Proposing a Method Reducing UGR Calculations for LED Luminaires with Diffusers in Indoor Applications
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. LEDs as Low-Energy Indoor Light Sources
1.2. Glare Evaluation by UGR
1.3. Paper Structure
2. Tabular Method for Reducing UGR Calculations, for Every Point on the Room Midline
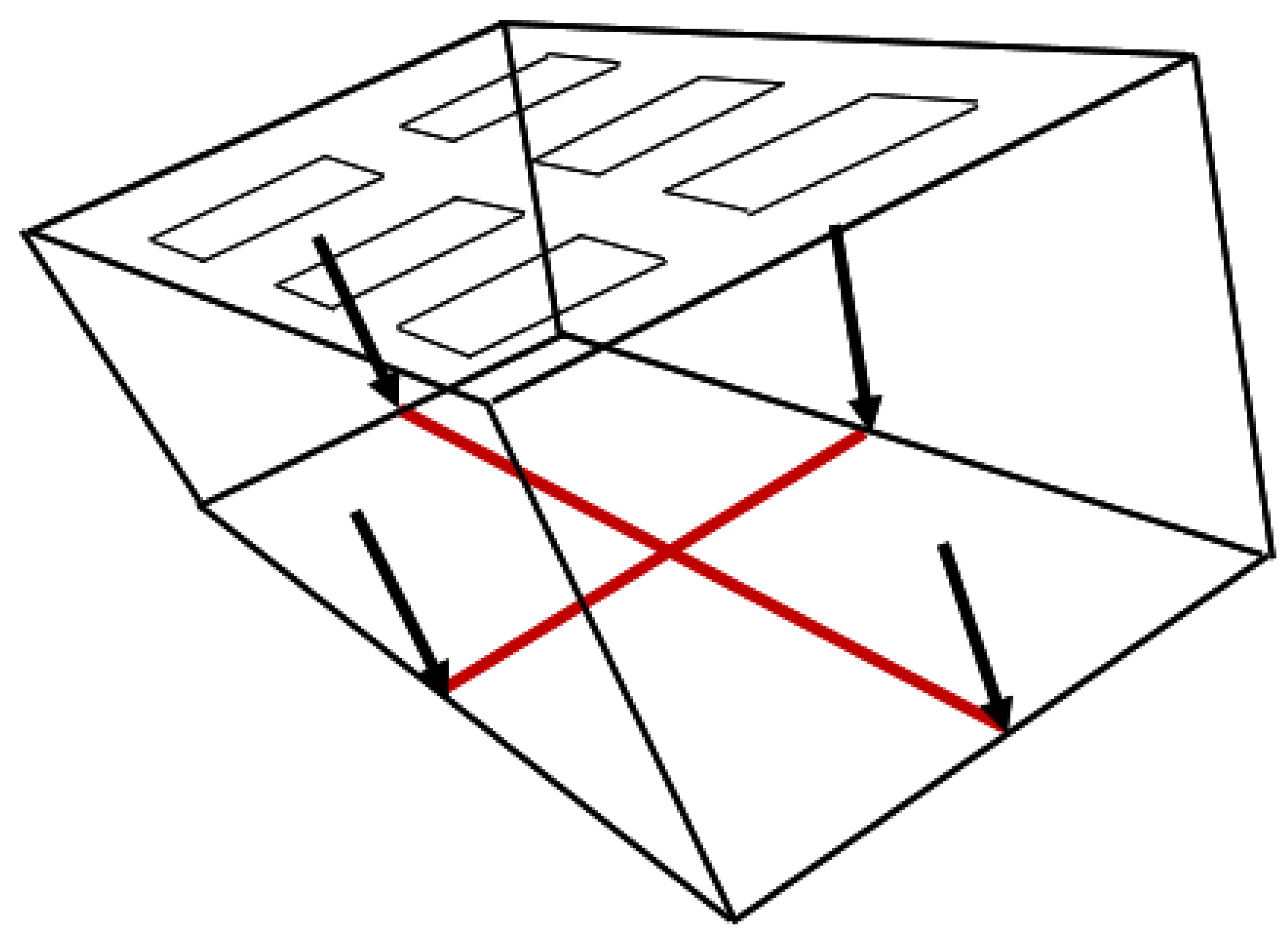
