BIM-Based Maintenance Data Processing Mechanism through COBie Standard Development for Port Facility
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review Focusing on the Use of COBie Data from Architecture to Civil Engineering
3. Port COBie Schema for Digital Data-Based Facility Management
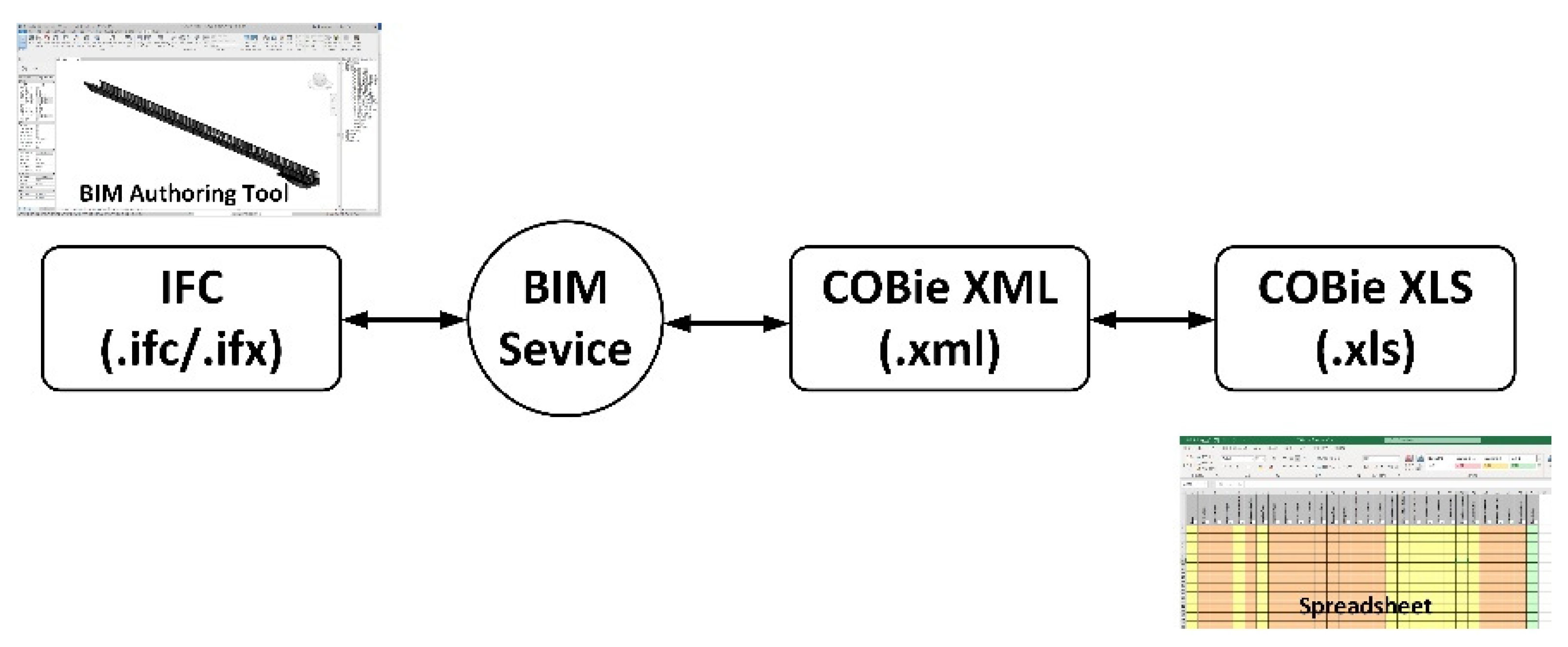
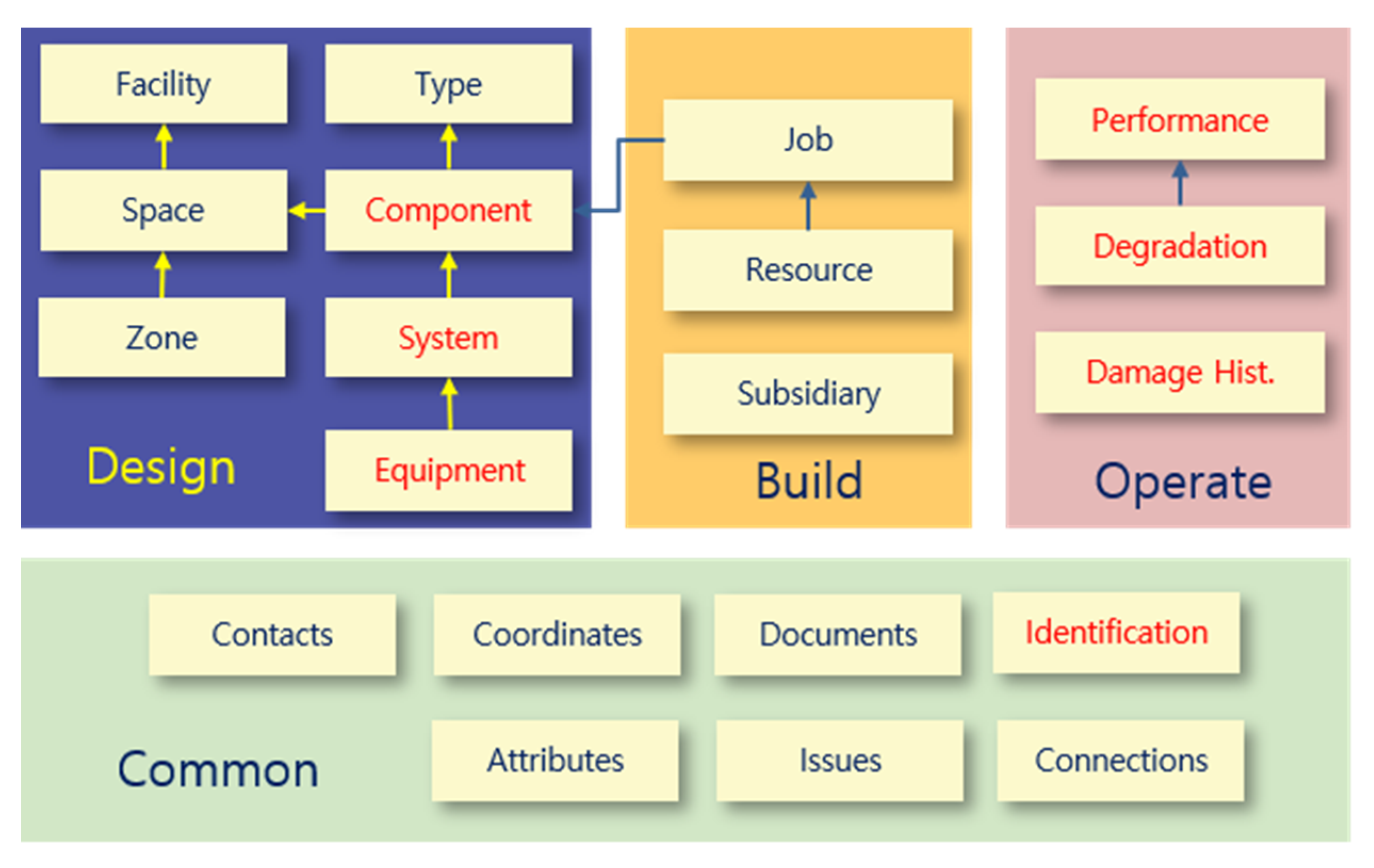
3.1. What Is the Existing COBie?
