Featured Application
New approaches to design efficient RF devices that use LCs.
Abstract
We evaluated hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (HTAB) for liquid crystals (LCs) in layered ITO cells with various cell gap conditions. HTAB is a surfactant that can self-align vertically on the surface of indium tin oxide (ITO) substrates and induce homeotropic alignment of the LC molecules. For implementing RF devices with HTAB and LCs, we should consider limitations caused by the design conditions which are different from conventional liquid crystal displays such as cell gap. We quantified the concentration of HTAB ([HTAB]) that is necessary to form and maintain a sufficiently dense vertical alignment of 5CB (4-Cyano-4′-pentylbiphenyl). The required [HTAB] for full-homeotropic alignment was increased to the cell gap until it was too large to support the transfer of the surface alignment to the LC molecules, due to the weak anchoring nature of HTAB. We also showed the phase-change characteristic of the LC mixture related to [HTAB] for the design of RF devices driven by light or heat. This study may help to guide the development of new approaches to designing efficient RF devices that use LCs.
1. Introduction
Liquid crystals (LCs) have a birefringence nature that permits tuning of their optical properties. The tunability of LCs is exploited in many photonics technologies; liquid crystal display [1,2,3,4], tunable lens [5,6,7], smart windows [8,9,10,11,12], etc. However, LCs are not only promising for photonics but also for millimeter-wave (mmWave) range applications such as future telecommunication technology over 5G and LC-based radars. LCs are favorable because of their lower loss characteristics at high frequencies than conventional radio frequency (RF) components [13,14]. LCs are competitive in price because LCD fabrication technologies are mature and can be used in lightweight structures that have a low profile and continuous steering capability [15].
In most radio frequency (RF) applications that use LCs, dielectric anisotropy in the frequency of the quasi-electrostatic range permits control of the orientation of LC molecules by an electric field [16,17,18]. When it comes to E-field driving by using DC bias or low-frequency AC voltage, since most of the LCs are positive type, only initial planar alignment is used for driving LC molecules. Recently, the light-driving method has been studied using LC mixtures and indium tin oxide (ITO) electrodes [19,20]. This method is attractive because it does not require designing a complex biasing line. Using light or heat-driving concurrently with a biasing line has the potential to improve the signal-control capability. The use of photoexcited trans-to-cis photoisomerization of a dopant or a thermal reaction of LCs may result in a nematic-to-isotropic phase transition of LCs, and, hence, a variation in the effective dielectric constant during interaction with a microwave signal [19]. With this driving method, both the planar and vertical alignment (VA, or homeotropic alignment) can change the effective dielectric constant of the RF structures.
A surface-active agent, such as hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (HTAB) and lecithin, can produce VA of LCs by surface treatment or mixing with LCs, because long aliphatic chains of these surfactants stand perpendicular to the surface [21,22,23]. Exploitation of this characteristic can eliminate the need for complex surface treatment (e.g., PI coating, rubbing) and thus effectively reduce manufacturing costs and processing time. These beneficial points are also effective in RF device processing if we can use them. However, conventional LCD industry and smart-window applications that use LCs typically use a small cell gap (defined as the distance between two ITO-coated substrates), ≤10 µm and ≤20 µm, respectively [8,10,16,24], and the display industry has a mature manufacturing capability for the cell gap. However, for RF applications, to maximize the tuning range of liquid crystal RF devices, a maximum thickness of 300 µm is needed [25]. Because of the weak anchoring force of HTAB, we have to evaluate the cell gap limitation of HTAB for VA alignment before using HTAB for other applications of different cell gap considerations.
