In-Gel Assay to Evaluate Antioxidant Enzyme Response to Silver Nitrate and Silver Nanoparticles in Marine Bivalve Tissues
Abstract
:1. Background
2. Materials and Methods
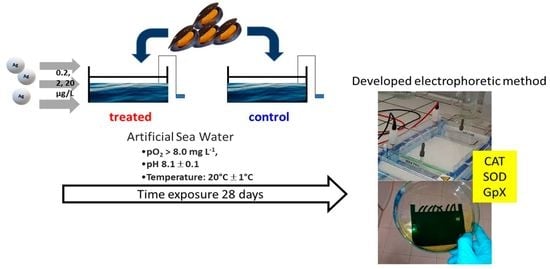
2.1. Animal Treatment and Experimental Design
2.2. In Gel Antioxidant Enzyme Assays
2.2.1. Catalase Assay
2.2.2. Superoxide Dismutase
2.2.3. Glutathione Peroxidase
2.3. HSP70 Evaluation
2.4. Digital Image Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
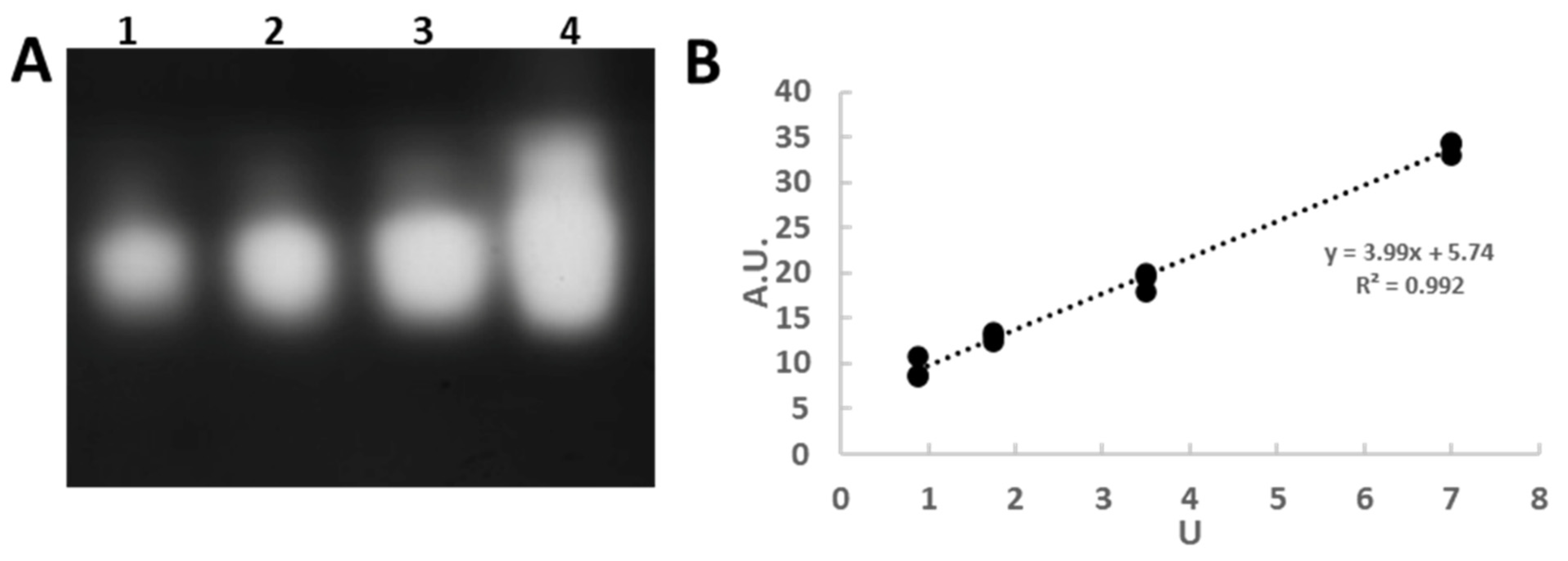
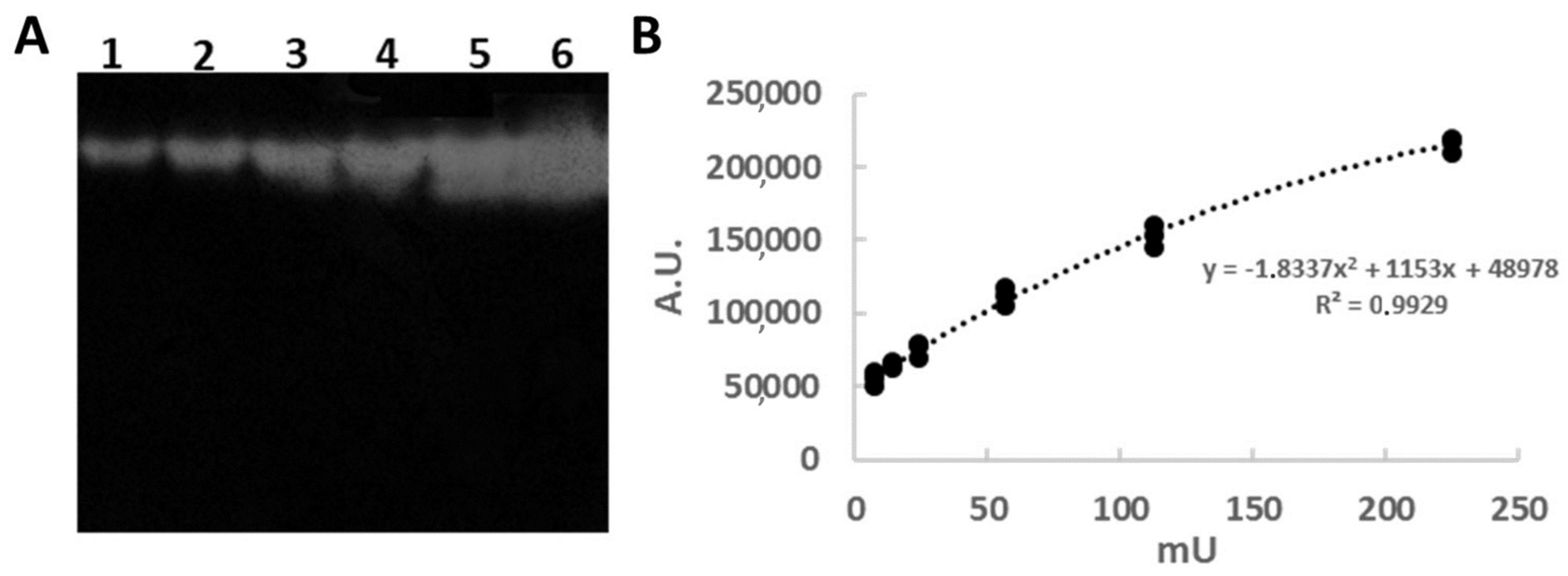
3.1. In-Gel Enzyme Protocol Development
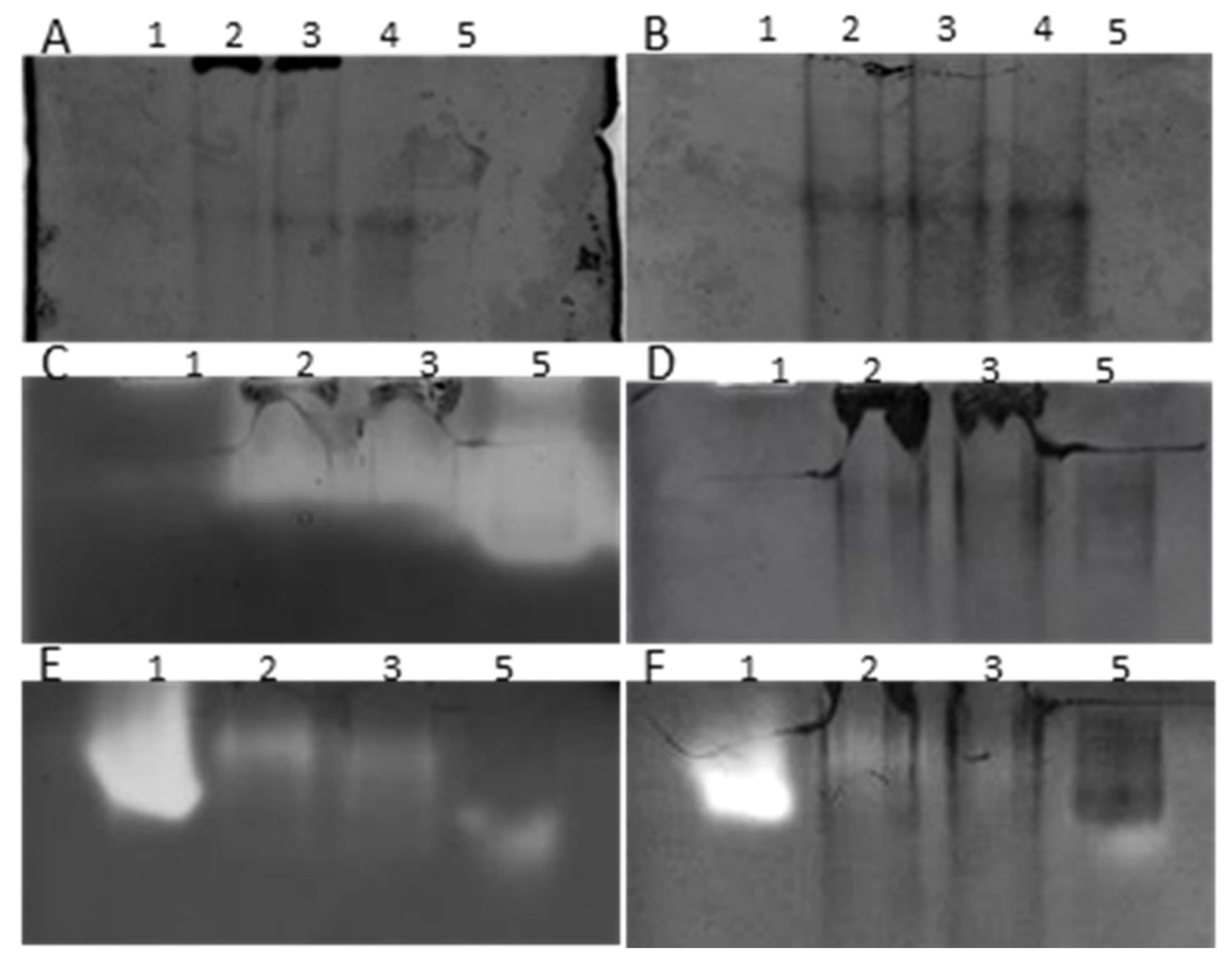
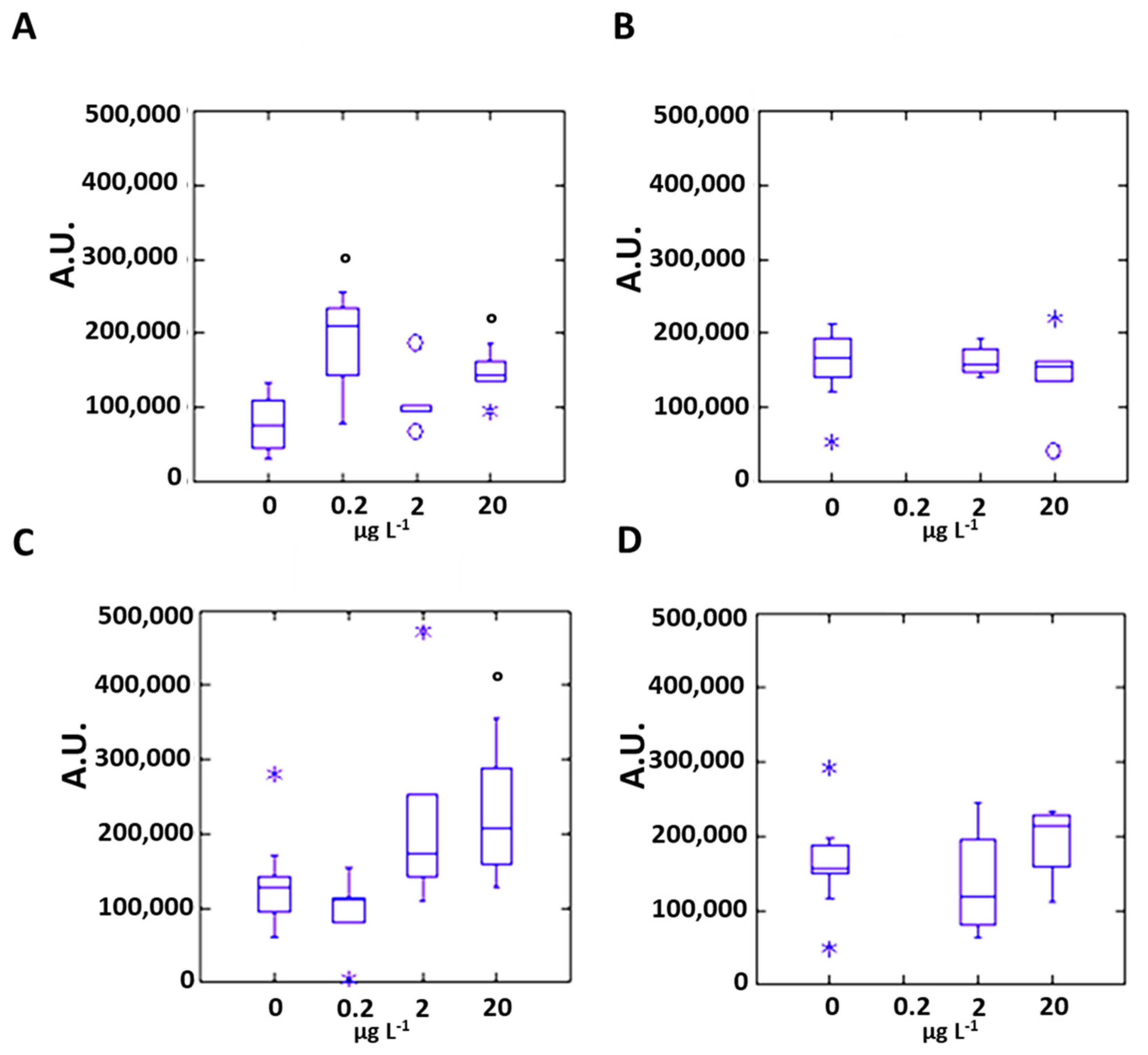
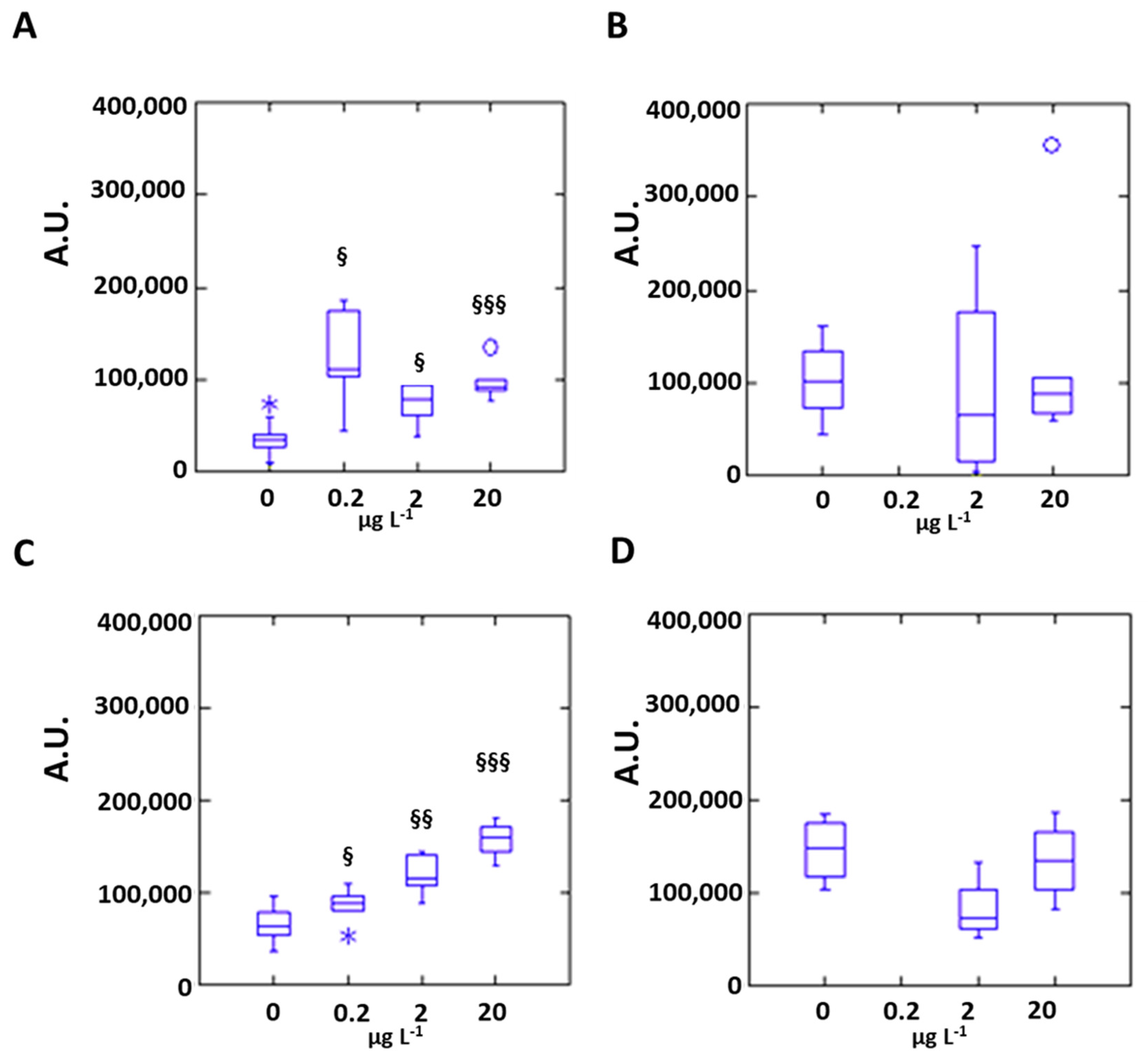
3.2. Silver Effects on Mussel Antioxidant System
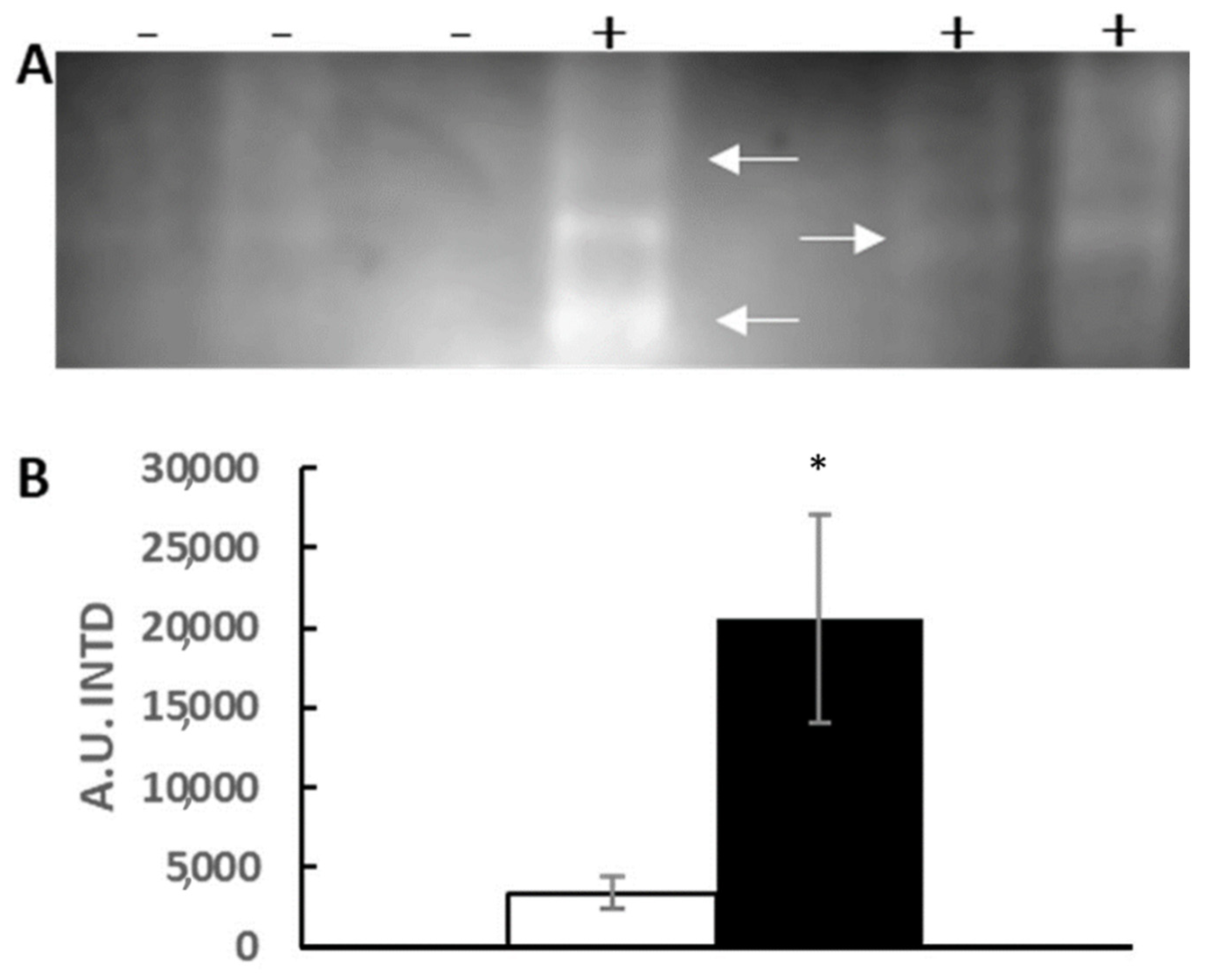
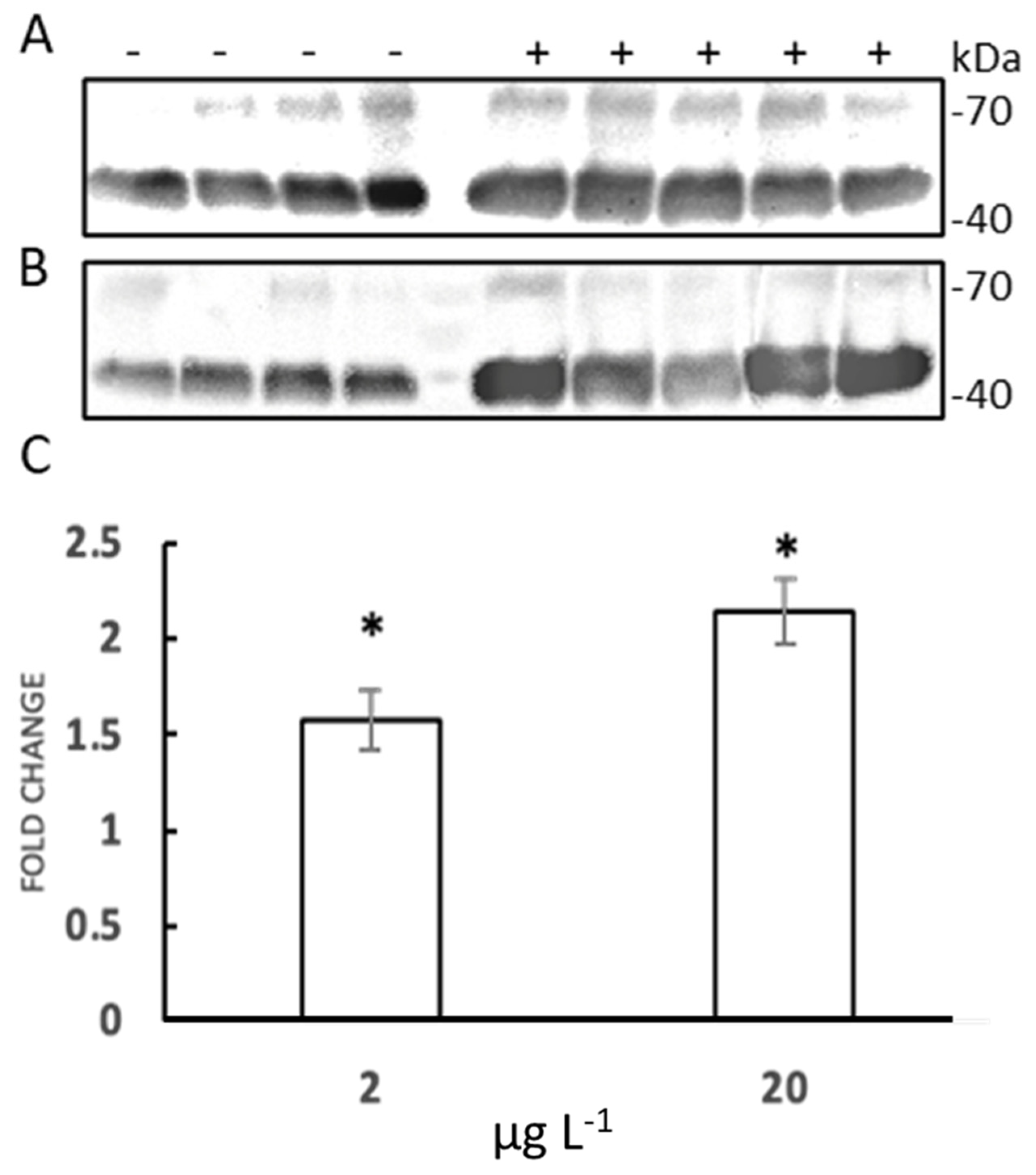
3.3. HSP70 Identification with Western Blot Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maanan, M.; Saddik, M.; Maanan, M.; Chaibi, M.; Assobhei, O.; Zourarah, B. Environmental and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Nador lagoon, Morocco. Ecol. Indic. 2005, 48, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Zrelli, R.; Rabaoui, L.; Alaya, M.B.; Daghbouj, N.; Castet, S.; Besson, P.; Michel, S.; Bejaoui, N.; Courjault-Radé, P. Seawater quality assessment and identification of pollution sources along the central area of Gabes Gulf (SE Tunisia): Evidence of industrial impact and implication for marine environment protection. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dondero, F.; Calisi, A. Evaluation of Pollution Effects in Marine Organisms: “Old” and “New Generation” Biomarkers. In Coastal Ecosystems: Experiences and Recommendations for Environmental Monitoring Programs; Sebastià, M.T., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 143–192. [Google Scholar]