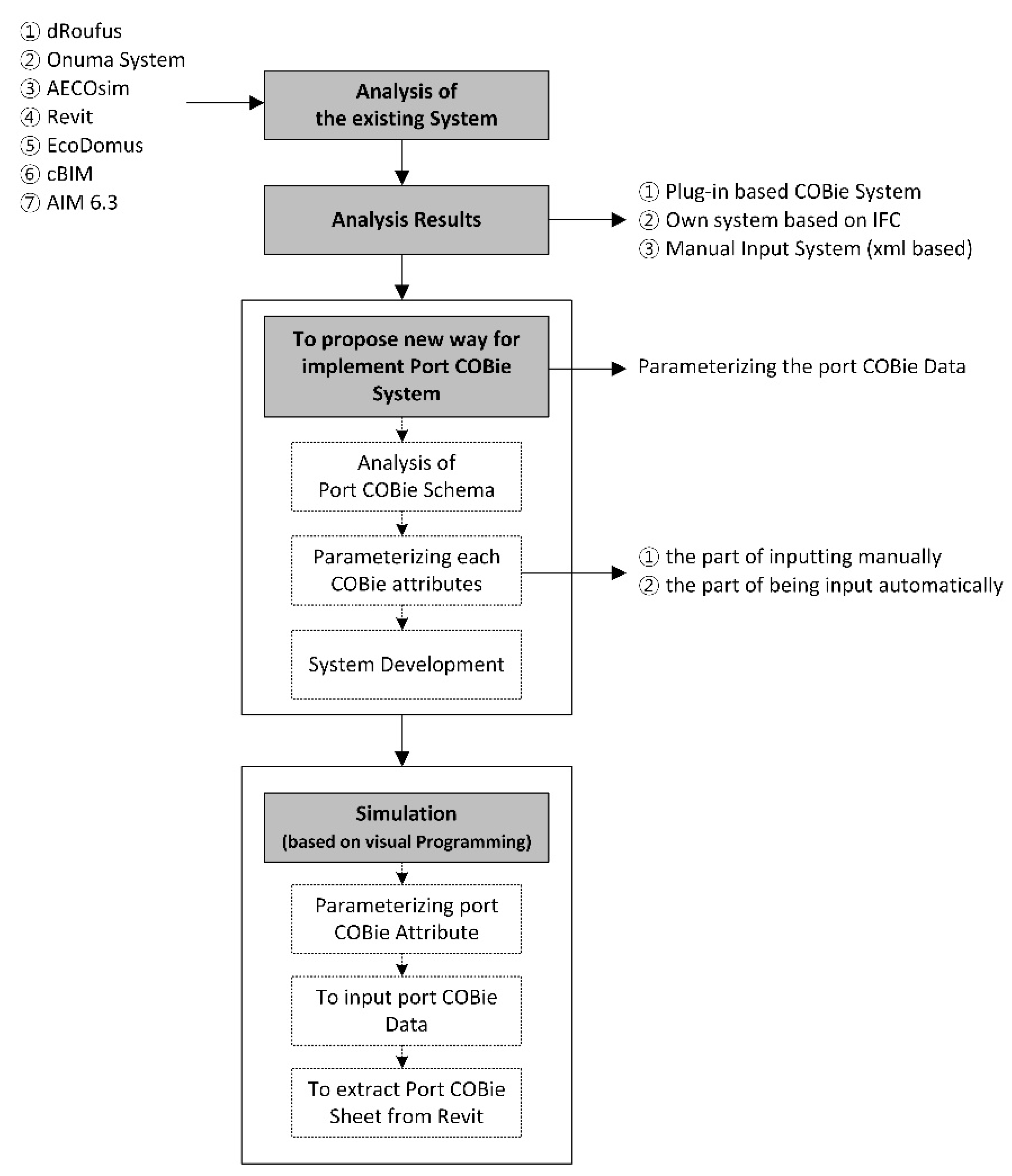
3.2. Commercial COBie System Analysis
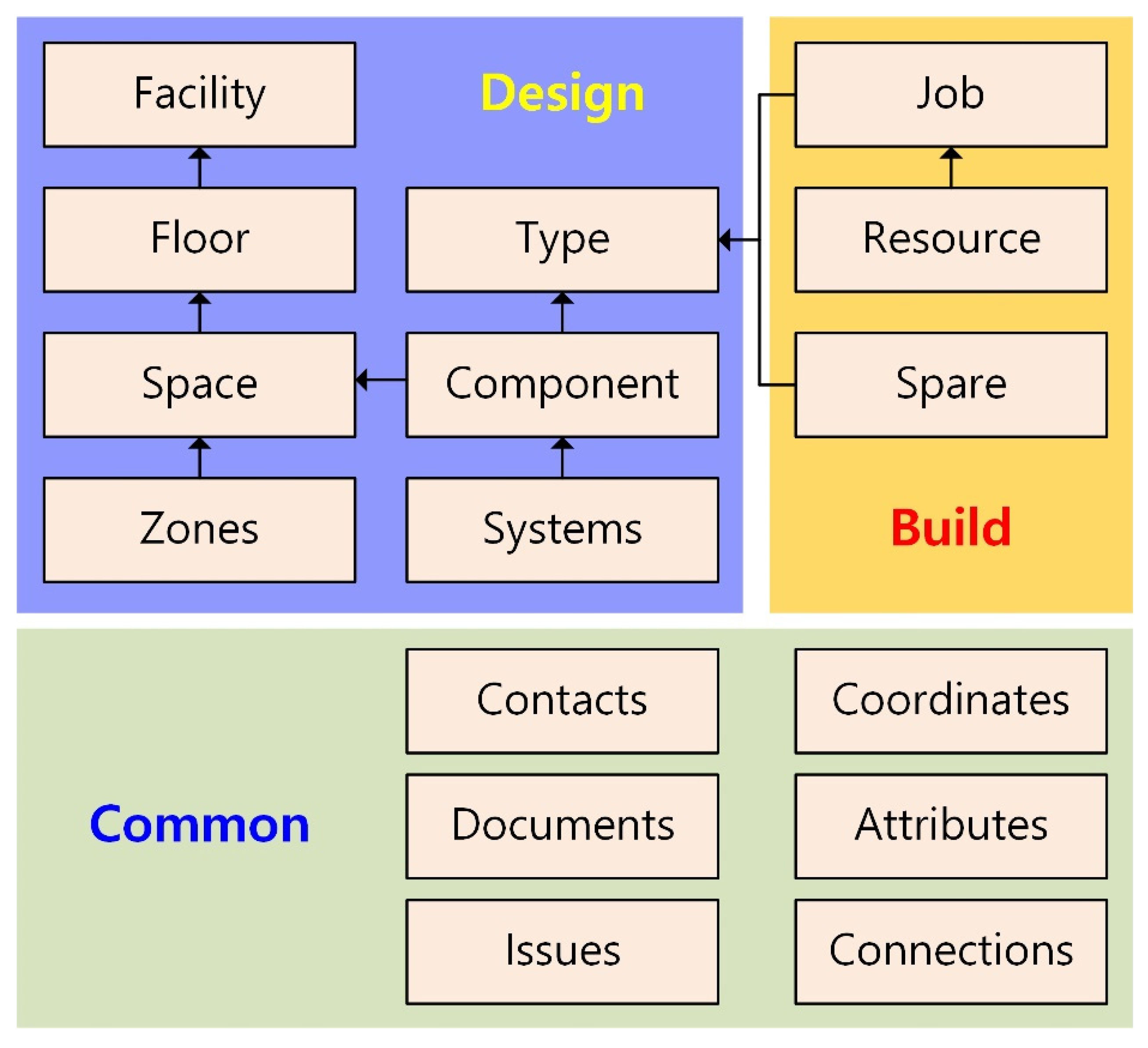
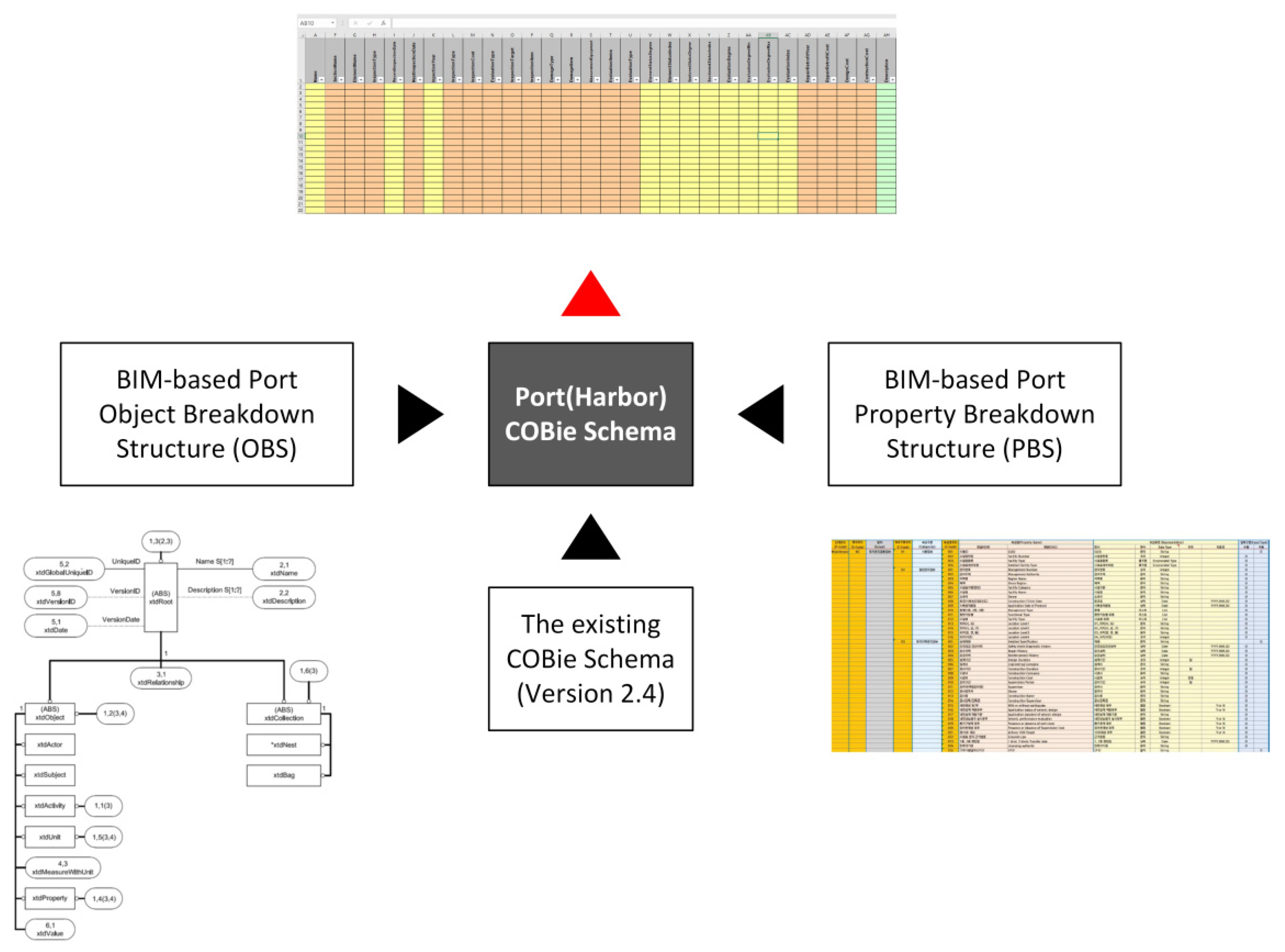
3.3. Development of Port COBie Schema
3.3.1. Background References for Developing Port COBie Schema
3.3.2. Port COBie Schema Developing Process
4. Implementation
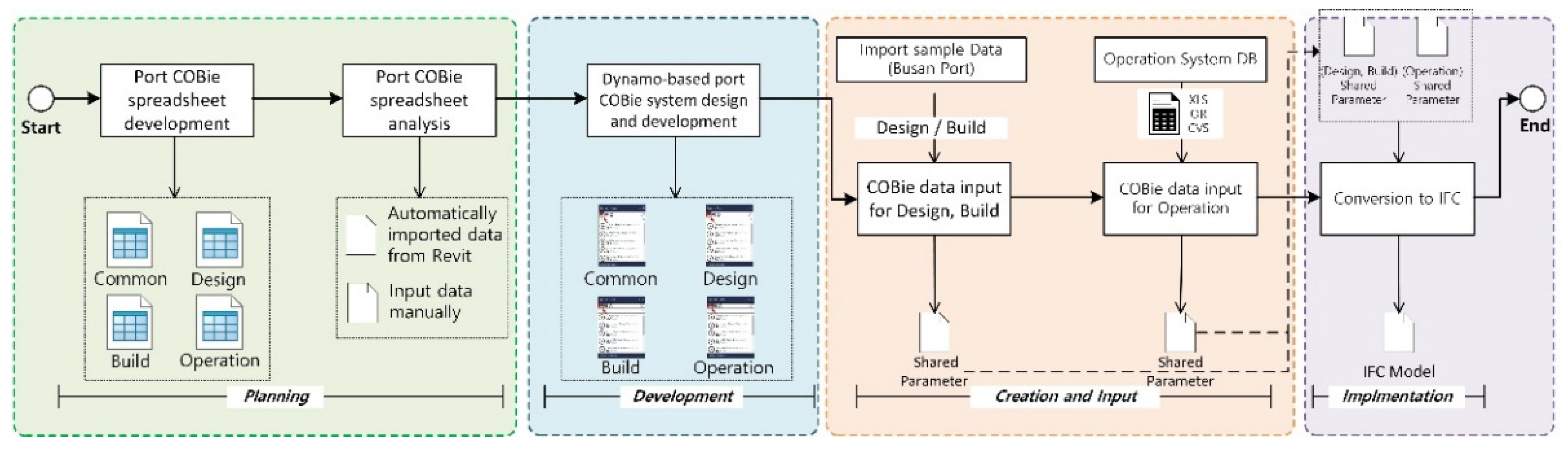
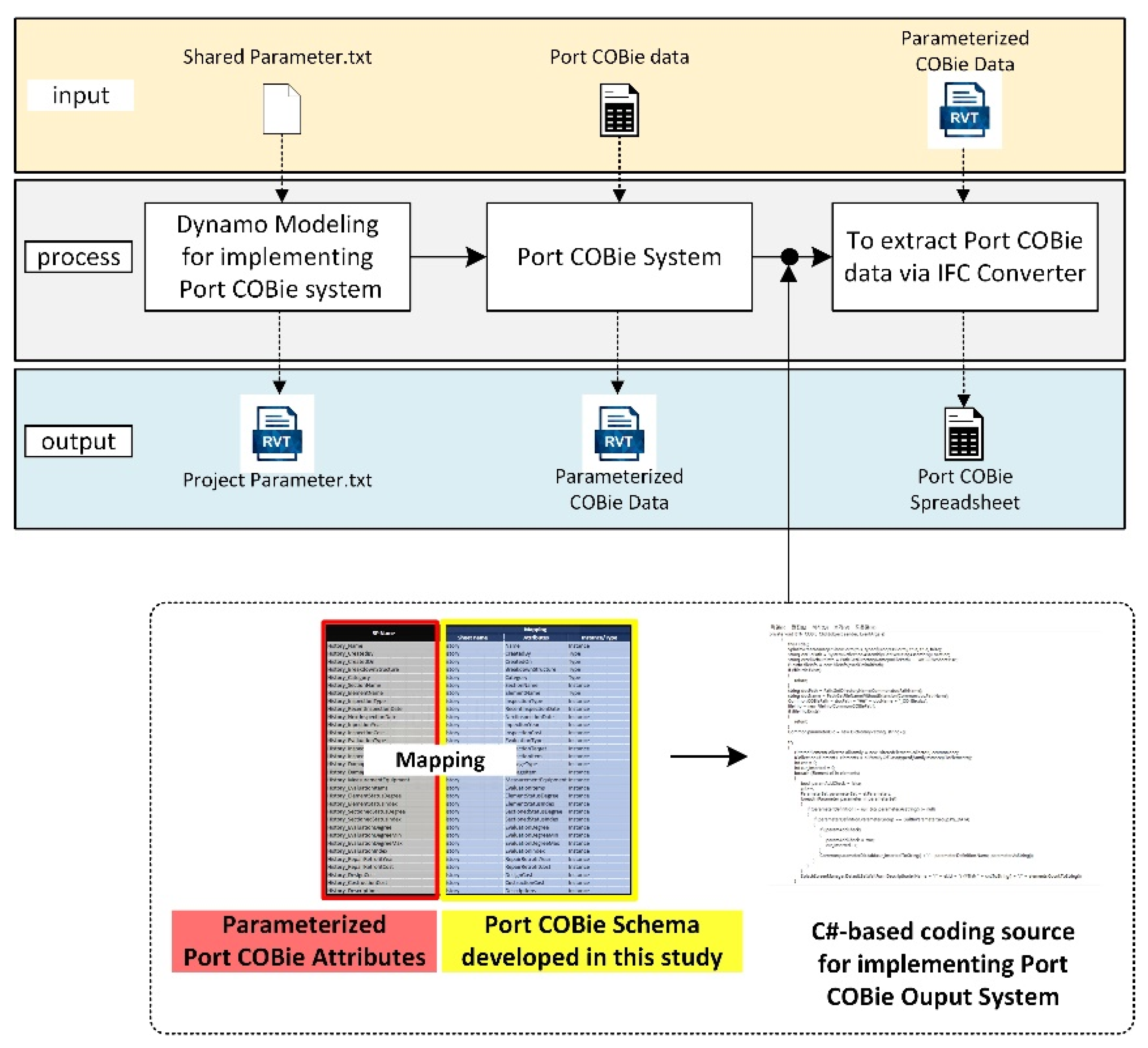
