Collaborative Mobile Robotics for Semantic Mapping: A Survey
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Single-Robot Semantic Mapping
2.1. Data Acquisition and Processing
2.1.1. Perception-Based Data Acquisition
2.1.2. HRI-Based Data Acquisition
2.1.3. Reasoning-Based Semantic Data Acquisition
2.2. Semantic-Map Representation
2.2.1. Visual Geometric-Semantic Representations
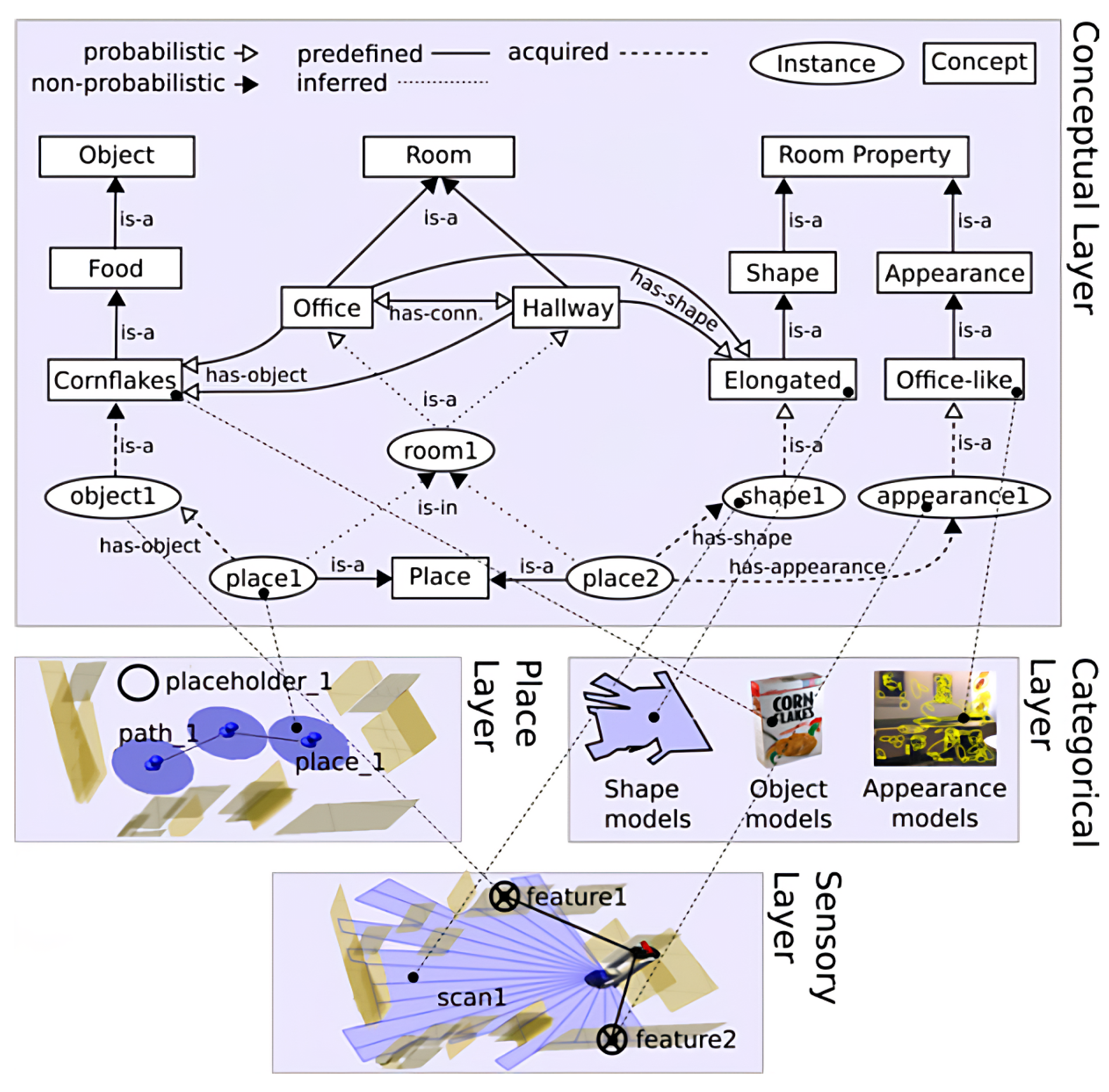