Therefore, in this work, we evaluated HTAB, which has a vertical self-alignment feature, for use in LCs that have various cell gap conditions. We confirmed the limitation of cell gap thickness with the HTAB for full-homeotropic alignment. However, this work is the first report that considers the cell gap of LC cells that use HTAB. Additionally, we showed that the required HTAB concentration ([HTAB]) for full-homeotropic alignment is proportional to the cell gap until the surface LC molecules’ alignment is not properly transferred into the LC medium due to the weak anchoring nature of HTAB. We also reported the effect of [HTAB] on the phase-change characteristic of the LC mixture by analyzing heat flow results from a differential scanning calorimeter (DSC). This result is meaningful because designing RF devices with HTAB driven by light or heat must consider this phase-change temperature tendency. We hope our work will be a milestone in the new approach to the efficient RF device design process using LCs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Basic Mechanism of RF Devices Using LCs and Consideration of the Cell Gap
The tunability of LCs is the main reason to use them in RF applications. Dielectric anisotropy of LCs permits control of their orientation by an electric field. The dielectric constants of devices can be regulated by changing the angle between the RF field and the LC’s directors. Typically, a dielectric constant can be considered using Gauss’s law
where [V m−1] is the electric field, [C m−3] is charge density, = 8.85 × 10−12 [F m−1] is the electric constant of the vacuum, and is a relative dielectric constant.
The wave-occupied volume ratio WoVR is helpful to analyze the dielectric constant of RF devices that use LCs [26]. Using this concept, it is easy to explain the E flux on the tunable region and tunability. WoVR can be induced by Gauss’s law as
where ΦE [V m] is electric flux, [C] is total enclosed charges, [F m−1] is the effective dielectric constant of the structure, and WoVRk is the wave-occupied volume ratio in region k.
WoVRk depends on the dielectric constant of the region and the conductor’s geometry. Usually, when we design tunable RF devices using LCs, we have to likely maximize ΦE of the LC’s tunable region, which is directly related to the tunability of the RF devices using LCs. The maximum obtainable differential phase shift is
where f [Hz] is the operating frequency, L [m] is the physical length of the phase shifter, c0 = 3 × 108 [m s−1] is the velocity of the light in a vacuum, is the effective relative dielectric constant with LCs biased by a saturated voltage, and is the effective relative dielectric constant of a phase shifter while biased by a reference voltage. Finally, tunability is evaluated with the tuning range TR [%] of the RF structure as
where is effective relative dielectric constant when the RF field is aligned with the LC molecular long axis, and is an effective relative dielectric constant when the RF field is aligned with the LC molecular short axis. Equation (4) demonstrates that the structure should be designed to maximize ( − ). The main consideration of this paper, the cell gap (=LC layer thickness), is also related to the WoVR [27].
The cell gap is important when designing RF devices with LCs, especially for liquid crystal phase shifters (LCPS). Two main types of transmission line topologies are used for passive LCPSs: the microstrip line (MSL) and the coplanar waveguide (CPW) [28,29,30,31]. The currently-used LC MSL phase shifter has a limitation in reducing the cell gap to ≤100 μm while matching the impedance, because the narrowness of the MSL inevitably causes a large amount of conduction loss [32]. The grounded-CPW LCPS type has the same limitation because of the conductor-backed design. The floating-electrode-free CPW (FE-free CPW) can be implemented with a cell gap ≤ 20 µm, but to achieve sufficient tuning range, it requires a cell gap ≥ 100 µm [25]. These considerations illustrate that responses at large cell gap must be considered before the HTAB method is adapted for RF applications.
2.2. Materials and Cell Fabrication
We used ITO as a glass substrate because ITO was used considering its transparency and conductivity as in the preceding research of light-driving LCPS [19,20]. We chose the HTAB as a surface-active agent because it has a high affinity with ITO [23]. HTAB is an organic compound containing hydrophilic groups at both ends of a prolate molecule-amphiphilic molecule (Figure 1a). HTAB has a bromide anion, which has a high affinity with ITO, and finally adheres to the ITO glass substrate. Owing to the polar nature of HTAB, the cyano groups of the LCs are expected to point towards HTAB [33]. Finally, LC molecules can be aligned vertically by the HTAB on the ITO glass substrates (Figure 1b). Some previous studies have considered LCPSs that use (4-cyano-4′-pentylbiphenyl) (5CB) LCs, and some studies have used HTAB and 5CB to achieve VA; these studies guarantee the validity of our experimental conditions [8,34,35].
