Featured Application
Characterization of the corneal nerve fibers is gaining popularity for objective assessment of anterior segment anomalies such as dry eye disease. Confocal microscopy provides high-resolution imaging of the sub-basal plexus; thus, several parameters such as corneal length, density or tortuosity can be analyzed. However, the analysis of these images is usually performed based on manual or semiautomated methods, many of which are subjective and time consuming. In this work, a fully automated tortuosity corneal nerve fiber analysis method is proposed. This new tool may be very useful to obtain an accurate evaluation of nerve alterations, to monitor changes over time and/or in response to treatment, to ensure comparisons across different studies or even to improve the diagnosis of ocular surface diseases.
Abstract
An automated tool for corneal nerve fiber tortuosity quantification from in vivo confocal microscopy (IVCM) is described and evaluated. The method is a multi-stage process based on the splitting of the corneal nerve fibers into individual segments, whose endpoints are an extreme or intersection of white pixels on a binarized image. Individual segment tortuosity is quantified in terms of the arc-chord ratio. Forty-three IVCM images from 43 laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) surgery patients were used for evaluation. Images from symptomatic dry eye disease (DED) post-LASIK patients, with () and without () ocular pain, and non-DED post-LASIK controls () were assessed. The automated tortuosity measure was compared to a manual grading one, obtaining a moderate correlation (Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient = , ). The new tortuosity index was significantly higher in post-LASIK patients with ocular pain than in control patients (), while no significant differences were detected with manual measurement (). The tortuosity quantification was positively correlated with the ocular surface disease index (OSDI) and a numeric rating scale (NRS) assessing pain ( and , respectively). The results show good performance of the proposed automated methodology for the evaluation of corneal nerve tortuosity.
1. Introduction
The cornea is the most highly innervated tissue in the human body [1,2]. Corneal nerves are located between Bowman’s layer and the basal epithelial layer, creating a nerve fiber network known as the corneal sub-basal nerve plexus [3]. In vivo confocal microscopy (IVCM) technology provides corneal visualization with high-quality resolution, allowing the evaluation of the corneal sub-basal nerve plexus [4]. This examination technique was reported to be clinically useful for corneal evaluation during the 1990s [5]. Later, several methods were developed for quantifying corneal IVCM image parameters. Oliveira-Soto and Efron [6] showed that the technique allows for the characterization of the sub-basal corneal plexus using the following parameters, among others: density, length, number, width, tortuosity or even reflectivity of corneal nerves. Subsequently, multiple studies [7,8,9] have confirmed that numerous properties of corneal nerves are linked to both ocular and systemic disorders. Thus, IVCM has naturally taken on new importance as the clinical method of choice to analyze corneal nerve structure [10].
The degree of curvature in the nerves of the corneal sub-basal plexus is known as corneal nerve tortuosity. A high-tortuosity nerve is meaningfully curved and has many twists (Figure 1a). In contrast, a low-tortuosity nerve appears approximately straight (Figure 1b). Estimating corneal nerve tortuosity from IVCM images is an important challenge for vision science [7]. Corneal tortuosity analysis could be useful to improve eye disease diagnosis because there is a relevant connection between some ocular and systemic diseases and corneal nerve tortuosity [11,12]. In particular, several studies have reported a strong positive correlation between corneal nerve tortuosity and dry eye disease (DED) [13,14,15,16,17]. In addition, it is commonly accepted that the structure and function of the ocular nerves are altered in DED combined with ocular pain [18,19,20]. Moreover, sub-basal nerve tortuosity is increased in the short term after corneal refractive surgery [21]. Tortuosity has also been investigated in healthy subjects [22], and in other diseases such as non-neurological autoimmune diseases [23], diabetic neuropathy [7,12,24], glaucoma [25], unilateral herpes zoster [26], acute acanthamoeba and fungal keratitis [27] and herpes simplex keratitis [28]. In order to establish a link between tortuosity and ocular or systemic anomalies, the degree of nerve fiber tortuosity has been commonly measured on an ordinal scale [8,29], which directly implies adding an element of subjectivity in the grading process.
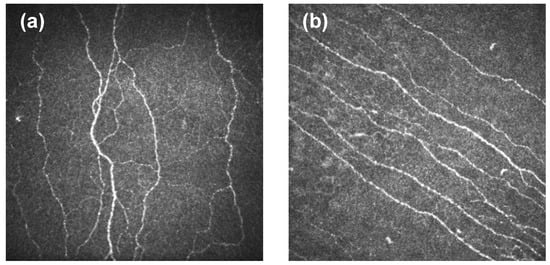
Figure 1.
Cornel nerve tortuosity. (a) High tortuosity. (b) Low tortuosity.