- Villarubia-Gómez, P.; Cornell, S.; Fabres, J. Marine plastic pollultion as a planetary boundary threat—The drifting piece in the sustainability puzzle. Mar. Policy 2018, 96, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.M.; Ledet, J.; Crowe, T.P.; Johnstone, E.L. Sublethal effects of contaminants on marine habitat-forming species: A review and meta-analysis. Biol. Rev. Cambrigde Philos. 2020, 95, 1554–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Stegeman, J.J.; Fleming, L.E.; Allemand, D.; Anderson, D.M.; Backer, L.C.; Brucker-Davis, F.; Chevalier, N.; Corra, L.; Czerucka, D.; et al. Human Health and Ocean Pollution. Ann. Glob. Health 2020, 86, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsi, I.; Cherr, G.N.; Lenihan, H.S.; Labille, J.; Hassellov, M.; Canesi, L.; Dondero, F.; Frenzilli, G.; Hristozov, D.; Puntes, V.; et al. Common strategies and technologies for ecosafety assesment and design of nanomaterials. Entering. The marine environment. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 9694–9709. [Google Scholar]
- Ale, A.; Rossi, A.S.; Bacchetta, C.; Gervasio, S.; de la Torre, F.R.; Cazenave, J. Integrative assessment of silver nanoparticles toxicity in Prochilodus lineatus fish. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ale, A.; Liberatori, G.; Vannuccini, M.L.; Bergami, E.; Ancora, S.; Mariotti, G.; Bianchi, N.; Galdopórpora, J.M.; Desimone, M.F.; Cazenave, J.; et al. Exposure to a nanosilver-enabled consumer product results in similar accumulation and toxicity of silver nanoparticles in the marine mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 211, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roma, J.; Matos, A.R.; Vinagre, C.; Duarte, B. Engineered metal nanoparticles in the marine environment: A review of the effects on marine fauna. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 161, 105110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmberg, C.; Dernis, H.; Miguet, C. Nanotechnology: An Overview Based on Indicators and Statistics; OECD Science, Technology and Industry Working Papers, No. 2009/07; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2009; p. 112. [Google Scholar]