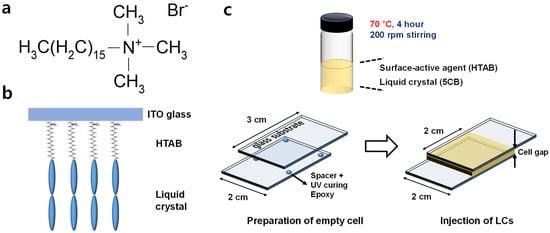
Figure 1.
Schematics of (a) chemical structure of HTAB, (b) principle of vertical alignment of LC molecules mixed with HTAB, and (c) cell fabrication.
We used a 2 cm × 3 cm sized superstrate and substrate, and we mixed 5CB with a surface-active agent HTAB. The materials were mixed in a glass vial by stirring continuously for 4 h at 70 °C, 200 rpm. We also mixed HTAB with 8CB to test whether other liquid crystals have similar responses to phase-change temperature and [HTAB]. These results will be discussed with the DSC results.
We fabricated the cells as follows (Figure 1c). First, we prepared empty cells and used spacers and UV-cured epoxy to establish a different cell gap. For a large cell gap ≥ 100 µm, we used 3M tapes to maintain the cell gap. To avoid degradation of optical transmittance (OT), we ensured that the spacer scattered region did not overlap the region in which the OT was measured. After preparing the empty cell, we injected the LC mixture into a 2 cm × 2 cm area by exploiting capillary action, then sealed the samples with UV-cured epoxy to prevent leakage of LCs, then cured it using UV to stiffen the samples.
2.3. Experimental Setup
We adjusted [HTAB] mixed into the 5CB to 0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, or 10 wt%. This set of [HTAB] was also used for DSC heat flow measurement. We also set the cell gap to 2.5, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, or 400 µm for quantification of the available level of the cell gap for homeotropic alignment using HTAB. We confirmed the uniformity of the cell gap with a micrometer (IP 65, Muitutoyo).
A good “dark” state under crossed polarizers can indicate successful VA. To confirm the good “dark” VA state of the cell, we cross-checked by using an optical microscope (Eclipse 50i POL, Nikon) in crossed-polarization mode and by measuring transmittance by using a multi-function optical power meter (Model 1835-C, Newport), with white light beamed in by a light source (DH-2000, Ocean Insight). Additionally, we used a white backlight panel (LP-100N, MEDALight) and two polarizer films to check whether HTAB assumed completely homeotropic alignment throughout the sample.
We used DSC to evaluate the dissolution of HTAB and 5CB LCs and to report how [HTAB] affects the phase-change nature of the LC mixture. Heat flow and heat capacity were analyzed using a thermal analysis instrument (DSC Q200, TA instruments).
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Insufficient HTAB Concentration
If [HTAB] was insufficient, the LC alignment was not uniform (Figure 2a). The use of polarizer films enables easy verification of the alignment state of the entire cell. The LC molecules did not align at all in the cell where pure 5CB was used, therefore black regions that imply vertical LC alignment were randomly distributed. However, the LC molecules started to be aligned along the HTAB in the cell where the surface-active agent HTAB is mixed. The results show that as the LCs mixture is injected by the capillary method, LC molecules are vertically aligned successfully near the injection spot, but LCs are not perfectly vertically aligned at the far region from the injection spot with the insufficient HTAB concentration (Figure 2b). Because the bromide ion in HTAB has a high affinity with ITO, HTAB can attach to the ITO glass substrate. Therefore, HTAB likely moves onto the ITO glass substrate [23]. If the concentration of HATB is insufficient, HTAB is out of stock before HTAB covers the entire ITO glass substrate, hence nonuniformity occurs. If the [HTAB] is insufficient, HTAB is depleted before it can cover the entire ITO glass substrate, so nonuniformity occurs. We confirmed this tendency with all the partially homeotropic-aligned samples (Figure 4, green triangles). Therefore, a method to minimize this non-uniformity must be developed; we leave this task for future work. This result also implies that although we used the same [HTAB] for LC solutions, the result can vary depending on the size of the LC filling region due to the non-uniform adhesion of HTAB to the ITO glass surface. This nonuniformity has been reported in other studies of surface-active agents for homeotropic alignment, and they support that explanation of the non-uniformity [23,36]. To avoid such a size-dependent influence, our LC-injection region was fixed at 2 cm by 2 cm for all cases.