Different criteria have been used to define and measure the tortuosity of different anatomical structures such as intracerebral vasculature [30] or retinal vessel [31]. Once the anatomical structure is identified in an image, it will be represented as a group of pixels with a curvilinear shape, and then its tortuosity can be measured. Designed measurements are based on different features such as length [30,31], angle [32,33,34] and curvature [35], but there is no standard measure for quantifying the tortuosity of nerve fibers [36].
Despite the advances in image analysis, manual or semiautomatic methodologies remain the most commonly used methods for analyzing corneal nerve tortuosity from IVCM images [37]. However, these techniques are subjective, time consuming and heavily dependent on the experience of the evaluator, which might not deliver reproducible outcomes [38]. These limitations show the need to create new automatic analysis systems that are able to provide reliable results. In 2004, Kallinikos et al. [12] were one of the first research groups that proposed an automated method for analyzing corneal nerve tortuosity in diabetic patients with neuropathy. Subsequently, in 2011, Scarpa et al. [29] provided several algorithms for the evaluation of corneal nerve tortuosity. More recently, automated approaches to grade the tortuosity of corneal nerves based on deep learning methodology have been developed (see [34,39] among others).
However, many of these methods focus on computing the tortuosity of individual fibers instead of calculating the global tortuosity of the whole image. These measurements are combined using the average of several fiber tortuosity degrees or the weighted average by fiber length. This approach does not take into account the fact that nerve fibers could exhibit considerably different tortuosity characteristics in the same image, i.e., highly twisted nerves coexisting with other very straight ones, which is usually labeled as highly tortuous by clinicians [29]. This may explain why an underestimation has been noted when fully automated algorithms are used [40]. In this work, a new index to quantify sub-basal nerve tortuosity using an automatic analysis of corneal IVCM images is proposed. The method is based on the segmentation of the image in individual segments between extreme or intersection points instead of nerve fibers. Thus, each fiber may be characterized by one or more segments depending on nerve fiber branching and length. Global tortuosity is calculated by taking into account the curvature of each identified segment regardless of the location of each fiber. The fully automated method is implemented in a fast and easy-to-use R [41] tool. Finally, the new index is compared to a manual grading method in laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) surgery patients, because they usually show an altered sub-basal nerve plexus and automatic nerve recognition might be more challenging [40].
2. Materials and Methods
The clinical study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Valladolid University Clinical Hospital and complied with the Tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. The nature of the research and protocols was explained to the patients before written consent was obtained.
Inclusion criteria were LASIK patients who underwent refractive surgery in both eyes and suffered from chronic DED in both eyes after the surgery procedure. Two case groups were created, one group composed of LASIK patients who suffered from DED symptoms (post-LASIK DED group), and another group composed of post-LASIK patients who reported suffering from pain in addition to other DED symptoms (post-LASIK DED-pain group). To be included in the post-LASIK DED group, patients should obtain a score in the Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI) questionnaire, and should also show one unbalanced homeostasis marker, either corneal fluorescein staining (CFS ) or tear break-up time (TBUT s), based on the TFOS DEWS II report regarding the diagnostic criteria for DED [42]. To be included in the post-LASIK DED-pain group, in addition to being diagnosed with DED, as mentioned above, patients should also suffer from ocular pain. Ocular pain was defined as a score of ≥2 on a numerical rating scale (NRS). Finally, a control group was also recruited; the inclusion criterion was a history of LASIK surgery in both eyes and the absence of DED symptoms (OSDI score ).
Exclusion criteria were failure to discontinue contact lens use at least 15 days before the study, presence of any active ocular disease, except DED, and history of any other ocular surgery, except LASIK.
2.1. Clinical Assessment
Clinical evaluation was always performed by the same examiner following this sequence.
- The OSDI questionnaire was administered to all volunteers. This instrument allows DED screening [42] and also DED severity classification: “mild” (score 13–22), “moderate” (score 23–32) and “severe” (score 33–100).
- A NRS was used to rate the severity of pain, as previously reported [43]. LASIK patients were indicated to rate their average ocular pain severity on a 10-point scale ranging from “no pain” (score 0) to “the most severe pain” (score 10). Scores ranging from 2 to 4 was considered “mild” pain, from 5 to 7 “moderate” pain, and from 8 to 10 “severe” pain.
- Corrected distance visual acuity (CDVA) was evaluated using an ETDRS chart at a 4 m distance.
- TBUT was assessed after the instillation of 5 mL of 2% sodium fluorescein. The measurement was repeated three times to obtain an average value.
- CFS was evaluated using the Oxford scheme (grade 0–5).
