Estimating Significant Wave Height from SAR with Long Integration Times
Abstract
:1. Introduction
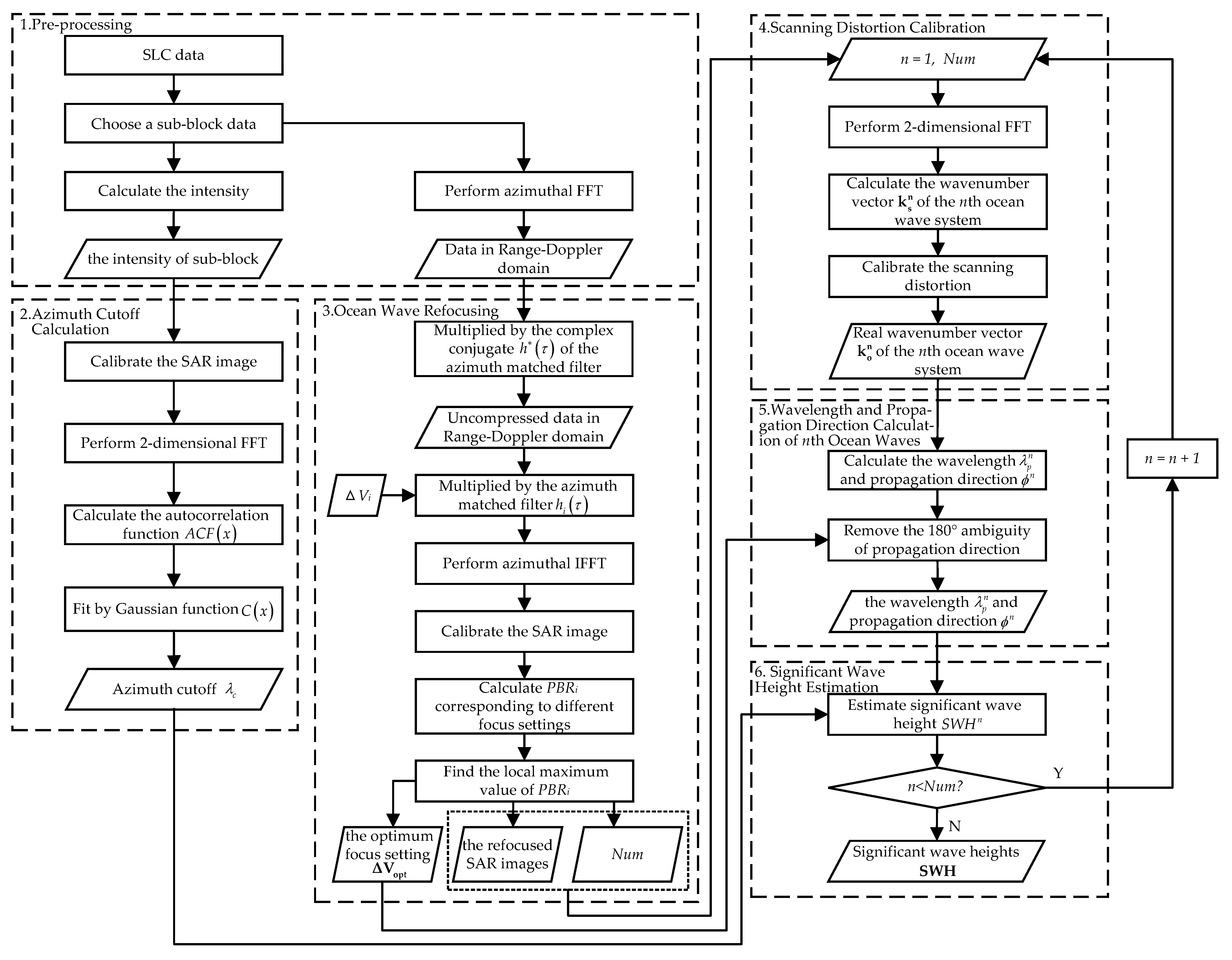
2. Estimating Significant Wave Height from SAR with Long Integration Times
2.1. Pre-Processing
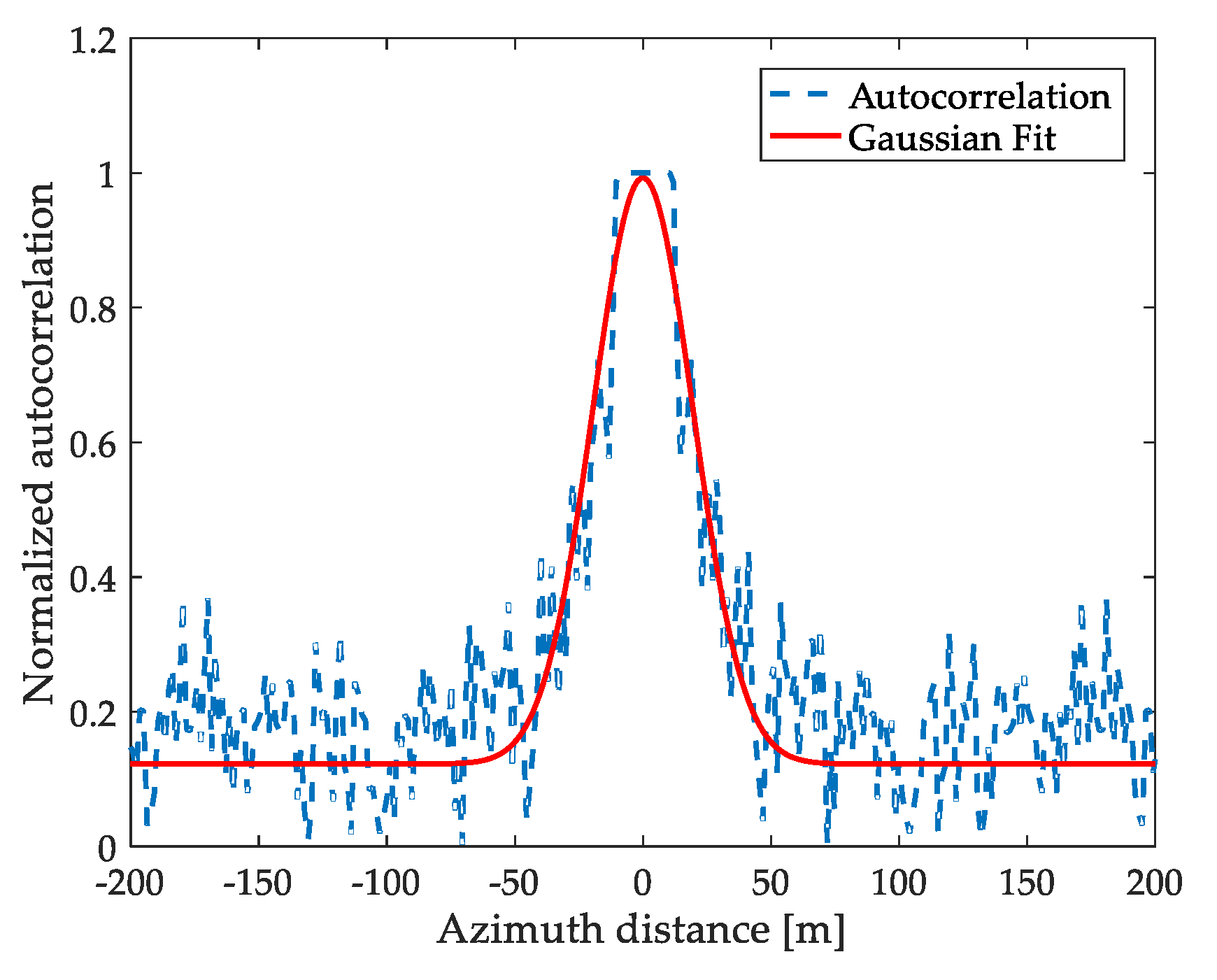
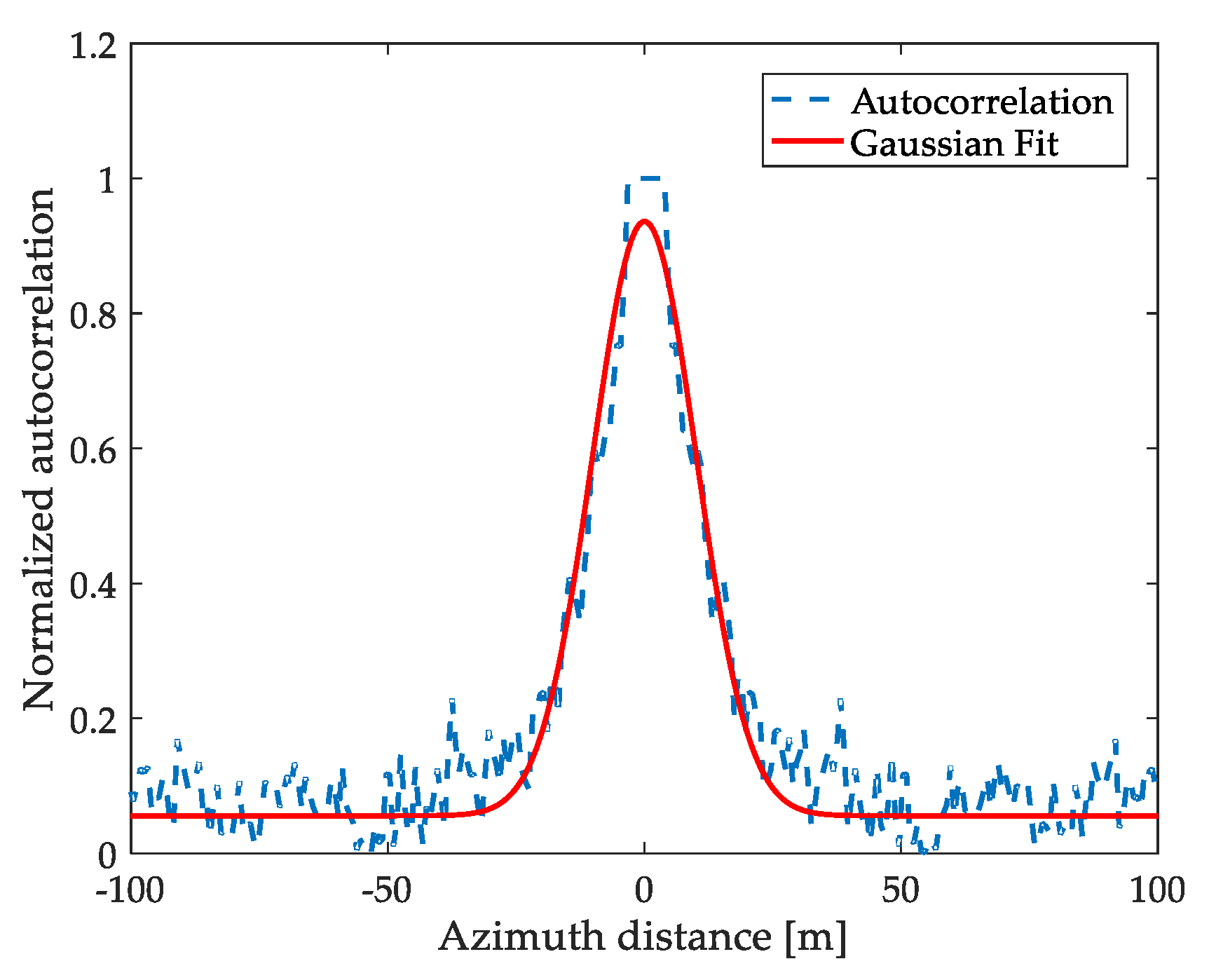
2.2. Azimuth Cutoff Calculation
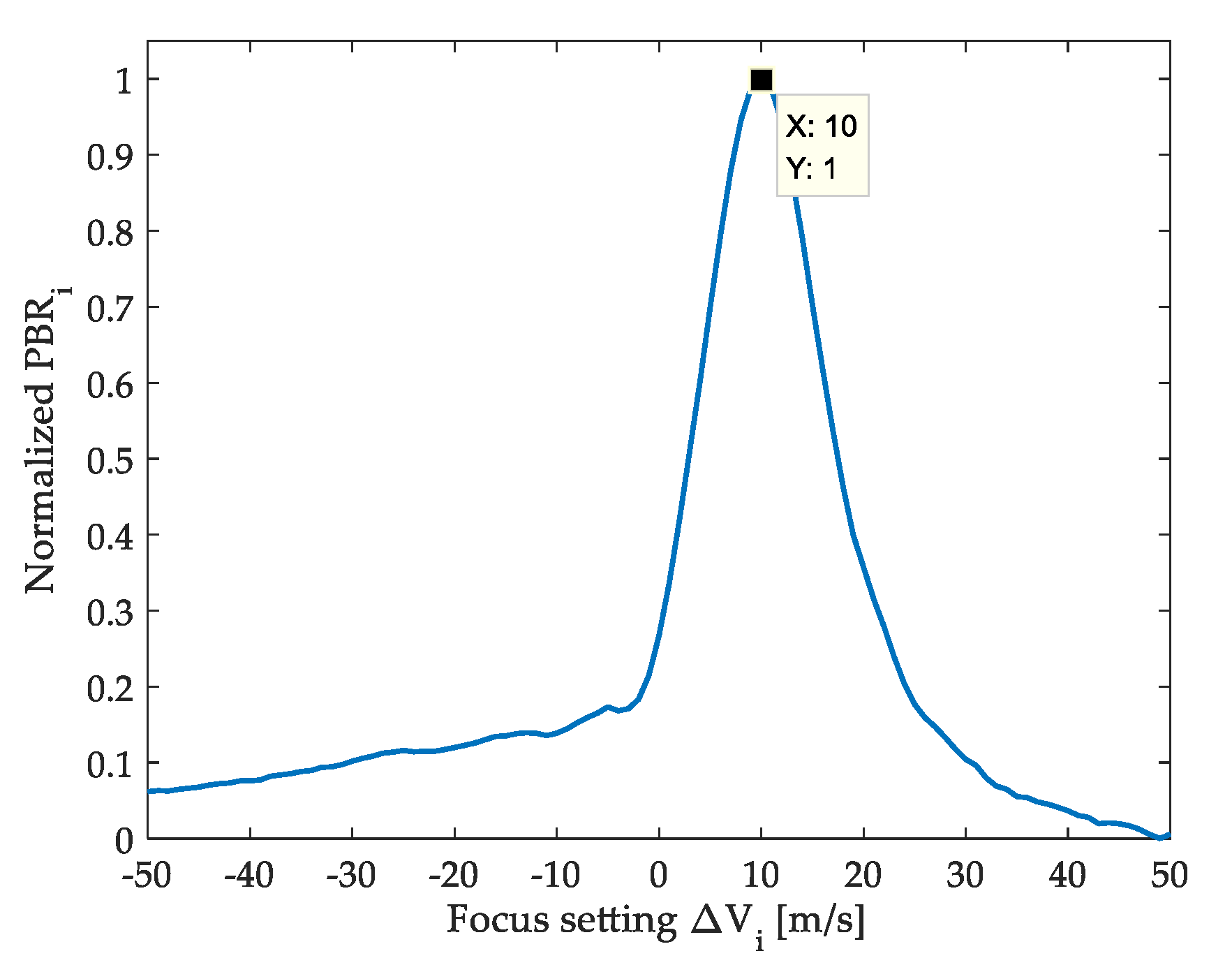
2.3. Ocean Wave Refocusing
2.4. Scanning Distortion Calibration
2.5. Wavelength and Propagation Direction Calculation of nth Ocean Waves
2.5.1. Wavelength Calculation of nth Ocean Wave
2.5.2. Propagation Direction Calculation of nth Ocean Wave
2.5.3. 180° Ambiguity Removal of Wave Propagation Direction
2.6. Significant Wave Height Estimation
3. Experiments of Estimating Significant Wave Height from SAR with Long Integration Times
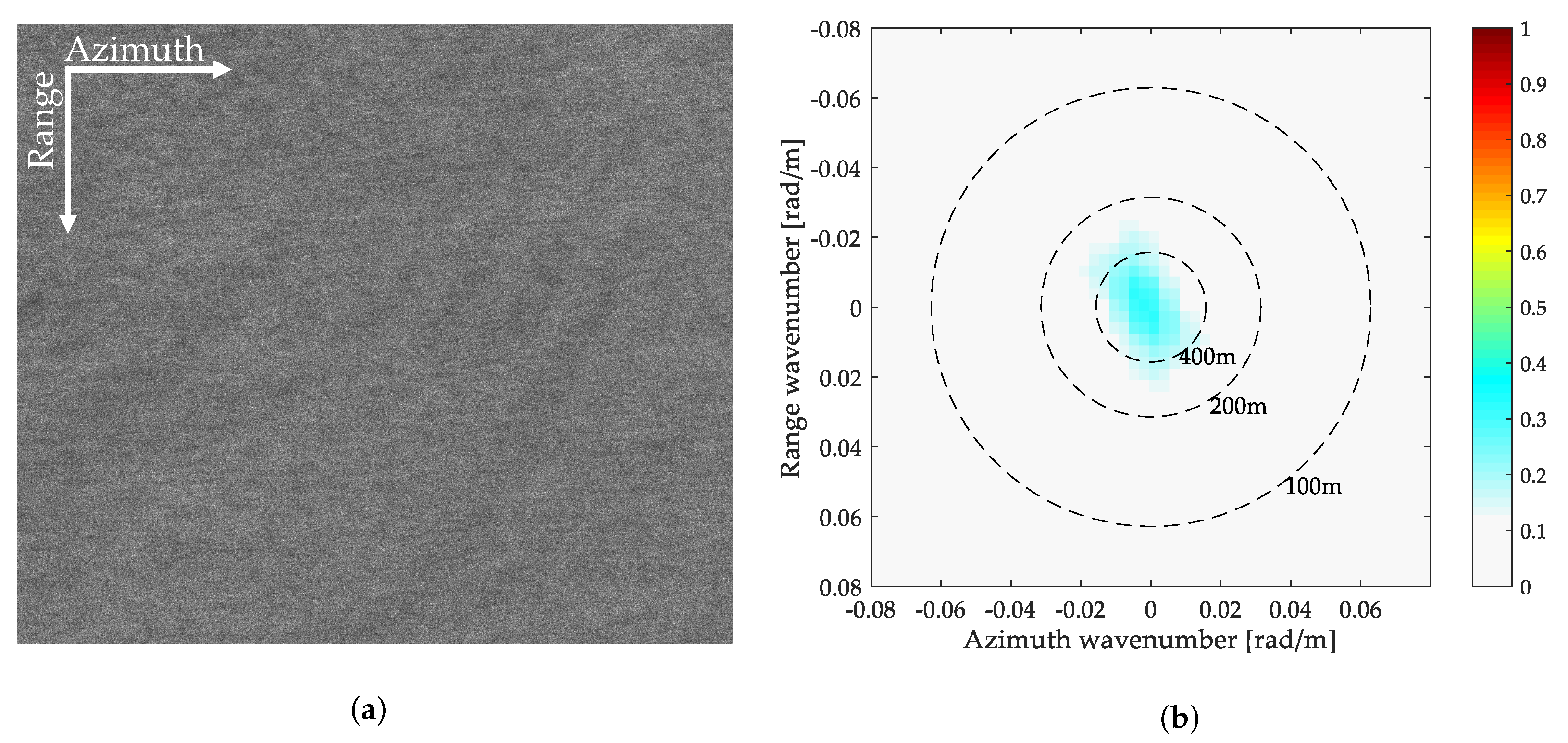
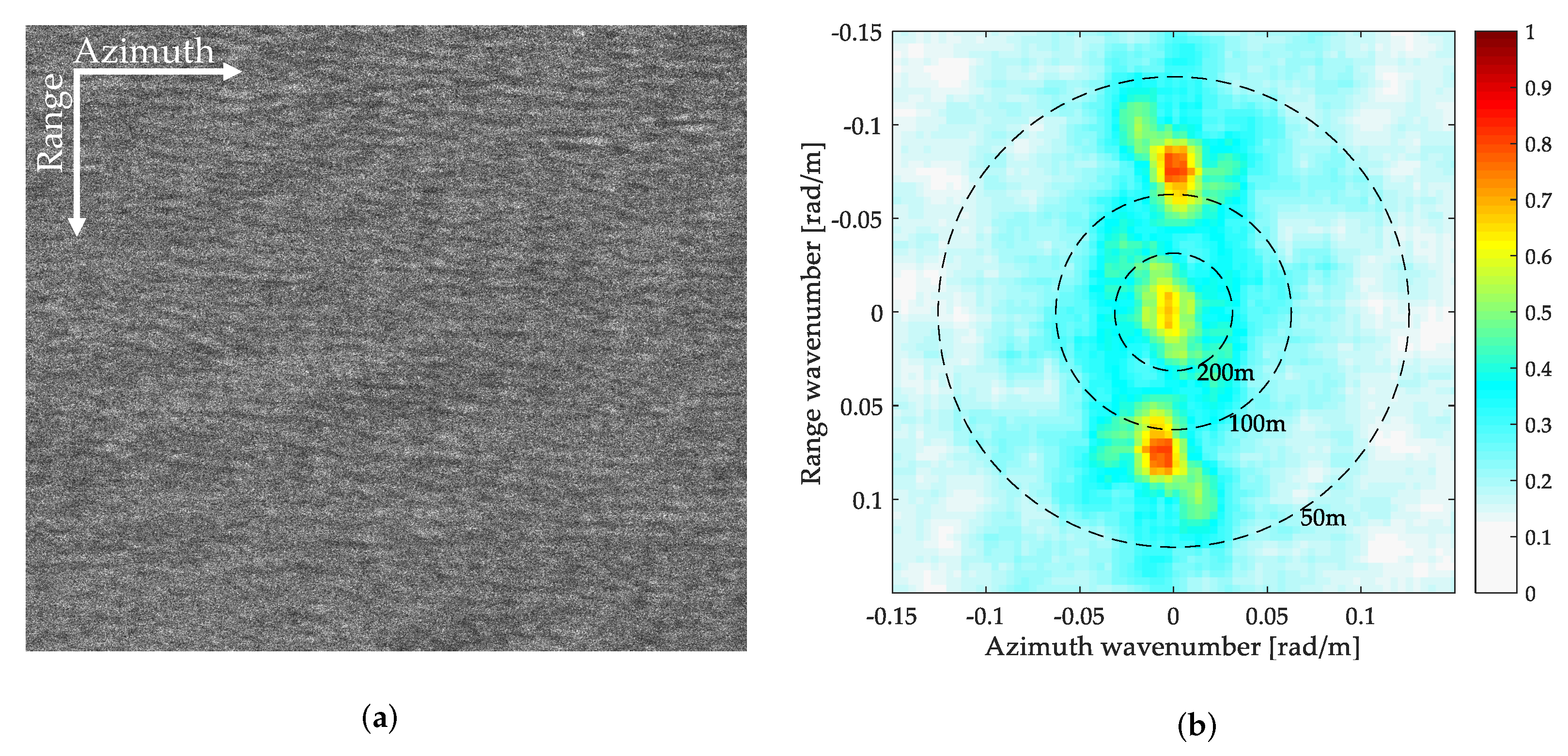
3.1. Case 1-Invisible Ocean Waves from SAR with Long Integration Times
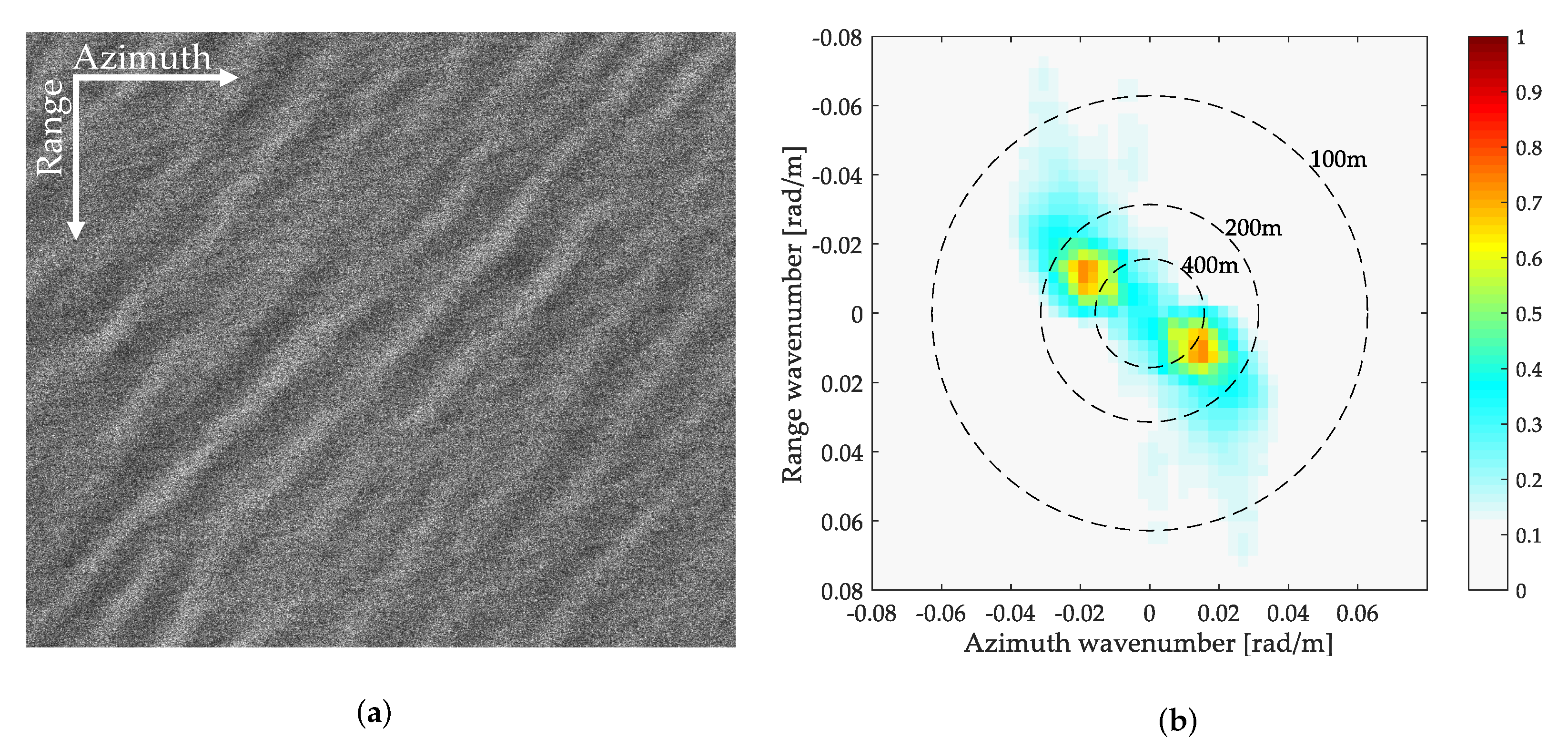
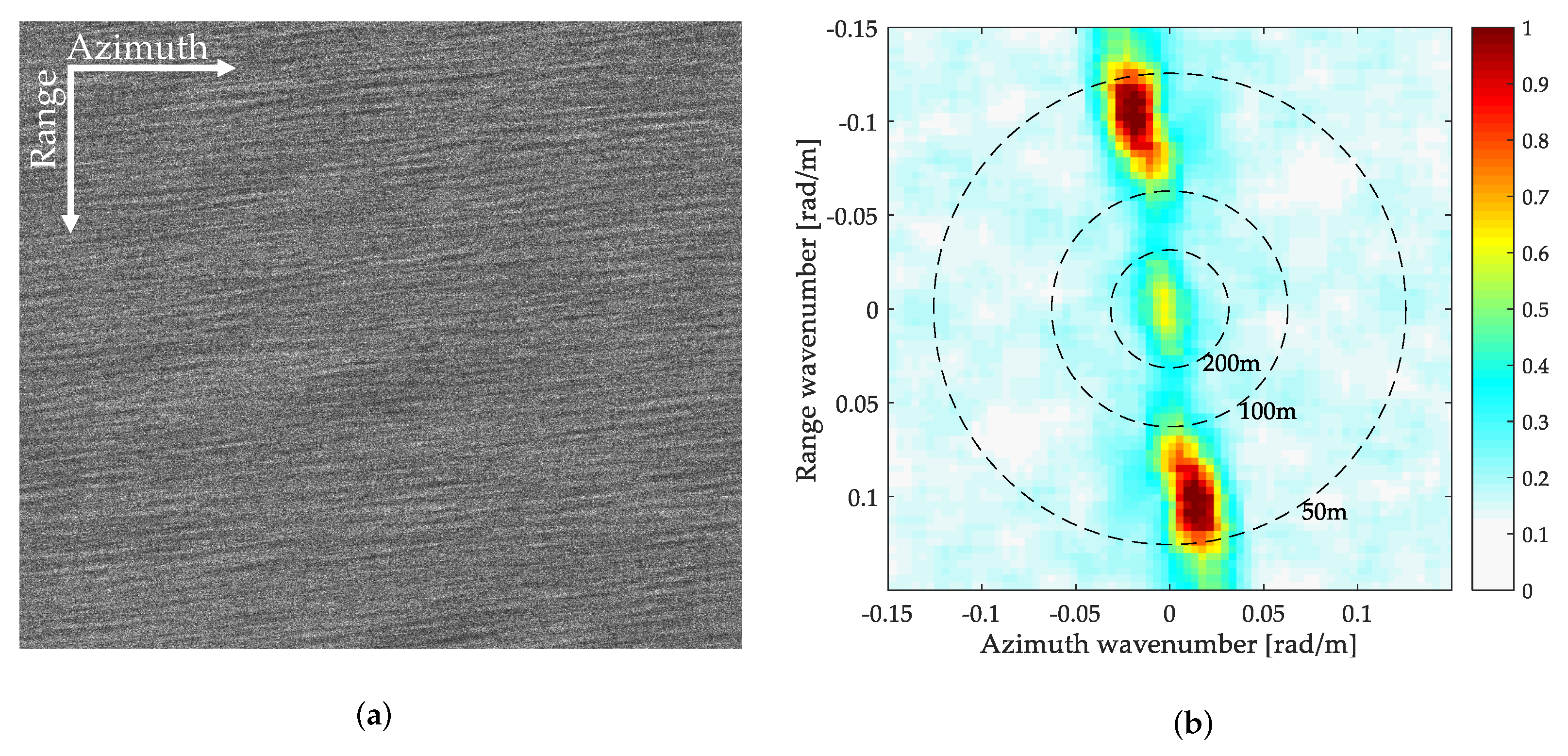
3.2. Case 2-Multiple Ocean Waves from SAR with Long Integration Times
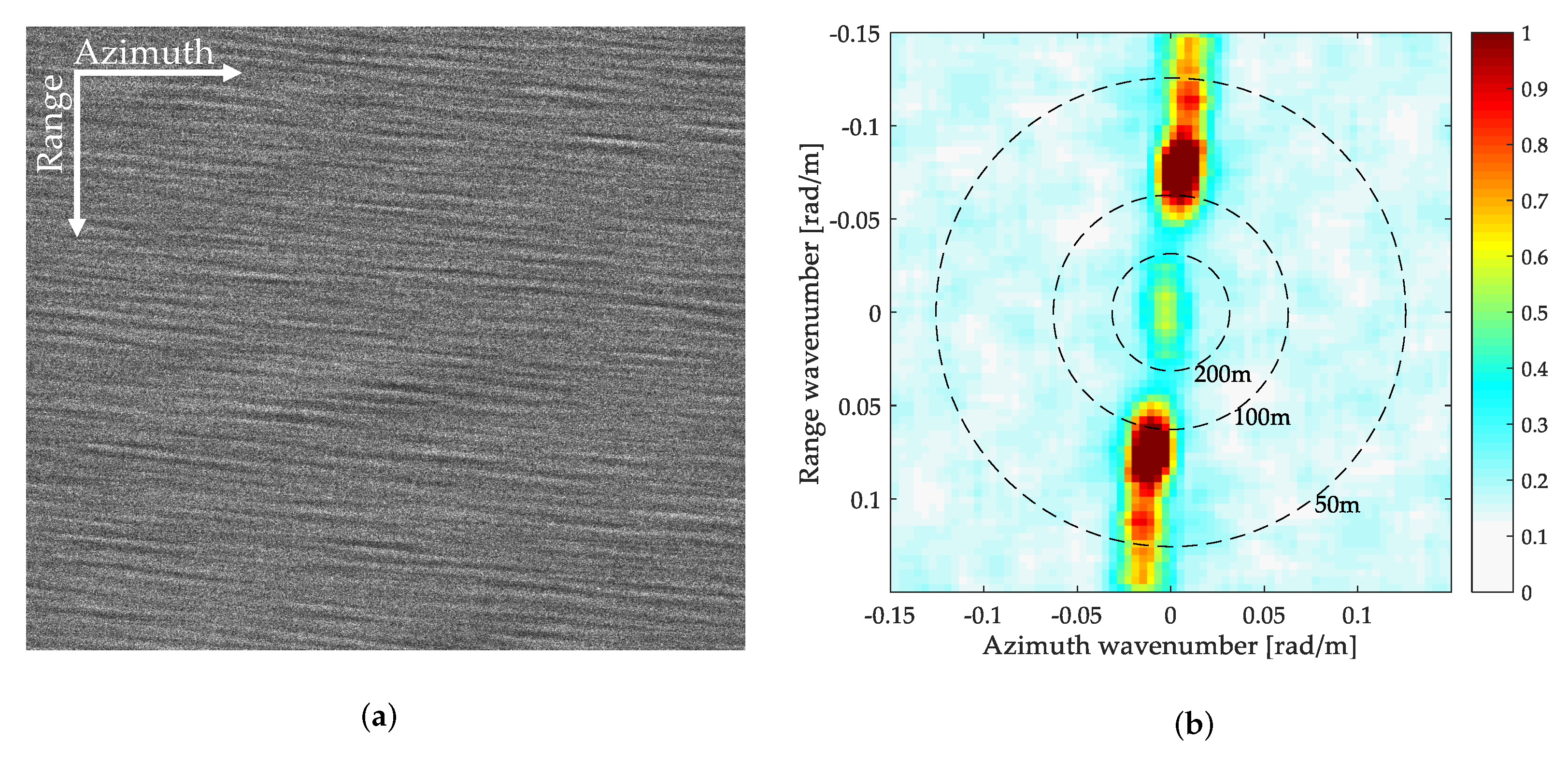
3.2.1. Experiment of Significant Wave Height Estimation of the First Ocean Waves
3.2.2. Experiment of Significant Wave Height Estimation of the Second Ocean Wave
4. Validation of the Experimental Results with ECMWF and Sensitivity Analysis
