Three-Dimensional Inversion of Semi-Airborne Transient Electromagnetic Data Based on a Particle Swarm Optimization-Gradient Descent Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theory and Method
2.1. Forward Simulation Theory
2.2. Theory of the PSO-GD Algorithm
2.2.1. α-Trimmed Filter Constraint
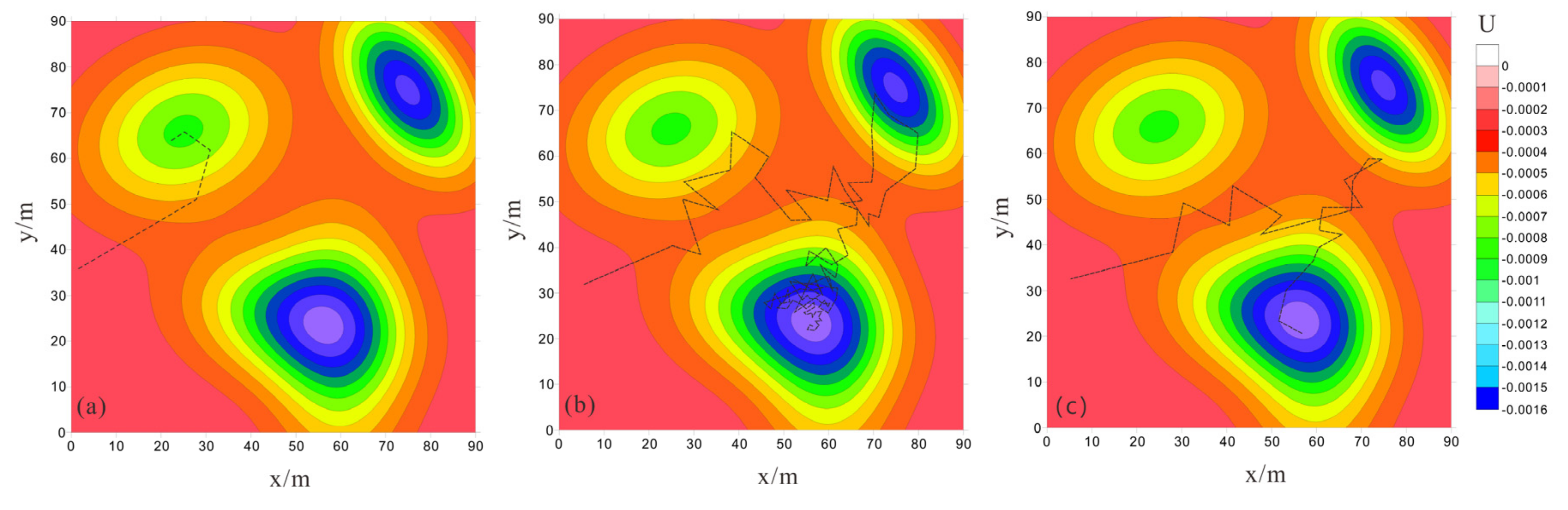
2.2.2. Experimental Function Testing
3. Numerical Simulations
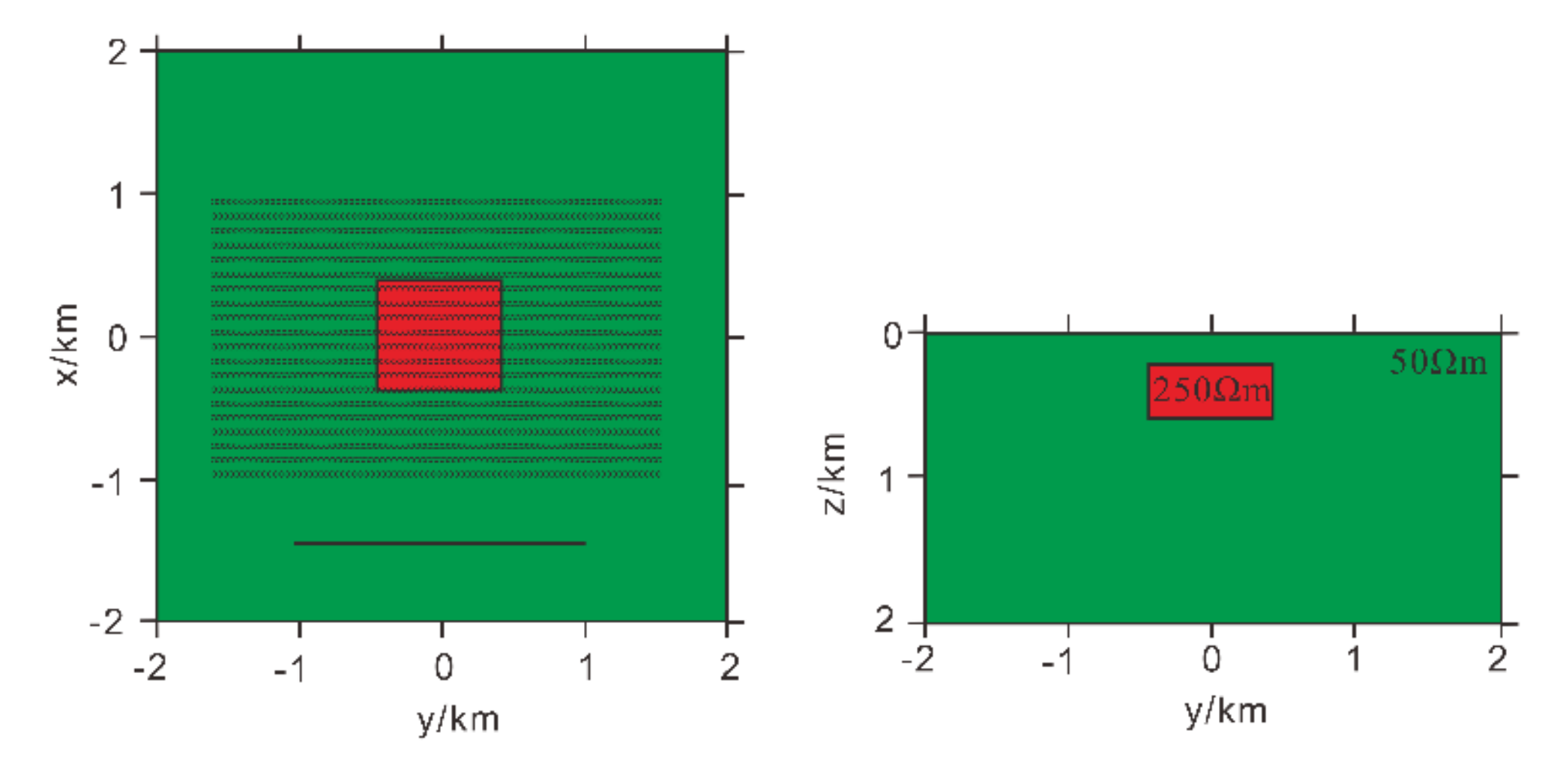
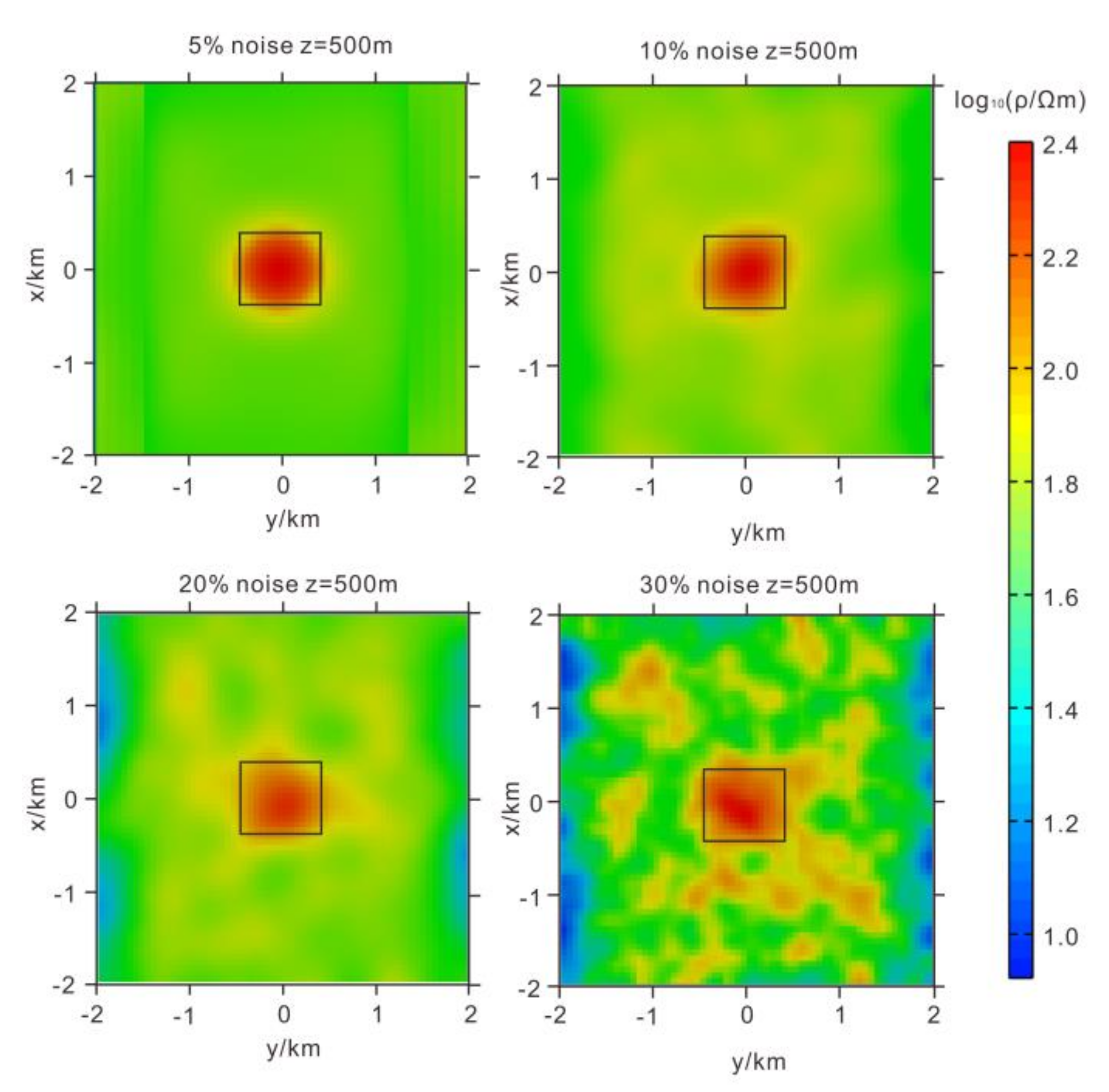
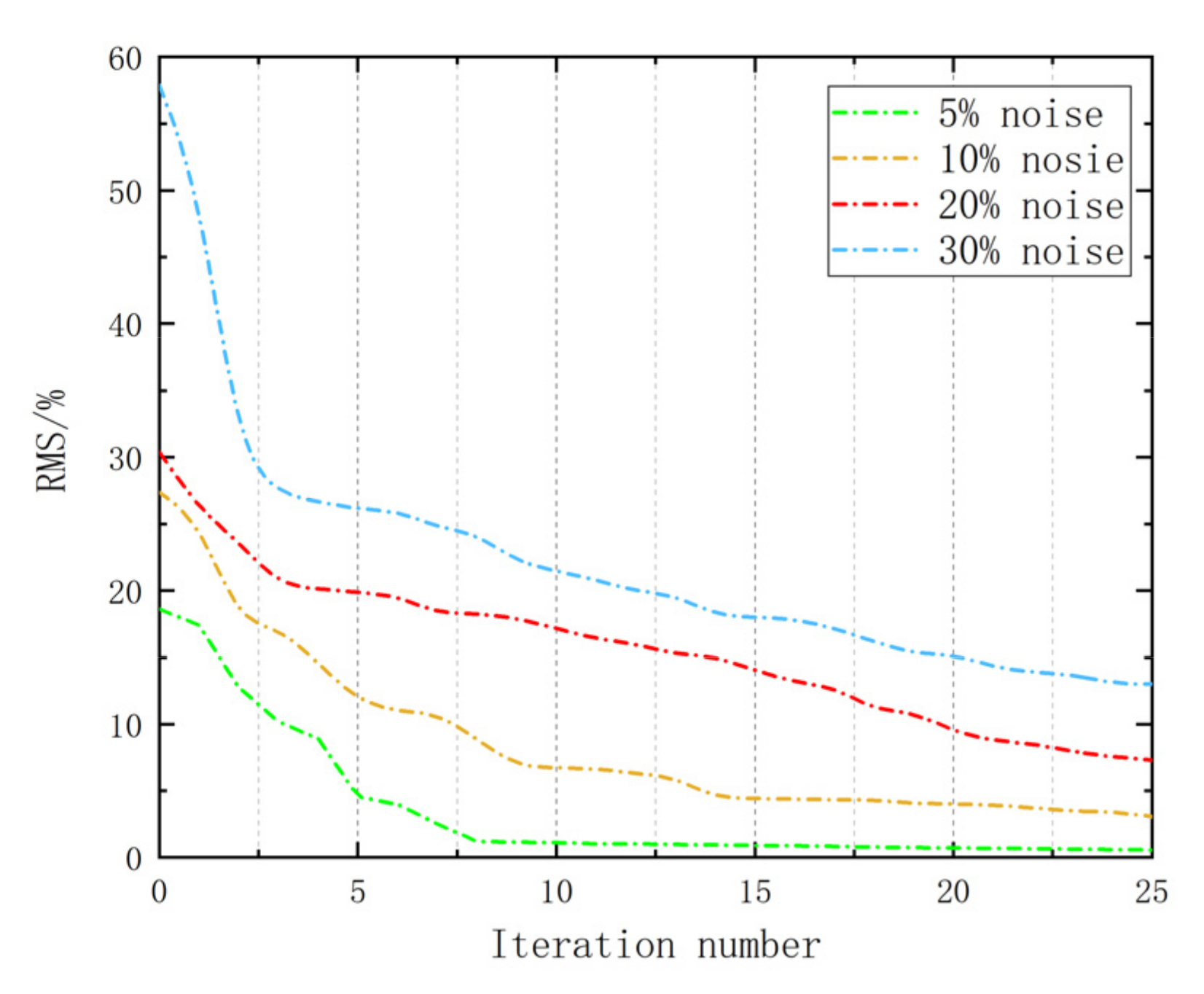
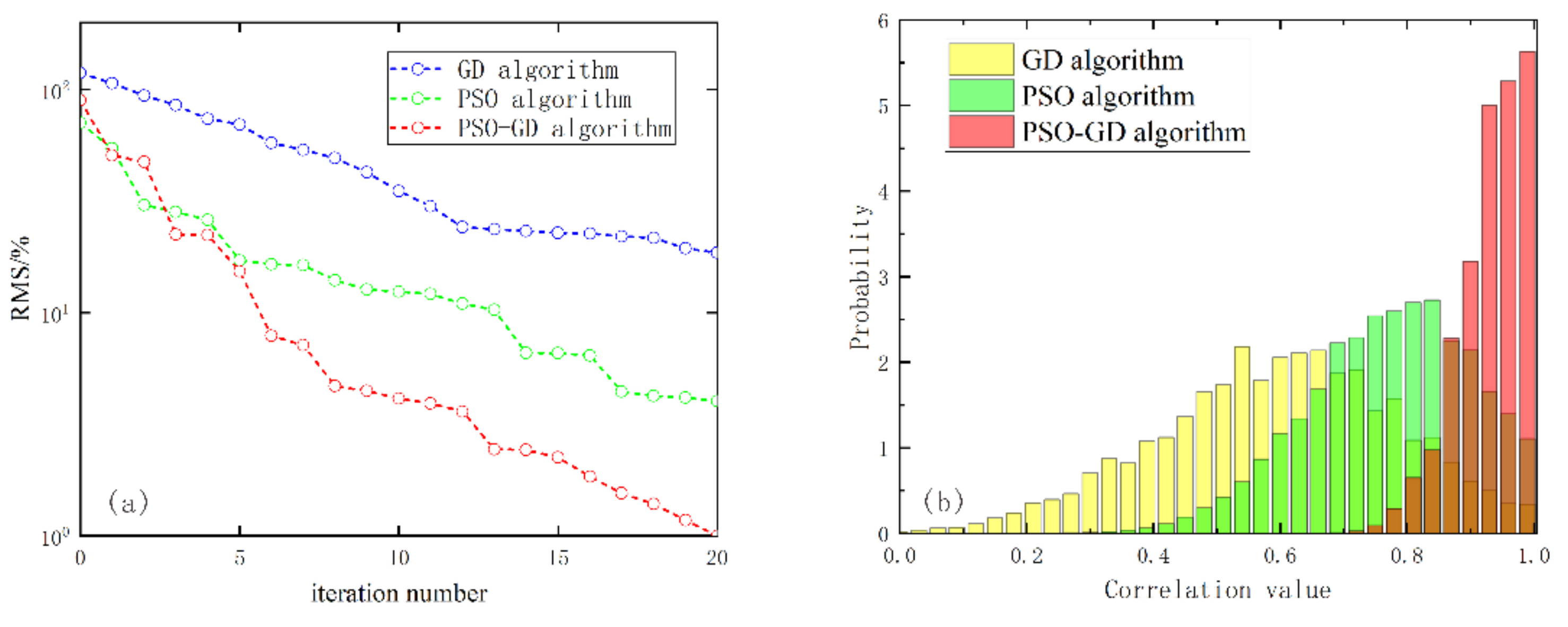
3.1. Noise Immunity Testing
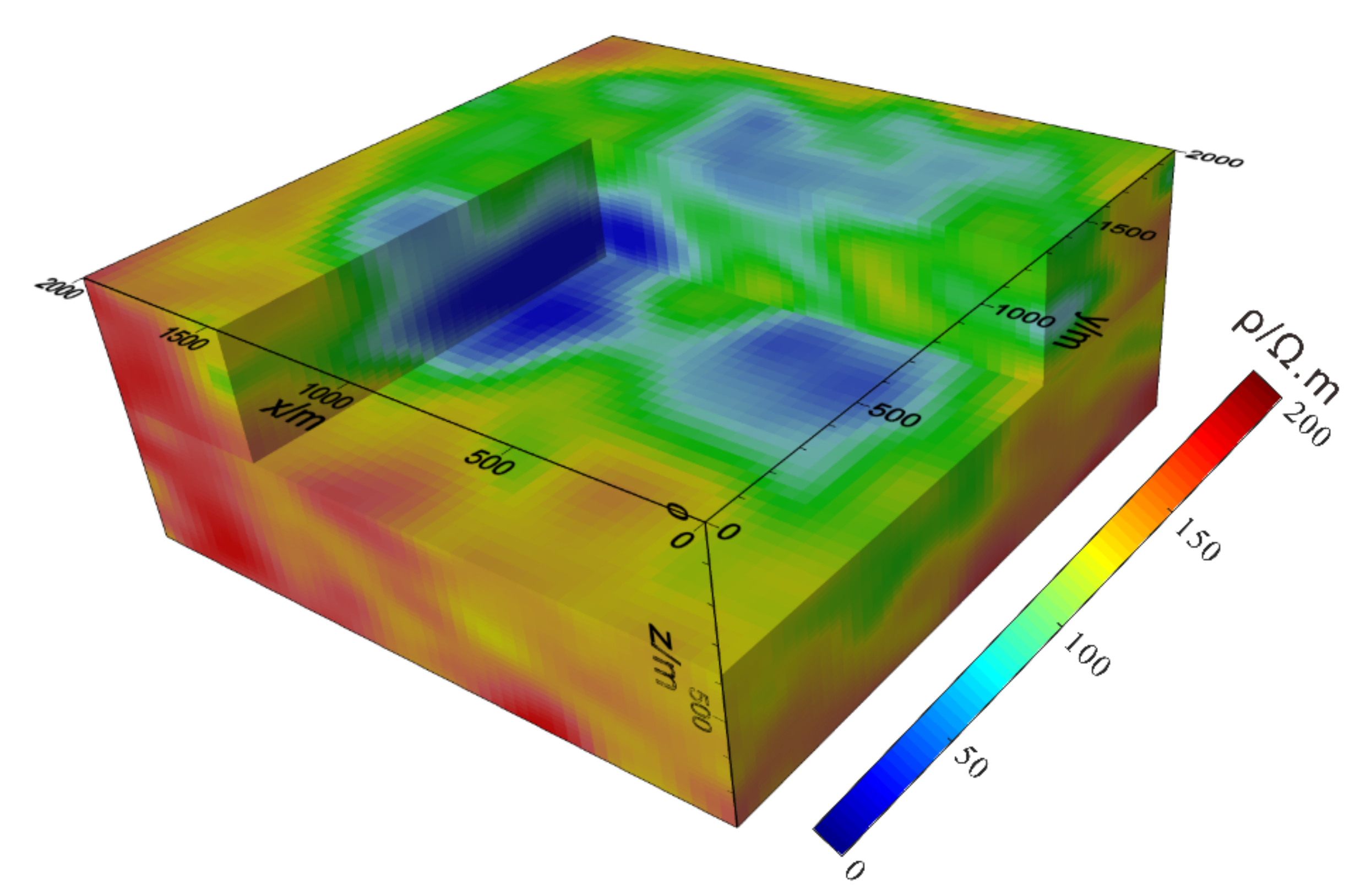
3.2. Complex Model Testing
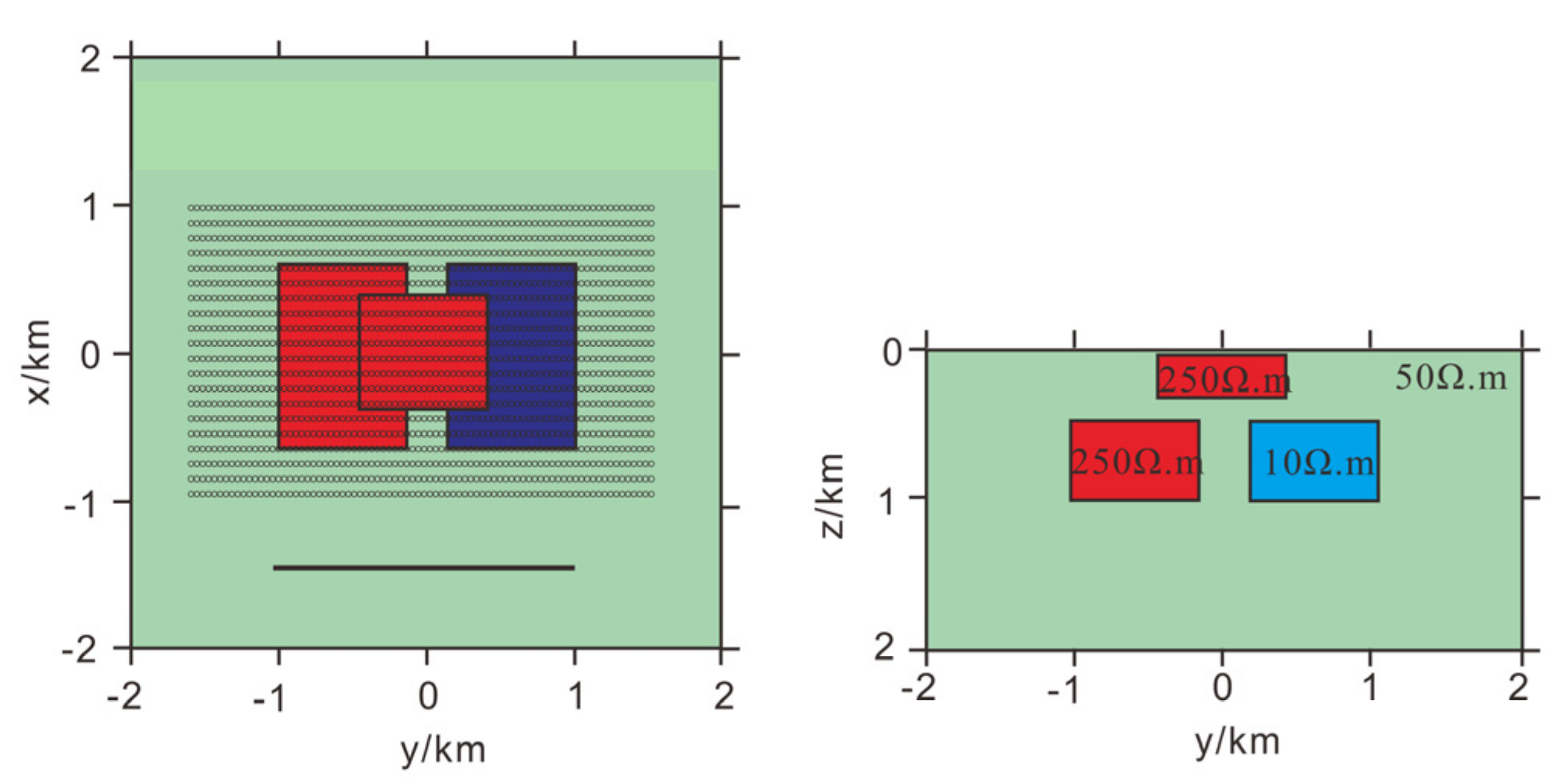
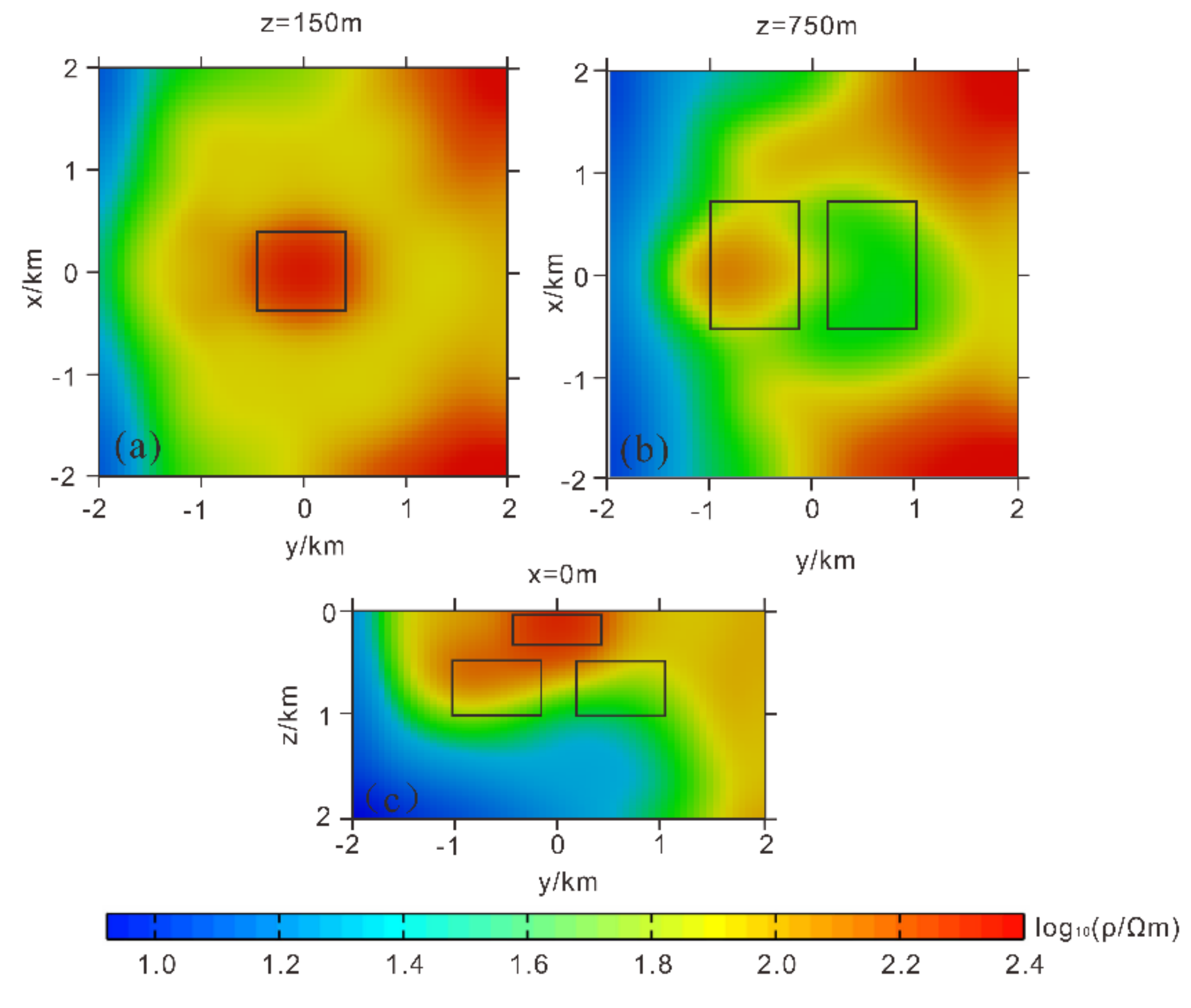
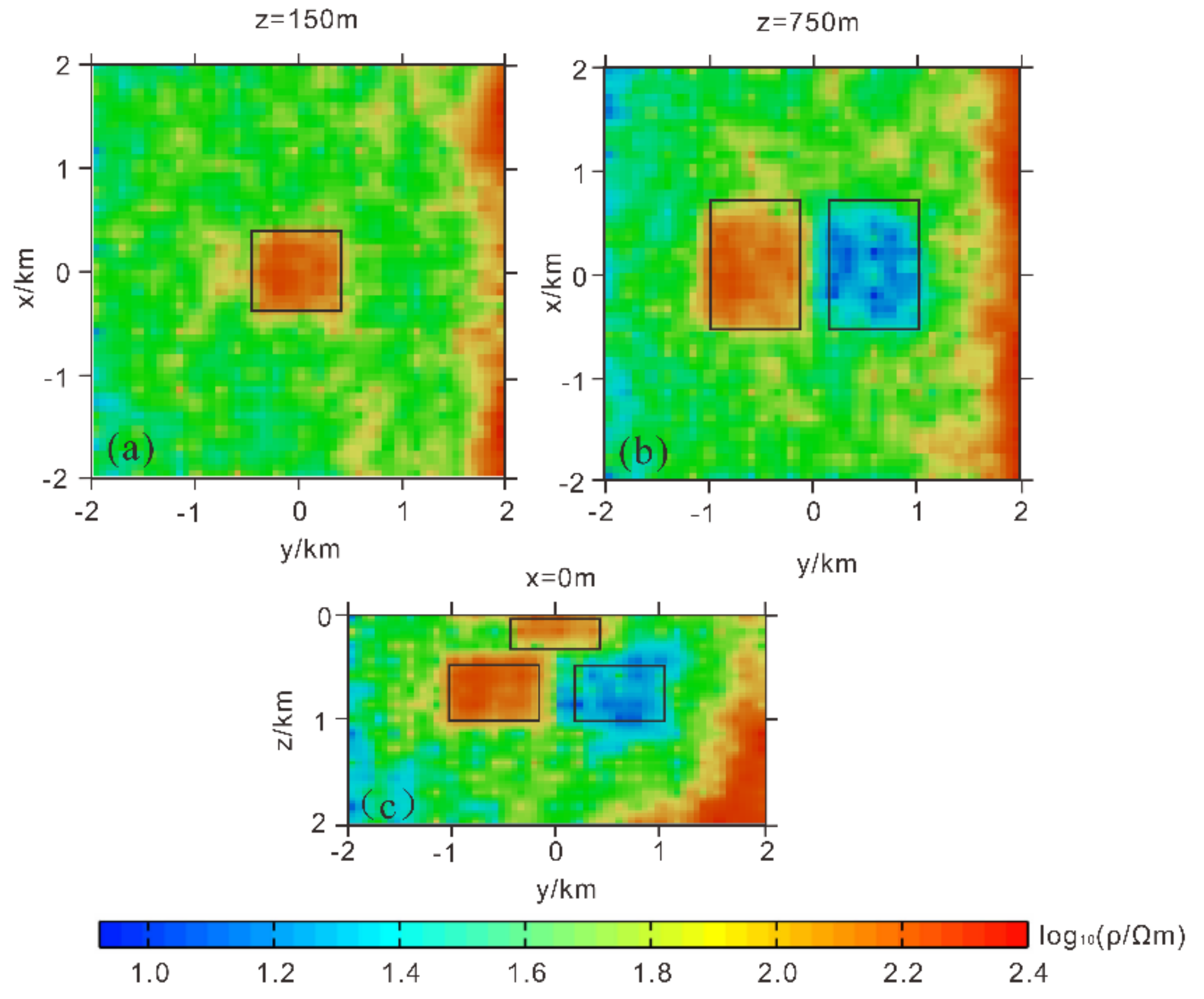
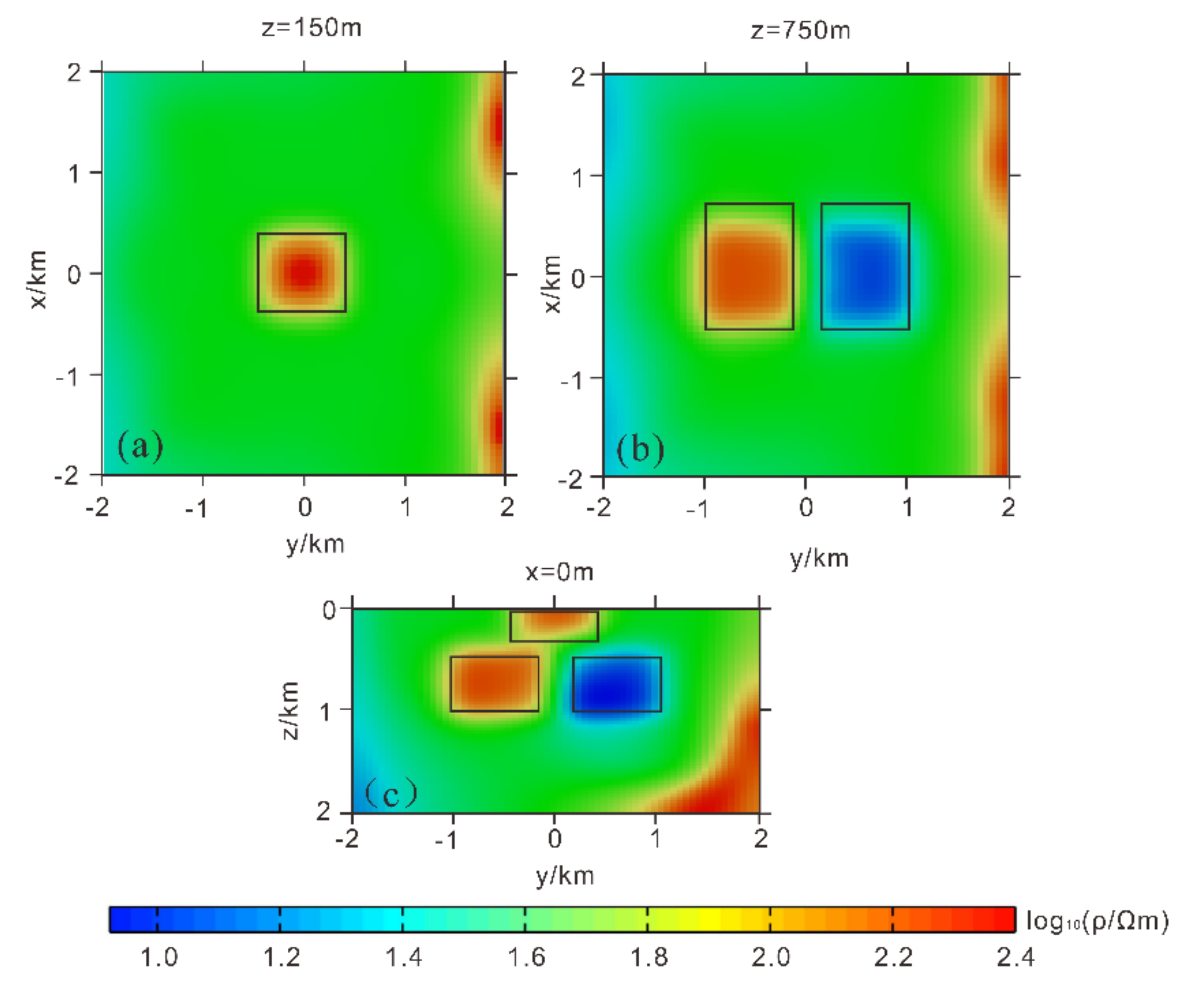
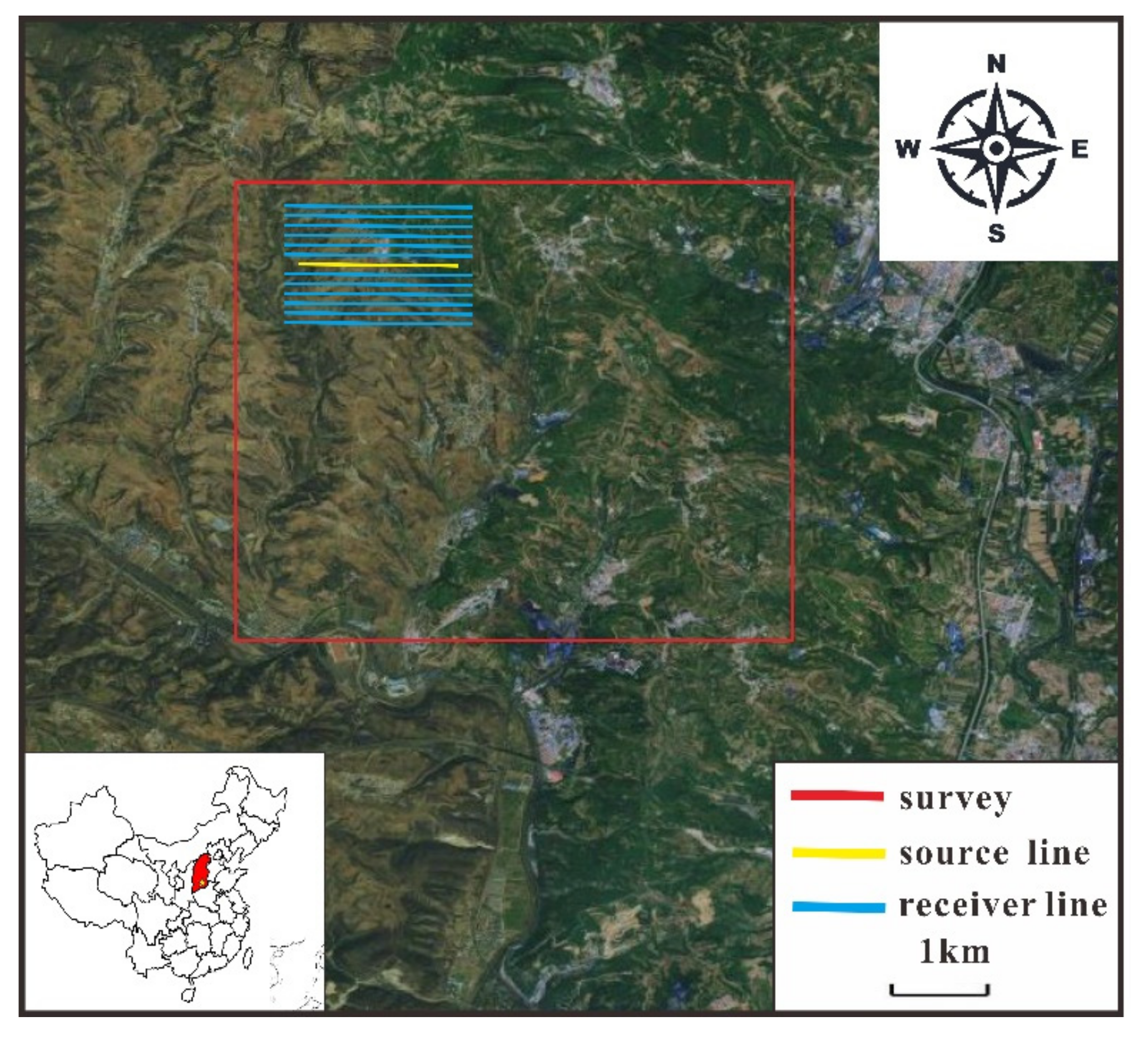
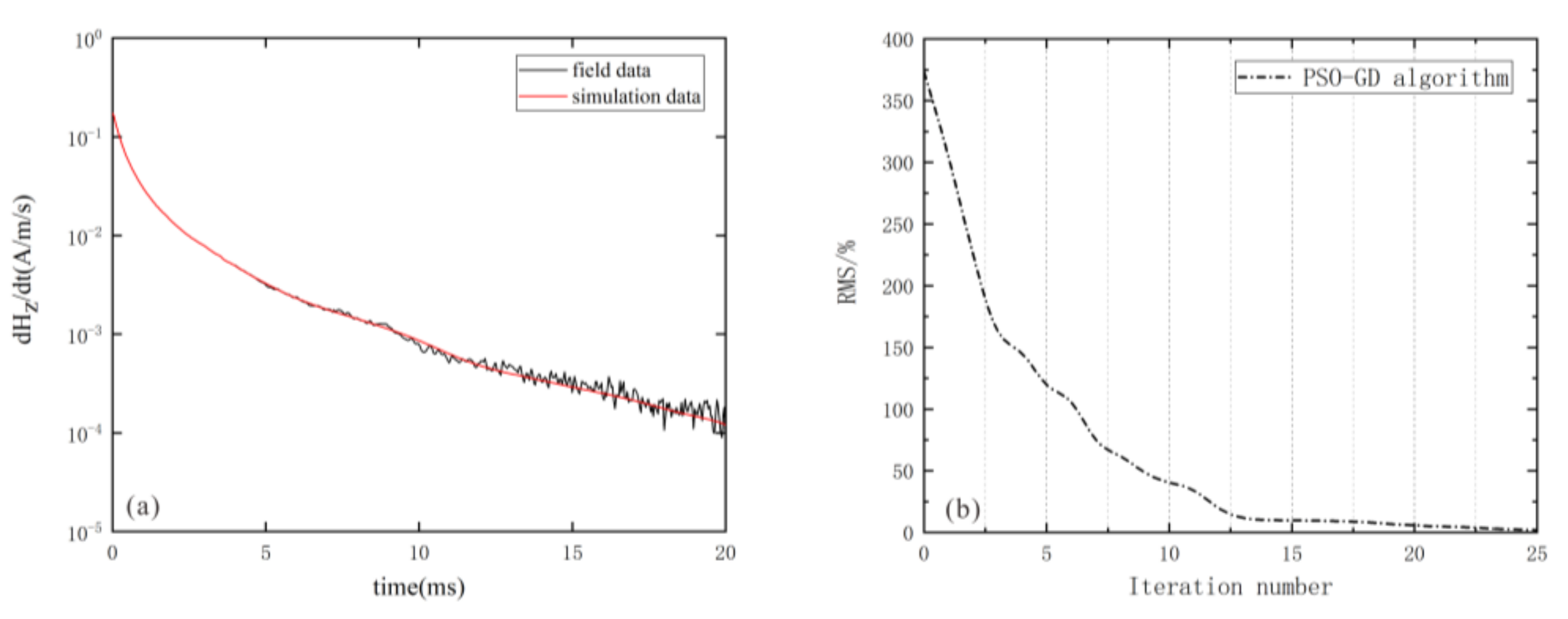
4. Case Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, R.S.; Annan, A.P.; Mcgowan, P.D. A comparison of data from airborne, semi-airborne, and ground electromagnetic systems. Geophysics 2001, 66, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogi, T.; Kusunoki, K.I.; Kaieda, H.; Ito, H.; Jomori, A.; Jomori, N.; Yuuki, Y. Grounded electrical-source airborne transient electromagnetic (GREATEM) survey of Mount Bandai, north-eastern Japan. Explor. Geophys. 2009, 40, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Kaieda, H.; Suzuki, K.; Kiho, K.; Mogi, T.; Yuuki, Y.; Jomori, A. A semi-airborne TEM (GREATEM) survey and its applicability to geo-hazards. In Proceedings of the 10th Asian Regional Conference of IAEG (2015), Kyoto, Japan, 26–29 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Y.; Yang, G.; Guan, S.; Zhang, X.; Tian, P. Interpretation research on electrical source of time domain