- Confocal microscopy assessment of the cornea. The IVCM images of the cornea were obtained using the Rostock cornea module of the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph III (Heidelberg Engineering GmbH, Heidelberg, Germany). Non-overlapping images of the central cornea focused on the sub-basal nerve plexus were obtained using sequence and/or volume scans. Each image was comprised of pixels, which represents a coronal section of μm (0.16 mm). The grade of nerve tortuosity was subjectively evaluated according to the scale (0–4) reported by Oliveira-Soto and Efron [6]. The observer who assessed each image was blinded to the LASIK group classification.
In the case of CDVA, TBUT and CFS, both eyes were assessed, and the mean was computed for analysis.
2.2. Automated Tortuosity Index
The proposed method was implemented in R statistical software [41] and provides automatic tortuosity indexes of the corneal nerve structure from IVCM images. The IVCM images were saved as JPEG monochrome, pixel digital images. An image was defined as a two-dimensional function , where x and y are spatial coordinates, and the value of f at any pair of coordinates is called the intensity of the image at that point.
2.2.1. Nerve Tracing
A multi-stage process was used to prepare the images for quantification. The details of each step are outlined below, and the complete sequence is summarized using a sample image from the dataset in Figure 2.

Figure 2.
Scheme of the nerve tracing process.
Pre-Processing. The first step in the preprocessing stage was an image-sharpening technique for emphasizing edges. A Gaussian filter was used to blur the edges of the image, and then it was subtracted from the original. The subtracted image was multiplied by a weighting factor and added back to the original.
In the second step, the images were binarized. This step began with a normalization procedure where pixels were classified into “nerve” and “background” pixels. The A k-means algorithm was applied to identify two pixel groups. The normalization of images was achieved by subtracting the mean and dividing the result by the standard deviation of the pixel intensity values of the “background” cluster. The normalized images were binarized by setting a threshold, which assumes that at least 95% of the pixels are background pixels. As this procedure increases the amplitude of noise, a median filter was also applied to reduce this artifact. In preprocessed images, nerve structures appear in white.
Post-Processing. The binarized images resulting from the preprocessing stage showed undesired noise and artefacts such as small white spots (that could correspond, for example, to dendritic cells). These undesired fragments were automatically removed in the postprocessing step. The removal of small fragments was followed by a dilation operation, which adds pixels to the nerve boundaries and fills small gaps. Finally, the dilated nerves were reduced to thin lines and skeletonized images were obtained.
2.2.2. Nerve Splitting
The nerve-splitting step consisted of breaking up the nerves. In this process, neighboring white pixels in a skeletonized image were grouped into individual segments.
First, the watershed algorithm [44] was used to segment the skeletonized images into different regions. A region in the image consisted of any group of connected pixels. Pixels were considered connected if they shared a side as and or and or touched at a corner as and . Then, in each region, the algorithm identified two types of pixel: nerve extremes and nerve intersections a nerve extreme is a white pixel connected to a single white pixel, while a nerve intersection is a white pixel connected to more than two white pixels.
The nerves were broken up into individual segments whose endpoints were an extreme and/or an intersection pixel. Hereinafter, K denotes the number of nerve segments in an image. Figure 3 shows the nerve splitting process in the sample image.
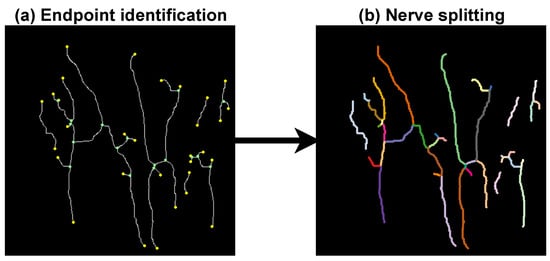
Figure 3.
Nerve splitting process. (a) The nerve extreme and the nerve intersection pixels are marked in yellow and green, respectively. (b) Individual nerve segments are displayed in different colors.
2.2.3. Tortuosity Characterization
Once the individual nerve segments were extracted, each one was individually examined to compute the local segment tortuosity. This segment tortuosity characterization was performed in terms of the arc-chord ratio, the simplest mathematical method to estimate tortuosity. For the segment, was defined as the ratio of the length of the segment (denoted by ) to the distance between its endpoints ():
Then, the individual evaluations of the K segments were combined as follows:
where L corresponds to the total length of the nerves calculated as the sum of the length of its K segments. This index was always greater than zero. It integrated the information about the number of individual segments and each individual segment tortuosity in such a way that higher number of segments and/or higher segment tortuosity implied higher global tortuosity. The quantification of tortuosity was similar to the metric proposed by Grisan et al. [31] to perform a characterization of retinal vascular tortuosity.