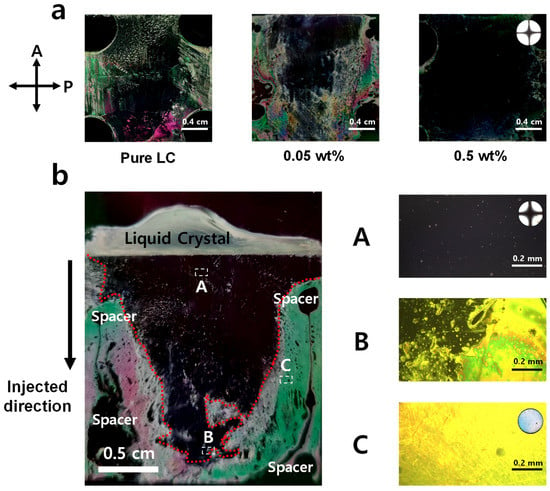
Figure 2.
Image of region near LC injection with the test cell between the two cross-polarized polarizer films; (a) injected pure LCs, insufficient [HTAB] for homeotropic alignment, and LCs mixture with sufficient [HTAB] to induce fully-vertical alignment at the cell gap = 20 µm. LC mixtures with insufficient [HTAB] develop nonuniform LC orientation; (b) nonuniform LC cell with an insufficient [HTAB]. (A) polarized optical microscopy images of vertically well-aligned part near the LC injection point, (B) division area, and (C) imperfectly-aligned part far from the LC injection point.
The non-uniformity of VA can be checked by measuring the OT (Figure 3a). By adjusting the placement of the samples, we can change the area that the light passes through. Under crossed polarizers, the vertically fully-aligned LC molecules with OT was <~0.83%, whereas the pure 5CB cell in which alignment was random had 15 ≤ OT ≤ 22%, depending on the measurement location. The non-uniformity was caused during the LC injection process. OT was lowest near the LC injection site (Figure 3bA), intermediate near the middle of the sample (Figure 3bB), and lowest farthest from the injection site (Figure 3bC). We double-checked the non-uniformity with the crossed-polarizers film image and transmittance with all of the partially homeotropic-aligned samples denoted with the green triangle case (Figure 4).
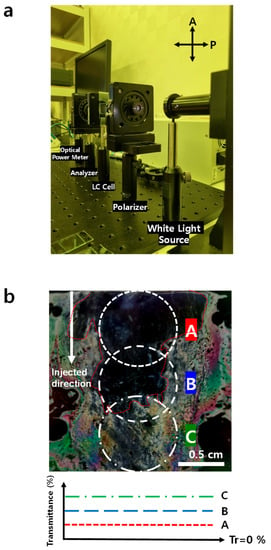
Figure 3.
(a) Experimental setup image to evaluate Optical transmittance. Cross-polarization is set for testing the homeotropic alignment. (b) Overall image with insufficient [HTAB] for fully-vertical alignment (Cell gap = 10 µm, [HTAB] = 0.01 wt%). White dotted line: area where white light is applied to the sample. Lower graph: transmittance non-uniformity caused by insufficient [HTAB].
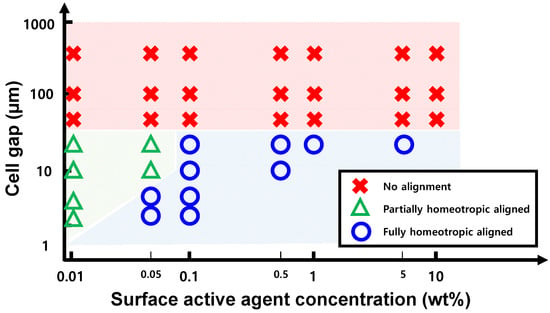
Figure 4.
Diagram of alignment states vs. cell gap and surface-active agent concentration. ✕: no alignment, Δ: non-uniform homeotropic alignment caused by insufficient [HTAB], ∘: fully-homeotropic alignment across the entire cell.
