Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone and Organosilica Layered Nanofiller for Sustainable Proton Exchange Membranes Fuel Cells (PEMFCs)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Sulfonation of Polyether Ether Ketone
2.3. Synthesis of Organo-Silica Layered Materials
2.4. Membranes Preparation
2.5. Ion Exchange Capacity (IEC) and Water Uptake
2.6. NMR (PFG and Relaxometry) Spectroscopy
2.7. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
2.8. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA)
3. Results and Discussion
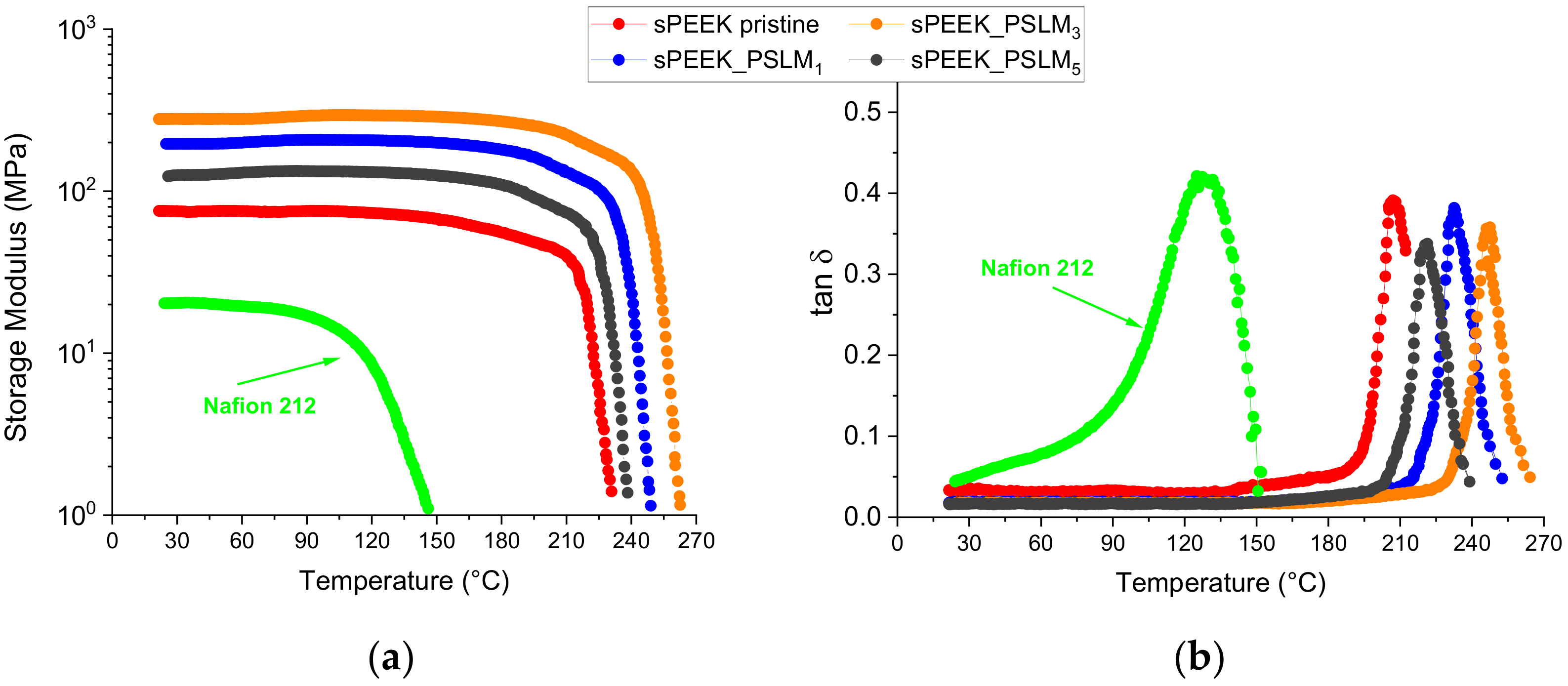
3.1. Mechanical Properties
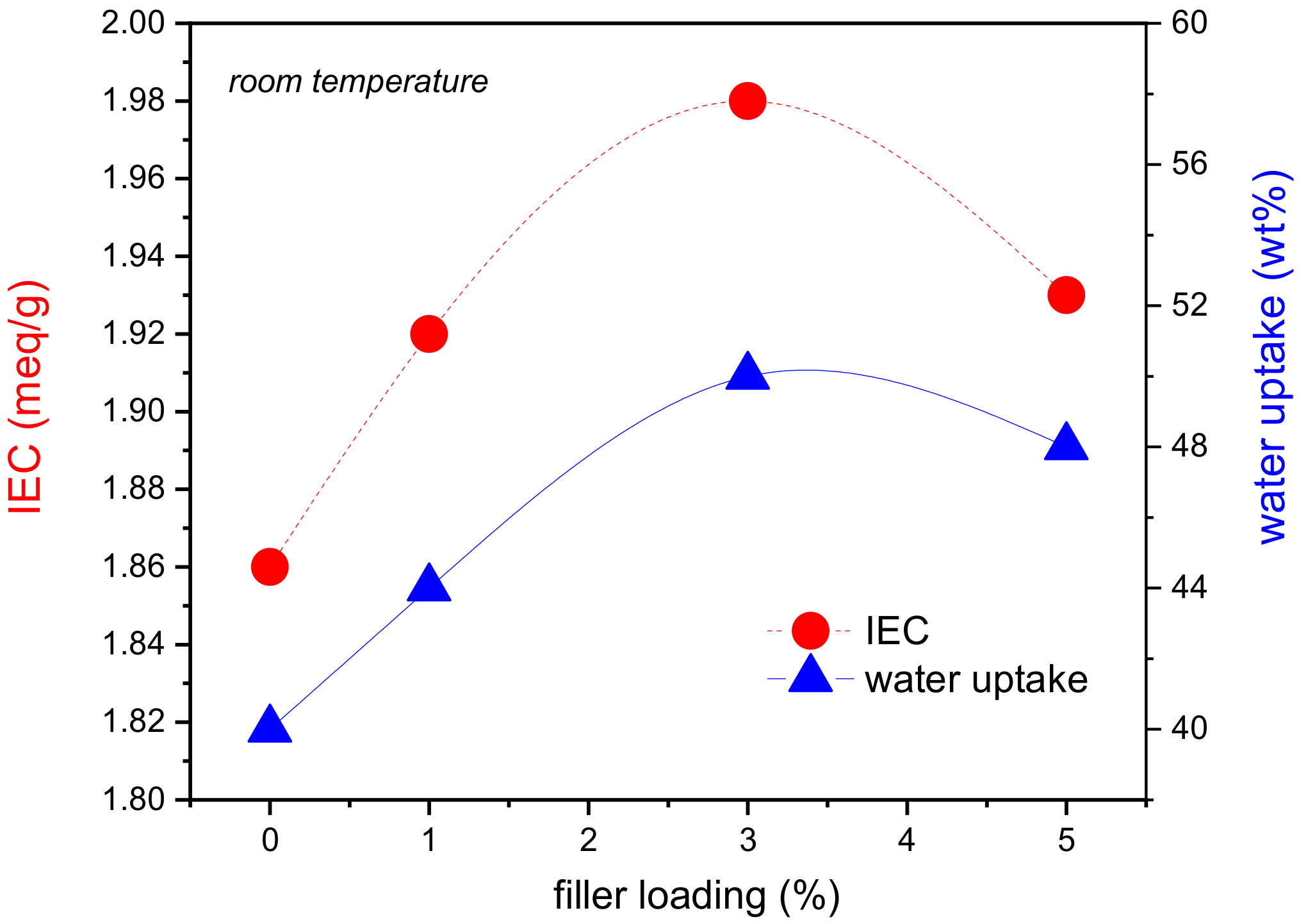
3.2. IEC and Water Uptake
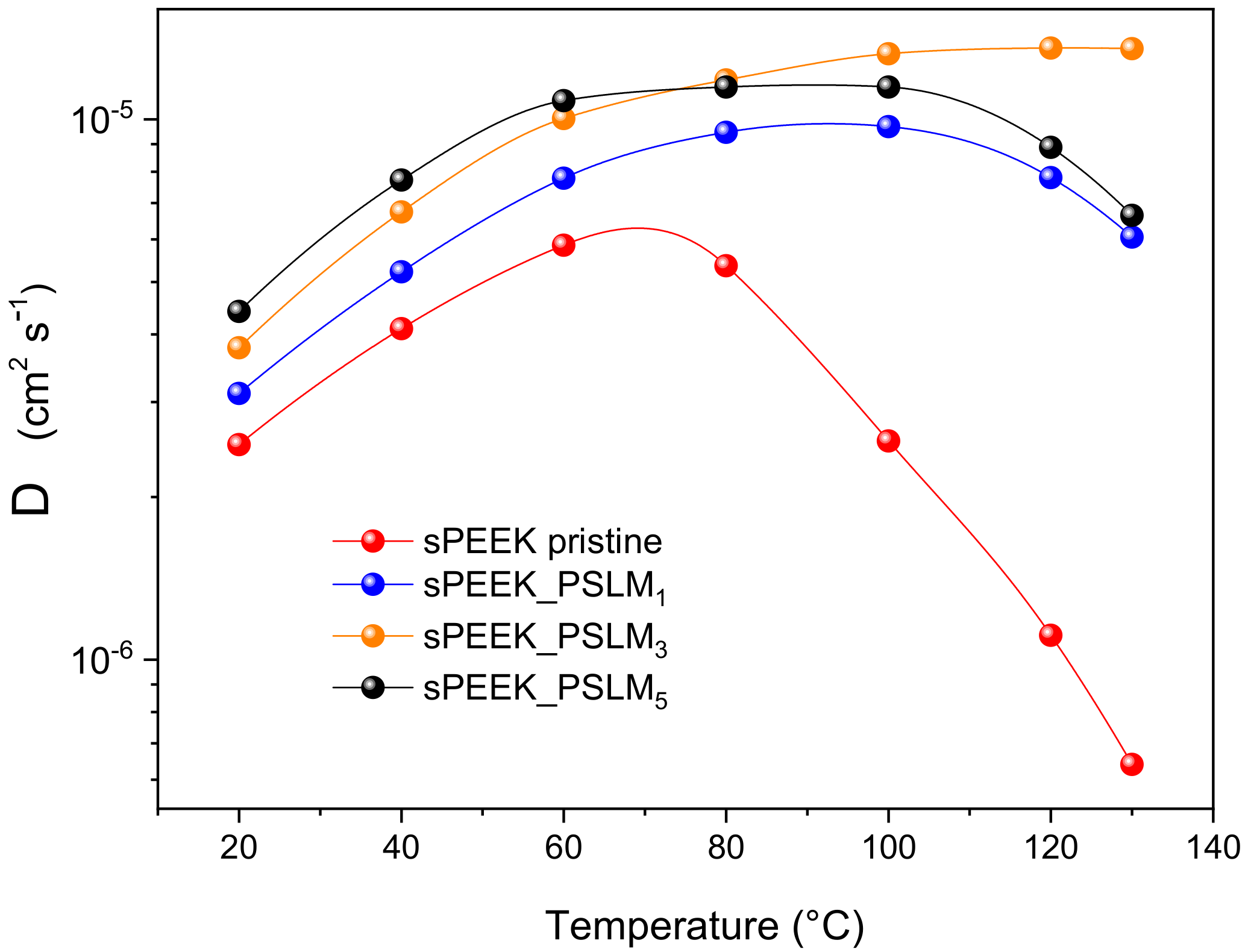
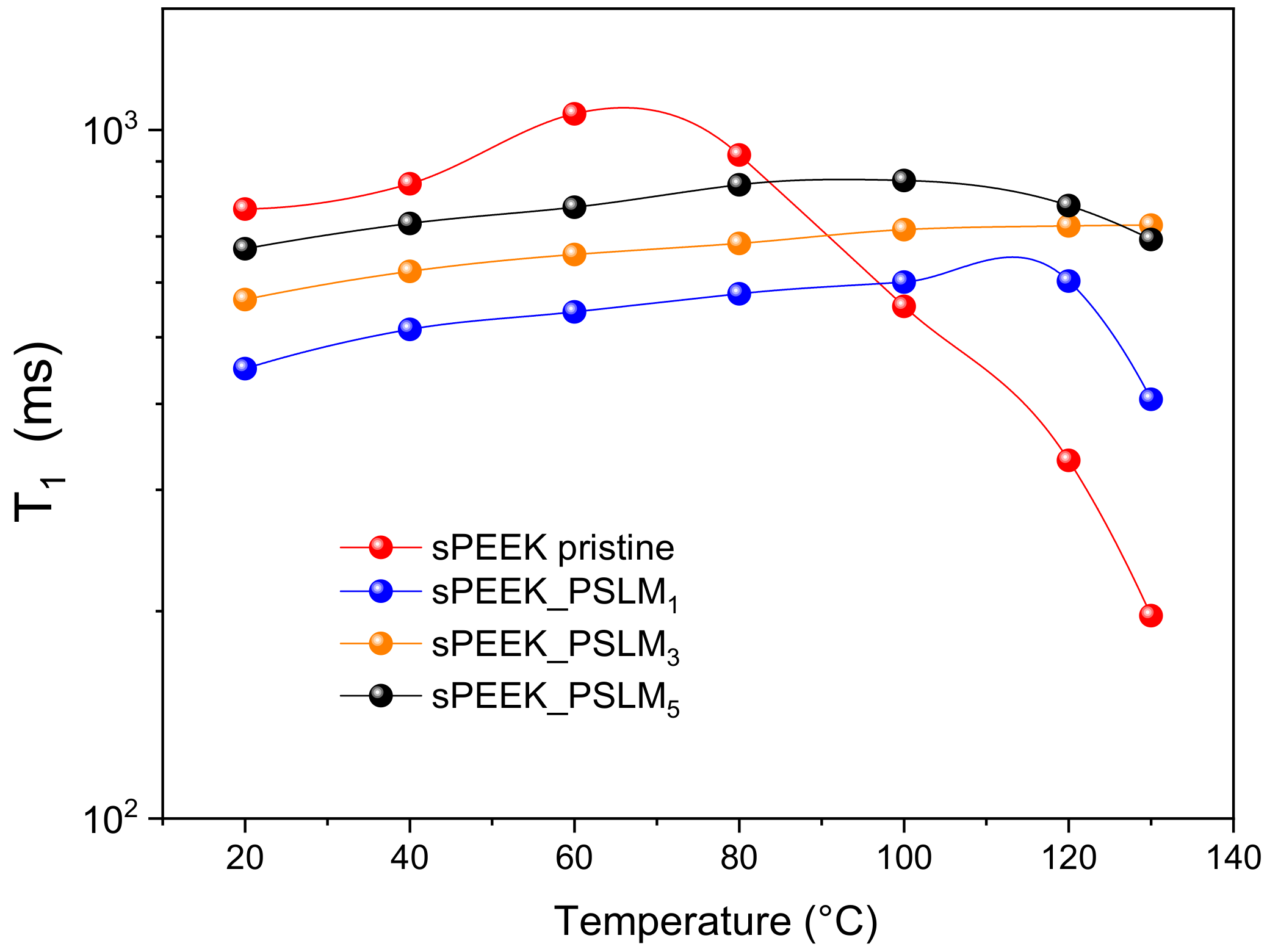
3.3. PFG-NMR Investigation
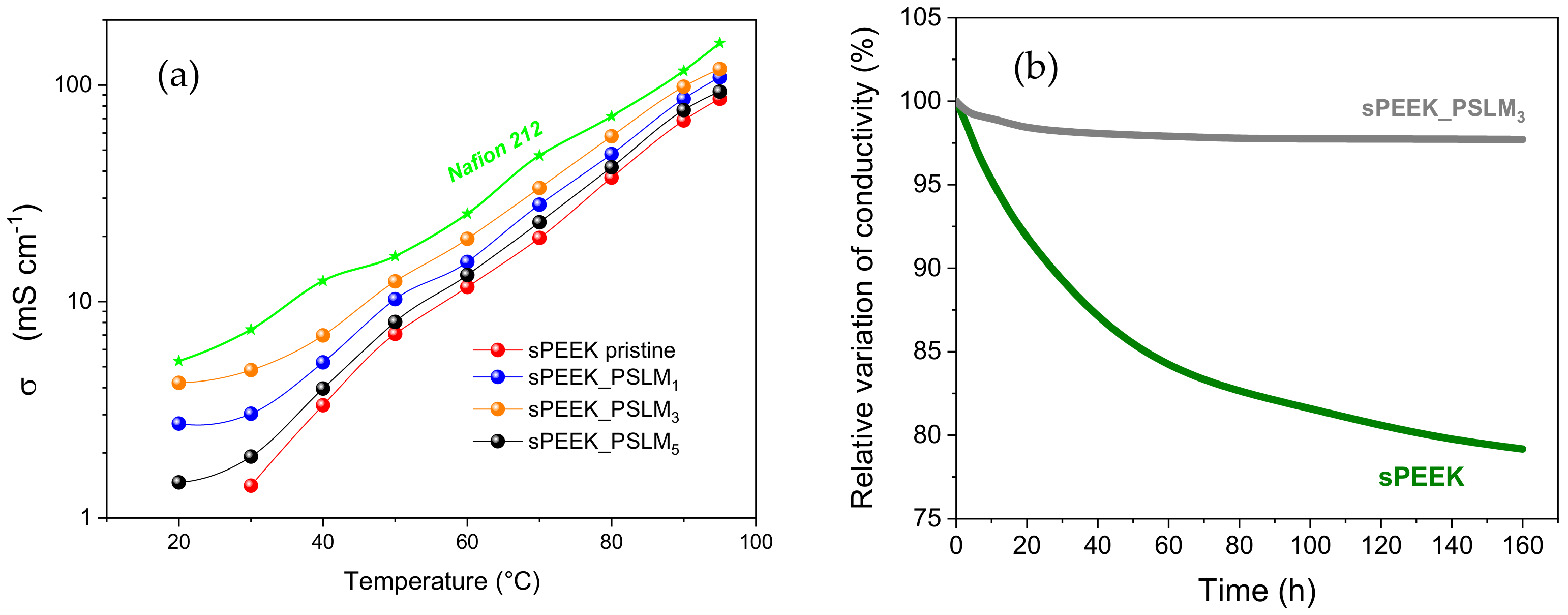
3.4. Proton Conductivities (σ) and Hydrolytic Stability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Shen, P.K. Recent development of polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cells. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2780–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Kang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Liang, Z.; He, X.; Li, X.; Tavajohi, N.; et al. A review of lithium-ion battery safety concerns: The issues, strategies, and testing standards. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 59, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.Z.; Mench, M.M.; Meyers, J.P.; Ross, P.N.; Gostick, J.T.; Liu, Q. Redox flow batteries: A review. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2011, 41, 1137–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garland, N.L.; Kopasz, J.P. The United States Department of Energy’s high temperature, low relative humidity membrane program. J. Power Sources 2007, 172, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, C.; Wan, Z.; Chen, X.; Chan, S.H.; Tu, Z. Progress and perspectives of integrated thermal management systems in PEM fuel cell vehicles: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 155, 111908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauritz, K.A.; Moore, R.B. State of understanding of Nafion. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4535–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Pan, M.; Yuan, R. Nafion/Silicon oxide composite membrane for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2012, 22, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lufrano, E.; Simari, C.; Di Vona, M.L.; Nicotera, I.; Narducci, R. How the morphology of nafion-based membranes affects proton transport. Polymers 2021, 13, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonkwo, P.C.; Ben Belgacem, I.; Emori, W.; Uzoma, P.C. Nafion degradation mechanisms in proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) system: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 27956–27973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Wei, Z. A Review of Water Management in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Energies 2009, 2, 1057–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, P.; Li, J.; Tang, H.; Wang, Z.; Pan, M. Physically stable and high performance Aquivion/ePTFE composite membrane for high temperature fuel cell application. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 442, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.B.; Mohammadi, F.; Hooshyari, K. Recent approaches to improve Nafion performance for fuel cell applications: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 28919–28938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellez-Cruz, M.M.; Escorihuela, J.; Solorza-Feria, O.; Compañ, V. Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (Pemfcs): Advances and challenges. Polymers 2021, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Zhu, G.; Li, J. Synthesis and properties of highly branched sulfonated poly(arylene ether)s as proton exchange membranes. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 1985–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusano, S.; Baglio, V.; Lufrano, F.; Staiti, P.; Aricò, A.S. Electrochemical characterization of a PEM water electrolyzer based on a sulfonated polysulfone membrane. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 448, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simari, C.; Vecchio, C.L.; Enotiadis, A.; Davoli, M.; Baglio, V.; Nicotera, I. Toward optimization of a robust low-cost sulfonated-polyethersulfone containing layered double hydroxide for PEM fuel cells. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.W.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, K.-S.; Park, C.H.; Mcgrath, J.E.; Zhang, M.; Moore, R.B.; Lingwood, M.D.; Madsen, L.A.; et al. Sulfonated Poly(arylene sulfide sulfone nitrile) Multiblock Copolymers with Ordered Morphology for Proton Exchange Membranes. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 7797–7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Cui, X.; Cai, H.; Fu, T.; Zhao, C.; Na, H. Crosslinked sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) proton exchange membranes for direct methanol fuel cell applications. J. Power Sources 2007, 164, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Ahn, Y.; Kim, D. Poly(arylene ether ketone) proton exchange membranes grafted with long aliphatic pendant sulfonated groups for vanadium redox flow batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 2261–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marani, D.; D’Epifanio, A.; Traversa, E.; Miyayama, M.; Licoccia, S. Titania nanosheets (TNS)/Sulfonated poly ether ether ketone (SPEEK) nanocomposite proton exchange membranes for fuel cells. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kesava, M.; Dinakaran, K. SnO2 nanoparticles dispersed carboxylated Poly(arylene ether sulfones) nanocomposites for proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.B.; Hooshyari, K.; Salarizadeh, P.; Beydaghi, H.; Ortiz-Martínez, V.M.; Ortiz, A.; Ortiz Uribe, I.; Mohammadi, F. A comprehensive review on the proton conductivity of proton exchange membranes (PEMs) under anhydrous conditions: Proton conductivity upper bound. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 34413–34437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simari, C.; Enotiadis, A.; Lo Vecchio, C.; Baglio, V.; Coppola, L.; Nicotera, I. Advances in hybrid composite membranes engineering for high-performance direct methanol fuel cells by alignment of 2D nanostructures and a dual-layer approach. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 599, 117858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bonis, C.; Simari, C.; Kosma, V.; Mecheri, B.; D’Epifanio, A.; Allodi, V.; Mariotto, G.; Brutti, S.; Suarez, S.; Pilar, K.; et al. Enhancement of proton mobility and mitigation of methanol crossover in sPEEK fuel cells by an organically modified titania nanofiller. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2016, 20, 1585–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.S.; Ruffmann, B.; Silva, H.; Silva, V.B.; Mendes, A.; Madeira, L.M.; Nunes, S. Zirconium oxide hybrid membranes for direct methanol fuel cells-Evaluation of