2.3. Data Analysis
Quantitative variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Median and interquartile range (IQR) were used to summarize distributions of ordinal variables. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed to test the differences among groups. When one-way ANOVA assumptions were not met, i.e., either a normal distribution and/or equal variance, the Kruskal–Wallis and Welch ANOVA was performed, respectively. Post hoc comparisons were performed using Student’s t-tests, Welch’s t-test or the Mann–Whitney U test when required. For all of them, the Benjamini and Hochberg procedure was applied to control the false discovery rate [45].
To evaluate the correlation between the new automated tortuosity index and the ocular parameters, the Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient was employed, along with a 95% confidence interval (CI) computed by 5000 bootstrap samples. The hypothesis tests of the correlation coefficients significance were performed.
3. Results
3.1. Ocular Parameters
Forty-three (21 males and 22 females) consecutive LASIK patients aged between 25 and 59 years (mean age: ) were recruited. Seven were classified into the post-LASIK DED group, 16 into the post-LASIK DED-pain group and 20 composed the control group. No recruited patient suffered from diabetes. The clinical tests are summarized in Table 1. There were significant () differences between control and both post-LASIK groups for OSDI scores. In addition, the post-LASIK DED-pain group showed significantly () higher NRS pain scores in comparison with the post-LASIK DED and the control group. There were no significant differences () among groups for the other ocular parameters and age.

Table 1.
Outcomes of the subjective and objective tests performed.
3.2. Tortuosity Measurements
The Spearman’s rank correlation coeffient between automated and subjective tortuosity indexes was (95%CI: ; ) (see Figure 4a). Table 2 shows the tortuosity outcomes of the three post-LASIK groups and the total length estimated by the automated procedure. The automated tortuosity index, ranging from 0 to 30, was significantly different among groups (). Post hoc analysis showed that this new tortuosity index was significantly increased in the post-LASIK DED-pain group compared with the control group (). In contrast, there were no significant differences among groups in the subjective tortuosity grading (). Regarding the total length of the automatically detected nerves, the control group showed a trend () for longer values than both case groups.
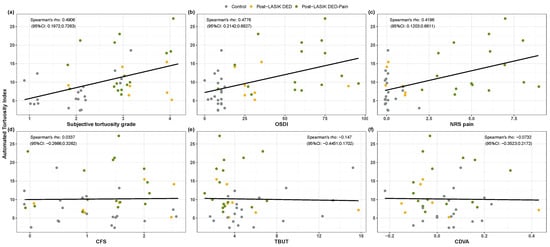
Figure 4.
Correlations between the automated tortuosity index and ocular parameters. Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients and 95% CI are shown on the scatterplots for the automated tortuosity index against (a) subjective tortuosity index, (b) OSDI score, (c) NRS pain score, (d) CFS, (e) TBUT and (f) CDVA. Values of the ordinal variables are jittered to prevent overplotting.

Table 2.
Tortuosity indexes obtained from IVCM images for control and post-LASIK DED patients.
Regarding the correlations between the automated tortuosity index and ocular parameters (Figure 4b–f), the Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients indicated that tortuosity was positively correlated with the OSDI and NRS pain scores (Figure 4b,c); and , respectively). However, the tortuosity index did not correlate with CFS, TBUT and CDVA (Figure 4d–f); , and ).
The execution time for the proposed automated procedure was seconds per image, and seconds for nerve tracing and splitting stages, respectively. The estimation was carried out using R coding on a machine equipped with an Intel 3770 CPU at GHz.
4. Discussion
IVCM is a non-invasive technique useful for the examination of the sub-basal nerve plexus [29]. Although the area observed in a single IVCM scan image may be too small to represent the whole corneal status, the analysis of these images and the objective measures that can be obtained from them have proven to be interesting biomarkers for different ocular disorders. In 2001, Oliveira and Efron [6] successfully applied IVCM to corneal nerve imaging. Since then, many authors have shown that several corneal nerve features are measurable from IVCM images and are related to both ocular and systemic diseases [7,8,9]. Among other features of nerve fibers, tortuosity has been outlined, since it can be used to interpret the degeneration and subsequent regeneration of nerves, which leads to active neural growth [9]. Many ocular disorders can be linked to the tortuosity of corneal nerve fibers. Particularly for DED, while there is contradictory information regarding some characteristics such as nerve density, including a decrease [15,16], no change [46,47] and an increase [48], increased tortuosity has been consistently related to this condition [15,16,47,48,49]. We therefore think that, among the different sub-basal corneal nerve measures, tortuosity could be one of the best parameters to evaluate corneal nerve health status.
