Abstract
The bluefin sea robin (Chelidonichthys spinosus), hereafter BSR, is one of the most important fish species in the South Sea of Korea. The production value of BSR in 2020 was USD 4,733,057. The production volume in Korea has shown an annual mean increase of 8.9% since 2010, but the efficiency of the fishing gear decreased due to excessive use. This has led to a decrease in the profitability of fishery operators, and as compensation, the use of fishing gear has further increased through competitive operations. Alternative measures for improving catch performance and reducing the use of fishing gear are needed. As one such measure, LED (Light-Emitting Diode) lights were attached to the pot, and the effects were determined. The field experiment results showed that the catch of BSR was higher for the experimental groups (n = 10–273) using fishing gear with LED lights (red, green, blue, and white) than for the control group (n = 2) (Kruskal–Wallis test, p < 0.05). Among the experimental groups, the pot with green light achieved the largest catch (n = 273). The use of LED lights was found to enhance the catch efficiency of pot fishing gear for BSR.
1. Introduction
The bluefin sea robin (Chelidonichthys spinosus), hereafter BSR, a fish species belonging to the family Triglidae, inhabits the sand or mud floor of 20–600 m depth in the waters of the coasts in Korea as well as Japan and East China. The main food source for BSR is benthic crustaceans [1,2]. BSR production in Korea in 2010 amounted to 979 tons, which increased to 2379 tons by 2020 with the recent increase in demand. BSR production in the last few decades has shown an annual increase of 8.9% on average. The economic value of BSR based on production was USD 2,919,200 in 2010; however, in 2020, it was USD 4,733,057, indicating an increase of 62% [3]. Despite such an economic value of BSR, most studies have focused mainly on the ecology of this species, investigating the main prey organisms of BSR in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea [4,5], and the feeding preference of BSR in the sea waters close to Busan and Jeju island in Korea [6,7]. To the best of our knowledge, no study has yet focused on the perspectives of the use of fishing gear.
The BSR in Korea is mainly caught by gillnet, pot, and longline. The pot catch, in particular, has a high economic value due to outstanding fish quality, which allows the distribution of live fish. Pot fishing is one of the traditional fishing methods used worldwide. It is categorized as an environmentally friendly fishing method compared to other methods. Pot fishing leads to relatively low bycatches with selectivity towards target species and size, and compared to towed gears such as trawl, its effect on the benthic ecosystem is relatively limited. Moreover, the bycatch can be returned to waters with low mortality and high survival rates. From the perspective of fishing vessel operations, compared to other fishing techniques, a relatively small-sized vessel with low fuel consumption is required for pot fishing [8,9].
However, compared to gillnet or trawl, pot fishing has a low catch rate. It is, thus, crucial that catch efficiency is improved to ensure profitability for fishery operators [10]. The development of pot fishing techniques has continuously advanced via studies on the reduction in bycatch and the improvement in size selectivity and pot design, as well as in comparing bycatch reductions in pots and other gears [11,12,13,14,15,16]. Recently, studies have been conducted on the application of light-emitting diode (LED) lights to the pot as a novel technique to increase catch rates [17,18].
With technological advancements, LED lights have been actively applied to fishing gear since the early 2000s, with studies mainly focused on squid jigging. The goals of these studies on the use of LED fish lamps in squid jigging were to improve energy efficiency, promote green growth, and lower carbon emissions, whereby the use of LED lights resulted in an equal catch performance compared to the use of conventional metal halide lamps but lowered energy demands, such as fuel cost [19,20,21,22]. Recently, the scope of the use of artificial LED lights in various fishing gear from gillnet to trawl and stationary gear has been extended to reduce bycatch and enhance catch rates [23,24,25,26]. Similarly, studies in pot fishing on the application of LED lights to improve catch efficiencies have been conducted. The most well-known studies are those on cod (Gadus morhua) and snow crabs (Chionoecetes opilio) in the Atlantic Ocean. These studies have shown increased catch efficiency at specific wavelengths compared to the use of conventional fishing gear [27,28,29]. As such, studies on fishing gear such as the use of pots with artificial light have been conducted with an aim to enhance catch efficiency or to reduce bycatch. In previous studies, LED lights are known to affect the catch efficiency of fishing gear or reduce the bycatch of specific species. Similarly, the application of LED lights is predicted to increase the catch of BSR via either a direct effect on the catch (e.g., phototaxis) of BSR or via an indirect effect on their prey organisms (e.g., attracting and phototaxis) [30,31,32,33,34,35].
