Asphalt Road Pavements to Address Climate Change Challenges—An Overview
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (a)
- Section 2 presents the most significant aspects of road asphalt pavements related to climate change issues, namely the materials that constitute the pavement, the design of the pavement structure, and the pavement condition.
- (b)
- Section 3 describes the three most relevant climate change challenges. They are the air temperature, the precipitation (floods), and the sea-level rise.
- (c)
- Section 4 presents solutions for mitigating climate change challenges, namely models to predict climate change and pavement solutions/developments to address the climate change challenges.
- (d)
- Conclusions and recommendations are suggested in Section 5.
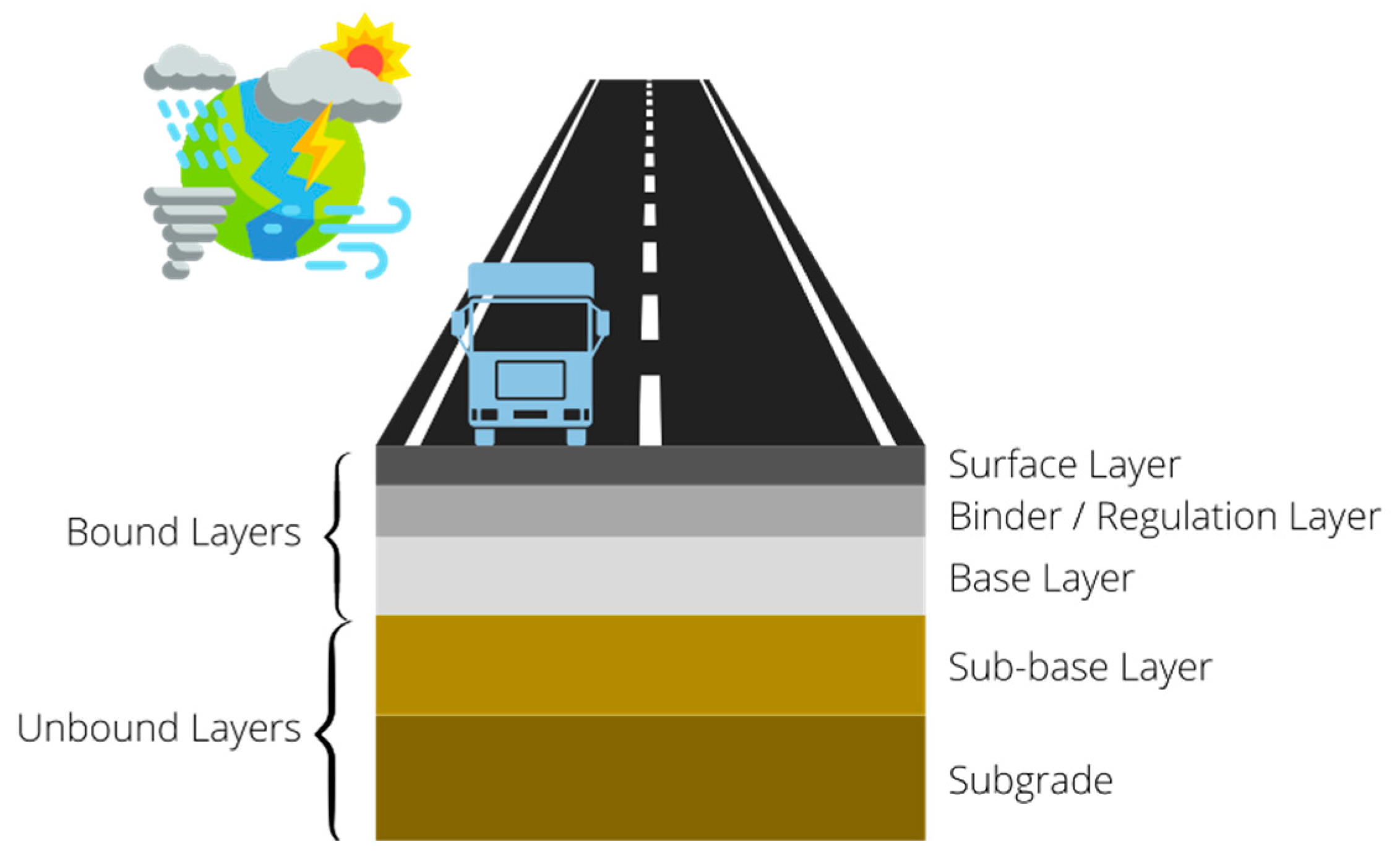
2. Asphalt Pavements
2.1. Materials
2.2. Design
2.3. Condition
3. Climate Change Challenges
3.1. Air Temperature
3.2. Rainfall and Floods
- (a)
- Flash floods—caused by heavy rainfall, resulting in a rapid rise of water height.
