Deep Learning-Based Human Action Recognition with Key-Frames Sampling Using Ranking Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We introduce a novel ranking-based approach for human action recognition using 3D-CNN with raw depth sequence.
- First, we use SSIM or CCM ranking metrics to select k-ranked frames that contain more spatial and temporal changes. This allows us to discard the redundant frames having the same or very similar information.
- Then, we use transfer learning to perform the recognition of human action. It helps maintain the knowledge of previous hand gesture datasets and applies them to human action datasets.
- We also adopt three different publicly available benchmark human action recognition datasets to emphasize the robustness of the proposed method.
2. Related Works
3. Proposed Methodology
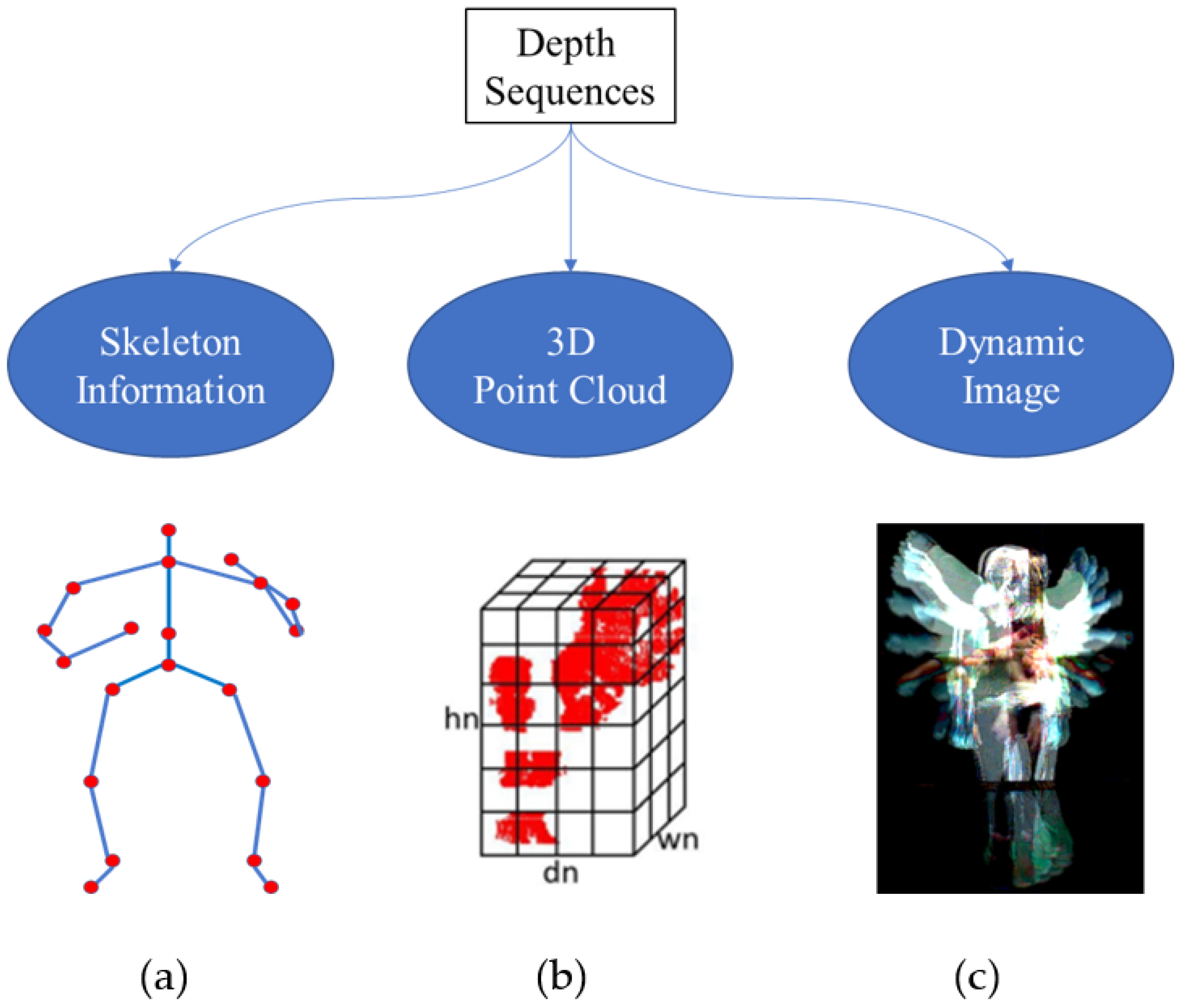
3.1. Motivation
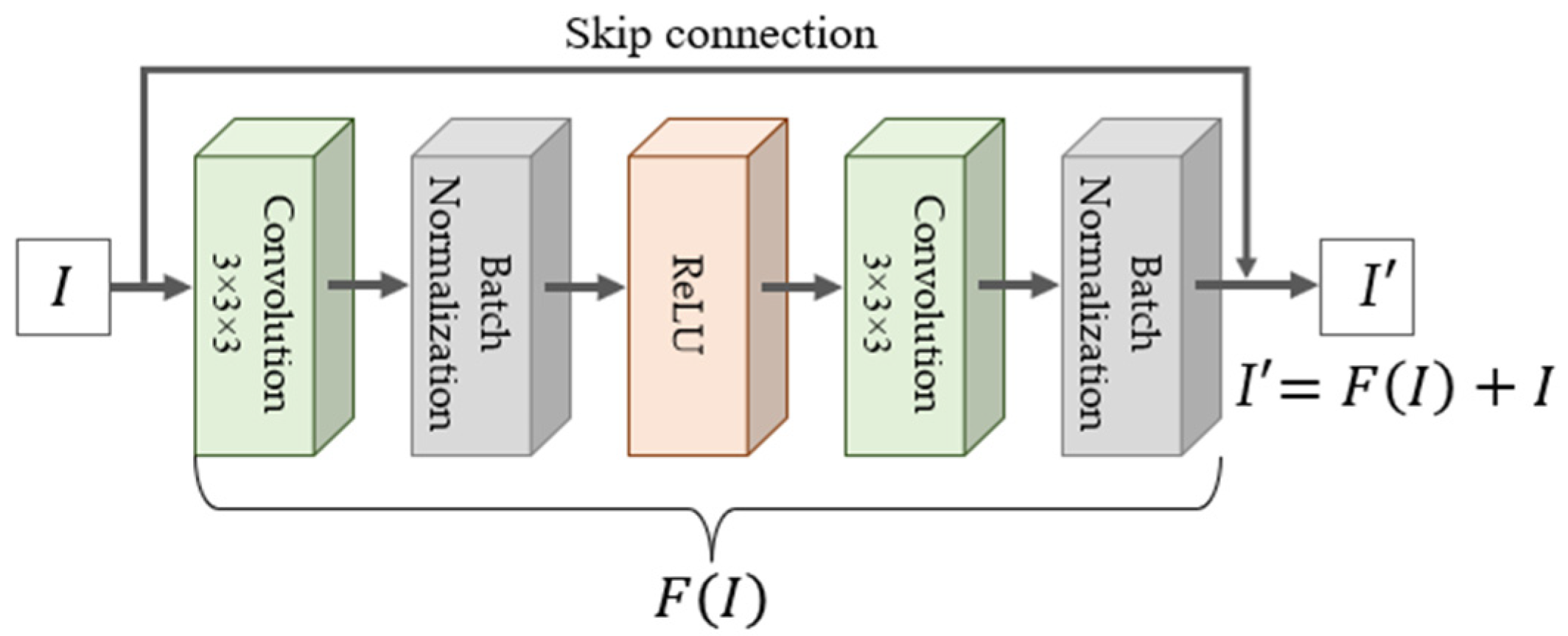
3.2. Architecture of the Proposed Method
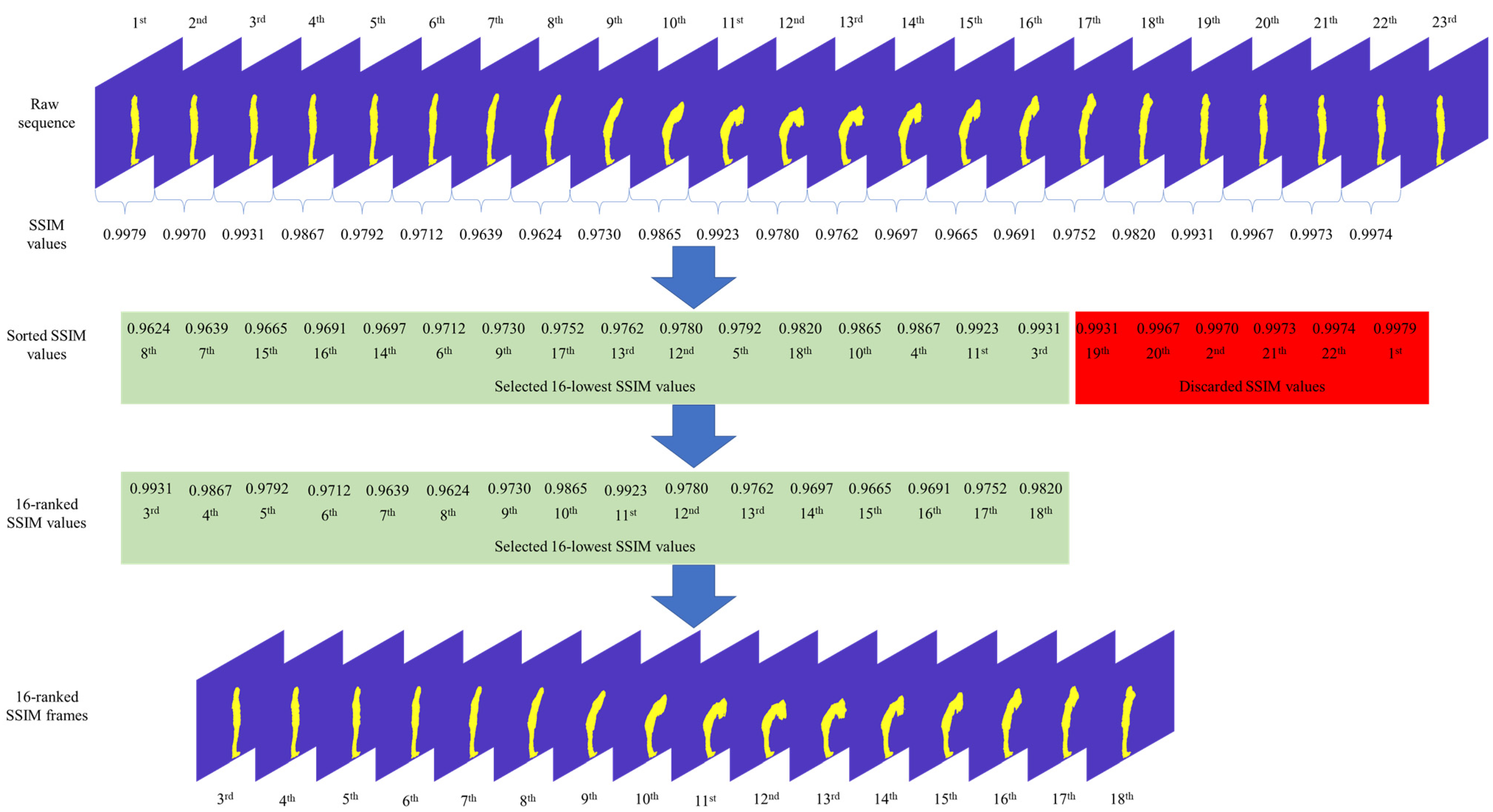
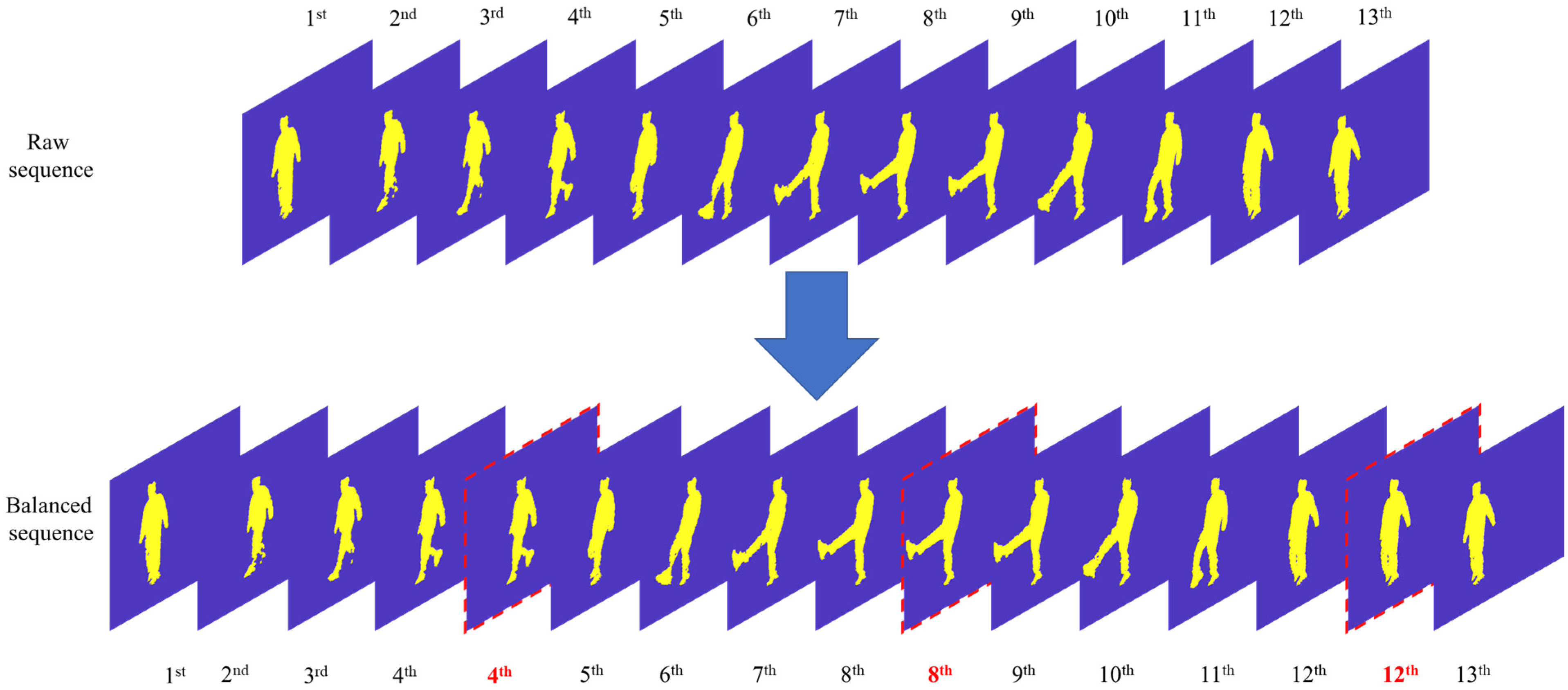
3.2.1. Key-Frames Sampling Using Ranking Methods
3.2.2. Deep Leaning for Human Action Classification
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Datasets
4.1.1. DHA Dataset
4.1.2. MSR-Action3D Dataset
4.1.3. UTD-MHAD Dataset
4.1.4. Settings of the Training and Testing Dataset
4.2. Environmental Setup and Evaluation Metrics
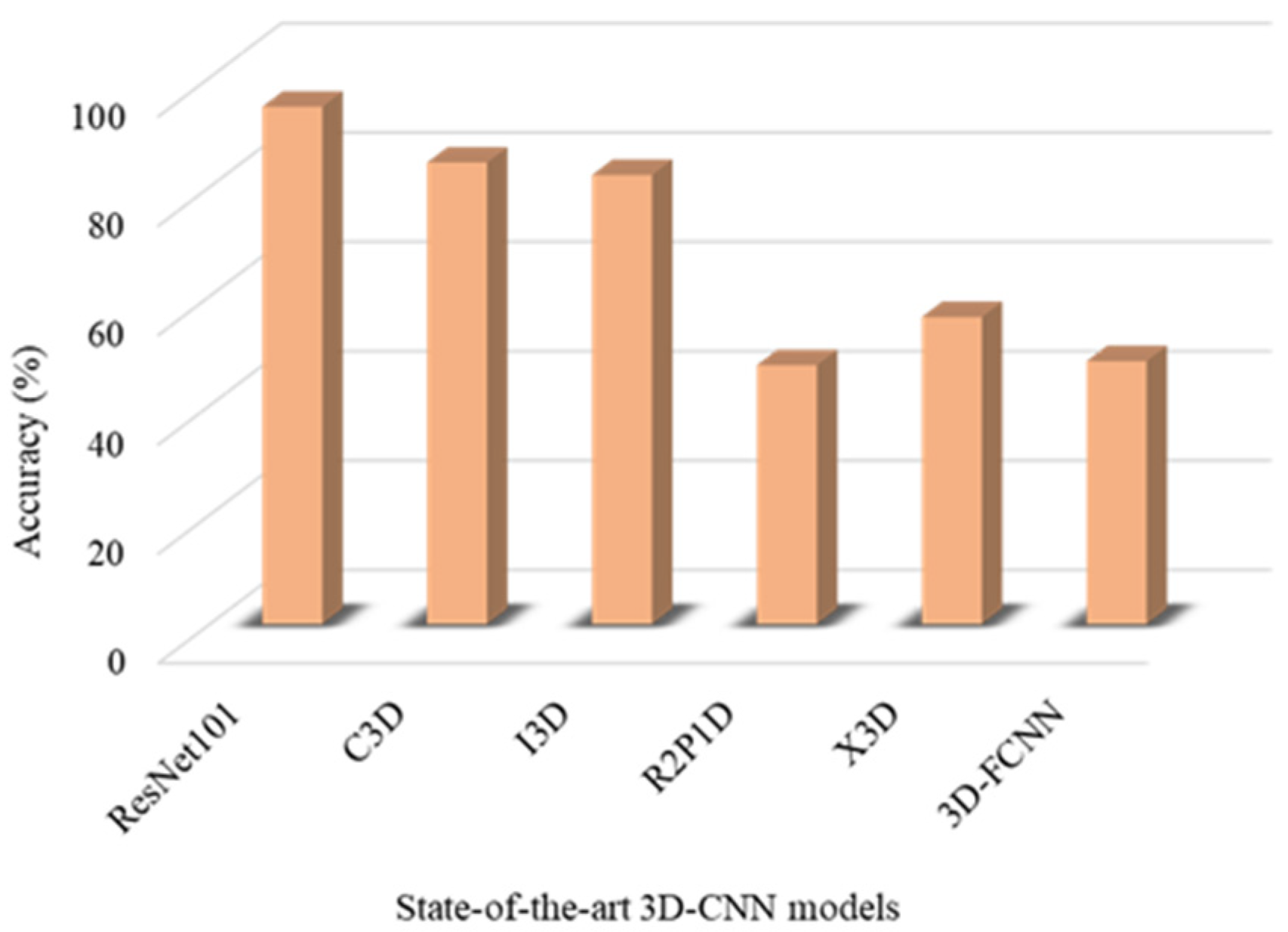
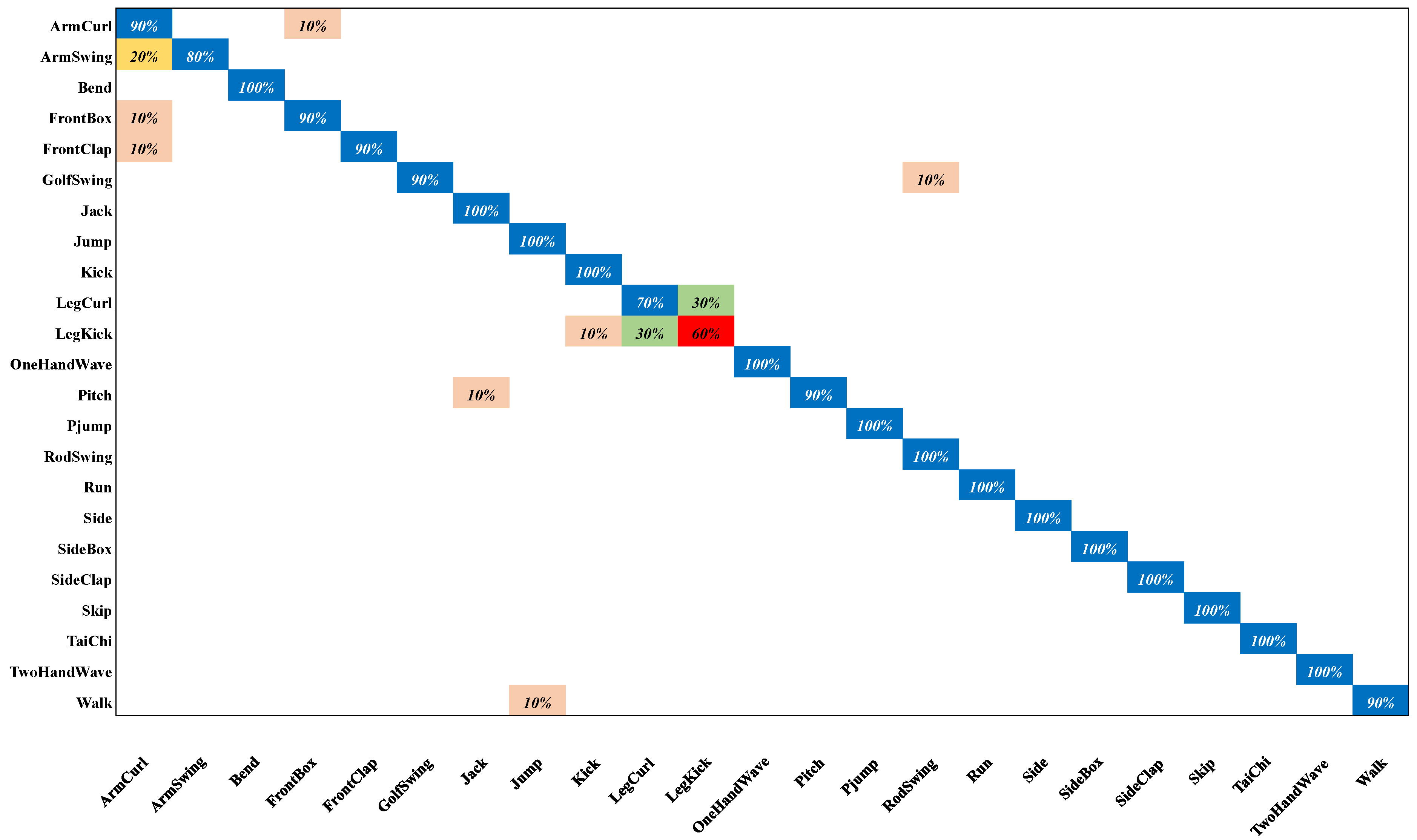
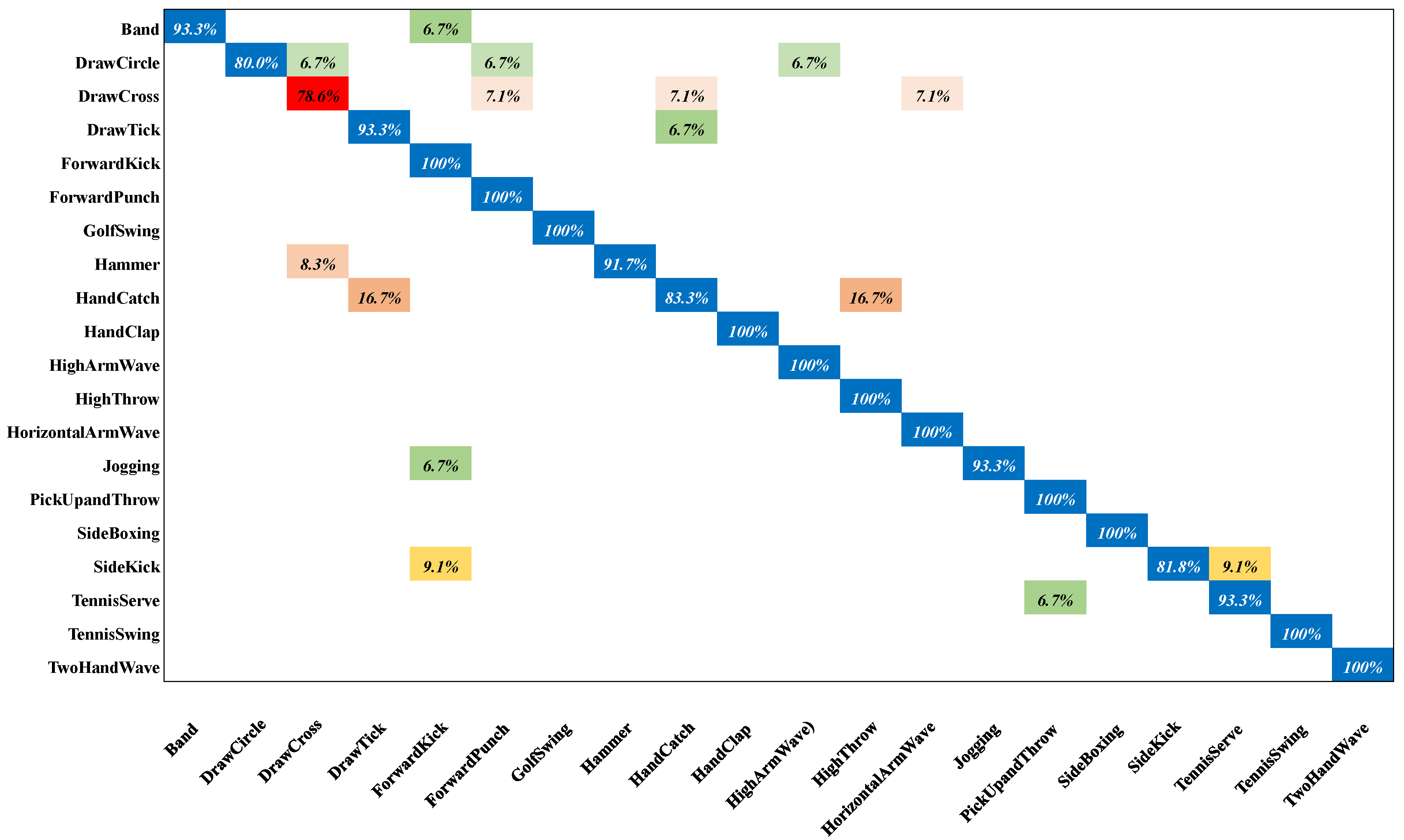
4.3. Performance Evaluations and Comparisons
4.4. Ablation Study
4.5. Complexity Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dawar, N.; Kehtarnavaz, N. Continuous detection and recognition of actions of interest among actions of non-interest using a depth camera. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Beijing, China, 17–20 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Vial, R.; Lu, S. Tornado: A spatio-temporal convolutional regression network for video action proposal. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.; Nguyen, B.P.; Chng, C.B.; Chui, C.K. In Situ Spatial AR Surgical Planning Using projector-Kinect System. In Proceedings of the Fourth Symposium on Information and Communication Technology, Da Nang, Vietnam, 5–6 December 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, R.T. A survey of augmented reality. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Environ. 1997, 6, 355–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangbemi, A.S.; Liu, B.; Yu, N.H. Efficient human action recognition interface for augmented and virtual reality applications based on binary descriptor. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality and Computer Graphics, Otranto, Italy, 24–27 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, A.; Kamal, S.; Kim, D. A Depth Video Sensor-Based Life-Logging Human Activity Recognition System for Elderly Care in Smart Indoor Environments. Sensors 2014, 14, 11735–11759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Ma, N.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Wang, P.; Pang, G.; Shi, X. Survey of pedestrian action recognition techniques for autonomous driving. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2020, 25, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, V.; Makris, D.; Argyriou, V. G3D: A gaming action dataset and real time action recognition evaluation framework. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tian, Y.; He, M. Monocular human pose estimation: A survey of deep learning-based methods. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2020, 192, 102897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Peng, X.; Yang, J.; Lu, S.; Qiao, Y. Suppressing uncertainties for large-scale facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Wu, T.; Luo, Z.; Duan, F.; Qiao, X.; Guo, P. Learning Behavior Analysis in Classroom Based on Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing (ICICIP), Marrakesh, Morocco, 14–19 December 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köpüklü, O.; Gunduz, A.; Kose, N.; Rigoll, G. Real-time hand gesture detection and classification using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recog. (FG), Lille, France, 14–18 May 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ameur, S.; Khalifa, A.B.; Bouhlel, M.S. A novel hybrid bidirectional unidirectional LSTM network for dynamic hand gesture recognition with leap motion. Entertain. Comput. 