A Direct-Current Triboelectric Nanogenerator Energy Harvesting System Based on Water Electrification for Self-Powered Electronics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
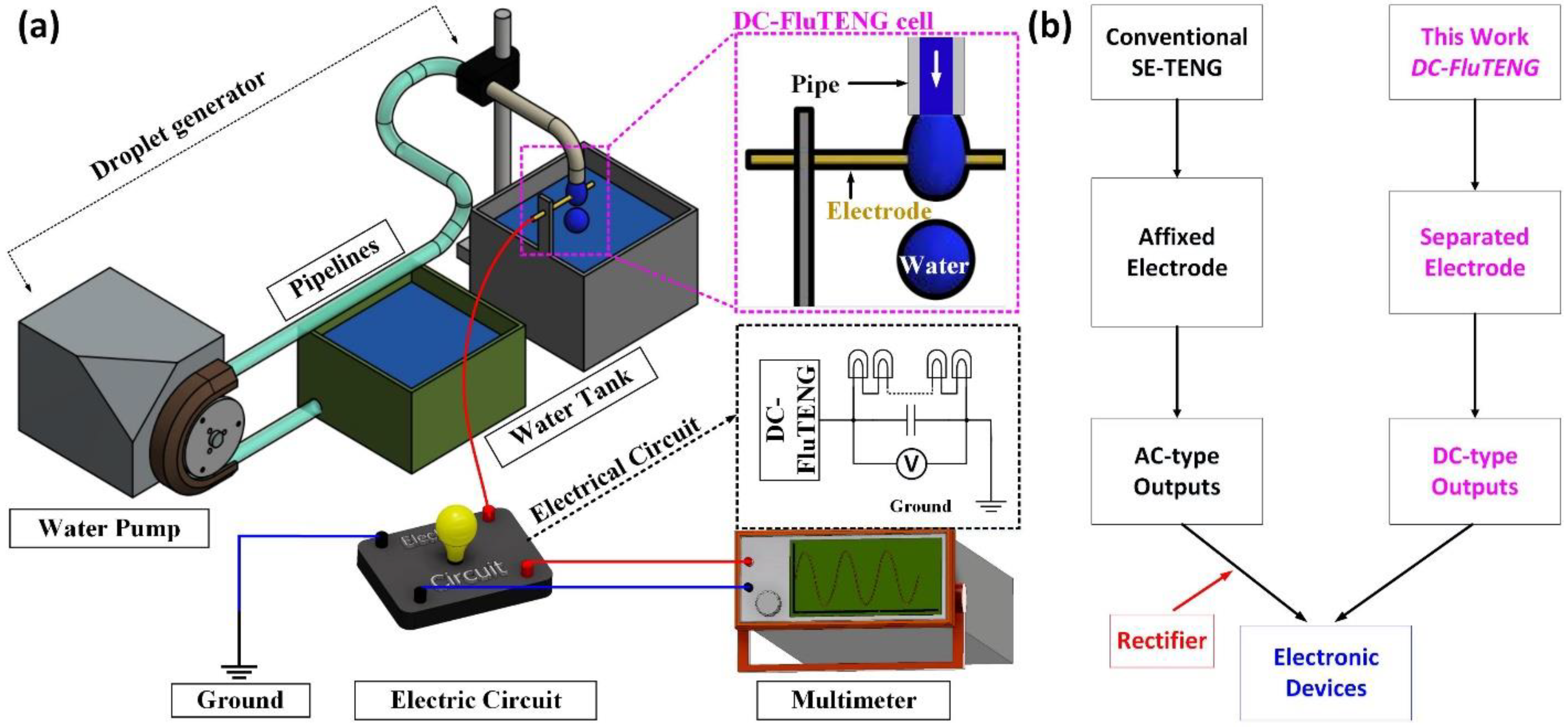
2.1. Experimental Installation and Process
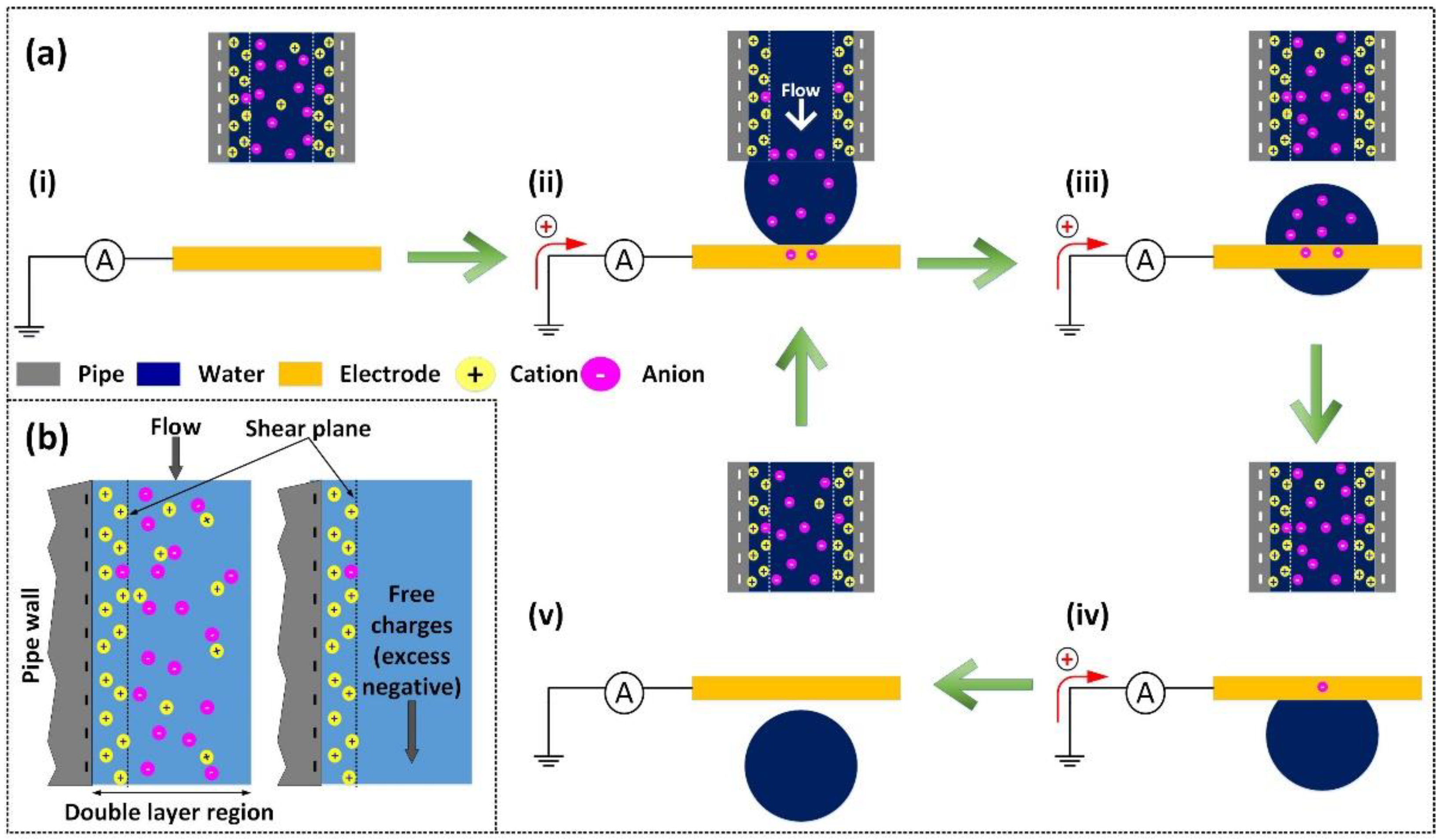
2.2. Working Principle of DC–FluTENG
3. Results and Discussion
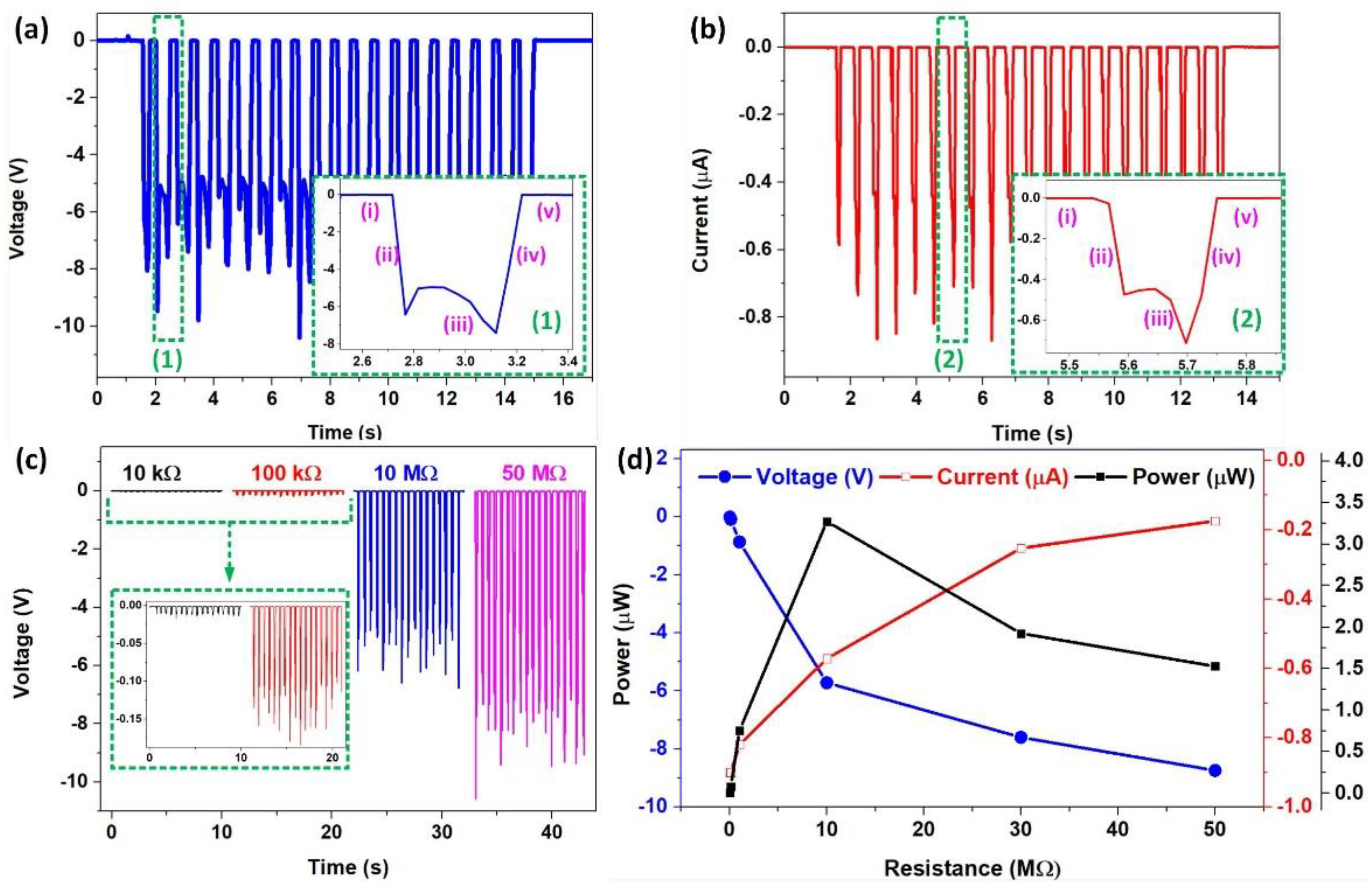
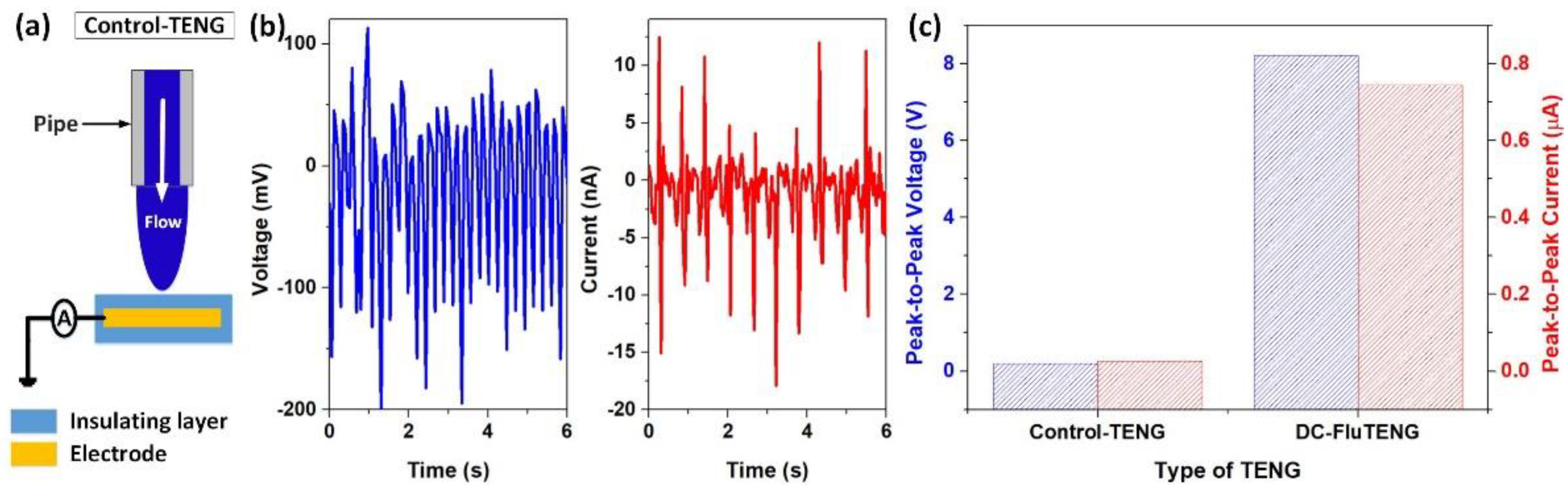
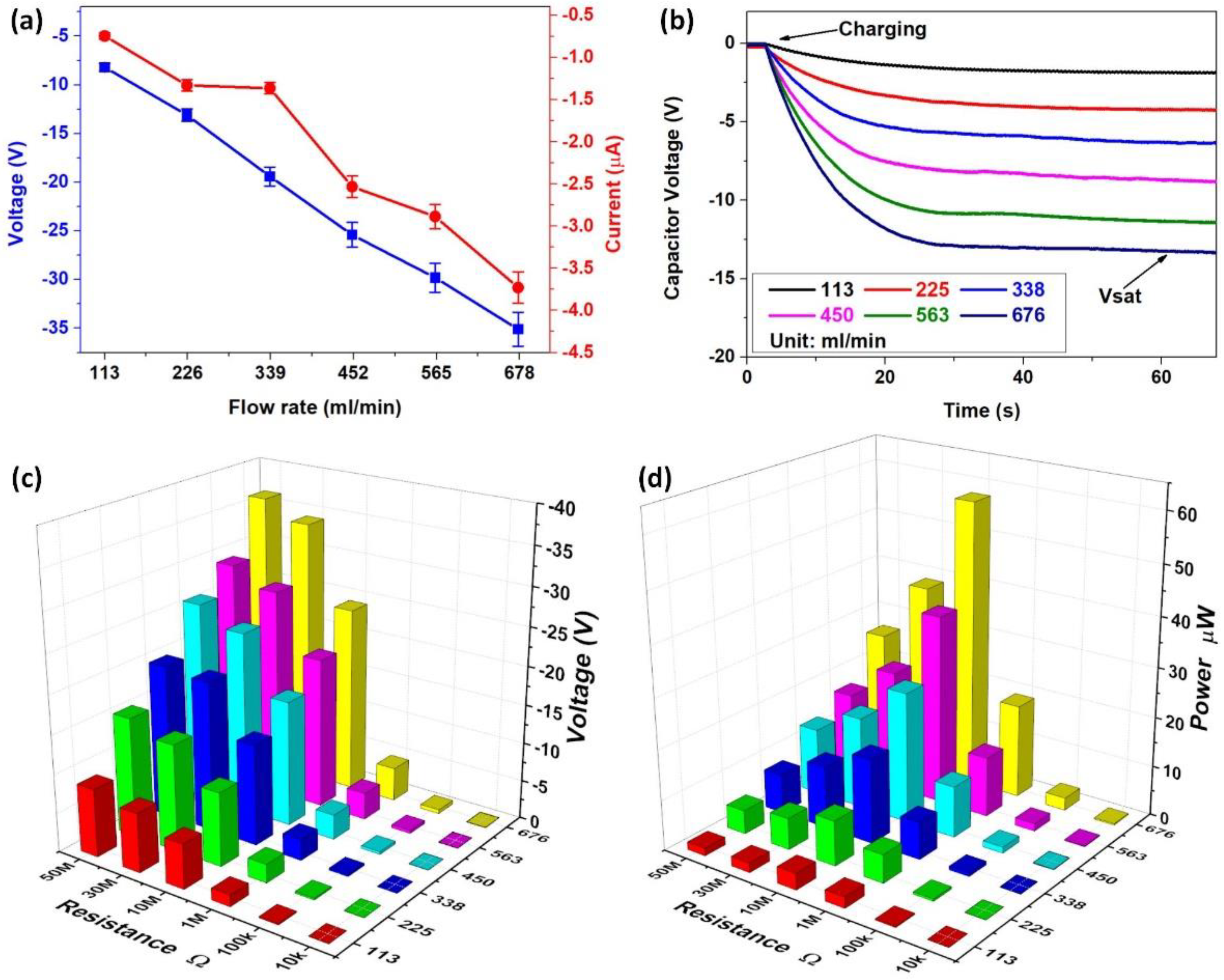
3.1. Electricity Generation of DC–FluTENG
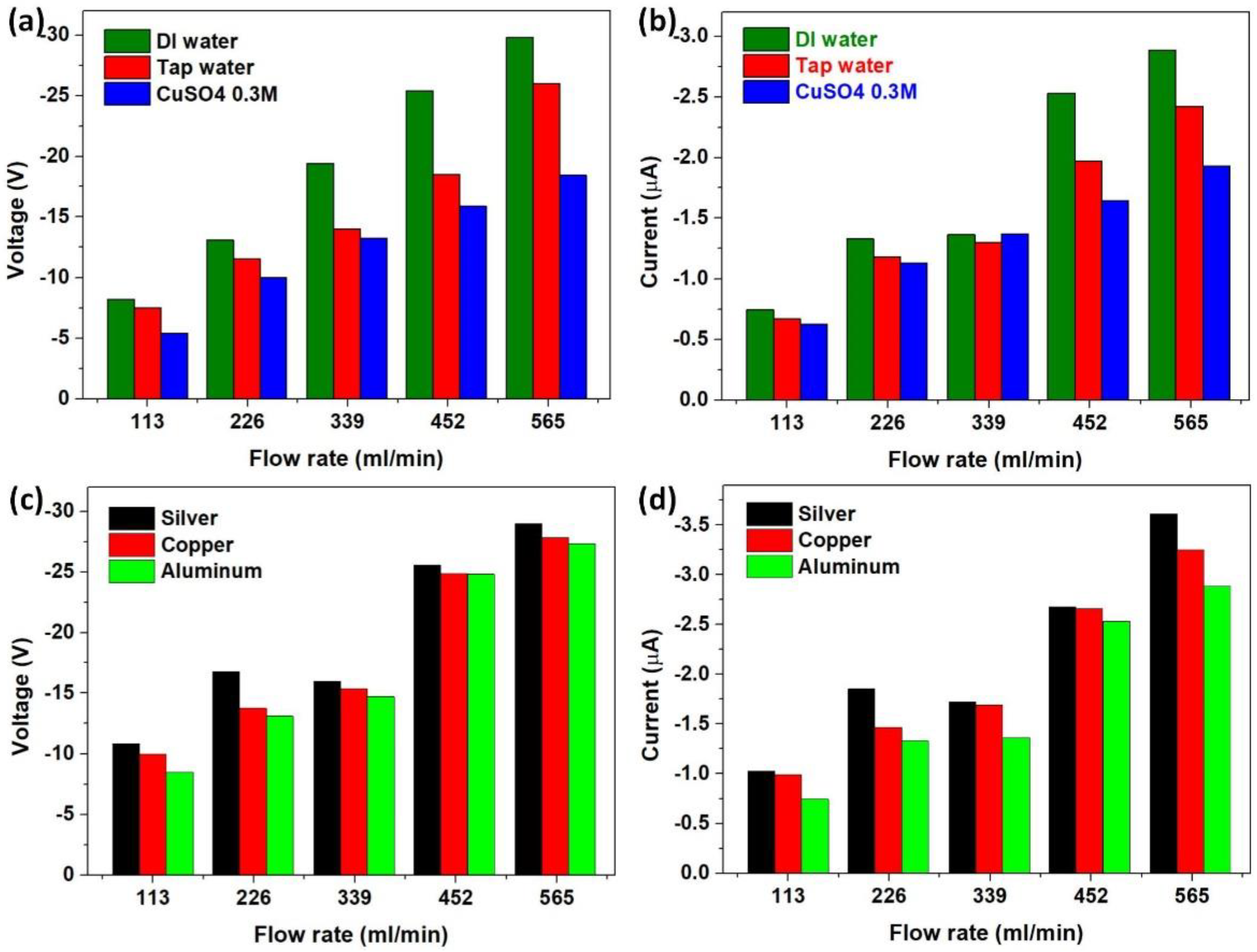
3.2. Factors Affecting the Output Performance
3.3. Application of DC–FluTENG
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raj, A.; Steingart, D. Review—Power Sources for the Internet of Things. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, B3130–B3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Wang, A.C. On the origin of contact-electrification. Mater. Today 2019, 30, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.L.; Yang, Y. Efficient Scavenging of Solar and Wind Energies in a Smart City. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 5696–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Hybridized Electromagnetic–Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Scavenging Biomechanical Energy for Sustainably Powering Wearable Electronics. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3521–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Zhong, Q.; Fan, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Hu, B.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhou, J. Finger typing driven triboelectric nanogenerator and its use for instantaneously lighting up LEDs. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liang, Q.; Liao, Q.; Ma, M.; Gao, F.; Zhao, X.; Song, Y.; Song, L.; Xun, X.; Zhang, Y. An Amphiphobic Hydraulic Triboelectric Nanogenerator for a Self-Cleaning and Self-Charging Power System. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1803117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, T.; Tang, W.; Han, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.L. Rotating-Disk-Based Direct-Current Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1301798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Pan, L.; Gao, R.; Zhang, B.; Yang, L.; Guo, H.; Liao, R.; Wang, Z.L. Direct-Current Rotary-Tubular Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Liquid-Dielectrics Contact for Sustainable Energy Harvesting and Chemical Composition Analysis. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 2587–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Jiang, T.; Liu, G.; Xiao, T.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Xi, F.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Networks Integrated with Power Management Module for Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Y. Effective energy storage from a hybridized electromagnetic-triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2017, 32, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wang, Z.L.; Yang, Y. Self-Powered Wireless Smart Sensor Node Enabled by an Ultrastable, Highly Efficient, and Superhydrophobic-Surface-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 9044–9052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, J. Triboelectric nanogenerator: From alternating current to direct current. iScience 2021, 24, 102018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.L. Direct-Current Triboelectric Generator. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3745–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Lee, J.H.; Khan, U.; Kwak, S.S.; Hinchet, R.; Kim, S.