- (b)
- River floods—caused when water (from rain or snow melt) rises above the river’s banks.
- (c)
- Coastal floods—caused by storms that surge, from a tropical cyclone to a tsunami.
3.3. Sea-Level Rise
4. Solutions for Mitigating Climate Change Challenges
4.1. Climate Change Prediction
4.2. Pavement Solutions
4.2.1. Permeable Pavements
4.2.2. Cool Pavements
4.2.3. Hydrophobic-Deicing Pavements
4.2.4. Less Temperature-Sensitive Pavements
4.2.5. Salt-Resistant Pavements
4.2.6. Final Remarks
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krishnan, J.M.; Rajagopal, K.R. On the mechanical behavior of asphalt. Mech. Mater. 2005, 37, 1085–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Zhou, X. Resilience assessment of asphalt pavement rutting under climate change. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2022, 109, 103395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudipudi, P.P.; Underwood, B.S.; Zalghout, A. Impact of climate change on pavement structural performance in the United States. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 57, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H. Pavement Analysis and Design; Pearson Education, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. WMO Warns of Frequent Heatwaves in Decades Ahead. Available online: https://news.un.org/en/story/2022/07/1122822 (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- United Nations. Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- Zhang, N.; Alipour, A. Flood risk assessment and application of risk curves for design of mitigation strategies. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. Prot. 2022, 36, 100490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Stoner, A.M.K.; Santos, J. Impacts of future climate change on flexible road pavement economics: A life cycle costs analysis of 24 case studies across the United States. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 103773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahpour, A.; El-Diraby, T. Incorporating climate change in pavement maintenance policies: Application to temperature rise in the Isfahan county, Iran. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 71, 102960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarna, S.T.; Hossain, K.; Mehta, Y.A.; Bernier, A. Climate change adaptation strategies for Canadian asphalt pavements; Part 1: Adaptation strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. AR5 Synthesis Report: Climate Change 2014; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. 2018 Revision of World Urbanization Prospects. Available online: https://population.un.org/wup/ (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- Hu, Y.; Si, W.; Kang, X.; Xue, Y.; Wang, H.; Parry, T.; Airey, G.D. State of the art: Multiscale evaluation of bitumen ageing behaviour. Fuel 2022, 326, 125045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speight, J.G. Chapter 9—Asphalt technology. In Asphalt Materials Science and Technology; Speight, J.G., Ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 361–408. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, S.; Blackman, B.R.K.; Kinloch, A.J.; Taylor, A.C. Durability of asphalt mixtures: Effect of aggregate type and adhesion promoters. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2014, 54, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.; Pais, J. Main flexible pavement and mix design methods in Europe and challenges for the development of an European method. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2017, 4, 316–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Thompson, J.; Kim, D.; Huynh, N.; Carroll, E. Evaluation of pavement service life using AASHTO 1972 and mechanistic-empirical pavement design guides. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adwan, I.; Milad, A.; Memon, Z.A.; Widyatmoko, I.; Ahmat, Z.N.; Memon, N.A.; Yusoff, N.I.M. Asphalt pavement temperature prediction models: A review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Picado-Santos, L. Design temperature on flexible pavements. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2000, 1, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shell. Addendum to the Shell Pavement Design Manual; Shell International Petroleum Company Ltd.: London, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Jitsangiam, P.; Kumlai, S.; Nikraz, H. New theoretical framework for temperature-effect integration into asphalt concrete pavement life prediction with respect to Australian pavement conditions. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2022, 23, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Nam, B.; Abdel-Aty, M. Effects of pavement surface conditions on traffic crash severity. J. Transp. Eng. 2015, 141, 04015020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Transportation Research Board; National Academies of Sciences Engineering Medicine. Estimating the Effects of Pavement Condition on Vehicle Operating Costs; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; p. 77. [Google Scholar]
- Piryonesi, S.M.; El-Diraby, T. Climate change impact on infrastructure: A machine learning solution for predicting pavement condition index. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 306, 124905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Thomas, N.E.; Wayne, L.K. Applicability of the international roughness index as a predictor of asphalt pavement condition1. J. Transp. Eng. 2007, 133, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Tighe, S.L.; Xie, W.-C. Impact of flood hazards on pavement performance. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 21, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-W.W.; Wilson, K.; Hassan, S.A. Prediction of performance and evaluation of flexible pavement rehabilitation strategies. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2017, 4, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AASHTO. AASHTOWare. Available online: https://www.aashtoware.org/ (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, K. Exploring the impact of climate and extreme weather on fatal traffic accidents. Sustainability 2021, 13, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Dawson, A.; Parry, T.; Flintsch, G. Life cycle cost of flexible pavements and climate variability: Case studies from Virginia. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2019, 15, 1665–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA. Climate Change: Global Temperature. Available online: https://www.climate.gov/news-features/understanding-climate/climate-change-global-temperature (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- Knott, J.F.; Sias, J.E.; Dave, E.V.; Jacobs, J.M. Seasonal and long-term changes to pavement life caused by rising temperatures from climate change. Transp. Res. Rec. 2019, 2673, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, F.; Celauro, C. Effect of climate change on asphalt binder selection for road construction in Italy. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2015, 37, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgadillo, R.; Arteaga, L.; Wahr, C.; Alcafuz, R. The influence of climate change in Superpave binder selection for Chile. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2020, 21, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulley, M.E. 5—The urban heat island effect: Causes and potential solutions. In Metropolitan Sustainability; Zeman, F., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 79–98. [Google Scholar]
