Bacterial Communities in Informal Dump Sites: A Rich Source of Unique Diversity and Functional Potential for Bioremediation Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Physicochemical Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction and Library Preparation
2.4. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.5. Assessment of Bacterial Catabolic Activities Using Biolog EcoplatesTM
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Variables
3.2. Bacterial Diversity of Different Informal Dump Sites
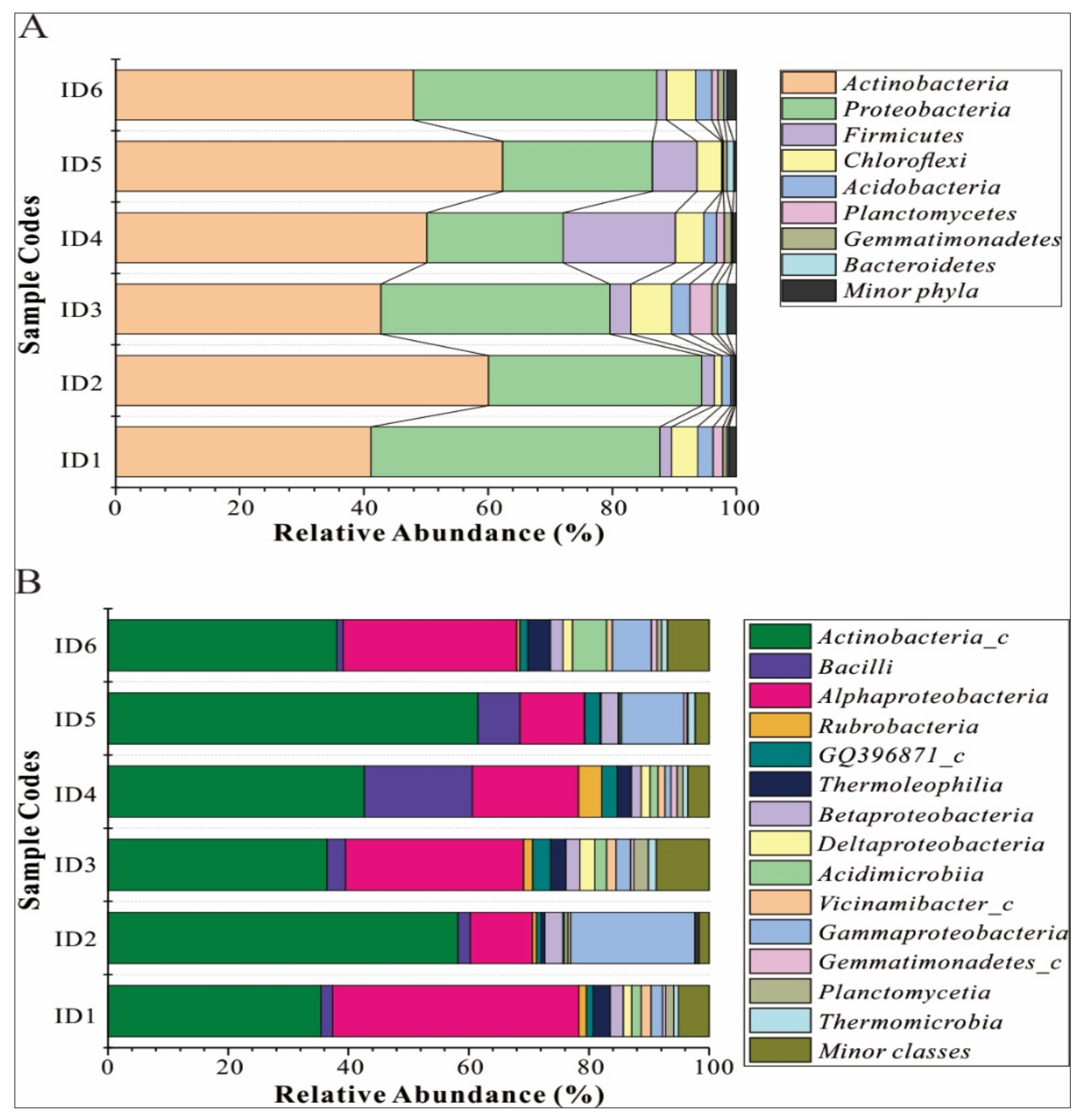
3.3. Bacterial Composition of Different Informal Dump Sites
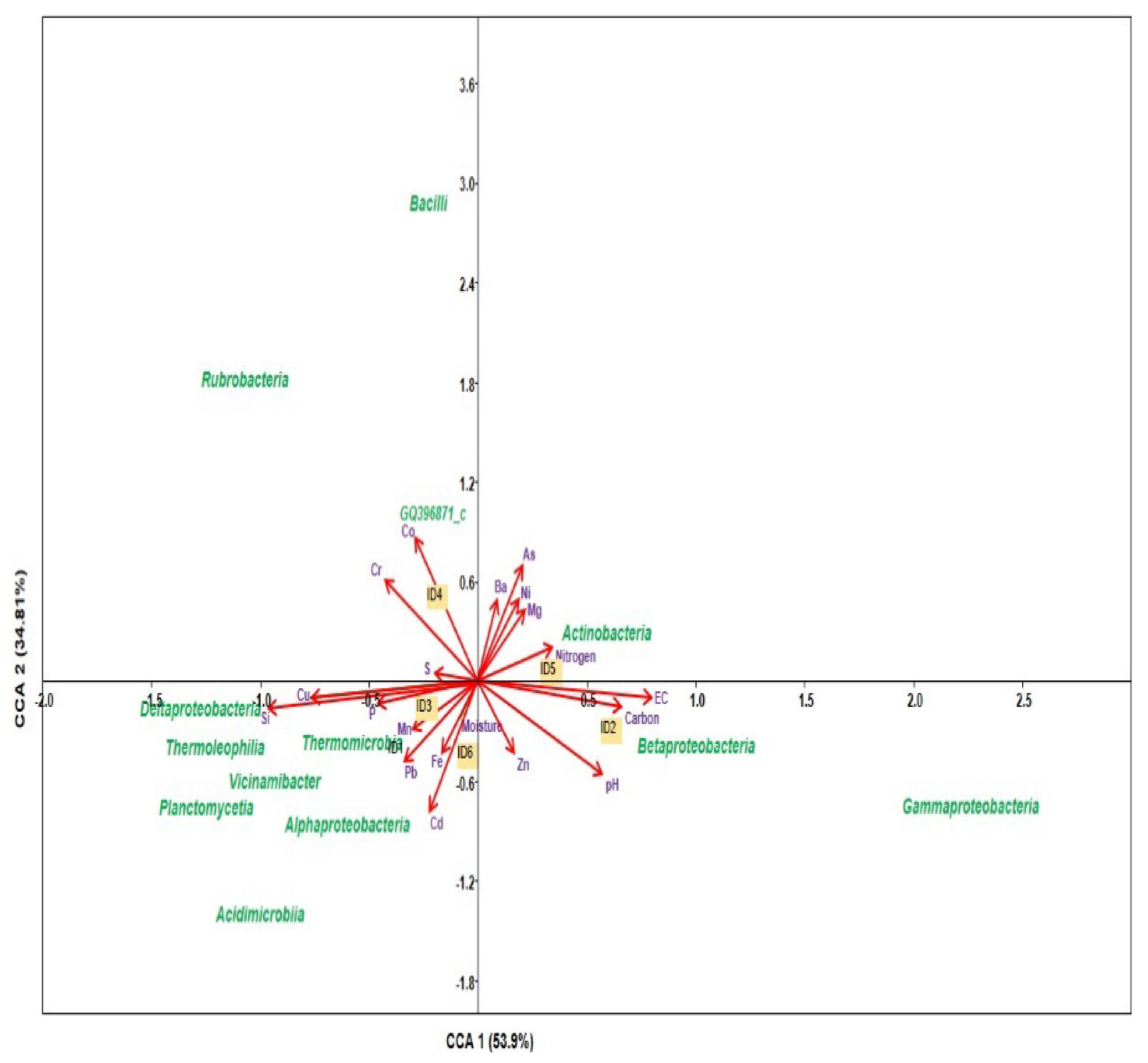
3.4. CCA Analysis
3.5. PICRUSt Predictive Function Profiling
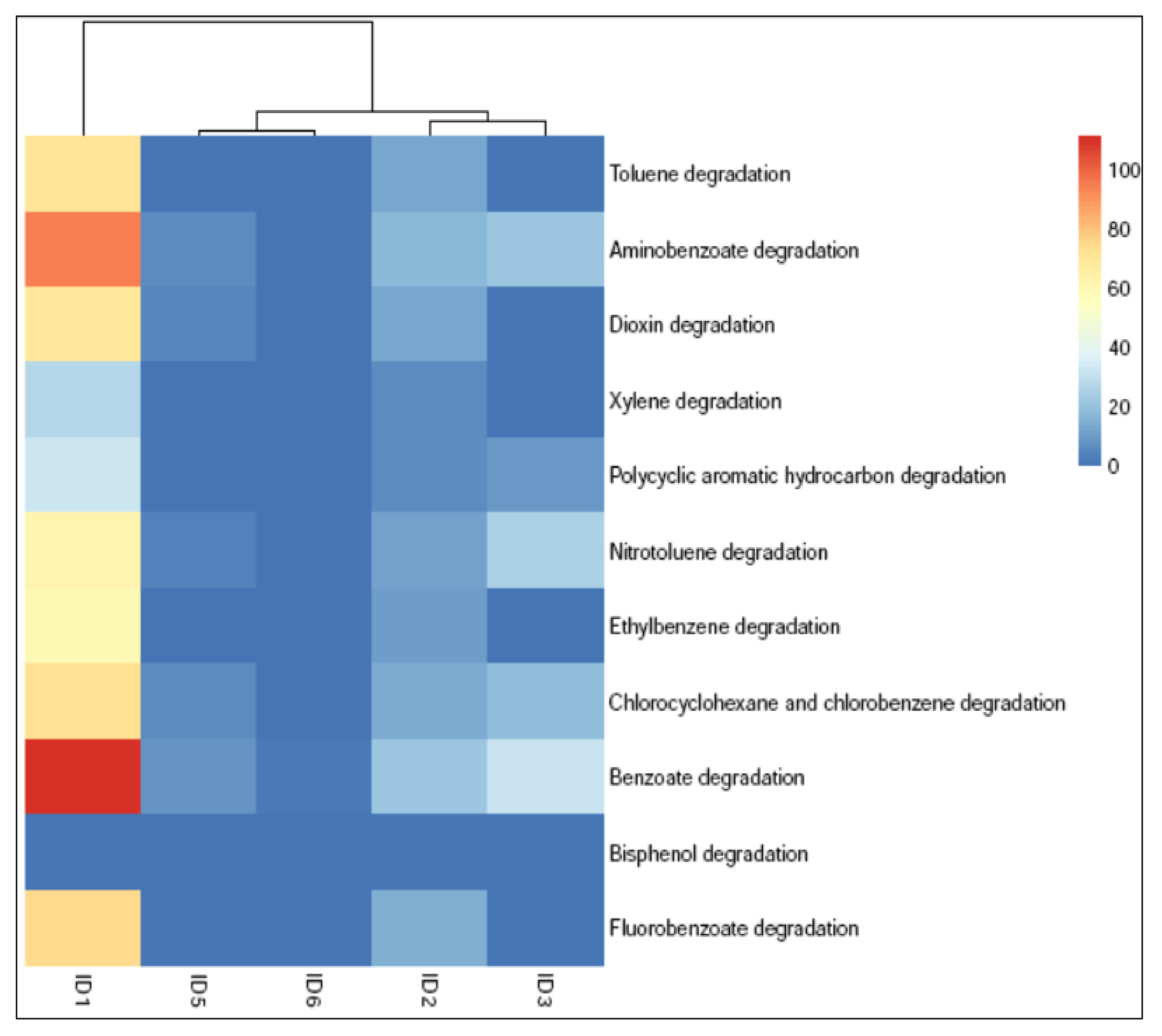
3.6. Catabolic Activity of Soil Bacterial Community in the Dumping Sites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, M.; Xu, P.; Zeng, G.; Yang, C.; Huang, D.; Zhang, J. Bioremediation of soils contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, petroleum, pesticides, chlorophenols and heavy metals by composting: Applications, microbes and future research needs. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frączek, K.; Ropek, D. Municipal waste dumps as the microbiological threat to the natural environment. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2011, 18, 93–110. [Google Scholar]
- Nagarajan, R.; Thirumalaisamy, S.; Lakshumanan, E. Impact of leachate on groundwater pollution due to non-engineered municipal solid waste landfill sites of erode city, Tamil Nadu, India. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2012, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo, T.; Clemente, R.; Epelde, L.; Garbisu, C.; Bernal, M.P. Evaluation of the phytostabilisation efficiency in a trace elements contaminated soil using soil health indicators. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 268, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, O.P. Impact of Environmental Contamination of Biodiversity. In Environmental Issues of North-East India; Regency Publications: New Delhi, India, 2013; ISBN 8187498692. [Google Scholar]
- Igbinosa, E.O. Effect of cassava mill effluent on biological activity of soil microbial community. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, N.B.; Maphosa, F.; Morillo, J.A.; Abu Al-Soud, W.; Langenhoff, A.A.M.; Grotenhuis, T.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M.; Smidt, H. Impact of Long-Term Diesel Contamination on Soil Microbial Community Structure. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventorino, V.; Sannino, F.; Piccolo, A.; Cafaro, V.; Carotenuto, R.; Pepe, O. Methylobacterium populi VP2: Plant growth-promoting bacterium isolated from a highly polluted environment for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) biodegradation. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 931793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourceret, A.; Cébron, A.; Tisserant, E.; Poupin, P.; Bauda, P.; Beguiristain, T.; Leyval, C. The bacterial and fungal diversity of an aged PAH-and heavy metal-contaminated soil is affected by plant cover and edaphic parameters. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 71, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida, F.; Jehmlich, N.; Lima, K.; Morris, B.E.L.; Richnow, H.H.; Hernández, T.; Von Bergen, M.; García, C. The ecological and physiological responses of the microbial community from a semiarid soil to hydrocarbon contamination and its bioremediation using compost amendment. J. Proteom. 2016, 135, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, L.; Zhang, R.; Lin, K. High throughput sequencing analysis of the joint effects of BDE209-Pb on soil bacterial community structure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 301, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Zhang, J.; Tian, L.; Guo, J. The effect of heavy metal contamination on the bacterial community structure at Jiaozhou Bay, China. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventorino, V.; Aliberti, A.; Faraco, V.; Robertiello, A.; Giacobbe, S.; Ercolini, D.; Amore, A.; Fagnano, M.; Pepe, O. Exploring the microbiota dynamics related to vegetable biomasses degradation and study of lignocellulose-degrading bacteria for industrial biotechnological application. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacquiod, S.; Cyriaque, V.; Riber, L.; Al-Soud, W.A.; Gillan, D.C.; Wattiez, R.; Sørensen, S.J. Long-term industrial metal contamination unexpectedly shaped diversity and activity response of sediment microbiome. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barragán, V.A.; Aveiga, I.; Trueba, G. Microbial community composition in petroleum-contaminated and uncontaminated soil from Francisco de Orellana, in the northern Ecuadorian Amazon. Int. Microbiol. 2008, 11, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.Y.; Dafforn, K.A.; Johnston, E.L.; Brown, M.V. Core sediment bacteria drive community response to anthropogenic contamination over multiple environmental gradients. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 2517–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanbille, M.; Gury, J.; Duran, R.; Tronczynski, J.; Agogué, H.; Ben Said, O.; Ghiglione, J.-F.; Auguet, J.-C. Response of core microbial consortia to chronic hydrocarbon contaminations in coastal sediment habitats. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhal, P.K.; Islam, E.; Kazy, S.K.; Sar, P. Culture-independent molecular analysis of bacterial diversity in uranium-ore/-mine waste-contaminated and non-contaminated sites from uranium mines. 