Landslide Susceptibility Modeling Using a Deep Random Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
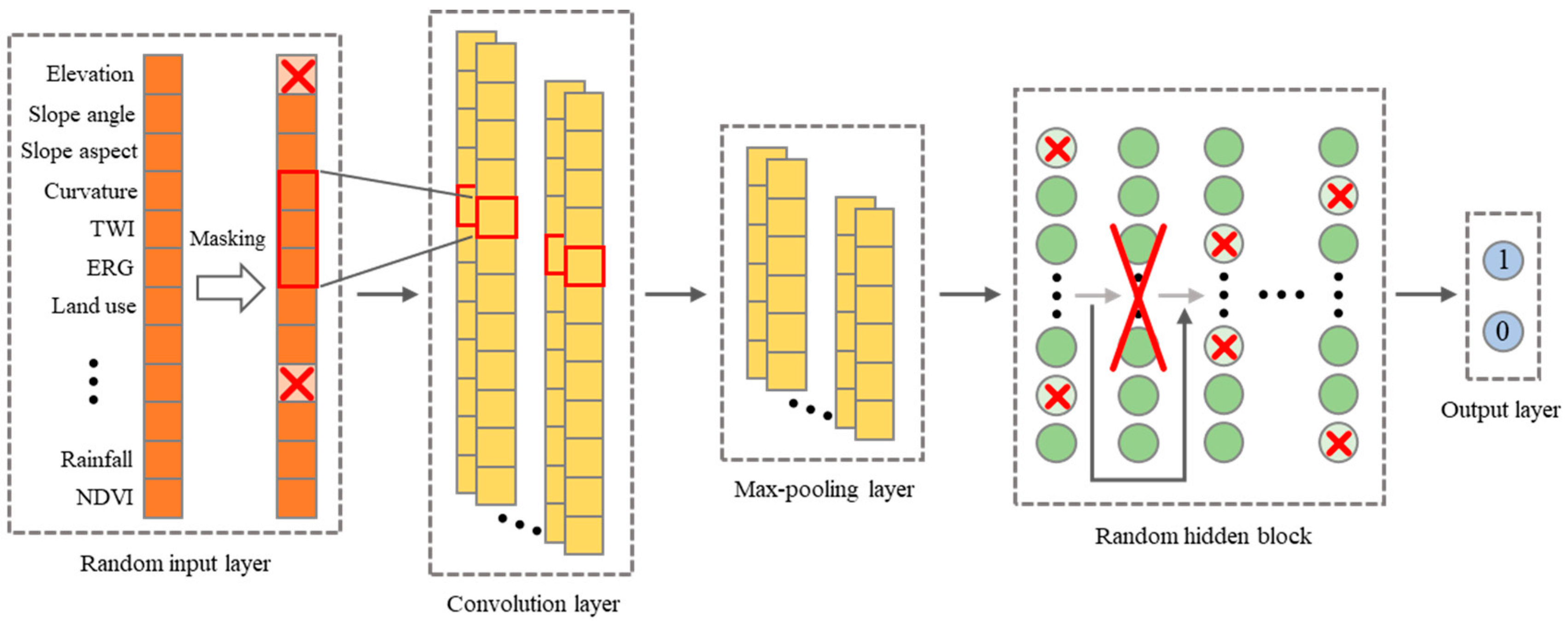
2.1. Whole Structure of the DRNN
2.2. Random Input Layer
2.3. Convolutional and Max-Pooling Layers
2.4. Random Hidden Block
2.5. Output Layer
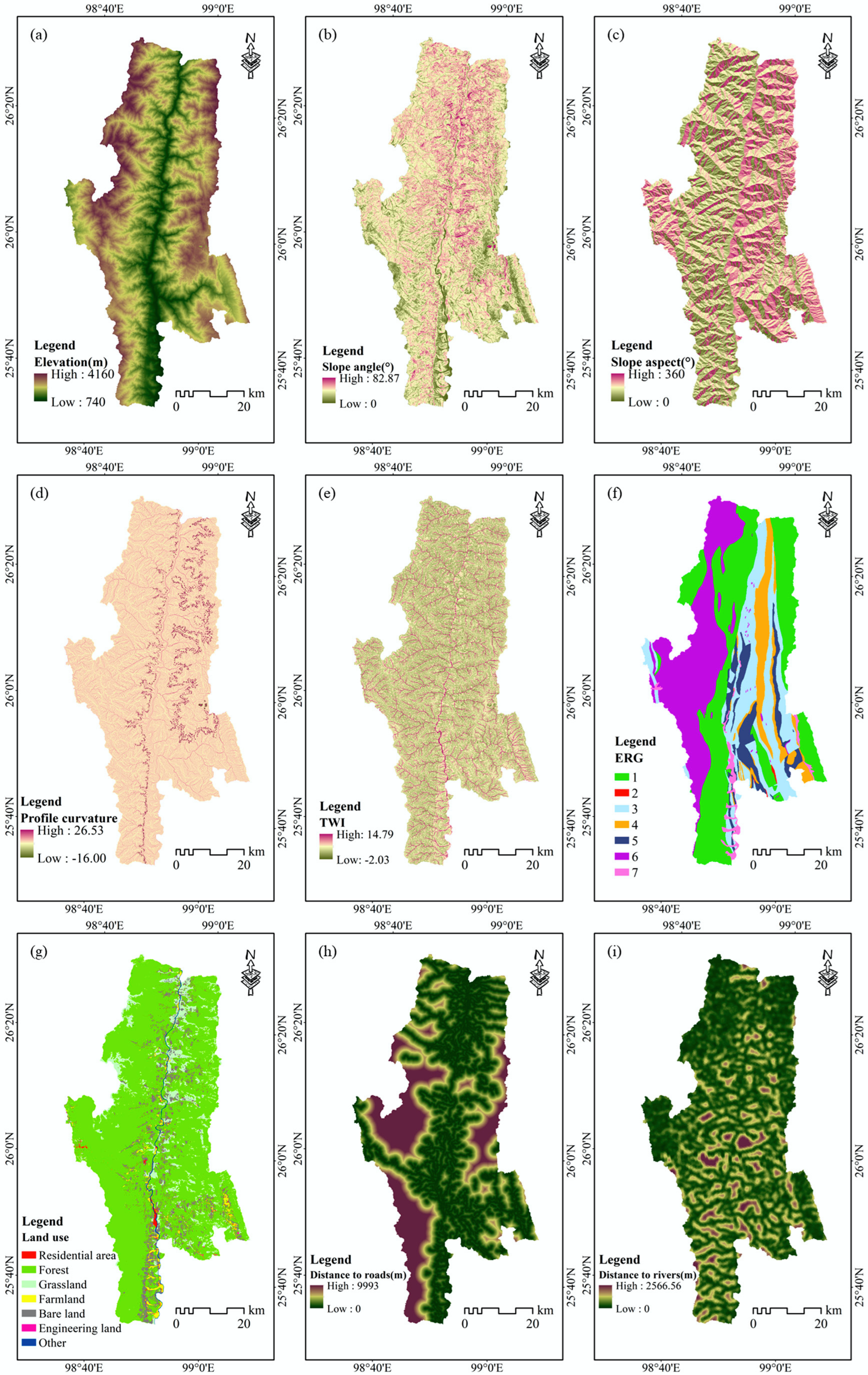
3. Study Area and Data Used
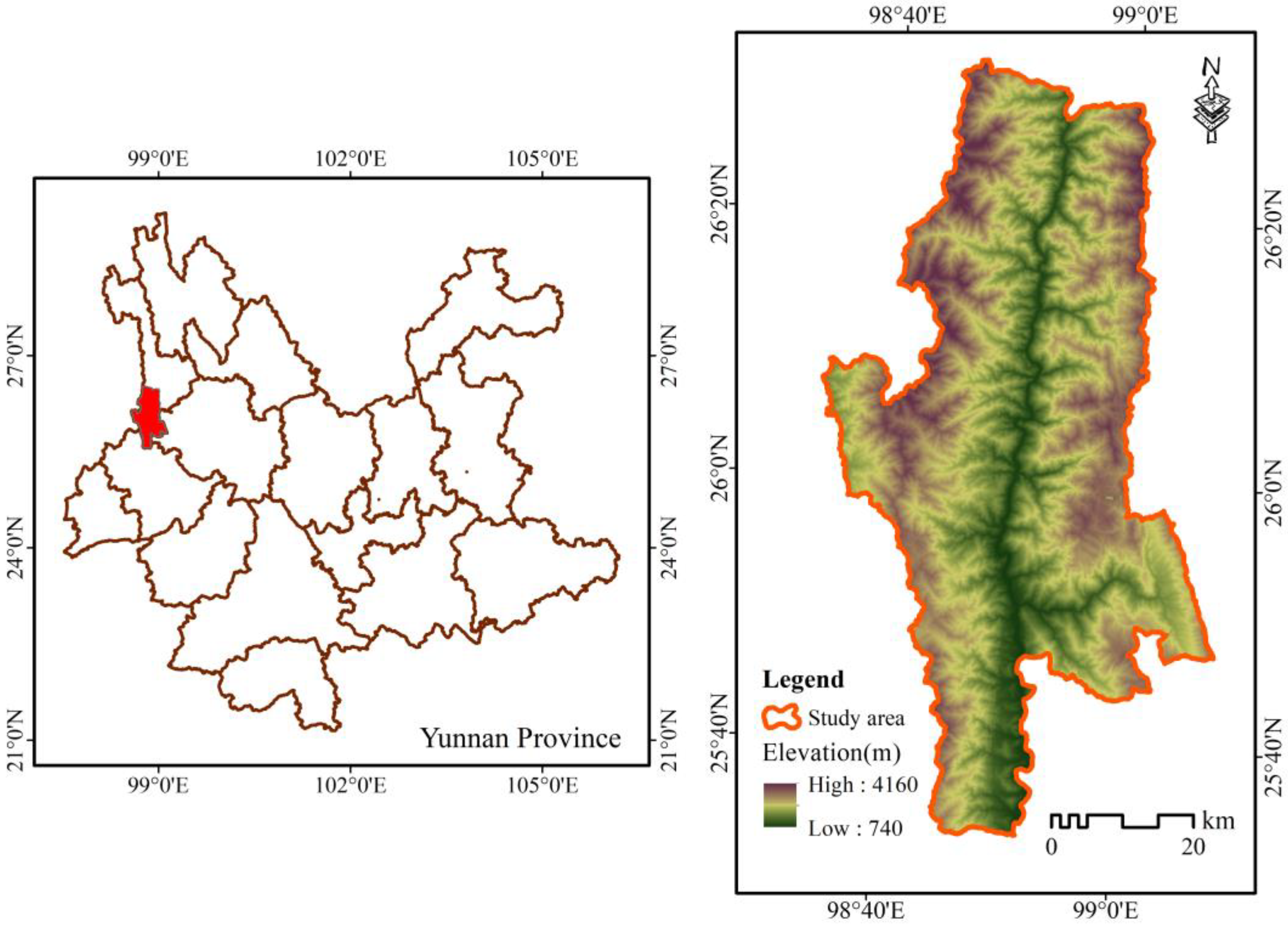
3.1. Study Area
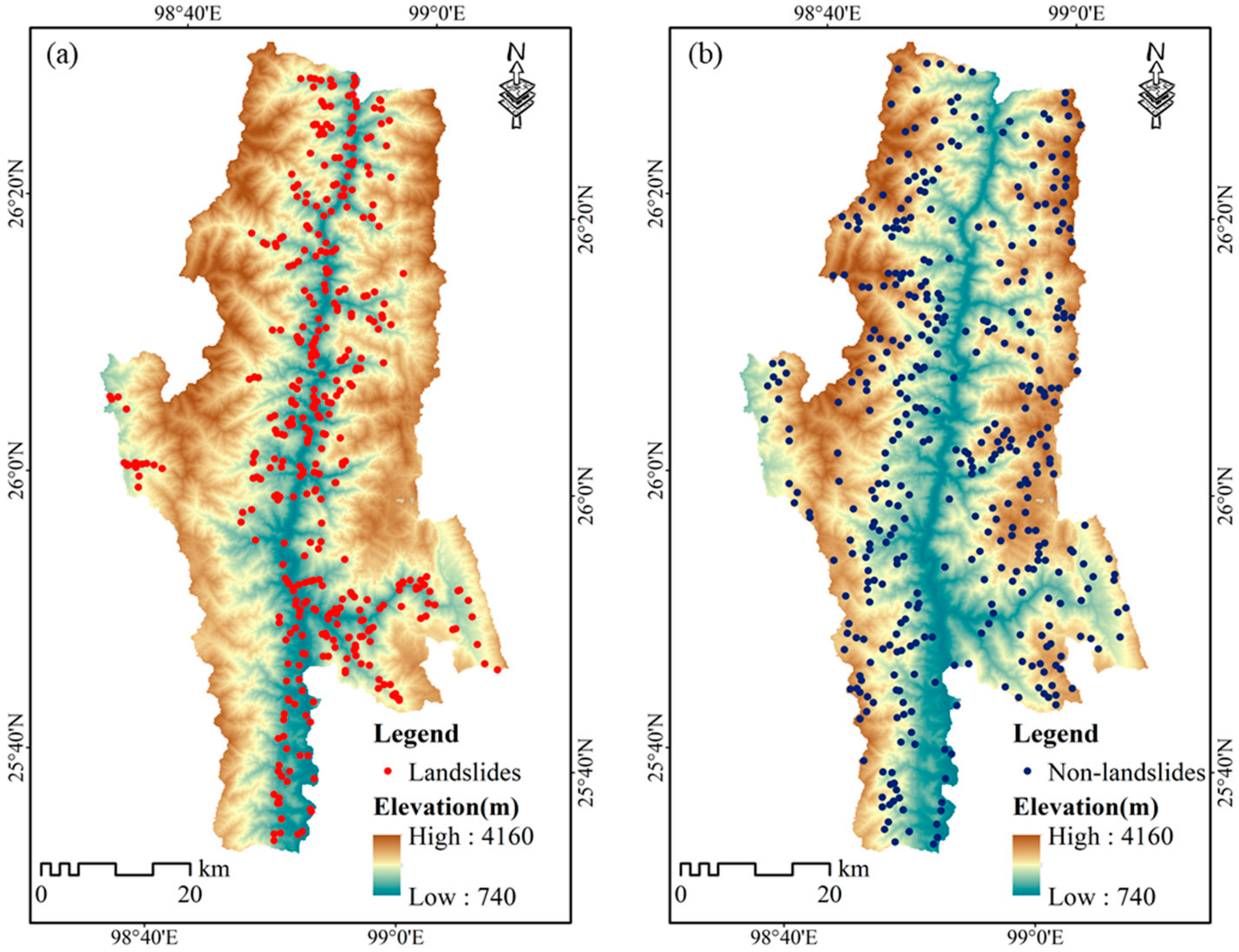
3.2. Landslide Inventory Map
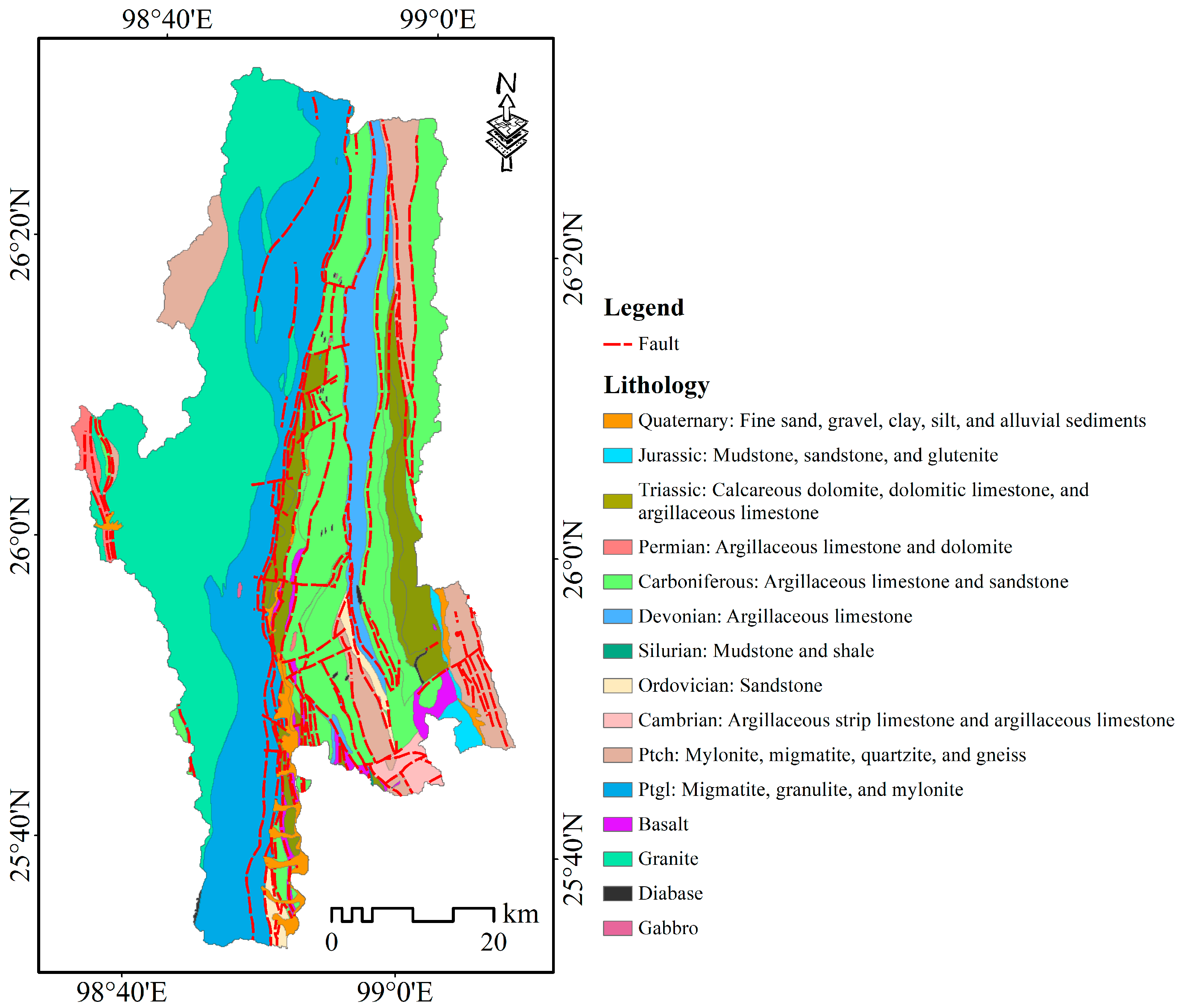
3.3. Landslide Conditioning Factors
4. Results and Discussion
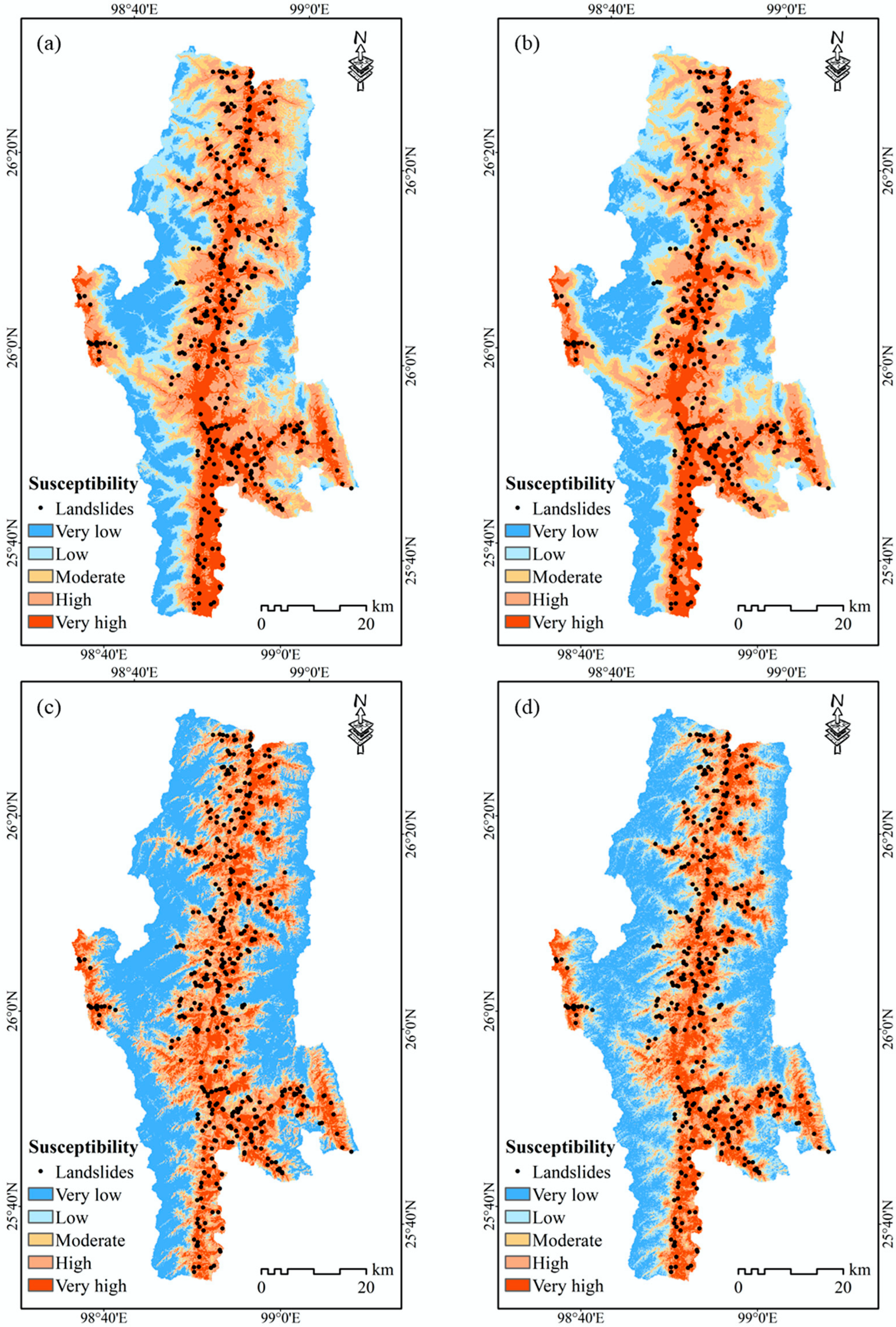
4.1. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping
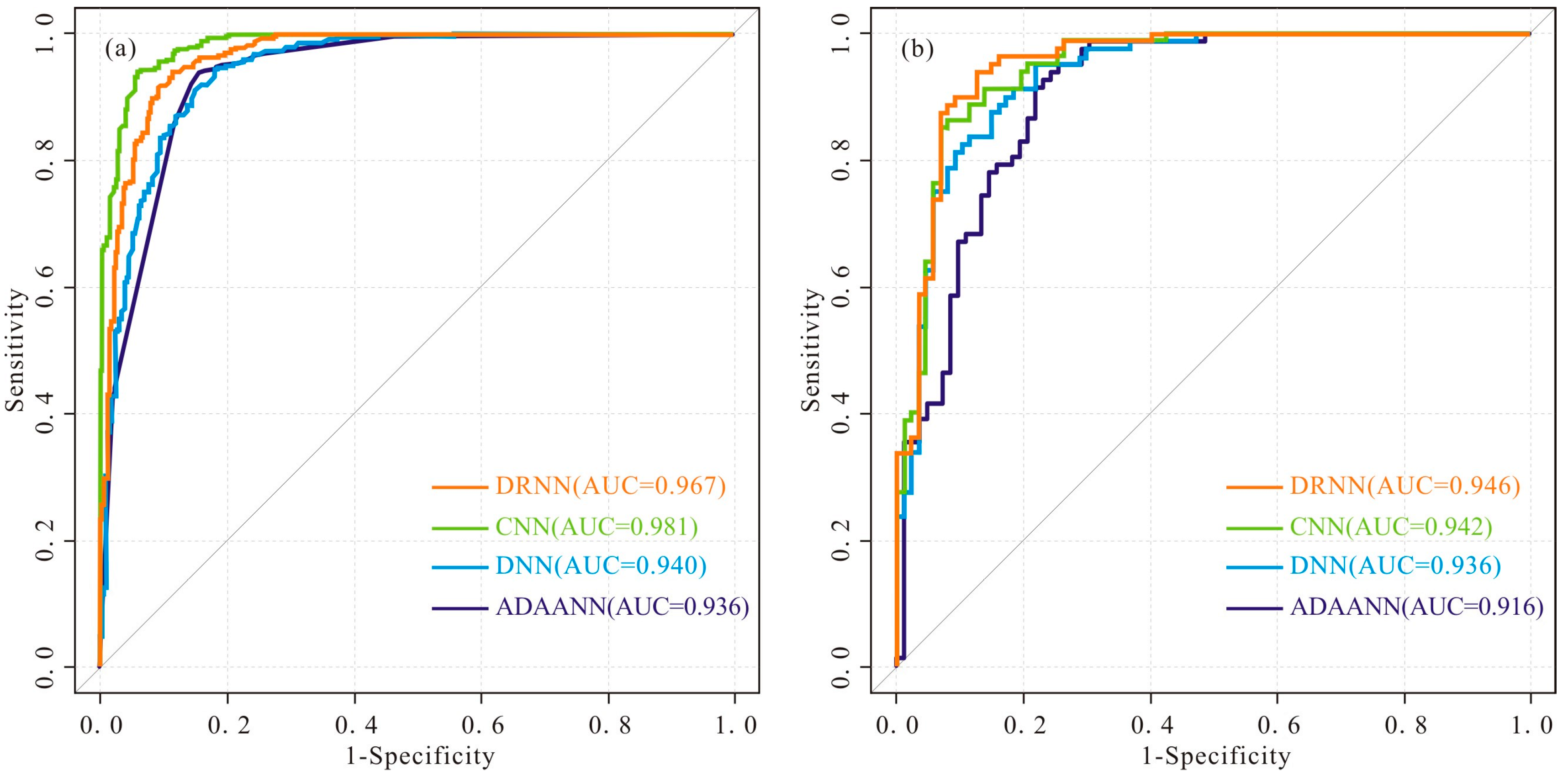
4.2. Performance Evaluation and Comparison
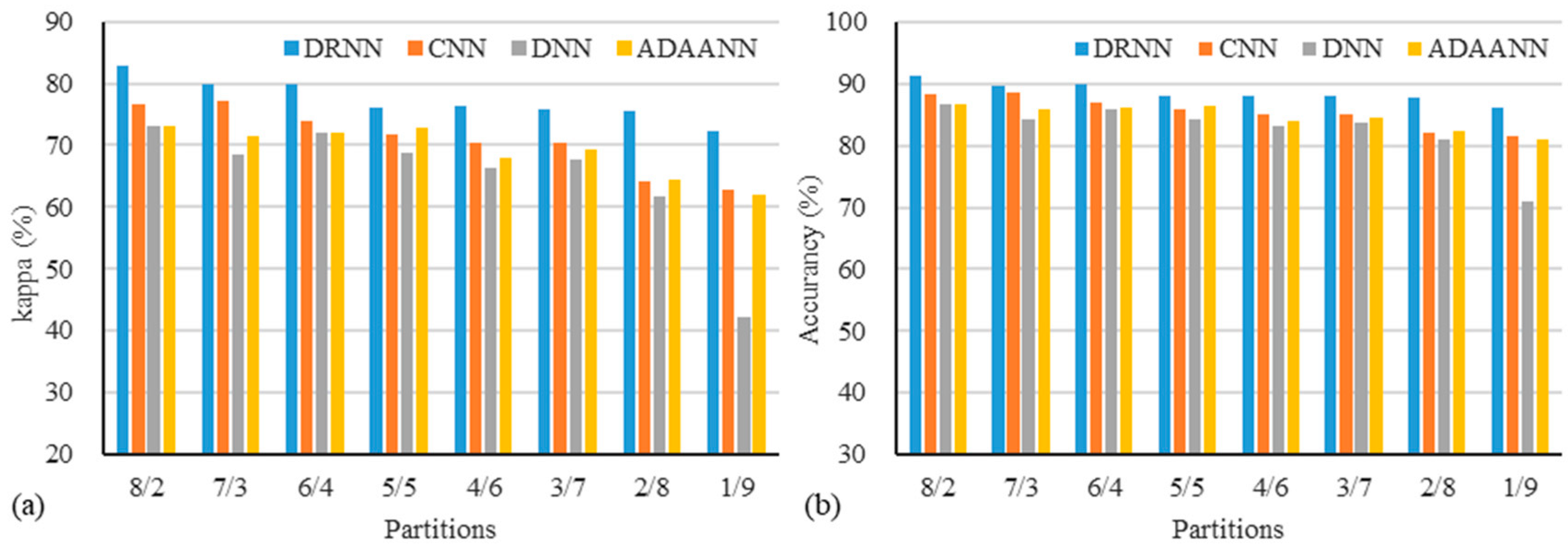
4.3. Robustness to Training Data Size
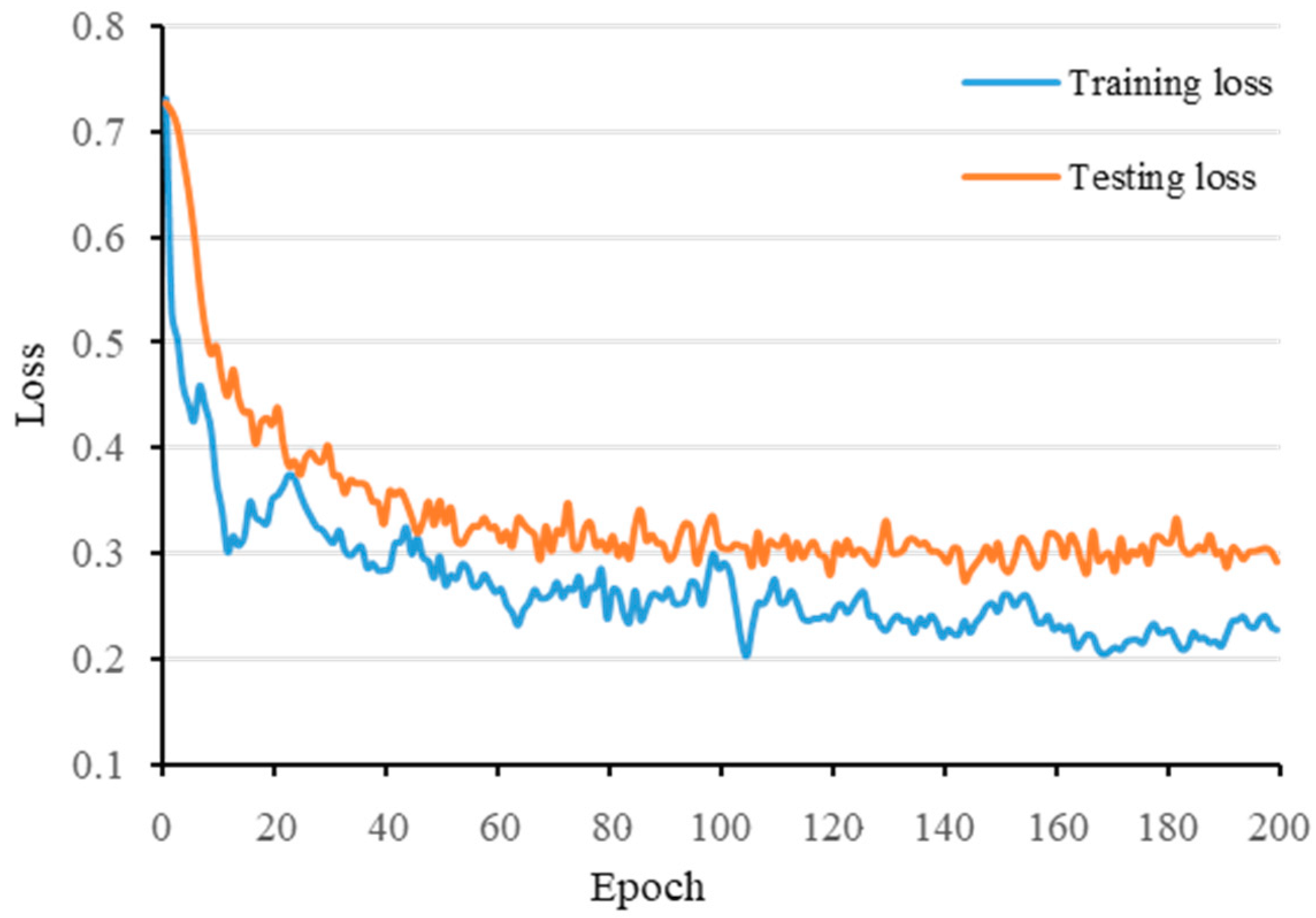
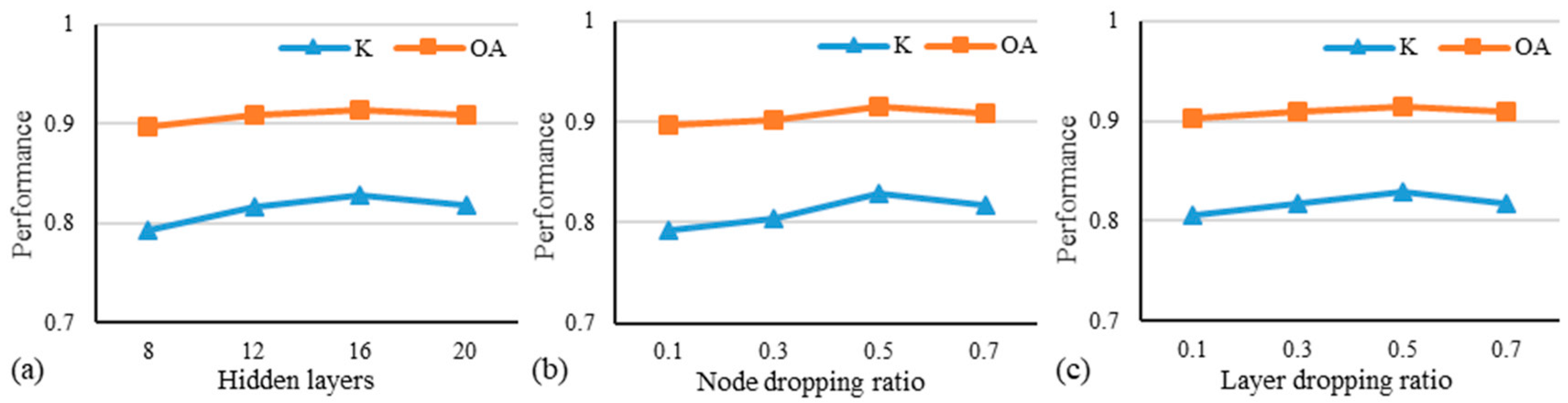
4.4. Influence of Critical Parameter Settings
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Korup, O. Geomorphic Hazard Assessment of Landslide Dams in South Westland, New Zealand: Fundamental Problems and Approaches. Geomorphology 2005, 66, 167–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Wang, W.D.; Han, Z. A Variable Weight Combination Model for Prediction on Landslide Displacement Using Ar Model, Lstm Model, and Svm Model: A Case Study of the Xinming Landslide in China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Yue, J.P.; Chen, C. Interval Estimation of Landslide Displacement Prediction Based on Time Series Decomposition and Long Short-Term Memory Network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 3187–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.X.; Huo, J.Y.; Li, C.J.; Zhang, Y.N. Landslide Displacement Prediction Based on a Two-Stage Combined Deep Learning Model under Small Sample Condition. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, F.S.; Calvello, M.; Liu, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.M.; Lacasse, S. Machine Learning and Landslide Studies: Recent Advances and Applications. Nat. Hazards 2022, 114, 1197–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.A.; Gu, X.; Tang, L.B.; Yin, Y.P.; Liu, D.S.; Zhang, Y.M. Application of Machine Learning, Deep Learning and Optimization Algorithms in Geoengineering and Geoscience: Comprehensive Review and Future Challenge. Gondwana Res. 2022, 109, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Saha, A.; Hembram, T.K.; Pradhan, B.; Alamri, A.M. Evaluating the Performance of Individual and Novel Ensemble of Machine Learning and Statistical Models for Landslide Susceptibility Assessment at Rudraprayag District of Garhwal Himalaya. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.P.; Patel, N.; Ghose, M.K.; Debnath, P. Application of Frequency Ratio and Likelihood Ratio Model for Geo-Spatial Modelling of Landslide Hazard Vulnerability Assessment and Zonation: A Case Study from the Sikkim Himalayas in India. Geocarto Int. 2014, 29, 128–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourghasemi, H.R.; Rossi, M. Landslide Susceptibility Modeling in a Landslide Prone Area in Mazandarn Province, North of Iran: A Comparison between Glm, Gam, Mars, and M-Ahp Methods. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 130, 609–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, R.K.; Hasegawa, S.; Nonomura, A.; Yamanaka, M.; Masuda, T.; Nishino, K. Gis-Based Weights-of-Evidence Modelling of Rainfall-Induced Landslides in Small Catchments for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping. Environ. Geol. 2008, 54, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.W. Using Maximum Entropy Modeling for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping with Multiple Geoenvironmental Data Sets. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 937–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, M.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Vafakhah, M.; Pradhan, B. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping at Vaz Watershed (Iran) Using an Artificial Neural Network Model: A Comparison between Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) and Radial Basic Function (RBF) Algorithms. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 2873–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.Q.; Gong, J.H.; Gao, S.; Wang, D.C.; Cui, T.J.; Li, Y.; Wei, B.Q. Susceptibility Assessment of Earthquake-Induced Landslides Using Bayesian Network: A Case Study in Beichuan, China. Comput. Geosci. 2012, 42, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Dai, F.C.; Xu, X.W.; Lee, Y.H. Gis-Based Support Vector Machine Modeling of Earthquake-Triggered Landslide Susceptibility in the Jianjiang River Watershed, China. Geomorphology 2012, 145, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xie, X.S.; Peng, J.B.; Wang, J.L.; Duan, Z.; Hong, H.Y. Gis-Based Landslide Susceptibility Modelling: A Comparative Assessment of Kernel Logistic Regression, Naive-Bayes Tree, and Alternating Decision Tree Models. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2017, 8, 950–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.M.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Pourtaghi, Z.S.; Al-Katheeri, M.M. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Random Forest, Boosted Regression Tree, Classification and Regression Tree, and General Linear Models and Comparison of Their Performance at Wadi Tayyah Basin, Asir Region, Saudi Arabia. Landslides 2016, 13, 839–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xie, X.S.; Wang, J.L.; Pradhan, B.; Hong, H.Y.; Bui, D.T.; Duan, Z.; Ma, J.Q. A Comparative Study of Logistic Model Tree, Random Forest, and Classification and Regression Tree Models for Spatial Prediction of Landslide Susceptibility. Catena 2017, 151, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, A.; Kardani, N.; Alzo’ubi, A.K.; Roy, B.; Samui, P.; Gandomi, A.H. Novel Integration of Extreme Learning Machine and Improved Harris Hawks Optimization with Particle Swarm Optimization-Based Mutation for Predicting Soil Consolidation Parameter. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2022, 14, 1588–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, P.; Loveson, V.J.; Das, B.; Kotha, M. Novel Ensemble Machine Learning Models in Flood Susceptibility Mapping. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 4571–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.F.; Meier, M.A.; Hauksson, E.; Zhan, Z.W.; Andrews, J. Machine Learning Seismic Wave Discrimination: Application to Earthquake Early Warning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 4773–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Chen, Y.Z.; Chen, W. Landslide Susceptibility Modeling Using Remote Sensing Data and Random Subspace-Based Functional Tree Classifier. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.D.; Mei, H.B.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, M.D. Performance Evaluation of Ensemble Learning Techniques for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping at the Jinping County, Southwest China. Nat. Hazards 2021, 105, 1663–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Bagging Predictors. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, Y.; Schapire, R.E. A Decision-Theoretic Generalization of on-Line Learning and an Application to Boosting. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 1997, 55, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.J.; Kuncheva, L.I. Rotation Forest: A New Classifier Ensemble Method. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.D.; Zhang, H.; Mei, H.B.; Xiao, D.H.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, M.D. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using the Stacking Ensemble Machine Learning Method in Lushui, Southwest China. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Ryu, J.H.; Won, J.S.; Park, H.J. Determination and Application of the Weights for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using an Artificial Neural Network. Eng. Geol. 2004, 71, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Peng, J.B.; Leng, Y.Q.; Lee, S.; Panahi, M.; Chen, W.; Zhao, X. Hybrids of Support Vector Regression with Grey Wolf Optimizer and Firefly Algorithm for Spatial Prediction of Landslide Susceptibility. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.D.; Huang, C.; Mei, H.B.; Zhang, H. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using an Ensemble Model of Bagging Scheme and Random Subspace-Based Naive Bayes Tree in Zigui County of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 5315–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokach, L. Taxonomy for Characterizing Ensemble Methods in Classification Tasks: A Review and Annotated Bibliography. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2009, 53, 4046–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.D.; Zhang, P.L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.Q. Improving Wetland Cover Classification Using Artificial Neural Networks with Ensemble Techniques. GISci. Remote Sens. 2021, 58, 603–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Z.C.; Hong, H.Y. Comparison of Convolutional Neural Networks for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping in Yanshan County, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 975–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renza, D.; Cardenas, E.A.; Martinez, E.; Weber, S.S. Cnn-Based Model for Landslide Susceptibility Assessment from Multispectral Data. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.C.; Wang, Y.; Peng, L.; Hong, H.Y. Integration of Convolutional Neural Network and Conventional Machine Learning Classifiers for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping. Comput. Geosci. 2020, 139, 104470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarafza, M.; Azarafza, M.; Akgun, H.; Atkinson, P.M.; Derakhshani, R. Deep Learning-Based Landslide Susceptibility Mapping. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.L.; Niu, R.Q. Displacement Prediction of Baijiabao Landslide Based on Empirical Mode Decomposition and Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network in Three Gorges Area, China. Comput. Geosci. 2018, 111, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep Learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, P.; Larochelle, H.; Lajoie, I.; Bengio, Y.; Manzagol, P.A. Stacked Denoising Autoencoders: Learning Useful Representations in a Deep Network with a Local Denoising Criterion. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 3371–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Fang, Z.C.; Wang, Y. Stacking Ensemble of Deep Learning Methods for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 36, 2207–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavzoglu, T.; Teke, A.; Yilmaz, E.O. Shared Blocks-Based Ensemble Deep Learning for Shallow Landslide Susceptibility Mapping. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Chen, T.; Dou, J.; Plaza, A. A Hybrid Ensemble-Based Deep-Learning Framework for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 108, 102713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Chen, J. A Hybrid Deep Learning Method for Landslide Susceptibility Analysis with the Application of Insar Data. Nat. Hazards 2022, 114, 1393–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhuri, I.; Pal, S.C.; Janizadeh, S.; Saha, A.; Ahmadi, K.; Chakrabortty, R.; Islam, A.M.T.; Roy, P.; Shit, M. Application of Novel Deep Boosting