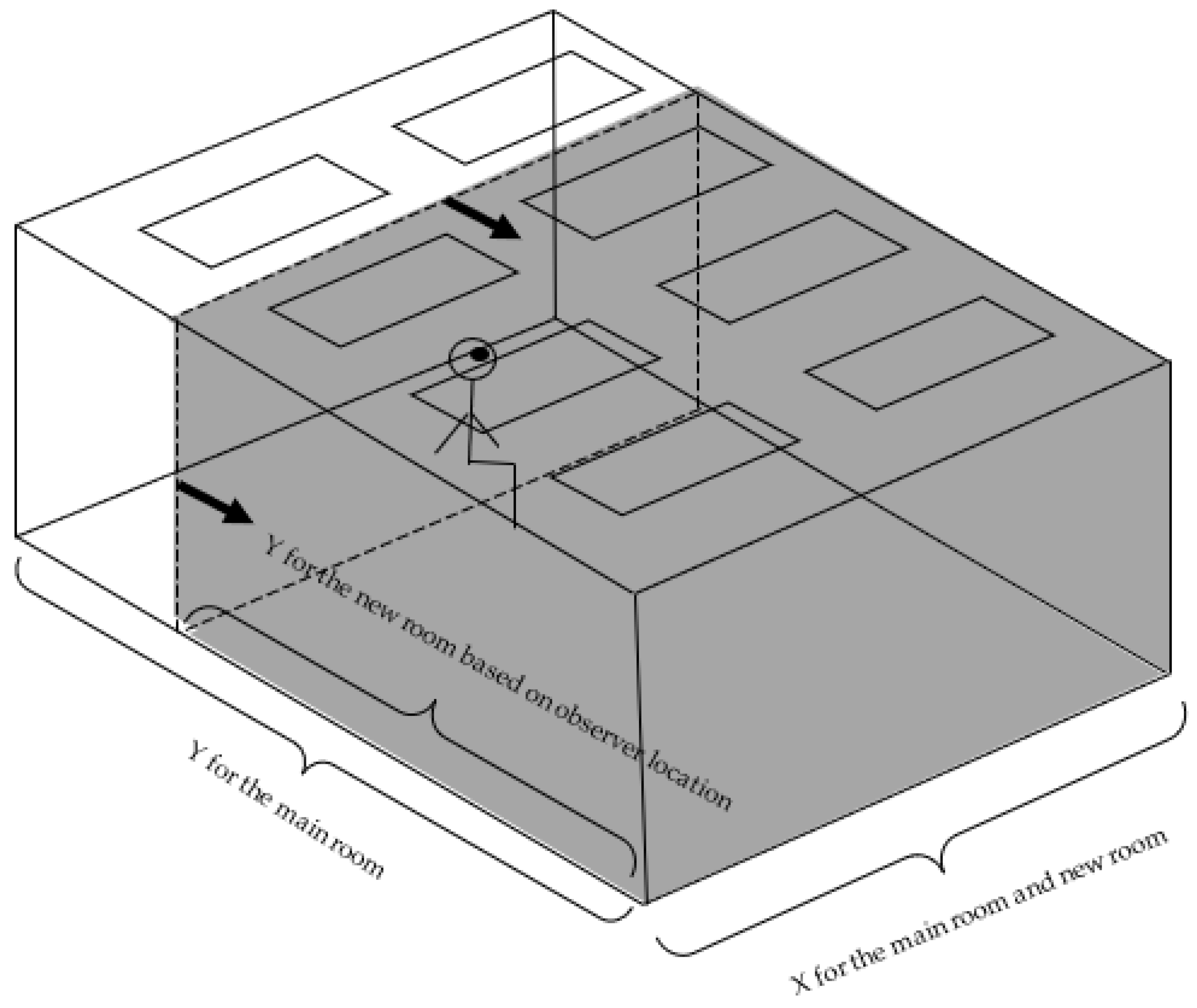
2.1. Introduction to the Method
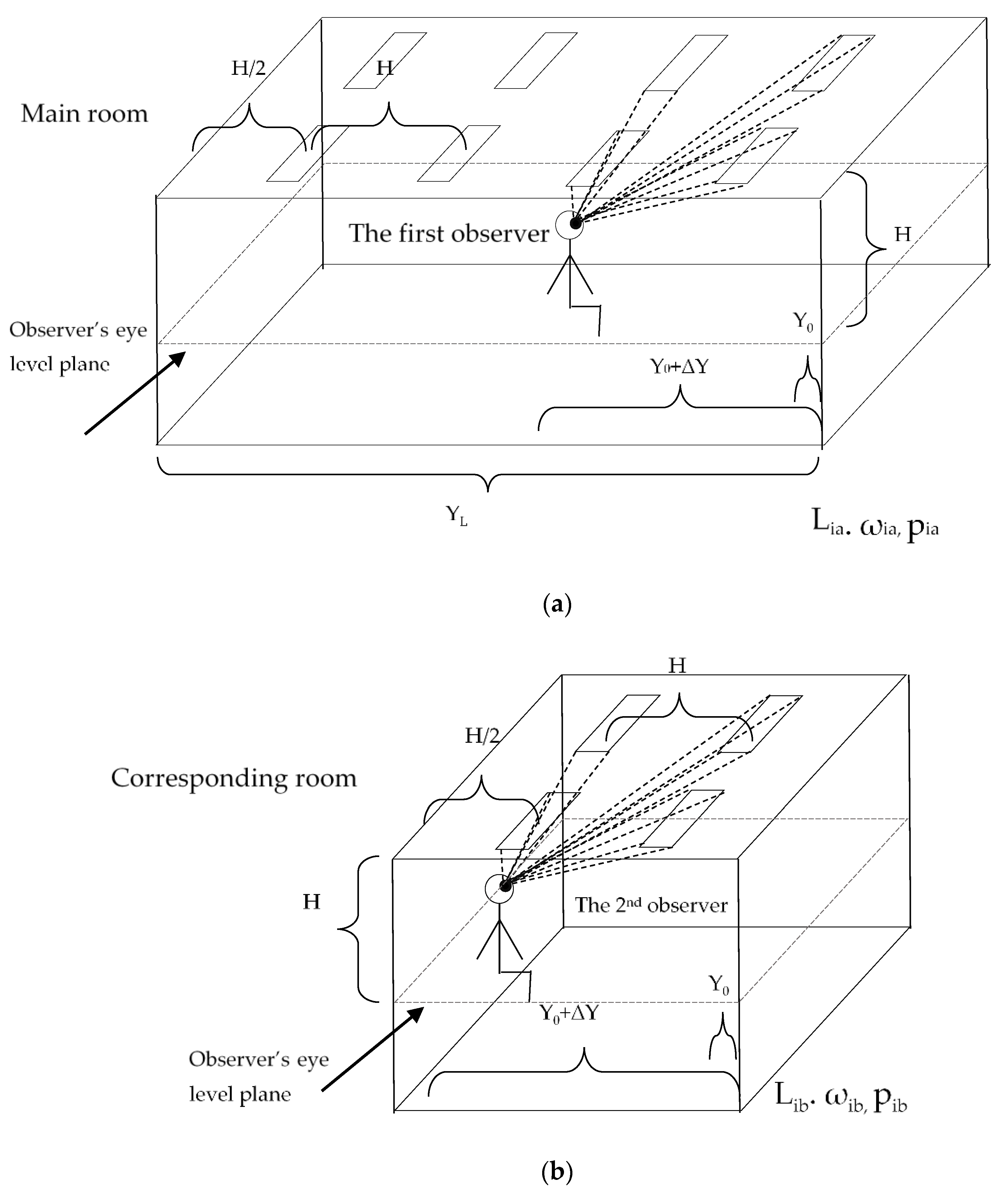
2.2. Method Explanation
2.3. Mathematical and Practical Proof