2.2.2. Hierarchical Representations
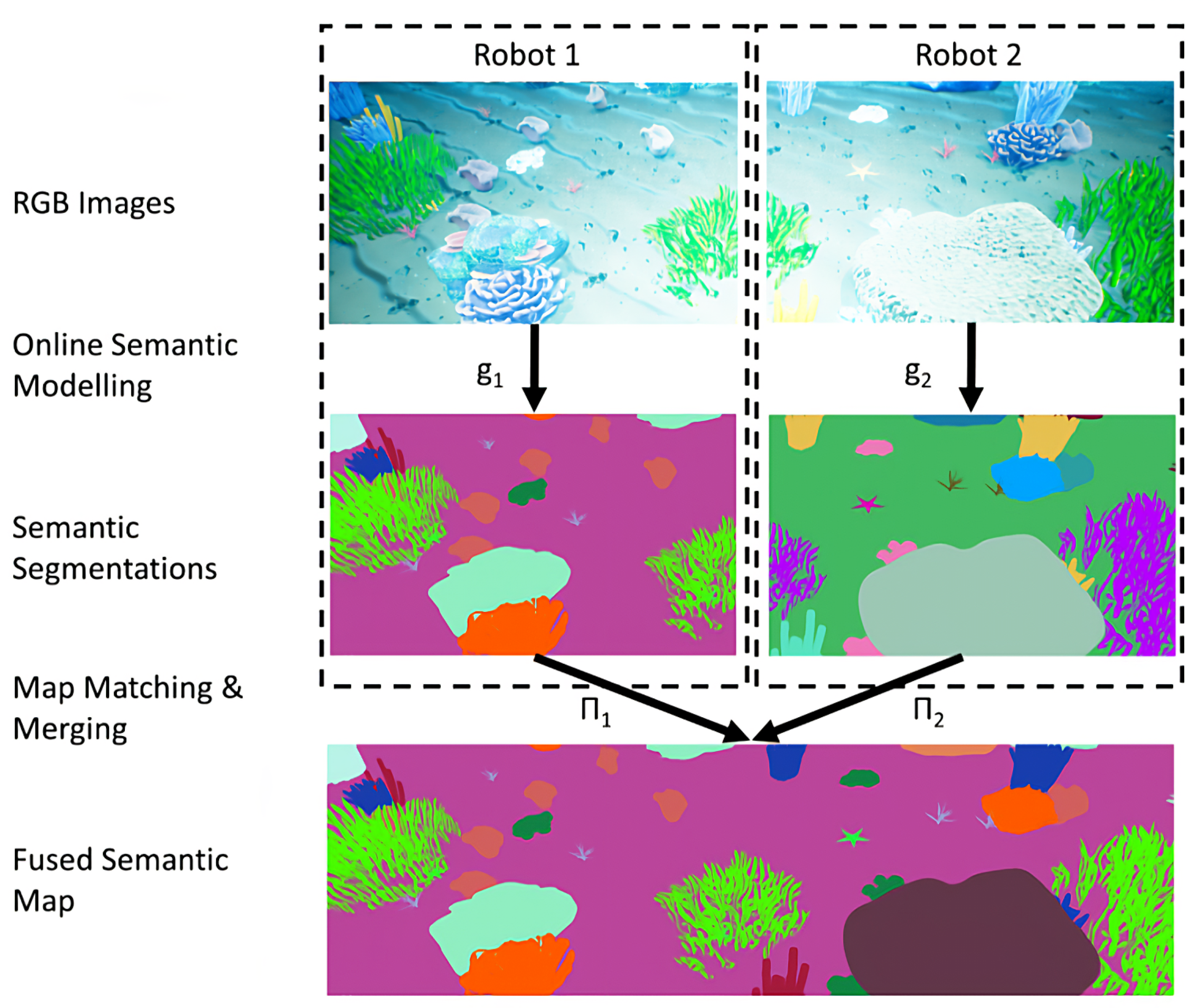
3. Collaborative Semantic Mapping
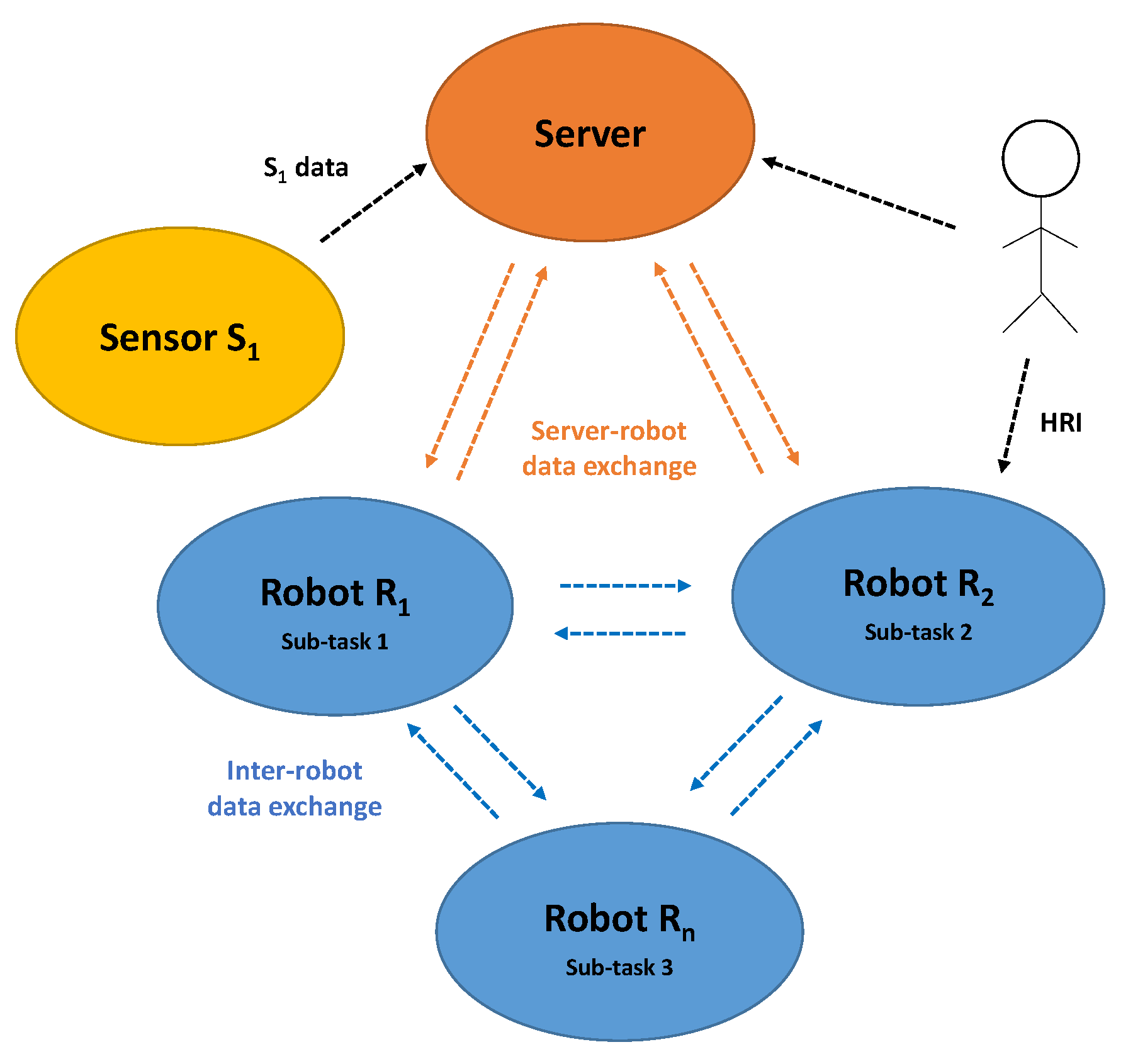
3.1. Multi-Robot Semantic-Mapping Pipeline
- The task and data distribution scheme: defines the system architecture, its components, the connections between them and the tasks assigned to each component.
- The communication policy:
- Defines the topology of the exchanges: the different agents with which each robot has the physical possibility and the authorization to communicate;
- Defines the type of communicated data: sensor data or partial semantic maps;
- Plans the exchanges: which information to send, to which robot and at which time.
- The multi-robot data association and fusion strategy: is the solution used to integrate the multi-robot exchanged data into a global semantic map.