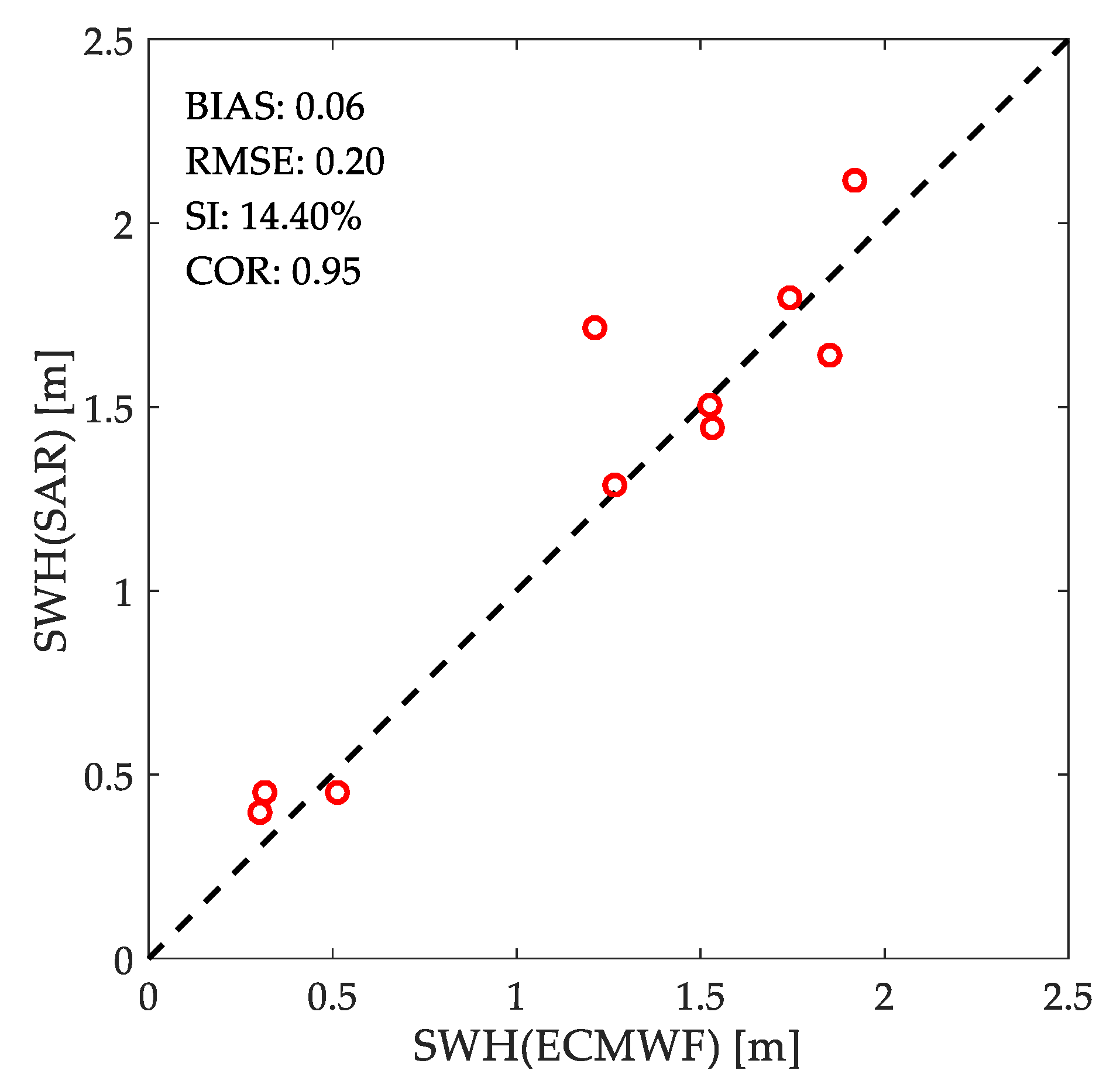
4.1. Validation of the Experimental Results with ECMWF
4.2. Sensitivity Analysis of Significant Wave Height Estimation
4.2.1. Sensitivity Analysis of Significant Wave Height to Azimuth Cutoff
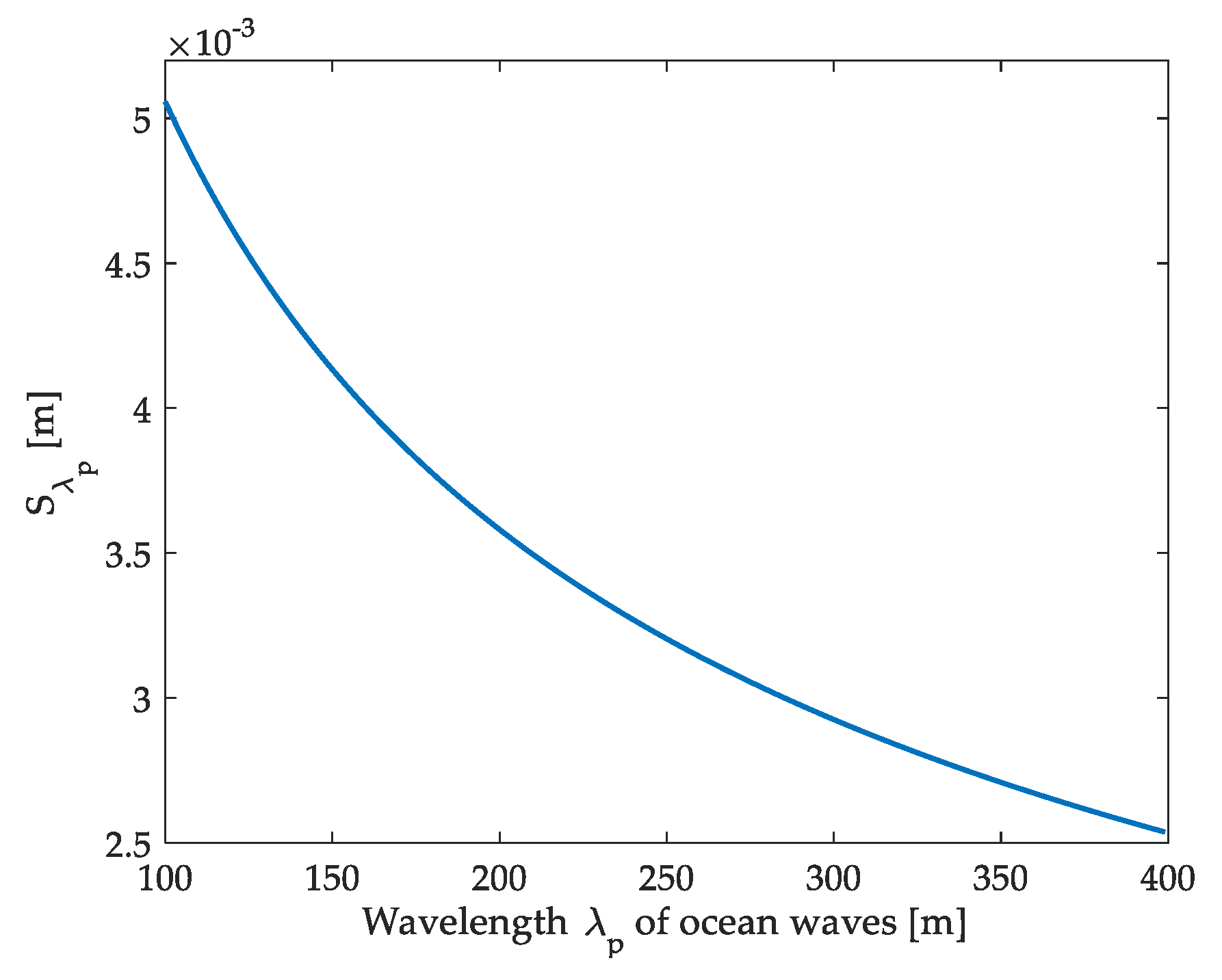
4.2.2. Sensitivity Analysis of Significant Wave Height to Wavelength of Ocean Waves
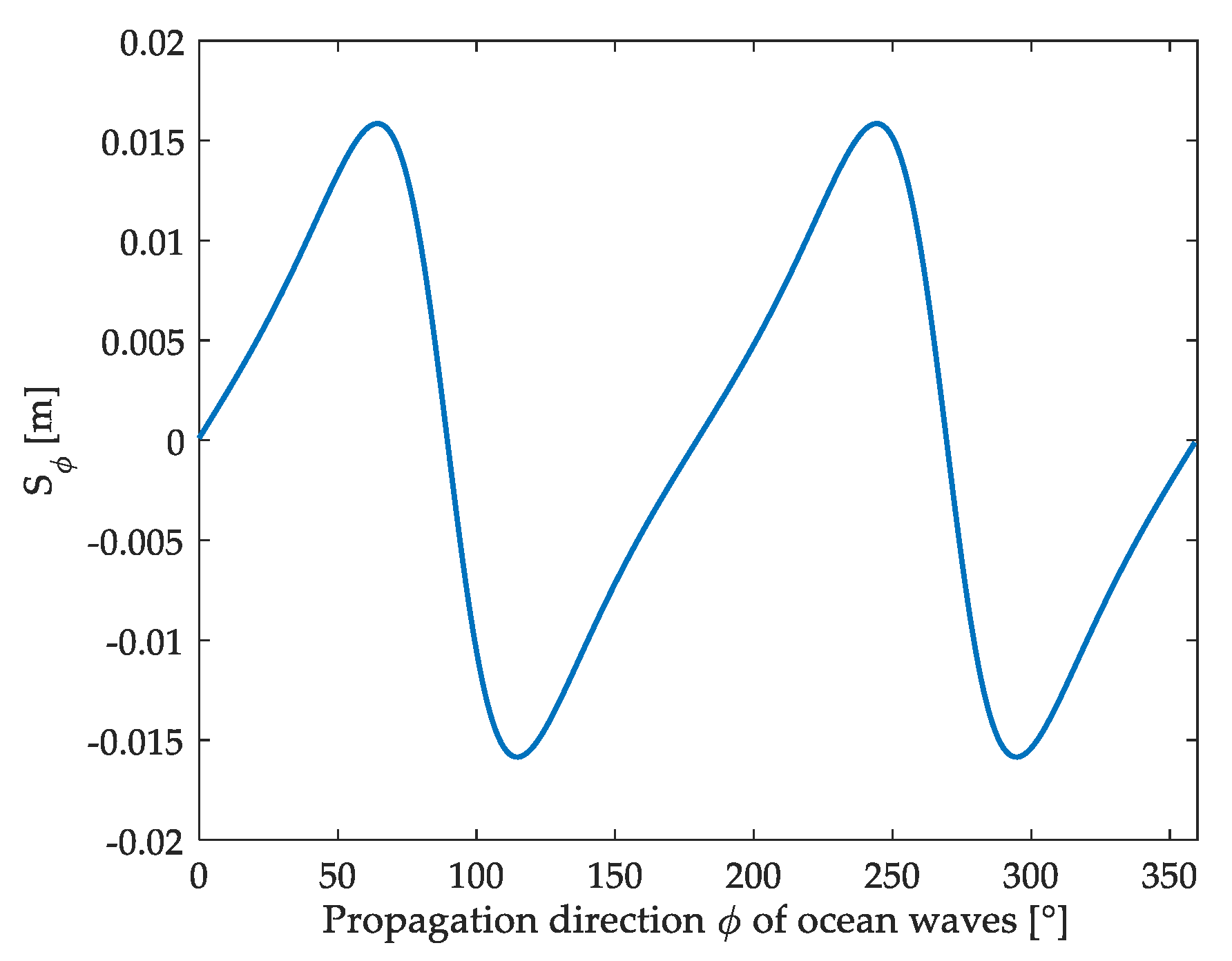
4.2.3. Sensitivity Analysis of Significant Wave Height to Propagation Direction of Ocean Waves
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vachon, P.W.; Monaldo, F.M.; Holt, B.; Lehner, S. Ocean surface waves and spectra. In Synthetic Aperture Radar: Marine User’s Manual; Jackson, C.R., Apel, J.R., Eds.; U.S. Department of Commerce National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; pp. 139–169. [Google Scholar]
- Hasselmann, K.; Hasselmann, S. On the nonlinear mapping of an ocean wave spectrum into a synthetic aperture radar image spectrum and its inversion. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1991, 96, 10713–10729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmann, S.; Brüning, C.; Hasselmann, K.; Heimbach, P. An improved algorithm for the retrieval of ocean wave spectra from synthetic aperture radar image spectra. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1996, 101, 16615–16629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmann, S.; Hasselmann, K.; Baure, E.; Janssen, P.A.E.M.; Komen, G.J.; Bertotti, L.; Lionello, P.; Guillaume, A.; Cardone, V.C.; Greenwood, J.A.; et al. The WAM model—A third generation ocean wave prediction model. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1988, 18, 1775–1810. [Google Scholar]
- Mastenbroek, C.; De Valk, C.F. A semiparametric algorithm to retrieve ocean wave spectra from synthetic aperture radar. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2000, 105, 3497–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Guan, C. Parameterized first-guess spectrum method for retrieving directional spectrum of swell-dominated waves and huge waves from SAR images. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2006, 24, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.; Yang, J.; Mouche, A.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, H. Preliminary analysis of Chinese GF-3 SAR quad-polarization measurements to extract winds in each polarization. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schulz-Stellenfleth, J.; König, T.; Lehner, S. An empirical approach for the retrieval of integral ocean wave parameters from synthetic aperture radar data. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2007, 112, C03019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lehner, S.; Bruns, T. Ocean wave integral parameter measurements using Envisat ASAR wave mode data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stopa, J.E.; Mouche, A. Significant wave heights from Sentinel-1 SAR: Validation and applications. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 1827–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Ren, L.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, X.; Xie, C. Empirical algorithm for significant wave height retrieval from wave mode data provided by the Chinese Satellite Gaofen-3. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, L.; Yang, J.; Zheng, G.; Wang, J. Significant wave height estimation using azimuth cutoff of C-band Radarsat-2 single-polarization SAR images. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2015, 34, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Li, H. Ocean wave parameters retrieval from Sentinel-1 SAR imagery. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pramudya, F.S.; Pan, J.; Devlin, A.T.; Lin, H. Enhanced estimation of significant wave height with dual-polarization Sentinel-1 SAR imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpers, W.; Rufenach, C. The effect of orbital motions on synthetic aperture radar imagery of ocean waves. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1979, 27, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raney, R. Wave orbital velocity, fade, and SAR response to azimuth waves. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1981, 6, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, R.C.; Tilley, D.G.; Monaldo, F.M. Large- and small-scale spatial evolution of digitally processed ocean wave spectra from Seasat synthetic aperture radar. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1983, 88, 1761–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachon, P.W.; Krogstad, H.E.; Paterson, J.S. Airborne and spaceborne synthetic aperture radar observations of ocean waves. Atmosphere-Ocean 1994, 32, 83–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajirian, E.K. Multifocus processing of L band synthetic aperture radar images of ocean waves obtained during the tower ocean wave and radar dependence experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1988, 93, 13849–13857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayt, D.W.; Alpers, W.; Burning, C.; Dewitt, R.; Henyey, F.; Kasilingam, D.P.; Keller, W.C.; Lyzenga, D.R.; Plant, W.J.; Schult, R.L.; et al. Focusing simulations of synthetic aperture radar ocean images. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1990, 95, 16245–16261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasilingam, D.P.; Hayt, D.W.; Shemdin, O.H. Focusing of synthetic aperture radar ocean images with long integration times. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 16935–16942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Chong, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Yao, X. Airborne SAR imaging algorithm for ocean waves based on optimum focus setting. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, A.; Shemdin, O.H. L band SAR ocean wave observations during MARSEN. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1983, 88, 9792–9808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyzenga, D.R. Numerical simulation of synthetic aperture radar image spectra for ocean waves. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1986, GE-24, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A.; Toporkov, J.V.; Sletten, M.A.; Menk, S.P. Mapping surface currents and waves with interferometric synthetic aperture radar in coastal waters: Observations of wave breaking in swell-dominant conditions. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2013, 43, 563–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engen, G.; Johnsen, H. SAR-ocean wave inversion using image cross spectra. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Alpers, W. On the cross spectrum between individual-look synthetic aperture radar images of ocean waves. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 922–932. [Google Scholar]