This study was based on the results of recent studies on the use of low-powered LED lights in the field of fishery with a previously uninvestigated target—BSR species (C. spinosus). By conducting field experiments, the effects of artificial LED lights (red, green, blue, and white) on the catch of BSR were investigated for pot fishing in the coasts of Korea. In contrast to previous conventional studies, this study conducted photometric and integrating sphere analyses to determine the properties of LED lights. Furthermore, the fish stomach contents were analyzed to determine the influence of LED light pots or prey items on the BSR catch between the control and experimental groups referring to the Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) research case. Thus, the application of LED lights in pots was verified as a method to increase pot fishing efficiency, and basic data were obtained for enhancing the profitability of fishery operators.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. LED Lights
For the LED lights in this study, we used DYP-200 (Dongyang Engineering Co., Jinhae, Korea), which is used in distant water longline fishery. The LED lights were made of polycarbonate (L 120 mm × H 43 mm, weight 130 g) material. The voltage was provided by two 1.5 V AA batteries (LR6) with light emitted to a maximum operating depth of 700 m and a maximum operating time of approximately 700 h. Four different colors of LED lights were used in this study. The properties of red, green, blue, and white LED lights, including peak wavelengths, color coordinates, and photometric curves, were measured in the integrating sphere and photometric analyses. The optical properties were analyzed by commission at the LED Marine Science Convergence Center at Pukyong National University with certified facilities and devices of the Korea Laboratory Accreditation Scheme (KOLAS). The analytical devices used to measure the optical properties were the integrating sphere analyzer (WithLight OPI-1000, Jeonju, Korea) and goniophotometer (Pimacs NeoLight 8000, Namyangju, Korea). The experiments were performed at a temperature of 25 ± 3 °C and a relative humidity 45 ± 15%. The results are shown in Table 1 and Figure 1. Each LED light was found to emit a unique color of light based on the peak wavelength and color coordinates from the integrating sphere analysis, as presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Specifications of LED lights used for the experiments.
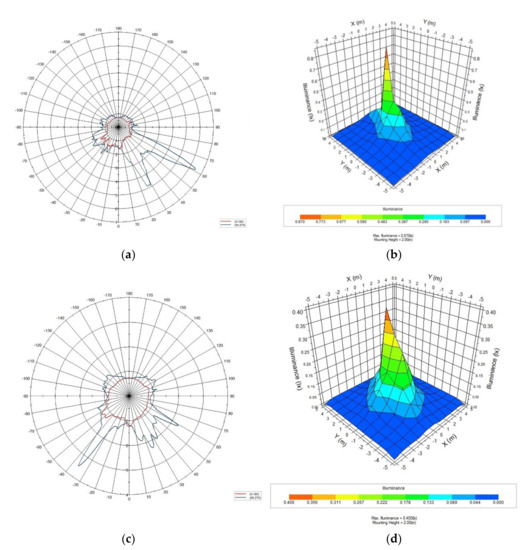
Figure 1.
The polar distribution and ISO lux diagrams for the LED lights used for the experiments by integrating the sphere device and goniophotometer system: (a) polar distribution of green LED; (b) ISO lux diagram of green LED; (c) polar distribution of white LED; (d) ISO lux diagram of green LED.
The photometric analysis showed that the LED lights used in the experiment had a high level of illuminance in a specific direction, as shown for the green light in Figure 1, unlike the common LED lights with uniform illuminance from the light source. The results for different LED light colors (red, blue, and white) were similar.
2.2. Experimental Fishing Gear
The experimental fishing gear comprised a foldable spring pot commonly used in the South Sea of Korea, as shown in Figure 2a. The nets were made using black nettings of polyethylene (PE) 230 Td with 21 threads of 35 mm mesh size; after making the nets, 200 pots (L 680 mm × W 330 mm, weight 710 g) were prepared. As shown in Figure 2b, the experimental fishing gear was arranged as 25 pots in a set, and a total of 100 pots as part of four sets were used in experimental fishing. Each pot was distinguished from the other by spray painting the circular entrance of the pot with one of five colors (red, yellow, green, blue, and white). To measure the mesh opening of the experimental fishing gear, 20 out of 200 pots were randomly selected, and the mesh of each pot was measured using Vernier calipers (Mitutoyo CD-20PS×, Kawasaki, Japan) 10 times. The measured mesh opening was 36.09 mm (Standard Deviation ± 0.56) on average.