of Feasibility of the Method
2.4. Case Study and Illustration of Implementation
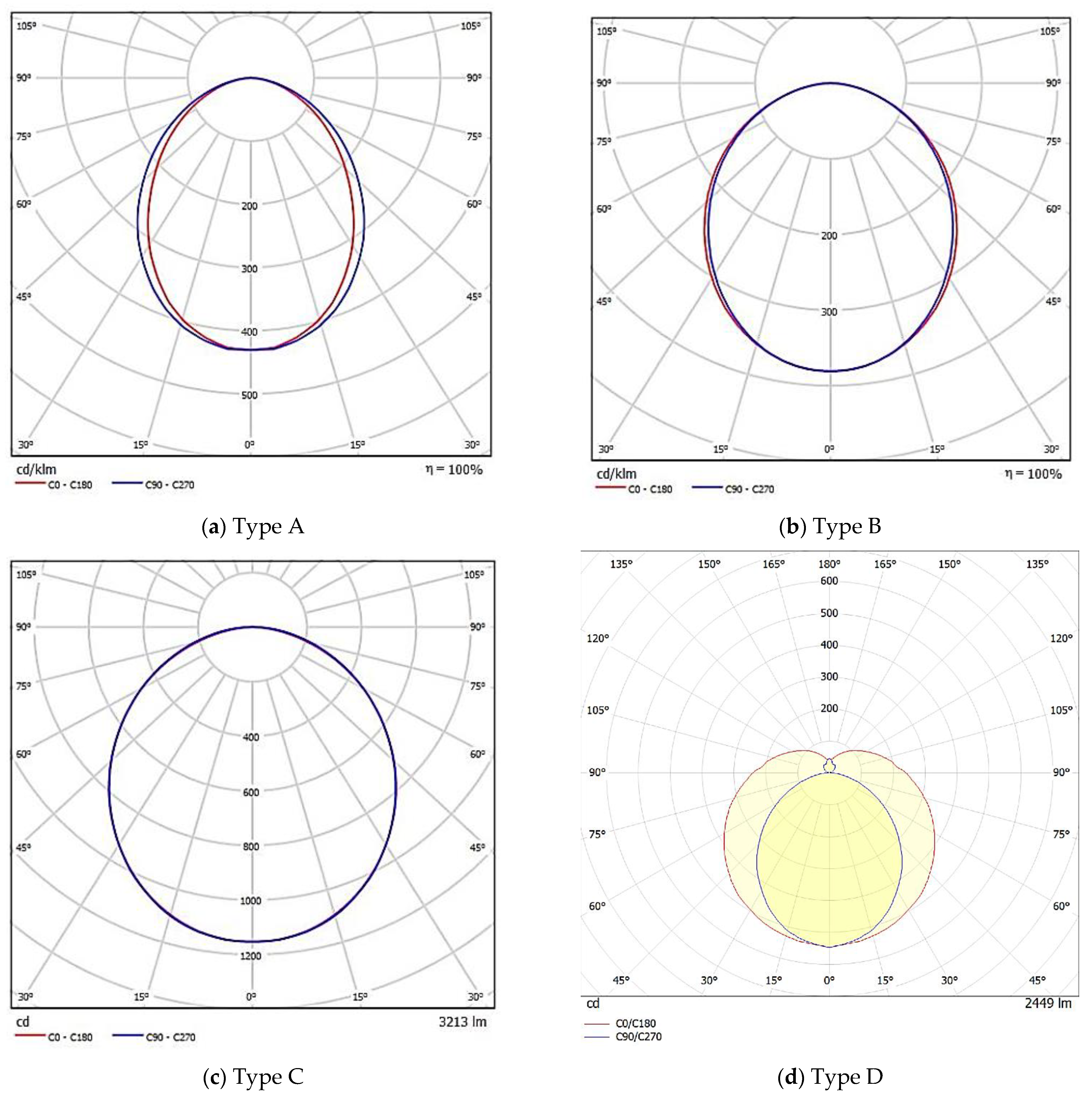
2.4.1. Luminaires Equipped with Diffusers (Uniform Luminous Intensity Distribution)
