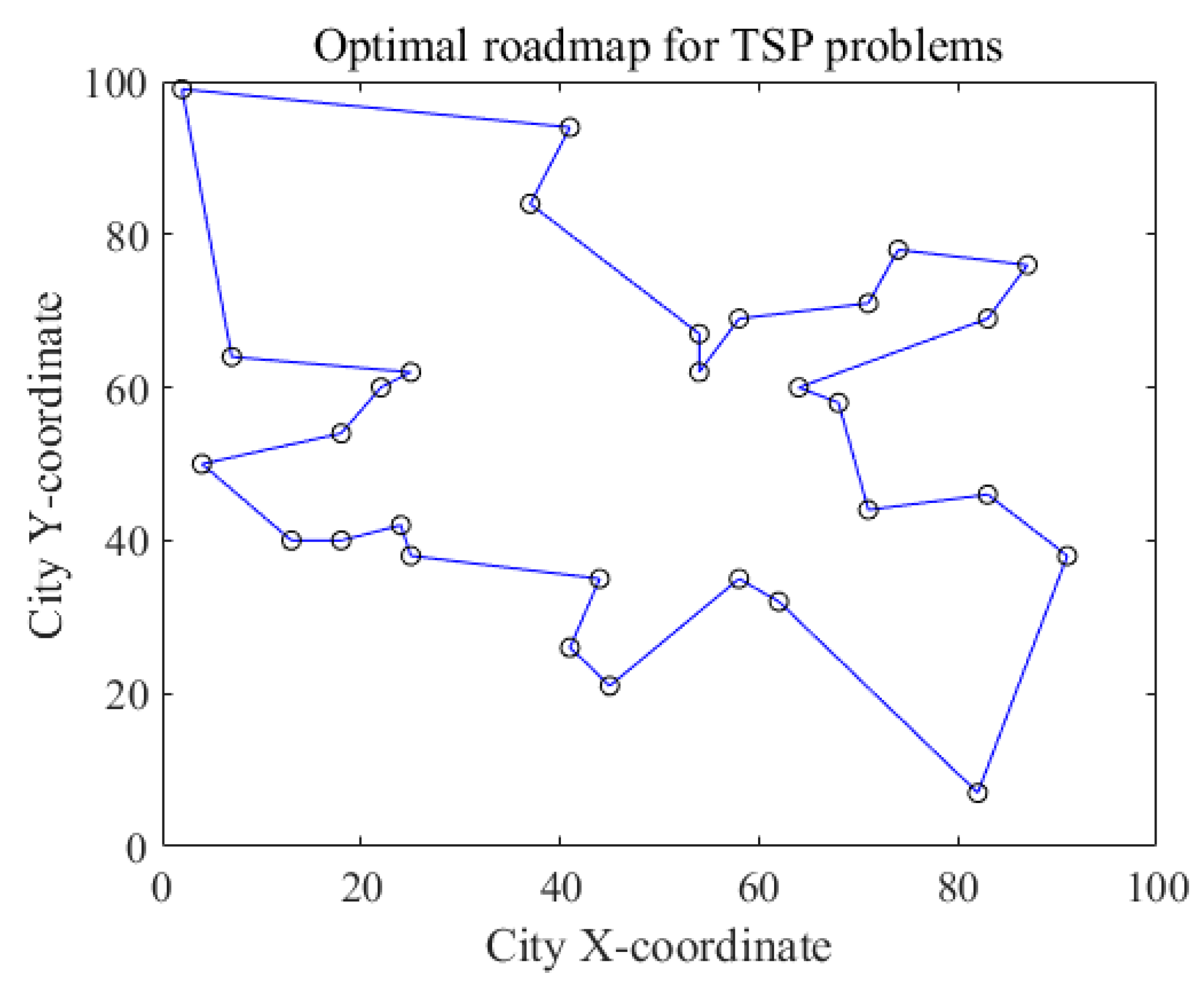
4.1.2. The Effect of Blue Noise on the Optimization Power of Neural Networks for Combinatorial Problems
4.2. Chaotic Neural Network Model Based on Blue Noise
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ran, X.; Zhou, X.; Lei, M.; Tepsan, W.; Deng, W. A Novel K-Means Clustering Algorithm with a Noise Algorithm for Capturing Urban Hotspots. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Gupta, A. Dealing with noise problem in machine learning data-sets: A systematic review. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 161, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, C.H.; Wong, M.S.; Chan, P.W. Spatio-Temporal Data Fusion for Satellite Images Using Hopfield Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezapour, S.; Kumar, P.; Erturk, V.S.; Etemad, S. A Study on the 3D Hopfield Neural Network Model via Nonlocal Atangana–Baleanu Operators. Complexity 2022, 2022, 6784886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, S. Single Neuronal Dynamical System in Self-Feedbacked Hopfield Networks and Its Application in Image Encryption. Entropy 2021, 23, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citko, W.; Sienko, W. Inpainted Image Reconstruction Using an Extended Hopfield Neural Network Based Machine Learning System. Sensors 2022, 22, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Q.; Zhen, X.X.; Tang, M. Dynamical System in Chaotic Neurons with Time Delay Self-Feedback and Its Application in Color Image Encryption. Complexity 2022, 2022, 2832104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, X.; Yan, D. Clustering Based on Continuous Hopfield Network. Mathematics 2022, 10, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillar, C.; Chan, T.; Taubman, R.; Rolnick, D. Hidden Hypergraphs, Error-Correcting Codes, and Critical Learning in Hopfield Networks. Entropy 2021, 23, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Jamaludin, S.Z.; Mohd Kasihmuddin, M.S.; Md Ismail, A.I.; Mansor, M.A.; Md Basir, M.F. Energy Based Logic Mining Analysis with Hopfield Neural Network for Recruitment Evaluation. Entropy 2021, 23, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, Z. An optimization routing protocol for FANETs. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2019, 2019, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandali, K.; Bennis, L.; Bennis, H. A new hybrid routing protocol using a modified K-means clustering algorithm and continuous hopfield network for VANET. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 47169–47183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X.; Cui, X.Q. Dynamic positioning colored noise influence function—A first order ar model as an example. J. Surv. Mapp. 2003, 2003, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Aviles-Espinosa, R.; Dore, H.; Rendon-Morales, E. An Experimental Method for Bio-Signal Denoising Using Unconventional Sensors. Sensors 2023, 23, 3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Xu, Y.; Luo, L.; Liu, H.; Lu, K.; Liu, J. Regularized Denoising Masked Visual Pretraining for Robust Embodied PointGoal Navigation. Sensors 2023, 23, 3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Yan, H.; Huang, T. Optimal tracking control of networked systems subject to model uncertainty and additive colored Gaussian noise. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 3209–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, N.F.; Zhao, D. Stochastic properties of thermoacoustic oscillations in an annular gas turbine combustion chamber driven by colored noise. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 480, 115423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, C.; Gnan, N.; Paoluzzi, M.; Zaccarelli, E.; Crisanti, A. Critical active dynamics is captured by a colored-noise driven field theory. Commun. Phys. 2022, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, N.; Hinojosa, C.; Arguello, H. Adaptive grayscale compressive spectral imaging using optimal blue noise coding patterns. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 117, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matt, G.; Lucy, T.; Ben, J.; Fiona, P.; James, M. The importance of noise colour in simulations of evolutionary systems. Artif. Life 2021, 27, 164–182. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z. Wavelet Analysis of Red Noise and Its Application in Climate Diagnosis. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5462965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatayama, A.; Matsubara, A.; Nakashima, S.; Nishifuji, S. Effect of Pink Noise on EEG and Memory Performance in Memory Task. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 10th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE), Kyoto, Japan, 12–15 October 2021; pp. 238–241. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Z.; Ma, K.; Tang, S.; Sarker, M.S.; Yamahara, H.; Tabata, H. Phase locking of ultra-low power consumption stochastic magnetic bits induced by colored noise. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 151, 111262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulcehre, C.; Moczulski, M.; Denil, M. Noisy Activation Functions. Proc. Mach. Learn. Res. 2016, 48, 3059–3068. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.; Li, W.; Xiang, H. Fault Diagnosis Method and Application Based on Multi-scale Neural Network and Data Enhancement for Strong Noise. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 2023, 2023, 2523–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Bijan, S.; Maria, R.; Masoud, M. Vision-based concrete crack detection using a hybrid framework considering noise effect. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 61, 2352–7102. [Google Scholar]
- Nagamani, G.; Soundararajan, G.; Subramaniam, R.; Azeem, M. Robust extended dissipativity analysis for Markovian jump discrete-time delayed stochastic singular neural networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 9699–9712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, S.; Nagamani, G.; Radhika, T. Further Results on Dissipativity Criterion for Markovian Jump Discrete-Time Neural Networks with Two Delay Components Via Discrete Wirtinger Inequality Approach. Neural Process. Lett. 2017, 45, 939–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, S.; Nagamani, G.; Gopalakrishnan, P. State estimation for discrete-time neural networks with two additive time-varying delay components based on passivity theory. Int. J. Pure Appl. Math. 2016, 106, 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Wang, Z. Stability analysis of fraction-order Hopfield neuron network and noise-induced coherence resonance. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 3520972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhivomirov, H. A Method for Colored Noise Generation. Rom. J. Acoust. Vib. 2018, 15, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.H.; Wang, Z.H.; Wu, G.Q. Full-phase filtered white noise generates colored noise and its power spectrum estimation. J. Circuits Syst. 2005, 2005, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.H.; Liu, Y.Y.; Chen, K. A review of detection signal-to-noise ratio calculation methods and principles. Electroacoust. Technol. 2016, 40, 37–43+57. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.; Guan, D.; Ma, T.; Khattak, A.M. Classification with class noises through probabilistic sampling. Inf. Fusion 2018, 41, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshgoftaar, T.M.; Van Hulse, J. Empirical case studies in attribute noise detection. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C (Appl. Rev.) 2009, 39, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fan, H.X.; Jiao, Y.H.; Xu, Y.Q.; Qin, F. Wavelet chaotic neural network with white noise and its application. J. Harbin Univ. Commer. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2011, 27, 177–181. [Google Scholar]
- Boykov, I.; Roudnev, V.; Boykova, A. Approximate Methods for Solving Problems of Mathematical Physics on Neural Hopfield Networks. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Manzano, C.; Segura-Navarrete, A.; Martinez-Araneda, C.; Vidal-Castro, C. Explainable Hopfield Neural Networks Using an Automatic Video-Generation System. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Ning, C.X.; Xu, Y.Q. A segmental annealing strategy for radial basis chaotic neural networks and applications. Comput. Appl. Softw. 2014, 31, 158–161. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.Q.; He, S.P.; Zhang, L. Research on chaotic neural networks with perturbation. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2008, 44, 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y. The White Noise Impact on the Optimal Performance of the Hopfield Neural Network. In Advanced Intelligent Computing Theories and Applications ICIC 2010; Huang, D.S., Zhao, Z., Bevilacqua, V., Figueroa, J.C., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 6215. [Google Scholar]