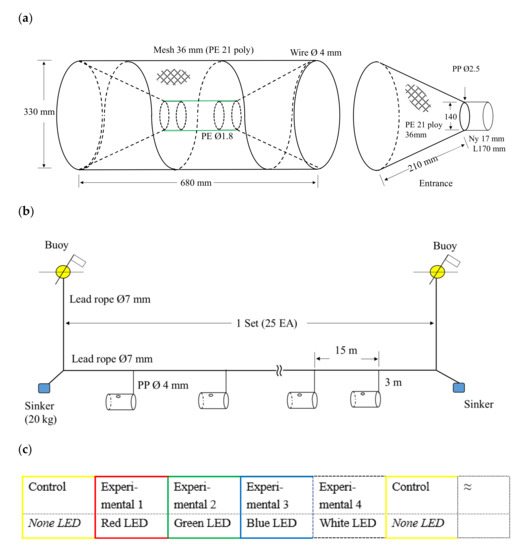
Figure 2.
Fishing pots for bluefin sea robin in the experiments: (a) schematic drawing of a single pot; (b) composition of experimental fishing gear; (c) the arrangement of control and experimental pots for fishing gear deployment.
2.3. Field Experiments
The field experiments were performed on a coastal pot fishing vessel Myeongseong (gross tonnage, 4.49 tonnes; diesel engine, 198 kW; length of all 9.4 m) during the period of May–December 2020, in the fishing ground near Saryang island in the coastal region of Goseong-gun, Gyeongsangnam-do, Korea (Figure 3). The experimental fishing gear was immersed in water for 3 days. The operation consisted of casting at 3–4 p.m. and hauling after approximately 3 days. One cast of experimental fishing gear contained 25 pots (5 each of bait, red LED, green LED, blue LED, and white LED pots). For the bait, approximately 100 g of sardine (Sardinia melanosticta) was used, and a plastic bait container was attached to the center of the pot interior.
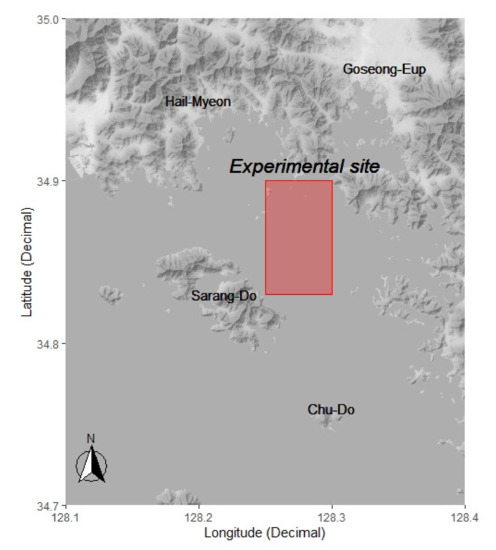
Figure 3.
Map of experimental site in the South Sea, Korea. The red rectangle box indicates the area of the fishing grounds for experimental fishing operations.
The LED lights were attached to the same place on each pot. For the experimental groups, the pots were composed of the bait and LED lights of the same color as the sprayed rim. For the control group with the bait only, a yellow pot was used. The experimental pots were lined up in repeated sequences of red, yellow (the control), green, blue, and white, as shown in Figure 2c. For the experimental groups, four casts (a total of 100 pots) were used in one field experiment. The pots had a main line at 15 m intervals and a branch line at 3 m intervals. The mean water depth of the fishing ground was approximately 25 m. If an experimental pot had a damaged mesh or LED light during hauling, it was replaced with an identical reserve pot or LED light.
The fish caught in the experimental fishing gear were sorted and categorized per type on the ship using a zippered net with a color label. The total length and weight were measured for the fish per species on the dock after port entry.
2.4. Stomach Contents
To verify the effects of LED lights on the feeding of BSR, fish stomach contents were analyzed and compared between the control and experimental groups. The BSRs caught during the experimental period of September–December 2020 were separated between the control and experimental groups and transferred to the Fisheries Resource Research Center of National Institute of Fisheries Science located close to the fishing ground on the day of the catch. Then, the prey organism was identified under a stereomicroscope (Olympus SZ×2-ILLD, Tokyo, Japan). The prey items were separated, identified at the lowest feasible taxonomic unit, counted, and the wet weight was measured using an electronic scale (Satorius Quintix 224, Goettingen, Germany) to a unit of 0.0001 g. The prey organism of each fish was further analyzed by estimating the frequency (%F), number of individuals (%N), weight ratio (%W), and the index of relative importance (%IRI), using the methods described by Baek et al. (2014) and Pinkas et al. (1971) and the following equations [36,37].
indicates the number of BSR from which the respective prey organism was found in the stomach contents; and indicate the count of individuals in the respective prey organism and the wet weight, respectively; and and indicate the total count and wet weight, respectively.