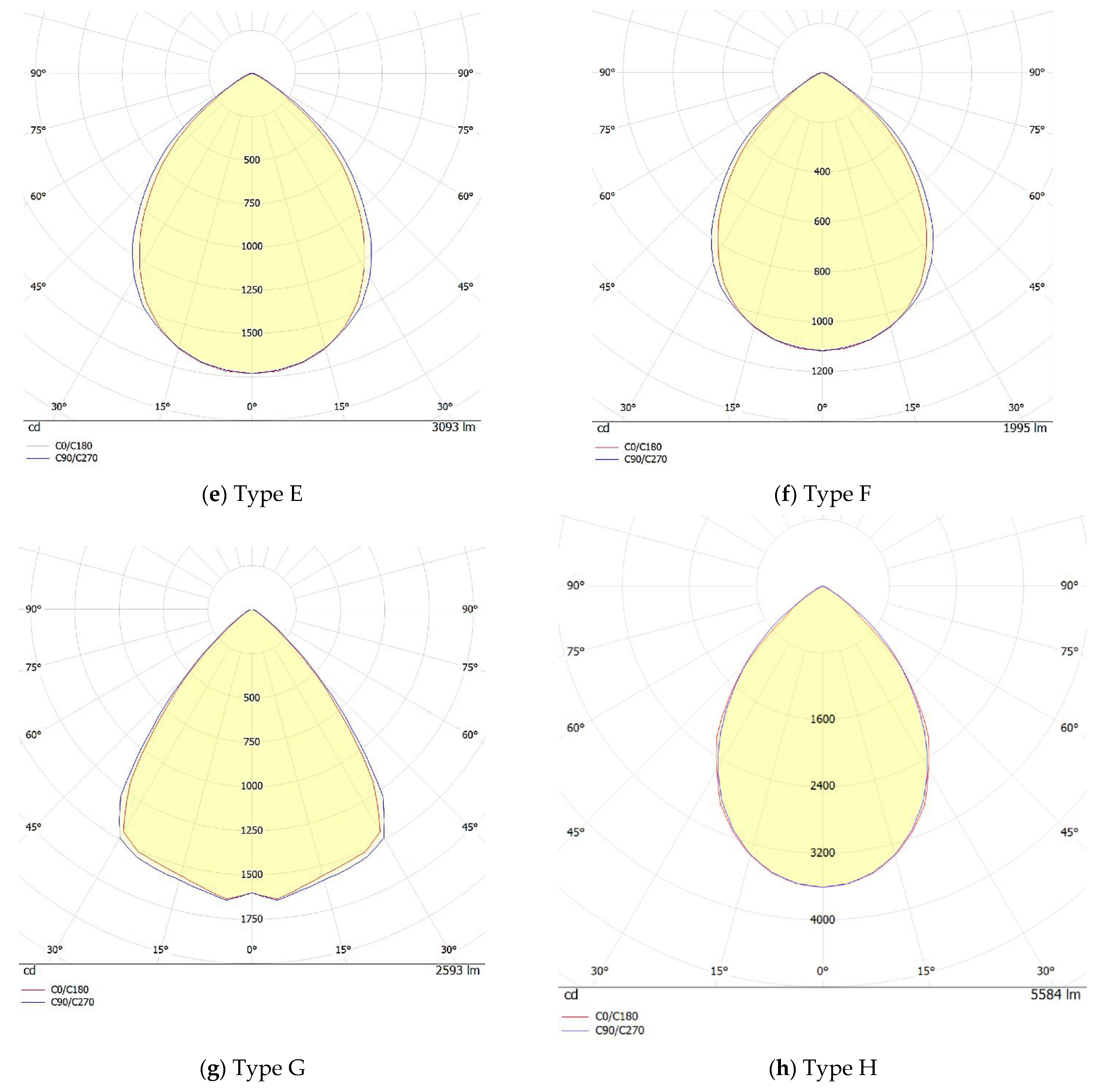
2.4.2. Luminaires Equipped with Lenses
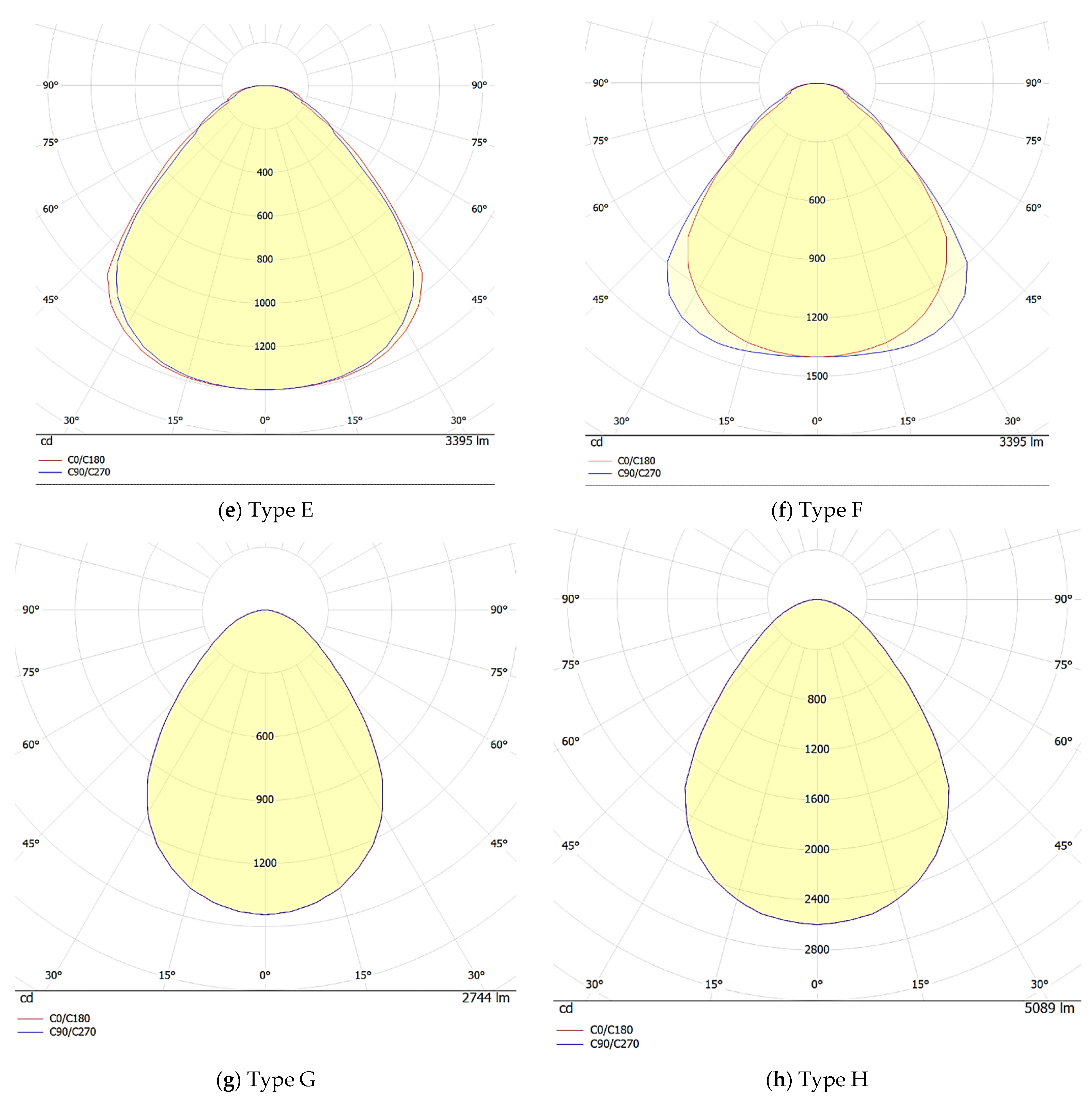
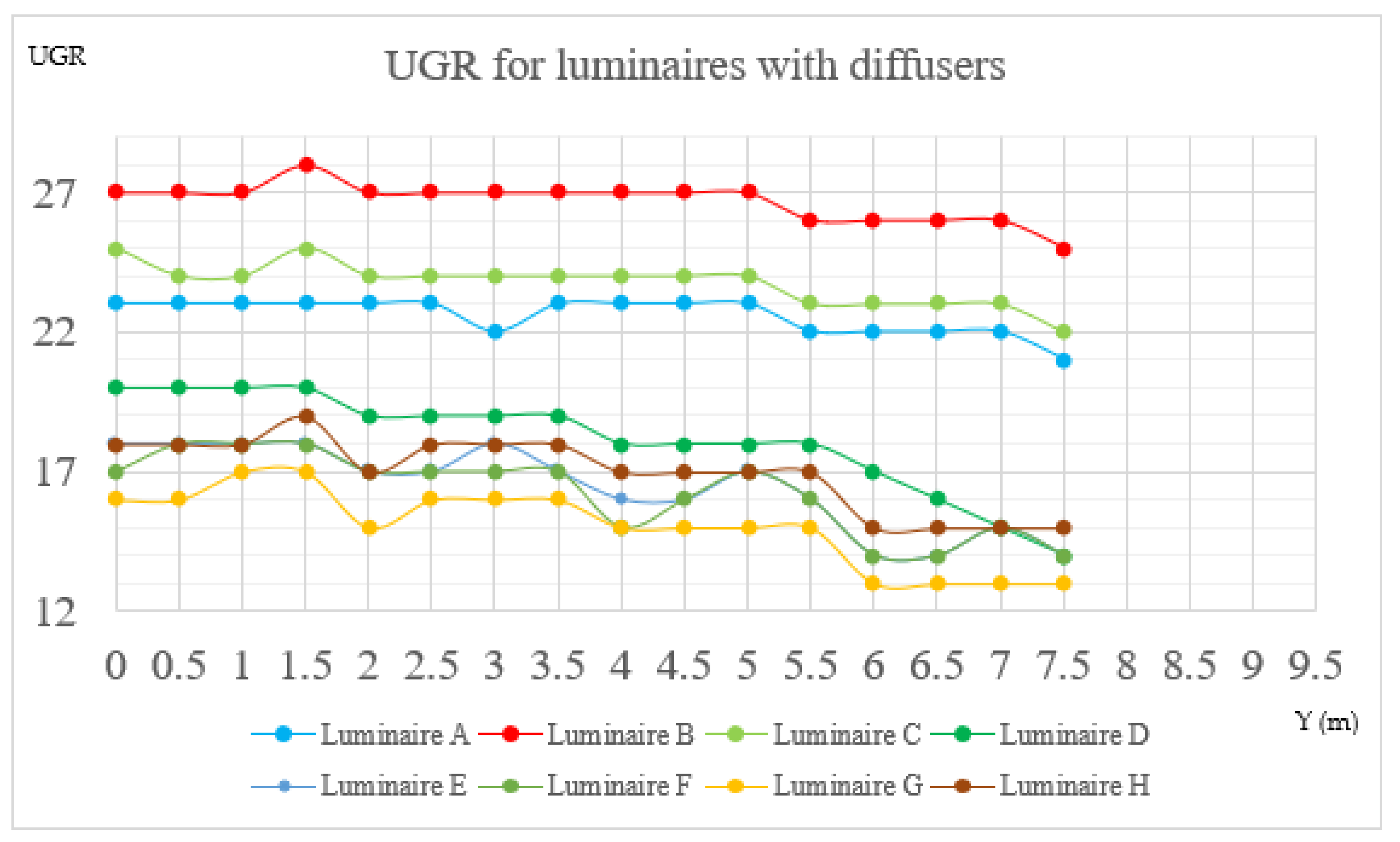