3.2. Tasks and Data Allocation Architectures
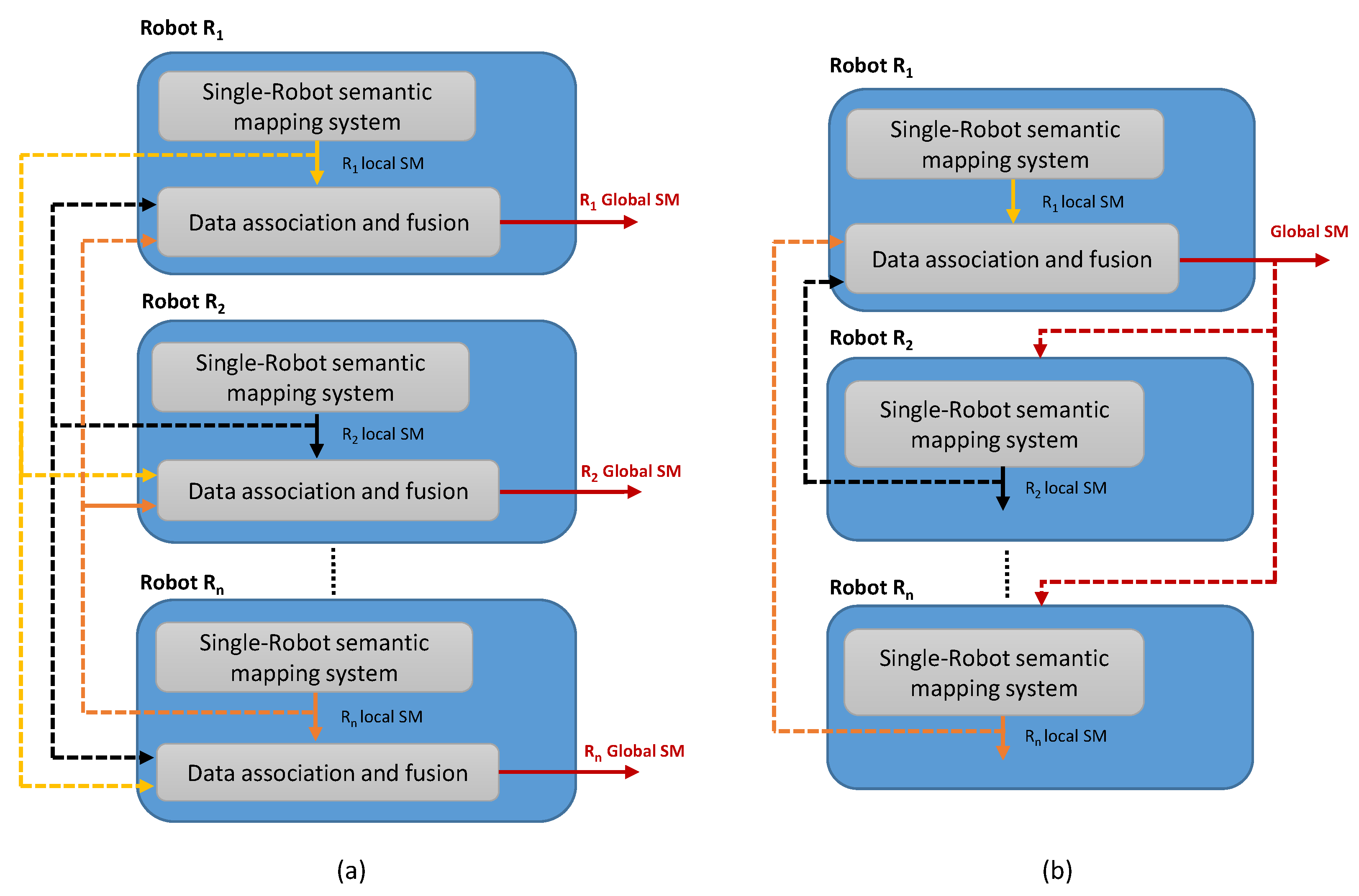
3.2.1. Centralized Semantic-Mapping Architecture
3.2.2. Distributed Semantic-Mapping Architecture
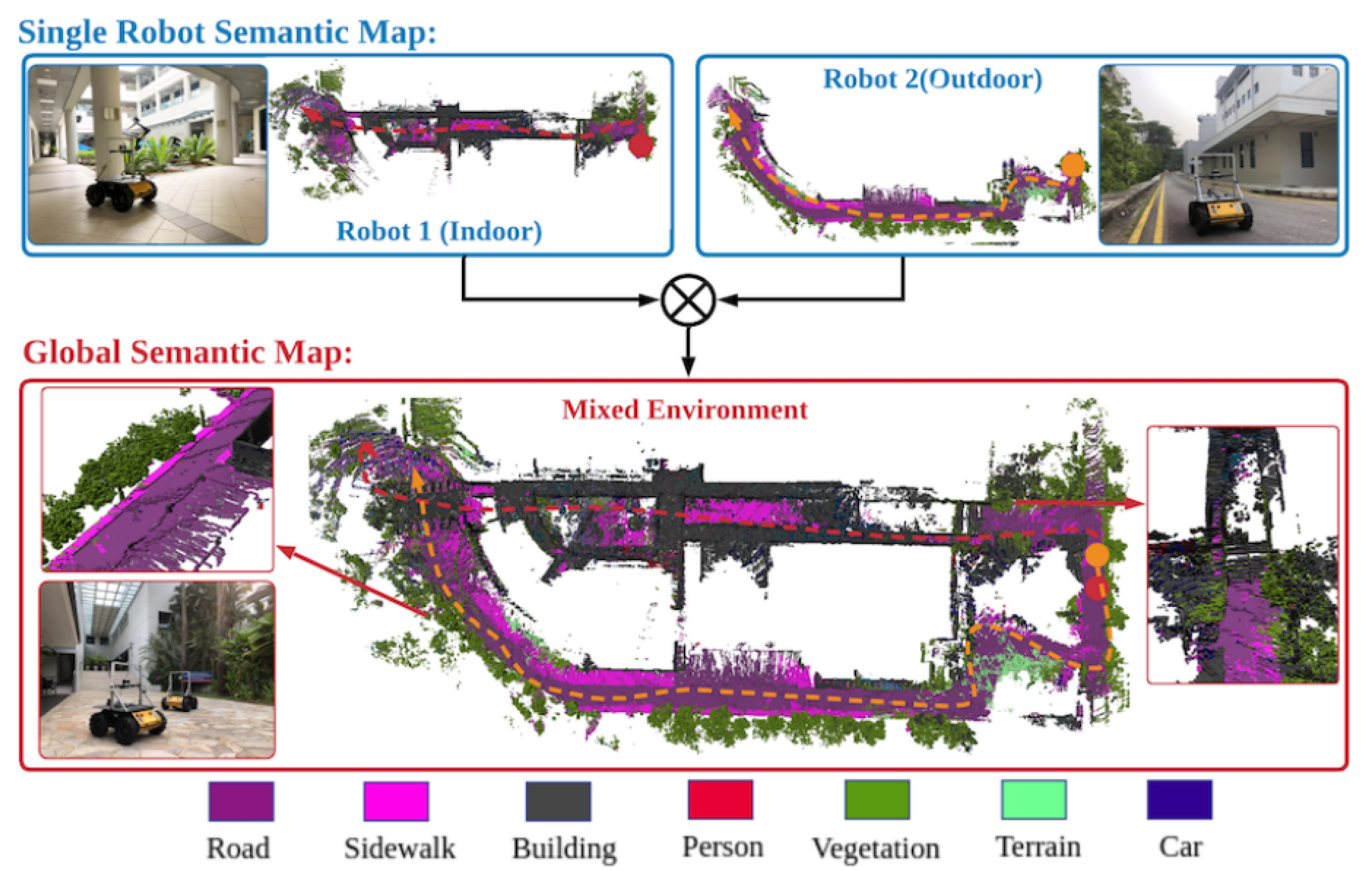
3.3. Multi-Robot Data Association and Semantic Maps Fusion
3.3.1. Data Association
3.3.2. Fusion and Optimization
4. Open Problems and Ongoing Trends
4.1. Semantic Data Gathering Challenges
4.2. Map Representation Challenges
4.2.1. Task-Oriented Map Representation
4.2.2. Context-Aware Map Representation
4.2.3. Knowledge Database Representation
4.3. Semantic Mapping of Dynamic Environments
4.4. Collaborative Semantic Mapping of Indoor Environments
4.5. Semantic-Map Fusion Challenges
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, F.; Zhang, C.; Tang, F.; Jiang, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y. Lightweight Object-level Topological Semantic Mapping and Long-term Global Localization based on Graph Matching. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.05977. [Google Scholar]
- Nüchter, A.; Hertzberg, J. Towards semantic maps for mobile robots. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2008, 56, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Mei, W.; Pan, W. Building a grid-semantic map for the navigation of service robots through human–robot interaction. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2015, 1, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Wang, W.; Yuan, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Xue, L.; Sun, Y. Building semantic grid maps for domestic robot navigation. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, C.; Fernández-Madrigal, J.A.; González, J.; Saffiotti, A. Robot task planning using semantic maps. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2008, 56, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantaros, Y.; Pappas, G.J. Optimal temporal logic planning for multi-robot systems in uncertain semantic maps. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 4127–4132. [Google Scholar]
- Kantaros, Y.; Kalluraya, S.; Jin, Q.; Pappas, G.J. Perception-based temporal logic planning in uncertain semantic maps. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostavelis, I.; Gasteratos, A. Semantic mapping for mobile robotics tasks: A survey. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2015, 66, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, R.; Hu, H.; Gu, D. Extracting semantic information from visual data: A survey. Robotics 2016, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadena, C.; Carlone, L.; Carrillo, H.; Latif, Y.; Scaramuzza, D.; Neira, J.; Reid, I.; Leonard, J.J. Past, present, and future of simultaneous localization and mapping: Toward the robust-perception age. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2016, 32, 1309–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo Herrero, J.; Castillo Montoya, J.C.; Martínez Mozos, Ó.; Barber Castaño, R.I. Semantic information for robot navigation: A survey. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, W. Semantic Mapping for Mobile Robots in Indoor Scenes: A Survey. Information 2021, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, S.; Trentini, M.; Seto, M.; Li, H. Multiple-robot simultaneous localization and mapping: A review. J. Field Robot. 2016, 33, 3–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, D.F.; Sukhatme, G.S. Semantic mapping using mobile robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2008, 24, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernuy, F.; Ruiz del Solar, J. Semantic mapping of large-scale outdoor scenes for autonomous off-road driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Fan, L.; Pan, Z.; Chen, L. Monocular Outdoor Semantic Mapping with a Multi-task Network. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 1992–1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, D.; Friedmann, S.; Hedrich, J.; Paulus, D. Semantic mapping for mobile outdoor robots. In Proceedings of the 2015 14th IAPR International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA), Tokyo, Japan, 18–22 May 2015; pp. 325–328. [Google Scholar]