2.5. Data Analysis
The effect of pot treatment on the CPUE (Catch Per Unit Effort) of BSR was estimated using a generalized linear mixed effect model (GLMM) based on Poisson regression. The model structure was as follows:
where the response variable is CPUE, the explanatory variable involves treatments, soaking time is used as an offset, and the trial number (trial no) is the random effect.
BSR Model = glmmadmb(CPUE ~ treatments + offset(log(soak)) + (1|trial no), family = “nbinom”, zeroInflation = TRUE, data = BSRdata)
Non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis tests were used to test the differences between the control and experimental pots’ catch rates. The used data were the sums of the control pots and experimental pots in each fleet. Comparisons were made for all total lengths pooled. The CPUE was considered count data and was calculated from dividing the catch number of BSR into its gear usage with comparisons made for pooling fish for all total lengths.
The statistical analyses were conducted in R software (R Core Team, 2019). The GLMM (generalized linear mixed effect model) was fit using R2admb package, moonBook package, and qcc package.
3. Results
3.1. Field Experiments
The field experiments were performed using experimental fishing gear for 24 operations across a total of 10 cruises. The results showed that the catch contained 575 BSR fish in total. The BSR catch varied according to the color of LED light attached to the pot. The BSR catch was the largest (n = 273) for the pot with green light, followed by blue light (n = 157), white light (n = 133), red light (n = 10), and the control without a light (n = 2) (Kruskal–Wallis test, p < 0.05) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Total catches of bluefin sea robin over the experimental period; May–December 2020.
The monthly catch count in accordance with the total length class for the target BSR species between the control and experimental groups during the field experiment period is shown in Figure 4. The monthly catch showed the highest catch frequency in the pots with green, blue, and white LED lights. The catch per unit effort (CPUE) for the BSR pot of the control group was compared according to the BSR catch count per the total use of fishing gear, as shown in Figure 5. CPUE was the highest for the pot with green LED (2.84 ± 3.21; mean ± standard deviation, hereafter), followed by blue LED (1.64 ± 3.21), white LED (1.39 ± 1.46), and red LED (0.02 ± 0.03). For BSR catch efficiency, the pots with green and blue LED lights showed the highest levels during the peak fishing season in October and December. The parameter estimates for the GLMM model for the BSR CPUE are shown in Table 3. The effect of treatment on CPUE was visualized using odds ratio plot in Figure 6.
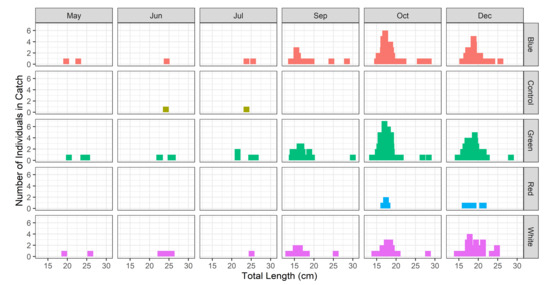
Figure 4.
Monthly total length distribution of bluefin sea robin by fishing gear types.
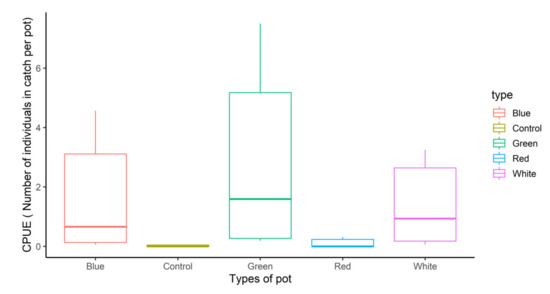
Figure 5.
Catch Per Unit Effort (CPUE) comparison between the control and treatment pots for BSR.

Table 3.
Parameter estimates, fit statistics, and variation from the random effects of a GLMM model for BSR based on trial number as a random factor (n = 21).
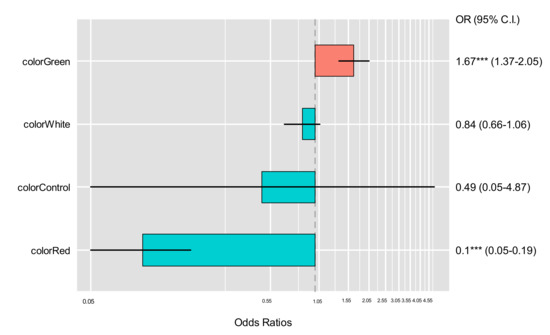
Figure 6.