Framework-Based Earthquake Induced Landslide Hazards Prediction Approach in Sikkim Himalaya. Geocarto Int. 2022, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.B.; Yin, K.L.; Lacasse, S.; Liu, Z.Q. Time Series Analysis and Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network to Predict Landslide Displacement. Landslides 2019, 16, 677–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameen, M.I.; Pradhan, B.; Lee, S. Application of Convolutional Neural Networks Featuring Bayesian Optimization for Landslide Susceptibility Assessment. Catena 2020, 186, 104249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, O.; Shanableh, T. Cnn and Hevc Video Coding Features for Static Video Summarization. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 72080–72091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.D.; Zhang, P.L.; Zhang, Q. A Novel Framework of Cnn Integrated with Adaboost for Remote Sensing Scene Classification. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; pp. 2643–2646. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.N.; Wei, Y.C.; Liang, X.D.; Dong, J.; Xu, T.F.; Feng, J.S.; Yan, S.C. Attentive Contexts for Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2017, 19, 944–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Su, M.C.; Azzizi, V.T.; Wang, T.K.; Lin, W.J. Smart Project Management: Interactive Platform Using Natural Language Processing Technology. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yang, X.; Xu, C.; Wei, L.S.; Zeng, X.Q. Comparative Study of Convolutional Neural Network and Conventional Machine Learning Methods for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Xiang, L.Y. Method for Meteorological Early Warning of Precipitation-Induced Landslides Based on Deep Neural Network. Neural Process. Lett. 2018, 48, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.Y.; Qin, S.W.; Qiao, S.S.; Che, W.C.; Chen, Y.; Su, G.; Miao, Q. Assessment of Landslide Susceptibility Combining Deep Learning with Semi-Supervised Learning in Jiaohe County, Jilin Province, China. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Baek, W.K.; Jung, H.S.; Lee, S. Susceptibility Mapping on Urban Landslides Using Deep Learning Approaches in Mt. Umyeon. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.B.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.T.; Wang, S.X.; Wang, J.M.; Ji, J.W.; Wang, Z.Q. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Ant Colony Optimization Strategy and Deep Belief Network in Jiuzhaigou Region. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 11042–11057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemian, B.; Shahabi, H.; Shirzadi, A.; Al-Ansari, N.; Jaafari, A.; Kress, V.R.; Geertsema, M.; Renoud, S.; Ahmad, A. A Robust Deep-Learning Model for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping: A Case Study of Kurdistan Province, Iran. Sensors 2022, 22, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Lin, X.K.; Qi, X.; Li, H.D.; Yang, J.J. Landslide Susceptibility Analysis Based on a Pso-Dbn Prediction Model in an Earthquake-Stricken Area. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Saha, A.; Hembram, T.K.; Kundu, B.; Sarkar, R. Novel Ensemble of Deep Learning Neural Network and Support Vector Machine for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping in Tehri Region, Garhwal Himalaya. Geocarto Int. 2022, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, B.; Zafar, A.; Khalil, U. Development of Integrated Deep Learning and Machine Learning Algorithm for the Assessment of Landslide Hazard Potential. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 13493–13512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, W.L.; Rezaie, F.; Nur, A.S.; Panahi, M.; Khosravi, K.; Lee, C.W.; Lee, S. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) with Metaheuristic Optimization Algorithms for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping in Icheon, South Korea. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 305, 114367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.B.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.T.; Wang, S.X.; Wang, Z.Q.; Ji, J.W.; Wang, J.M.; Zou, W.J.; You, D.; Qin, G. A Novel Intelligent Method Based on the Gaussian Heatmap Sampling Technique and Convolutional Neural Network for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, B.; Nefeslioglu, H.A.; Sezer, E.A.; Akcayol, M.A.; Gokceoglu, C. An Experimental Research on the Use of Recurrent Neural Networks in Landslide Susceptibility Mapping. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Peng, G.Z. Landslide Susceptibility Assessment Using Integrated Deep Learning Algorithm along the China-Nepal Highway. Sensors 2018, 18, 4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Huang, L.H.; Fan, L.Y.; Huang, J.S.; Huang, F.M.; Chen, J.W.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, Y.H. Landslide Susceptibility Prediction Modeling Based on Remote Sensing and a Novel Deep Learning Algorithm of a Cascade-Parallel Recurrent Neural Network. Sensors 2020, 20, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, K.; Wang, F.W. The Performance of Using an Autoencoder for Prediction and Susceptibility Assessment of Landslides: A Case Study on Landslides Triggered by the 2018 Hokkaido Eastern Iburi Earthquake in Japan. Geoenviron. Disasters 2019, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.M.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C.B.; Wang, Y.H.; Huang, J.S.; Zhu, L. A Deep Learning Algorithm Using a Fully Connected Sparse Autoencoder Neural Network for Landslide Susceptibility Prediction. Landslides 2020, 17, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.; Wang, F.W. An Extreme Rainfall-Induced Landslide Susceptibility Assessment Using Autoencoder Combined with Random Forest in Shimane Prefecture, Japan. Geoenviron. Disasters 2020, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cui, P.; Ye, C.M.; Marcato, J.; Zhang, Z.T.; Guo, J.; Li, J. Accurate Prediction of Earthquake-Induced Landslides Based on Deep Learning Considering Landslide Source Area. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.F.; Li, J.J.; Fan, F.L. Classification of Landslides on the Southeastern Tibet Plateau Based on Transfer Learning and Limited Labelled Datasets. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 12, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, B.T.; Bui, D.T.; Prakash, I.; Dholakia, M.B. Rotation Forest Fuzzy Rule-Based Classifier Ensemble for Spatial Prediction of Landslides Using Gis. Nat. Hazards 2016, 83, 97–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.S.; Zhang, W.B.; Xu, X.M.; Xing, X.F. Deep Networks with Stochastic Depth for Acoustic Modelling. In Proceedings of the 2016 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference, Jeju, Korea, 13–16 December 2016; pp. 646–661. [Google Scholar]
- Gustav, L.; Michael, M.; Shakhnarovich, G. Fractalnet: Ultra-Deep Neural Networks without Residuals. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1605.07648. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasi, G.; Lin, T.Y.; Le, Q.V. Dropblock: A Regularization Method for Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 31 (NIPS 2018), Montreal, QC, Canada, 2–8 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Juliev, M.; Mergili, M.; Mondal, I.; Nurtaev, B.; Pulatov, A.; Hubl, J. Comparative Analysis of Statistical Methods for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping in the Bostanlik District, Uzbekistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, A.; Bianchi, P. Convergence and Dynamical Behavior of the Adam Algorithm for Nonconvex Stochastic Optimization. SIAM J. Optim. 2021, 31, 244–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.B.; Zhuang, J.Q.; Mu, J.Q.; Zheng, J.; Zhan, J.W.; Wang, J.; Fu, Y.T. Evaluation of Landslide Susceptibility of the Ya’an-Linzhi Section of the Sichuan-Tibet Railway Based on Deep Learning. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, B.; Zafar, A.; Khalil, U. Comparative Analysis of Multiple Conventional Neural Networks for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping. Nat. Hazards 2022, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.Q.V.; Kim, Y.T. Landslide Spatial Probability Prediction: A Comparative Assessment of Naive Bayes, Ensemble Learning, and Deep Learning Approaches. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 4291–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.S.; Misko, O.; Salumaa, S.O.; Papkov, M.; Palo, K.; Fishman, D.; Parts, L. Evaluating Very Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Nucleus Segmentation from Brightfield Cell Microscopy Images. SLAS Discov. 2021, 26, 1125–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Basic structures | Method Descriptions | References |