ground-airborne electromagnetic data. In Proceedings of the World Automation Congress 2012, Puerto Vallarta, Mexico, 4 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nittinger, C.; Cherevatova, M.; Becken, M.; Martin, T.; Günther, T. A Novel Semi-airborne EM System for Mineral Exploration—First Results from Combined Fluxgate and Induction Coil Data. In Proceedings of the Second European Airborne Electromagnetics Conference, Malmö, Sweden, 3 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Guoqiang, X.; Weiying, C.; Shu, Y. Research study on the short offset time-domain electromagnetic method for deep exploration. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 155, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xue, G.; He, Y. The Progress of the Helicopter-Borne Transient Electromagnetic Method and Technology in China. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 32757–32766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Q.Y.; Zhu, R.X.; Xue, G.Q.; Yin, C.C.; Li, X. New development of the Electromagnetic (EM) methods for deep exploration. Chin. J. Geophys. 2019, 62, 2128–2138. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.S.; Xue, G.Q. Review of the key techniques on short-offset electromagnetic detection. Chin. J. Geophys. 2018, 61, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Xue, G.Q.; Fang, G.Y.; Li, X.; Ji, Y.J. The Development and Applications of the Semi-Airborne Electromagnetic System in China. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 104956–104966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tian, Z.; Ma, Y.; Gu, J.; Ji, Y.; Li, S. Application of Grounded Electrical Source Airborne Transient Electromagnetic (GREATEM) System in Goaf Water Detection. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2019, 24, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Liang, B.; Wang, J.; Han, F.; Liu, Q.H. 1-D Inversion of GREATEM Data by Supervised Descent Learning. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 99, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auken, E.; Christiansen, A.V. Layered and laterally constrained 2D inversion of resistivity data. Geophysics 2004, 69, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auken, E.; Christiansen, A.V.; Jacobsen, L.; Sørensen, K.I. Laterally Constrained 1D-Inversion of 3D TEM Data. In Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2005; pp. 514–518. [Google Scholar]
- Ley-Cooper, A.Y.; Viezzoli, A.; Guillemoteau, J.; Vignoli, G.; Macnae, J.; Cox, L.; Munday, T. Airborne electromagnetic modelling options and their consequences in target definition. Explor. Geophys. 2014, 46, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhdanov, M.S.; Alfouzan, F.A.; Cox, L.; Alotaibi, A.; Alyousif, M.; Sunwall, D.; Endo, M. Large-scale 3D modeling and inversion of multiphysics airborne geophysical data: A case study from the Arabian Shield, Saudi Arabia. Minerals 2018, 8, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McMillan, M.; Haber, E.; Marchant, D. Large scale 3D airborne electromagnetic inversion–recent technical improvements. ASEG Ext. Abstr. 2018, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steuer, A.; Smirnova, M.; Becken, M.; Schiffler, M.; Günther, T.; Rochlitz, R.; Yogeshwar, P.; Moerbe, W.; Siemon, B.; Costabel, S.; et al. Comparison of novel semi-airborne electromagnetic data with multi-scale geophysical, petrophysical and geological data from Schleiz, Germany. J. Appl. Geophys. 2020, 182, 104172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Seismic impedance inversion using I1-norm regularization and gradient descent methods. J. Inverse Ill Posed Probl. 