Odds ratios plot for GLMM pot treatment comparison. *** shows significancy of p-value.
3.2. Stomach Contents
A total of 190 BSR fish were used for analyzing stomach contents. Among them, 97 fish had an empty stomach, indicating a 51.05% fasting rate. The results of the stomach contents analysis of 93 fish are shown in Table 4. The frequency of shrimps was 68.42–83.72%. Shrimps accounted for 93.60–79.82% of the total weight of stomach contents. The %IRI was 78.84–97.59%. The length distribution of the shrimps was 0.2–30 mm, with a mean length of 9.09 mm.

Table 4.
Composition of the stomach contents of bluefin sea robins by frequency of occurrence, number of individuals, and index of relative importance.
4. Discussion
Bluefin sea robin catches can be increased with the use of pots with LED lights in pot fishing grounds in the South Sea of Korea. The greatest catch improvement was seen in pots with green LED lights compared to those with red, blue, or white lights and the conventional pots containing bait only. The results indicated that, compared to the conventional method of using only the bait in the pot, attaching green, blue, or white LED lights to the pots could increase the efficiency of bluefin sea robin fishing. Hence, this method could increase the profitability of fishery operators.
The difference in catch among the pots may be accounted for by the following reasons: the vision and behavior of fishery species to artificial light generally vary according to habitat conditions, target fish characteristics, and fishing gear composition. In certain species, the mechanism involves a combination of these factors [30,31,38,39,40]. The focus of previous studies on fishing gear with artificial lights, especially LED, has been a problem of bycatch. Low-powered LED lights were shown to reduce bycatch in studies on bottom shrimp trawl [23,25,35], while studies on trawls in the Barents Sea of Norway showed contrasting results [32,33].
Currently, the mechanism of the influence of LED fishing lights on catch variation remains unclear. The LED lights are known to increase the catch by the direct or indirect luring of the target fish or prey organism [28,29,41].
Pot fishing is known to be affected by various conditions from the target fish density to bait type and characteristics, immersion time, fishing season, fishing gear shape, and fishing ground environment [13,42]. The BSR pots, similarly, may capture fish as the artificial light directly affects fish entry, makes it easier for the fish to find the pot entrance, or as the prey organism of the target responds to the light. A study on cod (Gadus morhua) pot fishing in the Atlantic Ocean reported that green LED increased CPUE [27]. However, subsequent studies showed that the cod entered the pot to feed on the moving krill (Thysanoessa inermis) gathered around the LED inside the pot and not because of any direct response to the light [29,41].
Similarly to Atlantic cod, the bluefin sea robin catch may be attributed to the luring effect of the prey organism gathered around the light. This presumption is based on the results of stomach content analyses. In previous studies, bluefin sea robin was found to feed mainly on benthic shrimps as well as various other prey organism such as crabs, fish, and lugworms [6,7]. The bluefin sea robins inhabiting the East China Sea feed mainly on shellfish and fish, while the bluefin sea robins inhabiting the eastern side of the Mediterranean Sea feed mainly on tiny shrimps and decapods [5,43]. Although the bluefin sea robin species vary in their main prey organism according to region, they are known to prefer benthic crustaceans [6,7].
The results of bluefin sea robin stomach content analyses were in agreement with the results of previous studies. The dominant species in the stomach contents of bluefin sea robin was amphipods for both control and experimental groups. The variation in amphipod content in the stomach is presumed to have caused the differences in catch. The bluefin sea robin caught in pots with green LED lights showed a higher frequency and weight of amphipods in the stomach contents than those in other experimental pots. This could be attributed to the distribution of amphipods gathered around LED lights on the inside and the outside of the pot when the bluefin sea robin entered the pot for feeding.
This presumption is supported by previous studies on the phototaxis of amphipods that are known to show positive phototaxis to stimulation with low-intensity light [44]. The response spectrum of amphipods is known to show a low threshold during the night at 460–600 nm [45]. The LED spectrum used in this study was distributed within the response spectrum of amphipods. In addition, laboratory studies on marine invertebrates, such as amphipods, have shown that they gathered around low-intensity light rather than high-intensity light [46,47]. Artificial lights also enhanced the visibility of invertebrates to promote feeding by predators [48,49,50,51]. Based on these findings, the relationship between amphipods, light, and bluefin sea robin catch may be explained. However, the phototaxis of amphipods is known to be influenced simultaneously by other environmental factors, such as the sea’s current and tide in addition to light [45].