transport properties. J. Memb. Sci. 2006, 284, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simari, C.; Potsi, G.; Policicchio, A.; Perrotta, I.; Nicotera, I. Clay-Carbon Nanotubes Hybrid Materials for Nanocomposite Membranes: Advantages of Branched Structure for Proton Transport under Low Humidity Conditions in PEMFCs. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 2574–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enotiadis, A.; Boutsika, L.G.; Spyrou, K.; Simari, C.; Nicotera, I. A facile approach to fabricating organosilica layered material with sulfonic groups as an efficient filler for polymer electrolyte nanocomposites. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 9489–9496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Obaid, M.; Jang, J.; Ham, M.H.; Kim, I.S. Novel sulfonated graphene oxide incorporated polysulfone nanocomposite membranes for enhanced-performance in ultrafiltration process. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotera, I.; Enotiadis, A.; Angjeli, K.; Coppola, L.; Gournis, D. Evaluation of smectite clays as nanofillers for the synthesis of nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for fuel cell applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 6236–6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, H.; Luo, X.; Chen, N. A comparative study of Nafion and sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) membrane performance for iron-chromium redox flow battery. Ionics 2019, 25, 4219–4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotera, I.; Simari, C.; Boutsika, L.G.; Coppola, L.; Spyrou, K.; Enotiadis, A. NMR investigation on nanocomposite membranes based on organosilica layered materials bearing different functional groups for PEMFCs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 