3.2. Analysis of Limitations of 5CB and HTAB for Homeotropic Alignment
Despite the different design considerations between RF applications and LCDs, no prior research has evaluated the importance of the cell gap condition. Therefore, we analyzed the effectiveness of HTAB as a surface-active agent with 5CB at different cell gaps. We studied how the vertical self-assembly of 5CB LC molecules was affected by [HTAB] and by the cell gap (Figure 4). We plotted the evaluation of the effectiveness of the HTAB for each case. In the fully-homeotropic aligned state (Figure 4, blue circle), every part of the sample looked black between the crossed-polarizers, and OT was < ~0.83%. The partially homeotropically aligned state (Figure 4, green triangle) was caused by insufficient [HTAB], and a non-aligned state was caused by a large cell gap condition (Figure 4, red cross); these regions looked bright under the cross-polarized configuration and had high OT (Figure S1, Supporting information).
In this work, we proposed a reference for the minimum [HTAB] for fully VA to 20 µm. In this range of the cell gap, we found that for the higher cell gap, more [HTAB] is needed for a fully aligned state. For the cell gap = 2.5 µm and 5 µm, [HTAB] = 0.05 wt% is enough. However, at the cell gap = 10 µm and 20 µm, [HTAB] must be ≥ 1 wt%. This is because for a larger cell gap, stronger anchoring strength for a fully aligned state is necessary, which is related to the [HTAB]. This surfactant’s concentration dependency can be found in other studies [23,36]. The anchoring strength is related to the concentration of ions at the ITO glass surface [37]. If [HTAB] is too low in the solution, the molecules cannot orient well. There are some references to [HTAB] and the cell gap condition, using HTAB for VA (Table 1).

Table 1.
The references about the homeotropic alignment using HTAB.
At the cell gap ≥ 50 µm, HTAB could not form a homeotropic alignment (Figure S1, Supporting Information), because HTAB has a weak anchoring force. Although [HTAB] in 5CB was high enough and a sufficient number of layers formed to the ITO glass surface, when the cell gap was too large, the fluidity and interaction forces among the molecules disturbed the homeotropic alignment, so it was not maintained throughout the LC medium. This limitation imposed by the cell gap means that when HTAB is used as a surface-active agent for homeotropic alignment in RF structures, they must be designed to have the cell gap < 20 µm, perhaps by adjusting design parameters such as electrode conditions or using the RF technique such as loaded line design for a lower cell gap [25].
3.3. Effect of HTAB Concentration on the Phase-Change Characteristics
We investigated the effect of [HTAB] variation on the phase-change nature of the LC mixture. We analyzed thermal properties by using DSC (Figure 5); the results yield some important conclusions. DSC measurement was conducted under the condition; amount: ~3 mg, Gas1: Nitrogen 50.0 mL/min, Gas2: Air 50.0 mL/min, heating rate: 19.99 °C/min Heat Only, Pan: Tzero Aluminum Hermetic.
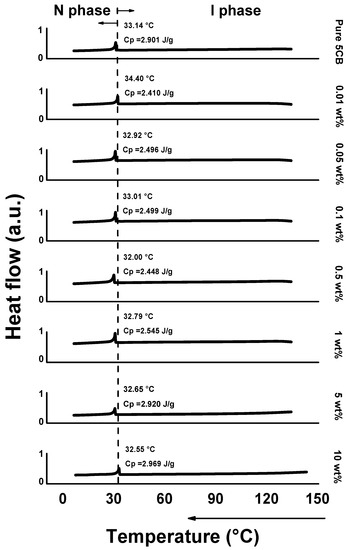
Figure 5.
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) heat flow results about 5CB+HTAB solutions over a wide temperature range from 0 to 150 °C with 0 ≤ [HTAB] ≤ 10 wt%. Cp: heat capacity. Heat flow was analyzed by cooling the samples.
First, the phase-change transition heat flow of HTAB was not detected, so we can be sure that 5CB and HTAB have good solubility and were well-mixed with our heating and stirring conditions. The good miscibility occurs because the cyano groups of the 5CB LCs are expected to be well matched with the polar nature of HTAB [33]. These results imply that injected LC mixtures are well dissolved in the LC host, so non-uniformity of mixtures does not affect the results.