- Senevirathne, D.M.; Jayasooriya, V.M.; Dassanayake, S.M.; Muthukumaran, S. Effects of pavement texture and colour on urban heat islands: An experimental study in tropical climate. Urban Clim. 2021, 40, 101024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Xu, H.; Tan, Y.; Lv, H.; Assogba, O.C. Low-temperature performance of asphalt mixture based on statistical analysis of winter temperature extremes: A case study of Harbin China. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 208, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandil, K.; Halim, A.O.A.E.; Hassan, Y.; Mostafa, A. Investigation of the effects of different polymer-modified asphalt cements on asphalt mixes at low temperature. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2007, 34, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, A.; Knight, M.A.; Soleymani, H.R. Field monitoring and comparison of thermal- and load-induced strains in asphalt pavement. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2012, 13, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ud Din, I.M.; Mir, M.S.; Farooq, M.A. Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on the properties of asphalt pavements in cold regions: A review. Transp. Res. Procedia 2020, 48, 3634–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, K.P.; Stipanovic, O.I.; ter Maat, H.; Hartmann, A.; Chinowsky, P.; Dewulf, G.P.M.R. Modeling cost impacts and adaptation of freeze–thaw climate change on a porous asphalt road network. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2020, 26, 04020022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Floods. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/floods/#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- Pregnolato, M.; Ford, A.; Wilkinson, S.M.; Dawson, R.J. The impact of flooding on road transport: A depth-disruption function. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 55, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, A.; Harvey, J.; Millan, M.; Wu, R.; Paniagua, F.; Paniagua, J. Full-scale experimental evaluation of the flood resiliency of thin concrete overlay on asphalt pavements. Transp. Res. Rec. 2021, 2676, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, M.; Mallick, R.; Nazarian, S. Numerical modeling of post-flood water flow in pavement structures. Transp. Geotech. 2021, 27, 100468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, P.; Guo, X.; Ge, W. Effects of moisture on the bonding performance of asphalt-aggregate system. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 295, 123667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plati, C.; Pomoni, M.; Stergiou, T. From mean texture depth to mean profile depth: Exploring possibilities. In Bituminous Mixtures and Pavements VII; CRC Press: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kogbara, R.B.; Masad, E.A.; Kassem, E.; Scarpas, A.; Anupam, K. A state-of-the-art review of parameters influencing measurement and modeling of skid resistance of asphalt pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 602–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, M.; Chai, G.; Chowdhury, S.; Martin, T.; Anissimov, Y.; Rahman, A. Rutting and roughness of flood-affected pavements: Literature review and deterioration models. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2018, 24, 04018006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairweather, H.; Yeaman, J. A study of the parameters affecting the performance of roads under an extreme rainfall event. Int. J. Geomate 2014, 7, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Transportation Research Board; National Academies of Sciences Engineering Medicine. Guide for Pavement Friction; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Afonso, M.L.; Dinis-Almeida, M.; Fael, C.S. Characterization of the skid resistance and mean texture depth in a permeable asphalt pavement. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 471, 022029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA. Climate Change: Global Sea Level. Available online: https://www.climate.gov/news-features/understanding-climate/climate-change-global-sea-level (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- Baldino, N.; Angelico, R.; Caputo, P.; Gabriele, D.; Rossi, C.O. Effect of high water salinity on the adhesion properties of model bitumen modified with a smart additive. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 225, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Ji, K.; Li, L.; Xiong, R. The durability of asphalt mixture with the action of salt erosion: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 315, 125749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tang, N.; Zhu, H. The effect of sea salt solution erosion on cohesion, chemical and rheological properties of SBS modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 318, 125923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, A.; Xing, C.; Tan, Y.; Xiao, S.; Li, J.; Li, G. Investigation on clogging characteristics of permeable asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 264, 120273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folland, C.K.; Karl, T.R.; Christy, J.R.; Clarke, R.A.; Gruza, G.V.; Jouzel, J.; Mann, M.E.; Oerlemans, J.; Salinger, M.J.; Wang, S.-W. Climate Change 2001—The Scientific Basis; Published for the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2001; 881p. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, D.; Petersen, J.; Eggert, B.; Alias, A.; Christensen, O.B.; Bouwer, L.M.; Braun, A.; Colette, A.; Déqué, M.; Georgievski, G.; et al. EURO-CORDEX: New high-resolution climate change projections for European impact research. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2014, 14, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Xie, P. Pavement temperature prediction: Theoretical models and critical affecting factors. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 158, 113755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, S.E.; Xiao, K.; Van Griensven, T.J.; Saad, M.; Farghaly, H.; Yang, S.X.; Gharabaghi, B. Hourly road pavement surface temperature forecasting using deep learning models. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarna, S.T.; Hossain, K.; Pandya, H.; Mehta, Y.A. Assessing climate change impact on asphalt binder grade selection and its implications. Transp. Res. Rec. 2021, 2675, 786–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopisetti, L.S.P.; Cetin, B.; Forman, B.A.; Durham, S.; Schwartz, C.W.; Ceylan, H. Evaluation of four different climate sources on pavement mechanistic-empirical design and impact of surface shortwave radiation. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 22, 1155–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, C.E.; Houston, W.N. Calibration and Validation of the Enhanced Integrated Climatic Model for Pavement Design National Cooperative Highway Research Program; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Sha, A.; Liu, X.; Luan, B.; Gao, J.; Jiang, W.; Ma, F. State-of-the-art of porous asphalt pavement: Experience and considerations of mixture design. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 119998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, E.; Pereira, P.; de Picado-Santos, L.; Santos, A. Traffic noise changes due to water on porous and dense asphalt surfaces. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2009, 10, 587–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCHRP. Construction and Maintenance Practices for Permeable Friction Courses; NCHRP: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Xu, H.; Chen, F.; Liu, K.; Tan, Y.; Leng, B. Evolution of water migration in porous asphalt due to clogging. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Yu, H.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Ding, Q.; Tong, B.; Wang, T. Energy analysis for evaluating durability of porous asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 326, 126819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ng, P.-L.; Gong, Y.; Su, H.; Du, J. Experimental study of low temperature performance of porous asphalt mixture. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; Hu, G.; Yang, T.; Du, C.; Oeser, M. Infiltration capacity and structural analysis of permeable pavements for sustainable urban: A full-scale case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 288, 125111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriminna, D.; Ferreri, G.B.; Noto, L.V.; Celauro, C. Numerical comparison of the hydrological response of different permeable pavements in urban area. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-Y.; Lo, S.-L.; Ho, C.-C.; Lin, J.-Y.; Yu, S.L. Field testing of porous pavement performance on runoff and temperature control in taipei city. Water 2019, 11, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Integrated life cycle assessment of permeable pavement: Model development and case study. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 85, 102381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.H.; Ibrahim, N.I.A.; Wahid, J.; Goh, N.A.; Koesmeri, D.R.A.; Nawi, M.N.M. The impact of road pavement on urban heat island (UHI) phenomenon. Int. J. Technol. 2018, 9, 291–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stempihar, J.J.; Pourshams, -M.T.; Kaloush, K.E.; Rodezno, M.C. Porous asphalt pavement temperature effects for urban heat island analysis. Transp. Res. Rec. 2012, 2293, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendel, M. 6—Cool pavements. In Eco-Efficient Pavement Construction Materials; Pacheco-Torgal, F., Amirkhanian, S., Wang, H., Schlangen, E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 97–125. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, K. The deterioration and performance improvement of long-term mechanical properties of warm-mix asphalt mixtures under special environmental conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 135, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badin, G.; Ahmad, N.; Ali, H.M.; Ahmad, T.; Jameel, M.S. Effect of addition of pigments on thermal characteristics and the resulting performance enhancement of asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 302, 124212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Peng, H. A new structure of permeable pavement for mitigating urban heat island. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Wang, Z.; Xie, J.; Liu, Y.; Jia, S. Simulation of the cooling effect of porous asphalt pavement with different air voids. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Qu, K.; Darkwa, J.; Calautit, J.K. Evaluating urban heat island mitigation strategies for a subtropical city centre (a case study in Osaka, Japan). Energy 2022, 250, 123721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Liang, M.; Jiao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Duan, Y.; Liu, H. A review of phase change materials in asphalt binder and asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 258, 119565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, A.; Zhang, J.; Jia, M.; Jiang, W.; Jiao, W. Development of polyurethane-based solid-solid phase change materials for cooling asphalt pavements. Energy Build. 2022, 259, 111873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, M.; Wu, S.; Liu, P. Effect of expanded graphite/polyethylene glycol composite phase change material (EP-CPCM) on thermal and pavement performance of asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 277, 122270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, D.S.N.M.; Hughes, B.R.; Calautit, J.K. Influence of urban form on the performance of road pavement solar collector system: Symmetrical and asymmetrical heights. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 149, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappou, S.; Souliotis, M.; Papaefthimiou, S.; Panaras, G.; Paravantis, J.A.; Michalena, E.; Hills, J.M.; Vouros, A.P.; Ntymenou, A.; Mihalakakou, G. Cool pavements: State of the art and new technologies. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, S. Europe’s Winter Temperatures Have Been Extreme This Year. Here‘s Why. Euronews, 23 February 2021. [Google Scholar]