- Atanasov, N.; Zhu, M.; Daniilidis, K.; Pappas, G.J. Semantic Localization Via the Matrix Permanent. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems, Berkeley, CA, USA, 12–16 July 2014; Volume 2, pp. 1–10. Available online: https://www.x-mol.com/paper/1477015746142314496 (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Reid, I. Towards semantic visual SLAM. In Proceedings of the 2014 13th International Conference on Control Automation Robotics & Vision (ICARCV), Singapore, 10–12 December 2014; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kundu, A.; Li, Y.; Dellaert, F.; Li, F.; Rehg, J.M. Joint semantic segmentation and 3d reconstruction from monocular video. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 703–718. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-10599-4_45citeas (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Bowman, S.L.; Atanasov, N.; Daniilidis, K.; Pappas, G.J. Probabilistic data association for semantic slam. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 1722–1729. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Lee, S.J.; Kölsch, M.; Chung, W.K. Enhanced maximum likelihood grid map with reprocessing incorrect sonar measurements. Auton. Robot. 2013, 35, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zender, H.; Mozos, O.M.; Jensfelt, P.; Kruijff, G.J.; Burgard, W. Conceptual spatial representations for indoor mobile robots. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2008, 56, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkesson, J.; Jensfelt, P.; Christensen, H.I. Vision SLAM in the measurement subspace. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Barcelona, Spain, 18–22 April 2005; pp. 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ekvall, S.; Kragic, D. Receptive field cooccurrence histograms for object detection. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2–6 August 2005; pp. 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto, R.; Adachi, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Ishida, H.; Kobayashi, S. Accuracy improvement of semantic segmentation using appropriate datasets for robot navigation. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies (CoDIT), Paris, France, 23–26 April 2019; pp. 1610–1615. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Belaroussi, R. Semi-dense 3d semantic mapping from monocular slam. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.04144. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, J.; Schöps, T.; Cremers, D. LSD-SLAM: Large-scale direct monocular SLAM. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 834–849. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-10605-2_54 (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Sünderhauf, N.; Pham, T.T.; Latif, Y.; Milford, M.; Reid, I. Meaningful maps with object-oriented semantic mapping. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 5079–5085. [Google Scholar]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Tardós, J.D. Probabilistic Semi-Dense Mapping from Highly Accurate Feature-Based Monocular SLAM. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems, Rome, Italy, 13–17 July 2015; Volume 2015. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/282807894_Probabilistic_Semi-Dense_Mapping_from_Highly_Accurate_Feature-Based_Monocular_SLAM (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Pronobis, A.; Jensfelt, P. Large-scale semantic mapping and reasoning with heterogeneous modalities. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Saint Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 3515–3522. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Garcia, A.; Orts-Escolano, S.; Oprea, S.; Villena-Martinez, V.; Garcia-Rodriguez, J. A review on deep learning techniques applied to semantic segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.06857. [Google Scholar]