- Ouchi, K.; Burridge, D.A. Resolution of a controversy surrounding the focusing mechanisms of synthetic aperture radar images of ocean waves. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 1004–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laface, V.; Arena, F.; Guedes Soares, C. Directional analysis of sea storms. Ocean. Eng. 2015, 107, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romolo, A.; Arena, F. On Adler space-time extremes during ocean storms. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 3022–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romolo, A.; Malara, G.; Laface, V.; Arena, F. “Space-time long-term statistics of ocean storms”, Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics. Probab. Eng. Mech. 2015, 44, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parametric Name | Parametric Symbol | Parametric Value |
|---|---|---|
| Radar wavelength (m) | 0.5 | |
| Platform height (m) | H | 8600 |
| Slant range of scene center (m) | 18,000 | |
| Platform speed (m/s) | V | 122 |
| Integration Times (s) | 23 |
| Parametric Name | Parametric Symbol | Parametric Value |
|---|---|---|
| Radar wavelength (m) | 0.23 | |
| Platform height (m) | H | 8100 |
| Slant range of scene center (m) | 13,000 | |
| Platform speed (m/s) | V | 117 |
| Integration Times (s) | 6 |
| Case 1-Invisible Waves | Case 2-Two Wave Systems | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SAR acquisition time (UTC) | 2014.10.11 01:22 | 2014.9.14 01:29 | |