In recent years, the interest in corneal nerve research has been growing rapidly and the analysis of IVCM images, where sub-basal nerves appear well defined, has become a common practice. Surprisingly, the increasing use of IVCM in ophthalmic clinical practice and the advances in image analysis have not led to the proliferation of fully automated approaches that can facilitate quantitative corneal nerve analysis. Conventionally, corneal nerve abnormalities have been commonly identified through arduous manual or semiautomatic evaluation processes [50,51,52]. Such approaches result in time-consuming and subjective outcomes, with limited inter-rater reliability across observers [38]. As expected, in this type of tool, the operator’s ability has a high impact on the accuracy of the measurements. In addition, manual and semiautomated software are inefficient when analyzing a high volume of IVCM images. Thus, the development of fully automated methods to quantify corneal nerve features from IVCM images is important in order to allow for an efficient and accurate evaluation of cornel nerve morphology. Although there are some automatic software developments, such as ACCMetrics (University of Manchester, Manchester, UK), an underestimation in their measurements compared to manual tools has been observed [40]. Regarding tortuosity, a possible reason for this discrepancy may be considering tortuosity at the single fiber level instead of at the whole image level, without taking into consideration that fibers with very different tortuosity patterns can be present in the same image [29]. The present research resulted in a fully automated tool for the quantification of corneal nerve tortuosity from IVCM images. The method computes the tortuosity at image level instead of fiber level, simplifying the tortuosity characterization to small length segments, rather than considering the wide variety of tortuosity patterns that can exhibit large fibers.
To assess the ability of this new automatic analysis system, and to evaluate its superiority over the manual one commonly used, we recruited LASIK patients with DED symptoms, because DED patients as well as LASIK subjects usually show an altered sub-basal corneal nerve plexus [10,53]. Thus, we used images with altered nerves instead of images from healthy subjects to further challenge the ability of this new automatic system. Moreover, we recruited two different groups of symptomatic LASIK patients (one group suffering from habitual DED symptoms and another also suffering from corneal pain), because we wanted to assess if the new automatic system could also detect differences in tortuosity among symptomatic LASIK patients. Although the observer was blind to the LASIK group classification when subjectively assessing nerve tortuosity, the obtained scores were not significantly different among groups (Table 2). In contrast, the automated tortuosity index showed that the LASIK pain group suffered significantly higher tortuosity than the non-symptomatic LASIK group (Table 2). However, the difference between both symptomatic LASIK groups was not significant, although the score of the LASIK pain group was higher. Guerrero-Moreno et al. [54] have reported that autoimmune DED patients suffering from corneal pain show increased nerve tortuosity in comparison with healthy controls. These authors used a subjective grading system, which might be the reason why they did not find increased tortuosity in Meibomiam gland dysfunction patients suffering from corneal pain, although their tortuosity values were also increased.
In the present study, we observed a moderate () correlation between the subjective and automated tortuosity grading methods, but the automated tool is expected to provide more reliable data. In addition, it was also observed that the values of the automated tortuosity index showed a positive relationship with OSDI and NRS pain scores (Figure 4). These findings show that subjective ocular surface perception is obviously related to the nervous system, specifically the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve. In fact, it has been reported that, after corneal refractive surgery, the regeneration of corneal nerves correlates strongly with the recovery of corneal sensation [55]. On the contrary, in the present study, CFS and TBUT did not show any relationship with the automated tortuosity index. This finding supports previous reports highlighting that, in LASIK patients suffering from chronic corneal pain, conventional DED tests do not explain the persistent ocular surface symptoms [56,57].
The limitations of the current study are related to the nature of the sample used to evaluate the automated method. First, our recruited volunteers were post-LASIK patients with DED symptoms. These selection criteria contributed to reducing the heterogeneity of the image features in the sample. However, it would be interesting to evaluate the performance of this new automatic tool in other patients suffering from different anomalies. Future studies should assess if the proposed automated method can perform similarly using corneal sub-basal plexus images with additional information such as inflammatory cells or gliomas. However, our tool could be optimized to detect these features on IVCM images to increase the accuracy of the outcomes in other anomalies. Second, the sample size was relatively small, especially in the post-LASIK DED group. This shortfall would have an impact on the statistical power of the hypothesis test to identify as significant the differences between groups. Despite these limitations, this proof-of-concept study designed to describe an automatic method has provided data showing its adequateness for the assessment of corneal nerve tortuosity. Future studies should corroborate this study’s findings using larger sample populations, including patients with diverse ocular anomalies.