- Minaee, S.; Boykov, Y.Y.; Porikli, F.; Plaza, A.J.; Kehtarnavaz, N.; Terzopoulos, D. Image segmentation using deep learning: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Li, W.; Wang, H. A brief survey on RGB-D semantic segmentation using deep learning. Displays 2021, 70, 102080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.; Lu, Z. A review of deep learning-based semantic segmentation for point cloud. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 179118–179133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhu, X.X. Linking points with labels in 3D: A review of point cloud semantic segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2020, 8, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisetti, G.; Stachniss, C.; Burgard, W. Improving grid-based slam with rao-blackwellized particle filters by adaptive proposals and selective resampling. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Barcelona, Spain, 18–22 April 2005; pp. 2432–2437. [Google Scholar]
- Grisetti, G.; Stachniss, C.; Burgard, W. Improved techniques for grid mapping with rao-blackwellized particle filters. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2007, 23, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randelli, G.; Bonanni, T.M.; Iocchi, L.; Nardi, D. Knowledge acquisition through human–robot multimodal interaction. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2013, 6, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastianelli, E.; Bloisi, D.D.; Capobianco, R.; Cossu, F.; Gemignani, G.; Iocchi, L.; Nardi, D. On-line semantic mapping. In Proceedings of the 2013 16th International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR), Montevideo, Uruguay, 25–29 November 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Crespo, J.; Barber, R.; Mozos, O. Relational model for robotic semantic navigation in indoor environments. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2017, 86, 617–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darlington, K. Common Sense Knowledge, Crucial for the Success of AI Systems. OpenMind BBVA 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Galindo, C.; Saffiotti, A.; Coradeschi, S.; Buschka, P.; Fernandez-Madrigal, J.A.; González, J. Multi-hierarchical semantic maps for mobile robotics. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE/RSJ International Conference On Intelligent Robots and Systems, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2–6 August 2005; pp. 2278–2283. [Google Scholar]
- Patel-Schneider, P.F.; Abrahams, M.; Resnick, L.A.; McGuinness, D.L.; Borgida, A. Neoclassic Reference Manual: Version 1.0; Artificial Intelligence Principles Research Department, AT&T Labs Research: 1996. Available online: http://www.bell-labs.com/project/classic/papers/NeoTut/NeoTut (accessed on 26 July 2022).