-W. Sustainable direct current powering a triboelectric nanogenerator via a novel asymmetrical design. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 2057–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Kim, D.Y.; Yun, J.; Kim, B.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, D.; Lee, S. Direct-current triboelectric nanogenerator via water electrification and phase control. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.-T.; Ahn, K.-K.K. Fluid-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators: A Review of Current Status and Applications. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2020, 8, 1043–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Xu, M.; Dong, M.; Guo, F.; Liu, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z.L. Water-solid triboelectric nanogenerators: An alternative means for harvesting hydropower. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 115, 109366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Burman, S.R.; Khan, I.; Saha, S.; Choi, D.; Lee, S.; Lin, Z.H. Recent advancements in solid-liquid triboelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting and self-powered applications. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 17663–17697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.; Park, S.-C.; Lee, S.; Sim, J.-Y.; Song, I.; Choi, D.; Lim, H.; Kim, D.S. Biomimetic anti-reflective triboelectric nanogenerator for concurrent harvesting of solar and raindrop energies. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helseth, L.E. Electrical energy harvesting from water droplets passing a hydrophobic polymer with a metal film on its back side. J. Electrost. 2016, 81, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.H.; Cheng, G.; Lee, S.; Pradel, K.C.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting water drop energy by a sequential contact-electrification and electrostatic-induction process. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4690–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stetten, A.Z.; Golovko, D.S.; Weber, S.A.L.; Butt, H.J. Slide electrification: Charging of surfaces by moving water drops. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 8667–8679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheedarala, R.K.; Shahriar, M.; Ahn, J.H.; Hwang, J.Y.; Ahn, K.K. Harvesting liquid stream energy from unsteady peristaltic flow induced pulsatile Flow-TENG (PF-TENG) using slipping polymeric surface inside elastomeric tubing. Nano Energy 2019, 65, 104017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Lin, Z.H.; Du, Z.L.; Wang, Z.L. Simultaneously Harvesting Electrostatic and Mechanical Energies from Flowing Water by a Hybridized Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 1932–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhang, H.; Cao, S.; Yuan, Z.; Ding, J.; Sang, S. Tube-based triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered detecting blockage and monitoring air pressure. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Pan, C.; Wang, Z.L. Networks of High Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Liquid–Solid Interface Contact Electrification for Harvesting Low-Frequency Blue Energy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.J.; Kuang, S.Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhu, G. Highly Adaptive Solid-Liquid Interfacing Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Diverse Water Wave Energy. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 4280–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.L.; Ding, W.; Kien, P.T.