5. Conclusions
The analysis of corneal nerve fiber tortuosity to better diagnose and monitor corneal diseases is beyond doubt. However, this tortuosity assessment has been traditionally performed through manual or semi-automated methods. In this work, a fully automated, quick and simple method to quantify corneal nerve tortuosity from IVCM images is proposed. The effectiveness of the proposed tortuosity index has been demonstrated on a sample of post-LASIK patients with DED symptoms.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology and original draft preparation: I.F. and A.L.-M.; software: I.F.; data collected: A.V., M.C. and M.J.M.; supervised and provided intellectual contributions: M.J.M. and M.C.; review and editing: I.F., A.V., M.C., M.J.M., A.d.l.M. and A.L.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The study was supported in part by Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Bioingeniería, Biomateriales y Nanomedicina (CIBER-BBN) (CB06/01/0003 grant).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institute of Applied Ophthalmobiology (IOBA) institutional review board and by the Ethics Committee of the University of Valladolid (Protocol code PI-15-301, approved on 25 May 2017).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author, I.F. The data are not publicly available, as they contain information that could compromise the privacy of research participants.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ANOVA | Analysis Of Variance. |
| CDVA | Corrected Distance Visual Acuity. |
| CFS | Corneal Fluorescein Staining. |
| CI | Confidence Interval. |
| DED | Dry Eye Disease. |
| IOBA | Institute of Applied Ophthalmobiology. |
| IQR | InterQuartile Range. |
| IVCM | In vivo confocal microscopy. |
| LASIK | Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis. |
| NRS | Numeric Rating Scale. |
| OSDI | Ocular Surface Disease Index. |
| SD | Standard Deviation. |
| TBUT | Tear Break-Up Time. |
References
- Müller, L.J.; Pels, L.; Vrensen, G. Ultrastructural organization of human corneal nerves. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1996, 37, 476–488. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, L.; Vrensen, G.; Pels, L.; Cardozo, B.N.; Willekens, B. Architecture of human corneal nerves. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1997, 38, 985–994. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, L.J.; Marfurt, C.F.; Kruse, F.; Tervo, T.M. Corneal nerves: Structure, contents and function. Exp. Eye Res. 2003, 76, 521–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokot, J.; Wylęgała, A.; Wowra, B.; Wójcik, Ł.; Dobrowolski, D.; Wylęgała, E. Corneal confocal sub-basal nerve plexus evaluation: A review. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018, 96, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, W.; Thaer, A.A.; Kroll, P.; Geyer, O.C.; Garcia, A.J. Optical sectioning of the cornea with a new confocal in vivo slit-scanning videomicroscope. Ophthalmology 1995, 102, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Soto, L.; Efron, N. Morphology of corneal nerves using confocal microscopy. Cornea 2001, 20, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, K.; Pritchard, N.; Vagenas, D.; Russell, A.; Malik, R.; Efron, N. Standardizing corneal nerve fibre length for nerve tortuosity increases its association with measures of diabetic neuropathy. Diabet. Med. 2014, 31, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, R.; Kheirkhah, A.; Aggarwal, S.; Hamrah, P.; Trucco, E. A fully automated tortuosity quantification system with application to corneal nerve fibres in confocal microscopy images. Med. Image Anal. 2016, 32, 216–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Markoulli, M. Automatic analysis of corneal nerves imaged using in vivo confocal microscopy. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2018, 101, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Xie, J.; Yang, T.; Su, P.; Liu, R.; Sun, T.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Feng, X.; Ma, S.; et al. Quantification of Increased Corneal Subbasal Nerve Tortuosity in Dry Eye Disease and Its Correlation With Clinical Parameters. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Hwang, J.; Mehra, D.; Galor, A. Corneal nerve abnormalities in ocular and systemic diseases. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 202, 108284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallinikos, P.; Berhanu, M.; O’Donnell, C.; Boulton, A.J.; Efron, N.; Malik, R.A. Corneal nerve tortuosity in diabetic patients with neuropathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, E.; Galimberti, D.; Viola, F.; Mapelli, C.; Mojana, F.; Pirondini, C.; Ratiglia, R. The cornea in Sjögren’s syndrome: An in vivo confocal study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbé, A.; Liang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Baudouin, C.; Sun, X. Corneal nerve structure and function in patients with non-Sjögren dry eye: Clinical correlations. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 5144–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, O.; Labbé, A.; Borderie, V.; Hamiche, T.; Dupas, B.; Laroche, L.; Baudouin, C.; Bouheraoua, N. Increased corneal sub-basal nerve density in patients with Sjögren syndrome treated with topical cyclosporine A. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2017, 45, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardigos, J.; Barcelos, F.; Carvalho, H.; Hipólito, D.; Crisóstomo, S.; Vaz-Patto, J.; Alves, N. Tear meniscus and corneal sub-basal nerve plexus assessment in primary Sjögren syndrome and Sicca syndrome patients. Cornea 2019, 38, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Zhao, K.; Ma, S.; Liu, R.; Gao, Y.; Hu, C.; Xie, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, H. Objective analysis of corneal subbasal nerve tortuosity and its changes in patients with dry eye and diabetes. Chin. J. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2019, 12, 638–644. [Google Scholar]