| SAR image central location | |||
| Corresponding time of ECMWF (UTC) | 2014.10.11 01:00 | 2014.9.14 01:00 | |
| SWH from SAR image (m) | 1.51 | 0.45 | 0.40 |
| Corresponding SWH from ECMWF (m) | 1.52 | 0.51 | 0.30 |
| Parametric Name | Parametric Symbol | Parametric Value |
|---|---|---|
| Azimuth cutoff (m) | 90 | |
| Wavelength of ocean waves (m) | 240 | |
| Propagation direction of ocean waves (°) | 300 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Chong, J.; Li, Z.; Wei, X.; Diao, L. Estimating Significant Wave Height from SAR with Long Integration Times. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052341
Zhao Y, Chong J, Li Z, Wei X, Diao L. Estimating Significant Wave Height from SAR with Long Integration Times. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(5):2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052341
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yawei, Jinsong Chong, Zongze Li, Xianen Wei, and Lijie Diao. 2022. "Estimating Significant Wave Height from SAR with Long Integration Times" Applied Sciences 12, no. 5: 2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052341
APA StyleZhao, Y., Chong, J., Li, Z., Wei, X., & Diao, L. (2022). Estimating Significant Wave Height from SAR with Long Integration Times. Applied Sciences, 12(5), 2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052341