2010, 18, 823–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Li, M.; Xiang, C.; Yang, F.; Abubakar, A. 2D Magnetotelluric Inversion using Supervised Descent Method. In Proceedings of the International Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society Symposium—China (ACES), Beijing, China, 29 July–1 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Scales, J.A. Tomographic inversion via the Conjugate Gradient method. Geophysics 1987, 52, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamoda, M.; Mamat, M.; Rivaie, M.; Salleh, Z. A Conjugate Gradient Method with Strong Wolfe-Powell Line Search for Unconstrained Optimization. Appl. Math. Sci. 2016, 10, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.H.; Dahlin, T. A comparison of the Gauss-Newton and quasi-Newton methods in resistivity imaging inversion. J. Appl. Geophys. 2002, 49, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, M.X.; Chen, J.B.; Cao, J. 1-Regularized full-waveform inversion with prior model information based on orthant-wise limited memory quasi-Newton method. J. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 142, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsopoulos, K.E.; Vrahatis, M.N. Applications in Bioinformatics and Medical Informatics. In Particle Swarm Optimization and Intelligence (Advances and Applications); IGI global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2010; Volume 9, pp. 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, M.K.; Stoffa, P.L. Global Optimization Methods in Geophysical Inversion; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Carbajal, M.; Linde, N.; Kalscheuer, T.; Vrugt, J.A. Two-dimensional probabilistic inversion of plane-wave electromagnetic data: Methodology, model constraints and joint inversion with electrical resistivity data. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 196, 1508–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hauser, J.; Gunning, J.; Annetts, D. Probabilistic inversion of airborne electromagnetic data under spatial constraints. Geophysics 2015, 80, E135–E146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.M.; Minsley, B.J. Inversion of airborne EM data with an explicit choice of prior model. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 218, 1348–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Vignoli, G.; Viezzoli, A.; Nevalainen, J.; Vacca, G. (Quasi-) Real-Time Inversion of Airborne Time-Domain Electromagnetic Data via Artificial Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Zhang, J.F.; Li, D.; Bai, Y. Resistivity-depth imaging with the airborne transient electromagnetic method based on an artificial neural network. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2020, 25, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, K.; Yoon, D.; Byun, J. Imaging subsurface resistivity structure from airborne electromagnetic induction data using deep neural network. Explor. Geophys. 2020, 51, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzyrev, V.; Swidinsky, A. Inversion of 1D frequency-and time-domain electromagnetic data with convolutional neural networks. Comput. Geosci. 2021, 149, 104681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minsley, B.J.; Foks, N.L.; Bedrosian, P.A. Quantifying model structural uncertainty using airborne electromagnetic data. Geophys. J. Int. 2021, 224, 590–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.L.; Li, M.X.; Xiao, Y.L.; Sun, X.Y.; Chen, D. Study on particle swarm optimization inversion of mine transient electromagnetic method in whole-space. Chin. J. Geophys. 2014, 57, 3478–3484. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Xue, G.; He, Y. Decoupling induced polarization effect from time domain electromagnetic data in Bayesian framework. Geophysics 2019, 84, A59–A63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Sun, B.; Sun, X. Inversion of Thermal Conductivity in Two-Dimensional Unsteady-State Heat Transfer System Based on Finite Difference Method and Artificial Bee Colony. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, T.; Hu, X.; Du, W.; Cheng, L.; Xiao, T.; Li, Q. Lp-Norm Inversion of Gravity Data Using Adaptive Differential Evolution. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, F.; Santilano, A.; Godio, A. A Review of Geophysical Modeling Based on Particle Swarm Optimization. Surv. Geophys. 2021, 42, 505–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, F.; Santilano, A.; Godio, A. Particle swarm optimization of 2D magnetotelluric data. Geophysics 2019, 84, E125–E141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Álvarez, J.P.; Fernández-Martínez, J.L.; García-Gonzalo, E.; Menéndez-Pérez, C.O. Application of the particle swarm optimization algorithm to the solution and appraisal of the Vertical Electrical Sounding inverse problem. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference of the International Association of Mathematical Geology (IAMG’06), Liège, Belgium, 12–14 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, R.; Srivastava, S. Particle swarm optimization: A new tool to invert geophysical data. Geophysics 2007, 72, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.; Gonzalo, E.; Álvarez, J.; Kuzma, H. PSO: A powerful algorithm to solve geophysical inverse problems: Application to a 1D-DC resistivity case. J. Appl. Geophys 2010, 71, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Li, F.; Peng, S.; Sun, X.; Zheng, J.; Jia, J. Joint inversion of TEM and DC in roadway advanced detection based on particle swarm optimization. J. Appl. Geophys. 