- Lambiase, A.; Micera, A.; Sacchetti, M.; Cortes, M.; Mantelli, F.; Bonini, S. Alterations of tear neuromediators in dry eye disease. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2011, 129, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galor, A.; Levitt, R.; Felix, E.; Martin, E.; Sarantopoulos, C. Neuropathic ocular pain: An important yet underevaluated feature of dry eye. Eye 2015, 29, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmonte, C.; Nichols, J.J.; Cox, S.M.; Brock, J.A.; Begley, C.G.; Bereiter, D.A.; Dartt, D.A.; Galor, A.; Hamrah, P.; Ivanusic, J.J.; et al. TFOS DEWS II pain and sensation report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 404–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, T.; Brahma, A.; O’Donnell, C.; Efron, N. Subbasal nerve fiber regeneration after LASIK and LASEK assessed by noncontact esthesiometry and in vivo confocal microscopy: Prospective study. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2007, 33, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roszkowska, A.M.; Wylęgała, A.; Gargano, R.; Spinella, R.; Inferrera, L.; Orzechowska-Wylęgała, B.; Aragona, P. Impact of corneal parameters, refractive error and age on density and morphology of the subbasal nerve plexus fibers in healthy adults. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Liu, X.; Yu, X.; Qin, Q.; Yu, N.; Ke, W.; Wang, K.; Chen, M. Corneal in vivo Confocal Microscopy for Assessment of Non-Neurological Autoimmune Diseases: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 809164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klisser, J.; Tummanapalli, S.S.; Kim, J.; Chiang, J.C.B.; Khou, V.; Issar, T.; Naduvilath, T.; Poynten, A.M.; Markoulli, M.; Krishnan, A.V. Automated analysis of corneal nerve tortuosity in diabetes: Implications for neuropathy detection. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2021, 105, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Rumpel, H.; Baskaran, M.; Tun, T.A.; Strouthidis, N.; Perera, S.A.; Nongpiur, M.E.; Lim, W.E.; Aung, T.; Milea, D.; et al. Optic nerve tortuosity and globe proptosis in normal and glaucoma subjects. J. Glaucoma. 2019, 28, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrah, P.; Cruzat, A.; Dastjerdi, M.H.; Prüss, H.; Zheng, L.; Shahatit, B.M.; Bayhan, H.A.; Dana, R.; Pavan-Langston, D. Unilateral herpes zoster ophthalmicus results in bilateral corneal nerve alteration: An in vivo confocal microscopy study. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbanyan, K.; Hoesl, L.; Schrems, W.; Hamrah, P. Corneal nerve alterations in acute Acanthamoeba and fungal keratitis: An in vivo confocal microscopy study. Eye 2012, 26, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrah, P.; Cruzat, A.; Dastjerdi, M.H.; Zheng, L.; Shahatit, B.M.; Bayhan, H.A.; Dana, R.; Pavan-Langston, D. Corneal sensation and subbasal nerve alterations in patients with herpes simplex keratitis: An in vivo confocal microscopy study. Ophthalmology 2010, 117, 1930–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpa, F.; Zheng, X.; Ohashi, Y.; Ruggeri, A. Automatic evaluation of corneal nerve tortuosity in images from in vivo confocal microscopy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 6404–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullitt, E.; Gerig, G.; Pizer, S.M.; Lin, W.; Aylward, S.R. Measuring tortuosity of the intracerebral vasculature from MRA images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2003, 22, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisan, E.; Foracchia, M.; Ruggeri, A. A novel method for the automatic grading of retinal vessel tortuosity. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2008, 27, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.G.; Hsu, W.; Li Lee, M.; Wang, H. ADRIS: An automatic diabetic retinal image screening system. Stud. Fuzziness Soft Comput. 2001, 60, 181–210. [Google Scholar]