- Dhouib, S. A new column-row method for traveling salesman problem: The dhouib-matrix-TSP1. Int. J. Recent Eng. Sci. 2021, 8, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta, I.I.; Neira, D.A.; Ortega, D.A.; Varas, V.; Godoy, J.; Asín-Achá, R. Improving the state-of-the-art in the traveling salesman problem: An anytime automatic algorithm selection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 187, 0957–4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cai, R.; Lin, M. Enhanced List-Based Simulated Annealing Algorithm for Large-Scale Traveling Salesman Problem. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 144366–144380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; He, R.; Zhu, Y.; Zuo, Y.; He, L. Active Debris Removal Mission Planning Method Based on Machine Learning. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Q.; Sun, Y.; Hao, Y.L. A chaotic Hopfield network and its application in optimization computing. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2002, 38, 41–42. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, N.; Liu, G.Y.; Xu, Y.Q. Chaotic neural networks with Gaussian perturbations and applications. J. Intell. Syst. 2014, 9, 444–448. [Google Scholar]
- Fogel, D.B. Applying evolutionay programming to selected traveling salesman problems. Cybern. Syst. 1993, 24, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Aihara, K. Chaotic simulated annealing by a neural network model with transient chaos. Neural Netw. 1995, 8, 915–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xiu, C. A novel hysteretic chaotic neural network and its applications. Neurocomputing 2007, 70, 2561–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
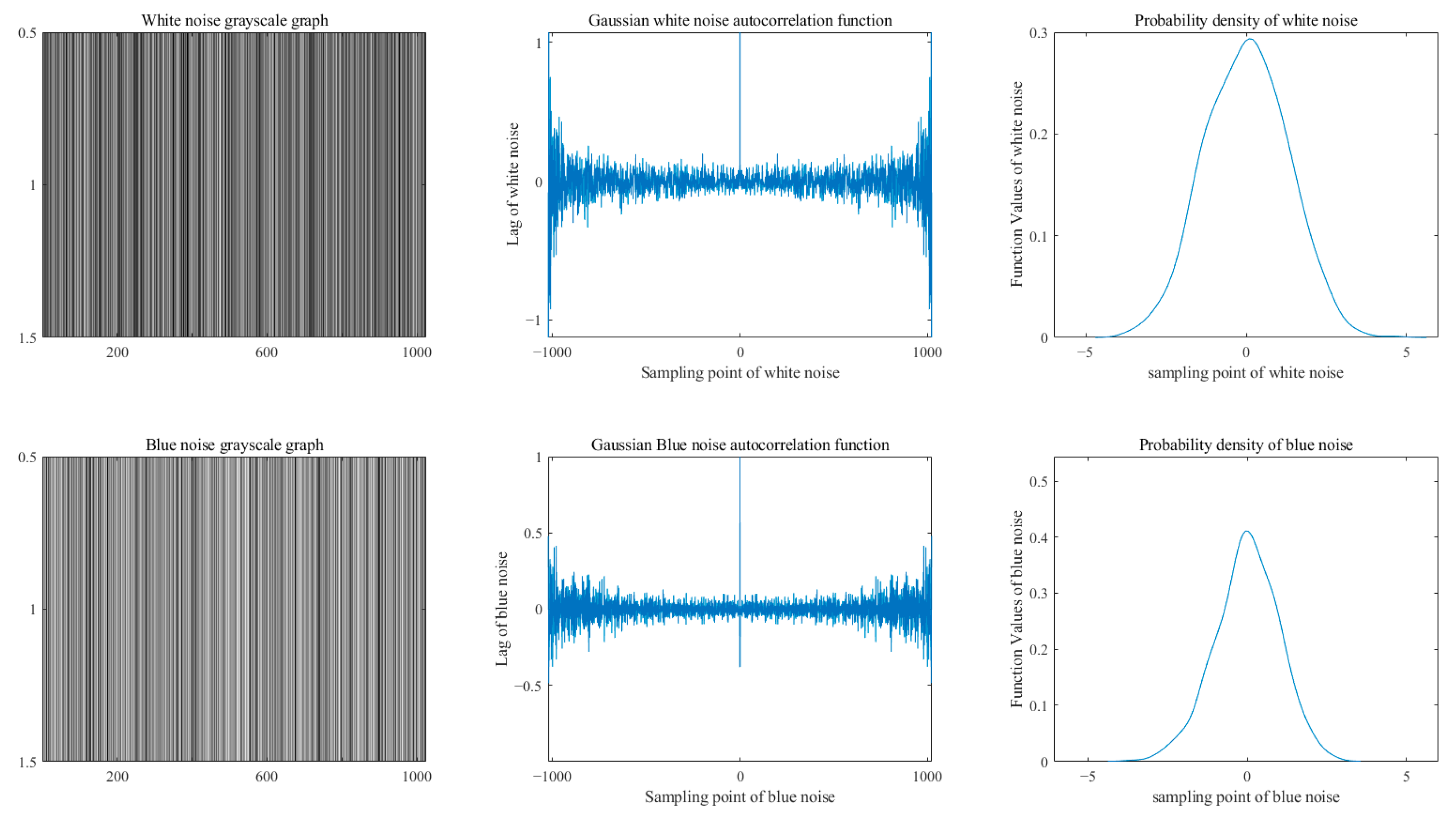
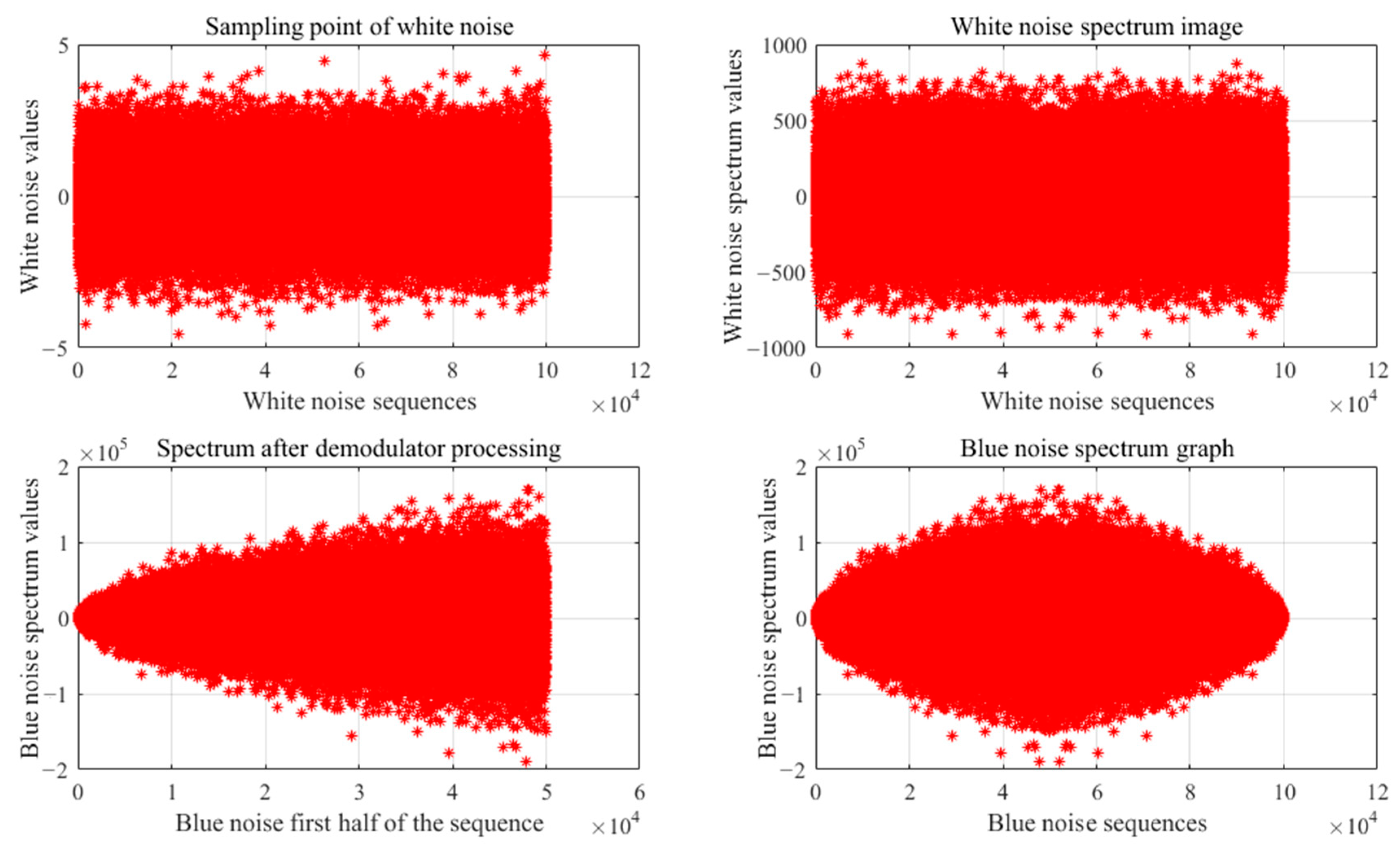
| Noise Type | PSD | Examples of Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Red noise | Identifying steady-state transitions in the integrated analysis of climate records | |
| Pink noise | Promotes neural oscillatory activity | |
| Blue noise | Multi-class blue noise sampling | |
| Violet noise | Acoustic thermal noise signal of water |
| SNR | Legal Path | Optimal Path | Legal Ratio | Optimal Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noiseless | 163 | 118 | 81.5% | 59.0% | |
| This paper | 40 | 40 | 7 | 20.0% | 3.5% |
| Reference [41] | 84 | 13 | 42.0% | 6.5% | |
| This paper | 50 | 118 | 54 | 59.0% | 27.0% |