- BBC. China: North-Eastern City Sees Highest Snowfall in 116 Years. BBC, 11 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- NOAA. Climate Change and Extreme Snow in the U.S. Available online: https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/news/climate-change-and-extreme-snow-us (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- Seeherman, J.; Liu, Y. Effects of extraordinary snowfall on traffic safety. Accid. Anal. Prevention 2015, 81, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wu, Y.; Xia, H.; Jing, B.; Zhang, Q. Review of ice-pavement adhesion study and development of hydrophobic surface in pavement deicing. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2018, 5, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, L.; Shi, X. Environmental impacts of chemicals for snow and ice control: State of the knowledge. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 2751–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, L.G.; Conaway, K.; Rebar, J.; Graettinger, A.J. Alternative deicers for winter road maintenance—A review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.D.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, Y.G.; Kim, I.S.; Yang, E.I. A comparison study of performance and environmental impacts of chloride-based deicers and eco-label certified deicers in South Korea. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2017, 143, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Geng, L.; Ding, X.; Zhang, D.; Huang, X. Experimental study of deicing asphalt mixture with anti-icing additives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 127, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Shi, X. Development and use of salt-storage additives in asphalt pavement for anti-icing: Literature review. J. Transp. Eng. Part B Pavements 2021, 147, 03121002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Hao, P. Modification mechanism and enhanced low-temperature performance of asphalt mixtures with graphene-modified phase-change microcapsules. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 320, 126301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, B.; Buttlar, W.G. Evaluation of polymer modification in asphalt mixtures through digital image correlation and performance space diagrams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 122, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengoz, B.; Isikyakar, G. Evaluation of the properties and microstructure of SBS and EVA polymer modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; You, Z.; Sharifi, N.P.; Yao, H.; Gong, F. Material selections in asphalt pavement for wet-freeze climate zones: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 510–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, P.; Porto, M.; Angelico, R.; Loise, V.; Calandra, P.; Oliviero, R.C. Bitumen and asphalt concrete modified by nanometer-sized particles: Basic concepts, the state of the art and future perspectives of the nanoscale approach. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 285, 102283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayfur, S.; Ozen, H.; Aksoy, A. Investigation of rutting performance of asphalt mixtures containing polymer modifiers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Birgisson, B.; Kringos, N. Polymer modification of bitumen: Advances and challenges. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 54, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picado-Santos, L.G.; Capitão, S.D.; Neves, J.M.C. Crumb rubber asphalt mixtures: A literature review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 247, 118577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chissama, K.S.S.; Picado-Santos, L.G. Assessment of crumb rubber Stone Mastic asphalt potential to be used in Angola. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarroukh, M.; Lahlou, K.; Farah, M. Effect of the bitumen type on the temperature resistance of hot mix asphalt. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 7428–7431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, M.; Capitão, S.; Almeida, A.; Picado-Santos, L. Influence of plastic waste on the workability and mechanical behaviour of asphalt concrete. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.; Capitão, S.; Estanqueiro, C.; Picado-Santosc, L. Possibility of incorporating waste plastic film flakes into warm-mix asphalt as a bitumen extender. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 291, 123384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.; Capitão, S.; Bandeira, R.; Fonseca, M.; Picado-Santos, L. Performance of AC mixtures containing flakes of LDPE plastic film collected from urban waste considering ageing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 232, 117253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crucho, J.; Picado-Santos, L.; Neves, J.; Capitão, S. A review of nanomaterials’ effect on mechanical performance and aging of asphalt mixtures. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamuye, Y.; Liao, M.-C.; Do, N.-D. Nano-Al2O3 composite on intermediate and high temperature properties of neat and modified asphalt binders and their effect on hot mix asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 331, 127304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, X.; Ji, X.; Li, J.; Li, K.; Shi, J. Investigating the rutting mechanism of asphalt mixtures based on particle tracking technology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Nian, T.; Zhou, F. Analysis of factors that influence anti-rutting performance of asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 254, 119237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouranian, M.R.; Imaninasab, R.; Shishehbor, M. The effect of temperature and stress level on the rutting performance of modified stone matrix asphalt. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2020, 21, 1386–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Yu, G. Material optimization and optimum asphalt content design of asphalt mixture in salty and humid environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 196, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

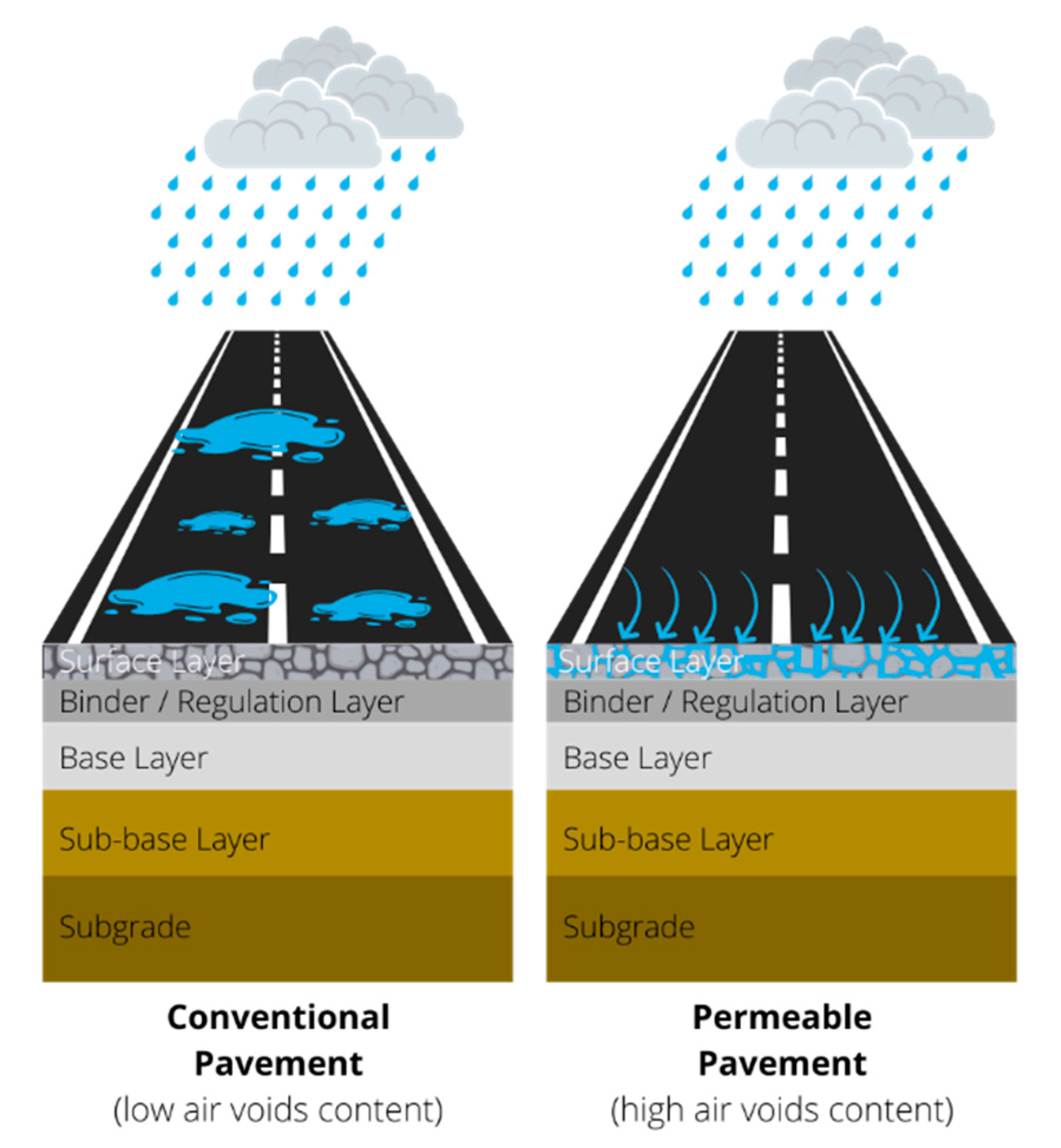
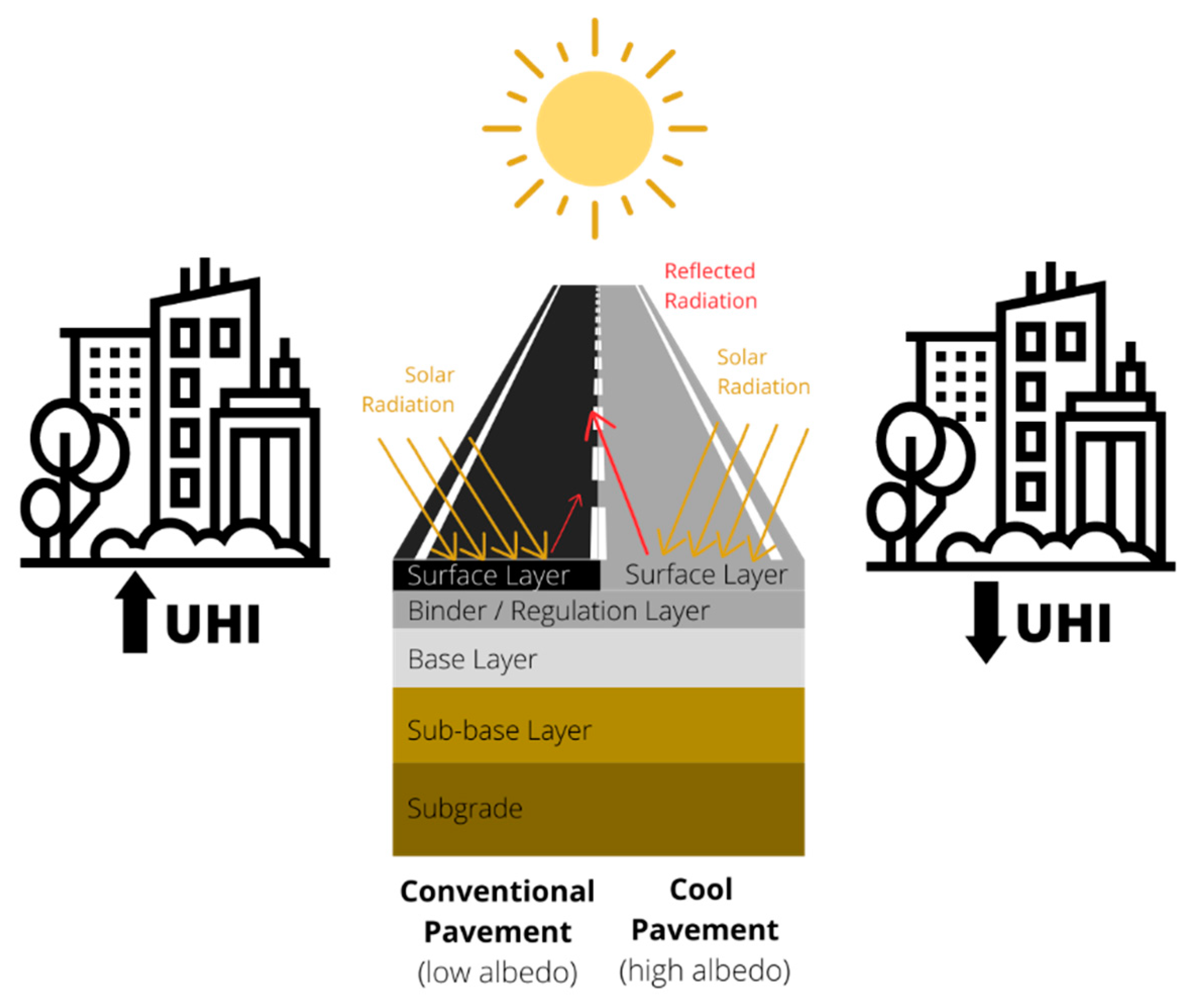
| High Temperature | Low Temperature | Rainfall and Floods | Sea-Level Rise |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decrease bitumen grade | Increase bitumen grade | Permeable pavements | Anti-stripping agents |
| Cool pavements | Hydrophobic-deicing pavements | ||
| Increase aggregate skeletons (e.g., use SMA) | Bitumen/Mixture modification | ||
| Bitumen/Mixture modification | Increase asphalt layer thickness | ||
| Increase asphalt layer thickness |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almeida, A.; Picado-Santos, L. Asphalt Road Pavements to Address Climate Change Challenges—An Overview. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12515. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412515
Almeida A, Picado-Santos L. Asphalt Road Pavements to Address Climate Change Challenges—An Overview. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(24):12515. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412515
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmeida, Arminda, and Luís Picado-Santos. 2022. "Asphalt Road Pavements to Address Climate Change Challenges—An Overview" Applied Sciences 12, no. 24: 12515. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412515
APA StyleAlmeida, A., & Picado-Santos, L. (2022). Asphalt Road Pavements to Address Climate Change Challenges—An Overview. Applied Sciences, 12(24), 12515. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412515