|---|---|---|
| Deep feedforward neural network (DNN) |
| [52] |
| [53] | |
| [54] | |
| [55] | |
| [56] | |
| [57] | |
| [58] | |
| Convolution neural network (CNN) |
| [33] |
| [46] | |
| [59] | |
| [60] | |
| [61] | |
| Recurrent neural network (RNN) |
| [62] |
| [63] | |
| [64] | |
| Auto-encoder |
| [65] |
| [66] | |
| [67] | |
| [68] | |
| Deep learning ensemble methods |
| [40] |
| [41] | |
| [42] | |
| [43] | |
| Other methods |
| [44] |
| [44] |
| Class | ADAANN | DNN | CNN | DRNN | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC(%) | PL(%) | LD | PC(%) | PL(%) | LD | PC(%) | PL(%) | LD | PC(%) | PL(%) | LD | |
| Very low | 19.73 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 19.76 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 40.17 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 34.15 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Low | 17.78 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 18.46 | 0.48 | 0.03 | 9.04 | 0.73 | 0.08 | 19.05 | 1.03 | 0.05 |
| Moderate | 14.51 | 1.45 | 0.10 | 14.99 | 1.94 | 0.13 | 10.36 | 2.42 | 0.23 | 11.08 | 5.93 | 0.53 |
| High | 29.21 | 30.51 | 1.04 | 28.60 | 30.99 | 1.08 | 23.46 | 33.90 | 1.44 | 19.06 | 36.34 | 1.91 |
| Very high | 18.57 | 68.04 | 3.66 | 18.22 | 66.59 | 3.65 | 16.98 | 62.95 | 3.71 | 16.66 | 63.14 | 3.79 |
| Models | On the Training Data | On the Testing Data | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA (%) | K | F | MCC | OA (%) | K | F | MCC | |
| ADAANN | 88.22 | 0.764 | 0.889 | 0.771 | 86.59 | 0.732 | 0.869 | 0.733 |
| DNN | 88.26 | 0.765 | 0.882 | 0.767 | 86.58 | 0.731 | 0.866 | 0.732 |
| CNN | 92.53 | 0.850 | 0.925 | 0.851 | 88.41 | 0.767 | 0.883 | 0.767 |
| DRNN | 91.16 | 0.823 | 0.912 | 0.823 | 91.46 | 0.829 | 0.914 | 0.828 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.; Li, F.; Wei, L.; Hu, X.; Yang, Y. Landslide Susceptibility Modeling Using a Deep Random Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12887. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412887
Huang C, Li F, Wei L, Hu X, Yang Y. Landslide Susceptibility Modeling Using a Deep Random Neural Network. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(24):12887. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412887
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Cheng, Fang Li, Lei Wei, Xudong Hu, and Yingdong Yang. 2022. "Landslide Susceptibility Modeling Using a Deep Random Neural Network" Applied Sciences 12, no. 24: 12887. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412887
APA StyleHuang, C., Li, F., Wei, L., Hu, X., & Yang, Y. (2022). Landslide Susceptibility Modeling Using a Deep Random Neural Network. Applied Sciences, 12(24), 12887. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412887