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Pan, X.; Wang, Z.L. A highly-sensitive wave sensor based on liquid-solid interfacing triboelectric nanogenerator for smart marine equipment. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Wang, Z.; Ren, Z.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Lin Wang, Z. Power generation from the interaction of a liquid droplet and a liquid membrane. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Xu, H.; Xu, B.; Li, D. Electric current generation of a droplet falling into an electrolyte solution. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 212, 112791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zheng, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.; Song, Y.; Deng, X.; Leung, M.; Yang, Z.; Xu, R.X.; et al. A droplet-based electricity generator with high instantaneous power density. Nature 2020, 578, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Gu, H.; Lu, K.; Ye, S.; Xu, W.; Zheng, H.; Song, Y.; Liu, C.; Jiao, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. A universal single electrode droplet-based electricity generator (SE-DEG) for water kinetic energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2021, 82, 105735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.-H.; Yu, J.-K.; Sheng, M.-K.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Yang, X. Influence Factors of the Generation and Accumulation of Electric Charge on the Oil-Delivery Metal Pipelines. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2017, 30, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Yu, J.; Sheng, M.; Yang, X. Influencing factors to the friction charging in water delivery metal pipeline. J. Electrost. 2016, 82, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hwang, J.Y.; Ahn, K.K. DC power harvesting system using streaming electrification and an opposite charge extractor. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, G.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Lee, G.H.; Vo, C.P.; Ahn, K.K. A New Pathway for Liquid–Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerator Using Streaming Flow by a Novel Direct Charge Transfer. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2020, 1, 2000031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, J.; Fan, Q.; Perez-Martinez, L.; Cuesta, A.; Cheng, J. Theoretical insight into the vibrational spectra of metal-water interfaces from density functional theory based molecular dynamics. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 11554–11558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Contact Electrification at the Liquid-Solid Interface. Chem. Rev. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauruzbayeva, J.; Sun, Z.; Gallo, A.; Ibrahim, M.; Santamarina, J.C.; Mishra, H. Electrification at water-hydrophobe interfaces. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Yang, J.; Kwok, D.Y. Flow Field Effect on Electric Double Layer during Streaming Potential Measurements. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 14970–14975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamee, C.E. Effect of a liquid flow on the forces between charged solid surfaces and the non-equilibrium electric double layer. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 266, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.L.; Li, D. Improved understanding of the effect of electrical double layer on pressure-driven flow in microchannels. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 531, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, N.; Liu, J.; Wen, Z.; Sun, X.; Lee, S.T.; Sun, B. Integrating a Silicon Solar Cell with a Triboelectric Nanogenerator via a Mutual Electrode for Harvesting Energy from Sunlight and Raindrops. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 2893–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Yan, X.; Liao, X.; Zhang, Y. Integrated multi-unit transparent triboelectric nanogenerator harvesting rain power for driving electronics. Nano Energy 2016, 25, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Lin, Z.H.; Cheng, G.; Wu, W.; Wen, X.; Lee, S.; Wang, Z.L. Silicon-based hybrid cell for harvesting solar energy and raindrop electrostatic energy. Nano Energy 2014, 9, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, Q.T.; Vo, C.P.; Nguyen, T.H.; Ahn, K.K. A Direct-Current Triboelectric Nanogenerator Energy Harvesting System Based on Water Electrification for Self-Powered Electronics. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052724
Nguyen QT, Vo CP, Nguyen TH, Ahn KK. A Direct-Current Triboelectric Nanogenerator Energy Harvesting System Based on Water Electrification for Self-Powered Electronics. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(5):2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052724
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Quang Tan, Cong Phat Vo, Thanh Ha Nguyen, and Kyoung Kwan Ahn. 2022. "A Direct-Current Triboelectric Nanogenerator Energy Harvesting System Based on Water Electrification for Self-Powered Electronics" Applied Sciences 12, no. 5: 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052724
APA StyleNguyen, Q. T., Vo, C. P., Nguyen, T. H., & Ahn, K. K. (2022). A Direct-Current Triboelectric Nanogenerator Energy Harvesting System Based on Water Electrification for Self-Powered Electronics. Applied Sciences, 12(5), 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052724