- Braunschweig, J.; Bosch, J.; Meckenstock, R.U. Iron oxide nanoparticles in geomicrobiology: From biogeochemistry to bioremediation. New Biotechnol. 2013, 30, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofacker, A.F.; Voegelin, A.; Kaegi, R.; Weber, F.A.; Kretzschmar, R. Temperature-dependent formation of metallic copper and metal sulfide nanoparticles during flooding of a contaminated soil. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 103, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, J.C.; Hiemstra, T.; Koopmans, G.F. Assessing the Reactive Surface Area of Soils and the Association of Soil Organic Carbon with Natural Oxide Nanoparticles Using Ferrihydrite as Proxy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 11990–12000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marambio-Jones, C.; Hoek, E.M.V. A rewiew of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 1531–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akmaz, S.; Adigüzel, E.D.; Yasar, M.; Erguven, O. The effect of Ag content of the Chitosan-silver nanoparticle composite material on the structure and antibacterial activity. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Ouay, B.; Stellacci, F. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: A surface science insight. Nano Today 2015, 10, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slavin, Y.N.; Asnis, J.; Häfeli, U.O.; Bach, H. Metal nanoparticles: Understanding the mechanism behind antibacterial activity. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 15, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rineesh, N.R.; Neelakandan, M.S.; Sabu, T. Applications of Silver Nanoparticles for Medicinal Purpose. JSM Nanotechnol. Nanomed. 2018, 6, 1063. [Google Scholar]