| Reference [41] | 126 | 64 | 63.0% | 32.0% | |
| This paper | 60 | 156 | 111 | 78.0% | 55.5% |
| Reference [41] | 144 | 92 | 72.5% | 47.0% | |
| This paper | 70 | 162 | 116 | 81.0% | 58.0% |
| Reference [41] | 145 | 94 | 80.0% | 56.0% | |
| This paper | 80 | 163 | 117 | 81.5% | 58.5% |
| Reference [41] | 160 | 112 | 75.5% | 53.0% | |
| This paper | 90 | 169 | 128 | 84.5% | 64.0% |
| Reference [41] | 151 | 106 | 74.5% | 51.5% | |
| This paper | 120 | 161 | 109 | 80.5% | 54.5% |
| Reference [41] | 149 | 103 | 74.5% | 51.5% | |
| This paper | 150 | 164 | 113 | 82.0% | 55.5% |
| Reference [41] | 149 | 104 | 74.5% | 52.0% | |
| This paper | 180 | 166 | 114 | 83.0% | 57.0% |
| Reference [41] | 152 | 103 | 76.0% | 51.5% |
| coef | SNR | Legal Path | Optimal Path | Legal Ratio | Optimal Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| coef = 0 | 0 | 91 | 21 | 91.0% | 21.0% |
| 30 | 87 | 12 | 87.0% | 12.0% | |
| 60 | 99 | 26 | 99.0% | 26.0% | |
| 90 | 93 | 22 | 93.0% | 22.0% | |
| coef = 1/250 | 0 | 100 | 27 | 100% | 27.0% |
| 30 | 100 | 21 | 100% | 21.0% | |
| 60 | 100 | 31 | 100% | 31.0% | |
| 90 | 100 | 27 | 100% | 27.0% |
| Algorithm | Optimal Solution | Index J |
|---|---|---|
| SCA | 14 | 5.37% |
| HCNN | 20 | 3.45% |
| CNNBN | 31 | 2.53% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Li, L.; Xu, Y.; Wei, S.; Wang, Y. The Effect of Blue Noise on the Optimization Ability of Hopfield Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6028. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106028
Zhang Y, Chen B, Li L, Xu Y, Wei S, Wang Y. The Effect of Blue Noise on the Optimization Ability of Hopfield Neural Network. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(10):6028. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106028
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yu, Bin Chen, Lan Li, Yaoqun Xu, Sifan Wei, and Yu Wang. 2023. "The Effect of Blue Noise on the Optimization Ability of Hopfield Neural Network" Applied Sciences 13, no. 10: 6028. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106028
APA StyleZhang, Y., Chen, B., Li, L., Xu, Y., Wei, S., & Wang, Y. (2023). The Effect of Blue Noise on the Optimization Ability of Hopfield Neural Network. Applied Sciences, 13(10), 6028. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106028