27940–27949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simari, C.; Enotiadis, A.; Nicotera, I. Transport properties and mechanical features of sulfonated polyether ether ketone/organosilica layered materials nanocomposite membranes for fuel cell applications. Membranes 2020, 10, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Kar, K.K. Impact of degree of sulfonation on microstructure, thermal, thermomechanical and physicochemical properties of sulfonated poly ether ether ketone. Polymer 2017, 109, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lufrano, E.; Simari, C.; Vecchio, C.L.; Aricò, A.S.; Baglio, V.; Nicotera, I. Barrier properties of sulfonated polysulfone/layered double hydroxides nanocomposite membrane for direct methanol fuel cell operating at high methanol concentrations. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 20647–20658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, J.E. Use of the stimulated echo in nmr diffusion studies. J. Chem. Phys. 1970, 52, 2523–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simari, C.; Lufrano, E.; Godbert, N.; Gournis, D.; Coppola, L.; Nicotera, I. Titanium dioxide grafted on graphene oxide: Hybrid nanofiller for effective and low-cost proton exchange membranes. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simari, C.; Lufrano, E.; Brunetti, A.; Barbieri, G.; Nicotera, I. Highly-performing and low-cost nanostructured membranes based on Polysulfone and layered doubled hydroxide for high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2020, 471, 228440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simari, C.; Lufrano, E.; Brunetti, A.; Barbieri, G.; Nicotera, I. Polysulfone and organo-modified graphene oxide for new hybrid proton exchange membranes: A green alternative for high-efficiency PEMFCs. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 380, 138214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slichter, C. (Ed.) Principles of Magnetic Resonance, 3rd ed.; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Simari, C.; Lufrano, E.; Corrente, G.A.; Nicotera, I. Anisotropic behavior of mechanically extruded sulfonated polysulfone: Implications for proton exchange membrane fuel cell applications. Solid State Ion. 2021, 362, 115581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lufrano, E.; Simari, C.; Enotiadis, A.; Nicotera, I. Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone and Organosilica Layered Nanofiller for Sustainable Proton Exchange Membranes Fuel Cells (PEMFCs). Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12030963
Lufrano E, Simari C, Enotiadis A, Nicotera I. Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone and Organosilica Layered Nanofiller for Sustainable Proton Exchange Membranes Fuel Cells (PEMFCs). Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(3):963. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12030963
Chicago/Turabian StyleLufrano, Ernestino, Cataldo Simari, Apostolos Enotiadis, and Isabella Nicotera. 2022. "Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone and Organosilica Layered Nanofiller for Sustainable Proton Exchange Membranes Fuel Cells (PEMFCs)" Applied Sciences 12, no. 3: 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12030963
APA StyleLufrano, E., Simari, C., Enotiadis, A., & Nicotera, I. (2022). Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone and Organosilica Layered Nanofiller for Sustainable Proton Exchange Membranes Fuel Cells (PEMFCs). Applied Sciences, 12(3), 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12030963