4.1. Implementation Process for COBie Data Input System Based on Port COBie Schema
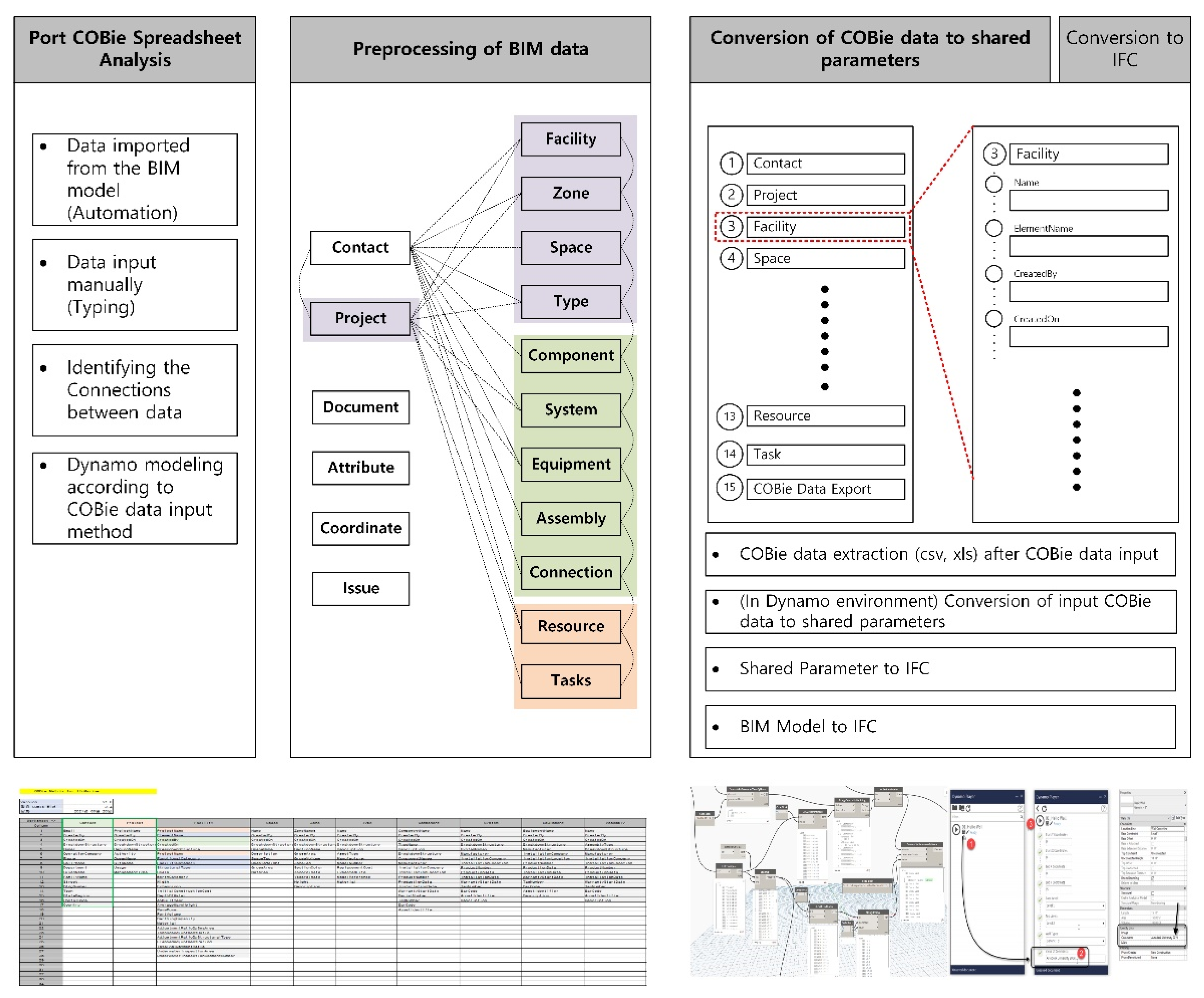
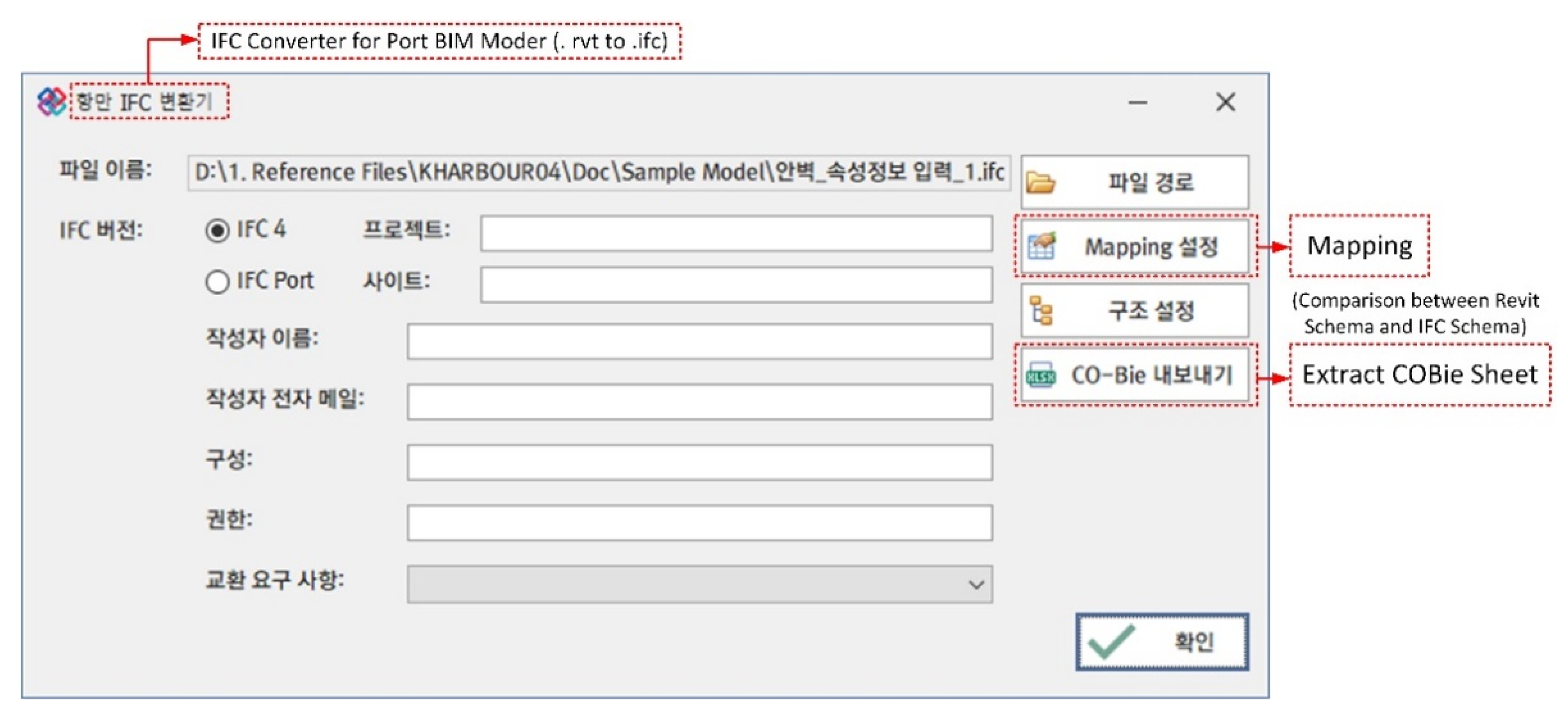
4.2. Development of Port COBie System Focusing on Revit Environment
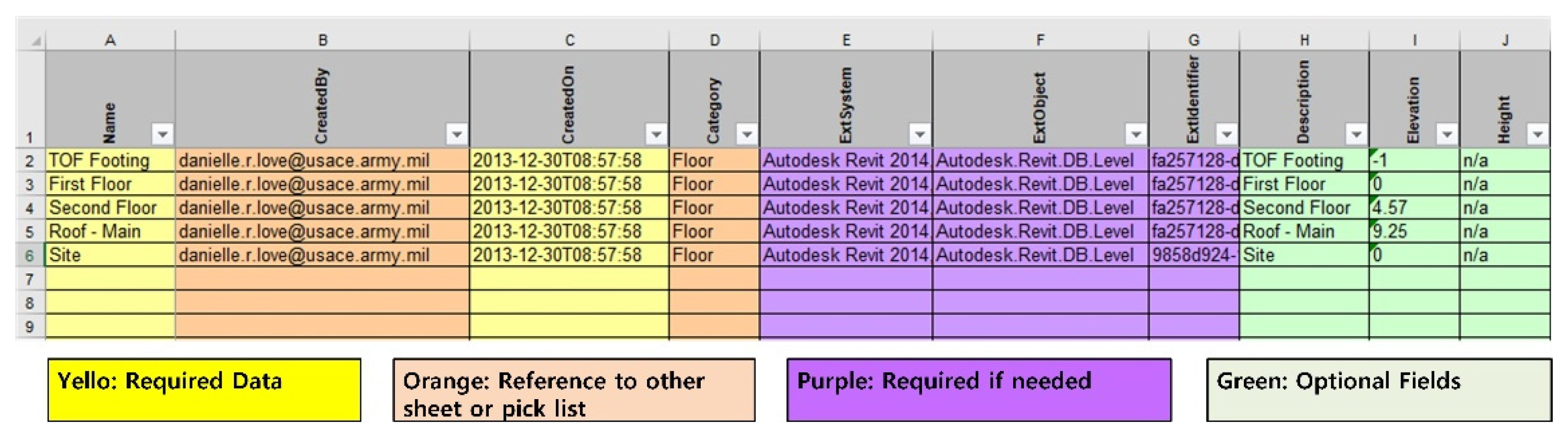
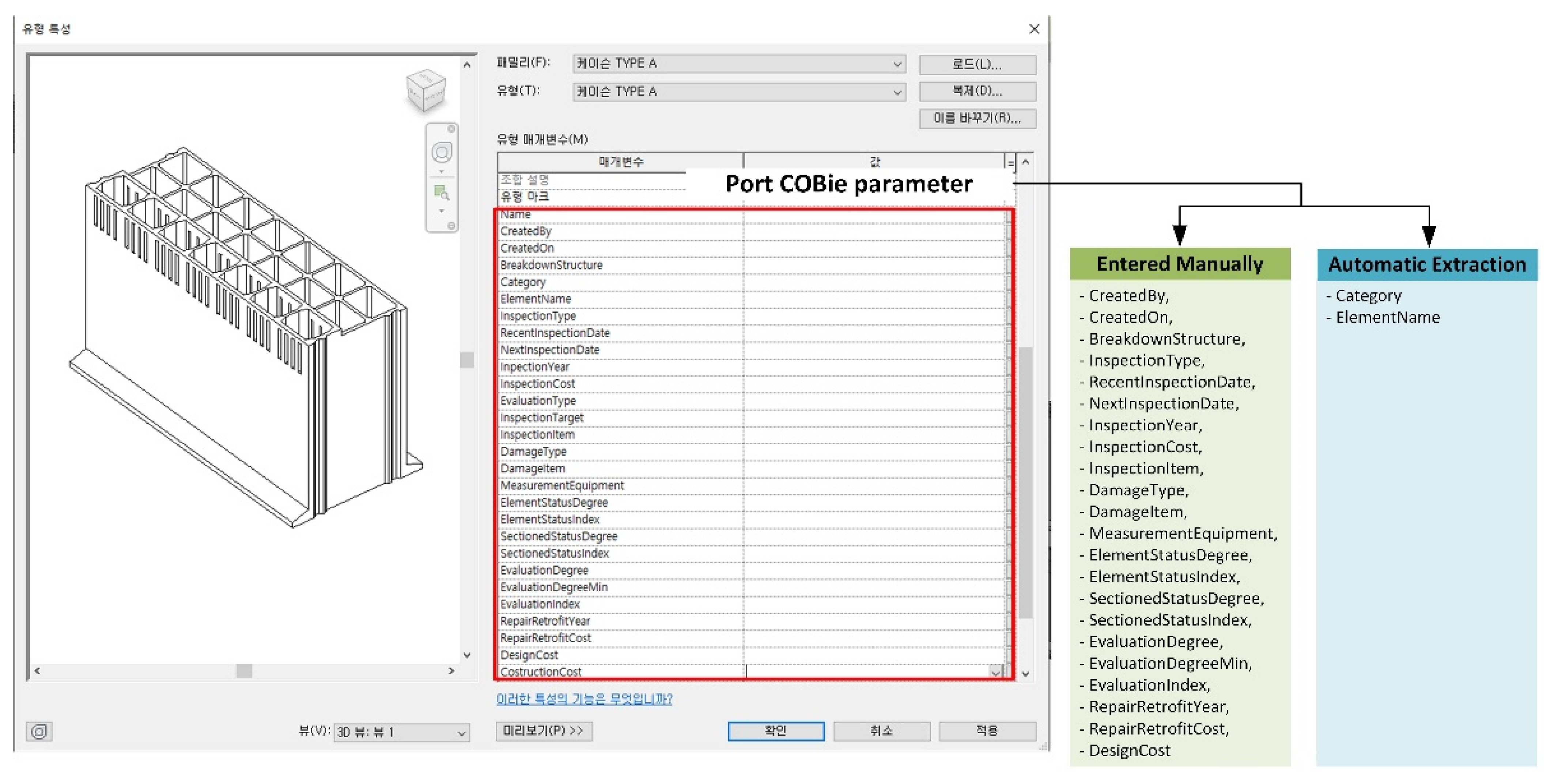
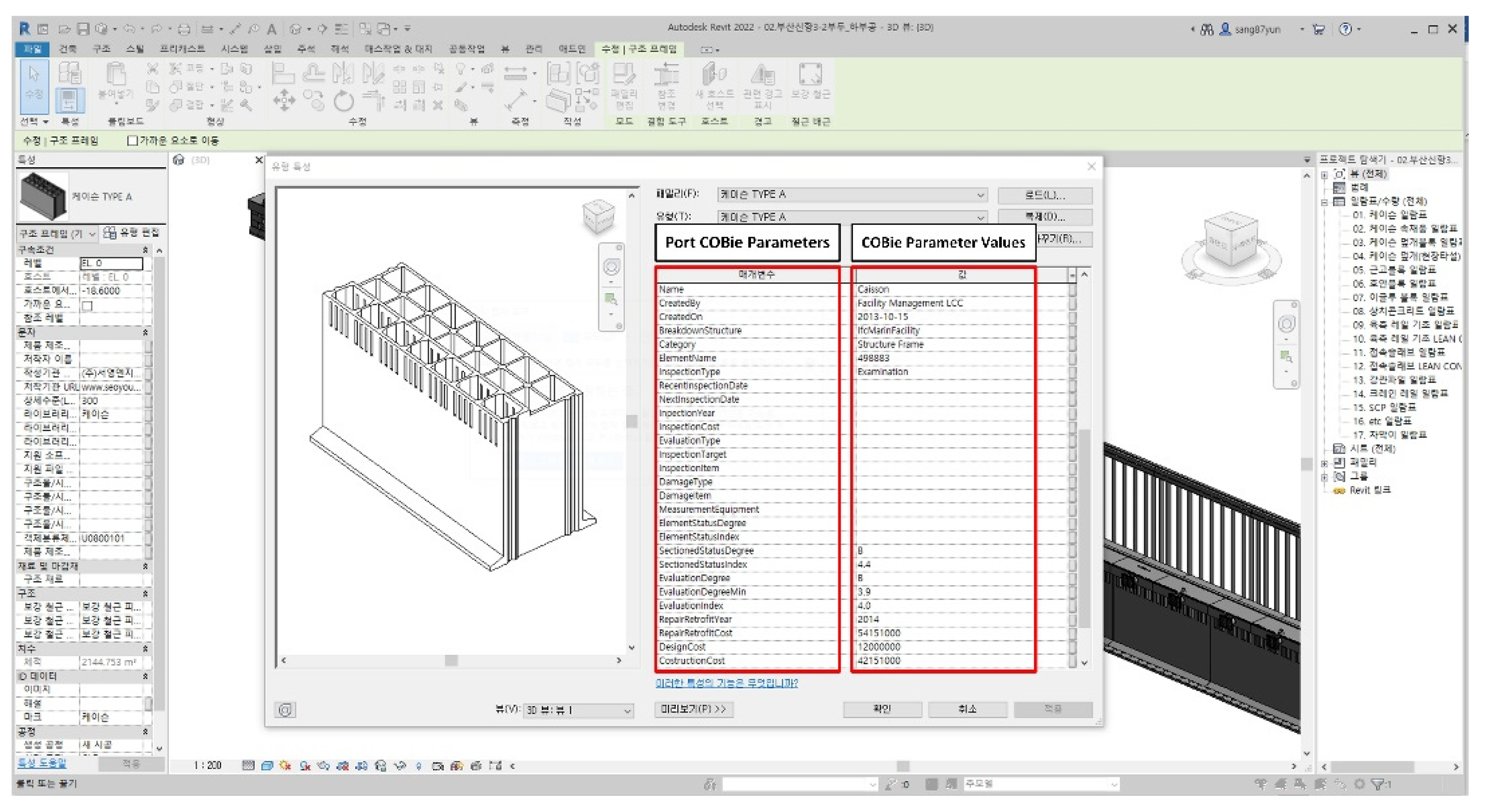
- Planning The port COBie schema developed in this study is analyzed during this stage. The COBie schema is analyzed because the types of data inputted to the COBie system are not homogenous. For example, the length, width, and height of a caisson (one of the port facilities) are automatically inputted according to the design when designing in Revit (see Figure 12). When entering COBie data, these values should be automatically inputted from Revit rather by the user. On the other hand, certain information (e.g., the company that constructed the caisson and its construction date and time) should be directly inputted by the user. Therefore, when developing the port COBie data processing system, it is essential to distinguish between the data to be imported from Revit and that to be manually inputted by the user. Such data classification takes place during the planning phase.