3 Biotech 2011, 1, 261–272. [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi, G.; Osman, S.; Vaishampayan, P.A.; Andersen, G.L.; Stetler, L.D.; Sani, R.K. Microbial diversity in uranium mining-impacted soils as revealed by high-density 16S microarray and clone library. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 59, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, H.F.; Cury, J.C.; do Carmo, F.L.; dos Santos, A.L.; Tiedje, J.; van Elsas, J.D.; Rosado, A.S.; Peixoto, R.S. Mangrove Bacterial Diversity and the Impact of Oil Contamination Revealed by Pyrosequencing: Bacterial Proxies for Oil Pollution. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanbille, M.; Gury, J.; Duran, R.; Tronczynski, J.; Ghiglione, J.-F.; Agogué, H.; Ben Saïd, O.; Taïb, N.; Debroas, D.; Garnier, C. Chronic polyaromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) contamination is a marginal driver for community diversity and prokaryotic predicted functioning in coastal sediments. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1303. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, J.; Rathour, R.; Dupont, C.; Mishra, A.; Thakur, I.S. Biogeochemical profiling and taxonomic characterization of municipal landfill site by metagenomic sequencing. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 351, 126936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbons, S.M.; Gilbert, J.A. Microbial diversity—Exploration of natural ecosystems and microbiomes. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2015, 35, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventorino, V.; Pascale, A.; Adamo, P.; Rocco, C.; Fiorentino, N.; Mori, M.; Faraco, V.; Pepe, O.; Fagnano, M. Comparative assessment of autochthonous bacterial and fungal communities and microbial biomarkers of polluted agricultural soils of the Terra dei Fuochi. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polasi, L.T. Factors Associated with Illegal Dumping in the Zondi Area, City of Johannesburg, South Africa. In Proceedings of the WasteCon 2018, Johannesburg, South Africa, 15–19 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Haywood, L.K.; Kapwata, T.; Oelofse, S.; Breetzke, G.; Wright, C.Y. Waste disposal practices in low-income settlements of South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debipersadh, S.; Sibanda, T.; Selvarajan, R.; Naidoo, R. Investigating toxic metal levels in popular edible fishes from the South Durban basin: Implications for public health and food security. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogola, H.J.O.; Selvarajan, R.; Tekere, M. Local Geomorphological Gradients and Land Use Patterns Play Key Role on the Soil Bacterial Community Diversity and Dynamics in the Highly Endemic Indigenous Afrotemperate Coastal Scarp Forest Biome. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 592725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajan, R.; Sibanda, T.; Venkatachalam, S.; Ogola, H.J.O.; Christopher Obieze, C.; Msagati, T.A. Distribution, Interaction and Functional Profiles of Epiphytic Bacterial Communities from the Rocky Intertidal Seaweeds, South Africa. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Glo, F.O.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Native Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Langille, M.G.I.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; Mcdonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Thurber, R.L.V.; Knight, R.; et al. Analysis Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandepitte, V.; Quataert, P.; de Rore, H.; Verstraete, W. Evaluation of the Gompertz function to model survival of bacteria introduced into soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1995, 27, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, L.W.; De Chaves, M.G.; Fonseca, M.d.C.; Mendes, R.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Tsai, S.M. Resistance breeding of common bean shapes the physiology of the rhizosphere microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Department of Environmental Affairs (DEA). South African State of Waste Report; Department of Environmental Affairs: Pretoria, South Africa, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Akbari, I.; Ajdari, M.; Shafiee, A. Mechanical properties of landfill components under low to medium stress levels. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G.T.; Giacobbo, A.; dos Santos Chiaramonte, E.A.; Rodrigues, M.A.S.; Meneguzzi, A.; Bernardes, A.M. The effect of sanitary landfill leachate aging on the biological treatment and assessment of photoelectrooxidation as a pre-treatment process. Waste Manag. 2015, 36, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.K.; Sharma, P.C. NGS-based characterization of microbial diversity and functional profiling of solid tannery waste metagenomes. Genomics 2020, 112, 2903–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukhele, T.; Ogola, H.J.O.; Selvarajan, R.; Oruko, R.O.; Nyoni, H.; Mamba, B.B.; Msagati, T.A.M. Metagenomic insights into taxonomic diversity and metabolic potential of bacterial communities associated with tannery waste-contaminated soils. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 2409–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitotaw, B.; Ayalew, F.; Girma, A.; Geta, K.; Kibret, M. High prevalence of Antibiotic Resistance Bacteria isolated from Municipal Solid Waste Dumpsite. Res. Sq. 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, G.; Lin, L.; Wang, H.; Lin, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jia, X. Relationship of soil pH value and soil Pb bio-availability and Pb enrichment in tea leaves. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakelin, S.A.; Macdonald, L.M.; Rogers, S.L.; Gregg, A.L.; Bolger, T.P.; Baldock, J.A. Habitat selective factors influencing the structural composition and functional capacity of microbial communities in agricultural soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.M.; Firestone, M.K. Mechanisms for soil moisture effects on activity of nitrifying bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, A.G.S.; Airoldi, C. The influence of moisture on microbial activity of soils. Thermochim. Acta 1999, 332, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imron, M.F.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Abdullah, S.R.S. Resistance of bacteria isolated from leachate to heavy metals and the removal of Hg by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain FZ-2 at different salinity levels in a batch biosorption system. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2021, 31, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, M.; Walter, U.; Rekers, V.; Gu, J.-D.; Denecke, M. More than a decade of experience of landfill leachate treatment with a full-scale anammox plant combining activated sludge and activated carbon biofilm. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhohola-Dlamini, L.; Selvarajan, R.; Ogola, H.J.O.; Tekere, M. Community diversity metrics, interactions, and metabolic functions of bacteria associated with municipal solid waste landfills at different maturation stages. Microbiologyopen 2021, 10, e1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.; Zhang, S.; Xie, S. Microbial community changes in aquifer sediment microcosm for anaerobic anthracene biodegradation under methanogenic condition. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 1498–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Xie, S. Anaerobic biodegradation of nonylphenol in river sediment under nitrate-or sulfate-reducing conditions and associated bacterial community. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Song, Y.; Zeng, P.; Duan, L.; Xiao, S. Characterization of bacterial communities in hybrid upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB)–membrane bioreactor (MBR) process for berberine antibiotic wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Wang, Y.; Tang, W.; Lei, Y. Bacterial community diversity in municipal waste landfill sites. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 7745–7756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.; Xiong, S.; Liang, S.; Hu, C.; Zhang, X.; Lu, J. Performance and bacterial compositions of aged refuse reactors treating mature landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 103, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamps, B.W.; Lyles, C.N.; Suflita, J.M.; Masoner, J.R.; Cozzarelli, I.M.; Kolpin, D.W.; Stevenson, B.S. Municipal solid waste landfills harbor distinct microbiomes. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, K.; Chownk, M.; Kumar, V.; Purohit, A.; Vashisht, A.; Kumar, V.; Yadav, S.K. Bioprospecting potential of microbial communities in solid waste landfills for novel enzymes through metagenomic approach. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, S.N.; Thakur, D. Actinobacteria-In Beneficial Microbes in Agro-Ecology; Academic Press: Cambridge, USA, 2020; pp. 443–476. [Google Scholar]
- Anandan, R.; Dharumadurai, D.; Manogaran, G.P. An introduction to actinobacteria. In Actinobacteria-Basics and Biotechnological Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 9535122487. [Google Scholar]
- Speirs, L.B.M.; Rice, D.T.F.; Petrovski, S.; Seviour, R.J. The Phylogeny, Biodiversity, and Ecology of the Chloroflexi in Activated Sludge. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Mondéjar, R.; Algora, C.; Baldrian, P. Lignocellulolytic systems of soil bacteria: A vast and diverse toolbox for biotechnological conversion processes. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 107374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Hanada, S.; Hugenholtz, P.; Kim, H.; Kamagata, Y.; Nakamura, K. Gemmatimonas aurantiaca gen. nov., sp. nov., a gram-negative, aerobic, polyphosphate-accumulating micro-organism, the first cultured representative of the new bacterial phylum Gemmatimonadetes phyl. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Pyrosequencing-based assessment of soil pH as a predictor of soil bacterial community structure at the continental scale. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5111–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnivetskaya, T.A.; Mosher, J.J.; Palumbo, A.V.; Yang, Z.K.; Podar, M.; Brown, S.D.; Brooks, S.C.; Gu, B.; Southworth, G.R.; Drake, M.M. Mercury and other heavy metals influence bacterial community structure in contaminated Tennessee streams. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapase, S.R.; Mawlankar, R.B.; Sundharam, S.S.; Krishnamurthi, S.; Dastager, S.G.; Kodam, K.M. Microvirga indica sp. nov., an arsenite-oxidizing Alphaproteobacterium, isolated from metal industry waste soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 3525–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, S.N.; Thakur, D. Actinobacteria; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; ISBN 9780128234143. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, G.; Shi, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, G. Skermanella stibiiresistens sp. nov., a highly antimony-resistant bacterium isolated from coal-mining soil, and emended description of the genus Skermanella. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, N.; Chandran, P. Microbial Degradation of Petroleum Hydrocarbon Contaminants: An Overview. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2011, 2011, 941810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibanda, T.; Selvarajan, R.; Tekere, M. Targeted 16S rRNA amplicon analysis reveals the diversity of bacterial communities in carwash effluents. Int. Microbiol. 2018, 22, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drzyzga, O. The strengths and weaknesses of Gordonia: A review of an emerging genus with increasing biotechnological potential. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 38, 300–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulenta, F.; Dionisi, D.; Majone, M.; Parisi, A.; Ramadori, R.; Tandoi, V. Effect of periodic feeding in sequencing batch reactor on substrate uptake and storage rates by a pure culture of Amaricoccus kaplicensis. Water Res. 2003, 37, 2764–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.X.; Gao, J.F.; Dai, H.H.; Zhang, W.Z.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.Q. DNA-based stable isotope probing identifies triclosan degraders in nitrification systems under different surfactants. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekar, A.; Sekar, R.; Medina-Roldan, E.; Bridge, J.; Moy, C.K.S.; Wilkinson, S. Next-generation sequencing showing potential leachate influence on bacterial communities around a landfill in China. Can. J. Microbiol. 2018, 64, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwuma, O.B.; Rafatullah, M.; Tajarudin, H.A.; Ismail, N. Bacterial diversity and community structure of a municipal solid waste landfill: A source of lignocellulolytic potential. Life 2021, 11, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenblatt, C.L.; Davis, A.; Clement, B.G.; Kitts, C.L.; Cox, T.; Cano, R.J. Diversity of microorganisms isolated from amber. Microb. Ecol. 1999, 38, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimviriyakul, P.; Chaiyen, P. Flavin-Dependent Dehalogenases, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 47, ISBN 9780128201374. [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi, E.; Romaniello, F.; Galletti, S.; Boccaleri, E.; Frache, A.; Cocconcelli, P.S. Selective bacterial colonization processes on polyethylene waste samples in an abandoned landfill site. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuźniar, A.; Banach, A.; Stȩpniewska, Z.; Frąc, M.; Oszust, K.; Gryta, A.; Kłos, M.; Wolińska, A. Community-level physiological profiles of microorganisms inhabiting soil contaminated with heavy metals. Int. Agrophys. 2018, 32, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | ID1 | ID2 | ID3 | ID4 | ID5 | ID6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physicochemical | ||||||
| pH | 5.51 | 8.09 | 6.6 | 5.3 | 6.7 | 8.03 |
| EC (μS/m) | 101.9 | 1196 | 547 | 297 | 498 | 313 |
| Moisture (%) | 5.7 | 20.52 | 23.7 | 14.62 | 1.3 | 22.19 |