Second, the results show almost the same phase-transition temperature (32.55 °C~34.40 °C) of the nematic-to-isotropic phase transition in each condition. This point can be slightly altered by experimental errors such as in sample weight and in rates of heating or cooling, so we can conclude that the phase-change temperature of the solution is stable for the range of [HTAB] tested [39]. For the general tendency of this result, we also checked another well-known LC, 8CB (4-cyano-4′-octylbiphenyl). The phase-change temperature of the 8CB mixture was stable at [HTAB] = 0, 1 wt% and 10 wt% (Figure S2, Supporting Information).
4. Discussion
We have performed the first analysis of non-uniformity caused by insufficient [HTAB] and the effectiveness of HTAB as a surface-active agent with 5CB LCs at different cell gaps, and measured the phase-change characteristics of the HTAB:5CB mixture. Minimizing [HTAB] is essential for several reasons.
The first is that the presence of dopants degrades the tunability of the LC. Previous studies for RF applications did not use LCs mixtures with dopants, and therefore did not consider the tunability of LC materials. Therefore, the first proposed concept of WoVR does not consider the tunability of LCs mixtures [26]. However, if a dopant is added to LC, WoVR on the tunable LCs region is reduced because the volume ratio of the tunable LC directors to the entire region is reduced. Therefore, if LCs are mixed with dopants, WoVR of the tunable LC region is reduced, so their tunability is reduced. However, this degradation can differ along materials and experimental conditions, so each case must be analyzed; we leave this task for future work, but it is essential for the exact design of the RF devices by simulation. Our results indicate that at a cell gap ≤20 µm, LCs can be aligned using only 0.1 wt% HTAB, so the VA for RF devices design can be carried out using a small amount of HTAB.
The second reason is the aggregation of the LC molecules’ alignment [23]. Excessive [HTAB] in LCs mixtures can cause aggregation in the alignment of LCs and cause imperfect VA. This aggregation of alignment reduces the tunability of RF devices that use LCs, and reduces the stability of the initial homeotropic alignment, so [HTAB] should be minimized.
The third consideration is the leakage current caused by the ionic dopant. An increase in [HTAB] causes an increase in the conductivity of the solution [40]. This high conductivity can degrade the operation of RF devices that use LCs that are driven by an applied electric field. To prevent this degradation, [HTAB] must be minimized in designs of RF devices. The specific effect of high [HTAB] on the degradation of the electrical characteristics of RF applications of LCs will be evaluated in future work.
These experiments confirmed the limitation of the HTAB anchoring force when the cell gap is large. Strengthening the surfactant’s anchoring force may be a solution to overcome this limitation. Some studies have sought methods to do this [36,41,42].
Additionally, if substrate materials other than ITO are used to achieve homeotropic self-alignment in RF applications, the adhesion between the substrate material and surfactant must be considered. If different LCs than HTAB are used, the polar characteristics between the LCs and surfactants must be checked.
The surface roughness of the substrate can also affect the arrangement of LCs. For a substrate that has a rough surface (e.g., PCB), coating it with dissolved HTAB as a VA alignment layer can be a solution, instead of using a mixture to avoid non-uniformity [21,43,44]. Furthermore, there is no prior study involving a morphological analysis of different temperature ranges or different concentrations when using HTAB for vertical alignment; we leave this task for future work.
Until now, LC antennas have been developed using LCs only with positive dielectric anisotropy. If previously-suggested vertically-aligned LC molecules with a surfactant are widely used, negative LCs for LC antennas can be also developed for E-field driving. If we can use LCs with high dielectric negative anisotropy, we can reduce the manufacturing time with HTAB and improve the tuning range of LC-based RF devices at the same time.