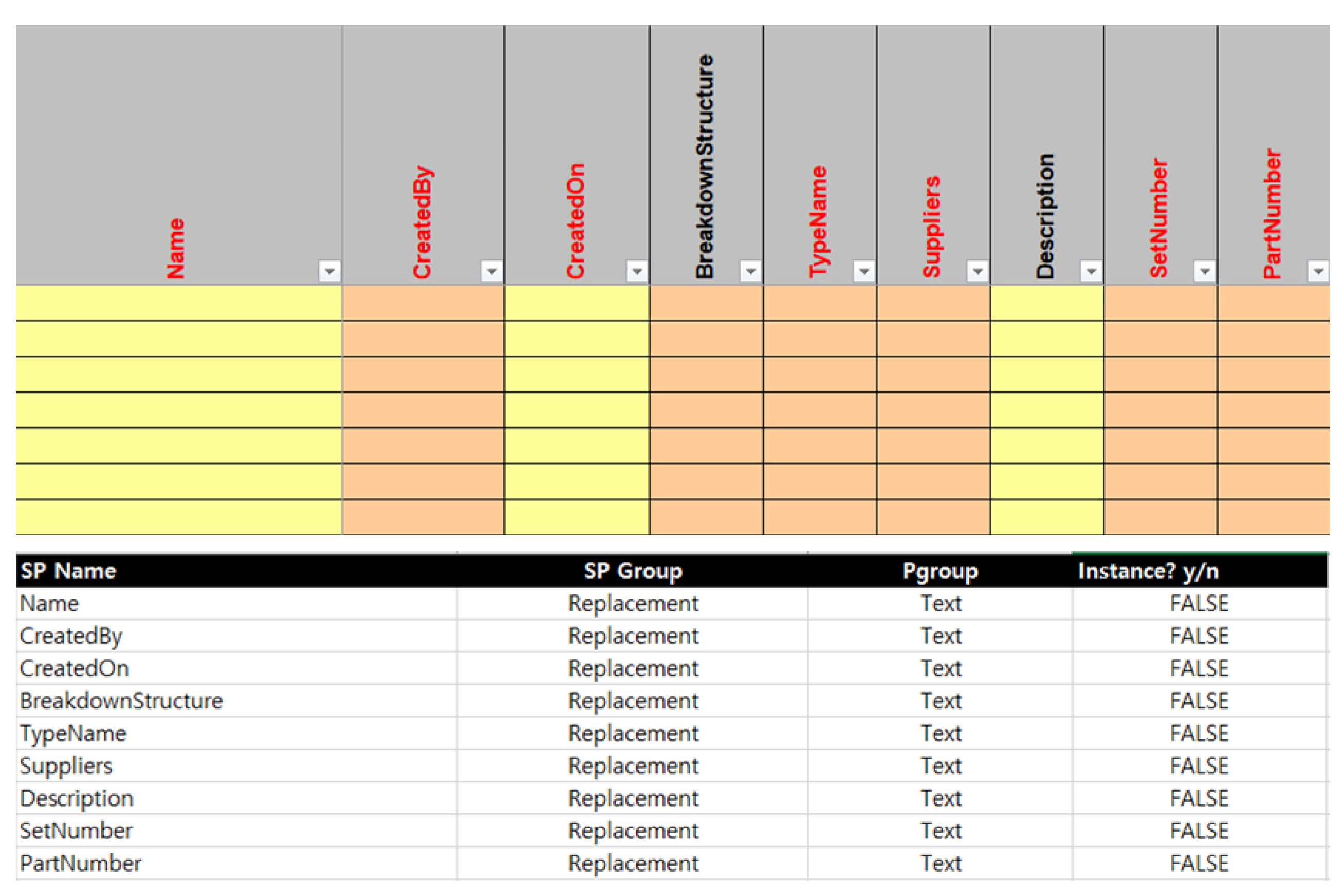
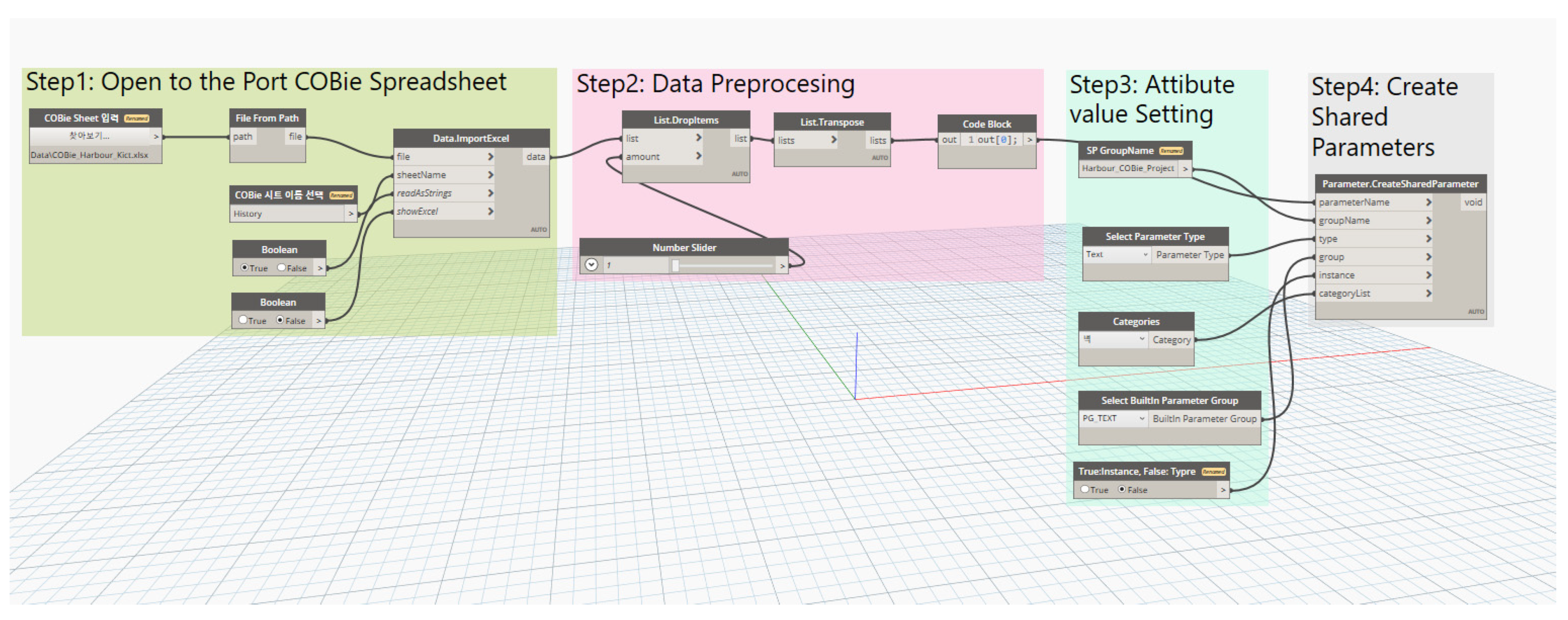
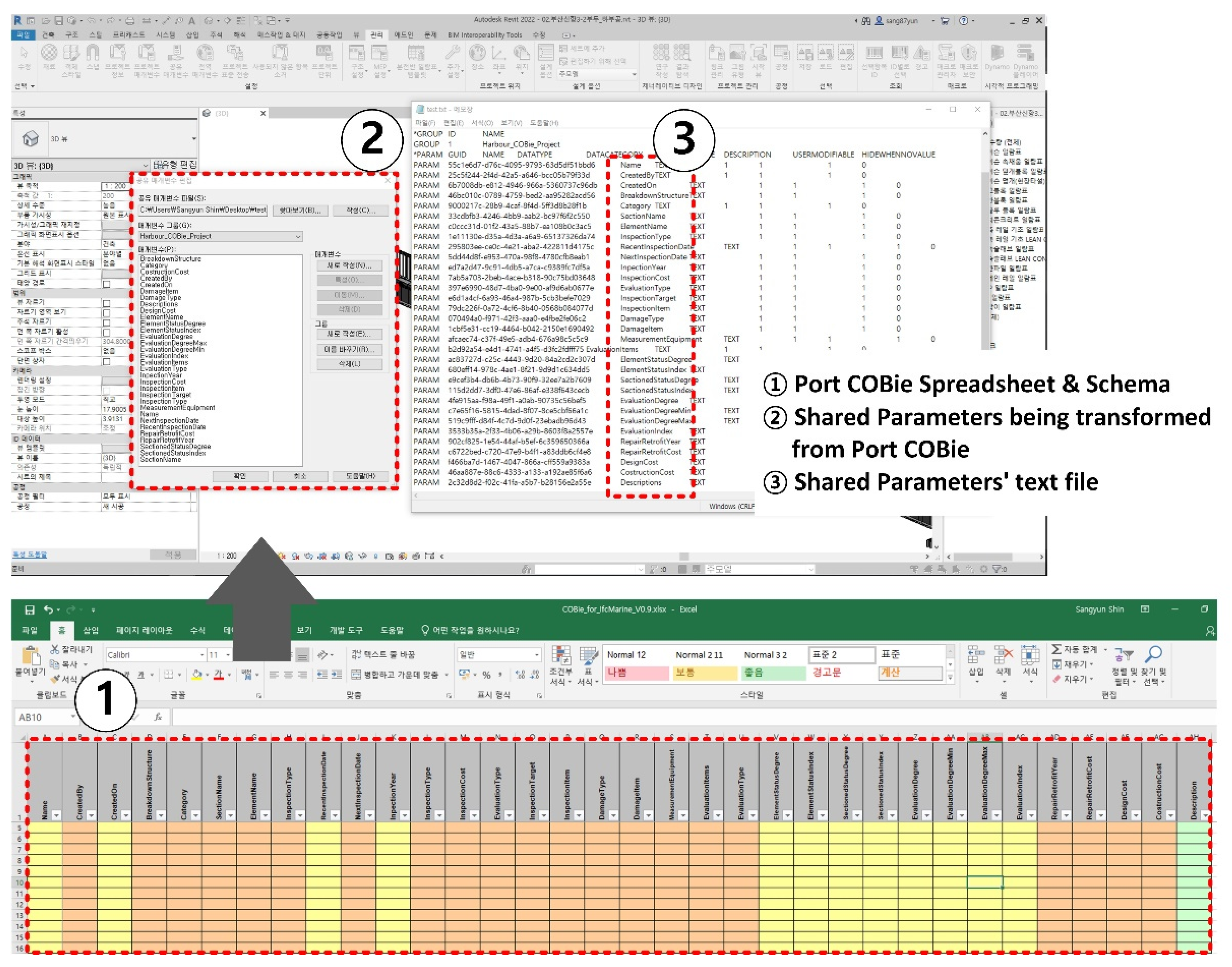
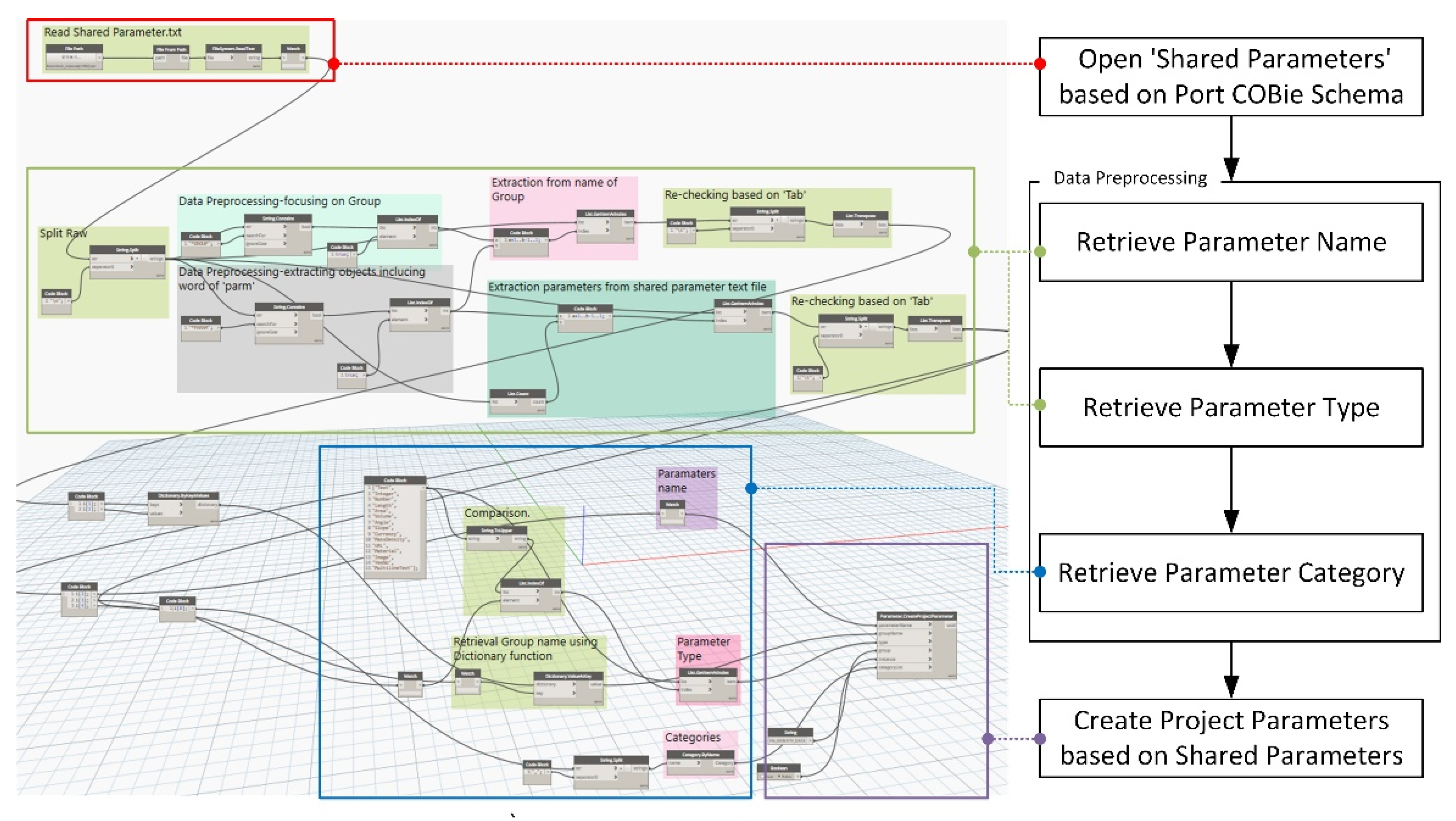
- Development When the COBie sheet analysis is completed (based upon the analysis results), information in each sheet should be parameterized so that attribute values can be inputted. In this study, the COBie sheet parameter algorithm was developed and implemented using Dynamo. Dynamo is a visual coding program available as an add-in program for Revit. To convert COBie into properties in Revit, the storage space into which COBie data can be inputted must be first created as a shared parameter. For example, properties such as “Name,” “CreateBy,” “CreateOn,” “BreakdownStructure,” “TypeName,” “Suppliers,” “Description,” “SetNumber,” and “PartNumber” were available in the Replacement tab of the port BIM COBie spreadsheet implemented in this study. Because these can hold individual property values, space is required to store these property values in Revit; such a space was implemented as a shared parameter in this study. Creating a shared parameter in Revit is an easy task; however, the port COBie developed in this study includes 24 sheets with a total of 332 properties. The task of creating a large number of shared parameters can be easily solved via Dynamo modeling. Figure 11 shows the process of converting the properties of the COBie shared parameters in Dynamo. The first step toward creating shared parameters through Dynamo is to reconfigure the sheet containing each property of the port COBie to match the shared parameters created (Figure 13).