2015, 123, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olalekan, F.; Di, Q. Particle Swarm Optimization Method for Stochastic Inversion of MTEM Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 1832–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liang, M.; Hu, X. Particle swarm optimization inversion of magnetic data: Field examples from iron ore deposits in ChinaParticle swarm optimization inversion. Geophysics 2018, 83, J43–J59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, J.M.; Shashkov, M. Mimetic Discretizations for Maxwell’s Equations. J. Comput. Phys. 1999, 151, 881–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cockett, R.; Kang, S.; Heagy, L.J.; Pidlisecky, A.; Oldenburg, D.W. SimPEG: An open source framework for simulation and gradient based parameter estimation in geophysical applications. Comput. Geosci. 2015, 85, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miranda, L.J. PySwarms: A research toolkit for Particle Swarm Optimization in Python. J. Open Source Softw. 2018, 3, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Networks IV, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ratnaweera, A.; Halgamuge, S.K.; Watson, H.C. Self-Organizing Hierarchical Particle Swarm Optimizer with Time-Varying Acceleration Coefficients. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2004, 8, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z.H.; Zhang, J. Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Ant Colony Optimization and Swarm Intelligence, Brussels, Belgium, 22–24 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pallero, J.L.G.; Fernández-Martínez, J.L.; Bonvalot, S.; Fudym, O. 3D gravity inversion and uncertainty assessment of basement relief via Particle Swarm Optimization. J. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 139, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednar, J.; Watt, T. Alpha-trimmed means and their relationship to median filters. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Processing 1984, 32, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| n | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50 | 25 | 15 | 10 | 0.2 |
| 2 | 60 | 20 | 10 | 20 | 0 |
| 3 | 75 | 75 | 10 | 12 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 10 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 0.1 |
| 5 | 25 | 66 | 15 | 12 | −0.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Y.; Xue, G.; Chen, W.; Tian, Z. Three-Dimensional Inversion of Semi-Airborne Transient Electromagnetic Data Based on a Particle Swarm Optimization-Gradient Descent Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12063042
He Y, Xue G, Chen W, Tian Z. Three-Dimensional Inversion of Semi-Airborne Transient Electromagnetic Data Based on a Particle Swarm Optimization-Gradient Descent Algorithm. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(6):3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12063042
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Yiming, Guoqiang Xue, Weiying Chen, and Zhongbin Tian. 2022. "Three-Dimensional Inversion of Semi-Airborne Transient Electromagnetic Data Based on a Particle Swarm Optimization-Gradient Descent Algorithm" Applied Sciences 12, no. 6: 3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12063042
APA StyleHe, Y., Xue, G., Chen, W., & Tian, Z. (2022). Three-Dimensional Inversion of Semi-Airborne Transient Electromagnetic Data Based on a Particle Swarm Optimization-Gradient Descent Algorithm. Applied Sciences, 12(6), 3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12063042