5. Conclusions
This was the first study to evaluate the surface-active agent HTAB, which has vertical self-alignment ability. We evaluated how this ability was affected by the cell gap and its phase-change characteristics to investigate its applicability to RF applications that use LCs. The cell gap is much smaller in RF applications than in displays, but no previous study of [HTAB] has considered whether successful homeotropic alignment is affected by the cell gap. We analyzed the non-uniformity caused by insufficient [HTAB], and the effectiveness of HTAB as a surface-active agent with 5CB in various cell gap conditions. The results indicated a minimum [HTAB] for fully-vertically aligned LC molecules up to 20 µm. To achieve fully-aligned LC molecules in this range of the cell gap, [HTAB] increases as the cell gap increases. However, for the cell gap ≥50 µm, we identified a limitation in achieving homeotropic alignment using HTAB because of its weak anchoring nature. We also investigated the effect of [HTAB] variation on the phase-change nature of LC mixtures (5CB and 8CB) and concluded that the phase-change temperature of the solutions is stable for all [HTAB] tested. We believe our work will be useful in the development of new design processes for RF devices that use LCs.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app122412582/s1, Figure S1: The POM images about the no-alignment state caused by a thick cell gap.; Figure S2: The differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) heat flow results about 8CB+HTAB solutions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and formal analysis, J.-S.M.; experiment and formal analysis, J.-Y.C., H.-J.S. and J.-H.L.; supervision, W.-S.K. and S.-W.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Samsung Research Funding Center of Samsung Electronics under Project Number SRFC-TE2013.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data that support the findings of this study are included within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Scheffer, J.; Nehring, J. A new, highly multiplexable liquid crystal display. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1984, 45, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koide, N. Liquid Crystal Display Story; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, Y.J. The world of liquid-crystal display TVs—Past, present, and future. Disp. Technol. 2007, 3, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Nam, S.; Choi, S.S. Analytical design of optical color filter using bi-layered chiral liquid crystal. Opt. Mater. Express 2022, 12, 949–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S. Liquid-crystal lens-cells with variable focal length. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1979, 18, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ye, M.; Honma, M.; Nose, T.; Sato, S. Liquid Crystal Lens with Spherical Electrode. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 41, L1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Fox, D.W.; Wu, B.; Wu, S.T. Liquid crystal lens with large focal length tunability and low operating voltage. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 11328–11335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.W.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, T.H. Self-shading by optical or thermal control of transmittance with liquid crystals doped with push-pull azobenzene. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 183, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.W.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, T.H. Control of transmittance by thermally induced phase transition in guest–host liquid crystals. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2018, 2, 1800066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.W.; Kim, S.H.; Baek, J.M.; Yoon, T.H. Optical and thermal switching of liquid crystals for self-shading windows. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2018, 2, 1700164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.H.; Eo, H.; Choi, T.H.; Kim, W.S.; Oh, S.W. A simulation of diffractive liquid crystal smart window for privacy application. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.W.; Nam, S.M.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, T.H.; Kim, W.S. Self-regulation of infrared using a liquid crystal mixture doped with push–pull azobenzene for energy-saving smart windows. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 5028–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadiku, M.N. Elements of Electromagnetics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, P.; Jakoby, R.; Karabey, O.H.; Rehder, G.P.; Maune, H. Reconfigurable Circuits and Technologies for Smart Millimeter-Wave Systems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Karabey, O.H. Electronic Beam Steering and Polarization Agile Planar Antennas in Liquid Crystal Technology; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, T.L. Technology of liquid crystal based antenna. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 17138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Shin, H.J.; Kim, W.S. Comparative Analysis of Liquid-Crystal Driving between the Grounded-Coplanar Waveguide and the Floating-Electrode-Free Coplanar Waveguide in Liquid-Crystal Phase Shifters. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting (Joint with AP-S Symposium), Denver, CO, USA, 10–15 July 2022; p. 118. [Google Scholar]