| Total nitrogen (TN) (%) | 0.13 | 0.176 | 0.295 | 0.16 | 0.345 | 0.125 |
| Total carbon (TC) (%) | 2.7 | 7.145 | 4.2 | 3.91 | 9.477 | 8.9 |
| Heavy metals (HMs) (ppm) | ||||||
| As | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.010 | 0.021 | 0.032 | 0.005 |
| Cd | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.005 |
| Pb | 0.044 | 0.007 | 0.013 | 0.018 | 0.020 | 0.115 |
| Mn | 1.316 | 0.454 | 0.274 | 0.292 | 0.106 | 0.047 |
| Co | 0.010 | 0.011 | 0.012 | 0.029 | 0.010 | 0.010 |
| Cu | 0.145 | 0.064 | 0.102 | 0.099 | 0.062 | 0.074 |
| Zn | 0.067 | 0.110 | 0.089 | 0.077 | 0.098 | 0.175 |
| Fe | 12.863 | 6.545 | 3.185 | 4.094 | 4.712 | 5.221 |
| Cr | 0.072 | 0.053 | 0.101 | 0.100 | 0.094 | 0.073 |
| Ni | 0.002 | 0.025 | 0.038 | 0.036 | 0.035 | 0.030 |
| Mg | 0.982 | 2.300 | 4.500 | 2.682 | 3.911 | 0.446 |
| Ba | 4.116 | 3.911 | 4.401 | 4.386 | 4.220 | 1.305 |
| P | 15.178 | 1.092 | 0.101 | 4.245 | 0.171 | 0.391 |
| S | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.016 | 0.013 | 0.015 | 0.013 |
| Sample | Quality Reads | Observed OTUs | ACE | CHAO | Shannon | Simpson | Good’s Coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID1 | 41,026 | 5658 | 6098 | 5808 | 7.29 | 0.00 | 98.04 |
| ID2 | 21,886 | 2364 | 2700 | 2502 | 5.57 | 0.02 | 97.72 |
| ID3 | 36,727 | 5058 | 5610 | 5308 | 7.41 | 0.00 | 97.56 |
| ID4 | 37,906 | 4605 | 5048 | 4784 | 6.99 | 0.00 | 98.00 |
| ID5 | 12,475 | 1595 | 1923 | 1767 | 6.05 | 0.01 | 96.74 |
| ID6 | 22,370 | 2850 | 3364 | 3137 | 6.55 | 0.01 | 96.88 |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Selvarajan, R.; Ogola, H.; Kalu, C.M.; Sibanda, T.; Obize, C. Bacterial Communities in Informal Dump Sites: A Rich Source of Unique Diversity and Functional Potential for Bioremediation Applications. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12862. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412862
Selvarajan R, Ogola H, Kalu CM, Sibanda T, Obize C. Bacterial Communities in Informal Dump Sites: A Rich Source of Unique Diversity and Functional Potential for Bioremediation Applications. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(24):12862. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412862
Chicago/Turabian StyleSelvarajan, Ramganesh, Henry Ogola, Chimdi M. Kalu, Timothy Sibanda, and Chinedu Obize. 2022. "Bacterial Communities in Informal Dump Sites: A Rich Source of Unique Diversity and Functional Potential for Bioremediation Applications" Applied Sciences 12, no. 24: 12862. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412862
APA StyleSelvarajan, R., Ogola, H., Kalu, C. M., Sibanda, T., & Obize, C. (2022). Bacterial Communities in Informal Dump Sites: A Rich Source of Unique Diversity and Functional Potential for Bioremediation Applications. Applied Sciences, 12(24), 12862. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412862