- Wang, Z.; Tian, G. Hybrid Offline and Online Task Planning for Service Robot Using Object-Level Semantic Map and Probabilistic Inference. Inf. Sci. 2022, 593, 78–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, R.; Eudes, A.; Frémont, V. Sharing visual-inertial data for collaborative decentralized simultaneous localization and mapping. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2022, 148, 103933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, R.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Wen, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D. A hierarchical framework for collaborative probabilistic semantic mapping. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 9659–9665. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, G.S.; Ferreira, J.F.; Portugal, D.; Couceiro, M.S. MoDSeM: Modular framework for distributed semantic mapping. In Poster Papers; 2019; p. 12. Available online: https://www.ukras.org.uk/publications/ras-proceedings/UKRAS19/pp12-15 (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Fernandez-Chaves, D.; Ruiz-Sarmiento, J.R.; Petkov, N.; Gonzalez-Jimenez, J. ViMantic, a distributed robotic architecture for semantic mapping in indoor environments. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2021, 232, 107440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Wen, M.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D. COSEM: Collaborative Semantic Map Matching Framework for Autonomous Robots. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 3843–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, S.; Fathian, K.; Khosoussi, K.; How, J.P.; Girdhar, Y. Multi-Robot Distributed Semantic Mapping in Unfamiliar Environments through Online Matching of Learned Representations. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 8587–8593. [Google Scholar]
- Potena, C.; Khanna, R.; Nieto, J.; Siegwart, R.; Nardi, D.; Pretto, A. AgriColMap: Aerial-ground collaborative 3D mapping for precision farming. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincon, J.L.S.; Carpin, S. Map Merging of Oriented Topological Semantic Maps. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Symposium on Multi-Robot and Multi-Agent Systems (MRS), New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 22–23 August 2019; pp. 202–208. [Google Scholar]
- Rincon, J.L.S.; Carpin, S. Time-constrained exploration using toposemantic spatial models: A reproducible approach to measurable robotics. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2019, 26, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornung, A.; Wurm, K.M.; Bennewitz, M.; Stachniss, C.; Burgard, W. OctoMap: An efficient probabilistic 3D mapping framework based on octrees. Auton. Robot. 2013, 34, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girdhar, Y.; Dudek, G. Modeling curiosity in a mobile robot for long-term autonomous exploration and monitoring. Auton. Robot. 2016, 40, 1267–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellaert, F. The Expectation Maximization Algorithm. Technical Report. Georgia Institute of Technology, 2002. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/543975 (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Hu, Y.; Song, R.; Li, Y. Efficient coarse-to-fine patchmatch for large displacement optical flow. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 5704–5712. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7780984 (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Huang, W.H.; Beevers, K.R. Topological map merging. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2005, 24, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanni, T.M.; Della Corte, B.; Grisetti, G. 3-d map merging on pose graphs. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrington, E.K. The selective impairment of semantic memory. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 1975, 27, 635–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathian, K.; Khosoussi, K.; Tian, Y.; Lusk, P.; How, J.P. Clear: A consistent lifting, embedding, and alignment rectification algorithm for multiview data association. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2020, 36, 1686–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Senarathne, P.N.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Wen, M.; Wang, D. Hierarchical probabilistic fusion framework for matching and merging of 3-d occupancy maps. IEEE Sensors J. 2018, 18, 8933–8949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macenski, S.; Jambrecic, I. SLAM Toolbox: SLAM for the dynamic world. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Ref. | Year | Semantic Data Sources | Approach | Collected Semantic Data | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| About Objects | About Places | ||||
| [23] | 2008 | Perception - HRI Reasoning | Vision-based SLAM, object recognition | Categories, instances | Categories, instances |
| [31] | 2012 | Perception - HRI Reasoning | EKF-SLAM, recognition and instance reasoning, properties classification | Categories, relationships with other concepts | Appearance, surface, shape |
| [40] | 2013 | HRI | Incremental approach by HRI | Categories, positions, sizes, properties | Categories, robot positions |
| [3] | 2015 | HRI | RBPF-SLAM, voice recognition | _ | Categories |
| [27] | 2016 | Perception | Monocular LSD-SLAM, 2D segmentation with CNN | Categories | _ |
| [41] | 2017 | Reasoning | _ | Instances, categories, utilities, characteristics, relationships with places | Instances, categories |
| [29] | 2017 | Perception | RGBD-based ORB-SLAM2, Object Detection, 3D Segmentation with CNN | Categories, instances | _ |
| [4] | 2020 | Perception | Sonar-based SLAM, object detection, triangulation | Categories | Categories |
| [45] | 2022 | Perception–reasoning | Monocular SLAM, object detection | Categories, relationships with other concepts | Categories |
| Ref. | Year | Fusion Mode | Input Data | Data Association and Fusion Methods | Map Representation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Association | Fusion | |||||
| [52] | 2019 | Incremental | Local grid-based multi-modal maps | Point-to-point matching | Map alignment | Global grid-based multi-modal map |
| [53] | 2019 | One-shot | Local OSTM [54] | Graph matching | Graph merging | Global OSTM |
| [47] | 2020 | Incremental | 3D Octree local maps [55] | Voxel-to-voxel matching | Bayesian fusion | 3D Octree global map |
| [51] | 2021 | One-shot | BNP-ROST unsupervised learning models [56] | Matching topics developed in individual robot models | Associating a single label to similar topics | Global semantic occupancy model |
| [49] | 2021 | Incremental | Coupled geometric and semantic informations | Grouping labels associated with the same physical element under a common virtual object | Assigning a parent label to each virtual object and linking it to the ontology | Labeled 3D virtual environment + Ontology |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Achour, A.; Al-Assaad, H.; Dupuis, Y.; El Zaher, M. Collaborative Mobile Robotics for Semantic Mapping: A Survey. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10316. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010316
Achour A, Al-Assaad H, Dupuis Y, El Zaher M. Collaborative Mobile Robotics for Semantic Mapping: A Survey. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(20):10316. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010316
Chicago/Turabian StyleAchour, Abdessalem, Hiba Al-Assaad, Yohan Dupuis, and Madeleine El Zaher. 2022. "Collaborative Mobile Robotics for Semantic Mapping: A Survey" Applied Sciences 12, no. 20: 10316. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010316
APA StyleAchour, A., Al-Assaad, H., Dupuis, Y., & El Zaher, M. (2022). Collaborative Mobile Robotics for Semantic Mapping: A Survey. Applied Sciences, 12(20), 10316. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010316