- Utsumi, Y.; Bach, N.T.; Kamei, T.; Ozaki, R.; Moritake, H. Comparison of microwave measurements and theoretical calculations of dielectric birefringence for a liquid crystal loaded CPW-FE phase shifter. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2009, 510, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. All-optically Controlled Microwave Analog Phase Shifter with Insertion Losses Balancing. Eng. Lett. 2020, 28, 663–667. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. Optically Steerable Phased Array Enabling Technology Based on Mesogenic Azobenzene Liquid Crystals for Starlink Towards 6G. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference (APMC), Hong Kong, China, 10–13 November 2020; p. 345. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, T.; Ishikawa, K.; Wada, M. Liquid crystal alignments and surface energy. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1980, 60, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Rosenblatt, C. Surface-anisotropy-induced linear electro-optic effect in a nematic liquid crystal. Phys. Rev. E 1996, 53, 2976–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Park, B.W.; Choi, S.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.; Shin, K.C.; Yoon, T.H. Vertical alignment of liquid crystals without alignment layers. Liq. Cryst. 2013, 40, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.W.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, T.H. Thermal control of transmission property by phase transition in cholesteric liquid crystals. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 6520–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Oh, S.W.; Kim, W.S. Liquid-crystal-based floating-electrode-free coplanar waveguide phase shifter with an additional liquid-crystal layer for 28-GHz applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2021, 55, 095106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Structure and Optimisation of Liquid Crystal based Phase Shifter for Millimetre-wave Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chu, D. Liquid Crystal-Based Enclosed Coplanar Waveguide Phase Shifter for 54–66 GHz Applications. Crystals 2019, 9, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuki, T.; Fujikake, H.; Nomoto, T. Microwave variable delay line using dual-frequency switching-mode liquid crystal. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2002, 50, 2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, R.; Kawakami, T.; Ito, Y.; Sasamori, T.; Isota, Y.; Honma, M.; Nose, T. Fundamental properties of novel design microstrip line type of liquid crystal phase shifter in microwave region. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 51, 044104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goelden, F.; Gaebler, A.; Goebel, M.; Manabe, A.; Mueller, S.; Jakoby, R. Tunable liquid crystal phase shifter for microwave frequencies. Electron. Lett. 2009, 45, 686–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzsch, C.; Giacomozzi, F.; Karabey, O.H.; Bildik, S.; Colpo, S.; Jakoby, R. Advanced characterization of a W-band phase shifter based on liquid crystals and MEMS technology. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2012, 4, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuki, T.; Fujikake, H.; Nomoto, T.; Utsumi, Y. Design of a microwave variable delay line using liquid crystal, and a study of its insertion loss. Electron. Commun. Jpn. 2002, 85, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.B.; Song, J.K.; Um, Y.; Kim, K.H. Pixel-division technology for high-quality vertical-alignment LCDs. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2010, 31, 987–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, F.; Krasinski, F.; Splingart, B.; Tentillier, N.; Legrand, C.; Spadlo, A.; Dabrowski, R. Large microwave birefringence liquid-crystal characterization for phase-shifter applications. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 47, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.R.; Chen, C.Y.; Pan, R.P.; Pan, C.L.; Zhang, X.C. Electrically controlled room temperature terahertz phase shifter with liquid crystal. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2004, 14, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, W.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Yu, Y.T.; Lee, H.; Jeong, K.U. Poly(trimethylene monothiocarbonate) from the Alternating Copolymerization of COS and Oxetane: A Semicrystalline Copolymer. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 8863–8868. [Google Scholar]
- Petrossian, A.; Residori, S. Surfactant enhanced reorientation in dye-doped nematic liquid crystals. Europhys. Lett. 2002, 60, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, K.H.; Rho, S.J.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.; Yoon, T.H. Ultrafast switching of randomly-aligned nematic liquid crystals. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 11659–11664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmann, W.; Walter, S.; Beckers, M.; Seide, G.; Gries, T. Applications of Calorimetry in a Wide Context—Differential Scanning Calorimetry; Isothermal Titration Calorimetry and Microcalorimetry: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bakshi, M.S.; Sachar, S. Surfactant polymer interactions between strongly interacting cationic surfactants and anionic polyelectrolytes from conductivity and turbidity measurements. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2004, 282, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, W.J.; Lee, K.M.; Evans, D.R.; McConney, M.E.; Kim, D.Y.; Jeong, K.U. Giant surfactants for the construction of automatic liquid crystal alignment layers. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 8500–8514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H. Vertical alignment of liquid-crystal molecules due to unilateral anchoring from charge accumulation at the semiconductor interface. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2019, 12, 064029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porte, G. Tilted alignment of MBBA induced by short-chain surfactants. J. Phys. 1976, 37, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanelli, A.R.; Scaramuzza, L. Hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide. Sect. C Cryst. Struct. Commun. 1986, 42, 1380–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).