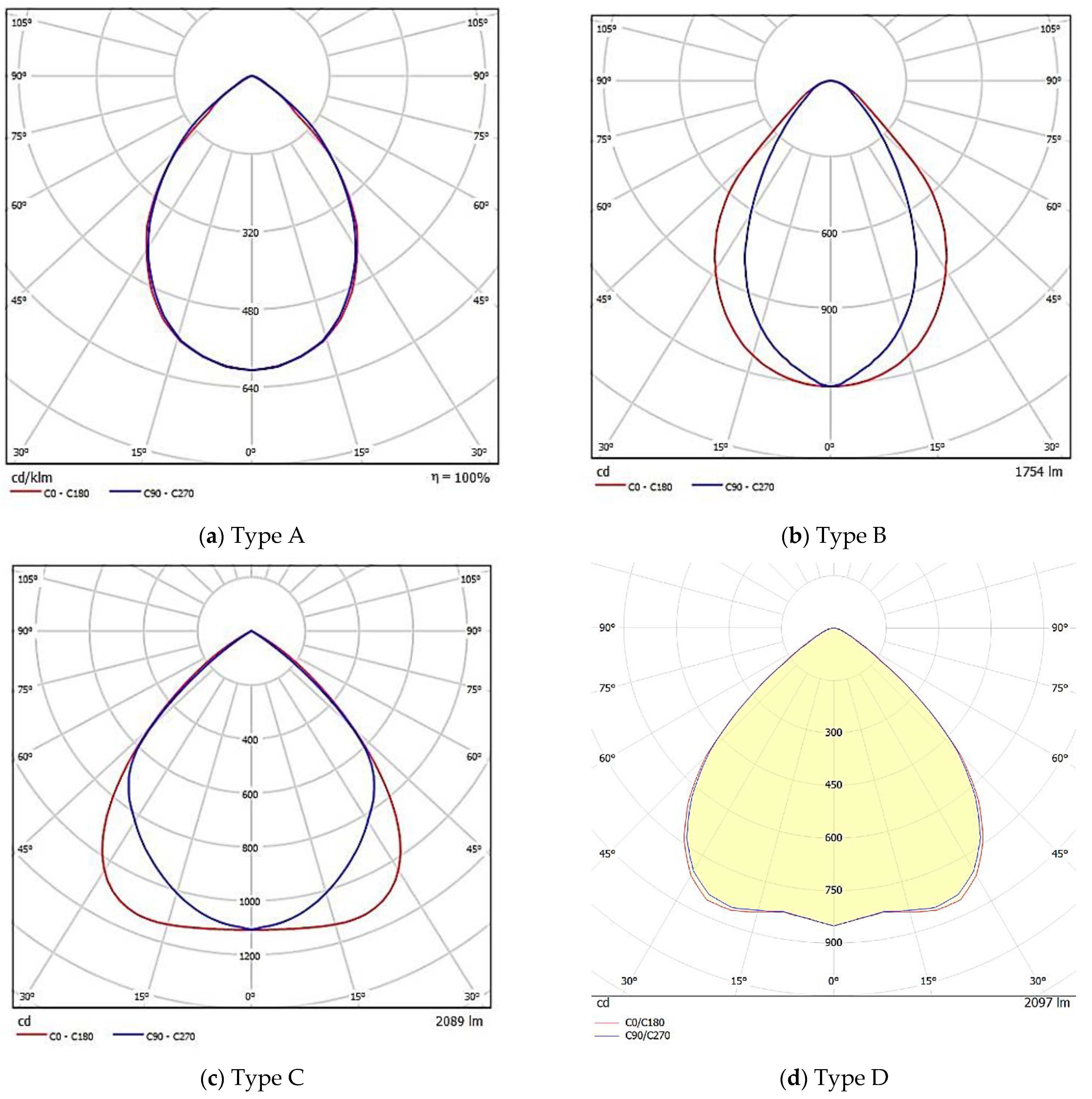
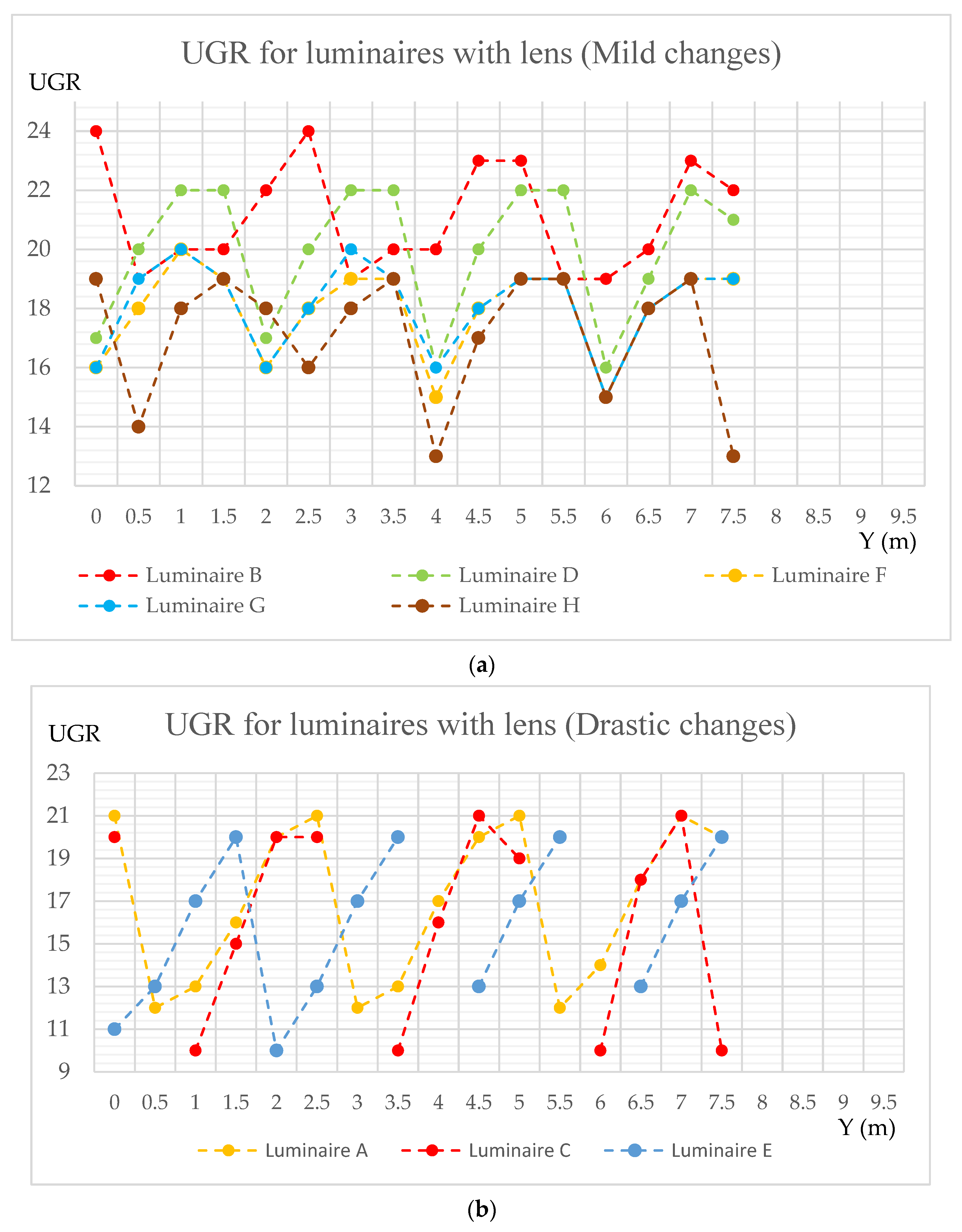
- Continuous curve represents lower contrast as UGR is a ratio of luminance (A, B, D, F, G and H).