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the pots attached to artificial LED fishing lights could increase the catch of bluefin sea robins by luring prey organism. The pots with green LED lights showed the highest catch, followed by pots with blue, white, and red LED lights. Compared to the control pot with bait only, the catch was 5–136-fold higher in the pots with lights. However, attaching LED lights to pots may lead to an increased cost in power, such as additional batteries and the purchase of LED lights as well as increased marine waste due to a possible loss of fishing gear. Nevertheless, the technology for fishing gear material is continuously advancing. Alkaline batteries are anticipated to be replaced with secondary sea water batteries developed using Na+ in sea water so as to reduce environmental pollution and the costs of operation. The plastic material constituting LED lights is likely to be replaced with a biodegradable material with further advancements in PBS (polybutylene succinate) and PBSAT (polybutylene succinate adipate-co-terephthalate) materials that allow degradation by microorganisms in sea water. If these conditions are satisfied, they will facilitate environmentally friendly pot fishing with high catch performance and a reduced usage of fishing gear.
Author Contributions
P.K. conceived and designed the experiments, analyzed the data, prepared the experiments, authored and reviewed drafts of the paper, and approved the final draft. H.K. contributed to the experimental design and supervision, provided editorial reviews of the manuscript, and approved the final draft. S.K. conceived and performed the experiments, analyzed the data, authored and reviewed drafts of the paper, and approved the final draft. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was conducted with the support of the Fisheries Research Project (R2022035) of the National Institute of Fisheries Science of Korea and the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries of Korea.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries of Korea. This research was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Fisheries Science R&D project (R2022035). They would like to thank Myeongkyu Kim, captain of F/V Myeongseong, and his crew for their help and assistance onboard the vessel. They also thank Hyeonji Kim and Jaemook Jeong for helping with stomach content analyses at Fisheries Resource Research Center, Korea, and Jaehyun Koo and Jiwon Cheong for assisting with onboard experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yamada, U. Fishes of the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea; Seikai Regional Fisheries Research Laboratory: Nagasaki, Japan, 1986; pp. 68–69. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, I.S.; Choi, Y.; Lee, C.L.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, J.H. Illustrated Book of Korean Fishes; Kyohak Publishing: Seoul, Korea, 2005; pp. 228–229. [Google Scholar]
- KOSIS (Korean Statistical Information Service). 2022, Volume 2022. Available online: https://kosis.kr/statHtml/statHtml.do?orgId=101&tblId=DT_1EW0005&vw_cd=MT_ZTITLE&list_id=K2_7&scrId=&seqNo=&lang_mode=ko&obj_var_id=&itm_id=&conn_path=MT_ZTITLE&path=%252FstatisticsList%252FstatisticsListIndex.do (accessed on 10 July 2021).
- Kunishige, N. On the age and growth of the gurnard, Chelidonichthys spinousus, in the East China and the Yellow Seas. Bull. Seikai Reg. Fish. Res. Lab. 1965, 34, 133–147. [Google Scholar]
- Kozo, S.; Tomiko, S.; Kunishige, N.; Junko, N. On feeding habit of gunard, Chelidonichthys spinousus, in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea. Bull. Seikai Reg. Fish Res. Lab. 1965, 33, 47–59. [Google Scholar]
- Huh, S.-H.; Park, J.M.; Baeck, G.W. Feeding Habits of Bluefin Searobin (Chelidonichthys spinosus) in the Coastal Waters off Busan. Korean J. Ichthyol. 2007, 19, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-B.; Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, D.-W.; Choi, J.-H. Feeding Habits of Bluefin Searobin (Chelidonichthys spinosus) around Jeju Island. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 44, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miller, R.J. Effectiveness of Crab and Lobster Traps. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1990, 47, 1228–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suuronen, P.; Chopin, F.; Glass, C.; Løkkeborg, S.; Matsushita, Y.; Queirolo, D.; Rihan, D. Low impact and fuel efficient fishing—Looking beyond the horizon. Fish. Res. 2012, 119–120, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.D.; Nguyen, L.T.; To, P.V.; Nguyen, K.Q. Effects of the trap entrance designs on the catch efficiency of swimming crab Charybdis feriata fishery. Fish. Res. 2020, 232, 105730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, R.N.; Taylor, D.I.; Connor, S.; Connor, G.; Jeffs, A. Factors affecting bycatch in a developing New Zealand scampi potting fishery. Fish. Res. 2017, 186, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hébert, M.; Miron, G.; Moriyasu, M.; Vienneau, R.; DeGrâce, P. Efficiency and ghost fishing of snow crab (Chionoecetes opilio) traps in the Gulf of St. Lawrence. Fish. Res. 2001, 52, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winger, P.D.; Walsh, P.J. The feasibility of escape mechanisms in conical snow crab traps. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2007, 64, 1587–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.-C.; Park, C.-D.; Park, S.-W.; Lee, J.-H.; Tokai, T. Size selectivity of trap for male red queen crab Chionoecetes japonicus with the extended SELECT model. Fish. Sci. 2000, 66, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, L.; Herrmann, B.; Grimaldo, E.; Sistiaga, M. Effect of pot design on the catch efficiency of snow crabs (Chionoecetes opilio) in the Barents Sea fishery. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petetta, A.; Vasapollo, C.; Virgili, M.; Bargione, G.; Lucchetti, A. Pots vs trammel nets: A catch comparison study in a Mediterranean small-scale fishery. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, K.Q.; Humborstad, O.-B.; Løkkeborg, S.; Winger, P.; Bayse, S.M. Effect of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) on snow crab catch rates in the Barents Sea pot fishery. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2019, 76, 1893–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.Q.; Winger, P. A trap with light-emitting diode (LED) lights: Evaluating the effect of location and orientation of lights on the catch rate of snow crab (Chionoecetes opilio). Aquac. Fish. 2019, 4, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, Y.; Azuno, T.; Yamashita, Y. Fuel reduction in coastal squid jigging boats equipped with various combinations of conventional metal halide lamps and low-energy LED panels. Fish. Res. 2012, 125–126, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Matsushita, Y.; Azuno, T. Catch performance of coastal squid jigging boats using LED panels in combination with metal halide lamps. Fish. Res. 2012, 113, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.-I.; Jeong, H.-G. Catching efficiency of LED fishing lamp and behavioral reaction of common squid Todarodes pacificus to the shadow section of color LED light. Bull. Korean Soc. Fish. Technol. 2011, 47, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.-I.; He, P.; Arimoto, T.; Jang, U.-J. Catch performance and fuel consumption of LED fishing lamps in the Korea hairtail angling fishery. Fish. Sci. 2017, 83, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, R.W.; Lomeli, M.J.; Jones, S.A. Tests of artificial light for bycatch reduction in an ocean shrimp (Pandalus jordani) trawl: Strong but opposite effects at the footrope and near the bycatch reduction device. Fish. Res. 2015, 170, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, N.; Mangel, J.C.; Wang, J.; Shigueto, J.A.; Pingo, S.; Jimenez, A.; Suarez-Yana, T.; Swimmer, Y.; Carvalho, F.; Godley, B. Reducing green turtle bycatch in small-scale fisheries using illuminated gillnets: The cost of saving a sea turtle. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 545, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomeli, M.J.M.; Groth, S.D.; Blume, M.T.O.; Herrmann, B.; Wakefield, W.W. Effects on the bycatch of eulachon and juvenile groundfish by altering the level of artificial illumination along an ocean shrimp trawl fishing line. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2018, 75, 2224–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virgili, M.; Vasapollo, C.; Lucchetti, A. Can ultraviolet illumination reduce sea turtle bycatch in Mediterranean set net fisheries? Fish. Res. 2018, 199, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryhn, A.C.; Königson, S.J.; Lunneryd, S.-G.; Bergenius, M.A. Green lamps as visual stimuli affect the catch efficiency of floating cod (Gadus morhua) pots in the Baltic Sea. Fish. Res. 2014, 157, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.Q.; Winger, P.D.; Morris, C.; Grant, S.M. Artificial lights improve the catchability of snow crab (Chionoecetes opilio) traps. Aquac. Fish. 2017, 2, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humborstad, O.-B.; Utne-Palm, A.C.; Breen, M.; Løkkeborg, S. Artificial light in baited pots substantially increases the catch of cod (Gadus morhua) by attracting active bait, krill (Thysanoessa inermis). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2018, 75, 2257–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesan, M.; Spoto, M.; Verginella, L.; Ferrero, E.A. Behavioural effects of artificial light on fish species of commercial interest. Fish. Res. 2005, 73, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.-I.; Jeong, H.-G.; Jung, B.-M. Behavioral reaction of common squid Todarodes pacificus to different colors of LED Light. Bull. Korean Soc. Fish. Technol. 