- Bribiesca, E. A measure of tortuosity based on chain coding. Pattern Recognit. 2013, 46, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrgardt, P.; Zandavi, S.M.; Poon, S.K.; Kim, J.; Markoulli, M.; Khushi, M. U-net segmented adjacent angle detection (USAAD) for automatic analysis of corneal nerve structures. Data 2020, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pereira, E.; Zheng, Y.; Su, P.; Xie, J.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Qi, H.; Liu, J.; et al. Automated tortuosity analysis of nerve fibers in corneal confocal microscopy. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2725–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Chen, T.; Xie, J.; Zheng, Y.; Qi, H.; Borroni, D.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J. Corneal nerve tortuosity grading via ordered weighted averaging-based feature extraction. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 4983–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Huang, X. Semiautomated and Automated Quantitative Analysis of Corneal Sub-Basal Nerves in Patients With DED With Ocular Pain Using IVCM. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 831307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannaccare, G.; Pellegrini, M.; Sebastiani, S.; Moscardelli, F.; Versura, P.; Campos, E.C. In vivo confocal microscopy morphometric analysis of corneal subbasal nerve plexus in dry eye disease using newly developed fully automated system. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2019, 257, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrgardt, P.; Khushi, M.; Poon, S.; Withana, A. Deep Learning Fused Wearable Pressure and PPG Data for Accurate Heart Rate Monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 27106–27115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, J.Y.; Yang, L.W.Y.; Ji, A.J.S.; Nubile, M.; Mastropasqua, L.; Allen, J.C.; Mehta, J.S.; Liu, Y.C. Validation of the use of automated and manual quantitative analysis of corneal nerve plexus following refractive surgery. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wolffsohn, J.S.; Arita, R.; Chalmers, R.; Djalilian, A.; Dogru, M.; Dumbleton, K.; Gupta, P.K.; Karpecki, P.; Lazreg, S.; Pult, H.; et al. TFOS DEWS II diagnostic methodology report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 539–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satitpitakul, V.; Kheirkhah, A.; Crnej, A.; Hamrah, P.; Dana, R. Determinants of ocular pain severity in patients with dry eye disease. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 179, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beucher, S.; Meyer, F. The morphological approach to segmentation: The watershed transformation. In Mathematical Morphology in Image Processing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 433–481. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R Stat. Soc. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoşal, B.; Örnek, N.; Zilelioğlu, G.; Elhan, A. Morphology of corneal nerves and corneal sensation in dry eye: A preliminary study. Eye 2005, 19, 1276–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, A.S.; Gurdal, C.; Arslan, N. Corneal confocal microscopy and dry eye findings in contact lens discomfort patients. Cont. Lens. Anterior. Eye 2018, 41, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Luo, L.; Xiao, Q.; Sun, M.; Liu, Z. Altered corneal nerves in aqueous tear deficiency viewed by in vivo confocal microscopy. Cornea 2005, 24, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, E.; Magnani, F.; Viola, F.; Santaniello, A.; Scorza, R.; Nucci, P.; Ratiglia, R. In vivo confocal evaluation of the ocular surface morpho-functional unit in dry eye. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2013, 90, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponirakis, G.; Ghandi, R.; Ahmed, A.; Gad, H.; Petropoulos, I.N.; Khan, A.; Elsotouhy, A.; Vattoth, S.; Alshawwaf, M.K.; Khoodoruth, M.A.S.; et al. Abnormal corneal nerve morphology and brain volume in patients with schizophrenia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitirgen, G.; Korkmaz, C.; Zamani, A.; Ozkagnici, A.; Zengin, N.; Ponirakis, G.; Malik, R.A. Corneal confocal microscopy identifies corneal nerve fibre loss and increased dendritic cells in patients with long COVID. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Dong, X.; Zhou, X.; Yan, L.; Wan, Q. Corneal subbasal nerve plexus changes in patients with episodic migraine: An in vivo confocal microscopy study. J. Pain. Res. 2019, 12, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gonzalez, M.; Cañadas, P.; Gros-Otero, J.; Rodriguez-Perez, I.; Cañones-Zafra, R.; Kozobolis, V.; Teus, M.A. Long-term corneal subbasal nerve plexus regeneration after laser in situ keratomileusis. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2019, 45, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Moreno, A.; Liang, H.; Moreau, N.; Luzu, J.; Rabut, G.; Parsadaniantz, S.M.; Labbé, A.; Baudouin, C.; Goazigo, A.R.L. Corneal Nerve Abnormalities in Painful Dry Eye Disease Patients. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.K.; Seo, K.Y.; Kim, E.K.; Lee, H.K. Comparison of corneal nerve regeneration and sensitivity between LASIK and laser epithelial keratomileusis (LASEK). Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2006, 141, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshirfar, M.; Bhavsar, U.M.; Durnford, K.M.; McCabe, S.E.; Ronquillo, Y.C.; Lewis, A.L.; Hoopes, P.C. Neuropathic corneal pain following LASIK surgery: A retrospective case series. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2021, 10, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theophanous, C.; Jacobs, D.S.; Hamrah, P. Corneal neuralgia after LASIK. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2015, 92, e233–e240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).