2020, 35, 100373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Eusanio, A.; Simoni, A.; Pini, S.; Borghi, G.; Vezzani, R.; Cucchiara, R. A Transformer-Based Network for Dynamic Hand Gesture Recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Fukuoka, Japan, 25–28 November 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Song, Y.; Gu, Y.; Li, A. Human action recognition based on depth images from Microsoft Kinect. In Proceedings of the Fourth Global Congress on Intelligent Systems, Hong Kong, China, 3–4 December 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Khan, N. Inertial Sensor Data to Image Encoding for Human Action Recognition. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 9, 10978–10988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, W. Skeleton optical spectra-based action recognition using convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2016, 28, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasnim, N.; Islam, M.; Baek, J.H. Deep Learning-Based Action Recognition Using 3D Skeleton Joints Information. Inventions 2020, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hou, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, W. Joint distance maps-based action recognition with convolutional neural networks. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2017, 24, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tasnim, N.; Islam, M.K.; Baek, J.H. Deep Learning Based Human Activity Recognition Using Spatio-Temporal Image Formation of Skeleton Joints. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjoub, A.B.; Atri, M. Human action recognition using RGB data. In Proceedings of the 11th International Design & Test Symposium (IDT), Tunisia, Hammamet, 18–20 December 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Sah, A.; Srivastava, R. Deep learning-based multi-modal approach using RGB and skeleton sequences for human activity recognition. Multimed. Syst. 2020, 26, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, C.; Vishwakarma, D.K. View-invariant deep architecture for human action recognition using two-stream motion and shape temporal dynamics. IEEE Trans. Image Proc. 2020, 29, 3835–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Tian, Y.L. Eigenjoints-based action recognition using naive-bayes-nearest-neighbor. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Chen, C.C.; Aggarwal, J.K. View invariant human action recognition using histograms of 3d joints. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Cheng, J.; Feng, W.; Tao, D. Skeleton embedded motion body partition for human action recognition using depth sequences. Signal Process. 2018, 143, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tian, Y.; Guo, X.; Liu, J. DAAL: Deep activation-based attribute learning for action recognition in depth videos. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2018, 167, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z. Action recognition based on a bag of 3d points. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahmani, H.; Mahmood, A.; Huynh, D.Q.; Mian, A. HOPC: Histogram of oriented principal components of 3D pointclouds for action recognition. In Proceedings of the European conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Jahan, H.; Huang, X.; Feng, Z. Human action recognition method based on historical point cloud trajectory characteristics. Vis. Comput. 2021, 37, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megavannan, V.; Agarwal, B.; Babu, R.V. Human action recognition using depth maps. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing and Communications (SPCOM), Bangalore, India, 22–25 July 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Aggarwal, J.K. Spatio-temporal depth cuboid similarity feature for activity recognition using depth camera. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eum, H.; Yoon, C.; Lee, H.; Park, M. Continuous human action recognition using depth-MHI-HOG and a spotter model. Sensors 2015, 15, 5197–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bulbul, M.F.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, J. Human action recognition based on DMMs, HOGs and Contourlet transform. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia Big Data, Beijing, China, 20–22 April 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tian, L.; Liu, M.; Tang, H. Sdm-bsm: A fusing depth scheme for human action recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 27–30 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulbul, M.F.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, J. DMMs-based multiple features fusion for human action recognition. Int. J. Multimed. Data Eng. Manag. 2015, 6, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, K.; Kehtarnavaz, N. Real-time human action recognition based on depth motion maps. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2016, 12, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Jiang, M.; Kong, J.; Huo, H.; Wang, X. Action recognition using vague division DMMs. J. Eng. 2017, 4, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, R.; Asadi-Aghbolaghi, M.; Kasaei, S.; Escalera, S. Dynamic 3D hand gesture recognition by learning weighted depth motion maps. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Video Technol. 2018, 12, 1729–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, F.; Leung, H.; Li, Q. Action recognition from depth sequence using depth motion maps-based local ternary patterns and CNN. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 19587–19601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Liu, D.; Qi, L.; Guan, L. Multi-modal human action recognition with sub-action exploiting and class-privacy preserved collaborative representation learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 39920–39933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huang, Q.; Li, X.; Wu, Q. Human Action Recognition Based on Multi-scale Feature Maps from Depth Video Sequences. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.07618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulbul, M.F.; Tabussum, S.; Ali, H.; Zheng, W.; Lee, M.Y.; Ullah, A. Exploring 3D Human Action Recognition Using STACOG on Multi-View Depth Motion Maps Sequences. Sensors 2021, 11, 3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareek, P.; Thakkar, A. RGB-D based human action recognition using evolutionary self-adaptive extreme learning machine with knowledge-based control parameters. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ding, Z.; Tao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Y. Generative multi-view human action recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Caballero, A.; de López-Diz, S.; Fuentes-Jimenez, D.; Losada-Gutiérrez, C.; Marrón-Romera, M.; Casillas-Perez, D.; Sarker, M.I. 3dfcnn: Real-time action recognition using 3d deep neural networks with raw depth information. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.07743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Bai, Y.; Qin, C.; Ding, Z.; Fu, Y. Generative View-Correlation Adaptation for Semi-supervised Multi-view Learning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Tao, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Yin, Y.; Fu, Y. Collaborative Attention Mechanism for Multi-View Action Recognition. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.06599. [Google Scholar]
- Jamshidi, M.B.; Talla, J.; Peroutka, Z. Deep Learning Techniques for Model Reference Adaptive Control and Identification of Complex Systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 19th International Conference on Mechatronics-Mechatronika (ME), Prague, Czech Republic, 2–4 December 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaj, O.; Jamshidi, M.B.; Saebnoori, E.; Mašek, B.; Štadler, C.; Svoboda, J. Hybrid Machine Learning Techniques and Computational Mechanics: Estimating the Dynamic Behavior of Oxide Precipitation Hardened Steel. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 156930–156946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, M.B.; Lalbakhsh, A.; Talla, J.; Peroutka, Z.; Roshani, S.; Matousek, V.; Roshani, S.; Mirmozafari, M.; Malek, Z.; Spada, L.L.; et al. Deep Learning Techniques and COVID-19 Drug Discovery: Fundamentals, State-of-the-Art and Future Directions. In Emerging Technologies during the Era of COVID-19 Pandemic; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreira, J.; Zisserman, A.; Quo, V. Action recognition? a new model and the kinetics dataset. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facebook Research. Available online: https://github.com/facebookresearch/pytorchvideo/tree/main/pytorchvideo/models (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Lin, Y.C.; Hu, M.C.; Cheng, W.H.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Chen, H.M. Human action recognition and retrieval using sole depth information. In Proceedings of the 20th ACM international conference on Multimedia, New York, NY, USA, 29 October–2 November 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Jafari, R.; Kehtarnavaz, N. UTD-MHAD: A Multimodal Dataset for Human Action Recognition Utilizing a Depth Camera and a Wearable Inertial Sensor. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 27–30 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

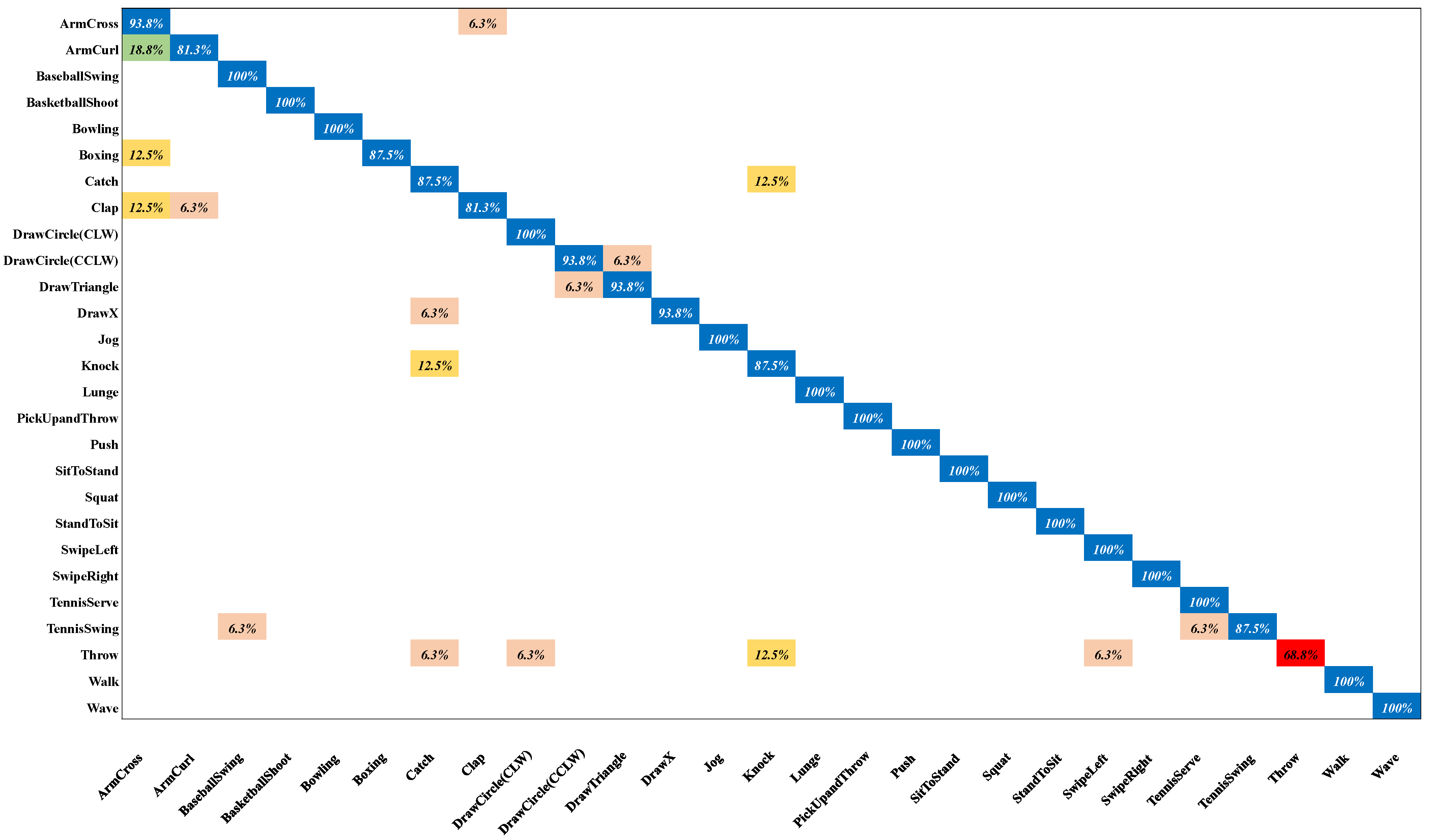
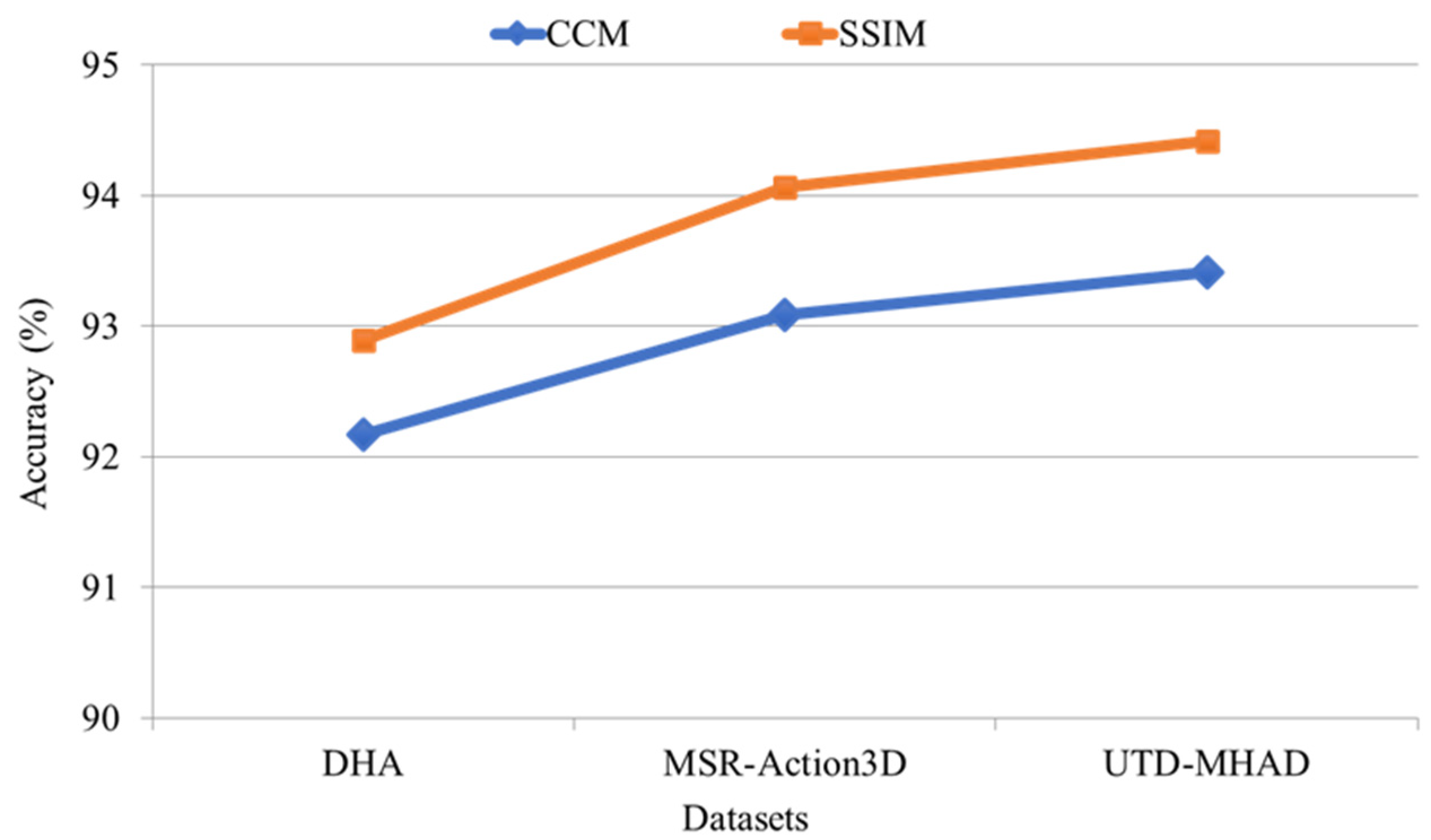
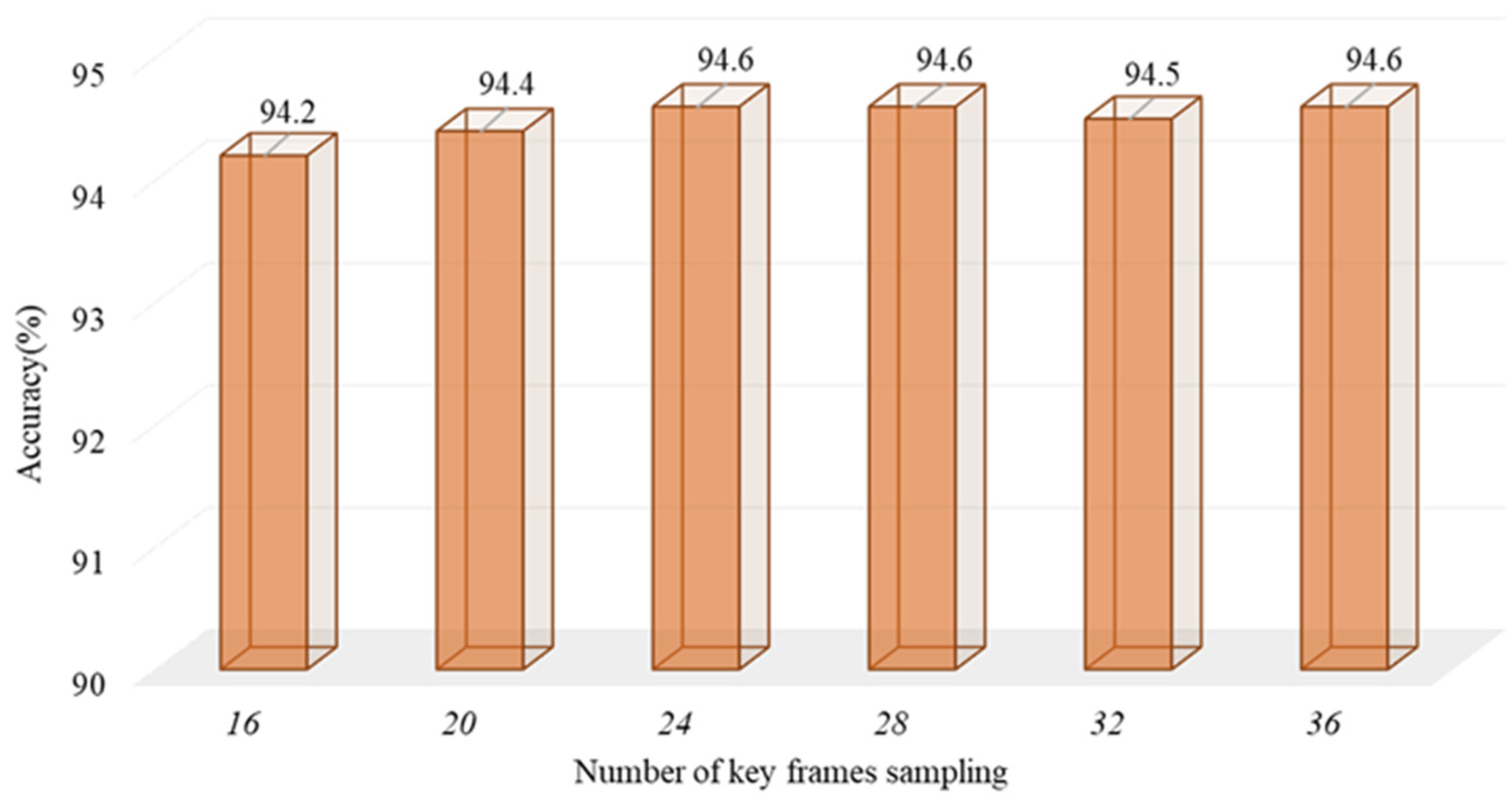
| Metric | Ranking | DHA Dataset | MSR-Action3D | UTD-MHAD | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k = 16 | 91.7% | 92.4% | 93.3% | 92.5% | |
| k = 20 | 92.6% | 93.1% | 93.5% | 93.1% | |
| k = 24 | 92.2% | 93.8% | 93.5% | 93.2% | |
| Average | 92.2% | 93.1% | 93.4% | 92.9% | |
| k = 16 | 92.2% | 93.5% | 94.2% | 93.3% | |
| k = 20 | 93.0% | 94.2% | 94.4% | 93.9% | |
| k = 24 | 93.5% | 94.6% | 94.7% | 94.2% | |
| Average | 92.9% | 94.1% | 94.4% | 93.8% |
| Methods | DHA Dataset | MSR-Action3D | UTD-MHAD |
|---|---|---|---|
| DAAL [27] | - | 92.3% | - |
| DSTIP+DCSF [32] | - | 89.3% | - |
| SDM-BSM [35] | 89.5% | - | - |