2009, 45, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, R.B.; Herrmann, B.; Sistiaga, M.; Brinkhof, J.; Tatone, I.; Langård, L. Performance of the Nordmøre Grid in Shrimp Trawling and Potential Effects of Guiding Funnel Length and Light Stimulation. Mar. Coast. Fish. 2017, 9, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, R.B.; Herrmann, B.; Sistiaga, M.; Brčić, J.; Brinkhof, J.; Tatone, I. Could green artificial light reduce bycatch during Barents Sea Deep-water shrimp trawling? Fish. Res. 2018, 204, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldo, E.; Sistiaga, M.; Herrmann, B.; Larsen, R.B.; Brinkhof, J.; Tatone, I. Improving release efficiency of cod (Gadus morhua) and haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus) in the Barents Sea demersal trawl fishery by stimulating escape behaviour. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 75, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melli, V.; Krag, L.A.; Herrmann, B.; Karlsen, J.D. Investigating fish behavioural responses to LED lights in trawls and potential applications for bycatch reduction in the Nephrops-directed fishery. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2018, 75, 1682–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeck, G.W.; Kim, H.J.; Jeong, J.M. Diet Composition of Bullet Mackerel, Auxis rochei (Risso, 1810) in the Coastal Waters of Iloilo, Philippines. Korean J. Ichthyol. 2014, 26, 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- Pinkas, L. Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna and bonito in California waters. Calif. Dept. Fish Game Fish Bull. 1971, 152, 1–105. [Google Scholar]
- Ciriaco, S.; Marchesan, M.; Verginella, L.; Vinzi, E.; Ferrero, E.A.; Spoto, M. Preliminary observations on the effects of artificial light on the marine environment, with special reference to three fish species of commercial value protected by Miramare Marine Reserve. Boll. Geof. Teor. App. 2003, 44, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Villamizar, N.; Blanco-Vives, B.; Migaud, H.; Davie, A.; Carboni, S.; Vázquez, F.J.S. Effects of light during early larval development of some aquacultured teleosts: A review. Aquaculture 2011, 315, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehayias, G.; Bouliopoulos, D.; Chiotis, N.; Koutra, P. A photovoltaic-battery-LED lamp raft design for purse seine fishery: Application in a large Mediterranean lake. Fish. Res. 2011, 109, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utne-Palm, A.C.; Breen, M.; Løkkeborg, S.; Humborstad, O.-B. Behavioural responses of krill and cod to artificial light in laboratory experiments. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winger, P.D.; Walsh, P.J. Selectivity, efficiency, and underwater observations of modified trap designs for the snow crab (Chionoecetes opilio) fishery in Newfoundland and Labrador. Fish. Res. 2011, 109, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrats, A.; Petrakis, G.; Papaconstantinou, C. Feeding habits of Aspitrigla cuculus (L., 1758) (red gurnard), Lepidotrigla cavillone (Lac., 1802) (large scale gurnard) and Trigloporus lastoviza (Brunn., 1768) (rock gurnard) around Cyclades and Dodecanese Islands (E. Mediterranean). Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2000, 1, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forward, R.B. Behavioral responses of a sand-beach amphipod to light and pressure. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1986, 102, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forward, R.B. Phototaxis of a sand-beach amphipod: Physiology and tidal rhythms. J. Comp. Physiol. A Sensory Neural Behav. Physiol. 1980, 135, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisp, D.J.; Ritz, D.A. Responses of cirripede larvae to light. I. Experiments with white light. Mar. Biol. 1973, 23, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forward, R.B., Jr. Diel vertical migration: Zooplankton photobiology and behaviour. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 1988, 26, 1–393. [Google Scholar]
- Batty, R.S.; Blaxter, J.H.S.; Richard, J.M. Light intensity and the feeding behaviour of herring, Clupea harengus. Mar. Biol. 1990, 107, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaxter, J.; Batty, R. Herring behaviour in the light and dark. In Light and Life in the Sea; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990; pp. 209–220. [Google Scholar]
- Nightingale, B.; Longcore, T.; Simenstad, C.A. Artificial night lighting and fishes. In Ecological Consequences of Artificial Night Lighting; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; pp. 257–276. [Google Scholar]
- McConnell, A.; Routledge, R.; Connors, B. Effect of artificial light on marine invertebrate and fish abundance in an area of salmon farming. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 419, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).