- The average UGR matters (UGR of G < UGR of B).
- Discontinuous curve introduces a “torch” effect to the design (C and E).
- If UGR is not available, there is a chance that its value reaches 30 (E).
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carlucci, S.; Causone, F.; De Rosa, F.; Pagliano, L. A review of indices for assessing visual comfort with a view to their use in optimization processes to support building integrated design. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 47, 1016–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- González-Torres, M.; Pérez-Lombard, L.; Coronel, J.F.; Maestre, I.R.; Yan, D. A review on buildings energy information: Trends, end-uses, fuels and drivers. Energy Rep. 2021, 8, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moadab, N.H.; Olsson, T.; Fischl, G.; Aries, M. Smart versus conventional lighting in apartments—Electric lighting energy consumption simulation for three different households. Energy Build. 2021, 244, 111009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, L.; Trampert, K.; Neumann, C. Evaluation of discomfort glare from LED lighting systems. Ing. Iluminatului 2012, 14, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Fontoynont, M. LED lighting, ultra-low-power lighting schemes for new lighting applications. Comptes Rendus. Phys. 2018, 19, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolska, A.; Sawicki, D. Practical application of HDRI for discomfort glare assessment at indoor workplaces. Measurement 2020, 151, 107179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacomussi, P.; Radis, M.; Rossi, G.; Rossi, L. Visual Comfort with LED Lighting. Energy Procedia 2015, 78, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CIE 117; Discomfort Glare in Interior Lighting, Technical Report; International Comission on Illumination: Vienna, Austria, 1995; ISBN 9783900734701.
- Slominski, S. Potential Resource of Mistakes Existing While Using the Modern Methods of Measurement and Calculation in the Glare Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Lighting Conference of the Visegrad Countries, Lumen V4, Karpacz, Poland, 13–16 September 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsankov, P.; Yovchev, M. Measurement and Determination of the Unified Glare Rating of Indoor Lighting Systems. In Proceedings of the 2018 Seventh Balkan Conference on Lighting (BalkanLight), Varna, Bulgaria, 20–22 September 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheir, G.; Hanselaer, P.; Ryckaert, W. Pupillary light reflex, receptive field mechanism and correction for retinal position for the assessment of visual discomfort. Light. Res. Technol. 2017, 51, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, G.; Wienold, J.; Khanie, M.S.; Erell, E.; Kaftan, E.; Tzempelikos, A.; Konstantzos, I.; Christoffersen, J.; Kuhn, T.; Andersen, M. Comparing performance of discomfort glare metrics in high and low adaptation levels. Build. Environ. 2021, 206, 108335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotios, S.; Kent, M. Measuring Discomfort from Glare: Recommendations for Good Practice. LEUKOS 2020, 17, 338–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, M.; Fotios, S.; Altomonte, S. Discomfort glare evaluation: The influence of anchor bias in luminance adjustments. Light. Res. Technol. 2017, 51, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, C.; Wienold, J.; Bodart, M. Review of Factors Influencing Discomfort Glare Perception from Daylight. LEUKOS 2018, 14, 111–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienold, J.; Iwata, T.; Khanie, M.S.; Erell, E.; Kaftan, E.; Rodriguez, R.; Garreton, J.Y.; Tzempelikos, T.; Konstantzos, I.; Christoffersen, J.; et al. Cross-validation and robustness of daylight glare metrics. Light. Res. Technol. 2019, 51, 983–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donners, M.A.H.; Vissenberg, M.; Geerdinck, L.M.; van den Broek-Cools, J.H.F.; Buddemeijer-Lock, A. A psychophysical model of discomfort glare in both outdoor and indoor applications. In Proceedings of the 28th CIE Session, Manchester, UK, 28 June–4 July 2015; Volume 216, p. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Porsch, T.; Funke, C.; Schmidt, F.; Schierz, C. Measurement of the Unified Glare Rating (UGR) Based on Using ILMD. In Proceedings of the 28th CIE Session, Manchester, UK, 28 June–4 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Scheir, G.H.; Hanselaer, P.; Bracke, P.; Deconinck, G.; Ryckaert, W.R. Calculation of the Unified Glare Rating based on luminance maps for uniform and non-uniform light sources. Build. Environ. 2015, 84, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheir, G.H.; Hanselaer, P.; Ryckaert, W.R. Defining the Actual Luminous Surface in the Unified Glare Rating. LEUKOS 2017, 13, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangali, J. Discomfort glare prediction by using Unified Glare Rating. Aust. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2018, 15, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyukhova, Y.; Waters, C.E. Discomfort Glare from Small, High-Luminance Light Sources When Viewed against a Dark Surround. LEUKOS 2018, 14, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Bhardwaj, A.; Sharma, M.; Mirza, A. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of discomfort glare due to artificial indoor lighting. Int. J. Product. Qual. Manag. 2019, 28, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, A.U. (Ed.) Application of Fluid Flow Equations to Gas Systems; Gulf Professional Publishing: Burlington, UK, 2003; Chapter 2; pp. 11–83. [Google Scholar]
- Maurin, A.; Kwapisz, L. Simplified method for calculating airborne sound transmission through composite barriers. Compos. Struct. 2021, 276, 114526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, A.; Mannan, S.; Cagin, T. (Eds.) Inherently Safer Design; Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; Chapter 8; pp. 339–396. [Google Scholar]
- Jarungthammachote, S. Simplified model for estimations of combustion products, adiabatic flame temperature and properties of burned gas. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2020, 17, 100393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AS/NZS 1680 Interior Lighting. 2009. Available online: www.standards.co.nz (accessed on 21 February 2022).