| DMM+CL-HOG [36] | - | 89.7% | 83.5% |
| DMM-MV [36] | - | 91.9% | 85.3% |
| DMM-LOGP [36] | - | 84.2% | 88.4% |
| VD-DMM [38] | - | - | 85.1% |
| WDMM-HOG [39] | - | 91.9% | - |
| EGSA [41] | - | 89.5% | 82.8% |
| TGSA [41] | - | 89.8% | 76.2% |
| LP-DMI-HOG [42] | 91.9% | 84.4% | 85.1% |
| LP-DMI-VGG [42] | 84.4% | 91.9% | 81.9% |
| ACG [43] | - | - | 87.7% |
| VCDN [45] | 79.8% | - | - |
| VCA [47] | 80.9% | - | - |
| VCA-Entropy [47] | 82.6% | - | - |
| SeMix [47] | 82.7% | - | - |
| LSTM [48] | 67.7% | - | - |
| Ours () | 92.2% | 93.1% | 93.4% |
| Ours () | 92.9% | 94.1% | 94.4% |
| Methods | Datasets | Parameters (M) | FLOPs (G) | Time (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State-of-the-art Methods | WDMM-HOG [38] | MSR- Action3D | - | - | 0.8 |
| LP-DMI-HOG [42] | DHA | - | - | 0.12 | |
| LP-DMI-HOG [42] | MSR- Action3D | - | - | 0.23 | |
| LP-DMI-HOG [42] | UTD-MHAD | - | - | 0.17 | |
| ACG [43] | UTD-MHAD | - | - | 508.9 | |
| Proposed | k = 16 | 47.58 | 9.67 | 0.036 | |
| k = 20 | 47.58 | 12.95 | 0.040 | ||
| k = 24 | 47.58 | 14.55 | 0.042 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tasnim, N.; Baek, J.-H. Deep Learning-Based Human Action Recognition with Key-Frames Sampling Using Ranking Methods. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4165. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094165
Tasnim N, Baek J-H. Deep Learning-Based Human Action Recognition with Key-Frames Sampling Using Ranking Methods. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(9):4165. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094165
Chicago/Turabian StyleTasnim, Nusrat, and Joong-Hwan Baek. 2022. "Deep Learning-Based Human Action Recognition with Key-Frames Sampling Using Ranking Methods" Applied Sciences 12, no. 9: 4165. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094165
APA StyleTasnim, N., & Baek, J.-H. (2022). Deep Learning-Based Human Action Recognition with Key-Frames Sampling Using Ranking Methods. Applied Sciences, 12(9), 4165. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094165