- Krutyakov, Y.A.; Kudrinskiy, A.A.; Olenin, A.Y.; Lisichkin, G.V. Synthesis and properties of silver nanoparticles: Advances and prospects. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2008, 77, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesser, M.P. Oxidative stress in marine environments: Biochemistry and Physiological Ecology. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 2006, 68, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lushchak, V.I. Environmentally induced oxidative stress in acquatic animals. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 101, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, C.; Pool, E.; Somerset, V. Nanotoxicity in aquatic invertebrates. In Invertebrates—Experimental Models in Toxicity Screening; Larramendy, M.L., Soloneski, S., Eds.; Intech Open: London, UK, 2016; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Bouallegui, Y.; Younes, R.B.; Turki, F.; Oueslati, R. Impact of exposure time, particle size and uptake patway on silver nanoparticle effects on circulating immune cells in Mytilus galloprovincialis. J. Immunol. 2017, 14, 116–124. [Google Scholar]
- Birnie-Gauvin, K.; Costantini, D.; Cooke, S.J. A comparative and evolutionary approach toon oxidative stress in fish: A review. Fish Fish. 2017, 18, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.C.; Xu, Z.; Wu, H.-Y.; Liu, G.L.; Cunningham, B.T. Surface-enhanced Raman nanodomes. Nanotecnology 2010, 21, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, T.; Pereira, C.G.; Cardoso, C.; Sousa, V.S.; Teixeira, M.R.; Pinheiro, J.P.; Bebianno, M.J. Effect of silver nanoparticles exposure in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 101, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouallegui, Y.; Younes, R.B.; Oueslati, R.; Sheehan, D. Role of endocytotic uptake routes in impacting the ros-related toxicity of silver nanoparticles to Mytilus galloprovincialis: A redox proteomic investigation. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 200, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baun, A.; Hartmann, N.B.; Grieger, K. Ecotoxicology of engineered nanoparticles to aquatic invertebrates: A brief review and recommendations for future toxicity testing. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canesi, L.; Ciacci, C.; Fabbri, R.; Marcomini, A.; Pojana, G.; Gallo, G. Bivalve mollusks as a unique target group for nanoparticle toxicity. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 76, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, T.L.; Gomes, T.; Sousa, V.S.; Mestre, N.C.; Bebianno, M.J. Ecotoxicological impact of engineered nanomaterials in bivalve mollusks: An overview. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 111, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.N. Do nanoparticles present ecotoxicological risks for the health of aquatic environment? Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagnino, A.; Allen, J.I.; Moore, M.N.; Broeg, K.; Canesi, L.; Viarengo, A. Development of an expert system for the integration of biomarker responses in mussels into an animal health index. Biomarkers 2007, 12, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banni, M.; Dondero, F.; Jebali, J.; Guerbej, H.; Boussetta, H.; Viarengo, A. Assessment of heavy metal contamination using real-time PCR analysis of mussel metallothionein mt10 and mt20 expression: A validation along the Tunisian coast. Biomarkers 2006, 12, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taze, C.; Panetas, I.; Kalogiannis, S.; Feidantsis, K.; Gallios, G.P.; Kastrinaki, G.; Konstandopoulos, A.G.; Václavíková, M.; Ivanicova, L.; Kaloyianni, M. Toxicity assessment and comparison between two type of iron oxide nanoparticles in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 172, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, J.; Green, N.W.; Brooks, S.; Allan, I.J.; Andres, R.; Gomes, T.; Bråte, I.L.N.; Schøyen, M. Blue mussel (Mytilus edulis spp.) as sentinel organisms in coastal pollution monitoring: A review. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 130, 338–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, G.; Akodad, M.; Baghour, M.; Layachi, M.; Moumen, A. The use of Mytilus spp. Mussels as bioindicators of heavy metal pollution in the coastal environment. A review. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2018, 9, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, F.; Gallego-Urrea, J.A.; Jurkschat, K.; Loureiro, S. Silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate induce high toxicity to Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata, Daphnia magna and Danio rerio. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466–467, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calisi, A.; Lorusso, C.; Gallego-Urrea, J.A.; Hasselov, M.; Dondero, F. Ecotoxicological effects of silver nanoparticles in marine mussels. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodbury, W.; Spencer, A.K.; Stahman, M.A. An improved procedure using ferricyanide for detecting catalase isozymes. Anal. Biochem. 1971, 44, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, C.; Fridovich, I. Superoxide Dismutase: Improved Assays and an Assay Applicable to Acrylamide Gels. Anal. Biochem. 1971, 44, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-L.; Chen, H.-J.; Hou, W.-C. Activity staining of glutathione peroxidase after electrophoresis on native and sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrilamide gels. Electrophoresis 2002, 23, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weydert, C.J.; Cullen, J.J. Measurement of superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase in cultured cells and tissue. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Livingstone, D.R.; Lips, F.; Martinez, P.G.; Pipe, R.K. Antioxidant enzymes in the digestive gland of the common mussel Mytilus edulis. Mar. Biol. 1992, 112, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.J. Disc electrophoresis. II. Method and application to human serum proteins. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1964, 121, 404–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornstein, L. Disc Electrophoresis. I. Background and Theory. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1964, 121, 321–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoma, S.N. Silver Nanotechnologies and the Environment: Old Problems or New Challenges? Project on Emerging Nanotechnologies; Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- Benn, T.M.; Westerhoff, P. Nanoparticle silver released into water from commercially available sock fabrics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4133–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toncelli, C.; Mylona, K.; Kalantzi, I.; Tsiola, A.; Pitta, P.; Tsapakis, M.; Pergantis, S.A. Silver nanoparticles in seawater: A dynamic mass balance at part per trillion silver concentrations. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondikas, A.; Gallego-Urrea, J.; Halbach, M.; Derrien, N.; Hassellöv, M. Nanomaterial fate in seawater: A rapid sink or intermittent stabilization? Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoma, S.N.; Ho, Y.B.; Bryan, G. Fate, bioavailability and toxicity of silver in estuarine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1995, 31, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukadida, K.; Cachot, J.; Clérandeaux, C.; Gourves, P.Y. Early and efficient induction of antioxidant defense system in Mytilus galloprovincialis embryos exposed to metal and heat stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 138, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffet, P.E.; Pan, J.F.; Poirier, L.; Amiard-Triquet, C.; Amiard, J.C.; Gaudin, P.; Risso-de Faverney, C.; Guibbolini, M.; Gilliland, D.; Valsami-Jones, E.; et al. Biochemical and behavioural responses of the endobenthic bivalve Scrobicularia plana to silver nanoparticles in seawater and microalgal food. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 89, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, G.; Somero, G. Evidence for protein damage at environmental temperatures: Seasonal changes in levels of ubiquitin conjugates and hsp70 in the intertidal mussel Mytilus trossulus. J. Exp. Biol. 1995, 198, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grösvik, B.E.; Goksöyr, A. Biomarker protein expression in primary cultures of salmon (Salmo salar L.) hepatocytes exposed to environmental pollutants. Biomarkers 1996, 1, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minier, C.; Borghi, V.; Moore, M.N.; Porte, C. Seasonal variation of MXR and stress proteins in the common mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2000, 50, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lorusso, C.; Calisi, A.; Sarà, G.; Dondero, F. In-Gel Assay to Evaluate Antioxidant Enzyme Response to Silver Nitrate and Silver Nanoparticles in Marine Bivalve Tissues. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12062760
Lorusso C, Calisi A, Sarà G, Dondero F. In-Gel Assay to Evaluate Antioxidant Enzyme Response to Silver Nitrate and Silver Nanoparticles in Marine Bivalve Tissues. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(6):2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12062760
Chicago/Turabian StyleLorusso, Candida, Antonio Calisi, Gianluca Sarà, and Francesco Dondero. 2022. "In-Gel Assay to Evaluate Antioxidant Enzyme Response to Silver Nitrate and Silver Nanoparticles in Marine Bivalve Tissues" Applied Sciences 12, no. 6: 2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12062760
APA StyleLorusso, C., Calisi, A., Sarà, G., & Dondero, F. (2022). In-Gel Assay to Evaluate Antioxidant Enzyme Response to Silver Nitrate and Silver Nanoparticles in Marine Bivalve Tissues. Applied Sciences, 12(6), 2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12062760