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jofré-Briceño, C.; Rivera, F.M.-L.; Atencio, E.; Herrera, R.F. Implementation of Facility Management for Port Infrastructure through the Use of UAVs, Photogrammetry and BIM. Sensors 2021, 21, 6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, J.S.; Cho, G.H.; Ju, K.B. Development method of BIM data modeling guide for facility management: Focusing on building mechanical system. Korean J. Air Cond. Refrig. Eng. 2013, 25, 216–224. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.H.; Lee, S.G. COBIE: Information Exchange Framework for Facility Management. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2012, 13, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Alnaggar, A.; Pitt, M. Towards a conceptual framework to manage BIM/COBie asset data using a standard project management methodology. J. Facil. Manag. 2019, 17, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, Y.; Hu, M. Research on information model of urban infrastructures intelligent O&M based on lifecycle. In Life-Cycle Civil Engineering: Innovation, Theory and Practice; Airong, C., Xin, R., Dan, M.F., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2021; pp. 1515–1520. [Google Scholar]
- An, H.K.; Yoo, J.H.; Lee, S.K.; Jang, H.S.; Son, B.S. Information Requirements Analysis for BIM-Based Facility Management System. J. Archit. Inst. Korea Plan. Des. 2012, 11, 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- East, E.W.; Nisbet, N.; Liebich, T. Facility Management Handover Model View. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2013, 27, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motawa, I.; Almarshad, A. A knowledge-based BIM system for building maintenance. Autom. Constr. 2013, 29, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerik-Gerber, B.; Jazizadeh, F.; Li, N.; Calis, G. Application areas and data requirements for BIM-enabled facilities management. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2012, 138, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Yu, J.H.; An, H.K. Improvement of information collection system in design and construction phases for efficient facility management. J. Archit. Inst. Korea Plan. Des. 2012, 28, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, S.-W.; Kim, S.-D.; Park, M.-K. Application of a 3D Graphic Model for Bridge Maintenance. Korean J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2011, 12, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, B.G.; Kim, J.W.; Ji, S.G.; Seo, J.W. A study on BIM guidelines for model-based infrastructure management. J. KIBIM 2012, 2, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, K.-W.; Kwon, T.-H.; Lee, S.-H. COBie Based Maintenance Document Generation of Railway Track. J. Comput. Struct. Eng. Inst. Korea 2017, 30, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.S.; Won, J.S.; Shin, J.Y. Development of IFC Standard for Securing Interoperability of BIM Data for Port Facilities. J. KIBIM 2020, 10, 9–22. [Google Scholar]
- Yalcinkaya, M.; Singh, V. Visual COBie for facilities management: A BIM integrated, visual search and information management platform for COBie extension. Facilities 2019, 37, 502–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- East, B.; Carrasquillo-Mangual, M. The COBie Guide, a Commentary to the NBIMS-US COBie Standard. 2012. Available online: https://www.bimpedia.eu/static/nodes/1010/COBie_Guide_-_Public_Release_3.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2021).
- East, W. bSa Construction Operations Building Information Exchange (COBie): Means and Methods; The National Institute of Building Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Teo, E.A.L. Perceived benefits and issues associated with COBie datasheet handling in the construction industry. Facilities 2021, 39, 321–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdepeñas, P.; Pérez, M.D.E.; Henche, C.; Rodríguez-Escribano, R.; Fernández, G.; López-Gutiérrez, J.-S. Application of the BIM Method in the Management of the Maintenance in Port Infrastructures. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, K. A technology trifecta: LiDAR, BIM, and GIS converge to bring business efficiencies to milwaukee metropolitan sewerage district. LiDAR Mag. ESRI 2012, 2. Available online: https://lidarmag.com/issue/volume-02-issue-06/ (accessed on 11 December 2021).
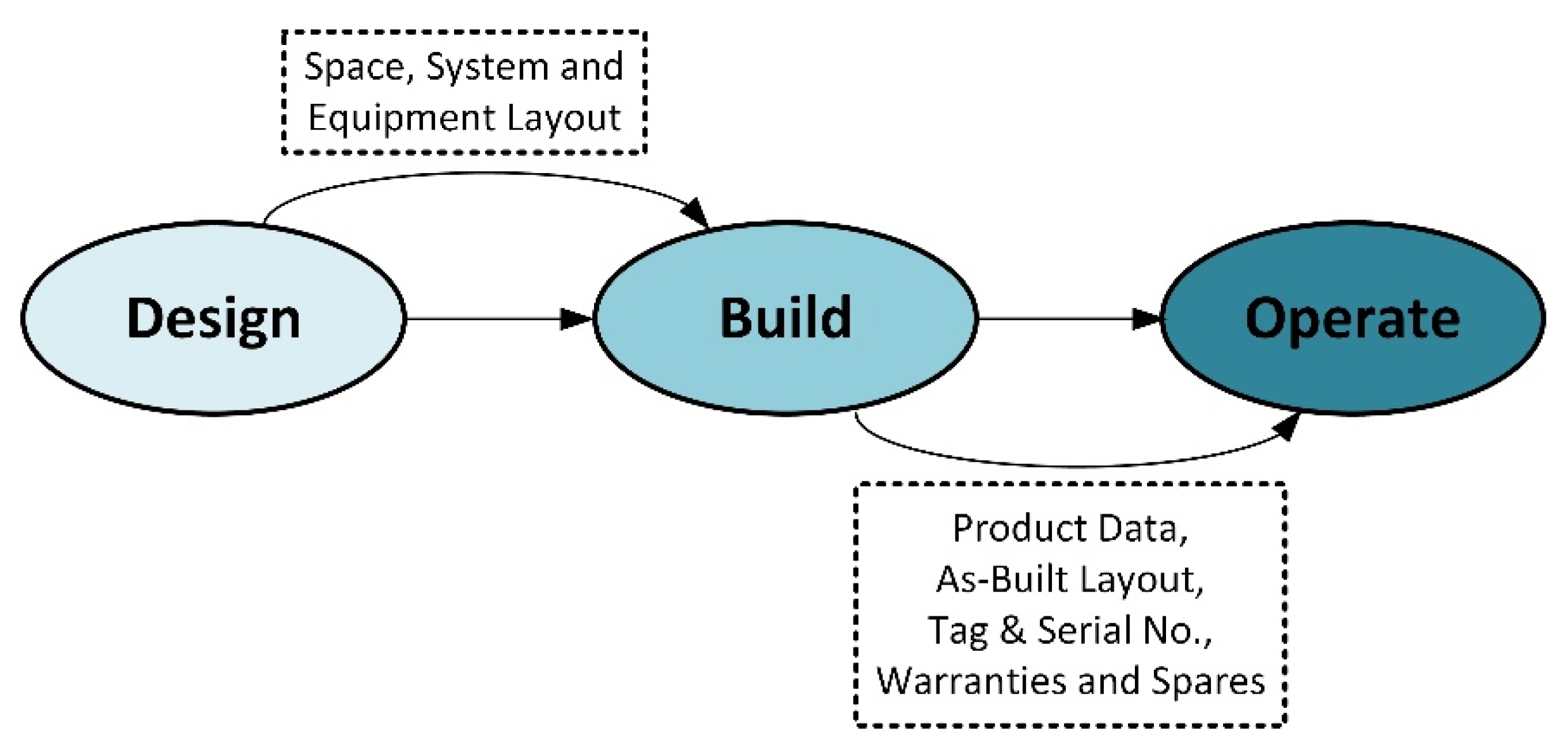


| Construction Phase | Stakeholders | Required Information |
|---|---|---|
| Architectural Programming | Designer | Contact, Facility, Floor, Space, Zone |
| Architectural Design | Designer | Type, Component, Attribute |
| Coordinated Design | Designer | Type, Component, Manufacturer Information (in Component), System, Coordinate, Connection |
| Construction Document | Designer | Spatial Assets, Manufacturer Information (in Component), Fixed Assets, Document, Attribute |
| Construction Mobilization | Contractor | Document |
| Construction 60% Complete | Contractor | Subcontractor Contract Information, Manufacturer Contract Information, Room Tag, Government Furnished Product, Bar Codes, Approved Submittals, Attribute |
| Beneficial Occupancy | Contractor | Spatial Assets, Equipment Assets, Parts and Warranty Contract, Replacement Parts, Detailed Parts Set |
| Fiscal Completion | Contractor | Updated previous phase information, as needed |
| System Name | Use Purpose | COBie Data Processing | Usage Phase |
|---|---|---|---|
| dRoufus | To generate COBie data | COBie data from spreadsheet were extracted from BIM tool, then are imported to the system. | Planning |
| Onuma System | To generate COBie data | IFC is extracted from BIM tool, then it is imported to the system, COBie data are generated using the system. COBie data formed spreadsheet were extracted from BIM tool, then are imported to the system. | Planning |
| AECOsim Building Designer | To generate COBie data | IFC is extracted from BIM tool, then it is imported to the system, COBie data are generated using the system. | Design |
| Revit, | To generate COBie data | COBie data are entered using Plug-in, then a spreadsheet is extracted. | Design |
| EcoDomus | Construction | ||
| cBIM, | To generate COBie data | First, COBie data are entered into COBie spreadsheet, then sheet is imported to the system. | Construction |
| AiM 6.3 | Operation |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, S.; Moon, H.; Shin, J. BIM-Based Maintenance Data Processing Mechanism through COBie Standard Development for Port Facility. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031304
Shin S, Moon H, Shin J. BIM-Based Maintenance Data Processing Mechanism through COBie Standard Development for Port Facility. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(3):1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031304
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Sangyun, Hyounseok Moon, and Jaeyoung Shin. 2022. "BIM-Based Maintenance Data Processing Mechanism through COBie Standard Development for Port Facility" Applied Sciences 12, no. 3: 1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031304
APA StyleShin, S., Moon, H., & Shin, J. (2022). BIM-Based Maintenance Data Processing Mechanism through COBie Standard Development for Port Facility. Applied Sciences, 12(3), 1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031304