- Kong, Q.; Siauw, T.; Bayen, A.M. Python Programming and Numerical Methods: Interpolation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Chapter 17; pp. 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farin, G. Tensor Product Patches; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 245–268. [Google Scholar]
- Calculation and Presentation of Unified Glare Rating Tables for Indoor Lighting Luminaires; CIE 190; CIE: Vienna, Austria, 2010.
- Ding, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Z.-R.; Gu, P.-F. Freeform LED lens for uniform illumination. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 12958–12966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| X | Y | ΔYFGL1 | ΔYFGL2 | ΔYFGL3 | ΔYFGL4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4~8 | −0.062 | −0.011 | 0.079 | 0.011 |
| 4 | 4~8 | −0.058 | −0.092 | 0.015 | 0.024 |
| 8 | 4~8 | −0.041 | −0.177 | 0.191 | 0.052 |
| 12 | 4~8 | −0.032 | −0.0209 | 0.199 | 0.071 |
| X | Y | ΔYFT,FW | ΔYFT,ww−1 | ΔYFT,CW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4~8 | −0.020 | −0.044 | −0.065 |
| 4 | 4~8 | −0.027 | −0.054 | −0.082 |
| 8 | 4~8 | −0.032 | −0.056 | −0.092 |
| 12 | 4~8 | −0.034 | −0.057 | −0.096 |
| X = 12 | X = 8 | X = 2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | 12 | 2 | 1 | 12 | 2 | 1 | 12 | 2 | 1 |
| EWID (calculated manually) | 25.5 | 28.38 | 12.65 | 31.2 | 21.4 | 13.21 | 28.46 | 26.00 | 19.59 |
| EWID Deviation from X = 12 | 0% | 11% | −50% | 0% | −31% | −58% | 0% | −9% | −31% |
| X = 12 | X = 8 | X = 2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | 12 | 2 | 1 | 12 | 2 | 1 | 12 | 2 | 1 |
| EWID (simulated) | 36.3 | 32.9 | 29.3 | 29.7 | 32.3 | 29.0 | 32.0 | 30.1 | 27.1 |
| EWID Deviation from X = 12 | 0% | −9% | −19% | 0% | 9% | −2% | 0% | −9% | −18% |
| Luminaire Type | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deviation of 2D-interpolated or extrapolated data from average of the simulated UGR as a percentage of 30 units of UGR. | −4.47% | −4.73% | −4.13% | −3.05% | 1.71% | 1.84% | 0.07% | 0.28% |
| Luminaire Type | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deviation of 2D-interpolated data average from average of the simulated UGR as a percentage of 30 units of UGR. | −3.59% | −23.4% | −12.83% | 6.86% | 5.40% | 3.35% | 3.10% | 3.52% |
| Difference between Proposed Method and Simulation Results as a Percentage of 30 Units of UGR | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Luminaire Type Observer Distance from Movement Starting Point (m) | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H |
| 2 | 13.33% | 36.5% | 12.17% | 17.00% | 24.33% | 10.27% | 10.67% | 0.60% |
| 4 | 3.33% | 23.33% | 7.67% | 20.33% | - * | 13.67% | 10.67% | 17.43% |
| 6 | 5.50% | 2.50% | 10.33% | 20.27% | - * | 13.00% | 13.33% | 10.77% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbasinejad, R.; Kacprzak, D. Proposing a Method Reducing UGR Calculations for LED Luminaires with Diffusers in Indoor Applications. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3462. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12073462
Abbasinejad R, Kacprzak D. Proposing a Method Reducing UGR Calculations for LED Luminaires with Diffusers in Indoor Applications. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(7):3462. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12073462
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbasinejad, Reza, and Dariusz Kacprzak. 2022. "Proposing a Method Reducing UGR Calculations for LED Luminaires with Diffusers in Indoor Applications" Applied Sciences 12, no. 7: 3462. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12073462
APA StyleAbbasinejad, R., & Kacprzak, D. (2022). Proposing a Method Reducing UGR Calculations for LED Luminaires with Diffusers in Indoor Applications. Applied Sciences, 12(7), 3462. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12073462







